PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE. Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician
|
|
|
- Margery Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 ABOUT THIS BOOKLET WHAT IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD) CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE TREATMENT OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE ANGIOPLASTY 7 8 BEFORE THE PROCEDURE INSTRUCTIONS DURING THE PROCEDURE ANGIOPLASTY OPENING A BLOCKED CORONARY VESSEL IMPLANTING THE STENT AFTER THE PROCEDURE CORONARY ARTERY STENTS 9 TAKING CARE OF YOURSELF AT HOME MEDICATIONS 5 THE EluNIR STENT CLINICAL DATA FOLLOW-UP EXAMINATIONS MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) WHO SHOULD NOT RECEIVE THE EluNIR STENT 6 POTENTIAL RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS OF TREATMENT WITH EluNIR RIDAFOROLIMUS ELUTING CORONARY STENT SYSTEM 10 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS GLOSSARY 2
3 ABOUT THIS BOOKLET Your doctor has recommended an EluNIR stent to help manage your coronary artery disease (CAD). The EluNIR Ridaforolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System (EluNIR ) is a drug- eluting stent (metal stent coated with a drug). It will be implanted into your coronary vessel following the angioplasty procedure. This stent will function as miniature scaffolding to help your vessel maintain its shape, strength and integrity. The information in this booklet will help to prepare you for your hospital stay, the stenting procedure and your recovery. It describes the EluNIR stent, how the stent is implanted and what you can do to facilitate your recovery. If you have any questions about the EluNIR stent or the stenting procedure after you read this booklet, be sure to ask your doctor. If you need additional information about the EluNIR stent, please call Customer Service at (800) WHAT IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD)? Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) affects the coronary arteries that surround the heart. These coronary arteries supply blood with oxygen to the heart muscle to allow it to function properly. CAD occurs when the inner walls of the coronary arteries thicken due to plaque, which is a buildup of cholesterol, fatty deposits, calcium, and other elements carried in the blood. As the plaque develops, the vessel narrows. When the vessel narrows, blood flow through the lumen, the center of the vessel, is restricted, so less oxygen and other nutrients reach the heart muscle. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, may lead to chest pain (angina pectoris) or a heart attack (myocardial infarction). SUPERIOR VENA CAVA RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY POSTERIOR DESCENDING ARTERY CORONARY ARTERIES CARRY BLOOD THAT SUPPLIES NUTRIENTS AND OXYGEN TO THE HEART CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE RISK FACTORS Common risk factors for CAD include: Being male or a postmenopausal female Increasing age High blood pressure Diabetes High blood cholesterol Smoking Obesity Family history of heart disease Lack of physical activity AORTA PULMONARY ARTERY PULMONARY VEINS LEFT CORONARY ARTERY CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY MARGINAL BRANCH LEFT DESCENDING ARTERY DIAGONAL BRANCHES SYMPTOMS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Symptoms of CAD differ from person to person; however, typical symptoms include pressure, tightness or pain in the chest, arm, back, shoulder, neck or jaws. Heartburn, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath and heavy sweating may also occur. HEALTHY CORONARY VESSEL LUMEN PLAQUE OCCLUDED (NARROWED) CORONARY VESSEL Women are more likely than men to have atypical chest pain, which may be fleeting or sharp and noticed in the abdomen, back or arm. Women also are somewhat more likely than men to experience other warning signs of a heart attack, including nausea and back or jaw pain. In some cases, a heart attack may occur without any apparent signs or symptoms. 3
4 DIAGNOSIS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE When making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and risk factors. Based on this information, your doctor may ask you to undergo a series of tests to see how healthy your arteries are. These will include some or all of the following: Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) This test measures your heart s electrical activity and may show whether parts of your heart muscle have been damaged by a heart attack caused by CAD. Stress test This test records your heart s electrical activity while you are exercising and may tell your doctor whether part of your heart muscle is damaged. Angiogram - This test is done by injecting a contrast dye into the coronary arteries so they can be seen on an X-ray screen. The X-ray will show if artery narrowing has occurred. Echocardiography Ultrasound evaluation of the heart muscle movements can identify areas of reduced or absent movements indicative of CAD. Nuclear Imaging / Scan The use of isotopes can identify areas of reduced blood flow. These areas may be caused by CAD. Troponin, CK-MB, CK Measurements of blood levels of various proteins originating from diseased heart muscle enable identification of patients with CAD. TREATMENT OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE To determine what treatment is right for you, your cardiologist will take a number of factors into consideration, including your overall medical condition, your cardiovascular condition, the condition of your coronary arteries, your age, your health history, and the results of the previously mentioned series of tests. Coronary artery disease may be managed through a combination of changes in lifestyle and physical activity, diet, and medical treatment. The therapy your doctor recommends will depend on the condition and severity of the disease. Medical treatments of the blockage may include medications, angioplasty, stent implantation or coronary artery bypass surgery. and the catheter is removed from the artery. PTCA can be performed with a balloon alone, or can involve the placement of a coronary stent (see Coronary Artery Stents, below). Some patients may develop re-narrowing of the vessel in the following months, a process which is termed restenosis. Vessel with plaque Opening vessel with balloon CORONARY ARTERY STENTS A stent is a small metallic mesh tube used to treat narrow or weak arteries. Stenting is a common procedure that helps maintain the patency of coronary arteries undergoing catheter based intervention. The stent is mounted onto a balloon, which is inflated inside of a coronary artery to push back plaque and to restore blood flow. After the plaque is compressed against the arterial wall, the stent is fully expanded into position, acting as a miniature "scaffold" for the artery. The balloon is then deflated and removed, and the stent is left behind in the artery to help keep the blood vessel open. For some patients it may be necessary to place more than one stent in one or more of their coronary arteries. Stent on delivery catheter before balloon inflation LUMEN LUMEN PLAQUE PLAQUE BALLOON BEFORE INFLATION BALLOON AFTER INFLATION VESSEL WALL ANGIOPLASTY Angioplasty, also known as Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA), is a minimally invasive treatment performed in the hospital to open the blocked coronary arteries. