PERINEAL & CATHETER CARE
|
|
|
- Gyles Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Client Care Module: PERINEAL & CATHETER CARE May be copied for use within each physical location that purchases this inservice.
2 Developing Top-Notch CNAs, One Inservice at a Time A Client Care Module: PERINEAL & CATHETER CARE We hope you enjoy this inservice, prepared by registered nurses especially for nursing assistants like you! Instructions for the Learner If you are studying the inservice on your own, please do the following: Read through all the material. You may find it useful to have a highlighting marker nearby as you read. Highlight any information that is new to you or that you feel is especially important. After finishing this inservice, you will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the urinary system, and identify key terms. If you have questions about anything you read, please ask. Take the quiz. Think about each statement and pick the best answer. Check with your supervisor for the right answers. You need 8 correct to pass! Print your name, write in the date, and then sign your name. Keep the inservice information for yourself and turn in the quiz page to no later than. Show your Inservice Club Membership Card to so that it can be initialed. In the Know at feedback@knowingmore.com with your comments and/or suggestions for improving this inservice. THANK YOU! Identify three ways aging effects the urinary system. Outline the procedure for providing excellent perineal care for both males and females. Discuss urinary tract infections, how they occur and how you can help prevent them. Discuss urinary catheters, reasons for cathing, types of caths, and how to care for a client with a catheter.
3 Developing Top-Notch CNAs, One Inservice at a Time Inside This Inservice: The Urinary System 2 Providing Peri-Care 3 The Aging Renal System 4 Understanding UTIs 5 Urinary Catheters 6 Caring for Catheters 7 Incontinent Clients 8 Bladder Retraining Techniques Peri-Care Tips 10 Final Thoughts on Peri-Care 2014 In the Know, Inc. May be copied for use within each physical location that purchases this inservice from In the Know. All other copying or distribution is strictly prohibited A Client Care Module: Perineal & Catheter Care THE IMPORTANCE OF PERINEAL CARE Everyone's favorite topic... perineal care! As you know, the perineum is the area that spans from the genitals to the anus. No other area of the body is more difficult to discuss, but, when it comes to client care, it is worth talking about! The number one healthcare associated infection is the urinary tract infection. Most healthcare associated UTI's are the result of catheterization or incontinence and can be avoided by providing regular peri-care and cath-care using proper technique. The perineal area is a dark, moist environment where bacteria love to live. The urethra, where urine comes out, provides the perfect route for bacteria to enter the bladder and cause an infection. In this inservice, you will review the urinary system, how urinary tract infections occur, and how you can help prevent them. You will also read about catheters: different types for different reasons and the best way to care for a catheter. As a CNA, you are entrusted to care for people in the most intimate way. Consider this: You may have some clients who spent their whole lives guarding their perineal area as a private place only their mothers have seen. Now, as they are older, possibly ill, and unable to care for this area on their own, they have to rely on you to do this for them. By providing discreet, thorough, and routine pericare, you give your clients the gift of health while maintaining their dignity.
4 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 2 ANATOMY OF THE RENAL (URINARY) SYSTEM RIGHT KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER LEFT KIDNEY URETHRA The main function of the urinary system is to rid the body of waste. Fluids in the blood are filtered by the kidneys. Excess water and waste combine to make urine and are flushed out of the body. The pathway: 1. Urine is produced in the kidneys. 2. The ureters drain the urine from the kidneys to the bladder where it collects. 3. Urine collects in the bladder until the bladder is full enough to trigger the sensation to urinate. 4. Urine travels from the bladder, through the urethra, to the outside of the body. TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW DID YOU KNOW? URINARY BLADDER - The hollow, muscular, balloon-shaped organ that stores urine until it is excreted. URETHRA - The canal that carries off the urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. KIDNEYS - A pair of bean shaped organs, about 4½ inches long, that filter blood and concentrate wastes and water into urine for excretion. NEPHRON - The functional unit of the kidney, the nephron is a microscopic filter that removes waste from blood. URETER - A tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. URINE - The yellow fluid that remains after the nephrons have cleaned the blood UREA - The main solid component that makes up urine. A problem with the kidneys can feel like a back injury! The kidneys are located toward the back of the body on each side of the spine. They are right about at the level of the twelfth rib. The left kidney is slightly higher than the right because the liver pushes the right kidney down.
