Radiofrequency Thermal Balloon Coronary Angioplasty : A New Device for Successful Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
|
|
|
- Anabel Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 336 JACC Vol. 23, No. 2 February 1994 : Radiofrequency Thermal Balloon Coronary Angioplasty : A New Device for Successful Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty KATSUHIRO YAMASHITA, MD, SHUTARO SATAKE, MD,* HIROSHI OHIRA, MD, KENICHIRO OHTOMO, MD, Yokohama and Tokyo, Japan angioy Objectives. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of thermal balloon perculanews transluminal coronary pwy using radistrequency energy in the treatment of patients with failed coronary angoplasty and complex lesions. In addition, we evaluated restenosis after radio frequency thermal balloon applications. Background. The efficacy of coronary angioplasty is limited by the relatively low success rate in complex lesions and the high frequency of restenosis. Few reports have studied the combined effects of pressure and laser the energy. This study describes a new device for coronary angioplasty using radiofrequency thermal energy. Methods. Thirty-two patients with failed conventional coronary angioplasty or complex lesions were treated with radiofrequency thermal balloon coronary angioplasty. Radiofrequency energy was delivered up to I I times in exposures ranging from 30 to OD s in duration. This combined effect allowed the vascular wall to be heated to temvratures ranging from 60 to 70 C. Follow-up coronary angiography was performed, on average, 6 months after the procedure. Results. Successful radiofrequency coronary angioplasty was achieved in 28 (82%) of 34 lesions. There was one abrupt coronary artery occlusion (3%) and no death, perforation or dissection. Angiographic restenosis occurred in 14 (56%) of 25 lesions. Conclusions. In patients with failed coronary angioplasty and difficult complex lesions, radiofrequency coronary angioplasty could potentially improve angioplasty success rates and may have important implications for bailout cases with abrupt occlusion. However, restenosis remains a significant problem. (J Am Coll Cordial 1994, ) Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty is an established, effective treatment for coronary vascular disease. However, its overall efficacy is limited by acute occlusion at the angioplasty site (1-4), the relatively low success rate in complex lesions (5-8) and the high frequency of restenosis (9-13). Recent reports of laser hot balloon angioplasty (14) have revealed that thermal treatment with balloon pressure was effective in improving lumen dimensions and arterial dissection caused by conventional balloon angioplasty. However, the restenosis rate has been reported to be higher with this method than with the conventional method. The purpose of this study was to assess whether the combination of radiofrequency thermal energy and low balloon pressure could improve angioplasty success rates and reduce the restenosis rate. From the Cardiovascular Department, Yokohama Red Cross Hospital, Yokohama and *The First Department of Internal of Medicine, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan. Manuscript received December 31, 1992; revised manuscript received August 25, 1993, accepted September 21, Address for corresggildence : Dr. Katsuhiro Yamashita, Cardiovascular Department, Yokohama Red Cross Hospital, 2-85 Negishi-cho, Naka-ku, Yokohama, Japan. (01994 by the American College of Cardiology Methods Between July 1989 and October 1992, radiofrequency balloon coronary angioplasty was performed in 32 patients in medically unstable condition who were referred for elective conventional balloon angioplasty. All patients gave informed consent, and the institutional committee on human research approved the study protocol (July 1989). Twenty patients were treated initially with balloon angioplasty in a conventional manner that required balloon inflation up to 8 atm for 30 to 60 s in the stenotic segment at least twice in each case. Because of inability to achieve an optimal angiographic result with this conventional procedure, radiofrequency thermal balloon coronary angioplasty was performed in these patients immediately after conventional angioplasty (sequential radiofrequency coronary angioplasty group). Five of these 20 patients required a second radiofrequency treatment because of dissection or intimal flaps, as did 15 patients with an insufficient lumen diameter because of initial insufficient balloon dilation and elastic recoil. The remaining 12 patients underwent direct radiofrequency coronary angioplasty without a preceding conventional angioplasty procedure. These patients all had type B lesions as classified by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force (5). A radiofrequency coronary angioplasty balloon catheter (Shutaro Satake Thermal Balloon Catheter, Japan Crescent) /94/$7.00
2 JACC Vol. 23, No. 2 February 1994 : YAMASHaA ET AL. RADIOFREQUENCY THERMAL BALLOON CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY 337 Figure 1. Radiolfrequency balloon angioplasty catheter. This sample balloon is 3 mm in diameter and 20 mm in length. The balloon is made of polyethylene terephthalate. The monopolar electrode is inside the balloon. is similar to a conventional coronary angioplasty balloon catheter except for its radiofrequency components (Fig. it The balloons used ranged in size from 2 to 3.5 mm in diameter and 15 to 20 mm in length, with -,,) 4.3F shaft size. The balloon membrane is made of polyethylene tereplithalate and the shaft is made of polybutylene tereplithalate. A helical monopolar electrode is mounted around the shaft inside the balloon to deliver the radiofrequency energy. To monitor the temperature during radiofrequency energy delivery, a thermocouple sensor is conjoined proximal to the balloon marker. For each dilation attempt, the balloon was filled with saline solution and contrast medium (ioxaglic acid) and inflated to 3 to 6 atm with use of a standard angioplasty inflation device. When the balloon pressure reached the desired range, radiofrequency current (13.56 MHz) (Interbase 7A3000, Japan Crescent) was delivered between the helical electrode inside the balloon and the electric plate positioned on the body surface. The energy was delivered at an output of 10 to 40 W for 30 to 60 s. During radiofrequency energy delivery, the temperature inside the balloon was constantly monitored and maintained between 60 to 70 C by regulating the output of radiofrequency energy. These procedures were performed up to I I times (average 3)/lesion until dilation of the stenosis was achieved. Angioplasty success was defined as a residual stenosis <50% without major complications and restenosis as a diameter stenosis ~t5o%. Percent diameter stenosis was calculated by computerized analysis of cineangiograms. Data are expressed as mean value t I Sr. A comparison between the groups was carried out by repeated measures analysis of variance. When statistical significance was obtained, group comparisons were performed using the Scheffd method. A p value < OR was considered statistically significant. 0"nal ~ (5)!CA LAD (8) (21) Figure 2. Baseline characteristics of coronary artery lesions in 26 patients (28 lesions). Left, Disease type. Middle, Lesion location. Right, Lesion type. A,B,C = types A, B and C lesion characteristics defined by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force. LAD = left anterior descending coronary artery ; RCA = right coronary ute. Primary angiographic success rates. Of the 34 lesions, 28 (82%) were successfully treated with radiofrequency coronary angioplasty. In the sequential radiofrequency angioplasty group, 17 (SV) of 20 patients were successfully treated. A significant reduction (p < 0.05) in mean percent stenosis was found after radiofrequency angioplasty compared with that after conventional angioplasty (Fig. 3). There was one acute occlusion (3%) caused by conventional coronary angioplasty ; it was immediately thermally welded by radiofrequency angioplasty, and success was achieved (Fig. 4). In the direct radiofrequency angioplasty group, It (78%) of 14 patients were successfully treated. Causes of unsuccessful angioplasty. Radiofrequency coronary angioplasty was unsuccessful in 6 of 34 lesions. In five of these six lesions, the residual stenosis ranged from 50% to 75%. There was one major complication entailing an abrupt coronary artery occlusion 8 h after radiofrequency angioplasty despi'e a =`-.L-c!nry initial angiographic result. Rate of rmtenosis. Follow-up angiography, averaging 6 months after radiofreque.-icy coronary angioplasty, was performed in 28 patients (88%) with 30 lesions (88%). The angiographic study indicated that radiofrequency angio- Figure 3. Percent diameter stenosis before and after radiofrequency coronary angioplasty (RFCA). A significant reduction in mean percent stenosis was found immediately after radiofrequency coronary angioplasty compared with that after conventional coronary angioplasty (PTCA). However, loss of the gain in lumen diameter was observed on follow-up angiography. Values presented are mean value ± I SD. Results Patient characteristics. There were 24 men and 8 women, with a mean age of 62 years (range 44 to 80). Of these 32 patients, 2 had 2 lesions, for a total of 34 lesions. Eight patients had a history of restenosis of the lesion of interest after conventional angioplasty. Lesion characteristics are shown in Figure 2. Fifty-six percent of the patients had single-vessel disease, and 62% of the lesions were located in the left anterior descending coronary artery. Seventy-six percent of the lesions were classified as type B. before PTCA after PTCA after RFCA 6 Months after RFCA (n-19)
