4 introduction. morbidity & mortality. ckd. volume. one. page e78
|
|
|
- Ami Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 chapter FOUR morbidity & mortality The day is short, the hour long. Motionless I retrace its steps, climbing its minor calvaries, I descend on stairs made of air, and am lost in transparent ' BML R LB KC and I don t see you. Octavio Paz, A Song Out of Tune translated from the Spanish by Eliot Weinberger e77
2 21 usrds annual data report volume one ckd e78 Assessing morbidity in patients with chronic kidney disease requires longitudinal data from a defined population, with relatively complete information on all-cause and cause-specific hospitalization. Such data are rarely available on a random sample of the U.S. population, since it is very difficult to track patients across multiple insurers. Health plan datasets from Medicare and from employer group health plans (EGHPs), however, can capture information well, particularly over a one-year period, and they provide a unique opportunity to assess morbidity. In this chapter we use data from three insurers which represent large populations. Medicare data, for instance, cover 95 percent of individuals age 65 and older. We also employ the Thomson Rueters MarketScan dataset and the Ingenix i3 LabRx dataset, both from large EGHPs. MarketScan data cover health plan expenditure claims for employers that are approximately 8 percent selfinsured, compared to just 2 percent in the Ingenix i3 data. For each dataset we use diagnosis codes to define CKD during a one-year entry period, noting hospitalizations and services in the one-year follow-up period. Because increasing recognition of CKD can create biases in the data, with a potentially lower disease burden in patients diagnosed earlier in the course of their disease, we have added information on comorbidity and disease severity. On the next, for example, we examine hospitalization rates in Medicare and MarketScan patients with and without CKD. Unadjusted rates in the CKD population reflecting its total disease burden are 3 5 times those of non-ckd patients. Once adjustments have been added for gender, prior hospitalizations, and comorbidity, rates for CKD patients are 1. times higher. This illustrates the net impact of CKD if the populations were to have similar comorbidity and severity of disease. CKD patients, however, carry a heavy burden of cardiovascular disease, which adjustments cannot fully address since CVD interacts so strongly with CKD itself. Hospitalization rates vary with comorbidity, and interact with degrees of CKD. Adjusted rates are 38 percent higher in Medicare CKD patients than in patients without the disease, 19 percent greater in patients with Stage 3 5 CKD than in those with CKD of Stages 1 2, and 2 percent higher in Stage 1 2 patients than in non-ckd patients illustrating the graded impact of advancing kidney disease. Not surprisingly, rates of cardiovascular hospitalization are greater for CKD patients, particularly those in more advanced stages of the disease. Both the CKD and non-ckd populations, however, have experienced a similar decline in adjusted mortality rates over the past 13 years. Secondary to multiple defects in the ability to kill bacteria, infectious complications are more frequent in the CKD and dialysis populations. Adjusted rates of hospitalization for pneumonia, for example, are percent higher among Medicare patients with CKD than in those without rec- morbidity & mortality introduction
3 ognized kidney disease. Hospitalizations secondary to bacteremia/sepsis show cyclical trends in both the CKD and non-ckd populations, a pattern whose cause is unknown, but which may reflect changes in the virulence of influenza over time. Overall rates of hospitalization for bacteremia/sepsis, however, now reach or exceed those noted more than a decade ago, which is a source of concern. We next compare mortality in CKD and non-ckd patients, illustrating the impact of adjustments for comorbidity and disease severity on absolute death rates. Adjusting for age, gender, race, comorbidity, and prior hospitalizations, mortality among CKD patients in 28 was 1.7 times greater than among non-ckd patients As with hospitalization, CKD is thus a risk multiplier for mortality. The decline in rates since 1i Admissions per 1, patient years Medicare (age 66+): no adjustment 1, MarketScan (5-6) Unadjusted & adjusted all-cause hospitalization rates in the Medicare & MarketScan populations, by CKD status may partially reflect increased recognition of CKD, as illustrated by the increasing percentage of patients carrying the diagnosis; it may also indicate classification bias rather than a true reduction. Adjustments over time, however, appear to mitigate some of these issues. Patterns in mortality by CKD stage parallel those seen with hospitalization; rates in patients with Adjusted for severity of disease Non-CKD CKD hospitalization rates in ckd & non-ckd patients 8 infectious hospitalizations 82 mortality rates 8 CKD of Stages 3 5, for example, are percent greater than those of non-ckd patients. The impact of diabetes and congestive heart failure as risk multipliers is also important, particularly given that cardiovascular risk factors are relatively under-treated in the U.S. see 168for analytical methods. Medicare: point prevalent patients on January 1 of the year, age 66 & older on December 31 of the prior year. MarketScan: point prevalent patients on January 1 of the year, age 5 6 on December 31 of the prior year. Adj: gender/prior hospitalization/13 comorbidities; ref: Medicare patients age 66 & older, 25. e79
4 Among Medicare patients age 66 and older, adjusted admission rates are greater for patients with CKD compared to those without, and for patients with Stage 3 5 CKD compared to those with CKD of Stages 1 2. By race, the highest rates for non- CKD patients, all CKD patients, and those with Stage 3 5 CKD occur among African Americans. By gender, rates for those with Stage 3 5 CKD are 5.2 percent higher in women than in men. see 168 for analytical methods. Medicare patients point prevalent on January 1, 28, age 66 & older on December 31, 27. Adj: age/gender/race/prior hospitalization/ comorbidity; rates presented by one factor are adjusted for the others; ref: Medicare patients age 66 & older, 28. ai Adjusted hospitalization rates (per 1, patient years at risk) in Medicare patients, by CKD diagnosis code, 28 No CKD claim All CKD /other Male Female African American All i Admissions per 1, patient years Comorbidity Adjusted hospitalization rates in Medicare patients, by comorbidity, race, & CKD diagnosis code, 28 All DM/NCHF DM+CHF NDM/NCHF CHF/NDM Race No CKD claim All CKD /other Af Am 21 usrds annual data report volume one ckd e8 In both the CKD and non-ckd populations, adjusted rates of hospitalization increase with greater comorbidity. In 28, for example, the rate for CKD patients with both diabetes and congestive heart failure was 726 per 1, patient years at risk 85 percent greater than the rate of 393 among patients with neither diagnosis. see 168 for analytical methods. Medicare patients point prevalent on January 1, 28, age 66 & older on December 31, 27. Adj: age/ gender/race/prior hospitalization/comorbidity; rates presented for one factor are adjusted for the others; ref: Medicare patients age 66 & older, 28. ICD-9-CM codes Chronic kidney disease, Stage Chronic kidney disease, Stage 2 (mild) Chronic kidney disease, Stage 3 (moderate) 585. Chronic kidney disease, Stage (severe) Chronic kidney disease, Stage 5 (excludes 585.6: Stage 5, requiring chronic dialysis.^) 585.9/oth. morbidity & mortality hospitalization rates in ckd & non-ckd patients ^ In USRDS analyses, patients with ICD-9-CM code are considered to have code 585.5; see Appendix A for details. CKD stage estimates are from a single measurement. For clinical case definition, abnormalities should be present 3 months.
