CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
|
|
|
- Norma Cecilia Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 2 Internal, external and secondary channels Lung, Pericardium & Heart Channels & Collateral Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007). A manual of acupuncture (2 ed.). Hove, East Sussex: Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications.
2 Group Discussion Report back on your conclusions after reading the CMBA Code of Conduct. o Which portions of the code affect your interactions in practical work throughout this subject? o How will you apply these in class? Endeavour College of Natural Health 2
3 OVERVIEW Internal Pathways Secondary Channels Extraordinary Channels Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 3
4 Channel Network Consists of: o Primary Channel o Secondary channels o Extraordinary channels Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 4
5 Primary Channels The 12 main channels have an exterior pathway on which acupuncture points are located Interior pathways that connect with the organs and other important structures Key Concept The pathway of a channel, internal and external connections dictate its function and pathology. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 5
6 The Eight Extraordinary Vessels o o o o o o Conception (Ren) Governing (Du) Thoroughfare (Chong) Belt (Dai) Yin & Yang Link (Wei) Yin & Yang Motility (Qiao) Note: The 8 extras will be covered in more depth in Sessions 6 & 13 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 6
7 Secondary Channels Numerous specialised pathways deviate from the main meridian and connect to the o internal organs o other meridians o Sinews o blood vessels o skin and other parts of the body Endeavour College of Natural Health 7
8 Secondary Channels o o o o o 15 Luo-Connecting 12 Divergent Channels 12 Sinew Channels 12 Cutaneous Regions Minute collaterals Practical exams will concentrate on the external 12 pathway of the main meridians. Final written exam will include all the channels. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 8
9 ANATOMICAL POSITION & DIRECTIONAL TERMS Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 9
10 Accuracy in Locating Channels Anatomical structures and landmarks Key acupuncture points Described using o Anatomical position o Directional terms o Cun measurements Endeavour College of Natural Health 10
11 Anatomical position is used when describing the pathway of channels and location of acupuncture points. Anatomical position: o Standing straight o Legs slightly apart o Eyes looking forward o Head faced forward Anatomical Position o Palms turned forward o Arms held slightly away from the body Anatomical position (Tortora & Derrickson, 2014, p. 13) Endeavour College of Natural Health 11
12 Anatomical Position Anterior Posterior Anatomical position (Tortora & Derrickson, 2014, p. 13) Endeavour College of Natural Health 12
13 Directional Terms Compass (García, 2008) Specific terminology is used to identify the locations of channels and points. o Used throughout your studies o In professional practice Example: The stomach channel runs lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia but medial to the fibula. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Endeavour College of Natural Health 13
14 Directional Terms Directional Terms (Tortora & Derrickson, 2014, p. 15) Endeavour College of Natural Health 14
15 Cun Measurements Specific to Acupuncture. Body inch is relative to the individual and specific body area. Used to measure from an acupoint or specific to anatomical landmarks. Proportional measurement is used for accuracy. View the following video in your own time. Arm Cun (Deadman, Al-Khafaji & Baker, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 15
16 CHANNELS & COLLATERALS OF THE ARM YIN Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 16
17 The Lung (LU) Hand Tai Yin Channels & Collaterals Deadman, Al-Khafaji & Baker (2007, pp ) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 17
18 Lung (Hand Tai Yin) Channel System o The Lung (Hand Tai Yin) Primary channel o The Lung Divergent channel o The Lung Luo-connecting collateral o The Lung Sinew channel o The Lung Cutaneous region Endeavour College of Natural Health 18
19 The Lung (LU) Hand Tai Yin Primary Channel Regular Points 11 points Lung Connecting Zang Fu Large Intestine Stomach Main Channel Connections with other channels Nil Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 19
20 Pathway of the Lung Channel Lu-1 Lu-2 Throat Lu-5 Lu-6 Lu-7 Lu-9 Lu-11 Stomach Lungs Large Intestine Lung Channel a (Deadman, Al-Khafaji & Baker, 2007, p. 73) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 20
21 Internal Pathway of the Lung Channel o Originates from the stomach region (the middle jiao/burner) o Descends and connects with the Large Intestine o Ascends past the stomach and diaphragm to enter the lungs o Continues superiorly to the throat o Descends to emerges at LU-1 (Zhongfu) Lung Channel b (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 21
