Doctor s assessment and evaluation of the pelvic floor in antenatal and postpartum women: routine or???
|
|
|
- Martin Grant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Doctor s assessment and evaluation of the pelvic floor in antenatal and postpartum women: routine or??? Dr Barry O Reilly Head of department of Urogynaecology Cork University Maternity Hospital Ireland
2 BACKGROUND Pregnancy and childbirth are recognised as major aetiological factors in the subsequent development of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) 1,2 However, the precise role of pre-pregnancy, antenatal and intrapartum events in the aetiology of PFD is poorly understood MacLennan AH et al. The prevalence of pelvic floor disorders and their relationship to gender, age, parity and mode of delivery. BJOG. 2000;107(12): Casey BM et al. Obstetric antecedents for postpartum pelvic floor dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(5):
3 BACKGROUND Available evidence shows that vaginal delivery appears to be principal causative factor for pelvic floor trauma and dysfunction However it is unclear whether such trauma is clinically relevant, and if it has an impact on pelvic floor morbidity later in life Main risk factors are considered : operative vaginal delivery long second stage macrosomia
4 BACKGROUND Considering the risk of PFD following childbirth, above mentioned symptoms are sometimes being cited as indications for elective caesarean section? To section?? Or NOT to section
5 Topic 1 Patient History The role of questionnaires (Pre-pregnancy and postnatal symptoms)
6 AIMS To identify the prevalence and risk factors for PFD in nullips To identify the group of the patients who might be at higher risk of having these complications
7 Population's demographics Age in years Alcohol consumption % 1 No 19% % Yes 81% % % Marital status Partner 89% BMI No Partner 11% Underweight 1% Normal 59% Annual income Overweight 28% <25 K 8% Obese 12% K 39% K 42% Education >124 K 11% <12 years 88% >=12 years 12% Mean values *Age in years 30.02(4.45) *BMI 24.87(4.13) Smoking Non smoking 73% *Weight in kg (12.07) Smoking 27% 1 All values presented as number of cases and ( %) of total * Data presented as mean value and Standard Deviation (SD)
8 METHODS A prospective, longitudinal, cohort study (part of the SCOPE study) SCOPE (Screening for Pregnancy Endpoints) Ireland study is an international, multicenter study with the aim of developing predictive tests for adverse pregnancy outcome (PET, IUD, IUGR) 870 low risk, primiparous women recruited for the SCOPE were analyzed All participants completed the standardised, validated Australian Pelvic Floor Questionnaire 1 twice: when recruited at 15 weeks gestation one year post delivery 1. Australian pelvic floor questionnaire: a validated interviewer-administered pelvic floor questionnaire for routine clinic and research. Int Urogynecol J (2009) 20:
9
10
11 RESULTS Background prevalence of PFD in Nonpregnant Prevalence of PFD at 1 Year postnatally Nullips Primips 1 st Pregnancy Persistent pre-natal onset PFD postnatally (PPPFD) Total postnatal PFD at 1 Year postnatally De Novo onset PFD Postnatally (DNPFD)
12 URINARY SYMPTOMS Pre-Pregnancy Postnatally N % N % Urinary Frequency ,5 % ,2 % Nocturia ,5 % 65 8,9 % Nocturnal enuresis % % Urgency ,6 % ,0 % x 2.5 x 2.3 Urge Incontinence 88 12,2 % ,5 % Stress Incontinence ,7 % ,0 % Weak Stream ,7 % ,5 % Incompletre Bladder Emptying ,1 % ,3 % Strain to Empty 87 12,0 % ,8 % Pad Usage 46 6,4 % ,0 % Reduced Fluid Intake 33 4,6 % 44 6,0 % Recurrent UTI 89 12,3 % 70 9,6 % Dysuria 71 9,8 % 58 8,0 % Impact on Social Life 32 4,4 61 8,4 % Bladder - How much of a bother 73 10,1 % ,4 % x 2 x 2
13 FAECAL SYMPTOMS Pre-Pregnancy Postnatally N % N % Defaecation Frequency ,5 % 95 13,0 % Consistency of Bowel Motion ,9 % ,6 % Defaecation Straining ,2 % ,4 % Laxative Use 56 7,7 % 53 7,3 % Do You Feel Constipated ,4 % ,1 % Flatus incontinence ,3 % ,3 % Faecal Urgency ,9 % ,2 % Faecal Incontinence wth diarrhoea 31 4,3 % 57 7,8 % Faecal Inconinence with normal stool % 12 1,6 % Incomplete Bowel Evacuation ,6 % ,4 % Obstructed Defaecation 42 5,8 % 44 6,1 % Bowel - How much of a bother ,9 % ,9 %
14 SEXUAL SYMPTOMS Pre-Pregnancy Postnatally N % N % Sexually active < 1/week ,9 % % Sexually active >= 1/week ,4 % ,0 % Sexually active most days/daily 66 9,0 % ,0 % Sexually active / No 21 2,9 % 38 5,2 % Sufficient lubrication ,7 % ,4 % Abnormal vaginal sensation during intercourse x ,4 % ,1 % x 4.2 Vaginal Laxity 35 4,9 % ,6 % Vaginal tightness/vaginismus ,2 % ,1 % x 1.3 Dyspareunia ,1 % ,7 % Coital Incontinence 11 1,5 % 35 4,9 % x 2.5 Sexual Function - How much of a bother 67 9,3 % ,5 %
15 PROLAPSE SYMPTOMS Pre-Pregnancy Postnatally N % N % Prolapse sensation 8 1,1 % 47 6,5 % Vaginal Pressure or heaviness 24 3,3 % 81 11,2 % Prolapse reduction to void % 13 1,8 % Prolapse reduction to defaecate 11 1,5 % 15 2,1 % Prolapse - How much of a bother 7 1,0 % 29 4,0 % x 6 x 3.5 x 4.5 x 4.0
16 Persistence of prepregnancy PFD postnatally
17 Postnatal persistence of prepregnancy symptoms Persistence Persistent rate worsened % N % N Frequency 44,6% 103 8,7% 9 Nocturia 32,1% 44 9,1% 4 Urgency 74,2% ,6% 45 Urge Incontinence 70,1% 75 32% 24 Stress Incontinence 82,6% ,3% 15 Flatus Incontinence 64,8% ,5% 37 Fecal Incontinence with diarrhoea 36,1% 13 15,4% 2 Fecal Incontinence with solid stool Obstructed Defecation 48,9% 23 13% 3 Prolapse Sensation 22,2% 2 50% 1 Vaginal Pressure or heaviness 34,6% 9 33,3% 3 Prolapse reduction to void 100,0% Prolapse reduction to defecate 20,0% Vaginal Laxity 56,1% 23 4,4% 1 Vaginal Tightness/Vaginismus 52,3% ,7% 19 Dyspareunia 68,0% ,9% 27