3 338 YAMASHITA ET AL. JACC Vol. 23, No. 2 RADIOFREQUENCY THERMAL BALLOON CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY February 1994 : complained of severe chest pain or discomfort similar to the severity of angina experienced during conventional balloon inflation. These symptoms were transient, and most patients could tolerate the pain once the temperature was lowered by reducing the level of radiofrequency energy. There was no perforation or dissection. All patients were hemodynamically stable during the procedure, and there were no malignant arrhythmias. However, one patient developed acute myocardial infarction secondary to late (8 h after radiofrequency angioplasty) abrupt coronary reocclusion despite an initial satisfactory angiographic result. Figure 4. Treatment of acute occlusion with radiofrequency coronary angioplasty. Coronary angiography (30 right anterior oblique view) shows severe eccentric stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery (A). During conventional coronary angioplasty, acute occlusion occurred at the treated site (B). Immediately thereafter, a radiofrequency coronary angioplasty balloon was inserted into the coronary vessel, the stenotic site was thermally welded and success was obtained (C). The true lumen was obliterated after radiofrequency angioplasty with six radiofrequency exposures, and reentry occurred, resulting in a marked increase in false lumen diameter. Follow-up angiography after 10 months revealed a patent coronary artery (D). plasty had achieved suboptimal success in 5 (17%) of the 30 lesions and that restenosis had occurred in 14 (56%) of the remaining 25 lesions. All four patients who were not restudied were asymptomatic with an average medication period of 10 months (range 6 to 18). Canplicsitions. The most common complication of the procedure was the development of chest symptoms. Eight (25%) of 32 patients experienced a burning sensation in the chest during radiofrequency energy applications. Others DISCUSS% Thirty-two patients were treated with a radiofrequency thermal balloon catheter. A total primary success rate was achieved in 28 (82%) of 34 lesions. The success rates in the sequential and direct radiofrequency coronary angioplasty groups were 85% and 78%, respectively. Thus, radiofrequency coronary angioplasty appears to be a highly effective treatment compared with conventional coronary angioplasty. It was unsuccessful in 6 of 34 lesions. Residual stenosis in five of these six lesions was <75%. Our results indicate that radiofrequency coronary angioplasty is highly effective for failed conventional coronary angioplasty and complex lesions. One major complication entailed an abrupt occlusion at the angioplasty site, with subsequent myocardial infarction. The lesion was eccentric and moderately angulated (type B) but had been initially successfully treated by direct radiofrequency coronary angioplasty (37% residual stenosis). However, 8 h later, the patient experienced abrupt coronary reocclusion and subsequent myocardial infarction. Anticoagulant therapy usually consisting of 200 to 300 mg/day of ticlopidine or 81 to 243 ing/day of aspirin administered orally before the procedure, and 8,000 to 10,000 U of intraarterial heparin were given at the start of the procedure, followed by 10,000 U of heparin administered intravenously for 24 h after the procedure. However, continuous venous heparin was not administered in this one patient, and the activated partial thromboplastin time was not measured. We speculate that the pathophysiology of abrupt closure in this case was thrombus formation. In our study, 20 patients were successfully treated by radiofrequency coronary angioplasty after unsuccessful treatment with conventional coronary angioplasty at balloon pressures up to 8 atm. When the arterial wall is heated to a temperature >70 C, tissue shrinkage will ordinarily occur (15). However, Lee et al. (16) reported that the stretched vessel wall can be maintained at a constant pressure by an inflated balloon used in combination with radiofrequency energy. Elastic recoil of the arterial wall can therefore be reduced with thermal treatment. This reduction in arterial recoil by radiofrequency coronary angioplasty is one mechanism of improvement. Another mechanism is the increment of plasticity on the vessel wall, which is increased by denaturing protein, which forms an indurated vessel wall.
4 JACC Vol. 23, No. 2 February 1994 : YAMASHITA ET AL RADIOFREQUENCY THERMAL BALLOON CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY These mechanisms entail the application of high frequency energy such that the stenotic area of the vessel can be dilated satisfactorily. Recently, Spears et al. (14) reported that laser balloon angioplasty was an effective procedure in increasing the minimal lumen diameter after conventional coronary angioplasty. A major mechanism of conventional coronary angioplasty is dissection of the arterial wall (17), which may lead to an abrupt closure of the vessel. In the lesions treated with radiofrequency coronary angioplasty, no arterial dissection was visible on angiography. Our results demonstrated that radiofrequency coronary angioplasty is also successful in thermally fusing tissue layers separated by conventional coronary angioplasty. Jenkins et al. (18) and Anand et al. (19) concluded that thermal tissue welding of arterial wall separation occurs at adventitial temperatures >80 C. Although the number of cases was small (Fig. 4), our study also revealed that adventitial temperatures <80 C with pressure can achieve similar effects. Radiofrequency coronary angioplasty could be important for bailout management of abrupt coronary artery occlusion, perhaps because of the uiiique capacitive heating mechanism of heating the vascular wall. This capacitive-type heating mechanism (20) has a more uniform heating effect on the stenotic area of the vessel in contrast to a bipolar radiofrequency thermal balloon, which generates heat convection strictly within the balloon. Our experimental result in a human model demonstrated that there was little thermal difference between the fluid around the shaft inside the balloon and the inner surface of the vessel in contact with the balloon membrane. We kept the temperature around the shaft inside the balloon between 60 and 70 C by regulating the output of radiofrequency wattage such that the temperature of the inner surface of the vessels could be maintained between 60 and 70 C for 30 to 60 s. Our previous investigation, using the external iliac artery of a rabbit, revealed that radiofrequency heating at a temperature of 60 to 70 C at 3 to 6 atm for 60 s created a coagulation necrosis within both the elastic lamina and the smooth muscle cells of the tunica media. The inner surface of the dilated lesions was smooth and showed no visible evidence of intimal tear, dissection or thrombus formation. We studied several frequencies and found that radiofrequency capacitive-type heating could not be produced by using lower frequencies, such as 350 to 700 khz, which were used in the catheter ablation of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Rate of restenosis. In our patients, the restenosis rate was 56%, which was relatively high compared with that of conventional coronary angioplasty (8-13). Several factors have been indicated as increasing the risk of restenosis. Complex coronary lesion morphology (21-23) and the severity of stenosis before coronary angioplasty (21,24,25) have been proposed as significant factors influencing restenosis. Residual stenosis (9,24,25), left anterior descending coronary artery lesions (21,23) and coronary artery dissection (arterial wall trauma) may all be associated with an increased rate of restenosis. Several studies have demonstrated that residual stenosis >30% (9,26) leads to higher percent stenosis immediately after the procedurc. In our patients, residual stenosis averaged 37%. We used relatively undersized balloons to prevent trauma to the vascular wall, a factor (27) that might have correlated with the relatively higher rate of restenosis in our case studies. In a report on the use of laser hot balloons, Spears et al. (14) noted that stenotic tissue was heated to temperatures >85 C in patients with a high rate of restenosis. However, their study revealed that the rate of restenosis was relatively low in patients treated at lower temperatures as compared with the rate in patients treated at higher temperatures. Given this report of lower temperatures with hot balloons, we speculated that lower temperatures might further reduce the restenosis rate. Therefore, we utilized lower temperatures (60 to 70 C) in our study and found that radiofrequency coronary angioplasty at lower temperatures was in fact effective in lowering the