5 3i Admissions per 1, patient years i Admissions per 1, patient years 5i Admissions per 1, patient years 6i Admissions per 1, patient years Adjusted all-cause hospitalization rates, by dataset & CKD diagnosis code, 28 Medicare (66+) Marketscan (5-6) Ingenix i3 (5-6) No CKD claim All CKD /other Adjusted rates of hospitalization for cardiovascular disease, by dataset & CKD diagnosis code, 28 Medicare (66+) Marketscan (5-6) Ingenix i3 (5-6) No CKD claim All CKD /other Adjusted rates of hospitalization for infection, by dataset & CKD diagnosis code, 28 Medicare (66+) Marketscan (5-6) Ingenix i3 (5-6) No CKD claim All CKD /other Adjusted rates of hospitalization for other causes, by dataset & CKD diagnosis code, 28 Medicare (66+) Marketscan (5-6) Ingenix i3 (5-6) No CKD claim All CKD /other Adjusted all-cause hospitalization rates, and rates of hospitalization for cardiovascular disease, infection, and other causes, are each highest among Medicare patients age 66 and older than in the younger MarketScan and Ingenix i3 populations. Rates are also greatest for CKD patients compared to those without CKD, and are generally higher in the later stages of CKD. All-cause rates, for example, are 19 percent higher among Medicare patients with Stage 3 5 CKD reaching nearly 76 admissions per 1, patient years than among their counterparts with CKD of Stages 1 2; in the MarketScan and Ingenix i3 populations, rates are 36 and 6.2 percent higher in those with later-stage CKD. Rates of admission for cardiovascular disease increase even more in the higher stages of CKD. Among Medicare patients, the rate of 11 admissions per 1, patient years for those with Stage 3 5 CKD is 26 percent higher than the rate of 112 reported for those with CKD of Stages 1 2. And the rates of 11 and 9 reported for MarketScan and Ingenix i3 patients with Stage 3 5 CKD are 8 and 16 percent greater, respectively, than those occurring in patients with early-stage CKD. In the Medicare and MarketScan populations, rates of admission for infection are 29 and 35 percent greater in those with Stage 3 5 CKD than in those with CKD of Stages 1 2. Among Ingenix i3 patients, in contrast, the rate is 19 percent lower in patients with later-stage CKD. Among Medicare patients, admission rates for all causes, cardiovascular disease, and infection are 38 6 percent higher for those with CKD than for those without. Similar differences are seen in the MarketScan and Ingenix i3 populations. see 168 for analytical methods. Medicare: point prevalent patients on January 1, 28, age 66 & older on December 31, 27. MarketScan & Ingenix i3: point prevalent patients on January 1, 28, age 5 6 on December 31, 27. Adj: gender/prior hospitalization/comorbidity; ref: Medicare patients age 66 & older, 28. e
6 7i Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for pneumonia in Medicare patients, by state, 28: CKD 8i 76.5 Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for pneumonia in Medicare patients, by state, 28: non-ckd i 11.7 Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for bacteremia/septicemia in Medicare patients, by state, 28: CKD 1i 5. Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for bacteremia/septicemia in Medicare patients, by state, 28: non-ckd i 5.5 Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for urinary tract infection in Medicare patients, by state, 28: CKD 12i.6 Unadjusted rates of hospitalization (per 1, patient years) for urinary tract infection in Medicare patients, by state, 28: non-ckd usrds annual data report volume one ckd e While geographic patterns of unadjusted hospitalization rates (per 1, patient years) for pneumonia, bacteremia/ septicemia, and urinary tract infections in 28 were similar between CKD and non-ckd patients age 66 and older, actual rates were much higher in those with CKD. Nationwide, rates for pneumonia in CKD patients, for instance, were nearly three times higher than those for non-ckd patients, and averaged 76.5 in the upper quintile compared to In patients hospitalized for bacteremia/septicemia, rates nation- 5.3 wide were nearly four times higher for CKD patients, averaging 5. in the upper quintile compared to 12.9 for those with no CKD. And rates of hospitalization for urinary tract infection were three-fold higher for CKD patients nationwide, averaging.6 compared to 12.1 in the upper quintile. p!dbpm@n see 169 for analytical methods. Point prevalent Medicare patients on January 1, 28, age 66 & older on December 31, 27; unadjusted. morbidity & hospitalizations mortality infectious
7 13i Admissions per 1, patient years 1i Admissions per 1, patient years 15i Admissions per 1, patient years CKD CKD Adjusted rates of hospitalization for pneumonia in Medicare patients, by CKD status & race CKD Non-CKD African American Adjusted rates of hospitalization for bacteremia/septicemia in Medicare patients, by CKD status & race Non-CKD African American Adjusted rates of hospitalization for urinary tract infection in Medicare patients, by CKD status & race Non-CKD African American In 28, adjusted rates of hospitalization for pneumonia in Medicare patients varied little by race in both the CKD and non-ckd populations. At 23.7 admissions per 1, patient years, the rate among white CKD patients was nearly 36 percent greater than that occurring among their non-ckd counterparts; for African Americans, the rate for CKD patients was more than 68 percent higher. Rates of hospitalization for bacteremia/septicemia vary more by race. In 28, for example, the rate among African Americans with CKD reached nearly 25 admissions per 1, patient years, 31 percent higher than the rate of 18.9 among whites. While admissions related to pneumonia have generally been declining since 2, those for bacteremia/septicemia have increased since falling in the beginning of the decade. The rate for white patients with CKD is now almost 25 percent greater than in The rate of hospitalizations for urinary tract infection has remained relatively steady for white CKD patients and, across races, for patients without CKD. In 28, the rate of 1. among white CKD patients was 59 percent greater than the rate of 9. among their non-ckd counterparts; rates for African Americans and for patients of other races were 22 and 29 percent greater, respectively, in the CKD population. see 169 for analytical methods. Point prevalent Medicare patients on January 1 of the year, age 66 & older on December 31 of prior year. Adj: age/gender/prior hospitalization/comorbidity; ref: Medicare patients age 66 & older, 25. e
8 16i Deaths per 1, patient years 2 1 Unadjusted & adjusted all-cause mortality rates in Medicare CKD & non-ckd patients, by age Unadjusted: CKD 5 Non-CKD Adjusted: CKD Non-CKD i Deaths per 1, patient years Unadjusted: CKD Non-CKD Adjusted: CKD Non-CKD Unadjusted & adjusted all-cause mortality rates in Medicare CKD & non-ckd patients, by gender Male Female All usrds annual data report volume one ckd e 18i Deaths per 1, patient years Unadjusted: CKD Non-CKD Adjusted: CKD Non-CKD Unadjusted & adjusted all-cause mortality rates in Medicare CKD & non-ckd patients, by race African American morbidity & mortality mortality rates These figures show mortality rates among Medicare patients age 66 and older. Unadjusted rates show what seem to be significant declines in mortality in the CKD population, with an overall decrease of 35 percent since 1995, and of 7 51 percent in those age But when rates are adjusted for factors which address patient complexity such as hospitalization and comorbidities they begin to flatten out, implying that decreasing comorbidity and severity of disease in the patient population may explain part of the decline in mortality. More complete models, containing patient information not currently available in the claims data, may make these rates flatten even more. see 169 for analytical methods. Point prevalent Medicare patients age 66 & older. Adj: age (.17 18)/gender (.16 &.18)/race (.16 17)/prior hospitalization/comorbidity; ref: 25 cohort.