18 The structure of postnatal PFD Pre-pregnancy PFD persisting postnatally De Novo onset PFD postnatally
19 Mode of delivery & Risk Factors for PFD Mode of delivery SVD ,3 % Kiwi ,6 % Forceps 80 11,0 % CS ,9 % Risk Factors OR [ CI ] Presence of prenatal symptoms 5.1 [3,28-7,86] Young maternal age 2.4 [ ] Induction of labour 2.1 [ ] Use of epidural 1.5 [1.08-2,17] Forceps delivery 1.4 [ ] Caesarean Section (p < 0.05 ) OR 0.1(Urinary) OR 0.3 (Prolapse) OR 0.5 (Faecal)
20 Conclusion This study demonstrated a high prevalence of different types of PFD before pregnancy Majority of postnatal PFD in primiparous women have been present prior to first pregnancy Persistent PFD tends to be more severe than De Novo PFD Caesarean Section seems to be more protective against worsened persistent PFD compared to DeNovo Emphasizes the importance of Pre-pregnancy PFD questionnaire
21 Topic 2 Examination of Patient Prolapse investigation (POP-Q)
22 Grading (Baden Walker +/- POP-Q) 1. First degree - descent of the prolapsing part into the vagina but not as far as the introitus 2. Second degree - prolapsing part reaches the introitus 3. Third degree - prolapsing part lies outside the introitus 4. Fourth degree total prolapse of the organ (procidentia).
23 Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification: POP-Q assessment
24 Examination Abdominal examination to exclude masses or organomegaly. Genital examination: 1. Examination in the dorsal position, when the patientin is bearing down (Valsalva maneuvre) Inspection of the introitus may reveal: An obvious second- or third-degree prolapse Stress incontinence Signs of atrophy 1. Examination in the Sims position with a Sims speculum 2. Vaginal examination 3. POPQ assesement
25 Prolapse symptoms postnatally POP-Q + Scan confirmed POP-Q Staging Prolapse grade Uterine Cystocele Rectocele Symptoms 0 11% (22) 10% (21) 30% (60) 1 89% (180) 32% (64) 47% (95) 2 0% 58% (117) 23% (47) 43% 57% Symptomatic No symptoms Swift, S. (2005). "Pelvic organ prolapse: is it time to define it? Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 16(6):
26
27 Topic 2 Prolapse investigation (Collagen studies)
28 Collagen Quantification 1. Pre-pro-Collagen synthesis 2. Pro- Collagen formation by Hydroxylation of Proline and Lysin residues 3. Collagen formation by cleaving the propeptides 4. Assembly of Collagen in ordered peptides 5. Stabilisation of Collagen by inter and intra molecule cross link formation
29 Beighton Hypermobility Score
30 ELISA Collagen type III RESULTS Uterine Prolapse grade of cases Collagen level ηg/ml * (25) (39) * Mean value (Standard Deviation) for uterine prolapse only Difference 32 ηg/ml p = 0.013
31 Risk factors Family history of uterine prolapse and cystocele Family history of varicose veins Personal history of varicose veins Personal history of Asthma Personal history of vertebral disk dislodgement
32 Conclusion This study demonstrated a high prevalence of different types of POP after one year post partum The majority of participants with prolapse were asymptomatic There is a link between the presence of uterine prolapse and collagen type 3 concentration Serum ELISA test can be a simple and acceptable test for collagen quantification
33 Topic 2 Prolapse investigation (2D Transperineal scan)
34 Transperineal scan technique
35 Prolapse quantification POP-Q vs. Ultrasound Scan Table Prevalence of various types of POP on POPQ and 3D transperineal US assessment ( 202) Prolapse Presence Cystocele Rectocele Uterine prolapse POP-Q* 3D-TpUS POP-Q* 3D-TpUS POP-Q 3D-TpUS No 118(58.4%) 174(86.1%) 155(76.7%) 153(75.7%) 75(37%) - Yes 84(41.6%) 28(13.9%) 47(23.3%) 49(24.3%) 127(63%) - * Prolapse grade 2 only according to POPQ shown as prolapse present Significant only prolapse according to Dietz et al. shown as prolapse present (Dietz et al 17 ) Prolapse grade 1-2 according to POPQ shown as prolapse present (according Dietz et al 14 ) Swift, S. (2005). "Pelvic organ prolapse: is it time to define it? Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 16(6):
36 Topic 3 Pelvic muscles trauma investigation (3D Transperineal scan)
37 Transperineal scan: Biometry of pelvic hiatus
38 Results Levator Ani Muscle trauma present in 29% of participants Levator Hiatal Ballooning present in 32% of participants Clinically significant POP present in 62% of participants
39 Results Table : Correlation between ultrasound diagnosed LAM avulsion and various antenatal / intrapartum factors (n= 202) Factors Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis OR CI (95%) p= OR CI (95%) p= Use of Oxytocin in labour 1.8 ( ) (0-1.63) Duration of 2nd stage of labour 1.01 ( ) ( ) Forceps delivery 4.5 ( ) < ( ) Emergency CS 0.6 ( ) Elective CS 0.7 ( ) ( ) 0.450
40 Conclusion More than half of relatively young premenopausal primiparous women were shown to have some form of clinically significant POP at 1-4 years after their first delivery. One third showed some degree of LAM trauma, which is associated with the presence of POP and symptoms related to it in later life.
