Constipation in Children
|
|
|
- Amie Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 7 Constipation in Children Constipation is a very common problem for children. For most children, constipation means passing hard stools, with difficulty, less frequently than normal. Regular soiling (often mistaken for runny diarrhoea) may indicate that a child has bad constipation with impaction (a blockage of stools/faeces). Where no particular disease or illness is the cause of the constipation, it is called idiopathic constipation. It is important that constipation be recognised and treated early, with laxatives, to prevent it from becoming a long-term (chronic) problem. Your child's bowels - what is normal? Parents often get very worried about their child's bowel habit. This anxiety can start when the child is a baby, with concern over the number of dirty nappies. The main thing to realise is that every child is different. Normal can vary quite a bit. It is a change in what is normal for your child, that suggests a problem. Babies will open their bowels anything from several times per day, to once every few days. The frequency of bowel movements is not particularly important. What is important is that the stools (motions, poo, faeces) are soft and easily passed. Breast-fed babies tend to pass runnier, mustard yellow-coloured stools. This is because breast milk is better digested than infant formula (bottle feeds). Newborn breast-fed babies may open their bowels with every feed. However, it is also normal for a breast-fed baby to go up to a week without a bowel movement. Bottle-fed babies often need to open their bowels daily, as the stools are bulkier. Bottle-fed baby stools smell worse (more like an adult's). It is not uncommon for your baby's stools to vary in colour and consistency from day to day. Any prolonged change to harder, less frequent stools might mean constipation. As babies are weaned to solid foods, their stools will change in colour and smell. The frequency may again change. Generally the stools become thicker, darker and a lot more smelly. You will notice that your baby's stools will alter depending upon what you have fed him or her. Some high-fibre foods, such as raisins, may even pass through your baby's bowels virtually unchanged, appearing in the nappy at the next change. As your baby grows up, into a toddler and then a young child, you may see further changes in their stool frequency and consistency, often dependent on what they are eating. Your child's bowels - what is abnormal? As you can see, there is great variation in a child's bowel habit, dependent on their age and what they are fed. As already mentioned, it is a change in what is normal for your child, that suggests a problem. Anything from three times a day to once every other day is common and normal. Less often than every other day means that constipation is likely. However, it can still be normal if the stools are soft and well formed, and passed easily. It may be normal for your baby to go a bit red in the face when straining to pass a stool. Constipation is more of a problem than this. Breast-fed babies seldom get constipated as breast milk contains exactly the right balance of nutrients to keep the stools soft and easily passed.
2 Page 2 of 7 Diarrhoea usually means very runny stools, often passed more frequently than normal. Breast-fed babies get diarrhoea less frequently than other babies, as breast milk has a protective effect against the germs that can cause diarrhoea. What is constipation? Constipation in children or babies can mean any, or all, of the following: Difficulty or straining when passing stools. Pain when passing stools, sometimes with a tiny amount of blood in the nappy or on the toilet paper, due to a small tear in the skin of the anus. Passing stools less often than normal. Generally, this is less than three complete (proper) stools per week. Stools that are hard, and perhaps very large, or pellet-like and small, like rabbit droppings. Other symptoms of constipation As well as less frequent, hard (and perhaps painful) stools, constipation can cause: Tummy ache (abdominal pain). Poor appetite. General malaise (feeling 'off colour'). Behavioural changes, such as being more irritable or unhappy. Fidgeting, restlessness and other signs that the child needs to go to the toilet. Feeling sick (nausea). Severe constipation can cause impaction (where a very large stool is stuck in the rectum). This can cause further symptoms. In particular, this can cause a child to soil their pants regularly with very soft faeces, or with faecal-stained mucus. This is often mistaken by parents as diarrhoea. Impaction is discussed in detail later. Types of constipation in children and babies 1. Idiopathic constipation. This is common. The word idiopathic means of unknown cause. Various factors may be involved (discussed later), but many children become constipated for no known reason. Short bouts of constipation. It is common for children and babies to have a bout of mild constipation for a day or so. This may settle quickly, often without the need for medical treatment. Long-term constipation. In about 1 in 3 children who become constipated, the problem becomes more long-term (persistent). This is also called chronic idiopathic constipation. 2. Constipation due to an underlying disease or condition. This is uncommon. The constipation is said to be secondary to this other problem. Some examples of conditions and problems that can cause constipation are: Some neurological conditions. Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid gland). Cystic fibrosis. Rare diseases with abnormal development of the bowel, such as Hirschsprung's disease. As a side-effect of certain medications that a child has to take for another condition. Treatment may involve treating the underlying condition (if that is possible) in addition to tackling the constipation.