restenosis rate. Study limitations and conclusions. Our study has several limitations. The patients in this study were highly selected and most had unsuccessful conventional coronary angioplasty and difficult lesions. Although primary success rates were favorable, patient numbers were small, and follow-up angiography was performed in only 28 patients. Because the profile of the radiofrequency coronary angioplasty balloon is larger than that of the conventional angioplasty balloon, use of the radiofrequency balloon as a primary device for tortuous lesions is limited. Nevertheless, we conclude from our study of radiofrequency coronary angioplasty that many stenotic coronary arteries can be dilated effectively and safely by combining radiofrequency thermal energy with low balloon pressures. References 1. Cowley MJ, Dovros G, Kelsey SF, Van Raden M, Detre KM. Emergency coronary bypass surgery after coronary angioplasty: the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute's Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Registry experience. Am J Cardiol 1984 ;53 :22C-6C. 2. Bredlau CE, Roubin GS, Leimgruber PP, Douglas JS Jr, King SB, Gruentzig AR. In-hospital morbidity and mortality in patdents undergoing elective coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1985 ;72 : Simpfendorfer C, Belardi J, Bellamy G, Galan K, Franco 1, Hollman J. Frequency, management and follow-up of patients with acute coronary occlusions after percutaneous coronary angioplasty. Am J Cardiol 1987 ; 59 : Sinclair IN, McCabe CH. Sipperly ME, Baim DS. Predictors, therapeutic options and long-term outcome of abrupt reclosure. Am J Cardiol 1989 ;61 : Ryan TJ, Faxon DP, Gunner RM, et al. Guidelines for percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty : a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Assessment of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Cardiovascular Procedures (Subcommittee on Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty). J Am Coll Cardiol 1988 ;12:529-45, 6. Meier B, Gruentzig AR, Hollman J, Ischinger T, Bradford JM. Does length or eccentricity of coronary stenoses influence the outcome of transluminal dilatation? Circulation 1983 ;67: Savage MP, Goldberg S, Hirshfeld JW, et al. Clinical and angiographic
5 340 YAMASHITA ET AL. JACC Vol. 23, No. 2 RADIOFREQUENCY THERMAL BALLOON CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY February 1994 : determinants of primary coronary angioplasty success. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991 ;17: Reiber JHC, Serruys PW, Kooijman CJ, et al. Assessment of short-, medium-, and long-term variations in arterial dimensions from computerassisted quantitation of coronary cineangiograms. Circulation 1985 ;71 : Leimguber PP, Roubin GS, Hotlman J, et al. Restenosis after successful coronary angioplasty in patients with single-vessel disease. Circulation 1986 ;73 : Nobuyoshi M, Kimura T, Nosaka H, et al. Restenosis after successful percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty : serial angiographic follow-up of 229 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 1 ;12 : Roubin GS, Douglas JS, King SB, et al. Influence of balloon size on initial success, acute complications, and restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1 ;78: Serruys PW, Lujjten HE, Beatt KJ, et al. Incidence of restenosis after successful coronary angioplasty : a time-related phenomenon. Circulation 1 ;77 : , Ellis SO, Roubin GS, King SB, Douglas JS, Cox WR. Importance of stenosis morphology in the estimation of restenosis risk after elective percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Am J Cardiol 1989 ;63 : Spears JR, Reyes VP, Wynne J, et al. Percutaneous coronary laser balloon angioplasty : initial results of a multicenter experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 1990 ;16: Gorisch W, Boergen KP. Heated induced contraction of blood vessels. Lasers Surg Med 1 2 ;2 : Lee BI, Becker GJ, Waller BF, et al. Thermal compression and molding of atherosclerotic vascular tissue with use of radiofrequency energy: implications for radiofrequency balloon angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol 1 ;13 : Wailer BF. Morphologic correlates of coronary angiographic ; atterns at the site of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Clin Cardiol 1 ;11 : Jenkins RD, Sinclair IN, Anand R, Kalil AG, Schoen FJ, Spears JR. Laser balloon angioplasty : effect of tissue temperature on weld strength of human postmortem intima-media separations. Lasers Surg ivied 1988 ;8 : Anand RK, Sinclair IN, Jenkins RD, Hiehle JF, James L, Spears JR. Laser balloon angioplasty : effect of constant temperature versus constant power on tissue weld strength. Lasers Surg Med 1988 ;8 : Ham S, Hasebe K. Behavior of metal piece placed in capacitive RF current path. In : Overgaard J, editor. Hyperthermic Oncology. London, Philadelphia : Taylor & Francis, 1984 ;1 : Mata LA, Bosch X, David PR, Rapold HJ, Corcos T, Bourassa MG. Clinical and angiographic assessment 6 months after double vessel percutaneous coronaary angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985 :6: Guiteras Val P, Bourassa MG, David PR, et al. Restenosis after successful percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty : the Montreal Heart Institute experience. Am J Cardiol 1987 ;60:50B-5B. 23. Vandormael MG, Deligonul U, Kern MJ, et al. Multilesion coronary angioplasty : clinical and angiographic follow-up. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987 ;10: Holmes DR Jr, Vlietstra RE, Smith HC, et al. Restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) : a report from the PTCA Registry of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Cardiol 1984 ;53 :77C-81C. 25. DiSciascio G, Cowley M, Vetrovec GW. Angiographic patterns of restenosis after angioplasty of multiple coronary arteries. Am J Cardiol 1986 ; 58 : Levine S, Ewels CJ, Rosing DR, Kent KM. Coronary angioplasty : clinical and angiographic follow-up. Am J Cardiol 1985 ;55 : Beatt KJ, Juijte HE, de Feyter PJ, et al. Change in diameter of coronary artery segments adjacent to stenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty : failure of percent diameter stenosis measurement to reflect morphologic changes induced by balloon dilatation. J Am Coll Card :ol19 ;12:15.23.
Intracoronary Serum Smooth Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain Levels Following PTCA may Predict Restenosis
 Clinical Studies Intracoronary Serum Smooth Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain Levels Following PTCA may Predict Restenosis Yasuhiro TSUCHIO,MD,ShigetoNAITO, MD, Akihiko NOGAMI,MD, Hiroshi HOSHIZAKI, MD, ShigeruOSHIMA,
Clinical Studies Intracoronary Serum Smooth Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain Levels Following PTCA may Predict Restenosis Yasuhiro TSUCHIO,MD,ShigetoNAITO, MD, Akihiko NOGAMI,MD, Hiroshi HOSHIZAKI, MD, ShigeruOSHIMA,
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of the Very Proximal Coronary Artery Stenosis
 Original Studies Catheterization and Cardiovascular Diagnosis 1387-92 (1987) Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of the Very Proximal Coronary Artery Stenosis Fred K. Nakhjavan, MD, Anthony
Original Studies Catheterization and Cardiovascular Diagnosis 1387-92 (1987) Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of the Very Proximal Coronary Artery Stenosis Fred K. Nakhjavan, MD, Anthony
Tear or Dissection After Coronary Angioplasty
 1035 Tear or Dissection After Coronary Angioplasty Morphologic Correlates of an Ischemic Complication Alexander J.R. Black, MB, BS, David L. Namay, MD, Alan L. Niederman, MD, Nicholas J. Lembo, MD, Gary
1035 Tear or Dissection After Coronary Angioplasty Morphologic Correlates of an Ischemic Complication Alexander J.R. Black, MB, BS, David L. Namay, MD, Alan L. Niederman, MD, Nicholas J. Lembo, MD, Gary
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of Occluded Coronary Arteries New Angiographic Features Related to Success
 Clinical Studies Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of Occluded Coronary Arteries New Angiographic Features Related to Success Simon M. HORNER, M.A., M.B., B.S., M.R.C.P. SUMMA Percutaneous
Clinical Studies Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty of Occluded Coronary Arteries New Angiographic Features Related to Success Simon M. HORNER, M.A., M.B., B.S., M.R.C.P. SUMMA Percutaneous
Morphological changes after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty of unstable plaques
 European Heart Journal (1996) 17, 1554-1559 orphological changes after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty of unstable plaques Insights from serial angioscopic follow-up C. Bauters, J.-. Lablanche,
European Heart Journal (1996) 17, 1554-1559 orphological changes after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty of unstable plaques Insights from serial angioscopic follow-up C. Bauters, J.-. Lablanche,
analysis demonstrated a large and highly significant reported results suggesting the optimal balloon: artery
 557 Influence of Balloon Size on Initial Success, Acute Complications, and Restenosis After Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty A Prospective Randomized Study Gary S. Roubin, MB, PhD, John S.