41 Conclusion Congenital factors seem to play little role in the aetiology of levator muscle trauma, whereas the main risk factor seems to be forceps delivery. Caesarean Section was demonstrated to be protective for presence of some symptoms. Avoidance of difficult vaginal deliveries may prevent severe pelvic floor trauma and associated symptoms.
42 Topic 4 Identify Risk factors
43 PFD in nullips: risk factors Table: Risk factors associated with various types of PFD in nulliparous women Risk factors Multivariate analysis OR [95% CI] P= Urinary dysfunction Stress Urinary Incontinence Recurrent UTI 1.6 ( ) Increased waist circumference ( ) <0.001 Frequent moderate exercising 1.8 ( ) <0.001 Diagnosed depression 2.1 ( ) Urge Urinary Incontinence Higher family income 0.7 ( ) Participant's birthweight <1500gm 15.9 ( ) No current alcohol user 0.5 ( ) Increased waist circumference 67 ( ) Diagnosed depression 1.9 ( ) 0.02 Urinary Urgency Education < 12 years 1.5 ( ) Recurrent UTI 1.5 ( ) 0.01 Current smoker 2.1 ( ) Vigorous exercising 1.3 ( ) Diagnosed depression 1.6 ( ) Urinary dysfunction combined Married 0.7 ( ) Education < 12 years 1.5 ( ) Trade workers 1.3 ( ) 0.03 Recurrent UTI 2.5 ( ) <0.001 Recent smoker (1-5 cigs.) 1.3 ( ) Diagnosed depression 1.9 ( ) 0.001
44 PFD in nullips: risk factors Risk factors Multivariate analysis OR [95% CI] P= Fecal dysfunction Flatus incontinence Student 2.3 ( ) Fecal dysfunction combined Higher family income 1.2 ( ) Diagnosed depression 2.1 ( ) <0.001 Sexual dysfunction Vaginal tightness Homekeeper 0.2 ( ) Associate professional/technical 1.4 ( ) Reduced sexual activity recently 1.5 ( ) Poor social support 1.8 ( ) Dyspareunia Immigrant 1st generation 1.7 ( ) <0.001 Recurrent UTI 1.5 ( ) Low BMI 2.7 ( ) Vigorous exercising 2.2 ( ) Diagnosed depression 1.6 ( ) Poor social support 2.1 ( ) Sexual dysfunction combined Education < 12 years 1.7 ( ) <0.001 Homekeeper 0.3 ( ) Low BMI 1.5 ( ) <0.001 Working paid employment 10 hours 3.2 ( ) Working paid employment 25 hours 4.2 ( ) Working paid employment 80 hours 89.4 ( ) Vigorous exercising 2.1 ( ) 0.02 Poor social support 2.2 ( ) 0.003
45 PFD in primips: risk factors Table: Risk factors for various PFD symptoms in primiparas Risk factors Multivariate analysis OR CI (95%) p= Urinary dysfunction Stress urinary incontinence Manual workers 24 ( ) 0.03 Office workers 5 ( ) Recurrent UTIs 2 ( ) Poor social support 1.6 ( ) Stress urinary incontinence pre-pregn. 17 ( ) <0.001 Elective Caesarean Section 0.5 ( ) Emergency Caesarean Section 0.3 ( ) <0.001 Induction of labour 1.7 ( ) Urgency urinary incontinence Recurrent UTIs 1.9 ( ) Smoking 1.8 ( ) Urgency urinary incontinence pre-pregn. 17 ( ) <0.001 Fetal head circumference 1.3 ( ) Vacuum delivery 0.5 ( ) Urinary urgency History of miscarriage 2.8 ( ) Urinary urgency pre-pregn. 27 ( ) <0.001 Induction of labour 1.6 ( ) Bladder dysfunction combined High hip circumference 3 ( ) Poor social support 3.3 ( ) Bladder section score pre-pregn. 8.2 ( ) <0.001 Elective Caesarean Section 0.5 ( ) Emergency Caesarean Section 0.4 ( ) <0.001 Induction of labour 3.3 ( ) 0.049
46 PFD in primips: risk factors Table: Risk factors associated with various PFD symptoms Risk factors Multivariate analysis OR CI (95%) p= Fecal dysfunction Flatus incontinence High hip circumference 1.6 ( ) Flatus incontinence pre-pregn. 7.3 ( ) <0.001 Induction of labour 2.7 ( ) Fecal urgency Smoker (former) (1-5 a day) 0.2 ( ) Faecal urgency pre-pregn. 43 ( ) <0.001 Vacuum delivery 0.7 ( ) Elective Caesarean Section 0.5 ( ) Fecal dysfunction combined Bowel section score pre-pregn. 1.6 ( ) <0.001 Diagnosed depression 2.4 ( ) 0.046
47 PFD in primips: risk factors Table: Risk factors associated with various PFD symptoms Risk factors Multivariate analysis OR CI (95%) p= Sexual dysfunction Vaginal laxity Participant born preterm 3.4 ( ) Diagnosed depression 0.2 ( ) 0.02 Poor social support 5.9 ( ) <0.001 Vaginal laxity pre-pregn. 4.9 ( ) <0.001 Emergency Caesarean Section 0.2 ( ) <0.001 Vaginal tightness / vaginismus Higher sitting height 0.9 ( ) Vigorous exercising 3.7 ( ) Dyspareunia Smoking 3.9 ( ) Higher gestation age at delivery 0.8 ( ) Dyspareunia pre-pregn. 15 ( ) <0.001 Sexual dysfunction combined Sexual section score pre-pregn. 9.1 ( ) <0.001 Induction of labour 0.1 ( ) Perineal tear grade ( ) Prolapse dysfunction Vaginal pressure or heaviness Forceps delivery 1.8 ( ) Elective Caesarean Section 0.3 ( ) Emergency Caesarean Section 0.2 ( ) Episiotomy 2 ( ) Prolapse section score postnatally Forceps delivery 8.3 ( ) 0.029
48 U - UI before pregnancy R - Race/ethnicity C - Child bearing started at what age? H - Height (mother s height) O - Overweight (weight of mother, BMI ) I - Inheritance (family history) C - Children (number of children desired) E - Estimated fetal weight
49 Conclusion The major risk factors for prepregnancy PFD are: 1. depression, 2. poor social support, 3. high BMI, 4. strenuous physical activity 5. recurrent UTI. For postnatal PFD most significant risk factors are: 1. presence of similar symptoms pre-pregnancy 2. Induction of labour 3. 3 rd degree perineal tear 4. high hip circumference 5. poor social support
50 Conclusion Apart from prolapse, SVD does not seem to increase the risk of PFD, where as CS is protective against majority PFD symptoms. Postnatal PFD in the majority of cases was associated with multiple prepregnancy symptoms, which confirms its multicompartment involvement and need for multilateral clinical investigations.
51 Conclusion An individual approach in selection of the mode of delivery is required in the group of patients with multiple risk factors prepregnancy. Further research is required to confirm how efficient avoidance of vaginal delivery is in the highlighted group, to prevent severe PFD.
52 Postnatal symptom s score in Persistent vs. De Novo PFD Urinary Faecal Sexual 3 (1-6) 4 (2-6) 2 (1-4) 1 (0-2) 2 (0-2) 1 (0-2) Median Score (Interquartile Range)
53 Definition Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP) Descent of a pelvic organ or structure into and sometimes outside the vagina