5 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 3 PROVIDING EXCELLENT PERI-CARE PERI-CARE FOR FEMALES 1. Prepare a basin of warm, clear water. If you are performing peri-care as part of a complete bed bath, take the time to change the water before you clean the perineal area. 2. Put on gloves. This protects you and the client. 3. Place a waterproof pad under the hips and buttocks and position the client on her back. 4. Wet a clean washcloth in the basin of clear water. Then, place soap on the washcloth, not in the basin. This will keep the basin water clear for rinsing. 5. Fold the washcloth in half, then in half again, making a square. Folding the washcloth into a square gives you four separate clean surfaces to work with. 6. Spread the labia majora, the outside folds, and wipe down the center, from front to back. 7. Turn the washcloth over and wipe each side of the perineal area, using a clean section of the washcloth for each wipe. 8. Once the perineal area is clean, set aside the dirty, soapy washcloth. Do not throw it in your clean water basin, There is no need to rinse it out. This will just contaminate your water. 9. Get a clean washcloth and wet it in the clean water. Rinse the perineal area with the same technique you used to wash only one wipe per each section of washcloth. 10. Thoroughly dry the area using a blotting motion. 11. Now, have client turn on side. Wash, rinse and dry the anal area. PERI-CARE FOR MALES The first 5 steps are the same for both men and women. Start with clean, clear water, a couple of clean washcloths and a towel for drying. Put on your gloves and place a waterproof pad under your client to protect the bed. 6. If your client is uncircumcised, retract the foreskin by sliding the skin gently toward the base of the penis. 7. Wash the penis in a circular motion, starting at the tip and working your way down. Use a different part of the wash cloth for each wipe. 8. Rinse with clean water, dry and replace foreskin (if present). 9. Next, clean the scrotum and the groin (just below the scrotum). 10. Thoroughly dry the area using a blotting motion. 11. Now, have client turn on side. Wash, rinse and dry the anal area. IT S JUST GOOD PRACTICE Excellent perineal care not only cleans and refreshes your client... it prevents infection! The perineal area should be cleaned EVERY DAY, whether the client gets a complete bath or not. It is important to use a clean area of the washcloth for each wipe because reusing the same area can cause infection. As you wipe from front to back, the wash cloth picks up bacteria. If you wipe again with the contaminated section of the washcloth, you are dragging that bacteria to the urethra where it can enter the opening, migrate up to the bladder and cause infection. Observe for redness, white discharge, pain or foul odor. Report any of these abnormal observations to the nurse right away!
6 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 4 EFFECTS OF AGE ON THE RENAL SYSTEM Just as in other parts of the body, age has an effect on the urinary system. KIDNEY FUNCTION DECREASES: Half the nephrons (the functional unit of the kidneys) are lost between the ages of 40 and 70 years. Between the ages of 30 and 90, the size and weight of the kidneys decrease by as much as 30 percent. The kidneys usually remain functional at the decreased level unless they are stressed by another illness such as high blood pressure or diabetes. THE BLADDER AND URETHRA ARE ALSO EFFECTED BY AGE: In women, the decrease in estrogen that occurs with menopause causes the walls of the bladder and the urethra to become less elastic. And, the muscles that support the bladder begin to relax. This causes older women to be more likely to have bladder infections and urinary incontinence. In men, the prostate gland begins to enlarge. The prostate surrounds the urethra, so as it enlarges, it can restrict the flow of urine coming from the bladder. This can cause difficulty or painful urination, and bladder infections. In both men and women there may be a weakening of the urinary sphincter. (This is the muscle that helps you hold it when you feel the urge to go, but need to wait.) This weakness can lead to stress incontinence. There may also be a decrease in the amount of urine the bladder can hold, leading to frequency (going more often) and nocturia (going often at night). DID YOU KNOW: Hundreds of years ago, Native Americans used cranberries to treat bladder infections. Now research indicates it really does work! Yogurt with live active cultures can help prevent yeast infections caused by antibiotic usage. What other natural remedies have you heard about? Ask your clients and family members about home remedies they grew up hearing about or using. Write down the interesting remedies you learn about and share them with your co-workers and supervisor! CONSTIPATION PLAYS A ROLE: A common complaint in the elderly is constipation. And, frequent or severe constipation can effect the urinary system. Stool that builds up in the rectum can put pressure on the urethra and possibly even obstruct flow, leading to painful urinary retention and bladder infections.