22 Pathway of the Lung Channel Lung Channel Human (Lian, Chen, Hammes & Kolster, 2005, p.80) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 22
23 External Pathway of the Lung Channel From LU-1, the channel ascends to LU-2 (Yunmen) located in the hollow of the delto-pectoral triangle Lung points (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 23
24 External Pathway of the Lung Channel Cont d Descends along the anterio-lateral aspect of the upper arm, to LU-5 at the cubital fossa of the elbow Lung points (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 24
25 External Pathway of the Lung Channel Cont d Passes through LU-6 on the antero-lateral aspect of the forearm, towards the styloid process of the radius. Lung points (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 25
26 External Pathway of the Lung Channel Cont d Connects with LU-7; between the tendons of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, 1.5 cun proximal to the palmar wrist crease (WHO, 2008). LU 7 (WHO, 2008) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 26
27 External Pathway of the Lung Channel Cont d oconnects with LU-9 on the lateral border of the radial artery Lung points (Deadman, 2007) o Passes over the thenar eminence o Concludes at the radial aspect of the thumbnail at LU-11 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 27
28 Branch of the Main Lung Channel Separates from the main channel at LU-7 Extends to the radial side of the tip of the index finger To the Large Intestine channel at LI-1 Lung Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 28
29 Clinical Uses Key Concept of the Lung Channel Actions and indications of any channel are dictated by the channel pathway and the functions of the organs that the channel connects with internally. Endeavour College of Natural Health 29
30 Group Discussion o Consider the pathway of the Lung Channel and the organs and structures it connects with. o What are some likely clinical uses of the Lung channel? Endeavour College of Natural Health 30
31 Pathologies of the Channels o Channels may be used to treat pathologies or disease states in the body o The channels themselves may also be damaged or become unhealthy. Endeavour College of Natural Health 31
32 Channel Vs Organ Pathologies Which of the following do you think are Lung channel pathologies and which are Lung organ pathologies? Distension of the chest Cough Pain in the infraclavicular fossa Asthma Pain in the shoulder Pain cold or numbness along the channel Endeavour College of Natural Health 32
33 Class discussion o What are some ways that the external Lung channel as distinct from the lung organ might develop a pathology? o How does the Lung channel s pathway explain its ability to treat throat and nasal disorders? Endeavour College of Natural Health 33
34 Luo-Connecting Channel Separates at LU-7 of the Lung Follows the main channel spreads through the thenar eminance Converges with the Large Intestine channel. Lung Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 34
35 Indications of the Luo-connecting channel of the Lung o Sensation of heat in the styloid process, wrist and thenar eminence o Yawning o Incontinence, increased frequency of urination Endeavour College of Natural Health 35
36 Divergent Channel of the Lung ascends across the throat converges with the LI channel Separates from the primary Lung channel at the axilla connects with the Lungs disperses into the Large Intestine Lung Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 36
37 Lung Sinew Channel Originates at LU-11 and ascends over the thumb then binds at the thenar eminence Follows the radial artery, then binds at the centre of the elbow Ascends along the antero-lateral aspect of the upper arm Enters the chest below the axilla and emerges at the supraclavicular fossa Travels laterally to bind at the shoulder Descends back to the supraclavicular fossa Descends into the chest and extends over the hypochondrium and diaphragm Starts at LU-11 Lung Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 37
38 Indications of the Sinew Channel of the Lung o Cramping, spasm and pain along the course of the channel. o If severe, accumulation of lumps and pain around the right hypochondrium, and haemoptysis (spitting blood) Endeavour College of Natural Health 38
39 Cutaneous Regions of the Tai Yin Taiyin Cutaneous (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 39
40 The Pericardium (PC) Hand Jue Yin Channels and Collaterals Deadman et al., 2007, pp Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 40
41 Pericardium (Hand Jue Yin) Channel System o The Pericardium (Hand Jue Yin) Primary channel o The Pericardium Divergent channel o The Pericardium Luo-connecting collateral o The Pericardium Sinew channel o The Pericardium Cutaneous region Endeavour College of Natural Health 41