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Postpartum Complications
 ACOG Postpartum Toolkit Postpartum Complications Introduction The effects of pregnancy on many organ systems begin to resolve spontaneously after birth of the infant and delivery of the placenta. The timeline
ACOG Postpartum Toolkit Postpartum Complications Introduction The effects of pregnancy on many organ systems begin to resolve spontaneously after birth of the infant and delivery of the placenta. The timeline
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)- herniation of pelvic organs into vaginal walls Common Huge impact on daily activities
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)- herniation of pelvic organs into vaginal walls Common Huge impact on daily activities
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse
 Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Northwest Rehabilitation Associates, Inc.
 Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging. Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague)
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Appendix B Protocol for management of obstetric anal sphincter injury THE MANAGEMENT OF THIRD- AND FOURTH-DEGREE PERINEAL TEARS
 Appendix B Protocol for management of obstetric anal sphincter injury Document Type: THE MANAGEMENT OF THIRD- AND FOURTH-DEGREE PERINEAL TEARS PURPOSE & SCOPE To provide a guideline that will assist in
Appendix B Protocol for management of obstetric anal sphincter injury Document Type: THE MANAGEMENT OF THIRD- AND FOURTH-DEGREE PERINEAL TEARS PURPOSE & SCOPE To provide a guideline that will assist in
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
Urogynaecology & Prolapse. Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings
 + Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
+ Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
Anal Sphincter Injuries: Acute Management
 Anal Sphincter Injuries: Acute Management Dr Stephen Jeffery Urogynaecology Consultant Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Groote Schuur Hospital Colorectal Surgeons Gynaecologists Gynaecologists Colorectal
Anal Sphincter Injuries: Acute Management Dr Stephen Jeffery Urogynaecology Consultant Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Groote Schuur Hospital Colorectal Surgeons Gynaecologists Gynaecologists Colorectal
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED
 By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
The Perineal Clinic: - the management of women following OASI
 The Perineal Clinic: - the management of women following OASI Miss Gillian Fowler Consultant Urogynaecologist MBChB, MD, MRCOG Liverpool Women s Hospital. Margie Polden University Memorial of Liverpool
The Perineal Clinic: - the management of women following OASI Miss Gillian Fowler Consultant Urogynaecologist MBChB, MD, MRCOG Liverpool Women s Hospital. Margie Polden University Memorial of Liverpool
OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION
 OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION COLM O HERLIHY, MD Professor and Chair University College Dublin Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology National Maternity
OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION COLM O HERLIHY, MD Professor and Chair University College Dublin Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology National Maternity
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients
 Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
2/25/2013. Speaker Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Ob/Gyn Conference Series: Urinary and Fecal Incontinence After Vaginal Childbirth
 Ob/Gyn Conference Series: Urinary and Fecal Incontinence After Vaginal Childbirth Jaime Sepulveda-Toro MD FACS FACOG Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery South Miami Hospital Speaker
Ob/Gyn Conference Series: Urinary and Fecal Incontinence After Vaginal Childbirth Jaime Sepulveda-Toro MD FACS FACOG Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery South Miami Hospital Speaker
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery
 Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care. Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner
 Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner Primary Care Womens Health Forum www.pcwhf.org.uk Useful websites RCN genital
Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner Primary Care Womens Health Forum www.pcwhf.org.uk Useful websites RCN genital
The Pelvic Floor: Expecting (and Delivering!) Susan Barr, MD Assistant Professor Saint Louis University Division of Urogynecology
 The Pelvic Floor: What She Can Expect After Expecting (and Delivering!) Susan Barr, MD Assistant Professor Saint Louis University Division of Urogynecology Objectives Understand risk factors and treatment
The Pelvic Floor: What She Can Expect After Expecting (and Delivering!) Susan Barr, MD Assistant Professor Saint Louis University Division of Urogynecology Objectives Understand risk factors and treatment
Women s and Men s Health Intake Form Comprehensive Physical Therapy Center
 Name: (Last, First) DOB: Date: Age: Referring Physician: Next Physician Appointment: Today s visit: What is the main reason you came to the office today? When did it start? What treatments have you had
Name: (Last, First) DOB: Date: Age: Referring Physician: Next Physician Appointment: Today s visit: What is the main reason you came to the office today? When did it start? What treatments have you had
Aetiology 1998 Bump & Norton Theoretical model
 Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Female Symptom Monitor
 Female Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Gynecological History: Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem What age
Female Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Gynecological History: Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem What age
Does delayed child-bearing increase the risk of levator injury in labour?
 Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2007; 47: 491 495 Blackwell Publishing Asia Original Article Delayed child-bearing and levator injury Does delayed child-bearing increase
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2007; 47: 491 495 Blackwell Publishing Asia Original Article Delayed child-bearing and levator injury Does delayed child-bearing increase
Female Symptom Monitor
 Occupation Female Symptom Monitor Presenting problems When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Gynecological History What age did your period start? Is your cycle
Occupation Female Symptom Monitor Presenting problems When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Gynecological History What age did your period start? Is your cycle
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Childbirth and prolapse: long-term associations with the symptoms and objective measurement of pelvic organ prolapse
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12075 www.bjog.org Epidemiology Childbirth and prolapse: long-term associations with the symptoms and objective measurement of pelvic organ prolapse C Glazener, a A Elders, a C MacArthur,
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12075 www.bjog.org Epidemiology Childbirth and prolapse: long-term associations with the symptoms and objective measurement of pelvic organ prolapse C Glazener, a A Elders, a C MacArthur,
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Content. Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management
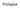 Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Provenance Rehabilitation Pelvic Intake Form
 Patient Name: Age: Weight: Gender: Male Female Provenance Rehabilitation Pelvic Intake Form Date: DOB: Occupation: Relationship Status: Hobbies / Leisure Activities: Exercise Routine: Briefly describe
Patient Name: Age: Weight: Gender: Male Female Provenance Rehabilitation Pelvic Intake Form Date: DOB: Occupation: Relationship Status: Hobbies / Leisure Activities: Exercise Routine: Briefly describe
Birth Trauma. H. P. Dietz. University of Sydney, Nepean Campus. Penrith, Australia
 Birth Trauma H. P. Dietz University of Sydney, Nepean Campus Penrith, Australia Procedures in US (2010): 1.6 Prolapse Urinary Incontinence Fecal Incontinence Prolapse 200.000 Urinary Incontinence 120.000
Birth Trauma H. P. Dietz University of Sydney, Nepean Campus Penrith, Australia Procedures in US (2010): 1.6 Prolapse Urinary Incontinence Fecal Incontinence Prolapse 200.000 Urinary Incontinence 120.000
Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications 23/ Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis
 Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis Consultant Obstetrician Gynaecologist & Urogynaecologist Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications Over eighty per cent of women sustain some degree of perineal trauma during childbirth.
Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis Consultant Obstetrician Gynaecologist & Urogynaecologist Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications Over eighty per cent of women sustain some degree of perineal trauma during childbirth.
Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma. Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center
 + Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center + Vaginal birth and the pelvic floor Mechanisms of injury Damage to
+ Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center + Vaginal birth and the pelvic floor Mechanisms of injury Damage to
Pregnancy and childbirth: the effects on pelvic floor muscles
 Page 1 of 9 Pregnancy and childbirth: the effects on pelvic floor muscles 26 February, 2009 Stress incontinence can follow childbirth as pelvic floor muscles are damaged AUTHOR Julia Herbert, MSc, MCSP,
Page 1 of 9 Pregnancy and childbirth: the effects on pelvic floor muscles 26 February, 2009 Stress incontinence can follow childbirth as pelvic floor muscles are damaged AUTHOR Julia Herbert, MSc, MCSP,
Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None
 Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None Financial Disclosures Jeremiah McNamara, MD, OBGYN Boulder Women s Care 303-500-1947 Boulder Women s Care Agenda: Prolapse & Urinary Incontinence The Pelvic Floor
Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None Financial Disclosures Jeremiah McNamara, MD, OBGYN Boulder Women s Care 303-500-1947 Boulder Women s Care Agenda: Prolapse & Urinary Incontinence The Pelvic Floor
5/29/2015. Objectives. Functions of the PFM. Various phases of PFM. Evaluation of the PFM
 The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
NEW POSTNATAL URINARY INCONTINENCE : OBSTETRIC AND OTHER RISK FACTORS IN PRIMIPARAE. New postnatal urinary incontinence in primiparae
 Author Posting. The Authors 2006. This is the author s version of the work. It is posted here for personal use, not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in BJOG, 113(2):208-17. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00840.x
Author Posting. The Authors 2006. This is the author s version of the work. It is posted here for personal use, not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in BJOG, 113(2):208-17. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00840.x
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics. Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
 Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
Faecal incontinence after childbirth
 Britisb Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 4650 Faecal incontinence after childbirth *Christine MacArthur Reader (Maternal and Child Epidemiology), *Debra E. Bick Research
Britisb Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 4650 Faecal incontinence after childbirth *Christine MacArthur Reader (Maternal and Child Epidemiology), *Debra E. Bick Research
Faecal incontinence persisting after childbirth: a 12 year longitudinal
 Author Posting. The Authors 2013. This is the authors version of the work. It is posted here for personal use, not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in British Journal of Obstetrics
Author Posting. The Authors 2013. This is the authors version of the work. It is posted here for personal use, not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in British Journal of Obstetrics
Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01751.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse HP Dietz, a JM Simpson b a Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01751.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse HP Dietz, a JM Simpson b a Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
FEMALE SYMPTOM MONITOR
 FEMALE SYMPTOM MONITOR Name: Occupation: Date: Age: Complaints: 1. 2. 3. GYNECOLOGICAL HISTORY: # pregnancies: # live births: Wt. heaviest baby: lbs oz Length pushing stage: hours Forceps? Yes No Episiotomies?