7 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 5 UNDERSTANDING THE URINARY TRACT INFECTION WHAT IS A URINARY TRACT INFECTION? A urinary tract infection, or UTI, develops when bacteria invade the urinary tract and multiply. Harmful bacteria usually enter the urinary tract through the urethra because this area is open to the outside of the body. The result is redness, swelling, pain, discharge and possibly a foul, "fishy" odor. If a UTI is not treated promptly, the bacteria can move up to the kidneys and cause a more serious kidney infection. WHO IS AT RISK? Women tend to get UTIs more easily than men do. The urethra in females is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. People with diabetes may be more likely to get UTI's because their bodies are unable to fight off the bacteria like they should. A male client with an enlarged prostate gland may have blocked urine flow, which can cause a UTI. Anyone with an indwelling catheter is at high risk of developing a UTI. COMMON SYMPTOMS OF UTI INCLUDE: Urgency - An urgent need to urinate, often with only a few drops of urine to pass. Pain - A burning feeling during urination, or lower abdominal pain. Abnormal Urine - Cloudy or blood-tinged urine, or urine with a strong odor. If the infection has spread to the kidneys, your client may have a fever, nausea, vomiting and complain of pain in the lower back. You may also notice behavioral changes in your elderly clients. Sometimes this is the only indication that something is wrong. A UTI can cause agitation, confusion and restlessness. HOW IS A UTI TREATED? Common, uncomplicated UTI s usually respond well to oral antibiotics. Some clients with more serious infections, or recurrent infections, may need IV antibiotics. Doctors may also prescribe pain medication if the pain and discomfort become severe. HOW YOU CAN HELP: It s much easier to prevent a UTI than it is to treat it. Providing excellent perineal care is one of the most important things you can do to help prevent urinary tract infections. Clients on antibiotics may develop upset stomach, diarrhea and even a yeast infection as a side effect of the antibiotic. Be sure your client drinks plenty of fluids, including cranberry juice. Be prepared for more frequent trips to the bathroom! Yogurt with live active cultures can help prevent diarrhea and yeast infections.
8 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 6 UNDERSTANDING URINARY CATHETERS WHO GETS CATHED? There are several reasons a client may have a catheter. Some common reasons include: Urinary retention where the client is unable to empty the bladder. Surgical procedures that may limit movement for a period of time. Accurate monitoring of input and output. Enlarged Prostate which impedes urinary output. Because of the documented risk for infection, healthcare providers are moving toward a more conservative approach to cathing. It is often only used as a last resort, and only when absolutely necessary. Urinary incontinence alone is never a reason to catheterize someone. While a catheter may be convenient for the staff, the risk of infection and the damage it can cause, far outweigh the benefits. TYPES OF CATHETERS Indwelling Catheters - Indwelling catheters are those that stay in place for a certain length of time. The Foley Catheter is an example of an indwelling catheter. Indwelling catheters consist of a flexible tube that is inserted into the urethra. The tube extends up into the bladder. A small balloon on the tip is inflated to keep the tube in place. The tubing drains urine from the bladder into a bag where it can be measured and observed for abnormalities on a regular basis. Straight Catheters - Straight caths, also known as In and Out caths are used for temporary relief from urinary retention. The tube is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. Urine is drained, measured and observed, then the tube is removed. There is less risk of infection with straight catheters, but the risk is not completely removed. Sterile technique is very important to ensure that no bacteria are introduced into the urinary system during catheterization. Some clients may be used to cathing themselves this way if they have had a chronic problem. A straight catheter may also be used to obtain a sterile urine specimen for laboratory tests. Condom Catheters - A condom catheter is a temporary, non-invasive catheter for men only. The condom cath is a condom that is placed over the penis and secured in place with adhesive. The condom is attached to tubing which drains the urine into a bag. Condom caths carry the least risk of infection and may be used as a solution for urinary incontinence in the male client who does not have any other problems, such as urinary retention or enlarged prostate. A BIT OF HISTORY The word "catheter" is Greek. It means to let or send down. Catheterization has been used to relieve urinary problems for thousands of years. Many materials have been used to form the tube of the catheter including straw, rolled up palm leaves, long, thin dried leaves of gold, silver, copper, brass and even lead! Ouch!