9 Adjusted mortality rates (per 1, patient years at risk) in Medicare patients, by CKD diagnosis code, 28 bi No CKD claim All CKD /oth Male Female African American All Adjusted mortality rates in Medicare patients, by comorbidity, race, & CKD diagnosis code, 28 19i Deaths per 1, patient years at risk Adjusted rates of mortality in 28 increased with age, and were highest in patients with advanced stages of CKD: percent higher, for example, in patients with Stage 3 5 CKD compared to those with no CKD. By gender, rates in men with CKD were 91.8 per 1, patient years at risk compared to 85.6 in women. Rates for CKD patients overall were similar in whites and African Americans, but in patients with Stage 3 5 CKD, rates for African Americans were 18 percent higher than those for whites, at 95. and 8.5 per 1, patient years, respectively. p /<=G@ = see 169 for analytical methods. Point prevalent Medicare patients age 66 & older, 28. Adj: age/gender/comorbidity; ref: 28 cohort. 25 Comorbidity Race No CKD claim All CKD /other All DM+CHF DM/NCHF NDM/NCHF CHF/NDM Af Am Patients with multiple comorbid conditions are at increased risk of mortality. In those with diabetes, congestive heart failure, and Stage 3 5 CKD, for example, the mortality rate in 28 was 169 per 1, patient years at risk, compared to 89.7 in Stage 3 5 patients with neither comorbid condition. p!dbpm@ see 169 for analyticalmethods. Point prevalent Medicare patients age 66 & older, 28. Adj: age/gender/comorbidity; ref: 28 cohort. ICD-9-CM codes Chronic kidney disease, Stage 1 Chronic kidney disease, Stage 2 (mild) Chronic kidney disease, Stage 3 (moderate) 585. Chronic kidney disease, Stage (severe) Chronic kidney disease, Stage 5 (excludes 585.6: Stage 5, requiring chronic dialysis.^) 585.9/oth.!FPMLGA IGBLCW BGQC?QC SLQNCAG CB ^ In USRDS analyses, patients with ICD-9-CM code are considered to have code 585.5; see Appendix A for details. CKD stage estimates are from a single measurement. For clinical case definition, abnormalities should be present 3 months. e
10 Adjustments for patient complexity imply that decreasing comorbidity and severity of disease may explain part of the decline in mortality among CKD patients since In patients with diabetes, congestive heart failure, and Stage 3 5 CKD, the mortality rate in 28 was 169 per 1, patient years at risk, compared to 89.7 in Stage 3 5 patients with neither comorbid condition. In 28, the adjusted hospitalization rate for CKD patients with both diabetes and congestive heart failure was 726 per 1, patient years at risk 85 percent greater than the rate of 393 among patients with neither diagnosis. Among Medicare patients age 66 and older, adjusted admission rates for all causes, cardiovascular disease, and infection are 38 6 percent higher for those with CKD than for those without. Adjusted rates of hospitalization for bacteremia/septicemia vary by race. In 28, for example, the rate among African Americans with CKD reached nearly 25 admissions per 1, patient years, 31 percent higher than the rate of 18.9 among whites. 21 usrds annual data report volume one ckd e morbidity & mortality summary
morbidity & mortality
 morbidity & mortality esrd introduction of ESRD treatment. We examine these concerns throughout the ADR, particularly in Chapter One. This year we focus on infectious complications, especially those related
morbidity & mortality esrd introduction of ESRD treatment. We examine these concerns throughout the ADR, particularly in Chapter One. This year we focus on infectious complications, especially those related
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality
 Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality Introduction In this chapter we evaluate the morbidity and mortality of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients continuously enrolled in Medicare. Each year s analysis
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality Introduction In this chapter we evaluate the morbidity and mortality of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients continuously enrolled in Medicare. Each year s analysis
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD
 Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD Introduction Determining the economic impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on the health care system is challenging on several levels. There is, for instance,
Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD Introduction Determining the economic impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on the health care system is challenging on several levels. There is, for instance,
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
5FM QFMUQ? AFGJB?Q FC PC?JJW GQ 5FM QCRQ FGK GL FGQ AMLQRCJJ?RGML?LB NSRQ RFC KC?QSPGLE PMB MD BGQR?LAC GL FGQ F?LB
 AF?NRCP $"#/ pediatric end-stage renal disease 5FM QFMUQ? AFGJB?Q FC PC?JJW GQ 5FM QCRQ FGK GL FGQ AMLQRCJJ?RGML?LB NSRQ RFC KC?QSPGLE PMB MD BGQR?LAC GL FGQ F?LB -
AF?NRCP $"#/ pediatric end-stage renal disease 5FM QFMUQ? AFGJB?Q FC PC?JJW GQ 5FM QCRQ FGK GL FGQ AMLQRCJJ?RGML?LB NSRQ RFC KC?QSPGLE PMB MD BGQR?LAC GL FGQ F?LB -
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD
 Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR) we introduce analysis of a new dataset. To provide a more comprehensive examination of morbidity patterns,
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR) we introduce analysis of a new dataset. To provide a more comprehensive examination of morbidity patterns,
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury
 Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury Introduction In recent years, acute kidney injury (AKI) has gained increasing recognition as a major risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury Introduction In recent years, acute kidney injury (AKI) has gained increasing recognition as a major risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Two: Chronic kidney disease identified in the claims data. Chapter
 Two: Chronic kidney disease identified in the claims data Though leaves are many, the root is one; Through all the lying days of my youth swayed my leaves and flowers in the sun; Now may wither into the
Two: Chronic kidney disease identified in the claims data Though leaves are many, the root is one; Through all the lying days of my youth swayed my leaves and flowers in the sun; Now may wither into the
Status of the CKD and ESRD treatment: Growth, Care, Disparities
 Status of the CKD and ESRD treatment: Growth, Care, Disparities United States Renal Data System Coordinating Center An J. Collins, MD FACP Director USRDS Coordinating Center Robert Foley, MB Co-investigator
Status of the CKD and ESRD treatment: Growth, Care, Disparities United States Renal Data System Coordinating Center An J. Collins, MD FACP Director USRDS Coordinating Center Robert Foley, MB Co-investigator
Levertovh CHAPTER. Denise
 Know the pinetrees. Know the orange dryness of sickness and death in needle and cone. Know them too in green health, those among whom your life is laid. Denise Levertovh The Runes Introduction Incidence
Know the pinetrees. Know the orange dryness of sickness and death in needle and cone. Know them too in green health, those among whom your life is laid. Denise Levertovh The Runes Introduction Incidence
Is it so small a thing To have enjoy d the sun, To have lived light in the spring, To have loved, to have thought, to have done e133
 chapter NINE costs of chronic kidney disease Is it so small a thing To have enjoy d the sun, To have lived light in the spring, To have loved, to have thought, to have done Matthew Arnold, From the Hymn