3 Page 3 of 7 Worrying symptoms or signs that may indicate a secondary cause include the following. These should be mentioned to your GP. It is also possible that some of these symptoms could mean your child is more seriously unwell: Vomiting. Weight loss or failure to gain weight (thrive). A swollen, stretched tummy. Severe pain. A baby that does not pass its first stool (called meconium) within the first 48 hours of life. Abnormalities of the anus - for example if it is closed over. Neurological (nervous system) problems such as weak or paralysed legs. Sores or ulcers near the anus. Excessive thirst. Urinary symptoms - such as passing huge volumes of urine, urine that is very dark or painful urination with smelly urine. Very pale-coloured stools (especially if the urine is very dark too). The rest of this leaflet is about idiopathic constipation. Does my child need any tests? Tests are not normally needed to diagnose idiopathic constipation. Your GP is likely to ask various questions and do a general examination to rule out secondary causes of constipation. By examining your child's abdomen (tummy), a GP can tell if there are lots of stools in the bowel. This can give an indication if impaction (discussed later) has developed. (If an underlying cause of constipation is suspected, your GP will refer your child to a paediatrician (children's doctor) and further tests may be done.) What causes idiopathic constipation? As mentioned, idiopathic means that there is no disease or known cause for the constipation. However, it is thought that various factors may contribute to constipation developing, or make it worse. These include diet, stool holding and emotional factors. Diet Dietary factors that may play a part in constipation are: Not eating enough foods with fibre (the roughage part of the food that is not digested and stays in the gut). Not having enough to drink. Stools tend to become harder, drier, and more difficult to pass if there is little fibre and fluid in the gut. Stool holding This means the child has the feeling of needing the toilet, but resists it. The child holds on to the stool, trying to ignore the desire to empty the bowels. This is quite common. You may see your child crossing their legs, sitting on the back of the heels, or doing similar things to help resist the feeling of needing the toilet. Your child may clench his or her buttocks to try to stop the stool from coming out, and may seem quite fidgety. You may notice smudges of stool on your child's pants, often when they are unable to hold on any longer. The longer the child holds on, the bigger the stool gets. Eventually the child has to go, but the large stool is more difficult to pass, and often more painful. This may lead to a bit of a vicious cycle where the child is even more reluctant to open his or her bowels the next time. There are a number of reasons why children may hold on to stools: A previous stool that they passed may have been a struggle or painful. So, they try
4 Page 4 of 7 and put off doing it again. Their anus may be sore or have a crack (anal fissure) from passing a previous large stool. It is then painful to pass further stools. So, the child may resist the urge to pass a stool. They may have a dislike of unfamiliar or smelly toilets, such as at school or on holiday. The child may want to put things off until they get home. Emotional problems Constipation problems may be made worse with upset due to change in surroundings or routine. Common examples are moving house and starting nursery. Potty training may be a factor if a child becomes scared of using the potty. Fears and phobias are usually the underlying reasons for these problems. What is idiopathic constipation with impaction? Impaction means that the bowel is, in effect, blocked by a large amount of hard stool. Idiopathic constipation with impaction most commonly develops in children between the ages of 2 and 4 years, but older or younger children can be affected. Symptoms and features include: Recurrent episodes when the child is uncomfortable or distressed trying to pass a stool. The child soils their pants regularly with very soft faeces, or with faecal-stained mucus. This is often mistaken by parents as diarrhoea. The child may also become irritable, not eat much, feel sick, have tummy pains from time to time, and may be generally out of sorts. A doctor can often feel a backlog of hard, lumpy stools when he or she examines the child's abdomen (tummy). The diagram below shows how a child may develop impaction, and the symptoms this may cause. Normally, stools build up in the lowest part of the bowel. When stools accumulate, they start to pass into the rectum (the last part of the bowel) which stretches. This sends nerve messages to the brain, telling you that you need to empty your bowels. If the stool is not passed out then more stools from higher up also reach the rectum.