FEMALE SYMPTOM MONITOR Name: Occupation: Date: Age: Complaints: 1. 2. 3. GYNECOLOGICAL HISTORY: # pregnancies: # live births: Wt. heaviest baby: lbs oz Length pushing stage: hours Forceps? Yes No Episiotomies?
Impact of Delivery Types on Women s Postpartum Sexual Health
 Reproduction & Contraception (2003) 14 (4):237~242 Impact of Delivery Types on Women s Postpartum Sexual Health Huan-ying WANG 1, Xiao-yang XU 2, Zhen-wei YAO 1, Qin ZHOU 1 Key words: postpartum; sexual
Reproduction & Contraception (2003) 14 (4):237~242 Impact of Delivery Types on Women s Postpartum Sexual Health Huan-ying WANG 1, Xiao-yang XU 2, Zhen-wei YAO 1, Qin ZHOU 1 Key words: postpartum; sexual
WELCOME TO COMPLETE WELLNESS CLINIC Take the first step to wellness!
 WELCOME TO COMPLETE WELLNESS CLINIC Take the first step to wellness! Your first appointment involves an assessment by a Registered Physiotherapist. Please read our website for more information. You may
WELCOME TO COMPLETE WELLNESS CLINIC Take the first step to wellness! Your first appointment involves an assessment by a Registered Physiotherapist. Please read our website for more information. You may
Pelvic organ prolapse. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
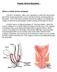 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic floor muscles?
 Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013; 53: 574 579 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12133 Original Article Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013; 53: 574 579 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12133 Original Article Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic
ICD-10 Common Codes for Pelvic Rehab Providers
 ICD-10 Common Codes for Pelvic Rehab Providers With ICD-10 changes taking place in 2015, we thought it would be helpful to put together a bit of a cheat sheet for our pelvic health providers. Keep in mind
ICD-10 Common Codes for Pelvic Rehab Providers With ICD-10 changes taking place in 2015, we thought it would be helpful to put together a bit of a cheat sheet for our pelvic health providers. Keep in mind
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND
 PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic organ prolapse
 Page 1 of 11 Pelvic organ prolapse Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about a pelvic organ prolapse, its causes and available treatments but does not replace advice given by
Page 1 of 11 Pelvic organ prolapse Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about a pelvic organ prolapse, its causes and available treatments but does not replace advice given by
The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12666 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction K van Delft, a AH Sultan, a R
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12666 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction K van Delft, a AH Sultan, a R
Guidelines on the Management of Complications related to Female Genital Mutilation
 Guidelines on the Management of Complications related to Female Genital Mutilation Scoping Survey Instructions The following is a list of 33 potential questions which could guide the evidence retrieval
Guidelines on the Management of Complications related to Female Genital Mutilation Scoping Survey Instructions The following is a list of 33 potential questions which could guide the evidence retrieval
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Ina S. Irabon, MD, FPOGS, FPSRM, FPSGE Obstetrics and Gynecology Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 Ina S. Irabon, MD, FPOGS, FPSRM, FPSGE Obstetrics and Gynecology Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson
Ina S. Irabon, MD, FPOGS, FPSRM, FPSGE Obstetrics and Gynecology Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
A. FALKERT, A. WILLMANN, E. ENDRESS, P. MEINT and B. SEELBACH-GÖBEL ABSTRACT
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 204 209 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11214 Three-dimensional ultrasound of pelvic floor: is there a correlation
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 204 209 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11214 Three-dimensional ultrasound of pelvic floor: is there a correlation
The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00819.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients HP Dietz, a AB Steensma b a
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00819.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients HP Dietz, a AB Steensma b a
Prolapse and Urogynae. By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell
 Prolapse and Urogynae By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell Anatomy and physiology of the pelvic supports The pelvic floor supports the pelvic viscera and vaginal, urethral and rectal openings Endopelvic fascial
Prolapse and Urogynae By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell Anatomy and physiology of the pelvic supports The pelvic floor supports the pelvic viscera and vaginal, urethral and rectal openings Endopelvic fascial
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Perineal Tears. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group
 Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
ijer.skums.ac.ir Risk factors of pelvic organ prolapse in Iranian women: a cross-sectional study
 International Journal of Epidemiologic Research, 2014; 1 (1): 29-34. ijer.skums.ac.ir Risk factors of pelvic organ prolapse in Iranian women: a cross-sectional study Ashraf Direkvand-Moghadam 1 ; Zeinab
International Journal of Epidemiologic Research, 2014; 1 (1): 29-34. ijer.skums.ac.ir Risk factors of pelvic organ prolapse in Iranian women: a cross-sectional study Ashraf Direkvand-Moghadam 1 ; Zeinab
Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria No of Patients included
 Table 1 Description of the studies included Inclusion and exclusion criteria and sample description Year First Author Country Type of UI Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria No of Patients included Age
Table 1 Description of the studies included Inclusion and exclusion criteria and sample description Year First Author Country Type of UI Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria No of Patients included Age
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 03 Page March 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Quality of Life among Patients after Vaginal Hysterectomy and Pelvic Floor Repair Operation ABSTRACT Authors S Lovereen 1, F A Suchi 2,
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Quality of Life among Patients after Vaginal Hysterectomy and Pelvic Floor Repair Operation ABSTRACT Authors S Lovereen 1, F A Suchi 2,
Urinary incontinence after obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIS) is there a relationship?