chapter NINE costs of chronic kidney disease Is it so small a thing To have enjoy d the sun, To have lived light in the spring, To have loved, to have thought, to have done Matthew Arnold, From the Hymn
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health
 Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health The painter who draws merely by practice and by eye, without any reason, is like a mirror which copies every thing placed in front of it without being
Chapter Five Clinical indicators & preventive health The painter who draws merely by practice and by eye, without any reason, is like a mirror which copies every thing placed in front of it without being
Arches National Park, Utah. hospitalization
 Arches National Park, Utah 237 212 USRDS annual data report 2volume 238 24 overall 242 re 244 admission rates by interdialytic interval 246 summary Remote from universal nature and living by complicated
Arches National Park, Utah 237 212 USRDS annual data report 2volume 238 24 overall 242 re 244 admission rates by interdialytic interval 246 summary Remote from universal nature and living by complicated
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury
 Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury In 2015, 4.3% of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries experienced a hospitalization complicated by Acute Kidney Injury (AKI); this appears to have plateaued since 2011
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury In 2015, 4.3% of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries experienced a hospitalization complicated by Acute Kidney Injury (AKI); this appears to have plateaued since 2011
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD
 Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Chapter six Outcomes: hospitalization & mortality. There is an element of death in life, and I am astonished
 INTRODUCTION 1 OVERALL HOSPITALIZATION & MORTALITY 1 hospital admissions & days, by primary diagnosis & patient vintage five-year survival mortality rates, by patient vintage expected remaining lifetimes
INTRODUCTION 1 OVERALL HOSPITALIZATION & MORTALITY 1 hospital admissions & days, by primary diagnosis & patient vintage five-year survival mortality rates, by patient vintage expected remaining lifetimes
chapter seven transplantation page
 chapter seven There been times that I thought I couldn t last for long But now I think I m able to carry on It s been a long, a long time coming But I know a change gonna come, oh yes it will Sam Cooke,
chapter seven There been times that I thought I couldn t last for long But now I think I m able to carry on It s been a long, a long time coming But I know a change gonna come, oh yes it will Sam Cooke,
patient characteriuics Chapter Two introduction 58 increasing complexity of the patient population 60 epo use & anemia in the pre-esrd period 62
 introduction 58 < increasing complexity of the patient population 6 < epo use & anemia in the pre-esrd period 62 < biochemical & physical characteristics at initiation 64 < estimated gfr at intiation &
introduction 58 < increasing complexity of the patient population 6 < epo use & anemia in the pre-esrd period 62 < biochemical & physical characteristics at initiation 64 < estimated gfr at intiation &
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
2017 USRDS ANNUAL DATA REPORT KIDNEY DISEASE IN THE UNITED STATES S611
 Healthy People 2020 In this chapter, we examine data for 11 Healthy People 2020 (HP2020) objectives 10 for CKD and one for diabetes spanning 20 total indicators for which the USRDS serves as the official
Healthy People 2020 In this chapter, we examine data for 11 Healthy People 2020 (HP2020) objectives 10 for CKD and one for diabetes spanning 20 total indicators for which the USRDS serves as the official
preventive health care measure
 introduction 98 < pre- & post-esrd preventive care 1 < diabetic care 12 < cancer screening 14 < chapter summary 16 Chapter Five preventive health care measure SSo neither ought you to attempt to cure the
introduction 98 < pre- & post-esrd preventive care 1 < diabetic care 12 < cancer screening 14 < chapter summary 16 Chapter Five preventive health care measure SSo neither ought you to attempt to cure the
CKD in the United States: An Overview of the USRDS Annual Data Report, Volume 1
 CKD in the United States: An Overview of the USRDS Annual Data Report, Volume 1 Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has received significant attention over the last decade, primarily since the consensus
CKD in the United States: An Overview of the USRDS Annual Data Report, Volume 1 Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has received significant attention over the last decade, primarily since the consensus
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD
 Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD Introduction Cardiovascular disease is an important comorbidity for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD patients are at high-risk for
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD Introduction Cardiovascular disease is an important comorbidity for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD patients are at high-risk for
Chapter 6: Mortality. Introduction 2016 USRDS ANNUAL DATA REPORT VOLUME 2 ESRD IN THE UNITED STATES
 Chapter 6: Mortality In 2014, adjusted mortality rates for ESRD, dialysis, and transplant patients, were 136, 166, and 30, per 1,000 patient-years, respectively. By dialysis modality, mortality rates were
Chapter 6: Mortality In 2014, adjusted mortality rates for ESRD, dialysis, and transplant patients, were 136, 166, and 30, per 1,000 patient-years, respectively. By dialysis modality, mortality rates were
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD
 Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD The prevalence of cardiovascular disease is 68.8% among patients aged 66 and older who have CKD, compared to 34.1% among those who do not have CKD
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With CKD The prevalence of cardiovascular disease is 68.8% among patients aged 66 and older who have CKD, compared to 34.1% among those who do not have CKD
ckd data sources 2013 USRDS annual data report data sources volume one
 138 140 140 140 141 data sources database definitions identification of major comorbidities ckd in the general population chapter one identification & care of ckd patients chapter two 142 hospitalization
138 140 140 140 141 data sources database definitions identification of major comorbidities ckd in the general population chapter one identification & care of ckd patients chapter two 142 hospitalization
Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence
 Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence Science is the observation of things possible, whether present or past. Prescience is the knowledge of things which may come to pass, though but slowly. LEONARDO da Vinci
Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence Science is the observation of things possible, whether present or past. Prescience is the knowledge of things which may come to pass, though but slowly. LEONARDO da Vinci
Ashberyh CHAPTER. John
 A knowledge that people live close by is, I think, enough. And even if only first names are ever exchanged The people who own them seem rock-true and marvelously self-suficient. John Ashberyh The Ongoing
A knowledge that people live close by is, I think, enough. And even if only first names are ever exchanged The people who own them seem rock-true and marvelously self-suficient. John Ashberyh The Ongoing
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart
Dialysis outcomes: can we do better?