9 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 7 CARING FOR CATHETERS Caring for a client with an indwelling catheter requires a few key tasks on the part of the CNA. These tasks include: EMPTYING THE BAG - The urinary drainage bag should be emptied at least once on every shift. It should always be emptied before becoming more than 3/4 full. If the bag is allowed to become too full, urine could back up in the tubing and drain back into the bladder. It's best to make a habit of draining the bag either at the beginning or end of your shift. That way you can accurately report the output over the duration of the shift. MEASURING THE OUTPUT - You are looking for a minimum of 30ml of output per hour. So, a typical client should put out at least 240 ml of urine on a typical eight hour shift. Remember 30 ml per hour is a minimum. That means it may be more and that's okay... but it should NOT be LESS! If you notice you client is putting out less than 30ml per hour, check the tubing for kinks. Make sure the client is not laying on the tubing and cutting off the flow. If no visible obstructions are found, notify the nurse immediately! ASSESSING THE URINE - As you empty the bag and measure the output, you can make a few important assessments. Note the color of the urine. Is it clear, straw, yellow, amber, red, or brown? Also assess the clarity. Notice if the urine is clear or cloudy. Is there sediment, or small particles, floating in it? And finally, notice the odor. Is it normal, strong or foul smelling? Report Your Findings - Once you empty the bag, measure the output and assess the urine, document your findings per your employer s protocol. If any of your findings are abnormal, report verbally to the nurse right away in addition to your documentation. POSITIONING - The drainage bag should always remain below the level of the bladder. This is particularly important to pay attention to when the client is ambulating or being transferred. If the bag is raised above the level of the bladder, the urine will back-flow into the bladder. This can be painful, and can cause infection. The tubing should be secured to the upper thigh with either a leg strap or tape to keep it from being tugged or pulled out of the bladder. The tubing should be coiled loosely, without kinks, and placed toward the foot of the bed where the client cannot lay on it and obstruct flow. CLEANING - Peri-care for the client with a catheter is the same as routine peri-care of other clients with one added step... cleaning the tubing. To clean the catheter tubing, hold the tubing firmly at the point of insertion with one hand. With your other hand, clean at least the first four inches of the tubing with a soapy washcloth. Use a clean area of the wash cloth for each swipe of the tubing, and move in only one direction (away from the body). Rinse with clean water in the same manner. Dry the tubing and the perineal area completely.