 DOI 10.1007/s00192-007-0431-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urinary incontinence after obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIS) is there a relationship? Inka Scheer & Vasanth Andrews & Ranee Thakar & Abdul H. Sultan
DOI 10.1007/s00192-007-0431-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urinary incontinence after obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIS) is there a relationship? Inka Scheer & Vasanth Andrews & Ranee Thakar & Abdul H. Sultan
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning
 Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ prolapse
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 693 697 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13222 Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 693 697 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13222 Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ
Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD
 How to protect the perineum and prevent obstetric perineal trauma Standards of OASIS diagnosis: Primary (clinical) and Secondary (ultrasound) Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD Obst/Gyne Dept Nîmes University Hospital
How to protect the perineum and prevent obstetric perineal trauma Standards of OASIS diagnosis: Primary (clinical) and Secondary (ultrasound) Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD Obst/Gyne Dept Nîmes University Hospital
The effect of physical activity on pelvic organ prolapse
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02112.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The effect of physical activity on pelvic organ prolapse NS Ali-Ross, ARB Smith, G Hosker The Warrell Unit, St Mary
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02112.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The effect of physical activity on pelvic organ prolapse NS Ali-Ross, ARB Smith, G Hosker The Warrell Unit, St Mary
Pregnancy and delivery: a urodynamic viewpoint
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2000, Vol107, pp. 1354-1359 Pregnancy and delivery: a urodynamic viewpoint *C. Chaliha Research Fellow (Urogynaecology),** J. M. Bland Professor (Medical
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2000, Vol107, pp. 1354-1359 Pregnancy and delivery: a urodynamic viewpoint *C. Chaliha Research Fellow (Urogynaecology),** J. M. Bland Professor (Medical
Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Anal incontinence after childbirth is more common than was previously believed. Anal incontinence after childbirth. Methods
 Anal incontinence after childbirth Research Recherche From *the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ont.; the Departments of Family Medicine and Social and Preventive
Anal incontinence after childbirth Research Recherche From *the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ont.; the Departments of Family Medicine and Social and Preventive
Degree of uterine prola pse
 by R. MITRA,* M.S., D.G.O. J Before the middle of the nineteenth century very little attention was directed towards the advancement of knowledge about the anatomical supports of the genital organs or towards
by R. MITRA,* M.S., D.G.O. J Before the middle of the nineteenth century very little attention was directed towards the advancement of knowledge about the anatomical supports of the genital organs or towards
POSTGRADUATE COURSE IN REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POSTPARTUM INFECTION
 POSTGRADUATE COURSE IN REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POSTPARTUM INFECTION INTRODUCTION Postpartum infection continue to be one of the major recognisable post- natal complications in developing countries Due to lack
POSTGRADUATE COURSE IN REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POSTPARTUM INFECTION INTRODUCTION Postpartum infection continue to be one of the major recognisable post- natal complications in developing countries Due to lack
Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks
 1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial ultrasound findings: implications for definition of normal pelvic organ support
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 216; 47: 36368 Published online 29 January 216 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14872 Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 216; 47: 36368 Published online 29 January 216 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14872 Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial
Options for Vaginal Prolapse. What is prolapse? What is prolapse? Disclosures 10/23/2013. Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. None
 Options for Vaginal Prolapse Disclosures None Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology Kaiser, San Francisco Assistant Professor, Volunteer Faculty Department of Ob/Gyn, UCSF What is prolapse?
Options for Vaginal Prolapse Disclosures None Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology Kaiser, San Francisco Assistant Professor, Volunteer Faculty Department of Ob/Gyn, UCSF What is prolapse?