 Dialysis outcomes: can we do better? Allan J. Collins, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Director, Chronic Disease Research Group Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation Director,
Dialysis outcomes: can we do better? Allan J. Collins, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Director, Chronic Disease Research Group Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation Director,
04 Chapter Four Treatment modalities. Experience does not err, it is only your judgement that errs in expecting from her what is not in her power.
 Chapter Four Treatment modalities Experience does not err, it is only your judgement that errs in expecting from her what is not in her power. LEONARDO da Vinci Vol 2 esrd Ch pg 29 Contents 22 Incident
Chapter Four Treatment modalities Experience does not err, it is only your judgement that errs in expecting from her what is not in her power. LEONARDO da Vinci Vol 2 esrd Ch pg 29 Contents 22 Incident
Section K. Economic costs of ESRD. Vol 3 esrd. pg 731. K tables
 Section K Economic costs of ESRD Vol 3 esrd pg 731 Table K.1 733 Total costs ($) of reported ESRD per calendar year all ESRD with at least one claim, & Table K.2 734 Total costs ($) of reported ESRD :
Section K Economic costs of ESRD Vol 3 esrd pg 731 Table K.1 733 Total costs ($) of reported ESRD per calendar year all ESRD with at least one claim, & Table K.2 734 Total costs ($) of reported ESRD :
Cost Analysis of the Creation and Maintenance of Functional Arteriovenous Grafts for Hemodialysis
 Cost Analysis of the Creation and Maintenance of Functional Arteriovenous Grafts for Hemodialysis Neeraja Konuthula BS, Steven D. Abramowitz MD, Harry Schanzer MD, Peter L. Faries MD, Michael L. Marin
Cost Analysis of the Creation and Maintenance of Functional Arteriovenous Grafts for Hemodialysis Neeraja Konuthula BS, Steven D. Abramowitz MD, Harry Schanzer MD, Peter L. Faries MD, Michael L. Marin
Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers
 Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2014 the two largest dialysis organizations, Fresenius and DaVita, collectively treated 69% of patients in 65% of all dialysis units (Figure 10.2). Nearly 90% of all dialysis
Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2014 the two largest dialysis organizations, Fresenius and DaVita, collectively treated 69% of patients in 65% of all dialysis units (Figure 10.2). Nearly 90% of all dialysis
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2013, collectively the three large dialysis organizations treated 71% of patients in 67% of all dialysis units. In the Small Dialysis
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2013, collectively the three large dialysis organizations treated 71% of patients in 67% of all dialysis units. In the Small Dialysis
Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD
 Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in adult ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart failure being the most common conditions
Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in adult ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart failure being the most common conditions
Peer Kidney Care Initiative
 Patient Populations Hospitalizations Mortality Cardiovascular Benchmarks Peer Kidney Care Initiative Peer Report Dialysis Care & Outcomes in the United States, 216 Financial support for the Peer Kidney
Patient Populations Hospitalizations Mortality Cardiovascular Benchmarks Peer Kidney Care Initiative Peer Report Dialysis Care & Outcomes in the United States, 216 Financial support for the Peer Kidney
The University of Mississippi School of Pharmacy
 LONG TERM PERSISTENCE WITH ACEI/ARB THERAPY AFTER ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: AN ANALYSIS OF THE 2006-2007 MEDICARE 5% NATIONAL SAMPLE DATA Lokhandwala T. MS, Yang Y. PhD, Thumula V. MS, Bentley J.P.
LONG TERM PERSISTENCE WITH ACEI/ARB THERAPY AFTER ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: AN ANALYSIS OF THE 2006-2007 MEDICARE 5% NATIONAL SAMPLE DATA Lokhandwala T. MS, Yang Y. PhD, Thumula V. MS, Bentley J.P.
Zuni Health Initiative
 ZUNI JEWELRY Zuni Health Initiative Raj Shah-University of New Mexico vshah@salud.unm.edu Do' tse'mak i:k'oshudu, elek'yanna!!! May you feel better, everything will be alright!!! OBJECTIVES Describe the
ZUNI JEWELRY Zuni Health Initiative Raj Shah-University of New Mexico vshah@salud.unm.edu Do' tse'mak i:k'oshudu, elek'yanna!!! May you feel better, everything will be alright!!! OBJECTIVES Describe the
KEEP S u m m a r y F i g u r e s. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 53, No 4, Suppl 4, 2009:pp S32 S44.
 28 S u m m a r y F i g u r e s American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 53, No 4, Suppl 4, 29:pp S32 S44. S32 Definitions S33 Data Analyses Diabetes Self-reported diabetes, self reported diabetic retinopathy,
28 S u m m a r y F i g u r e s American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 53, No 4, Suppl 4, 29:pp S32 S44. S32 Definitions S33 Data Analyses Diabetes Self-reported diabetes, self reported diabetic retinopathy,
Chapter 6: Transplantation
 Chapter 6: Transplantation Introduction During calendar year 2012, 17,305 kidney transplants, including kidney-alone and kidney plus at least one additional organ, were performed in the United States.
Chapter 6: Transplantation Introduction During calendar year 2012, 17,305 kidney transplants, including kidney-alone and kidney plus at least one additional organ, were performed in the United States.
Disparities in Transplantation Caution: Life is not fair.