42 The Pericardium (PC) Hand Jue Yin Pericardium Primary Channel Regular Points 9 points Connecting Zang Fu Triple Energizer Main Channel Connections with other channels Nil Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 42
43 Pathway of the Pericardium Channel PC-1 Pericardium PC-3 PC-6 PC-7 Diaphragm Upper Jiao Middle Jiao Lower Jiao PC-9 Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 43
44 o Originates in the chest o Connects with the Pericardium o Descends through the diaphragm o Connects with the upper, middle, and lower jiao to the abdomen o One branch emerges at the fourth intercostal space, at PC-1 Internal Pathway of the Pericardium Channel Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 44
45 Pathway of the Pericardium Channel Pericardium Channel Human (Lian et al., 2005, p.191) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 45
46 External Pathway of the Pericardium Channel From PC-1, in the fourth intercostal space lateral to the nipple, the main channel arcs over the axilla Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 46
47 External Pathway of the Pericardium Channel cont d Traverses the anterio-medial aspect of the upper arm to PC-3 at the cubital fossa of the elbow Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 47
48 External Pathway of the Pericardium Channel cont d o Runs between the tendons palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis, o passing through PC 6, 2 cun proximal to the distal wrist. Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 48
49 External Pathway of the Pericardium Channel cont d Runs between the Lung and Heart channels, to the wrist PC-7. Terminates at the tip of the middle finger at PC-9. Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 49
50 Branch of the Main Pericardium Channel Separates from the main channel at PC-8 And follows the radial side of the ring finger to its tip. Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 50
51 Actions & Indications of the Pericardium Channel o Cardiac pain, palpitation, arrhythmias o Pain of the chest o Pain of the lateral costal region o Disorders of the Stomach (vomiting) o Febrile diseases o Disorders of the spirit (Shen) o Swelling and pain in the axilla Endeavour College of Natural Health 51
52 Luo-Connecting Channel of the Pericardium Separates at PC-6 Follows the main channel Converges with the Pericardium and Heart Pericardium Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 52
53 Indications of the Luo-connecting channel of the Pericardium o Cardiac Pain o Restlessness/ Vexation Endeavour College of Natural Health 53
54 Divergent Channel of the Pericardium throat emerges posterior to the ear to unite with the Triple Energizer channel connects to the Triple Energizer Separates from the primary Pericardium channel 3 cun inferior to the axilla PC Divergent (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 54
55 Pericardium Sinew Channel Originates at PC-9 Ascends the forearm and binds at the medial elbow Continues along the anteriomedial aspect of the upper arm and binds at the axilla Spreads over the anterior and posterior aspects of the hypochondriac region A branch enters and diffuses at the chest; binding at the diaphragm. Starts at PC-9 PC Sinew (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 55
56 Indications of the Pericardium Sinew Channel o Stiffness and spasm along the course of the channel o Pain in the chest o Xi Ben disorder (dyspnoea with a cup size swelling on the right hypochondriac region) Endeavour College of Natural Health 56
57 Cutaneous Regions of the Jue Yin Jueyin Cutaneous (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 57
58 The Heart (HT) Hand Shao Yin Channels & Collaterals Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 58
59 Heart (Hand Shao Yin) Channel System o The Heart (Hand Shao Yin) Primary channel o The Heart Divergent channel o The Heart Luo-connecting collateral o The Heart Sinew channel o The Heart Cutaneous region Endeavour College of Natural Health 59
60 The Heart (HT) Hand Shao Yin Primary Channel Regular Points 9 points Connecting Zang Fu Heart Lungs Small Intestine Main Channel Connections with other channels Nil Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 60
61 Pathway of the Heart Channel Tissue surrounding eye HT-1 Lung Oesophagus HT-4 HT-3 Diaphragm Heart HT-7 HT-9 Small Intestine Heart Channel (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 61
62 Internal Pathway of the Heart Channel Heart Channel (Deadman, Al-Khafaji & Baker 2007, p. 209) o Originates in the Heart and spreads throughout the network of blood vessels around the Heart o Descends through the diaphragm and connects with the Small Intestine o One branch ascends past the oesophagus to the face, connecting with the surrounding eye tissue o Another branch exits the Heart and travels to the Lungs before emerging at HT-1 at the axilla Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 62
63 Pathway of the Heart Channel HT Channel Human (Lian et al., 2005, p.99) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 63