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and at times under monitored sedation, in a cardiac catheterization laboratory. A thin tube known as a catheter is inserted, under X-ray guidance, through the radial artery (wrist) or femoral artery (groin) and is then guided to the site of the blockage. A small balloon, located on the tip of the catheter, is expanded to reduce the blockage by compressing the plaque. The balloon is then deflated Stent expands as balloon is inflated Once the balloon is fully inflated, the stent is expanded, fitting the vessel size and contour IMPLANTING STENT 4
5 THE EluNIR STENT The decision as to which type of stent suits your needs best depends on various medical parameters that your doctor has considered. Your doctor has determined that the EluNIR drug eluting stent is suitable for you. The EluNIR is a Drug Eluting Stent, coated with an elastic polymer (elastomer). A drug called ridaforolimus is incorporated in the elastomer coating, which helps control the release of the drug into the arterial wall. The drug is released over time and helps block cell proliferation and prevent restenosis. When the balloon is inflated, the stent expands until it has made full contact with the vessel wall, adapting to fit the shape, size, and bends of the vessel. Once in place, the stent will remain in your artery. Over time, the lining of the artery wall will grow around the stent as the stent continues to support the vessel. vessel treated by the stent, or treatment of the lesion due to vessel renarrowing was 5.4% for both EluNIR and Resolute. Additionally, the EluNIR stent had a low rate of stent trombosis/occlusion with no events beyond 30 days. All patients are undergoing follow up for a period of five (5) years. The NIREUS study was conducted at 28 medical centers in Europe and Israel. A total of 302 patients participated in the study. This study also compared the EluNIR stent to the Resolute stent; however, the main purpose of this study was to observe the occurrence of re-narrowing of the artery after six (6) months. This was done using a repeat angiogram test. The study results showed that the EluNIR is similar to the Resolute stent in reducing the re-narrowing of the artery where the stent was placed. All patients are undergoing follow up for a period of five (5) years. The BIONICS-Israel clinical study was conducted to assess the EluNIR stent with a modified delivery system (the catheter leading the stent to its location within the artery). In this study, a total of 58 patients participated at three (3) medical centers in Israel. The EluNIR with the modified delivery system was successfully implanted in all patients. All patients are undergoing follow up for a period of 1 year. No safety signals of concern were identified in all EluNIR clinical studies. WHO SHOULD NOT RECEIVE THE EluNIR STENT Coronary artery stenting is generally contraindicated for: Patients who cannot take blood thinning medications (anticoagulants/ antiplatelets), such as heparin or bivalirudin, clopidogrel (also called Plavix), prasugrel, ticagrelor or aspirin. CLINICAL DATA EluNIR STENT The safety and effectiveness of the EluNIR stent was substantiated by data collected from two global clinical studies and a supplemental clinical study. The clinical studies include the BIONICS study and the NIREUS study, in which the EluNIR Stent was compared to another approved drug eluting stent, Medtronic s Resolute drug eluting stent. Approximately 2,300 patients participated in these studies, over half of which received the EluNIR Stent. Patients judged to have a lesion which prevents complete inflation of an angioplasty balloon or proper placement of the stent or delivery system. Patients with hypersensitivity (allergy) to ridaforolimus, the polymer or its individual components CarboSil 20 55D (Thermoplastic Silicone- Polycarbonate-Urethane) and Poly n-butyl Methacrylate (PBMA), or compounds in a metallic stent, such as nickel, cobalt, chromium and molybdenum or hypersensitivity (allergy) to contrast media. The BIONICS study was conducted at 76 medical centers in the US, Canada, Europe, and Israel. A total of 1,919 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) participated in the study, 958 patients received the EluNIR stent and 961 patients received the Resolute stent. The study results after 1 year showed that the EluNIR stent was similar to the Resolute stent in clinical outcomes. The observed rate of cardiac death, heart attack associated with the blood 5
6 POTENTIAL RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS OF TREATMENT WITH EluNIR RIDAFOROLIMUS ELUTING CORONARY STENT SYSTEM Angioplasty and stent placement for CAD have become increasingly common but, as with any invasive procedure, there are potential risks and complications. Use of the EluNIR stent carries the same risks as those associated with standard stent placements. The following complications may occur during or after placement of a coronary stent in the patient's body (in alphabetical order): Air, tissue or clots which can block the vessel Allergic reaction, which may be due to contrast dye, antiplatelet therapy, stent material (nickel, cobalt, chromium, molybdenum), drug or the polymer or its individual components CarboSil 20 55D (Thermoplastic Silicone-Polycarbonateurethane) and Poly n-butyl Methacrylate (PBMA) coating the stent Anxiety Blood Vessel spasm Bleeding around the heart Bleeding complications which may require transfusions or surgery Bruising, bleeding or pain at the catheter insertion site in the leg, wrist or arm Cardiac arrest due to electrical imbalance of the heart Chest pain or discomfort during or after the stenting procedure Coronary artery complications: Including re-narrowing of the artery, artery blockage / injury / puncture / tearing, that may require a repeat procedure to re-open the artery Death Delay in growth of artery wall cells after stent implantation Discomfort or fainting mediated by the vagus nerve Excess body fluids Failure of the heart with/without low blood pressure Failure of the lungs to adequately supply oxygen to the body Failure to deliver the stent to the correct place in the artery Fever Fluid accumulation around the heart Formation of blood clots inside the stent Heart attack High/low blood pressure Inadequate supply of blood to