 Disparities in Transplantation Caution: Life is not fair. Tuesday October 30 th 2018 Caroline Rochon, MD, FACS Surgical Director, Kidney Transplant Program Hartford Hospital, Connecticut Outline Differences
Disparities in Transplantation Caution: Life is not fair. Tuesday October 30 th 2018 Caroline Rochon, MD, FACS Surgical Director, Kidney Transplant Program Hartford Hospital, Connecticut Outline Differences
The Burden Report: Cardiovascular Disease & Stroke in Texas
 The Burden Report: Cardiovascular Disease & Stroke in Texas Texas Cardiovascular Health and Wellness Program www.dshs.state.tx.us/wellness Texas Council on Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke www.texascvdcouncil.org
The Burden Report: Cardiovascular Disease & Stroke in Texas Texas Cardiovascular Health and Wellness Program www.dshs.state.tx.us/wellness Texas Council on Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke www.texascvdcouncil.org
In each hospital-year, we calculated a 30-day unplanned. readmission rate among patients who survived at least 30 days
 Romley JA, Goldman DP, Sood N. US hospitals experienced substantial productivity growth during 2002 11. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(3). Published online February 11, 2015. Appendix Adjusting hospital
Romley JA, Goldman DP, Sood N. US hospitals experienced substantial productivity growth during 2002 11. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(3). Published online February 11, 2015. Appendix Adjusting hospital
ESRD Analytical Methods Contents
 ESRD Analytical Methods Contents Volume 2: ESRD Analytical Methods... 227 Introduction... 230 Data Sources... 230 Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-enabled Network... 230 CMS Medicare Enrollment Database...
ESRD Analytical Methods Contents Volume 2: ESRD Analytical Methods... 227 Introduction... 230 Data Sources... 230 Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-enabled Network... 230 CMS Medicare Enrollment Database...
Narender Goel et al. Middletown Medical PC, Montefiore Medical Center & Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York
 Narender Goel et al. Middletown Medical PC, Montefiore Medical Center & Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York 4th International Conference on Nephrology & Therapeutics September 14, 2015 Baltimore,
Narender Goel et al. Middletown Medical PC, Montefiore Medical Center & Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York 4th International Conference on Nephrology & Therapeutics September 14, 2015 Baltimore,
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with CKD
 Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with CKD The prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) was 65.8% among patients aged 66 and older who had chronic kidney disease (CKD), compared to 31.9%
Chapter 4: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with CKD The prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) was 65.8% among patients aged 66 and older who had chronic kidney disease (CKD), compared to 31.9%
Big Data Challenges & Opportunities. L. Miriam Dickinson, PhD
 Big Data Challenges & Opportunities L. Miriam Dickinson, PhD An Example from the Primary Care Setting NIDDK-funded pragmatic trial to test two approaches to improving care for stage 3 and 4 CKD patients
Big Data Challenges & Opportunities L. Miriam Dickinson, PhD An Example from the Primary Care Setting NIDDK-funded pragmatic trial to test two approaches to improving care for stage 3 and 4 CKD patients
FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 92 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access
 INTRODUCTION ANEMIA TREATMENT hemoglobin levels epo treatment iron treatment FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 2 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access EPO DOSING PATTERNS 4 epo dosing per kg
INTRODUCTION ANEMIA TREATMENT hemoglobin levels epo treatment iron treatment FULFILLMENT OF K/DOQI GUIDELINES 2 anemia treatment dialysis therapy vascular access EPO DOSING PATTERNS 4 epo dosing per kg
chapter two clinical indicators and preventive care page
 chapter two clinical indicators and preventive care If you believe in magic don t bother to choose If it s jug band music or rhythm and blues Just go and listen it ll start with a smile It won t wipe off
chapter two clinical indicators and preventive care If you believe in magic don t bother to choose If it s jug band music or rhythm and blues Just go and listen it ll start with a smile It won t wipe off
Alameda County Public Health Department. Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group
 Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group Abstract Preventable hospitalizations occur when persons are hospitalized for a medical condition that could have
Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group Abstract Preventable hospitalizations occur when persons are hospitalized for a medical condition that could have
Yeatsh CHAPTER. William Butler
 Sickness brought me this Thought, in that scale his: Why should I be dismayed Though Lame had burned the whole World, as it were a coal, Now I have seen it weighed Against a soul? William Butler Yeatsh
Sickness brought me this Thought, in that scale his: Why should I be dismayed Though Lame had burned the whole World, as it were a coal, Now I have seen it weighed Against a soul? William Butler Yeatsh
The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in North Carolina June 2009 Update
 The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in North Carolina June 2009 Update Sara L. Huston, Ph.D. Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section Division of Public Health North Carolina
The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in North Carolina June 2009 Update Sara L. Huston, Ph.D. Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section Division of Public Health North Carolina
Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims:
 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non- Medical Switching August 2017 THE MORAN COMPANY 1 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non-Medical
Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non- Medical Switching August 2017 THE MORAN COMPANY 1 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non-Medical
Chapter 8: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with ESRD
 Chapter 8: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with ESRD Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is common in adult end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients, with coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure (HF)
Chapter 8: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with ESRD Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is common in adult end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients, with coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure (HF)
Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population
 0 Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population In youth acquire that which may restore the damage of old age; and if you are mindful that old age has wisdom for its food, you
0 Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population In youth acquire that which may restore the damage of old age; and if you are mindful that old age has wisdom for its food, you
Key Findings. Mortality Rates
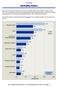 Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Advancing the management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Employee Benefits Planning Association- December s Program 12/6/2017 1
 Advancing the management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Employee Benefits Planning Association- December s Program 12/6/2017 1 Today s Topics Chronic Kidney Disease Causes & Financial Impact Managing comorbid
Advancing the management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Employee Benefits Planning Association- December s Program 12/6/2017 1 Today s Topics Chronic Kidney Disease Causes & Financial Impact Managing comorbid
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART. Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009
 TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters. Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA General Objectives Topics to discuss What are the key outcomes of CKD? What progress
Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA General Objectives Topics to discuss What are the key outcomes of CKD? What progress
REIMBURSEMENT AND ITS IMPACT ON YOUR DIALYSIS PROGRAM Tony Messana Executive Director Renal Services St. Joseph Hospital - Orange
 REIMBURSEMENT AND ITS IMPACT ON YOUR DIALYSIS PROGRAM Tony Messana Executive Director Renal Services St. Joseph Hospital - Orange Agenda History of the Medicare ESRD Program Cost of Care for ESRD Patients
REIMBURSEMENT AND ITS IMPACT ON YOUR DIALYSIS PROGRAM Tony Messana Executive Director Renal Services St. Joseph Hospital - Orange Agenda History of the Medicare ESRD Program Cost of Care for ESRD Patients
KEEP 2009 Summary Figures
 S4 29 Summary Figures American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 55, No 3, Suppl 2, 21:pp S4-S57 S41 Definitions DATA ANALYSES DIABETES Self-reported diabetes, self reported diabetic retinopathy, receiving
S4 29 Summary Figures American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 55, No 3, Suppl 2, 21:pp S4-S57 S41 Definitions DATA ANALYSES DIABETES Self-reported diabetes, self reported diabetic retinopathy, receiving
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center
 Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 8: Pediatric ESRD 1,462 children in the United States began end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care in 2013. 9,921 children were being treated for ESRD on December
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 8: Pediatric ESRD 1,462 children in the United States began end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care in 2013. 9,921 children were being treated for ESRD on December
FOUR. Clinical Indicators of Care
 Clinical Indicators of Care T FOUR The great questions of the time are not decided by speeches and majority decisions but by iron and blood. Otto von Bismarck, Speech to the Prussian Diet 78 ž 2000 ATLAS
Clinical Indicators of Care T FOUR The great questions of the time are not decided by speeches and majority decisions but by iron and blood. Otto von Bismarck, Speech to the Prussian Diet 78 ž 2000 ATLAS
Hu J, Gonsahn MD, Nerenz DR. Socioeconomic status and readmissions: evidence from an urban teaching hospital. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(5).