5 Page 5 of 7 Eventually, large hard stools may build up in the rectum. The rectum may then stretch and enlarge (dilate) much more than normal, to cope with the excessive amount of stools. A very large stool may develop and get stuck (impacted) in an enlarged rectum. If the rectum remains enlarged then the normal sensation of needing the toilet is reduced. The power to pass out a large stool is also reduced (the rectum becomes 'floppy'). More stools build up in the colon behind the impacted stool in the rectum. The lowest part of an impacted stool lies just above the anus. Some of this stool liquefies (becomes runny) and leaks out of the anus. This soils the child's pants or bedclothes. Also, some softer, more liquid stools from higher up the colon may bypass around the impacted hard stool. This also leaks out and soils the pants or bedclothes and can be mistaken for diarrhoea. The child has no control of this leaking and soiling. When a stool is eventually passed, because the rectum is distended and weakened, it simply fills up fairly quickly again with more hard stool from the backlog behind. What is the treatment of idiopathic constipation? Laxatives Idiopathic constipation that has lasted for more than a few days is usually treated with laxatives. Your doctor will advise on the type and strength needed. This may depend on factors such as the age of the child, severity of the constipation and the response to the treatment. Laxatives for children commonly come either as sachets or a powder that is made up into a drink, or as liquid/syrup. The laxatives used for children are broadly divided into two types. Macrogols (also called polyethylene glycols) are a type of laxative that pulls fluid into the bowel, keeping the stools soft. They are also known as osmotic laxatives. For example, Movicol Paediatric Plain is one brand that is commonly used first. This is mixed into water to make a drink to which cordial, such as blackcurrant squash, can be added to make it taste nicer. Lactulose is another type of osmotic laxative. Stimulant laxatives. These stimulate (encourage) the bowel to pass the stools out. There are several different types of stimulant laxative. Sodium picosulfate, bisacodyl, senna and docusate sodium are all examples. A stimulant laxative tends to be added in addition to a macrogol if the macrogol is not sufficient on its own. Laxatives are normally continued for several weeks after the constipation has eased and a regular bowel habit has been established. This is called maintenance treatment. So, in total, the duration of treatment may be for several months. Do not stop the laxatives prescribed abruptly. Stopping laxatives abruptly might cause the constipation to quickly recur. Your doctor will normally advise a gradual reduction in the dose over a period of time depending on how the stools have become in their consistency and frequency. Some children may even require treatment with laxatives for several years. Treatment of impaction - if needed Similar treatments are used for the the treatments listed above. The main difference is that higher doses of laxatives are needed initially to clear the large amount of faeces blocking the rectum. Secondly, laxatives are also usually needed for much longer, as maintenance treatment. The aim is to prevent a build-up of hard stools recurring again, which will prevent impaction returning. As a result of maintenance treatment: The enlarged rectum can gradually get back to a normal size and function properly again. Constipation is then unlikely to recur.