the heart Infections: Infection of the inner layer of the heart; Infection of the lungs and upper airways Irregular heartbeat Kidney failure Need for heart surgery; emergent or non-emergent Puncturing of the heart or great vessels Stent compression Stent misplacement in the artery / movement of the stent from where it was placed or from the balloon into the artery Stroke or other neurological events Weakening and enlargement of a portion of the wall of a blood vessel Ridaforolimus is a drug originally developed for patients with cancer. Patient exposure to ridaforolimus is directly related to the number of implanted stents (total stent surface area). The risks of the Ridaforolimus drug are not yet fully known. The risks that might occur include, but are not limited to (in alphabetical order): Anemia Anorexia Constipation Dehydration Diarrhea Distortion of the sense of taste Fatigue Fever Hair loss High levels of Glucose/Fat/Potassium/Phosphate in the blood High levels of liver enzymes in the blood High levels of muscle enzymes due to damage to muscle cells Inflammation of mucous membranes Irritation of the stomach Itching Low levels of white/ platelet blood cells Low levels of Potassium/Phosphate in the blood Lung infection/ inflammation Nausea and Vomiting Nail disorder Rash Renal injury Skin inflammation Severe loss of white blood cells Tingling sensation Weight decrease 6
7 BEFORE THE PROCEDURE INSTRUCTIONS Your doctor will instruct you on how to prepare for the angioplasty and stent implantation procedures prior to your admission to the hospital. Your doctor may ask you to take aspirin and other prescribed medications for several days before the procedure. This is done to thin the blood to prevent blood clots (thrombus) from forming during the stenting procedure. It is important to tell your doctor if you cannot take aspirin or have a history of bleeding problems. Your doctor also needs to know if you are taking any other medications or if you have any drug allergies. DURING THE PROCEDURE Your angioplasty procedure and the stent implantation will be performed in a specially equipped area of the hospital called the cardiac catheterization laboratory. The procedure will be performed by an Interventional Cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in angioplasty and stenting. The procedure usually lasts about 60 minutes. For the most part, you will be comfortable, but you may feel some pressure or chest pain when the balloon is inflated. This is normal and will quickly fade when the balloon is deflated. After the stent is implanted, you will be moved to a cardiology ward for a short period where you can be monitored closely as you begin to recover. ANGIOPLASTY OPENING A BLOCKED CORONARY VESSEL Your doctor will decide which site on your body would be the best place from which to access one of your arteries your wrist or groin area. The selected area will be shaved and cleaned with antiseptic and you will be given a local anesthetic to numb the area. During the procedure, you will have to lie flat on your back and you will remain awake, allowing you to follow your cardiologist s instructions (e.g. breathe deeply ). You may be given a mild sedative to help you relax. Devices will monitor your heart rate and blood pressure. The procedure will begin with an angiography test to determine the number and exact location of blockages. To obtain access to the artery, a short smooth catheter, called a sheath, is inserted via the groin or wrist. A thin tube called a guiding catheter is inserted into the sheath and maneuvered up to the heart. The guiding catheter acts as a conduit or pathway to the coronary arteries for subsequent devices (including the stent) and contrast fluid. With the area being observed on an X-ray screen, contrast dye is injected through the guiding catheter and the coronary arteries become visible on the screen. After the exact position of the narrowing has been determined, a small wire is advanced through the artery and past the narrowing. Then, over this wire, a balloon catheter is advanced and when positioned within the narrowing, the balloon is inflated. By inflating the balloon, the stenosis (blockage) is dilated (opened), and the vessel is widened (this part of the procedure is called predilatation). Let your doctor know if you are experiencing any pain. IMPLANTING THE STENT 1. After the artery is widened, your doctor will pass the stent, mounted on a balloon catheter used as the delivery catheter, into the coronary artery through the same guiding catheter. 2. Your doctor will then carefully position the stent at the place where the blockage was detected, known as the target site. By using a type of X-ray machine called a fluoroscope your doctor will be able to see the EluNIR inside the vessel. This helps to position the stent at exactly the right location. 3. Once the stent is in place, your doctor will inflate the balloon and expand the stent using an inflation device, and then position it to the inner wall of the artery. The stent will shape itself to the size and contours of your vessel and keep the artery open. It is common for patients to feel some mild discomfort when the balloon is inflated because the artery is being stretched. 4. When the stent is in place, the balloon is deflated and the delivery catheter is removed. The stent will remain in place and continue to keep the artery open. 5. Your doctor may choose to expand the stent further by using another balloon. If required, the balloon catheter is inserted inside the stent and then inflated to allow the stent to make better contact with the vessel wall. This part of the procedure is called post-dilatation. 6. The stent achieves full contact with the vessel wall and provides unobstructed blood flow, just like a healthy vessel does. When the stent is flush with the vessel wall physicians call this proper stent apposition. Once in place, the EluNIR will remain in your artery permanently. Post-dilatation with balloon catheter Final result FURTHER EXPANSION OF STENT 7