 Appendix Definitions of Index Admission and Readmission Definitions of index admission and readmission follow CMS hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission (HWR) measure as far as data are available.
Appendix Definitions of Index Admission and Readmission Definitions of index admission and readmission follow CMS hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission (HWR) measure as far as data are available.
PALLIATIVE CARE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES LIVING WITH CKD AND ESRD
 PALLIATIVE CARE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES LIVING WITH CKD AND ESRD Karen Solcher, MSN, APRN, NP-C, CNN-NP Nephrology Nurse Practitioner Stormont-Vail Health DISCLAIMER Adult population Clinical practice
PALLIATIVE CARE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES LIVING WITH CKD AND ESRD Karen Solcher, MSN, APRN, NP-C, CNN-NP Nephrology Nurse Practitioner Stormont-Vail Health DISCLAIMER Adult population Clinical practice
Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
 Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The number of children beginning end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care decreased by 6% in 2014, totaling 1,398 (Figure 8.1.a). 9,721 children
Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The number of children beginning end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care decreased by 6% in 2014, totaling 1,398 (Figure 8.1.a). 9,721 children
Chapter 1: Incidence, Prevalence, Patient Characteristics, and Treatment Modalities
 Chapter 1: Incidence, Prevalence, Patient Characteristics, and Treatment Modalities INCIDENCE In 2016, there were 124,675 newly reported cases of ESRD; the unadjusted (crude) incidence rate was 373.4 per
Chapter 1: Incidence, Prevalence, Patient Characteristics, and Treatment Modalities INCIDENCE In 2016, there were 124,675 newly reported cases of ESRD; the unadjusted (crude) incidence rate was 373.4 per
ICD-10CM, HCC and Risk Adjustment Factor
 ICD-10CM, HCC and Risk Adjustment Factor Not everyone is aware of what CMs calls the risk adjustment model. It was developed under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as the PACA)
ICD-10CM, HCC and Risk Adjustment Factor Not everyone is aware of what CMs calls the risk adjustment model. It was developed under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as the PACA)
Potentially Preventable Hospitalizations
 Potentially Preventable Hospitalizations What does kidney disease have to do with it? Elaine Braslow, MEd September 29, 2015 About your kidneys What do the kidneys do? Prevent buildup of wastes and extra
Potentially Preventable Hospitalizations What does kidney disease have to do with it? Elaine Braslow, MEd September 29, 2015 About your kidneys What do the kidneys do? Prevent buildup of wastes and extra
Supplementary appendix: Oral polio vaccination and hospital admissions with non-polio infections in Denmark: Nationwide retrospective cohort study
 Supplementary appendix: Oral polio vaccination and hospital admissions with non-polio infections in Denmark: Nationwide retrospective cohort study Signe Sørup, Lone G. Stensballe, Tyra G. Krause, Peter
Supplementary appendix: Oral polio vaccination and hospital admissions with non-polio infections in Denmark: Nationwide retrospective cohort study Signe Sørup, Lone G. Stensballe, Tyra G. Krause, Peter
Study Exposures, Outcomes:
 GSK Medicine: Coreg IR, Coreg CR, and InnoPran Study No.: WWE111944/WEUSRTP3149 Title: A nested case-control study of the association between Coreg IR and Coreg CR and hypersensitivity reactions: anaphylactic
GSK Medicine: Coreg IR, Coreg CR, and InnoPran Study No.: WWE111944/WEUSRTP3149 Title: A nested case-control study of the association between Coreg IR and Coreg CR and hypersensitivity reactions: anaphylactic
Medicare Severity-adjusted Diagnosis Related Groups (MS-DRGs) Coding Adjustment
 American Hospital association December 2012 TrendWatch Are Medicare Patients Getting Sicker? Today, Medicare covers more than 48 million people, and that number is growing rapidly baby boomers are reaching
American Hospital association December 2012 TrendWatch Are Medicare Patients Getting Sicker? Today, Medicare covers more than 48 million people, and that number is growing rapidly baby boomers are reaching
State Profile for FY 2018 for Dialysis Patients and Facilities - STATE SAMPLE
 Dear State Surveyor: State Profile for FY 2018 for Dialysis Patients and Facilities - STATE SAMPLE This report is designed to provide a comparative summary of treatment patterns and patient outcomes for
Dear State Surveyor: State Profile for FY 2018 for Dialysis Patients and Facilities - STATE SAMPLE This report is designed to provide a comparative summary of treatment patterns and patient outcomes for
ECU, Center for Health Services Research and Development, 2000
 Map 12.1 Progress Towards Pneumonia and Influenza Mortality Objective Northampton Gates Currituck Camden Pasquotank Halifax Hertford Perquimans Nash Bertie Chowan Edgecombe Martin Washington Tyrrell Dare
Map 12.1 Progress Towards Pneumonia and Influenza Mortality Objective Northampton Gates Currituck Camden Pasquotank Halifax Hertford Perquimans Nash Bertie Chowan Edgecombe Martin Washington Tyrrell Dare
Update on Kidney Allocation
 Update on Kidney Allocation 23rd Annual Conference Association for Multicultural Affairs in Transplantation Silas P. Norman, M.D., M.P.H. Associate Professor Division of Nephrology September 23, 2015 Disclosures
Update on Kidney Allocation 23rd Annual Conference Association for Multicultural Affairs in Transplantation Silas P. Norman, M.D., M.P.H. Associate Professor Division of Nephrology September 23, 2015 Disclosures
Introduction to Volume 2: ESRD in the United States
 Introduction to Volume 2: ESRD in the United States Introduction Volume 2 of the USRDS Annual Data Report (ADR) offers a detailed descriptive epidemiology of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in the United
Introduction to Volume 2: ESRD in the United States Introduction Volume 2 of the USRDS Annual Data Report (ADR) offers a detailed descriptive epidemiology of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in the United
Arkansas Health Care Payment Improvement Initiative Congestive Heart Failure Algorithm Summary
 Arkansas Health Care Payment Improvement Initiative Congestive Heart Failure Algorithm Summary Congestive Heart Failure Algorithm Summary v1.2 (1/5) Triggers PAP assignment Exclusions Episode time window
Arkansas Health Care Payment Improvement Initiative Congestive Heart Failure Algorithm Summary Congestive Heart Failure Algorithm Summary v1.2 (1/5) Triggers PAP assignment Exclusions Episode time window
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Medicine. The Department of Public Health Sciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Medicine The Department of Public Health Sciences EVALUATION OF TWO PROCEDURES FOR TREATMENT OF KNEE PROSTHETIC JOINT INFECTION (PJI) A
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Medicine The Department of Public Health Sciences EVALUATION OF TWO PROCEDURES FOR TREATMENT OF KNEE PROSTHETIC JOINT INFECTION (PJI) A
The impact of respiratory disease in New Zealand: 2018 update
 The impact of respiratory disease in New Zealand: 2018 update Dr Lucy Telfar Barnard Jane Zhang This report was prepared for the Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Contents 1. List of Figures... 5 2.