10 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 8 CARING FOR INCONTINENT CLIENTS USING INCONTINENCE PRODUCTS Since catheters are not the best option for those with incontinence alone, you probably care for many clients who use a variety of incontinence products. These products are designed to keep moisture off the skin and to absorb embarrassing odors. Perineal care is more important in the incontinent client than any other. Urine and feces are extremely harsh on the skin. Without prompt and thorough care, the skin will break down, develop sores, and potentially become infected. Some common incontinence products include: PADS AND LINERS Clients with mild incontinence problems may use pads or liners. They are absorbent, with adhesive backing so they can be worn with regular underwear. Pads and liners are discreet and most people can continue regular activities without any risk of embarrassment. Most clients who use pads or liners are able to change them on their own. However, you may be asked to assist. DISPOSABLE BRIEFS OR ADULT DIAPERS Clients who are incontinent of both stool and urine may need disposable briefs. They can either be pull-up style, or with tabs like a diaper. Some clients can do the pull-ups on their own, but most will need help with the tabbed style briefs. It s best not to refer to these products as diapers. Your clients are not children and the term may be offensive. WATER PROOF PADS OR CHUX Waterproof pads should be placed under the incontinent client to protect surfaces from leakage. These pads can be reusable or disposable. In the healthcare facility, the pads help protect surfaces from the leakage that can transmit microorganisms to other clients. In the home, pads help protect furniture from stains and odors. Washable pads may be the best option in the home, however disposables are available in most pharmacies, in the aisle where disposable briefs are sold. MOISTURE BARRIER CREAMS Barrier creams help protect the skin from the moisture and harshness of urine and feces. It s a small step that will make a big difference! Family caregivers who make the decision to care for a loved one at home often find incontinence the most stressful part of their job. Caregivers often site the stress of caring for an incontinent family member as the reason for seeking the help of a Home Health Nurse or long-term care. Sometimes, just being trained in the proper technique for changing a brief is all that's needed. But, some family members may need more. What advice, training, or words of encouragement would you give family caregivers to help them deal with this difficult situation?
11 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 9 BLADDER RETRAINING Sometimes incontinence is a temporary symptom of an illness or injury and can be reversed. If bladder retraining is ordered, follow the plan outlined for your client. Usually, bladder retraining consists of taking the client to the bathroom at regular intervals and keeping an accurate ongoing record of bowel and bladder patterns. KEGEL EXERCISES Kegel exercises help strengthen the muscles that help you "hold" urine when the bladder becomes full. The best way to teach a client how to do Kegel exercises is to have them try to stop the urine midstream. Explain that the muscle contraction needed to stop the urine is the actual exercise. Then, ask the client to try to do that same muscle contraction while just sitting and watching TV, or standing in the kitchen. Ask your supervisor if you need more information on Kegel exercises. REGULAR TRIPS TO THE BATHROOM Have your client start the day with a trip to the bathroom. Most people have to urinate as soon as they wake up in the morning. Write down the time of the first morning urine and make a note of whether the client was able to make it through the night and stay dry. Set a timer for one hour from the first morning urine. Take the client to the bathroom when the timer goes off, even if there is no urge to urinate. Make a note if urine was produced. Again, set the timer for one hour. Take client to the bathroom every hour for a few days. After a few days of going every hour, you should notice a pattern. You can cut back on the trips to the bathroom to every two or three hours, depending on your client's particular pattern. SOME PRACTICAL BLADDER RETRAINING TIPS Always encourage your client to completely empty the bladder with each trip to the bathroom. Provide privacy. Knowing someone is watching or listening makes urination difficult, if not impossible! Encourage clients to drink plenty of fluids. Withholding fluids may mean fewer trips to the bathroom, but will not solve the problem of incontinence. If your client has difficulty getting urine started, run the water. Leaning forward, placing pressure on the bladder, may also help. Remember: just because your client is learning to use the toilet independently does not mean you should stop helping with perineal care. Always assess perineal hygiene and assess skin for breakdown. Never rush your client, show frustration or anger. Incontinence is embarrassing and frustrating enough. Your patience and support is all that is needed. Never punish, yell or mock a client for having an accident. Treat the problem very matter-offactly. Clean up the mess and reassure your client that it is nothing to be ashamed or embarrassed about. Since your client will be spending a LOT of time in the bathroom, create a clean and relaxing environment. Clean on a regular basis to eliminate odors. Put out hand soaps and towels. Make sure the lighting is good. Take time to review the successes of the day and praise your client's efforts at bladder retraining.
