Urinary incontinence in women
|
|
|
- Byron Edwin Owens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urinary incontinence in women Lauren N Wood, 1 Jennifer T Anger 2 1 Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology, Los Angeles, CA, USA 2 Urologic Reconstruction, Urodynamics, and Female Urology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology, Los Angeles, CA 90211, USA Correspondence to: J T Anger jennifer.anger@cshs.org Cite this as: BMJ:2014;349:g4531 doi: /bmj.g4531 Introduction Urinary incontinence in women is a common and costly problem. Many treatment options are available, from simple lifestyle modifications to invasive surgery. This review describes the most common types of urinary incontinence, appropriate clinical investigations, and the treatment options available. Recent advances, including new pharmacologic and surgical therapies, have reshaped the treatment of incontinence. Overall, level I evidence supports the use of these treatments, and clinicians have a wide range of treatment options to choose from. Epidemiology and prevalence The International Continence Society defines urinary incontinence as any involuntary leakage of urine. 1 2 Ur inary incontinence is estimated to affect 200 million people worldwide. 3 The prevalence of urinary incontinence in women is variable in the literature, but it is reported to be as high as 55%. 4 This number may be an underestimate, because up to half of women may fail to report urinary incontinence to their healthcare provider. 5 This may be due to embarrassment, lack of knowledge about treatment options, or a belief that urinary incontinence is a normal inevitable part of aging. 6 According to the 2010 International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report, stress urinary incontinence is defined as voluntary loss of urine on effort, physical exertion, or on sneezing or coughing. 2 Depending on age, the prevalence of stress incontinence ranges from 29% to 75%, with a mean of 48%. 7 The prevalence of daily stress u rinary incontinence is 10% in community dwelling m iddle aged women. 8 A third of women with stress u rinary incontinence report leakage weekly. 8 Urgency urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency. 2 Urgency incontinence is part of a larger symptom complex known as overactive bladder syndrome, which is defined as urinary urgency, usually accompanied by frequency and nocturia, with or without urgency urinary incontinence, in the absence of urinary tract infection or other obvious disease. 2 The National Overactive Bladder Evaluation (NOBLE) study, in which investigators conducted telephone interviews with more than 5000 adults, with a follow-up nested study, found the prevalence of overactive bladder syndrome to be 16.9% in women and 16% in men. 9 People with overactive bladder syndrome-dry (without leakage) have frequency and urgency without leakage, whereas people with overactive bladder syndrome-wet (with leakage) experience overactive bladder syndrome with urgency urinary incontinence. The overall prevalence of urgency urinary incontinence is estimated at 7-33%. 7 Women are more likely to experience urgency urinary incontinence (overactive bladder syndrome-wet) SOURCES AND SELECTION CRITERIA In November 2013, we searched PubMed and the Cochrane databases using the keywords female urinary incontinence, stress urinary incontinence, urgency urinary incontinence, mixed urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, pelvic floor muscle training, tibial nerve stimulation, percutaneous sacral nerve modulation, suburethral bulking agents, and midurethral slings. For individual sections, further keywords related to the overall subjects were searched in the same databases. For example, mirabegron for overactive bladder, cost of urinary incontinence, or behavioral modification for stress urinary incontinence. We searched for published guidelines on the American Urological Association, American Urogynecologic Society, Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogenital Reconstruction, and National Institute for Health and Care Excellence websites. We considered all clinical trials and review articles published in English. We prioritized randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses. than men, with 9.3% of women experiencing this condition versus 2.6% of men. 9 The prevalence of mixed urinary incontinence (both stress urinary incontinence and urgency urinary incontinence) ranges from 14% to 61%. 7 Socioeconomic burden The burden of urinary incontinence is high in both human and financial terms. 10 Urinary incontinence has a negative impact on health related quality of life (HRQOL), 11 and it contributes to depression, falls, 14 and admission to a nursing home. 15 The adjusted risk of nursing home admission with urinary incontinence is 2.0 for women and 3.2 for men. 15 The total annual cost of urinary incontinence in the United States is estimated to be as high as $32bn ( 18.7bn; 23.5bn). 16 Furthermore, costs for women over the age of 65 years are twice those for their younger counterparts. 17 The cost of overactive bladder syndrome in the US alone has been estimated at $65.9bn. 18 Although costs of care include medical care and treatment, the largest contributor for urinary incontinence is the cost of pads, diapers, and bedding. Risk factors Established risk factors vary by type of urinary incontinence. Pregnancy and childbirth Pregnancy and childbirth are established risk factors for stress urinary incontinence. 19 Although vaginal delivery and caesarean delivery increase the risk of stress urinary incontinence, the risk is higher in women who deliver vaginally. In a study of more than women, the prevalence of urinary incontinence among nulliparous 26 6 December 2014 the bmj