6 Page 6 of 7 If laxatives are stopped too soon, a large stool is likely to recur again in the weakened 'floppy' rectum which has not had time to get back to a normal size and strength. Treatment to clear impacted stools from the rectum can be a difficult time for you and your child. It is likely that your child will actually have a few more tummy pains than before, and that there will be more soiled pants. It is important to persevere, as these problems are only temporary. Clearing the impacted stools is an essential part of treatment. In rare instances, where treatment of impacted stools has failed, a child may be treated in hospital. In hospital, stronger medicines to empty the bowel, called enemas, can be given via the rectum. For very hard to treat cases, a child can have a general anaesthetic and the bowel can be cleared out manually by a surgeon. Diet Dietary measures should not be used on their own to treat idiopathic constipation as it will be unlikely to solve the problem. However, it is still important to get a child into a habit of eating a good balanced diet. This is to include plenty of drinks (mainly water) and foods with fibre. This will help to prevent a recurrence of constipation once it has cleared. How can constipation in children be prevented? Eating foods with plenty of fibre and drinking plenty makes stools that are bulky, but soft and easy to pass out. Getting plenty of exercise is also thought to help. Food and fibre This advice applies to babies who are weaned, and children. Foods which are high in fibre are: fruit, vegetables, cereals, wholemeal bread. A change to a high-fibre diet is often 'easier said then done', as many children are fussy eaters. However, any change is better than none. Listed below are some ideas to try and increase your child's fibre intake: A meal of jacket potatoes with baked beans, or vegetable soup with bread. Dried (or semi-dried) apricots or raisins for snacks. Porridge or other high-fibre cereals (such as Weetabix, Shredded Wheat or All Bran ) for breakfast. Offering fruit with every meal - perhaps cut up into little chunks to make it look more appealing. Perhaps do not allow sweets or desserts until your child has eaten a piece of fruit. Another tip for when children are reluctant to eat high-fibre foods is to add powdered bran to yoghurt. The yoghurt will feel grainy, but powdered bran is tasteless. Drink If a bottle-fed baby has a tendency to become constipated you can try offering water between feeds. (Never dilute infant formula (milk) that is given to bottle-fed babies.) Although it is unusual for a breast-fed baby to become constipated, you can also offer water between feeds. Older, weaned babies can be given diluted fruit juice (preferably without added sugar). Pureed fruit and vegetables are the usual starting points for weaning, after baby rice, and these are good for preventing constipation. Encourage children to drink plenty. However, some children get into the habit of only drinking squash, fizzy drinks or milk to quench their thirst. These may fill them up, and make them less likely to eat proper meals with food that contains plenty of fibre. Try to limit these kinds of drinks. Give water as the main drink. However, fruit juices that contain fructose or sorbitol have a laxative action (such as prune, pear, or apple juice). These may be useful from time to time if the stools become harder than usual and you suspect constipation may be developing. Some other tips which may help Try to get children into a regular toilet habit. After breakfast, before school or nursery,
7 Page 7 of 7 is often best. Try to allow plenty of time so they don't feel rushed. Some kind of reward system is sometimes useful in younger children prone to holding on to stools. You could give a small treat, or use stickers or star charts to reinforce the message. Praise your child for passing a stool in the potty or toilet, but do not punish accidents. It is easy to become frustrated with soiled pants or a child who refuses to pass a stool. Try to keep calm and not make a fuss over the toilet issue. If your child can see that you are stressed or upset, they will pick up on this feeling, and the toileting issue can become even more of a fraught battle. The aim is to be 'matter of fact' and relaxed about it. Further information Your GP, practice nurse and health visitor are good sources of advice and information about childhood constipation. The school nurse may also be able to give some practical support and help. References Constipation in children and young people, NICE Clinical Guideline (May 2010); Diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care Bardisa-Ezcurra L, Ullman R, Gordon J; Diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation: summary of NICE BMJ Jun 1;340:c2585. doi: /bmj.c2585. Constipation, Clinical Knowledge Summaries (January 2008) No authors listed; Managing constipation in children. Drug Ther Bull Aug;38 (8): [abstract] Comprehensive patient resources are available at Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but make no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other health care professional for diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. For details see our conditions. EMIS 2010 Reviewed: 11 Aug 2010 DocID: 4584 Version: 40 For the planned review period see the Data Creation and Quality Control Process.
Advice for Parents and Carers
 Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives. HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians.
 NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Constipation usually is not a cause for concern, and easy to avoid by adopting healthy eating and exercise habits.