557 Influence of Balloon Size on Initial Success, Acute Complications, and Restenosis After Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty A Prospective Randomized Study Gary S. Roubin, MB, PhD, John S.
Restenosis, Reocclusion and Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Successful Balloon Angioplasty of Occluded Versus Nonoccluded Coronary Arteries
 JACC Vol. 27, No. 1 1 January 1996:1-7 CLINICAL STUDIES INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY Restenosis, Reocclusion and Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Successful Balloon Angioplasty of Occluded Versus Nonoccluded
JACC Vol. 27, No. 1 1 January 1996:1-7 CLINICAL STUDIES INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY Restenosis, Reocclusion and Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Successful Balloon Angioplasty of Occluded Versus Nonoccluded
Influence of Planned Six-Month Follow-Up Angiography on Late Outcome After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention A Randomized Study
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 38, No. 4, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01476-0 Influence
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 38, No. 4, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01476-0 Influence
Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis
 1630 JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis SHUNJI KASAOKA, MD, JONATHAN M. TOBIS, MD, FACC, TATSURO AKIYAMA, MD,* BERNHARD REIMERS, MD,* CARLO
1630 JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis SHUNJI KASAOKA, MD, JONATHAN M. TOBIS, MD, FACC, TATSURO AKIYAMA, MD,* BERNHARD REIMERS, MD,* CARLO
Prevention of Coronary Stent Thrombosis and Restenosis
 Prevention of Coronary Stent Thrombosis and Restenosis Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 9/12/03 Coronary
Prevention of Coronary Stent Thrombosis and Restenosis Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 9/12/03 Coronary
Protection of side branch is essential in treating bifurcation lesions: overview
 Angioplasty Summit TCT Asia Pacific Seoul, April 26-28, 2006 Protection of side branch is essential in treating bifurcation lesions: overview Alfredo R Galassi, MD, FACC, FSCAI, FESC Head of the Catetherization
Angioplasty Summit TCT Asia Pacific Seoul, April 26-28, 2006 Protection of side branch is essential in treating bifurcation lesions: overview Alfredo R Galassi, MD, FACC, FSCAI, FESC Head of the Catetherization
Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion
 lacc Vol. 3. NO.3 845 REPORTS ON THERAPY Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion DAVID R. HOLMES, Jr., MD, FACC, RONALD E. VLIETSTRA, MD, FACC, GUY S. REEDER, MD, JOHN F. BRESNAHAN, MD, HUGH C.
lacc Vol. 3. NO.3 845 REPORTS ON THERAPY Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion DAVID R. HOLMES, Jr., MD, FACC, RONALD E. VLIETSTRA, MD, FACC, GUY S. REEDER, MD, JOHN F. BRESNAHAN, MD, HUGH C.
Comparison of Long-term Efficacy of Medical Treatment versus Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) in Single-vessel Disease
 Comparison of Long-term Efficacy of Medical Treatment versus Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) in Single-vessel Disease Shinichiro NISHIYAMA, M.D., Takashi IWASE, M.D., Sugao ISHIWATA,
Comparison of Long-term Efficacy of Medical Treatment versus Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) in Single-vessel Disease Shinichiro NISHIYAMA, M.D., Takashi IWASE, M.D., Sugao ISHIWATA,
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 2, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /00/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 2, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00567-7 Greater
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 2, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00567-7 Greater
Intracoronary Stenting for Acute and Threatened Closure Complicating Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
 96 Intracoronary Stenting for Acute and Threatened Closure Complicating Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Gary S. Roubin, MB, BS, PhD; Adam D. Cannon, MB, BS; Subodh K. Agrawal, MB, BS; Peter
96 Intracoronary Stenting for Acute and Threatened Closure Complicating Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Gary S. Roubin, MB, BS, PhD; Adam D. Cannon, MB, BS; Subodh K. Agrawal, MB, BS; Peter
Gianturco-Roubin Stent Placement
 1126 Major Clinical Events After Coronary Stenting The Multicenter Registry of Acute and Elective Gianturco-Roubin Stent Placement Joseph M. Sutton, MD; Stephen G. Ellis, MD; Gary S. Roubin, MB, PhD; Cass
1126 Major Clinical Events After Coronary Stenting The Multicenter Registry of Acute and Elective Gianturco-Roubin Stent Placement Joseph M. Sutton, MD; Stephen G. Ellis, MD; Gary S. Roubin, MB, PhD; Cass
Distal Coronary Artery Dissection Following Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
 Distal Coronary rtery Dissection Following Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary ngioplasty Douglas. Murphy, M.D., Joseph M. Craver, M.D., and Spencer. King 111, M.D. STRCT The most common cause of acute
Distal Coronary rtery Dissection Following Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary ngioplasty Douglas. Murphy, M.D., Joseph M. Craver, M.D., and Spencer. King 111, M.D. STRCT The most common cause of acute
Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with successful angioplasty and longterm patency result
 DOI 10.7603/s40602-014-0017-x ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.aseanheartjournal.org/ Vol. 22, no. 1, 116 121 (2014) ISSN: 2315-4551 Case Report Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with
DOI 10.7603/s40602-014-0017-x ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.aseanheartjournal.org/ Vol. 22, no. 1, 116 121 (2014) ISSN: 2315-4551 Case Report Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E39-E41 A Case With Successful Retrograde Stent Delivery via AC Branch for Tortuous Right Coronary Artery Yoshiki Uehara, MD, PhD, Mitsuyuki Shimizu, MD, PhD,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E39-E41 A Case With Successful Retrograde Stent Delivery via AC Branch for Tortuous Right Coronary Artery Yoshiki Uehara, MD, PhD, Mitsuyuki Shimizu, MD, PhD,
preliminary clinical experience
 372 BrHeart)' 1994;71:372-377 TECHNIQUE Department of Invasive Cardiology, Royal Brompton National Heart and Lung Hospital, London J S R Gibbs U Sigwart N P Buller Correspondence to: Dr N P Buller, Department
372 BrHeart)' 1994;71:372-377 TECHNIQUE Department of Invasive Cardiology, Royal Brompton National Heart and Lung Hospital, London J S R Gibbs U Sigwart N P Buller Correspondence to: Dr N P Buller, Department
One-year Outcome of Stenting for Long Coronary Lesions, a Prospective Clinical Trial
 Tabriz University of Medical Sciences Original Article One-year Outcome of Stenting for Long Coronary Lesions, a Prospective Clinical Trial Samad Ghaffari MD, Mohammad Reza Hasanian MD, Leili Pourafkari
Tabriz University of Medical Sciences Original Article One-year Outcome of Stenting for Long Coronary Lesions, a Prospective Clinical Trial Samad Ghaffari MD, Mohammad Reza Hasanian MD, Leili Pourafkari
Adjunctive Stent Implantation Following Directional Coronary Atherectomy in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease
 JACC Vol. 32, No. 7 December 1998:1855 60 1855 Adjunctive Stent Implantation Following Directional Coronary Atherectomy in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease EZIO BRAMUCCI, MD,* LUIGI ANGOLI, MD,* PIERA
JACC Vol. 32, No. 7 December 1998:1855 60 1855 Adjunctive Stent Implantation Following Directional Coronary Atherectomy in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease EZIO BRAMUCCI, MD,* LUIGI ANGOLI, MD,* PIERA
Will Bioresorbable Scaffolds Change How We Think About Left Main PCI?