64 External Pathway of the Heart Channel From HT-1 the channel proceeds medially along the arm to HT-3 at the transverse cubital crease of the elbow HT points (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 64
65 External Pathway of the Heart Channel Proceeds along the anterio-medial aspect of the forearm through HT-4 to HT-7 at the pisiform bone of the wrist HT points (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 65
66 External Pathway of the Heart Channel HT points (Deadman, 2007) Continues along the palm to the radial aspect of the fifth metacarpal to end at HT-9 at radial corner of nail Endeavour College of Natural Health 66
67 Branch of the Main Heart Channel There are no branches from the main channel of the Heart meridian Endeavour College of Natural Health 67
68 Actions & Indications of the Heart Channel o Disorders of the chest/heart o Calm the spirit o Treating tongue and speech disorders o Throat conditions (pain, swelling) o Eye conditions o Disorders along the channel o Various conditions of the complexion Endeavour College of Natural Health 68
69 Luo-Connecting Channel of the Heart Separates at HT-5 Connects with the Small Intestine channel Returns to the Heart meridian Travels to the Heart Zang Links with the root of the tongue and eye HT Luo (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 69
70 Indications of the Luo-connecting channel of the Heart o Fullness or distension of the chest o Aphasia Endeavour College of Natural Health 70
71 Divergent Channel of the Heart Connects with the Small Intestine channel at inner canthus of the eye Enters chest Connects to the Heart Separates from primary Heart channel at the axillary fossa HT Divergent (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 71
72 Originates at HT-9 on the fifth metacarpal and binds at the wrist (pisiform bone) Sinew Channel of the Heart Follows the course of the primary channel and binds at the elbow and axilla Intersects Lung Sinew channel Spreads over the breast region to the centre of chest Travels over the diaphragm to the umbilicus HT Sinew (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 72
73 Indications of the Sinew Channel of the Heart o Internal cramping o Spasm and pain along the course of the channel. o Accumulation (lumps) below the chest Endeavour College of Natural Health 73
74 Arm Yin Sinew Channels Try this quick experiment Flex your biceps. What other muscles do you notice that you tense at the same time. How does that relate to the sinew channels of the arm yin? Endeavour College of Natural Health 74
75 Cutaneous Regions of the Shao Yin Shaoyin Cutaneous (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 75
76 Three Arm Yin Summary of Indications Portion of Lung Pericardium Heart Channel Chest Chest & lung Heart & chest N/A Hand & Arm Throat, chest,lung Heart, chest, stomach Mental disorders Heat disease Heart, chest Mental disorders Ellis, Wiseman, Boss & Cleaver (2004, pp. 57,88, 172, 276) (Ellis, Wiseman & Boss, 2004) Endeavour College of Natural Health 76
77 Case Study Brad presents with pain in the chest and shortness of breath. When severe the pain sometimes causes vomiting. What is the first question you ask Brad? Heart Pain Cliparts # (Clipart Library, n.d.) Endeavour College of Natural Health 77
78 Case Study cont d Discuss when it would be appropriate to proceed with treatment. Endeavour College of Natural Health 78
79 Case Study Which of the three arm yin channels could be used to treat the chest? If the chest pain is related to coughing- Which would be the channel of choice to treat Belinda? If the chest pain is accompanied by palpitations- Which would be the channel/s of choice to treat Belinda? Which channel/s would you use to address the vomiting? Endeavour College of Natural Health 79
80 Demonstration Lecturer demonstrates tracing external channels (marked in a solid line) on a student model. Lung Pericardium Heart Arm Yin (Deadman, 2007) Endeavour College of Natural Health 80
81 Group Work Divide into groups of 2 and, using a chinagraph pencil, eyeliner or water based marker, trace the pathway of the specified channels on a student partner using main points as landmarks Endeavour College of Natural Health 81
82 References Clipart library. (n.d.). Heart pain cliparts # [Image}. Retrieved January 30, 2018, from Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007). A manual of acupuncture (2 ed.). Hove, East Sussex: Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications. [Available as web app 2013, mobile app 2009 or text 2007] Ellis, A., Wiseman, N., Boss, K. & Cleaver, J. (2004). Fundamentals of Chinese Acupuncture. revised edn, Paradignm Publications, Taos. García, L., (2008). A 18th century azimuthal compass from Spain [Image]. Retrieved June 2, 2015, from Lian, Y., Chen, C., Hammes, M. & Kolster, B. (2005). Pictorial Atlas of Acupuncture, H.G.Ullmann, Marburg. Maciocia, G. (2015). The foundations of Chinese medicine, (3rd ed.). Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh. World Health Organisation. (2008). WHO standard acupuncture point locations in the Western Pacific Region. Manila, Philippines: World Health Organization. Endeavour College of Natural Health 82