Pelvic Floor and More.. Urinary Continence. Urinary Incontinence. Normal Bladder Function
 Pelvic Floor and More.. Jo Pitts Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapist Milton Keynes University Hospital Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapy at MKUH Pregnancy-related back and pelvic girdle pain
Pelvic Floor and More.. Jo Pitts Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapist Milton Keynes University Hospital Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapy at MKUH Pregnancy-related back and pelvic girdle pain
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/160830
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/160830
PROLAPSE. By Charlotte Robinson Women s Health Speciality Attachment
 PROLAPSE. By Charlotte Robinson Women s Health Speciality Attachment Introduction Case example Pelvic organ prolapse - Epidemiology - Aetiology - Anatomy - Types of prolapse/ severity - Examination/Investigation
PROLAPSE. By Charlotte Robinson Women s Health Speciality Attachment Introduction Case example Pelvic organ prolapse - Epidemiology - Aetiology - Anatomy - Types of prolapse/ severity - Examination/Investigation
Among parous women, cesarean birth reduces the
 Pelvic Floor Disorders After Vaginal Birth Effect of Episiotomy, Perineal Laceration, and Operative Birth Victoria L. Handa, MD, MHS, Joan L. Blomquist, MD, Kelly C. McDermott, BS, Sarah Friedman, MD,
Pelvic Floor Disorders After Vaginal Birth Effect of Episiotomy, Perineal Laceration, and Operative Birth Victoria L. Handa, MD, MHS, Joan L. Blomquist, MD, Kelly C. McDermott, BS, Sarah Friedman, MD,
Physiotherapy advice following your third or fourth degree perineal tear
 Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline. Mr David Sim Ms Patricia McStay. Dr Martina Hogan Dept./Division Only: YES-IMWH Directorate Only: NO
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline Author: Dr Foteini Verani Designation: Specialist Doctor Speciality / Division: Obstetrics-IMWH Directorate: Acute Services
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline Author: Dr Foteini Verani Designation: Specialist Doctor Speciality / Division: Obstetrics-IMWH Directorate: Acute Services
Women's physiotherapy
 The women s health physiotherapy outpatient team treats a variety of conditions affecting women: chronic pelvic pain urinary incontinence birth-related perineal trauma antenatal and postnatal musculoskeletal
The women s health physiotherapy outpatient team treats a variety of conditions affecting women: chronic pelvic pain urinary incontinence birth-related perineal trauma antenatal and postnatal musculoskeletal
THE PELVIC FLOOR, EPISIOTOMY AND PERINEAL REPAIR AND VAGINAL/RECTAL MEDICATIONS
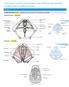 THE PELVIC FLOOR, EPISIOTOMY AND PERINEAL REPAIR AND VAGINAL/RECTAL MEDICATIONS MID2010 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 - REVIEW THE ANATOMY OF THE PELVIC FLOOR Superficial layers cavernosus Deep layer Coccygeus
THE PELVIC FLOOR, EPISIOTOMY AND PERINEAL REPAIR AND VAGINAL/RECTAL MEDICATIONS MID2010 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 - REVIEW THE ANATOMY OF THE PELVIC FLOOR Superficial layers cavernosus Deep layer Coccygeus
K. Jundt 1, I. scheer 2, v. von Bodungen 1, F. Krumbachner 1, K. Friese 1, U. M. Peschers 3
 362 EU Ro PE an JoUR nal of MED I cal RE search Eur J Med Res (2010) 15: 362-366 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2010 WHat HaRM DoEs a second DElIvERy to the PElvIc FlooR? K. Jundt 1, I. scheer 2, v. von Bodungen
362 EU Ro PE an JoUR nal of MED I cal RE search Eur J Med Res (2010) 15: 362-366 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2010 WHat HaRM DoEs a second DElIvERy to the PElvIc FlooR? K. Jundt 1, I. scheer 2, v. von Bodungen
Sexual Function and Dysfunction
 Sexual Function and Dysfunction Angie Rantell Lead Nurse / Nurse Cystoscopist Kings College Hospital, London, UK In the real world Sexual practices are changing! Sexual identities and behaviours change
Sexual Function and Dysfunction Angie Rantell Lead Nurse / Nurse Cystoscopist Kings College Hospital, London, UK In the real world Sexual practices are changing! Sexual identities and behaviours change
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Care of your Perineum following 3 rd and 4 th degree tears
 Maternity Services Care of your Perineum following 3 rd and 4 th degree tears Introduction This leaflet aims to give you information about the repair and aftercare of the third or fourth degree tear you
Maternity Services Care of your Perineum following 3 rd and 4 th degree tears Introduction This leaflet aims to give you information about the repair and aftercare of the third or fourth degree tear you
Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015
 Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015 Disclosures I have none Objectives Identify the basic Anatomy and causes of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Examine office diagnosis
Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015 Disclosures I have none Objectives Identify the basic Anatomy and causes of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Examine office diagnosis
ENTRY INTO SPECIALTY TRAINING USING THE CESR (CP) ROUTE DETAILS OF PREVIOUS POSTS IN OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY PRIOR TO APPOINTMENT TO NTN
 ENTRY INTO SPECIALTY TRAINING USING THE CESR (CP) ROUTE DETAILS OF PREVIOUS POSTS IN OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY PRIOR TO APPOINTMENT TO NTN PERSONAL DETAILS Trainee name Surname Forename(s) NTN Details NTN
ENTRY INTO SPECIALTY TRAINING USING THE CESR (CP) ROUTE DETAILS OF PREVIOUS POSTS IN OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY PRIOR TO APPOINTMENT TO NTN PERSONAL DETAILS Trainee name Surname Forename(s) NTN Details NTN
Study of correlation between symptoms and signs in women with anterior vaginal wall prolapse
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Bijwe SA et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Jul;6(7):3155-3159 www.ijrcog.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20172953
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Bijwe SA et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Jul;6(7):3155-3159 www.ijrcog.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20172953
CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT OF UTEROVAGINAL PROLAPSE WITH LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOM (LUTS)
 CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT OF UTEROVAGINAL PROLAPSE WITH LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOM (LUTS) *S BEGUM 1, S SHARMIN 2, P SULTANA 3, AN CHOWDHURY 4, P SULTANA 5, S NABI 6, MN UDDIN 7, MM HASAN 8 Abstract:
CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT OF UTEROVAGINAL PROLAPSE WITH LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOM (LUTS) *S BEGUM 1, S SHARMIN 2, P SULTANA 3, AN CHOWDHURY 4, P SULTANA 5, S NABI 6, MN UDDIN 7, MM HASAN 8 Abstract:
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