 TCT 2014 13 Sep 2014-17 Sep 2014, Washington, DC - U.S.A Will Bioresorbable Scaffolds Change How We Think About Left Main PCI? Robert-Jan van Geuns, MD, PhD Professor of Interventional Cardiology, Thoraxcenter,
TCT 2014 13 Sep 2014-17 Sep 2014, Washington, DC - U.S.A Will Bioresorbable Scaffolds Change How We Think About Left Main PCI? Robert-Jan van Geuns, MD, PhD Professor of Interventional Cardiology, Thoraxcenter,
Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion: Experience in 76 Consecutive Patients
 526 JACC Vol. 6, No.3 Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion: Experience in 76 Consecutive Patients DEAN J. KEREAKES, MD, MATTHEW R. SELMON, MD, BRUCE J, McAULEY, MD, DAVD B. McAULEY, MD, MPH,
526 JACC Vol. 6, No.3 Angioplasty in Total Coronary Artery Occlusion: Experience in 76 Consecutive Patients DEAN J. KEREAKES, MD, MATTHEW R. SELMON, MD, BRUCE J, McAULEY, MD, DAVD B. McAULEY, MD, MPH,
Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases
 Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases Satoru Sumituji,M.D. Rinku General Medical Center IVUS is can provide images of the vessel wall and the tissue around the vessel which cannot be viewed by angiography.
Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases Satoru Sumituji,M.D. Rinku General Medical Center IVUS is can provide images of the vessel wall and the tissue around the vessel which cannot be viewed by angiography.
Artery Stenting for Failed Percutaneous
 812 Emergent Use of Balloon-Expandable Coronary Artery Stenting for Failed Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Howard C. Herrmann, MD; Maurice Buchbinder, MD; Michael W. Clemen, MD; David Fischman,
812 Emergent Use of Balloon-Expandable Coronary Artery Stenting for Failed Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Howard C. Herrmann, MD; Maurice Buchbinder, MD; Michael W. Clemen, MD; David Fischman,
Outcome of Coronary Bypass Surgery Versus Coronary Angioplasty in Diabetic Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease
 10 CLINICAL STUDIES JACC Vol. 31, No. 1 INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY Outcome of Coronary Bypass Surgery Versus Coronary Angioplasty in Diabetic Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease WILLIAM S.
10 CLINICAL STUDIES JACC Vol. 31, No. 1 INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY Outcome of Coronary Bypass Surgery Versus Coronary Angioplasty in Diabetic Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease WILLIAM S.
Coronary Artery Dissection Following Angioplasty Evaluated by Fractional Flow Reserve: Report of Three Cases
 J Cardiol 2001 Dec; 386: 337 342 : 3 Coronary Artery Dissection Following Angioplasty Evaluated by Fractional Flow Reserve: Report of Three Cases Kazutaka AMAYA, MD Kenji TAKAZAWA, MD, FJCC Nobuhiro TANAKA,
J Cardiol 2001 Dec; 386: 337 342 : 3 Coronary Artery Dissection Following Angioplasty Evaluated by Fractional Flow Reserve: Report of Three Cases Kazutaka AMAYA, MD Kenji TAKAZAWA, MD, FJCC Nobuhiro TANAKA,
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial
 Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts and Future Directions
 REVIEW DOI 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.53 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright 2011 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts
REVIEW DOI 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.53 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright 2011 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts
Coronary Aneurysms After Stent Placement: A Suggestion of Altered Vessel Wall Healing in the Presence of Anti-inflammatory Agents
 1524 JACC Vol. 18,. 6 Coronary Aneurysms After Stent Placement: A Suggestion of Altered Vessel Wall Healing in the Presence of Anti-inflammatory Agents S. TANVEER RAB, MD, FACC,* SPENCER B. KING III, MD,
1524 JACC Vol. 18,. 6 Coronary Aneurysms After Stent Placement: A Suggestion of Altered Vessel Wall Healing in the Presence of Anti-inflammatory Agents S. TANVEER RAB, MD, FACC,* SPENCER B. KING III, MD,
The New England Journal of Medicine CORONARY-ARTERY STENTING COMPARED WITH BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR RESTENOSIS AFTER INITIAL BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY
 CORONARY-ARTERY STENTING COMPARED WITH BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR RESTENOSIS AFTER INITIAL BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY RAIMUND ERBEL, M.D., MICHAEL HAUDE, M.D., HANS W. HÖPP, M.D., DAMIAN FRANZEN, M.D., HANS JÜRGEN
CORONARY-ARTERY STENTING COMPARED WITH BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR RESTENOSIS AFTER INITIAL BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY RAIMUND ERBEL, M.D., MICHAEL HAUDE, M.D., HANS W. HÖPP, M.D., DAMIAN FRANZEN, M.D., HANS JÜRGEN
Multicenter Study of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty for Right Coronary Artery Ostial Stenosis
 1214 JACC Vol. 9, No.6 Multicenter Study of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty for Right Coronary Artery Ostial Stenosis ERC J. TOPOL, MD, FACC,* STEPHEN G. ELLS, MD,* JOD FSHMAN, RN, MS,:j: PERRE LEMGRUBER,
1214 JACC Vol. 9, No.6 Multicenter Study of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty for Right Coronary Artery Ostial Stenosis ERC J. TOPOL, MD, FACC,* STEPHEN G. ELLS, MD,* JOD FSHMAN, RN, MS,:j: PERRE LEMGRUBER,
Time Course of Restenosis During the First Year After Emergency Coronary Stenting
 1498 Time Course of Restenosis During the First Year After Emergency Coronary Stenting Adnan Kastrati, MD; Albert Schomig, MD; Rainer Dietz, MD; Franz-Josef Neumann, MD; and Gert Richardt, MD Background.
1498 Time Course of Restenosis During the First Year After Emergency Coronary Stenting Adnan Kastrati, MD; Albert Schomig, MD; Rainer Dietz, MD; Franz-Josef Neumann, MD; and Gert Richardt, MD Background.
Endovascular beta-irradiation with a liquid 188 Re-filled balloon to reduce restenosis after coronary angioplasty.