 From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis)
 Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis) Page 1 of 5 Diverticula of the colon are common in older people. They commonly cause no symptoms, and in most cases no treatment
Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis) Page 1 of 5 Diverticula of the colon are common in older people. They commonly cause no symptoms, and in most cases no treatment
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Patient information - Constipation
 Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Dietary advice for people with colostomies
 Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Specialist Continence Advisory Service Local Partnerships. Constipation
 Patient Experience Team contact details: Phone: 0115 993 4542 Email: complaints@nottshc.nhs.uk Write to: Patient Experience Team, Moorgreen House, Highbury Hospital, Highbury Vale, Bulwell, Nottingham
Patient Experience Team contact details: Phone: 0115 993 4542 Email: complaints@nottshc.nhs.uk Write to: Patient Experience Team, Moorgreen House, Highbury Hospital, Highbury Vale, Bulwell, Nottingham
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Preparing for your colonscopy or sigmoidoscopy (afternoon appointment)
 These are instructions telling you how to take Klean Prep. What is Klean Prep? Klean Prep is a strong laxative that you need to take before your colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. Klean Prep will give you diarrhoea
These are instructions telling you how to take Klean Prep. What is Klean Prep? Klean Prep is a strong laxative that you need to take before your colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. Klean Prep will give you diarrhoea
Constipation in Children
 Lanarkshire Acute Hospitals Constipation in Children Information for patients What is constipation? Constipation refers to bowel movements which are infrequent, hard and difficult to pass. There are a
Lanarkshire Acute Hospitals Constipation in Children Information for patients What is constipation? Constipation refers to bowel movements which are infrequent, hard and difficult to pass. There are a
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Information for patients Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy (an Examination of the Left Lower Part of Your Colon) Endoscopy Unit Tel: 01473 702352 DPS ref: 01086-18(RP)
The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Information for patients Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy (an Examination of the Left Lower Part of Your Colon) Endoscopy Unit Tel: 01473 702352 DPS ref: 01086-18(RP)
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines. Version 1 November 2016
 Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Rotavirus. Children s Ward Macclesfield District General Hospital.
 Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
Constipation. AL amyloidosis Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems;
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems;
Dietary management of Gastroparesis
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Dietary management of Gastroparesis Nutrition and Dietetics Department The information in this leaflet tells you what Gastroparesis
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Dietary management of Gastroparesis Nutrition and Dietetics Department The information in this leaflet tells you what Gastroparesis
Constipation. What are the signs and symptoms of constipation? Less than three bowel movements per week. Pain or discomfort when opening your bowels
 Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients
 Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients 1 This patient information is written to provide patients with information and advice on how to manage
Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients 1 This patient information is written to provide patients with information and advice on how to manage
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Constipation. Myeloma Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Urinary tract infection
 Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included.
 Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
CONSTIPATION. Patient Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. Microbiology Department Pathology Laboratory
 CONSTIPATION Patient Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is constipation? Constipation is infrequent or difficult passing of hard, dry faeces. In most cases, it is harmless,
CONSTIPATION Patient Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is constipation? Constipation is infrequent or difficult passing of hard, dry faeces. In most cases, it is harmless,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
AL amyloidosis Infosheet
 AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises
 MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
About Parachoc. To Mum and Dad. Colour me in! Please take the time to read this book. Using the Parachoc training diary...
 Parachoc Training Diary About Parachoc Parachoc is a lubricating laxative containing liquid paraffin. It contains no bowel stimulant, so it is a gentle treatment for constipation. This diary is designed
Parachoc Training Diary About Parachoc Parachoc is a lubricating laxative containing liquid paraffin. It contains no bowel stimulant, so it is a gentle treatment for constipation. This diary is designed
Coping with tummy bugs. Advice for parents/carers on dealing with an episode of diarrhoea and/or vomiting
 Coping with tummy bugs Advice for parents/carers on dealing with an episode of diarrhoea and/or vomiting www.dettol.co.uk www.unitetheunion.org/cphva Looking after your child, Healthy hygiene With over
Coping with tummy bugs Advice for parents/carers on dealing with an episode of diarrhoea and/or vomiting www.dettol.co.uk www.unitetheunion.org/cphva Looking after your child, Healthy hygiene With over
EATING WELL AND CANCER
 EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
Biofeedback Program. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Managing your Bowels. Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System:
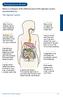 Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward. Hirschsprung Disease. Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward Hirschsprung Disease Information for parents What is Hirschsprung disease? Hirschsprung disease is a rare disorder of the bowels, most commonly the large bowel (colon).