83 Endeavour College of Natural Health 83
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 9 Four Examination Methods in Channel Diagnosis Channels & Collaterals of the Kidney Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 9 Four Examination Methods in Channel Diagnosis Channels & Collaterals of the Kidney Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman,
PRACTICAL EXAM REVISION AND PREPARATION GUIDE
 PRACTICAL EXAM REVISION AND PREPARATION GUIDE SUBJECT: CMAC Acupuncture Channel Theory EXAM: Practical exam LENGTH OF EXAM: 3 minutes WEIGHT: 3% TOTAL MARKS: 3 marks SESSIONS COVERED: SN 2-5 EXAM: Practical
PRACTICAL EXAM REVISION AND PREPARATION GUIDE SUBJECT: CMAC Acupuncture Channel Theory EXAM: Practical exam LENGTH OF EXAM: 3 minutes WEIGHT: 3% TOTAL MARKS: 3 marks SESSIONS COVERED: SN 2-5 EXAM: Practical
Acupuncture Channel Theory
 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 6 Conception, Governor, Belt & Thoroughfare Vessels Review Arm Channel Pathways Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji,
Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 6 Conception, Governor, Belt & Thoroughfare Vessels Review Arm Channel Pathways Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji,
Pericardium Channel and Points
 Pericardium Channel and Points Primary channel pathway Center of the chest (hypochondriac area) Emerge in the P1 PC SJ arches over the axilla The midline of the upper arm and fore arm (between the tendons
Pericardium Channel and Points Primary channel pathway Center of the chest (hypochondriac area) Emerge in the P1 PC SJ arches over the axilla The midline of the upper arm and fore arm (between the tendons
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL
 ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions
 Chapter 3 Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions 1 Characteristics of Luo Vessels Connect external/internal pairs Distribute qi throughout the body Harmonize circulation 2 In all, there are fifteen
Chapter 3 Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions 1 Characteristics of Luo Vessels Connect external/internal pairs Distribute qi throughout the body Harmonize circulation 2 In all, there are fifteen
CMPR121. Session 13. Small Intestine
 CMPR121 Session 13 Small Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Small Intestine o Separates the pure from the impure o Receives & transports food o Separates fluids o Is responsible
CMPR121 Session 13 Small Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Small Intestine o Separates the pure from the impure o Receives & transports food o Separates fluids o Is responsible
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
MASTER CHART. Guide to 60 Transformational Acupoints 1. bigtreehealing.com
 MASTER CHART GUIDE TO 60 TRANSFORMATIONAL ACUPOINTS Guide to 60 Transformational Acupoints 1 LU 5 LU 7 LU 9 On elbow crease, thumb side of tendon of biceps brachii. Lung Meridian On thumb side of forearm,
MASTER CHART GUIDE TO 60 TRANSFORMATIONAL ACUPOINTS Guide to 60 Transformational Acupoints 1 LU 5 LU 7 LU 9 On elbow crease, thumb side of tendon of biceps brachii. Lung Meridian On thumb side of forearm,
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Small Intestine Channel 1 THE SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND TAIYANG
 Small Intestine Channel 1 THE SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND TAIYANG Small Intestine Channel 2 THE SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND TAIYANG meets with Dazhui DU-14, Fufen BL-41 and Dazhu BL-11 meets with
Small Intestine Channel 1 THE SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND TAIYANG Small Intestine Channel 2 THE SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND TAIYANG meets with Dazhui DU-14, Fufen BL-41 and Dazhu BL-11 meets with
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Tracking the Dragon. Dr. Janice Walton-Hadlock, DAOM
 Tracking the Dragon Dr. Janice Walton-Hadlock, DAOM Tracking the Dragon Dr. Janice Walton-Hadlock, DAOM, LAc Illustrated by Ben Bateson Published by Fastpencil, Cupertino, CA First edition: 2010 Janice
Tracking the Dragon Dr. Janice Walton-Hadlock, DAOM Tracking the Dragon Dr. Janice Walton-Hadlock, DAOM, LAc Illustrated by Ben Bateson Published by Fastpencil, Cupertino, CA First edition: 2010 Janice
Contents. Basic Theory of Acupuncture. (Page 1) Acupuncture Points. (Page 31) Side Effects of Acupuncture. (Page 51)
 VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Symptomology of the EV. Flow of the EV and it characteristics
 Symptomology of the EV Flow of the EV and it characteristics Diagnosis by symptomology and pathology Main points of each EV s pathology (1) Dū Mài or Governing Vessel It has the strongest Yang factor.