 Endovascular beta-irradiation with a liquid 188 Re-filled balloon to reduce restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Peix A., Llerena L., Ponce F., López A., López L., Guerrero I., Cabrera L.O., Maltas A.M.,
Endovascular beta-irradiation with a liquid 188 Re-filled balloon to reduce restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Peix A., Llerena L., Ponce F., López A., López L., Guerrero I., Cabrera L.O., Maltas A.M.,
Role of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in the treatment of patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: a review
 224 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 84 April 1991 Role of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in the treatment of patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: a review
224 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 84 April 1991 Role of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in the treatment of patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: a review
THE CURRENT SITUATION AND FUTURE OF THE PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION FOR ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROM IN RUSSIAN FEDERATION
 : 616.127-005.8 -..,.. -...,, ( ), 2011, 581 182. 195 592 ( ) 385 590 -. 4,3 % 8,8 % ( ). 2011 62 329,, 24 931 (40 %) -. : - - ; ; 70 % ST ( ST); ST - 24. : ST,. THE CURRENT SITUATION AND FUTURE OF THE
: 616.127-005.8 -..,.. -...,, ( ), 2011, 581 182. 195 592 ( ) 385 590 -. 4,3 % 8,8 % ( ). 2011 62 329,, 24 931 (40 %) -. : - - ; ; 70 % ST ( ST); ST - 24. : ST,. THE CURRENT SITUATION AND FUTURE OF THE
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF PTCA IN THE TREATMENT OF CORONARY TOTAL OCCLUSION
 PAKISTAN HEART JOURNAL VOL. 34 No. 1-4 JAN-DEC 2001 SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF PTCA IN THE TREATMENT OF CORONARY TOTAL OCCLUSION SUMMARY AFSAR RAZA* Background: In recent years several centers have published
PAKISTAN HEART JOURNAL VOL. 34 No. 1-4 JAN-DEC 2001 SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF PTCA IN THE TREATMENT OF CORONARY TOTAL OCCLUSION SUMMARY AFSAR RAZA* Background: In recent years several centers have published
Angiographic and histologic consequences of laser thermal angioplasty: comparison with balloon angioplasty
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION PERPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Angiographic and histologic consequences of laser thermal angioplasty: comparison with balloon angioplasty TIMOTHY A. SANBORN, M.D., CHRISTIAN C. HAUDENSCHILD,
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION PERPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Angiographic and histologic consequences of laser thermal angioplasty: comparison with balloon angioplasty TIMOTHY A. SANBORN, M.D., CHRISTIAN C. HAUDENSCHILD,
Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System
 Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
Innovation by design. Technology that sets a new standard
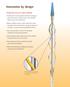 Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
Accurate characterization of the degree of risk
 Angiographic Characterization of Lesion Morphology Are the AHA/ACC and SCAI lesion classifications still useful? BY LLOYD W. KLEIN, MD, AND RONALD J. KRONE, MD Accurate characterization of the degree of
Angiographic Characterization of Lesion Morphology Are the AHA/ACC and SCAI lesion classifications still useful? BY LLOYD W. KLEIN, MD, AND RONALD J. KRONE, MD Accurate characterization of the degree of
Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered Stent Implantation
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 212851, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/212851 Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 212851, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/212851 Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered
NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
Coronary artery stenting in unstable angina pectoris: a comparison with stable angina pectoris
 Heart 1999;81:393 397 393 Coronary artery stenting in unstable angina pectoris: a comparison with stable angina pectoris P B M Clarkson, M Halim, K K Ray, S Doshi, M Been, H Singh, M F Shiu Department
Heart 1999;81:393 397 393 Coronary artery stenting in unstable angina pectoris: a comparison with stable angina pectoris P B M Clarkson, M Halim, K K Ray, S Doshi, M Been, H Singh, M F Shiu Department
RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
866 JACC gol. 25, No. 4 March 15, 1995:866-70
 866 JACC gol. 25, No. 4 Stent Implantation of Saphenous Vein Graft Aorto-Ostial Lesions in Patients With Unstable Ischemic Syndromes: Immediate Angiographic Results and Long-Term Clinical Outcome ELDAD
866 JACC gol. 25, No. 4 Stent Implantation of Saphenous Vein Graft Aorto-Ostial Lesions in Patients With Unstable Ischemic Syndromes: Immediate Angiographic Results and Long-Term Clinical Outcome ELDAD
Percutanous revascularization of chronic total occlusion of diabetic patients at Iraqi center for heart diseases, a single center experience 2012
 www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2015; 2(2):76-82 Percutanous revascularization of chronic total occlusion of diabetic patients at Iraqi center for heart diseases, a single center experience 2012
www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2015; 2(2):76-82 Percutanous revascularization of chronic total occlusion of diabetic patients at Iraqi center for heart diseases, a single center experience 2012
Current Non-Surgical Cardiac Interventions. By Pam Bayles, RN, BSN
 Current Non-Surgical Cardiac Interventions By Pam Bayles, RN, BSN Balloon Angioplasty & DES A balloon-tipped catheter was first used in 1964 to treat a cause of atherosclerotic disease in a patient s leg
Current Non-Surgical Cardiac Interventions By Pam Bayles, RN, BSN Balloon Angioplasty & DES A balloon-tipped catheter was first used in 1964 to treat a cause of atherosclerotic disease in a patient s leg
REBEL. Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
Sex dilferences in early and long-term results of
 THERPY ND PREVENTION PTC Sex dilferences in early and long-term results of coronary angioplasty in the NHLI PTC Registry MICHEL J. COWLEY, M.D., SUZNNE M. MULLIN, RN., M.P.H., SHERYL F. KELSEY, PH.D.,
THERPY ND PREVENTION PTC Sex dilferences in early and long-term results of coronary angioplasty in the NHLI PTC Registry MICHEL J. COWLEY, M.D., SUZNNE M. MULLIN, RN., M.P.H., SHERYL F. KELSEY, PH.D.,
Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING
 Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING 1 2013 Spectranetics. All Rights Reserved. Approved for External
Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING 1 2013 Spectranetics. All Rights Reserved. Approved for External
Formation of and countermeasures for subacute coronary stent thrombosis in elderly diabetic patients
 Formation of and countermeasures for subacute coronary stent thrombosis in elderly diabetic patients Z.-F. Li 1, Y.-P. Zhang 2, Z.-Q. Qin 2, X.-L. Li 1, C.-H. Gao 1, S. Yang 1 and Z.-J. Chen 1 1 Department
Formation of and countermeasures for subacute coronary stent thrombosis in elderly diabetic patients Z.-F. Li 1, Y.-P. Zhang 2, Z.-Q. Qin 2, X.-L. Li 1, C.-H. Gao 1, S. Yang 1 and Z.-J. Chen 1 1 Department
PCI TO CHRONIC TOTAL OCCLUSION, LIAQUAT NATIONAL HOSPITAL EXPERINCE
 SUMMARY PCI TO CHRONIC TOTAL OCCLUSION, LIAQUAT NATIONAL HOSPITAL EXPERINCE INTRODUCTION GHAZALA IRFAN*, MANSOOR AHMAD**, DAD JAN BALOCH @, ABDUL RASHEED @@ BACKGROUND PCI of chronic total occlusion represents
SUMMARY PCI TO CHRONIC TOTAL OCCLUSION, LIAQUAT NATIONAL HOSPITAL EXPERINCE INTRODUCTION GHAZALA IRFAN*, MANSOOR AHMAD**, DAD JAN BALOCH @, ABDUL RASHEED @@ BACKGROUND PCI of chronic total occlusion represents
Contemporary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Versus Balloon Angioplasty for Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease
 Contemporary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Versus Balloon Angioplasty for Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease A Comparison of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Dynamic Registry and the
Contemporary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Versus Balloon Angioplasty for Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease A Comparison of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Dynamic Registry and the
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention?
 Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta
 389 Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta L. LUANN MINICH, MD, ROBERT H. BEEKMAN Ill, MD, FACC, ALBERT P. ROCCHINI, MD, KATHLEEN
389 Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta L. LUANN MINICH, MD, ROBERT H. BEEKMAN Ill, MD, FACC, ALBERT P. ROCCHINI, MD, KATHLEEN
In-hospital morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing elective coronary angioplasty
 THERAPY AND PREVENTION PTCA In-hospital morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing elective coronary angioplasty CLAYTON E. BREDLAU, M.D., GARY S. ROUBIN, M.B., PH.D., PIERRE P. LEIMGRUBER, M.D., JOHN
THERAPY AND PREVENTION PTCA In-hospital morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing elective coronary angioplasty CLAYTON E. BREDLAU, M.D., GARY S. ROUBIN, M.B., PH.D., PIERRE P. LEIMGRUBER, M.D., JOHN
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /00/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 5, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00546-5 CLINICAL
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 5, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00546-5 CLINICAL
Acute Biological Response to Laser Balloon Angioplasty in the At herosclerotic Rabbit
 Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 14:7-12 (1994) Acute Biological Response to Laser Balloon Angioplasty in the At herosclerotic Rabbit Dimitrios Alexopoulos, MD, FACC, FESC, Timothy A. Sanborn, MD, FACC,
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 14:7-12 (1994) Acute Biological Response to Laser Balloon Angioplasty in the At herosclerotic Rabbit Dimitrios Alexopoulos, MD, FACC, FESC, Timothy A. Sanborn, MD, FACC,
Coronary Plaque Sealing: The DEFER Study and more...