8 AFTER THE PROCEDURE After the procedure, you may be instructed to lie flat for several hours. You will go to a special care unit where medical staff will monitor your heart rate and blood pressure closely. Before you return to your room, the sheath that was used to enter the vessel may be removed and pressure applied to the puncture site until the bleeding has stopped. The catheter insertion site may be bruised and sore. If the sheath was inserted into your wrist, it will be removed and the site will be bandaged. If the catheter was inserted into your groin, you will be asked to lie in bed with your leg straight for several hours. In some cases, your doctor may use a device that seals the small hole in the artery; this may allow you to move around sooner. The place on your body where the catheter was inserted will be monitored for any changes in color, temperature, or sensation. Antiplatelet medication such as Aspirin, or any other blood thinning medications, will be prescribed for you before and after stent placement. They help prevent a blood clot (thrombus) from forming and blocking the stent lumen. Your doctor or nurse will give you instructions about your medications. Your blood will be frequently tested to monitor and regulate medication levels that control the clotting of your blood. Your hospital stay may be less than one day or up to three days. TAKING CARE OF YOURSELF AT HOME Contact your doctor or the hospital immediately if you experience pain, bleeding, discomfort, or changes such as severity or frequency in angina symptoms (chest pain). Follow your doctor s instructions exactly regarding the use and dosage of medications prescribed. CAUTION Do not stop taking your medications unless you are asked to stop by your cardiologist. Tell your dentist or other medical personnel that you are on blood thinners prior to any treatment. Postpone dental work until after your recovery. Avoid strenuous exercise unless approved by your doctor. Return to normal activities gradually, pacing your return to activity as you feel better. Check with your doctor about strenuous activities. Report side effects from medications to your doctor immediately. These may include headaches, nausea, vomiting or rash. Keep all follow-up appointments, including laboratory blood testing. Keep your Implant Card handy. Show it if you report to an emergency room. This card identifies you as a patient who has had a scaffold implanted (see MRI section below). MEDICATIONS Your doctor may prescribe a number of medications which thin the blood to prevent blood clots from forming and adhering to the surface of the stent. These medications may include: Aspirin and other antiplatelet medications (e.g. clopidogrel, ticagrelor, prasugrel). CAUTION Early cessation of your blood thinners may cause abrupt blockage of your stent and result in heart attack or even death. Do not stop these medications without consulting your doctor. Your doctor may prescribe other medications to treat your heart and risk factors, which may include drugs to lower your heart rate, to lower your blood pressure and to optimize your blood cholesterol levels. Your doctor will let you know when you can stop taking this medication. Until then, it is extremely important to follow your medication regimen. Check with your doctor before taking antacids as they may decrease absorption of aspirin and other medications. FOLLOW- UP EXAMINATIONS You will need to see the doctor who implanted your stent for routine follow-up examinations. During these visits, your doctor will monitor your progress and evaluate your medications, the clinical status of your CAD, and how the stent is working for you. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) If you require a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, tell your doctor or MRI technician that you have an EluNIR and present your patient Implant Card. The technician will need to operate the machine within certain limits. Let your doctor know about any changes in lifestyle you make during your recovery period. 8
9 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS If you are a candidate for stenting to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), you will most likely have a lot of questions to discuss with your doctor. Here are some questions and answers to get you started. Keep in mind that your doctor is your best source of information and advice about CAD and treatment for CAD. Be sure to bring up any additional questions and concerns you may have about CAD with your doctor. WILL I FEEL THE STENT? No. You will not feel the stent inside you. HOW LONG WILL THE STENT STAY IN MY BODY? Stents are designed to stay permanently. CAN I PLAY SPORTS? Yes, but be cautious! Your doctor will tell you what sports you can play and when you can start. WHAT SHOULD I CHANGE IN MY DIET? Your doctor may recommend specific dietetic changes to help to reduce your risk for future events. WILL I EXPERIENCE THE SYMPTOMS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE AGAIN, SUCH AS CHEST PAIN? It is possible that you will experience symptoms again, either because of a new blockage in the treated coronary artery or a new blockage in a different place. If you experience these symptoms, notify your doctor immediately. CAN THE STENT MOVE OR RUST? Once the stent is opened and presses into the inside wall of your coronary artery, it will remain in place permanently; the stent does not move on its own. Vessel tissue will grow around the stent and hold it in place. It will not rust because it is made of non-corroding metal. CAN I WALK THROUGH METAL DETECTORS WITH A STENT? Yes, without any fear of setting them off. The stent is made of nonmagnetic metals. HOW WILL I KNOW IF MY ARTERY RE-NARROWS? Although the stents are intended to reduce restenosis, it is still possible for your artery to re-narrow. If this happens, you may experience symptoms similar to those experienced when you first noticed you had coronary artery disease or before your stent procedure. These symptoms may include chest pain or shortness of breath, especially during physical activity. If you experience pain, inform your doctor immediately. WHY HAS MY DOCTOR RECOMMENDED STENTING? Based on your individual CAD progression and symptoms, your doctor feels that placing one or more stents is the best treatment option for you. HOW LONG SHOULD I TAKE MY MEDICATIONS? The most important thing that you can do to minimize the risk of stent thrombosis is to take the medications your doctor prescribes. Do not stop taking these medicines until your cardiologist tells you to, even if you are feeling better. WHAT IF I STILL GET PAINS? If you experience pain, inform your cardiologist or the center where the procedure was performed immediately. 9