Symptomology of the EV Flow of the EV and it characteristics Diagnosis by symptomology and pathology Main points of each EV s pathology (1) Dū Mài or Governing Vessel It has the strongest Yang factor.
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 1 Overview of Channel Theory Work Health & Safety/ Infection control Chinese Medicine Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Welcome
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 1 Overview of Channel Theory Work Health & Safety/ Infection control Chinese Medicine Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Welcome
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
LU/METAL 3-5A English Location Notes. LI/METAL 5-7A English Location Notes
 LU/METAL 3-5A English Location Notes LU-1 LU-5 LU-7 LU-9 LU-11 Center of gathering Indentation in the stream Broken Sequence Great stagnation Young merchant (Sound of metal element) 6 cun lateral to the
LU/METAL 3-5A English Location Notes LU-1 LU-5 LU-7 LU-9 LU-11 Center of gathering Indentation in the stream Broken Sequence Great stagnation Young merchant (Sound of metal element) 6 cun lateral to the
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Commonly Used Canine Transpositional Acupuncture Points
 Commonly Used Canine Transpositional Acupuncture Points Dr. Carla Leon Assisted by Dr. Lisa Travisanello, Dr. Cheryl Chrisman, Solo, Brittany and Hurricane Frances 2004 Chinese Inch=Cun The width of the
Commonly Used Canine Transpositional Acupuncture Points Dr. Carla Leon Assisted by Dr. Lisa Travisanello, Dr. Cheryl Chrisman, Solo, Brittany and Hurricane Frances 2004 Chinese Inch=Cun The width of the
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Week 8 : Pericardium / Triple Warmer
 Week 8 : Pericardium / Triple Warmer Begin in the shoulder rotation position......transition to an arm rotation... Then bring the arm back into the first Pericardium stretch. Hold the arm to your body,
Week 8 : Pericardium / Triple Warmer Begin in the shoulder rotation position......transition to an arm rotation... Then bring the arm back into the first Pericardium stretch. Hold the arm to your body,
Commonly Used and Important Acupuncture Points
 Commonly Used and Important Acupuncture Points (These are just a few points that can be taken home and used in treatment and by no means are exclusive.) Abstract: This lecture will go over some commonly
Commonly Used and Important Acupuncture Points (These are just a few points that can be taken home and used in treatment and by no means are exclusive.) Abstract: This lecture will go over some commonly
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Traditional Thai Acupressure Points. The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS
 Traditional Thai Acupressure Points The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS lines of the SHOULDER BLADES AND POSTERIOR ARM Scapula Line This line runs through landmarks: 1. Above the midpoint
Traditional Thai Acupressure Points The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS lines of the SHOULDER BLADES AND POSTERIOR ARM Scapula Line This line runs through landmarks: 1. Above the midpoint
A N OTHER - 04 September :16 - Source Points. A N OTHER - 04 September :16 - Source Points 11AM-3PM 3PM-7PM
 Exam Findings A N OTHER - 04 September 2008 19:16 - Source Points 200 A N OTHER - 04 September 2008 19:16 - Source Points 175 150 131134 125 126 116 101 100 75 112 130 138136 124 118 148 132 128130 122
Exam Findings A N OTHER - 04 September 2008 19:16 - Source Points 200 A N OTHER - 04 September 2008 19:16 - Source Points 175 150 131134 125 126 116 101 100 75 112 130 138136 124 118 148 132 128130 122
TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE OUTLINE The Theory of Yin and Yang, Five Element Theory, and Fundamental Substances (Qi, Blood, and Body Fluids)
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE OUTLINE The Theory of Yin and Yang, Five Element Theory, and Fundamental Substances (Qi, Blood, and Body Fluids)
Zhen/Jiu. Have a pleasant treatment with VedaPulse! Patient: John Smith Age: 34 Data: :50:36
 Zhen/Jiu Patient: John Smith Age: 34 Data: 29-08-2018 10:50:36 Nosology: Digestive system diseases - acute gastritis Recipe: Zhen prescription (acupuncture, acupressure, tsubo/seed therapy, application
Zhen/Jiu Patient: John Smith Age: 34 Data: 29-08-2018 10:50:36 Nosology: Digestive system diseases - acute gastritis Recipe: Zhen prescription (acupuncture, acupressure, tsubo/seed therapy, application
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla.