 Coronary Plaque Sealing: The DEFER Study and more... How Waiting Can Be Beneficial in Stable Coronary Artery Disease Patients ESC, Stockholm, 2005 M. Romanens, 21.09.2005 at www.kardiolab.ch DEFER Study:
Coronary Plaque Sealing: The DEFER Study and more... How Waiting Can Be Beneficial in Stable Coronary Artery Disease Patients ESC, Stockholm, 2005 M. Romanens, 21.09.2005 at www.kardiolab.ch DEFER Study:
Transcoronary Chemical Ablation of Atrioventricular Conduction
 757 Transcoronary Chemical Ablation of Atrioventricular Conduction Pedro Brugada, MD, Hans de Swart, MD, Joep Smeets, MD, and Hein J.J. Wellens, MD In seven patients with symptomatic atrial fibrillation
757 Transcoronary Chemical Ablation of Atrioventricular Conduction Pedro Brugada, MD, Hans de Swart, MD, Joep Smeets, MD, and Hein J.J. Wellens, MD In seven patients with symptomatic atrial fibrillation
Predictors of 6-Month Angiographic Restenosis inside Bare-Metal Stent in Chinese Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2009;25:1 6 Coronary Artery Disease Predictors of 6-Month Angiographic Restenosis inside Bare-Metal Stent in Chinese Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Yung-Lung Chen,
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2009;25:1 6 Coronary Artery Disease Predictors of 6-Month Angiographic Restenosis inside Bare-Metal Stent in Chinese Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Yung-Lung Chen,
Original Research Article. S. Praveen 1, Baiju R. 1 *, V. V. Radhakrishnan 1, Sarosh Kumar K. K. 2
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Praveen S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Feb;6(2):448-454 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20180029
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Praveen S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Feb;6(2):448-454 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20180029
Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries. Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL
 Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Definition: transcatheter opening of
Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Definition: transcatheter opening of
Pathology. The exact mechanism by which balloon dilatation relieves stenosis is poorly understood. The atherosclerotic
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1987) 63, 327-335 Review Article Coronary angioplasty I.C. Cooper, M. Signy, M.M. Webb-Peploe and D.J. Coltart Department of Cardiology, St Thomas' Hospital, Lambeth Palace
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1987) 63, 327-335 Review Article Coronary angioplasty I.C. Cooper, M. Signy, M.M. Webb-Peploe and D.J. Coltart Department of Cardiology, St Thomas' Hospital, Lambeth Palace
Stenting In Small Coronary Arteries (SISCA) Trial A Randomized Comparison Between Balloon Angioplasty and the Heparin-Coated bestent
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 38, No. 6, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01602-3 Stenting
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 38, No. 6, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01602-3 Stenting
Optimal Coronary Balloon Angioplasty With Provisional Stenting Versus Primary Stent (OCBAS)
 1351 Optimal Coronary Balloon Angioplasty With Provisional Stenting Versus Primary Stent (OCBAS) Immediate and Long-Term Follow-up Results ALFREDO RODRÍGUEZ, MD, PHD, FACC,* FRANCISCO AYALA, MD,* VICTOR
1351 Optimal Coronary Balloon Angioplasty With Provisional Stenting Versus Primary Stent (OCBAS) Immediate and Long-Term Follow-up Results ALFREDO RODRÍGUEZ, MD, PHD, FACC,* FRANCISCO AYALA, MD,* VICTOR
Current PTCA practice and clinical outcomes in the Netherlands: the real world in the pre-drug-eluting stent era
 3 Current PTCA practice and clinical outcomes in the Netherlands: the real world in the pre-drug-eluting stent era Pascalle S. Monraats, Willem R.P. Agema, Aeilko H. Zwinderman, Robbert J. de Winter, René
3 Current PTCA practice and clinical outcomes in the Netherlands: the real world in the pre-drug-eluting stent era Pascalle S. Monraats, Willem R.P. Agema, Aeilko H. Zwinderman, Robbert J. de Winter, René
Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction
 lacc ol. 16. No.4 807 Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Severe Left entricular Dysfunction AND S. KOHL, MD, DM, GMANO DSCASCO, MD, FACC, MCHAL J. COWLY, MD, FACC, AMA NATH, MD, FACC, LYN GOUDAU, MD,
lacc ol. 16. No.4 807 Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Severe Left entricular Dysfunction AND S. KOHL, MD, DM, GMANO DSCASCO, MD, FACC, MCHAL J. COWLY, MD, FACC, AMA NATH, MD, FACC, LYN GOUDAU, MD,
The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Acute and Late Clinical Outcomes Following Coronary Stent Implantation
 584 JACC Vol. 32, No. 3 The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Acute and Late Clinical Outcomes Following Coronary Stent Implantation ALEXANDRE ABIZAID, MD, RAN KORNOWSKI, MD, GARY S. MINTZ, MD, FACC, MUN
584 JACC Vol. 32, No. 3 The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Acute and Late Clinical Outcomes Following Coronary Stent Implantation ALEXANDRE ABIZAID, MD, RAN KORNOWSKI, MD, GARY S. MINTZ, MD, FACC, MUN
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 4, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /00/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 4, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00639-7 Immediate
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 35, No. 4, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00639-7 Immediate
MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION
 MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION C. Graidis, D. Dimitriadis, A. Ntatsios, V. Karasavvides Euromedica Kyanous Stavros, Thessaloniki.
MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION C. Graidis, D. Dimitriadis, A. Ntatsios, V. Karasavvides Euromedica Kyanous Stavros, Thessaloniki.
Angioplasty remains the most common method
 When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart
 Prognostic Value of the Modified American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Stenosis Morphology Classification for Long-Term Angiographic and Clinical Outcome After Coronary Stent Placement
Prognostic Value of the Modified American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Stenosis Morphology Classification for Long-Term Angiographic and Clinical Outcome After Coronary Stent Placement
PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis
 PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis Why do you hesitate PCI for LAD ostial stenosis? LAD Ostial Lesion Limitations of PCI High elastic recoil Involvement of the distal left main coronary
PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis Why do you hesitate PCI for LAD ostial stenosis? LAD Ostial Lesion Limitations of PCI High elastic recoil Involvement of the distal left main coronary
Subject Review. Advances in Interventional Cardiology
 Subject Review Advances in Interventional Cardiology DAVID R. HOLMES, Jr., M.D., RONALD E. VLIETSTRA, M.B.,Ch.B.,* STEVEN J. REITER, M.D.,t DENNIS R. BRESNAHAN, M.D.,i Division of Cardiovascular Diseases
Subject Review Advances in Interventional Cardiology DAVID R. HOLMES, Jr., M.D., RONALD E. VLIETSTRA, M.B.,Ch.B.,* STEVEN J. REITER, M.D.,t DENNIS R. BRESNAHAN, M.D.,i Division of Cardiovascular Diseases
Comparative Results of Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Dynamic Versus Fixed Coronary Stenosis
 0 lacc Vol. 8, No.3 September 1986:0-8 Comparative Results of Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Dynamic Versus Fixed Coronary Stenosis MCHEL E. BERTRAND, MD, FACC, JEAN M.
0 lacc Vol. 8, No.3 September 1986:0-8 Comparative Results of Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty in Patients With Dynamic Versus Fixed Coronary Stenosis MCHEL E. BERTRAND, MD, FACC, JEAN M.