10 GLOSSARY ANGINA PECTORIS Discomfort, pain, tightness or pressure in the chest, usually due to interference with blood flow to the heart muscle and precipitated by excitement or effort. May also cause profuse sweating, nausea, shortness of breath and associated pain in the neck, jaw, back, or arm. CATHETER A small thin plastic tube used to provide access to parts of the body, such as into the coronary arteries of the heart. CLOPIDOGREL A medicine that thins the blood and helps prevent clot formation. ANGIOGRAPHY An imaging test performed by injecting contrast dye into the coronary arteries so that the vessels can be seen on an x-ray screen. The x-ray will show if any blockages and/or artery narrowing has occurred and if the blocked coronary arteries can be treated with angioplasty or stenting. ANGIOPLASTY A minimally invasive treatment that uses a balloon to open blocked arterial vessels, also known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). ANTICOAGULANT Medicine such as heparin, which slows or prevents blood from clotting by interfering with blood clotting agents. ANTIPLATELET Medicine such as aspirin, which acts against blood platelets in order to prevent the release of blood clotting agents. APPOSITION Refers to the positioning of the stent against the vessel wall. ATHEROSCLEROSIS A disease in which the flow of blood to the heart is restricted with plaque deposits (a build-up of cholesterol and other fats, calcium and certain other elements carried in the blood) causing less oxygen and other nutrients to reach the heart muscle. This may lead to chest pain (angina pectoris) or to a heart attack (myocardial infarction). CORONARY Related to arteries that supply blood to the heart. CORONARY ANGIOGRAM A test that can determine if CAD is present. Contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries and a fluoroscope allows the doctor to see the narrowed or blocked vessels, a stent, or catheter on an x-ray screen. CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD) Disease affecting the coronary arteries that surround the heart and supply blood to the heart muscle. CAD occurs when the lumen of the coronary arteries becomes narrowed with plaque deposits (a build up of cholesterol and other fats, calcium, and other elements carried in the blood). CORONARY ARTERIES The arteries that surround the heart and supply blood containing oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. Oxygen deprivation to the heart restricts heart function and may lead to chest pain (angina pectoris) or to a heart attack (myocardial infarction). CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT SURGERY (CABG) Open heart or bypass surgery. ECG Electrocardiogram. See stress test. EXERCISE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM See Stress test. 10
11 ISCHEMIA A condition that results from reduced oxygen supply to cells, usually due to an obstruction that reduces blood flow. LUMEN The inner channel of a vessel or tube. MINIMALLY INVASIVE A minimally invasive procedure is any procedure (surgical or otherwise) that is less invasive than an open surgery used for the same purpose. MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Permanent damage to the heart muscle due to the interruption of blood supply to the area, commonly referred to as a heart attack; can occur when blood clots form within the coronary arteries. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) A non-invasive way to take pictures of the body. MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves, unlike x-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, which use radiation. PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION (PCI) A non-surgical procedure used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. PERCUTANEOUS TRANSLUMINAL CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY (PTCA) See Angioplasty. PLAQUE An accumulation or build-up of cells, cellular debris, cholesterol, calcium, fatty deposits, and/or collagen in a blood vessel that leads to narrowing of the lumen. POST-DILATATION After the stent has been expanded, another balloon catheter may be inserted inside the stent and inflated to size the stent more precisely to the normal diameter of the blood vessel. RESTENOSIS Recurrent blockage or narrowing of a previously treated vessel. STENT A small, expandable, metal tube that is inserted into a coronary artery to support the blood vessel wall and maintain healthy blood flow through the opened vessel. STENT THROMBOSIS Stent thrombosis is a rare condition that occurs when a blood clot forms on the surface of a stent, raising the risk of blood flow in an artery being reduced or cut off. STRESS TEST A test to measure electrical activity in the patient s heart (ECG) while the patient is performing controlled exercise. The results help determine if there is damage to the heart muscle or if blood flow has been restricted to areas of the heart. TRANSLUMINAL Through the lumen which is the inner channel of a vessel. VESSEL A vein or artery. PRE-DILATATION Before the stent is placed, a balloon catheter may be inserted inside the lesion and inflated to exert pressure against the arterial wall. 11
12 Distributed by: Cordis Corporation North West 60th Avenue Miami Lakes, Florida USA Manufactured by : Medinol Ltd. PO Box 45026, Beck Tech Bldg. Har-Hotzvim B, Hartom St. 8 Jerusalem ISRAEL Cordis A Cardinal Health Compamy November Rev 3
13 220mm 230mm
A PATIENT`S GUIDE TO CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE. AND YOUR NIRxcell CoCr CORONARY Stent on RX System
 A PATIENT`S GUIDE TO CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE AND YOUR NIRxcell CoCr CORONARY Stent on RX System TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS BOOKLET PAGE 3 WHAT IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD) CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
A PATIENT`S GUIDE TO CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE AND YOUR NIRxcell CoCr CORONARY Stent on RX System TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS BOOKLET PAGE 3 WHAT IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD) CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
TAXUS Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System
 Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each product. CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law and governing law outside the U.S.A. restricts
Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each product. CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law and governing law outside the U.S.A. restricts
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
TAXUS Express 2. Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 TAXUS Express 2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease.................................. 2 Who is at Risk?.......................................3
TAXUS Express 2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease.................................. 2 Who is at Risk?.......................................3
Coronary angioplasty and stents
 Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Understanding Peripheral
 Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
Patient Information Guide
 TM - Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)...5 Your Heart...5 What is Coronary Artery Disease?...5 What are the Symptoms of CAD?...6 What are the Risk Factors of CAD?...8
TM - Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)...5 Your Heart...5 What is Coronary Artery Disease?...5 What are the Symptoms of CAD?...6 What are the Risk Factors of CAD?...8
UNDERSTANDING TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR HEART DISEASE. Visit
 Visit www.absorbstent.com UNDERSTANDING TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR HEART DISEASE UNDERSTANDING YOUR BLOCKED ARTERIES CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE MAY BE AFFECTING YOU OR SOMEONE YOU LOVE. Your heart needs a constant