The impact of respiratory disease in New Zealand: 2018 update Dr Lucy Telfar Barnard Jane Zhang This report was prepared for the Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Contents 1. List of Figures... 5 2.
Appendix Identification of Study Cohorts
 Appendix Identification of Study Cohorts Because the models were run with the 2010 SAS Packs from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)/Yale, the eligibility criteria described in "2010 Measures
Appendix Identification of Study Cohorts Because the models were run with the 2010 SAS Packs from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)/Yale, the eligibility criteria described in "2010 Measures
Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
 Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The one-year end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient mortality among the 0-4 year age group has declined approximately 41.6% over the past decade.
Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The one-year end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient mortality among the 0-4 year age group has declined approximately 41.6% over the past decade.
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 3 Episodes
 TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 3 Episodes Respiratory Infection (RI); Pneumonia (PNA); Inpatient Urinary Tract Infection (UTI-I; Outpatient Urinary
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 3 Episodes Respiratory Infection (RI); Pneumonia (PNA); Inpatient Urinary Tract Infection (UTI-I; Outpatient Urinary
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population In light of the 2017 blood pressure guidelines from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA), this year we examine hypertension control
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population In light of the 2017 blood pressure guidelines from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA), this year we examine hypertension control
JAMA, January 11, 2012 Vol 307, No. 2
 JAMA, January 11, 2012 Vol 307, No. 2 Dementia is associated with increased rates and often poorer outcomes of hospitalization Worsening cognitive status Adequate chronic disease management is more difficult
JAMA, January 11, 2012 Vol 307, No. 2 Dementia is associated with increased rates and often poorer outcomes of hospitalization Worsening cognitive status Adequate chronic disease management is more difficult
Prevalence And Trends In Obesity Among Aged And Disabled U.S. Medicare Beneficiaries,
 Trends Prevalence And Trends In Obesity Among Aged And Disabled U.S. Medicare Beneficiaries, 1997 2002 The rise in obesity among beneficiaries, along with expansions in treatment coverage, could greatly
Trends Prevalence And Trends In Obesity Among Aged And Disabled U.S. Medicare Beneficiaries, 1997 2002 The rise in obesity among beneficiaries, along with expansions in treatment coverage, could greatly
Medication Trends in Dialysis Patients Focus on Medicare Part D
 Medication Trends in Dialysis Patients Focus on Medicare Part D Wendy L. St. Peter, PharmD, FASN, FCCP Professor, College of Pharmacy, University of Minnesota Co-investigator, USRDS Collaborators USRDS
Medication Trends in Dialysis Patients Focus on Medicare Part D Wendy L. St. Peter, PharmD, FASN, FCCP Professor, College of Pharmacy, University of Minnesota Co-investigator, USRDS Collaborators USRDS
QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room
 QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room msix PEDIATrIC ESrD 18 ž 21 ATLAS OF ESRD IN THE UNITED STATES Incident rates of ESRD in children have risen two
QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room msix PEDIATrIC ESrD 18 ž 21 ATLAS OF ESRD IN THE UNITED STATES Incident rates of ESRD in children have risen two
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Figure S1. Cohort definition flow chart.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Cohort definition flow chart. Supplementary Table S1. Baseline characteristics of study population grouped according to having developed incident CKD during the follow-up or not
Supplementary Figure S1. Cohort definition flow chart. Supplementary Table S1. Baseline characteristics of study population grouped according to having developed incident CKD during the follow-up or not
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Volume 2: ESRD Analytical Methods Contents Introduction...352 Data Sources...352 Renal Management Information System...353 CROWNWeb and Standard Information Management
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Volume 2: ESRD Analytical Methods Contents Introduction...352 Data Sources...352 Renal Management Information System...353 CROWNWeb and Standard Information Management
PP-US-DSE Relypsa, Inc. All rights reserved. Relypsa and the Relypsa logo are trademarks of Relypsa, Inc.
 1 2 There are 4 main objectives that I d like to cover with you today: First, to review the definition, prevalence, and risk of hyperkalemia in certain populations Second, to review why RAASi are recommended
1 2 There are 4 main objectives that I d like to cover with you today: First, to review the definition, prevalence, and risk of hyperkalemia in certain populations Second, to review why RAASi are recommended
Estimating Medicaid Costs for Cardiovascular Disease: A Claims-based Approach
 Estimating Medicaid Costs for Cardiovascular Disease: A Claims-based Approach Presented by Susan G. Haber, Sc.D 1 ; Boyd H. Gilman, Ph.D. 1 1 RTI International Presented at The 133rd Annual Meeting of
Estimating Medicaid Costs for Cardiovascular Disease: A Claims-based Approach Presented by Susan G. Haber, Sc.D 1 ; Boyd H. Gilman, Ph.D. 1 1 RTI International Presented at The 133rd Annual Meeting of