Stent Thrombosis in Bifurcation Stenting
 Summit TCT Asia Pacific 2009 Stent Thrombosis in Bifurcation Stenting Associate Professor Tan Huay Cheem MBBS, M Med(Int Med), MRCP, FRCP(UK), FAMS, FACC, FSCAI Director, National University Heart Centre,
Summit TCT Asia Pacific 2009 Stent Thrombosis in Bifurcation Stenting Associate Professor Tan Huay Cheem MBBS, M Med(Int Med), MRCP, FRCP(UK), FAMS, FACC, FSCAI Director, National University Heart Centre,
Stent Trials in Acute Myocardial Infarction
 IAGS 1998 Proceedings Stent Trials in Acute Myocardial Infarction Alfredo Rodríguez MD, PhD Primary angioplasty in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction has been demonstrated to reduce in-hospital
IAGS 1998 Proceedings Stent Trials in Acute Myocardial Infarction Alfredo Rodríguez MD, PhD Primary angioplasty in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction has been demonstrated to reduce in-hospital
Safety and Efficacy of Angioplasty with Intracoronary Stenting in Patients with Unstable Coronary Syndromes. Comparison with Stable Coronary Syndromes
 Original Article Safety and Efficacy of Angioplasty with Intracoronary Stenting in Patients with Unstable Coronary Syndromes. Comparison with Stable Coronary Syndromes Luís C. L. Correia, José Carlos Brito,
Original Article Safety and Efficacy of Angioplasty with Intracoronary Stenting in Patients with Unstable Coronary Syndromes. Comparison with Stable Coronary Syndromes Luís C. L. Correia, José Carlos Brito,
Anthony Main 1, William L. Lombardi 2, Jacqueline Saw 3. Introduction. Case presentation
 Case Report Cutting balloon angioplasty for treatment of spontaneous coronary artery dissection: case report, literature review, and recommended technical approaches Anthony Main 1, William L. Lombardi
Case Report Cutting balloon angioplasty for treatment of spontaneous coronary artery dissection: case report, literature review, and recommended technical approaches Anthony Main 1, William L. Lombardi
Safety and Efficacy of Coronary Stent Implantation. Acute and Six Month Outcomes of 1,126 Consecutive Patients Treated in 1996 and 1997
 Original Article Safety and Efficacy of Coronary Stent Implantation. Acute and Six Month Outcomes of 1,126 Consecutive Patients Treated in 1996 and 1997 Luiz Alberto Mattos, Ibraim Pinto, Alexandre Abizaid,
Original Article Safety and Efficacy of Coronary Stent Implantation. Acute and Six Month Outcomes of 1,126 Consecutive Patients Treated in 1996 and 1997 Luiz Alberto Mattos, Ibraim Pinto, Alexandre Abizaid,
Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in
 Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in in-progress Department of Cardiology, Hideo Tamai, M.D. Metallic stents... Background induce a varing degree of thrombogenesis eg, subacute thrombosis in complex
Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in in-progress Department of Cardiology, Hideo Tamai, M.D. Metallic stents... Background induce a varing degree of thrombogenesis eg, subacute thrombosis in complex
Role of New Devices for Angioplasty in the Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery
 J Cardiol 21 Nov; 38 5 : 245 253 Role of New Devices for Angioplasty in the Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Kunihiko Hideo Eisho Tatsuhiko Masaharu Takuji Shinya Hidenori Takafumi Shinsaku Seiichiro
J Cardiol 21 Nov; 38 5 : 245 253 Role of New Devices for Angioplasty in the Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Kunihiko Hideo Eisho Tatsuhiko Masaharu Takuji Shinya Hidenori Takafumi Shinsaku Seiichiro
The New England Journal of Medicine INTRAVASCULAR GAMMA RADIATION FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS IN SAPHENOUS-VEIN BYPASS GRAFTS
 INTRAVASCULAR GAMMA RADIATION FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS IN SAPHENOUS-VEIN BYPASS GRAFTS RON WAKSMAN, M.D., ANDREW E. AJANI, M.D., R. LARRY WHITE, M.D., ROSANNA C. CHAN, M.D., LOWELL F. SATLER, M.D., KENNETH
INTRAVASCULAR GAMMA RADIATION FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS IN SAPHENOUS-VEIN BYPASS GRAFTS RON WAKSMAN, M.D., ANDREW E. AJANI, M.D., R. LARRY WHITE, M.D., ROSANNA C. CHAN, M.D., LOWELL F. SATLER, M.D., KENNETH
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 55, No. 9, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /10/$36.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 55, No. 9, 2010 2010 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/10/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.09.052
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 55, No. 9, 2010 2010 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/10/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.09.052
Bifurcation stenting with BVS
 Bifurcation stenting with BVS Breaking the limits or just breaking the struts? Maciej Lesiak Department of Cardiology University Hospital in Poznan, Poland Disclosure Speaker s name: Maciej Lesiak I have
Bifurcation stenting with BVS Breaking the limits or just breaking the struts? Maciej Lesiak Department of Cardiology University Hospital in Poznan, Poland Disclosure Speaker s name: Maciej Lesiak I have
Percutaneous Revascularization of Ostial Saphenous Vein Graft Stenoses
 JACC Vol. 26, No. 4 955 October 1995:955-60 Percutaneous Revascularization of Ostial Saphenous Vein Graft Stenoses ALAA E. ABDEL-MEGUID, MD, PI-ID, FACC, PATRICK L. WHITLOW, MD, FACC, CONRAD SIMPFENDORFER,
JACC Vol. 26, No. 4 955 October 1995:955-60 Percutaneous Revascularization of Ostial Saphenous Vein Graft Stenoses ALAA E. ABDEL-MEGUID, MD, PI-ID, FACC, PATRICK L. WHITLOW, MD, FACC, CONRAD SIMPFENDORFER,
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /05/$30.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 5, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.06.009
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 5, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.06.009
SAMMPRIS. Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis. Khalil Zahra, M.D
 SAMMPRIS Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis Khalil Zahra, M.D Major points Patients with recent TIA or stroke and intra-cranial artery
SAMMPRIS Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis Khalil Zahra, M.D Major points Patients with recent TIA or stroke and intra-cranial artery
Resolute in Bifurcation Lesions: Data from the RESOLUTE Clinical Program
 Resolute in Bifurcation Lesions: Data from the RESOLUTE Clinical Program Prof. Ran Kornowski, MD, FESC, FACC Director - Division of Interventional Cardiology Rabin Medical Center and Tel Aviv University,
Resolute in Bifurcation Lesions: Data from the RESOLUTE Clinical Program Prof. Ran Kornowski, MD, FESC, FACC Director - Division of Interventional Cardiology Rabin Medical Center and Tel Aviv University,
Stent For An Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysm Of The Left Main Coronary Artery Tatsuya Amano* and Sunao Nakamura
 Journal of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine Casereport A Case of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Using A Polytetrafluorethylene-Covered Stent For An Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysm Of The Left Main Coronary
Journal of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine Casereport A Case of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Using A Polytetrafluorethylene-Covered Stent For An Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysm Of The Left Main Coronary
Percutaneous Coronary Interventions Without On-site Cardiac Surgery
 Percutaneous Coronary Interventions Without On-site Cardiac Surgery Hassan Al Zammar, MD,FESC Consultant & Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiology Department European Gaza Hospital Palestine European
Percutaneous Coronary Interventions Without On-site Cardiac Surgery Hassan Al Zammar, MD,FESC Consultant & Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiology Department European Gaza Hospital Palestine European
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions. Body and Disease 2011
 Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access
 Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
DEB experience in Gachon Universtiy Gil Hospital (in ISR) Soon Yong Suh MD., PhD. Heart Center Gachon University Gil Hospital Seoul, Korea.
 DEB experience in Gachon Universtiy Gil Hospital (in ISR) Soon Yong Suh MD., PhD. Heart Center Gachon University Gil Hospital Seoul, Korea. In-stent restenosis (ISR) Remains important issue even in the
DEB experience in Gachon Universtiy Gil Hospital (in ISR) Soon Yong Suh MD., PhD. Heart Center Gachon University Gil Hospital Seoul, Korea. In-stent restenosis (ISR) Remains important issue even in the
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 34, No. 4, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /99/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00324-1 Final
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00324-1 Final
A Case of Recoiling of Everolimus - eluting Stent at the Ostium of the Right Coronary Artery by Out - stent Plaque Progression
 Jikeikai Med J 2016 ; 63 : 71-6 Case Report A Case of Recoiling of Everolimus - eluting Stent at the Ostium of the Right Coronary Artery by Out - stent Plaque Progression Haruka Kimura, Tetsuya Ishikawa,
Jikeikai Med J 2016 ; 63 : 71-6 Case Report A Case of Recoiling of Everolimus - eluting Stent at the Ostium of the Right Coronary Artery by Out - stent Plaque Progression Haruka Kimura, Tetsuya Ishikawa,