Visit www.absorbstent.com UNDERSTANDING TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR HEART DISEASE UNDERSTANDING YOUR BLOCKED ARTERIES CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE MAY BE AFFECTING YOU OR SOMEONE YOU LOVE. Your heart needs a constant
REBEL. Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Understanding Peripheral
 Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Table of Contents Glossary...2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?...4 Treating Peripheral Artery
Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Table of Contents Glossary...2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?...4 Treating Peripheral Artery
Carotid Artery Stenting
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage cardiovascular health. All decisions about the management of Carotid Artery Disease must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage cardiovascular health. All decisions about the management of Carotid Artery Disease must be made in conjunction with
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Angioplasty and Vascular Stenting
 Scan for mobile link. Angioplasty and Vascular Stenting Angioplasty uses imaging guidance to insert a balloon-tipped catheter into a narrow or blocked blood vessel where the balloon is inflated to open
Scan for mobile link. Angioplasty and Vascular Stenting Angioplasty uses imaging guidance to insert a balloon-tipped catheter into a narrow or blocked blood vessel where the balloon is inflated to open
Introduction 3. What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5. What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
Cardiac Catheterization
 Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Patient Brochure. Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland. PK Rev. 0 05/17
 Patient Brochure Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland PK1411100 Rev. 0 05/17 LIFESTREAM Patient Brochure If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with
Patient Brochure Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland PK1411100 Rev. 0 05/17 LIFESTREAM Patient Brochure If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES
 CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
Cheltenham General Hospital
 Page 1 of 5 Coronary angioplasty Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients undergoing coronary angioplasty also known as PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). What is coronary artery
Page 1 of 5 Coronary angioplasty Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients undergoing coronary angioplasty also known as PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). What is coronary artery
Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)...5 Your Heart...5 What is CAD?...5 What are the Symptoms of CAD?...5 What are the Risk
Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)...5 Your Heart...5 What is CAD?...5 What are the Symptoms of CAD?...5 What are the Risk
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
PATIENT TEACHING GUIDE FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION
 FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION Percutaneous Intervention for Coronary Artery and Peripheral Vascular Diseases START TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Your Heart and Circulatory System... 3 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION Percutaneous Intervention for Coronary Artery and Peripheral Vascular Diseases START TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Your Heart and Circulatory System... 3 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
Cordis S.M.A.R.T. and S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Nitinol System For the Iliac Arteries
 Endovascular Cordis S.M.A.R.T. and S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Nitinol System For the Iliac Arteries A Patient s Guide to Peripheral Vascular Disease in the Iliac Arteries this guidebook... This guidebook is proudly
Endovascular Cordis S.M.A.R.T. and S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Nitinol System For the Iliac Arteries A Patient s Guide to Peripheral Vascular Disease in the Iliac Arteries this guidebook... This guidebook is proudly
Coronary Artery Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Patient Information. Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon. Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care
 Patient Information Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care Contents Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Patient Information Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care Contents Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Intravascular Ultrasound
 Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Treatment for blocked heart arteries DRAFT. What are arteries? How do heart arteries become blocked?
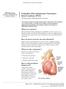 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up
 Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
Neuroform Microdelivery Stent System
 Neuroform Microdelivery Stent System Patient Information Booklet TABLE OF CONTENTS What is the Purpose of This Booklet?...2 What is a Wide Neck, Intracranial Aneurysm?...2 What is the Treatment for Wide
Neuroform Microdelivery Stent System Patient Information Booklet TABLE OF CONTENTS What is the Purpose of This Booklet?...2 What is a Wide Neck, Intracranial Aneurysm?...2 What is the Treatment for Wide
Percutaneous coronary intervention. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Percutaneous coronary intervention Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Percutaneous coronary intervention Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Therapy
 Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Therapy With the Edwards SAPIEN XT Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients and Caregivers This booklet was created to help you learn more about the Edwards SAPIEN XT Transcatheter
Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Therapy With the Edwards SAPIEN XT Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients and Caregivers This booklet was created to help you learn more about the Edwards SAPIEN XT Transcatheter
California Cardiovascular Consultants Medical Associates
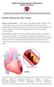 Patient information: Heart Attack What is a heart attack? A heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, or MI, is what happens when one of the arteries that supply blood to the heart gets blocked.
Patient information: Heart Attack What is a heart attack? A heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, or MI, is what happens when one of the arteries that supply blood to the heart gets blocked.