12 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 10 FACTS & TIPS ON PERINEAL CARE INTERESTING FACTS HELPFUL TIPS In women, the perineum goes from the vagina to the anus. In men, it is the area from the scrotum to the anus. Physicians often describe the perineal muscles as diamond shaped, made up of two triangles, the urinary-genital triangle in the front and the anal triangle in the back. The pelvic muscles (called the pelvic floor ) play an important role in movement, balance and good body posture. Weak pelvic floor muscles can result in incontinence, prolapsed organs, poor posture, back problems and imbalance. Remember the number one rule of perineal care always go from clean to dirty! Remember to maintain the client s dignity at all times. Cover the client as much as possible. Pull the curtain around the client s bed and/or shut the door to the room before beginning perineal care. If your client is in a hospital or adjustable bed, remember to raise it to a good working level for you. Putting warm water on the perineal area may trigger the need to urinate, so offer your client a bedpan/urinal or assist him or her to the bathroom before starting. DID YOU KNOW? On average, skin is only 1/20 of an inch thick. Yet, it contains nerves, blood vessels, hair follicles, glands, and sensory receptors. Remember that the perineal area is more sensitive to temperature than the rest of the body. You may want to use water that is slightly cooler than regular bath water. Raising the hips with a towel or padded bedpan may help you visualize the area better. The average human being has about 300 million skin cells. Skin is constantly renewing itself, from the bottom layer up. A new layer of skin replaces the old layer approximately every 27 days, so each of us gets about 1,000 new outer layers of skin during our lives. Humans shed thousands of skin particles every hour. Throughout a lifetime, most people lose about 50 pounds of skin! Be very gentle when washing the delicate perineal area. (If your client is elderly, his or her skin is more fragile than a younger person s.) Be sure to rinse any soap off the skin thoroughly. If soap is left on the perineum, it can be extremely irritating. Be sure to leave the client in a comfortable position after perineal care is complete.
13 2014 In the Know, Inc. Page 11 FINAL THOUGHTS ON PERINEAL CARE No one enjoys caring for other people s perineal area. And your clients don t enjoy having to rely on you to do it, either. But, the fact is that it is a critical element in the overall health of your client. Keeping the perineal area clean and dry eliminates the risk of infection, skin breakdown, bed sores. And, it alleviates the discomfort and embarrassment that comes from unpleasant odors and wetness. Make perineal care your habit. Every client needs perineal care everyday. And, incontinent clients need it after every urination or bowel movement. Use of incontinence products like pads or briefs work to keep bedding and clothing clean. But, they also keep urine and stool in constant contact with the skin. Over time, this can damage the skin. It's important to continuously monitor your incontinent client and keep the skin clean and dry. The length of a film should be directly related to the endurance of the human bladder. ~ Alfred Hitchcock Be sensitive to your incontinent client s feelings. Never show anger or impatience at having to clean up a messy bed or change a dirty gown. No one wants to urinate or stool uncontrollably. It s embarrassing. Your judgment will not help. Never punish a client for having an accident. I don't need you to remind me of my age. I have a bladder to do that for me. ~ Stephen Fry Remain patient and positive during bladder retraining. It can take up to six weeks to regain full control. Working with clients in the home often requires coming up with creative solutions to common problems. THE PROBLEM: You are assigned to care for a client with mild but progressive dementia who is having trouble remembering to go to the bathroom on her own. She has moments when she can express the need to urinate or have a bowel movement, but can also go hours without asking for help, and eventually has an accident. WHAT YOU KNOW: This client lives with her daughter and sonin-law. Someone is usually at home with her. The daughter is growing tired and stressed from cleaning up the accidents and asks for your advice. GET CREATIVE: Think of 3 creative solutions you could try to help your client and her daughter through this difficult situation. TALK ABOUT IT: Share your ideas with your co-workers and supervisor and find out how they would solve the problem.