The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward Hirschsprung Disease Information for parents What is Hirschsprung disease? Hirschsprung disease is a rare disorder of the bowels, most commonly the large bowel (colon).
How to Prepare for your. Colonoscopy using. Bowel Preparation. Type 2 Oral Medication. Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
 How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation Type 2 Oral Medication Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 12 Page 2 of 12 Contents Introduction Page 4 What is the bowel preparation?
How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation Type 2 Oral Medication Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 12 Page 2 of 12 Contents Introduction Page 4 What is the bowel preparation?
Ulster Council GAA. Health Booklet. Name: Class: School: supported by
 Ulster Council GAA Health Booklet Name: Class: School: supported by The Food Pyramid 5 a Day Fruit & Vegetables Drink Plenty of Water HEALTH PROMOTION UNIT DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND CHILDREN What counts
Ulster Council GAA Health Booklet Name: Class: School: supported by The Food Pyramid 5 a Day Fruit & Vegetables Drink Plenty of Water HEALTH PROMOTION UNIT DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND CHILDREN What counts
Adult barium enema. X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing. What is a barium enema? Are there alternatives to Barium enema?
 Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
Dietary. Ostomists. Advice. National: Scotland:
 Ostomists Dietary Advice www.fittleworth.com DTRY315-1 Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Dietary Advice for Ostomists Giving
Ostomists Dietary Advice www.fittleworth.com DTRY315-1 Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Dietary Advice for Ostomists Giving
Patient Information Leaflet. Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel
 Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Your guide to taking PLENVU
 Your guide to taking PLENVU Morning only dosing PLENVU is different to other bowel preparations you may have taken before. Please follow the instructions in this booklet carefully and also read the Patient
Your guide to taking PLENVU Morning only dosing PLENVU is different to other bowel preparations you may have taken before. Please follow the instructions in this booklet carefully and also read the Patient
BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE)
 BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE) This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child
BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE) This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child
DIVERTICULAR DISEASE DIET INFORMATION
 #wearenhft DIVERTICULAR DISEASE DIET INFORMATION 01604 745036 (Northampton) 01536 492317 (Kettering) nhft.nhs.uk/dietetics MAKING A DIFFERENCE FOR YOU, WITH YOU WHAT IS DIVERTICULAR DISEASE? A diverticulum
#wearenhft DIVERTICULAR DISEASE DIET INFORMATION 01604 745036 (Northampton) 01536 492317 (Kettering) nhft.nhs.uk/dietetics MAKING A DIFFERENCE FOR YOU, WITH YOU WHAT IS DIVERTICULAR DISEASE? A diverticulum
Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
Bowel Washouts Using an Antegrade Colonic Enema (ACE)
 This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child need bowel washouts? Bowel washouts are a method of
This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child need bowel washouts? Bowel washouts are a method of
Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery
 Lady Sobell Gastrointestinal Unit Wexham Park Hospital Introduction Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery This leaflet contains general information to help you with eating after surgery. If you need
Lady Sobell Gastrointestinal Unit Wexham Park Hospital Introduction Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery This leaflet contains general information to help you with eating after surgery. If you need
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Diverticulosis / Diverticulitis
 Diverticulosis / Diverticulitis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with Diverticulosis and / or Diverticulitis. The information
Diverticulosis / Diverticulitis Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with Diverticulosis and / or Diverticulitis. The information
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel. June st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota
 Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Gastroenteritis in Adults
 Gastroenteritis in Adults Page 1 of 5 Gastroenteritis is an infection of the gut (intestines). It causes diarrhoea and may also cause you to be sick (vomit), and have tummy (abdominal) pain and other symptoms.