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
 Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Coming in for angioplasty and stent. Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel:
 Coming in for angioplasty and stent Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel: 0118 322 6502 This booklet has been produced by the staff to help answer some of the questions you may have about
Coming in for angioplasty and stent Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel: 0118 322 6502 This booklet has been produced by the staff to help answer some of the questions you may have about
Advice to patients having an angioplasty
 What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY
 CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY What is Coronary Angioplasty? Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to remove the obstruction caused by plaque or fatty build up on the inner walls of the arteries to your heart. It
CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY What is Coronary Angioplasty? Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to remove the obstruction caused by plaque or fatty build up on the inner walls of the arteries to your heart. It
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels
 Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Coronary artery disease develops because of hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) that supply blood to the heart muscle. In the diagnosis of coronary artery disease,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Coronary artery disease develops because of hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) that supply blood to the heart muscle. In the diagnosis of coronary artery disease,
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
YOUR GUIDE TO. Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment
 YOUR GUIDE TO Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
YOUR GUIDE TO Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
EDUCATION. Peripheral Artery Disease
 EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
 Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE
 AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting
 Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
This information explains the advice about the care and treatment of people with stable angina that is set out in NICE clinical guideline 126.
 Information for the public Published: 1 July 2011 nice.org.uk About this information NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Information for the public Published: 1 July 2011 nice.org.uk About this information NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Patient Information Booklet
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction 1 Anatomy of the Thoracic Aorta 2 What Is an Aneurysm?
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction 1 Anatomy of the Thoracic Aorta 2 What Is an Aneurysm?
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW
 CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW Your heart is a strong muscular pump that is responsible for moving about 3,000 gallons of blood through your body every day. Like other muscles, your heart requires a
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW Your heart is a strong muscular pump that is responsible for moving about 3,000 gallons of blood through your body every day. Like other muscles, your heart requires a
Coronary Angioplasty. Feedback. Further Information. We appreciate and encourage feedback from patients and the public. Patient Information
 Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback from patients and the public If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of your care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the
Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback from patients and the public If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of your care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Golden Jubilee National Hospital Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting
 Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000
Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000
Promus ELITE. Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide CV01
 Promus ELITE Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide CV01 Promus ELITE Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE
Promus ELITE Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide CV01 Promus ELITE Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE
A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty
 A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty Welcome Contents If you have this booklet then, like many other New Zealanders, heart disease has touched your life. Whether it is you or a loved one who
A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty Welcome Contents If you have this booklet then, like many other New Zealanders, heart disease has touched your life. Whether it is you or a loved one who
Percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty) +/- rotablation
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Why do I need this procedure? If you are coming into hospital for a cardiac procedure
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Why do I need this procedure? If you are coming into hospital for a cardiac procedure
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Carry this card with you at all times. Show this card to any medical professional treating you. Patient Implant Card. Option ELITE Vena Cava Filter.
 Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
PATIENT EDUCATION. Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease
 PATIENT EDUCATION Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease General Information The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout your body. The blood vessels that supply oxygen to your
PATIENT EDUCATION Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease General Information The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout your body. The blood vessels that supply oxygen to your
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty
 Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08)
 S PATIENT INFORMATION oregon surgical specialists Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08) Abdominal aortic and iliac artery occlusive disease occurs when the arteries in your abdomen
S PATIENT INFORMATION oregon surgical specialists Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08) Abdominal aortic and iliac artery occlusive disease occurs when the arteries in your abdomen
Angioplasty Your quick guide
 Angioplasty Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Angioplasty Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Facing Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Coronary Artery Disease Coronary artery disease is a form of heart disease that affects your arteries.
Facing Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Coronary Artery Disease Coronary artery disease is a form of heart disease that affects your arteries.
YES. Your Guide to Getting WATCHMAN. Is a life without blood thinners possible?
 Your Guide to Getting WATCHMAN Is a life without blood thinners possible? YES. WATCHMAN is for people with atrial fibrillation not caused by a heart valve problem who need an alternative to warfarin for
Your Guide to Getting WATCHMAN Is a life without blood thinners possible? YES. WATCHMAN is for people with atrial fibrillation not caused by a heart valve problem who need an alternative to warfarin for
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Transcatheter Heart Valve. Replacement. With the Edwards SAPIEN 3. for Patients & Caregivers
 For Patients With a Failing Surgical Bioprosthetic Heart Valve Transcatheter Heart Valve Replacement With the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve for Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is
For Patients With a Failing Surgical Bioprosthetic Heart Valve Transcatheter Heart Valve Replacement With the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve for Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is
Superior vena cava stent
 Radiology department Superior vena cava stent Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as superior vena cava (SVC) stent insertion. It explains what is involved and what the benefits
Radiology department Superior vena cava stent Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as superior vena cava (SVC) stent insertion. It explains what is involved and what the benefits
INL No. A0083 Project Medtronic Thoracic patients guide Description Version 18
 INL No. A0083 Project Medtronic Thoracic patients guide Description Version 18 www.inl-agency.com PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Endovascular Stent Grafts: A treatment for Thoracic Aortic disease Table of
INL No. A0083 Project Medtronic Thoracic patients guide Description Version 18 www.inl-agency.com PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Endovascular Stent Grafts: A treatment for Thoracic Aortic disease Table of