 1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION
 MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Introduction to Acupuncture
 Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020 Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020 Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Course: Meridians and Energetics Date: 10/10/07. Study Questions Exam 1
 Course: Meridians and Energetics Date: 10/10/07 Study Questions Exam 1 Which are Yin and which are Yang? Above the waist Yang Inferior Yin Back of the Body Skin and muscles Body in general Superior Front
Course: Meridians and Energetics Date: 10/10/07 Study Questions Exam 1 Which are Yin and which are Yang? Above the waist Yang Inferior Yin Back of the Body Skin and muscles Body in general Superior Front
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
"Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Course: Acupuncture Treatment of Disease 3 Date: May 11, 2009 Class #: 5 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Sciatica and Tennis Elbow
 Course: Acupuncture Treatment of Disease 3 Date: May 11, 2009 Class #: 5 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Sciatica and Tennis Elbow Characterized by pain and numbness on palmar side median nerve is compressed
Course: Acupuncture Treatment of Disease 3 Date: May 11, 2009 Class #: 5 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Sciatica and Tennis Elbow Characterized by pain and numbness on palmar side median nerve is compressed
 Acupoints And Meridians The theory of meridians and acupoints is the basic theory of Tai Chi and Qi Gong therapy. The science of meridians expounds the routes that connect different parts of the body based
Acupoints And Meridians The theory of meridians and acupoints is the basic theory of Tai Chi and Qi Gong therapy. The science of meridians expounds the routes that connect different parts of the body based
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS. Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac
 INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S17 Discussion on the Essentials of Pulse S18 Discussion on the Pulse Conditions of Healthy People
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S17 Discussion on the Essentials of Pulse S18 Discussion on the Pulse Conditions of Healthy People
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Course: Energetics 1 Exam 2 Date: Study Questions Exam 2
 Course: Energetics 1 Exam 2 Date: 11-6-07 Study Questions Exam 2 To know for test: Point Categories Will ask all pt categories! Fill in blanks write about diff pt categories. I.e., which is the Yuan source
Course: Energetics 1 Exam 2 Date: 11-6-07 Study Questions Exam 2 To know for test: Point Categories Will ask all pt categories! Fill in blanks write about diff pt categories. I.e., which is the Yuan source
大 dà 可 kě horse. 口 kŏu mouth. 奇 qí extraordinary; wonder; strange; queer; rare. 經 jīng channels. 八 bā eight. 脈 mài vessels; arteries and veins; pulse.
 Qí Jīng Bā Mài 奇經八脈 Eight Extra Ordinary Channel System In different places of the Nàn Jīng, the channels of the 奇經八脈, qí jīng bā mài are described. The eight extraordinary channel system, or the bā qí
Qí Jīng Bā Mài 奇經八脈 Eight Extra Ordinary Channel System In different places of the Nàn Jīng, the channels of the 奇經八脈, qí jīng bā mài are described. The eight extraordinary channel system, or the bā qí
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone
 *the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
Subacromial Bursa Injection
 Subacromial Bursa Injection 5 cc syringe, 21 gauge 1.5 inch needle 1% lidocaine - 4cc 40mg triamcinolone - 1 cc of 40mg/ml identify site-seat the patient with weight of arm hanging down, palpate the lateral
Subacromial Bursa Injection 5 cc syringe, 21 gauge 1.5 inch needle 1% lidocaine - 4cc 40mg triamcinolone - 1 cc of 40mg/ml identify site-seat the patient with weight of arm hanging down, palpate the lateral
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING
 DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
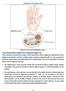 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Systematic Anatomy (For international students)
 Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy
 The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Introduction and anatomy History: discovered by Prof. Zhang, Yingqing firstly in 1973. Shandong University, China. ECIWO
The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Introduction and anatomy History: discovered by Prof. Zhang, Yingqing firstly in 1973. Shandong University, China. ECIWO
ANATOMY. Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date :
 ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