14 Developing Top-Notch CNAs, One Inservice at a Time EMPLOYEE NAME (Please print): DATE: I understand the information presented in this inservice. I have completed this inservice and answered at least eight of the test questions correctly. EMPLOYEE SIGNATURE: SUPERVISOR SIGNATURE: A Client Care Module: Perineal & Catheter Care Are you in the know about perineal and catheter care? Circle the best choice. Then check your answers with your supervisor! 1. True or False The number one healthcare associated infection is the UTI. 2. True or False The main function of the renal system is to rid the body of waste. 3. True or False When providing perineal care, you should wash the anal area first to avoid dragging germs to the cleaner areas. 4. True or False Cleaning the perineal area every day is not necessary; it only causes irritation. 5. Harmful bacteria that cause urinary tract infections usually enter the body through the: A. Ureter C. Urethra B. Vagina D. A break in the skin Inservice Credit: Self Study Group Study 1 hour 1 hour 6. True or False Age has no effect on the urinary system. 7. A client with a UTI may have all the following symptoms, EXCEPT: A. Back and abdominal pain C. Excessive thirst B. Urgency D. Agitation and confusion 8. True or False Urinary incontinence is a good reason to catheterize someone. File completed test in employee s personnel file. 9. True or False The minimum amount of urine output that is considered acceptable is 30 ml/hr. 10. True or False Catheter tubing should always be kept above the level of the bladder.
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
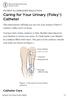 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems
 If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS
 Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Bladder Management. Why is a Bladder Program so Important?
 Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6. All Things Urinary Catheters
 FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Continence Promotion. CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS
 Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Indwelling urinary catheter
 Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients
 Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) for Bladder Emptying FAQ What
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) for Bladder Emptying FAQ What
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter
 Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients This information is produced by the Continence, Urology and Colorectal Service Leeds Community Healthcare NHS Trust Having a urinary
Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients This information is produced by the Continence, Urology and Colorectal Service Leeds Community Healthcare NHS Trust Having a urinary
My Urinary Catheter Passport Looking after my urinary catheter
 Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS
 SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
Your catheter. Information for patients and carers. NHS Grampian Continence Service
 Your catheter Information for patients and carers NHS Grampian Continence Service Healthcare professional details Name: Contact number:. GP: Telephone number: Reason for catheterisation:... Date of initial
Your catheter Information for patients and carers NHS Grampian Continence Service Healthcare professional details Name: Contact number:. GP: Telephone number: Reason for catheterisation:... Date of initial
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy
 Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Urinary sheaths. Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Extra Long Cure Medical Pocket Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest
 Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST
 CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST INTRODUCTION The human body is designed to move. And just as the human body thrives on movement, it suffers when for one reason or another there is enforced immobility.
CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST INTRODUCTION The human body is designed to move. And just as the human body thrives on movement, it suffers when for one reason or another there is enforced immobility.
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Twist
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization. Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre
 2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery
 Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Looking after your bladder
 Looking after your bladder A guide for men after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people
Looking after your bladder A guide for men after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people
advice on prevention
 Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Self Catheterisation for Men
 Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Coping with incontinence
 Coping with incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia and stressful for the carer. But approaching the problem with understanding, matter-of-factness and humour
Coping with incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia and stressful for the carer. But approaching the problem with understanding, matter-of-factness and humour
Self-Catheterization for Females
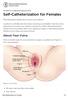 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women
 CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Urinary Catheter Passport
 Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: be a last resort when all suprapubic catheter in CAUTI
 Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: Name: DOB Address: Indwelling Urinary Catheter (Urethral/ Suprapubic) Date Assessed Need GOAL INTERVENTION Evaluation of intervention/
Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: Name: DOB Address: Indwelling Urinary Catheter (Urethral/ Suprapubic) Date Assessed Need GOAL INTERVENTION Evaluation of intervention/
Looking after your suprapubic catheter. Information for patients
 Looking after your suprapubic catheter Information for patients What is a suprapubic catheter? A catheter is a soft hollow tube, which is used to drain urine from the bladder. The catheter is inserted
Looking after your suprapubic catheter Information for patients What is a suprapubic catheter? A catheter is a soft hollow tube, which is used to drain urine from the bladder. The catheter is inserted
Lee Jackson, M.D. Post-Operation Information and Instructions
 Post-Operation Information and Instructions While a robotic prostatectomy is performed routinely, it is still a relatively major surgery that will take some time and effort to recover from. The following
Post-Operation Information and Instructions While a robotic prostatectomy is performed routinely, it is still a relatively major surgery that will take some time and effort to recover from. The following
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
NHS Urinary Catheter Passport
 South Sefton Care Home Innovation Programme (CHIP) PROTOCOL 07:Urinary Catheter Passport NHS Urinary Catheter Passport Information for patients and carers The passport is a hand held patient document for
South Sefton Care Home Innovation Programme (CHIP) PROTOCOL 07:Urinary Catheter Passport NHS Urinary Catheter Passport Information for patients and carers The passport is a hand held patient document for
Instruction Guide to Sterile Intermittent Catheterization For Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~
 TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
Wellness education. The basics of intermittent self-catheterization
 Wellness education The basics of intermittent self-catheterization Coloplast Consumer Care Advisors can assist you with your intimate healthcare needs. They are available Monday through Friday from 7 a.m.
