The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Shauna Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 26 The Urinary System
2 Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood ph Prevents the loss of valuable nutrients Eliminates organic matter Synthesizes calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) Prevents dehydration Aids the liver with some of its functions
3 Introduction The urinary system consists of: Kidneys And the associated nephrons Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra
4 Figure 26.1a An Introduction to the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary bladder Temporarily stores urine prior to elimination Suprarenal gland Renal artery and vein Inferior vena cava Aorta Urethra Conducts urine to exterior; in males, transports semen as well Anterior view showing the components of the urinary system
5 The Kidneys The left kidney is positioned higher than the right kidney Both kidneys are capped with the suprarenal glands There are layers of connective tissue that serve to protect the kidneys
6 The Kidneys Superficial Anatomy of the Kidney The medial indentation is the hilum Renal arteries enter at the hilum Renal veins and ureters exit at the hilum
7 Figure 26.2a The Urinary System in Gross Dissection Diaphragm Inferior vena cava Celiac trunk Right suprarenal gland Right kidney Hilum Quadratus lumborum muscle Iliacus muscle Psoas major muscle Peritoneum (cut) Rectum (cut) Esophagus (cut) Left suprarenal gland Left kidney Left renal artery Left renal vein Superior mesenteric artery Left ureter Abdominal aorta Left common iliac artery Gonadal artery and vein Urinary bladder Diagrammatic anterior view of the abdominopelvic cavity showing the kidneys, suprarenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, and blood supply to the kidneys
8 The Kidneys Sectional Anatomy of the Kidney Consists of: Renal cortex Renal medulla, which consists of: Renal pyramids Renal papillae Renal columns Renal lobe, which consists of: Minor calyx Major calyx Renal pelvis
9 Figure 26.3a Structure of the Kidney Inner layer of fibrous capsule Renal sinus Adipose tissue in renal sinus Renal pelvis Hilum Renal papilla Cortex Medulla Renal pyramid Connection to minor calyx Minor calyx Renal lobe Medulla Hilum Renal columns Ureter Outer layer of fibrous capsule Renal pyramids Renal sinus Inner layer of fibrous capsule Renal pelvis Major calyx Minor calyx Renal papilla Ureter Major calyx Outer layer of fibrous capsule Frontal section through the left kidney showing major structures. The outlines of a renal lobe and a renal pyramid are indicated by dotted lines. Renal lobe Fibrous capsule
10 The Kidneys The Blood Supply to the Kidneys Beginning with blood in the renal arteries Segmental arteries Interlobar arteries Arcuate arteries Cortical radiate arteries Afferent arterioles Glomerular capillaries Waste is dropped in the nephrons
11 The Kidneys The Blood Supply to the Kidneys (continued) After waste is dropped off at the nephrons, blood leaves the kidneys via the following vessels: Glomerular capillaries Efferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries or vasa recta capillaries Arcuate veins Interlobar veins Renal vein
12 Figure 26.4a Blood Supply to the Kidneys Interlobular veins Cortical radiate arteries Interlobar arteries Segmental artery Suprarenal artery Renal artery Renal vein Interlobar veins Arcuate veins Arcuate arteries Sectional view showing major arteries and veins. Compare with Figures 26.3 and 26.8.
13 Figure 26.7ac Histology of the Nephron Proximal convoluted tubule Renal corpuscle Cortical nephron Distal convoluted tubule Juxtamedullary nephron Cortex Connecting tubules Visceral epithelium Parietal epithelium Glomerulus Nephron loop Thin descending limb Thick ascending limb Medulla Capsular space Distal convoluted tubule Proximal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Renal corpuscle The renal corpuscle LM 140 Papillary duct Renal papilla Minor calyx Orientation of cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons
14 The Kidneys Functions of the PCT Absorbs organic nutrients, ions, and plasma protein from the filtrate Water is absorbed from the PCT to the bloodstream The capillaries in the PCT region are called the peritubular capillaries
15 The Kidneys Functions of the Nephron Loop Descending portion Water leaves this portion and enters the bloodstream (thereby preventing dehydration) The capillaries surrounding the nephron loop are called the vasa recta Ascending portion Pumps ions (sodium ions and chloride ions) out of the ascending loop thereby preventing the loss of these ions
16 The Kidneys Functions of the DCT Active secretion of ions and acids Selective reabsorption of sodium and calcium ions Very little reabsorption of water
17 The Kidneys Functions of the Collecting Duct The DCTs of several nephrons drain into the collecting duct The cells of the collecting ducts make final adjustments to the concentration of the urine that is about to exit the kidneys
18 The Kidneys Structure and Function of the Nephron Waste (glomerular filtrate) material leaves the glomerular capillaries and enters: Glomerular capsule Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) Nephron loop Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
19 The Kidneys Structure and Function of the Nephron Filtrate enters the DCT of several nephrons and empties into a common tube called the collecting duct Filtrate enters the papillary duct Minor calyx Major calyx Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra
20 Figure 26.7ac Histology of the Nephron Proximal convoluted tubule Renal corpuscle Cortical nephron Distal convoluted tubule Juxtamedullary nephron Cortex Connecting tubules Visceral epithelium Parietal epithelium Glomerulus Nephron loop Thin descending limb Thick ascending limb Medulla Capsular space Distal convoluted tubule Proximal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Renal corpuscle The renal corpuscle LM 140 Papillary duct Renal papilla Minor calyx Orientation of cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons
21 Figure 26.6 A Typical Nephron NEPHRON COLLECTING SYSTEM DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE Nucleus Microvilli Mitochondria Reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients Efferent arteriole Secretion of ions, acids, drugs, toxins Variable reabsorption of water, sodium ions, and calcium ions (under hormonal control) Renal tubule Connecting tubules Collecting duct CONNECTING TUBULES AND COLLECTING DUCT Parietal (capsular) epithelium Capsular space Visceral (glomerular) epithelium RENAL CORPUSCLE Afferent arteriole Descending limb of loop ends Descending limb Ascending limb of loop ends Ascending limb Variable reabsorption of water and reabsorption or secretion of sodium, potassium, hydrogen, and bicarbonate ions Capillaries of glomerulus PAPILLARY DUCT Production of filtrate Thin descending limb NEPHRON LOOP Thick ascending limb Minor calyx Delivery of urine to minor calyx Further reabsorption of water (descending limb) and both sodium and chloride ions (ascending limb)
22 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination The Ureters Exit the kidney at the hilum area Extend to the urinary bladder Enter the urinary bladder on the posterior/inferior side The entrance to the urinary bladder is the ureteral openings in the trigone area
23 Figure 26.10c Organs Responsible for the Conduction and Storage of Urine Median umbilical ligament (urachus) Ureter Lateral umbilical ligament Detrusor muscle Rugae Ureteral openings Internal urethral sphincter External urethral sphincter (in urogenital diaphragm) Anatomy of the urinary bladder in a male Prostate gland Prostatic urethra Membranous urethra Trigone Center of trigone Neck of urinary bladder
24 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination Histology of the Ureters Each ureter consists of three layers Inner mucosa Middle muscular layer (consisting of longitudinal and circular muscles) Adventitia (this is continuous with the fibrous capsule)
25 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination The Urinary Bladder Males The base of the urinary bladder is between the rectum and the symphysis pubis Females The base of the urinary bladder is inferior to the uterus and anterior to the vagina
26 Figure 26.10a Organs Responsible for the Conduction and Storage of Urine Peritoneum Left ureter Rectum Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Prostate gland External urethral sphincter Spongy urethra External urethral orifice Urethra [see part c] Urogenital diaphragm Position of the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra in the male
27 Figure 26.10b Organs Responsible for the Conduction and Storage of Urine Rectum Right ureter Uterus Peritoneum Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Internal urethral sphincter Urethra External urethral sphincter (in urogenital diaphragm) Vagina Vestibule Position of the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra in the female
28 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination Histology of the Urinary Bladder The muscular layer of the urinary bladder is called the detrusor muscle At the exit of the urinary bladder and entrance to the urethra is a smooth muscle that makes up the internal urethral sphincter This is under involuntary control
29 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination Histology of the Urinary Bladder (continued) As the urethra passes through the urogenital diaphragm there is a skeletal muscle that makes up the external urethral sphincter This is under voluntary control this is the sphincter we learned to control as an infant We lose control as we age We lose control due to some spinal cord injuries
30 Figure 26.10c Organs Responsible for the Conduction and Storage of Urine Median umbilical ligament (urachus) Ureter Lateral umbilical ligament Detrusor muscle Rugae Ureteral openings Internal urethral sphincter External urethral sphincter (in urogenital diaphragm) Anatomy of the urinary bladder in a male Prostate gland Prostatic urethra Membranous urethra Trigone Center of trigone Neck of urinary bladder
31 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination The Urethra Female 3 to 5 cm in length The external urethral orifice is near the anterior wall of the vagina Male 18 to 20 cm in length Subdivided to form the prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, and spongy urethra
32 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination The Urethra Male (continued) Prostatic urethra passes through the prostate gland Membranous urethra is a short segment that goes through the urogenital diaphragm Spongy urethra (penile urethra) extends through the penis to the external urethral orifice
33 Figure Organs Responsible for the Conduction and Storage of Urine Peritoneum Left ureter Rectum Rectum Right ureter Urinary bladder Uterus Peritoneum Pubic symphysis Prostate gland External urethral sphincter Spongy urethra Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Internal urethral sphincter Urethra External urethral orifice Urethra [see part c] Urogenital diaphragm External urethral sphincter (in urogenital diaphragm) Vagina Vestibule Position of the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra in the male Position of the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra in the female Median umbilical ligament (urachus) Ureter Peritoneum Lateral umbilical ligament Detrusor muscle Rugae Ureteral openings Internal urethral sphincter External urethral sphincter (in urogenital diaphragm) Anatomy of the urinary bladder in a male Prostate gland Prostatic urethra Membranous urethra Trigone Center of trigone Neck of urinary bladder Right ureter The male urinary bladder and accessory reproductive structures as seen in posterior view Base of urinary bladder Ductus deferens Seminal gland Posterior surface of prostate gland Prostatic urethra
34 Structures for Urine Transport, Storage, and Elimination The micturition reflex and urination The first urge to urinate is when the urinary bladder fills to about 200 ml Greater than 200 ml will cause the internal urethral sphincter to open The external urethral sphincter will open (voluntarily) to expel the stored urine Between 500 ml and 800 ml, even the external urethral sphincter will open
35 Aging and the Urinary System Age related problems include: Nephrons decrease in number Glomerular filtration rate declines Reduced sensitivity to hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) resulting in frequent urination Micturition problems Urethral sphincters lose muscle tone leading to incontinence Urinary retention may lead to infections
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
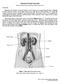 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms
 209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
1. The Fibrous Capsule covers the outside of the kidney. It is made of fat and fibers.
 Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Urinary System VASTACCESS, INC.
 Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily.
 1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
Bio 230 Lecture Notes: THE URINARY SYSTEM
 Bio 230 Lecture Notes: THE URINARY SYSTEM NOTE: You must follow along in your text book or the powerpoint supplied while reading through these lecture notes. A picture is worth a thousand words. Urinary
Bio 230 Lecture Notes: THE URINARY SYSTEM NOTE: You must follow along in your text book or the powerpoint supplied while reading through these lecture notes. A picture is worth a thousand words. Urinary
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Chapter 25: Urinary System
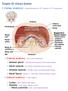 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12. Urinary System INTRODUCTION. Main functions of the kidneys are
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Unit 15: The Urinary System
 Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones
 4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Pearson Education, Inc.
 24 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Anatomy of the Urinary System Learning Outcomes 24.1 Identify the organs of the urinary system, and cite a primary function of each.
24 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Anatomy of the Urinary System Learning Outcomes 24.1 Identify the organs of the urinary system, and cite a primary function of each.
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
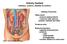 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
active transport of! Na. C. Tubular Reabsorption of Nutrients, Water, and Ions (p. 979; Fig )
 The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1
 Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1 I. Unit 15: The Urinary System A. Functions of the Urinary System 1. Elimination of waste products a) Nitrogenous wastes b) Toxins c) Drugs 2. Regulate aspects of homeostasis
Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1 I. Unit 15: The Urinary System A. Functions of the Urinary System 1. Elimination of waste products a) Nitrogenous wastes b) Toxins c) Drugs 2. Regulate aspects of homeostasis
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Kidneys. Urinary System. Overview of the Urinary System. Principal organs = Kidneys. Accessory organs = Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra
 Urinary System Overview of the Urinary System Principal organs = Kidneys Accessory organs = Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra The Urinary System regulates the content of blood plasma to maintain homeostasis
Urinary System Overview of the Urinary System Principal organs = Kidneys Accessory organs = Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra The Urinary System regulates the content of blood plasma to maintain homeostasis
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Urinary System
 Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C.
 Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R. The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 18 The Urinary System Chapter 18 Learning Outcomes 18-1 18-2 18-3 18-4 Identify the components of the urinary system,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 18 The Urinary System Chapter 18 Learning Outcomes 18-1 18-2 18-3 18-4 Identify the components of the urinary system,
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Urinary system. Aleš Hampl
 Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Chapter 14 The Urinary System. Anatomy
 Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
The Urinary System: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Func%ons of the Urinary System
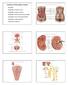 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Diaphragm Regula%on of blood volume 11th and 12th ribs Adrenal gland Renal artery Renal vein Regula%on of blood pressure Kidney Vertebra L2 Aorta Inferior vena cava
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Diaphragm Regula%on of blood volume 11th and 12th ribs Adrenal gland Renal artery Renal vein Regula%on of blood pressure Kidney Vertebra L2 Aorta Inferior vena cava
11/8/2017. Urinary System Functions. Organs and Vessels of the Urinary System Hepatic veins (cut)
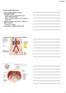 Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
The kidneys (Figure 28,1), which are the principal organs. natomy of the Urinary System. Anatomy of the Urinary System.
 Exercise 28 natomy of the Urinary System Laboratory Objectives n ompletion of the activities in this exercise, you will be able to: Describe the gross and microscopic anatomy of the urinary svstem, Trace
Exercise 28 natomy of the Urinary System Laboratory Objectives n ompletion of the activities in this exercise, you will be able to: Describe the gross and microscopic anatomy of the urinary svstem, Trace
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