Results of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
 I N T E R M E D I AT E O R G R E AT E R R I S K Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is for those who
I N T E R M E D I AT E O R G R E AT E R R I S K Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is for those who
Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease)
 1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options
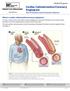 www.hrh.ca Medical Program Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options What is a cardiac catheterization/coronary angiogram? A cardiac catheterization (also called a
www.hrh.ca Medical Program Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options What is a cardiac catheterization/coronary angiogram? A cardiac catheterization (also called a
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) PROOF. Patient Information leaflet. Lancashire Cardiac Centre
 Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) Patient Information leaflet Lancashire Cardiac Centre Welcome to the Lancashire Cardiac Centre During your admission you will be admitted to Ward 37. Ward
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) Patient Information leaflet Lancashire Cardiac Centre Welcome to the Lancashire Cardiac Centre During your admission you will be admitted to Ward 37. Ward
THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM
 THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM 1 A Guide for Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis medtronic.com/tavr Table of Contents 2 3 We have created this booklet to help you learn
THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM 1 A Guide for Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis medtronic.com/tavr Table of Contents 2 3 We have created this booklet to help you learn
Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line) is most often used to deliver medication over a long period. The doctor or nurse inserts
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line) is most often used to deliver medication over a long period. The doctor or nurse inserts
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram
 Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting
 Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Peripheral Vascular Disease Patient Awareness
 Peripheral Vascular Disease Patient Awareness Interventional Radiology: your minimally invasive alternative www.cirse.org Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe Cardiovascular
Peripheral Vascular Disease Patient Awareness Interventional Radiology: your minimally invasive alternative www.cirse.org Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe Cardiovascular
Patient Information Coronary Angiogram
 Patient Information Coronary Angiogram Cardiac Suite Cardiology Department What is a coronary angiogram? A coronary angiogram is an invasive investigation to detect signs of heart disease, such as narrowing
Patient Information Coronary Angiogram Cardiac Suite Cardiology Department What is a coronary angiogram? A coronary angiogram is an invasive investigation to detect signs of heart disease, such as narrowing
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder A Patient s Guide to the Non-Surgical Closure of the Atrial Septal Defect Using the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder System leadership through innovation TM AGA Medical Corporation 5050
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder A Patient s Guide to the Non-Surgical Closure of the Atrial Septal Defect Using the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder System leadership through innovation TM AGA Medical Corporation 5050
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Coronary artery disease and as anticoagulant (inhibiting the clotting of the blood) in patients undergoing surgery to treat blockages
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Coronary artery disease and as anticoagulant (inhibiting the clotting of the blood) in patients undergoing surgery to treat blockages
Femoro-femoral bypass surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Femoro-femoral bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Femoro-femoral bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Carotid and Intracranial Stenosis Angioplasty and Stenting
 Carotid and Intracranial Stenosis Angioplasty and Stenting UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what carotid and intracranial stenosis are about angioplasty and stenting
Carotid and Intracranial Stenosis Angioplasty and Stenting UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what carotid and intracranial stenosis are about angioplasty and stenting
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
 INTERMEDIATE OR GREATER RISK Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is for those who are suffering from
INTERMEDIATE OR GREATER RISK Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve For Patients & Caregivers This patient booklet is for those who are suffering from
all about your heart...
 For a healthy heart If you smoke, stop smoking. Eat lots of fruit and vegetables and less fat. Be more active every day. Be a healthy weight. Relax take time out for yourself. Local contact: For more information
For a healthy heart If you smoke, stop smoking. Eat lots of fruit and vegetables and less fat. Be more active every day. Be a healthy weight. Relax take time out for yourself. Local contact: For more information
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
 Northwestern Memorial Hospital Patient Education TESTS AND PROCEDURES Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) A percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) may be used to treat stenosis (narrowing) of a
Northwestern Memorial Hospital Patient Education TESTS AND PROCEDURES Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) A percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) may be used to treat stenosis (narrowing) of a
You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you.
 Mitral Clip Procedure You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you. 2 Mitral Clip Procedure What is mitral
Mitral Clip Procedure You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you. 2 Mitral Clip Procedure What is mitral
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers
 CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Introduction to Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Ron Blankstein, MD Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers to a combination of methods that can be used to obtain images related to the structure
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Introduction to Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Ron Blankstein, MD Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers to a combination of methods that can be used to obtain images related to the structure
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Learning About. Peripheral Artery Disease
 SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting
 Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting Your Carotid Artery Problem The carotid arteries are blood vessels in the neck that carry blood to the brain. One or both of your carotids is narrowed due to a buildup
Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting Your Carotid Artery Problem The carotid arteries are blood vessels in the neck that carry blood to the brain. One or both of your carotids is narrowed due to a buildup
Dear patient and family,
 The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Division of Interventional Neuroradiology Dear patient and family, Welcome to Johns Hopkins Medicine! Your doctor has referred you to Johns Hopkins Pediatric Interventional
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Division of Interventional Neuroradiology Dear patient and family, Welcome to Johns Hopkins Medicine! Your doctor has referred you to Johns Hopkins Pediatric Interventional
BRING LIVING BACK TO LIFE. An Educational Booklet for Recipients of the Abbott Portico Transcatheter Aortic Valve
 BRING LIVING BACK TO LIFE An Educational Booklet for Recipients of the Abbott Portico Transcatheter Aortic Valve TABLE OF CONTENTS Your role in the management of your health is very important. This information
BRING LIVING BACK TO LIFE An Educational Booklet for Recipients of the Abbott Portico Transcatheter Aortic Valve TABLE OF CONTENTS Your role in the management of your health is very important. This information
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms
 WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
Coronary heart disease
 1 of 9 12/30/2012 10:58 PM PubMed Health. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M.; 2011. Coronary heart disease
1 of 9 12/30/2012 10:58 PM PubMed Health. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M.; 2011. Coronary heart disease