Gastroenteritis in Adults Page 1 of 5 Gastroenteritis is an infection of the gut (intestines). It causes diarrhoea and may also cause you to be sick (vomit), and have tummy (abdominal) pain and other symptoms.
About barium meals and swallows. Information for patients Radiology
 About barium meals and swallows Information for patients Radiology What is a barium meal or barium swallow? A barium meal or swallow is a procedure that allows a doctor, called a radiologist, to look at
About barium meals and swallows Information for patients Radiology What is a barium meal or barium swallow? A barium meal or swallow is a procedure that allows a doctor, called a radiologist, to look at
What should my toddler be eating?
 Contents What should my toddler be eating? 1 Can my toddler eat the same food as us? 2 Semi-skimmed and skimmed milk 3 What foods should be avoided? 4 Sweet drinks 5 Food allergy 6 Vegetarian diets 7 Where
Contents What should my toddler be eating? 1 Can my toddler eat the same food as us? 2 Semi-skimmed and skimmed milk 3 What foods should be avoided? 4 Sweet drinks 5 Food allergy 6 Vegetarian diets 7 Where
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery
 Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Diet advice for patients with a stoma
 Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
GROUP PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION IN PATIENTS IN CLOZAPINE CLINICS. Version 1 (reviewed unchanged January 2018)
 GROUP PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION IN PATIENTS IN CLOZAPINE CLINICS Version 1 (reviewed unchanged January 2018) RATIFYING COMMITTEE Drugs and Therapeutics Group DATE ORIGINALLY 29 th October2014
GROUP PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION IN PATIENTS IN CLOZAPINE CLINICS Version 1 (reviewed unchanged January 2018) RATIFYING COMMITTEE Drugs and Therapeutics Group DATE ORIGINALLY 29 th October2014
Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia
 Information for parents and carers Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia What is hypoglycaemia? Hypoglycemia is having a blood glucose (also known as blood sugar) level that is too low
Information for parents and carers Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia What is hypoglycaemia? Hypoglycemia is having a blood glucose (also known as blood sugar) level that is too low
Session 1: Fibre and Health
 Learning outcomes Session 1: Fibre and Health At the end of the session the group should: Know that they should eat foods that are high in fibre Be able to list the foods that are high in fibre Be aware
Learning outcomes Session 1: Fibre and Health At the end of the session the group should: Know that they should eat foods that are high in fibre Be able to list the foods that are high in fibre Be aware
UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS
 UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS Structures 3.0 Objectives 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Conditions Affecting Digestive System 3.2.1 Chronic Liver Failure
UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS Structures 3.0 Objectives 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Conditions Affecting Digestive System 3.2.1 Chronic Liver Failure
Understanding childhood constipation
 Understanding childhood constipation Advice for parents, carers and healthcare professionals Introduction Constipation is a common problem in childhood. It can develop for a number of reasons and not usually
Understanding childhood constipation Advice for parents, carers and healthcare professionals Introduction Constipation is a common problem in childhood. It can develop for a number of reasons and not usually
Barium Enema Examination
 Radiology Department Barium Enema Examination Information for patients Barium Enema examination The X-ray department has received a request for you to have a Barium Enema examination. This leaflet tells
Radiology Department Barium Enema Examination Information for patients Barium Enema examination The X-ray department has received a request for you to have a Barium Enema examination. This leaflet tells
Taking bowel preparation (Picolax/CitraFleet or Moviprep) prior to a Virtual Colonoscopy (VC)
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Taking bowel preparation (Picolax/CitraFleet or Moviprep) prior to a Virtual Colonoscopy (VC) Radiology Department Information
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Taking bowel preparation (Picolax/CitraFleet or Moviprep) prior to a Virtual Colonoscopy (VC) Radiology Department Information
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse
 Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Talk about Constipation
 This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
Session 1: Fibre and health
 Session 1: Fibre and health Learning outcomes At the end of the session the group should: know that they should eat foods that are high in fibre be able to list the foods that are high in fibre be aware
Session 1: Fibre and health Learning outcomes At the end of the session the group should: know that they should eat foods that are high in fibre be able to list the foods that are high in fibre be aware
Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment
 Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment Paediatric Continence Assessment Form LEVEL 1. Completed by... Date:... Designation... Contact no... Abbreviations used in this document to be listed here with
Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment Paediatric Continence Assessment Form LEVEL 1. Completed by... Date:... Designation... Contact no... Abbreviations used in this document to be listed here with
General Surgery. Haemorrhoids
 General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Laxido Paediatric Plain 6.9 g, powder for oral solution
 Package Leaflet: Information for the user Laxido Paediatric Plain 6.9 g, powder for oral solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you give this medicine to your child because it contains important
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Laxido Paediatric Plain 6.9 g, powder for oral solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you give this medicine to your child because it contains important
How to feed your children healthily
 It can be tricky to make sure children are eating a healthy balanced diet, and for some parents it may seem like an impossible task. After all, how many children can resist the idea of a plate of pizza
It can be tricky to make sure children are eating a healthy balanced diet, and for some parents it may seem like an impossible task. After all, how many children can resist the idea of a plate of pizza
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
advice on prevention
 Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i
 Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS. The Right to
 HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
How to Prepare for your. Colonoscopy using. Bowel Preparation YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
 How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Contents Introduction Page 3 What is the bowel preparation? Page 3 What can I expect? Page
How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Contents Introduction Page 3 What is the bowel preparation? Page 3 What can I expect? Page
Small bowel atresia. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
opyright 2017 SAMPLE COPY Property of Hayward Bell Ltd Copyright 2017 Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone
 Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone This booklet could be your first positive step to a full and active life Contents 1. Introduction 2. A bladder 3. The most common problems 5. A bowel 6. Functional
Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone This booklet could be your first positive step to a full and active life Contents 1. Introduction 2. A bladder 3. The most common problems 5. A bowel 6. Functional
CT colonography. Information for patients Radiology
 CT colonography Information for patients Radiology This information booklet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a CT colonography. What is computed tomography
CT colonography Information for patients Radiology This information booklet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a CT colonography. What is computed tomography
Patient Information Leaflet. Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems
 Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN RECESSIVE DYSTROPHIC EB (RDEB) - SEVERE GENERALIZED
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN RECESSIVE DYSTROPHIC EB (RDEB) - SEVERE GENERALIZED 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN RECESSIVE DYSTROPHIC EB (RDEB) - SEVERE GENERALIZED 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This
Radiotherapy to the pelvis. (bladder, prostate, rectum)
 Radiotherapy to the pelvis (bladder, prostate, rectum) General advice Everyone having radiotherapy is different. Your treatment is specific to you and so is the way you react to treatment. If you are worried
Radiotherapy to the pelvis (bladder, prostate, rectum) General advice Everyone having radiotherapy is different. Your treatment is specific to you and so is the way you react to treatment. If you are worried
The Intragastric Balloon
 The Intragastric Balloon Bariatric Dietitians Musgrove Park Hospital TAUNTON Somerset TA1 5DA Tel. No. 01823 343394 September 2010 16 2 15 NOTES: The Intragastric Balloon The intragastric balloon is a
The Intragastric Balloon Bariatric Dietitians Musgrove Park Hospital TAUNTON Somerset TA1 5DA Tel. No. 01823 343394 September 2010 16 2 15 NOTES: The Intragastric Balloon The intragastric balloon is a
15 Ileostomy. Eating and drinking with an ileostomy
 5 Ileostomy Eating and drinking with an ileostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an ileostomy either temporarily
5 Ileostomy Eating and drinking with an ileostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an ileostomy either temporarily
Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years
 Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years Description Content Review Date: August 2005 Printable Version / View Related Services Constipation is stool that is dry, hard and difficult or painful to pass. The number
Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years Description Content Review Date: August 2005 Printable Version / View Related Services Constipation is stool that is dry, hard and difficult or painful to pass. The number