Wellness education The basics of intermittent self-catheterization Coloplast Consumer Care Advisors can assist you with your intimate healthcare needs. They are available Monday through Friday from 7 a.m.
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Sacrospinous Vault Suspension
 gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Sacrospinous Vault Suspension Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Sacrospinous Vault Suspension Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
Tips & Tricks for Usage
 Life. Not leaks. BLADDER SUPPORT FOR WOMEN Tips & Tricks for Usage Based on feedback from users and clinicians, here are some questions and answers that might help with using your uresta bladder support
Life. Not leaks. BLADDER SUPPORT FOR WOMEN Tips & Tricks for Usage Based on feedback from users and clinicians, here are some questions and answers that might help with using your uresta bladder support
Urinary Catheter Passport SAMPLE COPY. A guide to looking after a urinary catheter. (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition
 Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors
 DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
University College Hospital. Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate 2 If you would like this document in another language or format, or require
University College Hospital Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate 2 If you would like this document in another language or format, or require
WHAT TYPES OF CONTINENCE PRODUCTS ARE THERE?
 15 CAN HELP MANAGE WHAT ARE? Continence products help manage the symptoms of poor bladder and bowel control. They may be used for a short time during treatment. They can also be used long term if poor
15 CAN HELP MANAGE WHAT ARE? Continence products help manage the symptoms of poor bladder and bowel control. They may be used for a short time during treatment. They can also be used long term if poor
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Device and Activator. Table of Contents INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Device and Activator INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Table of Contents 1. Purpose of the inflow Device...2 2. Description of the inflow Device...2 3. When Should This Device Not Be Used?...3
Device and Activator INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Table of Contents 1. Purpose of the inflow Device...2 2. Description of the inflow Device...2 3. When Should This Device Not Be Used?...3
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
ISC. (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information. Women and Children Gynaecology
 44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
Anterior And Posterior Repair
 gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Anterior And Posterior Repair Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Anterior And Posterior Repair Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
Urinary catheter passport
 Urinary catheter passport The aim of this passport is to provide you with the all the necessary information to enable you to care for your urinary catheter. It will also provide a useful form of communication
Urinary catheter passport The aim of this passport is to provide you with the all the necessary information to enable you to care for your urinary catheter. It will also provide a useful form of communication
After care following insertion of suprapubic catheter
 After care following insertion of suprapubic catheter Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign
After care following insertion of suprapubic catheter Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign
Guide to strengthening the pelvic floor muscles
 Exercise Cones Pelvic Exercise Made Easy Exercise Cones Pelvic Exercise Made Easy This system is clinically proven to strengthen the pelvic floor muscle to help with the control and prevention of stress
Exercise Cones Pelvic Exercise Made Easy Exercise Cones Pelvic Exercise Made Easy This system is clinically proven to strengthen the pelvic floor muscle to help with the control and prevention of stress
Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy
 RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