2 women was 10.1%, versus 15.9% in the caesarean d elivery group and 21% in the vaginal delivery group. 20 This may be due to a combination of injury to the pelvic floor musculature and connective tissue, as well as nerve damage as a result of pregnancy and labor. Hysterectomy Hysterectomy has been associated with the development of urinary incontinence, particularly stress urinary incontinence. 19 Hysterectomy may damage the muscles of the pelvic floor and lead to incontinence, although this is poorly understood. Stress urinary incontinence has also been associated with vaginal prolapse, including cystocele (prolapse of the bladder), rectocele (prolapse of the rectum), 23 uterine prolapse, 24 and vaginal vault prolapse after hysterectomy, probably from the common risk factor of the weakening of the pelvic floor muscles. Weakening of the structures of the pelvic floor can contribute to both prolapse and incontinence, and the two problems may be inter-related because they often share a common cause. 25 Other risk factors Recurrent urinary tract infection is independently associated with urgency urinary incontinence and is a readily treatable cause of this condition. 26 Higher body mass index and advancing age 27 are associated with both stress and urgency urinary incontinence. Family history is important because women whose mothers or older sisters are incontinent are more likely to develop stress and mixed urinary incontinence. 28 Smoking has been associated with urgency urinary incontinence in women, 29 possibly because of the irritative effects on the bladder. Smoking is also associated with chronic cough, which can contribute to stress urinary incontinence. 30 Caffeine has a diuretic effect and may also play a role in urgency urinary incontinence. 31 A cross sectional national survey of more than 4300 women found that daily caffeine intake of greater than 204 mg (roughly the amount of caffeine in one cup of coffee) was Box 1 Levels of evidence for urinary incontinence risk factors 33 Level 1 Pregnancy, labor, and vaginal delivery Body mass index Genetics and family history Oral estrogen Level 2 Physical function Diabetes Hysterectomy Dementia and loss of cognitive function Level 3 Smoking Caffeine Constipation Urinary tract infections Depression Exercise Box 2 Evaluation of women with urinary incontinence History Urinary symptoms (frequency, urgency, hematuria, urinary tract infections, nocturia) Presence of stress urinary incontinence, urgency urinary incontinence, or mixed urinary incontinence Pad usage Daily fluid intake Presence of a vaginal bulge Physical examination Pelvic examination: assess for atrophy, prolapse, ability to perform Kegel exercises Stress test for stress urinary incontinence Presence of edema in the lower extremities Cognitive status Neurologic examination associated with a prevalence of 40% of any type of incontinence, most commonly stress urinary incontinence. 32 Many other factors increase the risk of urinary incontinence, and box 1 provides a summary of the levels of evidence for all established risk factors. Evaluation Because of the lack of self reporting and the high incidence of urinary incontinence and bother, it could be argued that all women presenting to their primary care physician should be screened for symptoms of urinary incontinence. 34 However, professional organizations, such as the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Urological Association (AUA), provide no specific screening recommendations, and many women experience leakage that is infrequent and do not seek medical attention. Hence, screening for urinary incontinence is likely to be of maximum benefit to women whose quality of life is affected by urinary incontinence (box 2). History The investigation of a patient with urinary incontinence should begin with a specific history. Associated urinary symptoms such as frequency, urgency, hematuria, recurrent urinary tract infections, and nocturia should be elucidated and explored. To tailor treatment to the individual, it is necessary to determine whether symptoms of stress, urgency, or both types of incontinence are present. 34 Symptom severity can be assessed by inquiry about daily pad usages, including pad size (pantiliner v menses pad v incontinence pads or diapers). It is important to ask about fluid intake because many women exacerbate symptoms by drinking six to eight glasses of water a day, regardless of thirst. 34 Symptoms of a vaginal bulge may indicate pelvic organ prolapse, which is highly associated with stress urinary incontinence and can also contribute to urgency urinary incontinence. 25 Questionnaires Several validated tools are available to assess the severity of urinary incontinence and measure condition specific HRQOL. The urogenital distress inventory (UDI-6) and the the bmj 6 December
3 incontinence impact questionnaire (IIQ-7) encompass the urinary domain components of the pelvic floor distress inventory-short form (PFDI-20) and the pelvic floor impact questionnaire short form (PFIQ-7). They are popular questionnaires among specialists and measure symptom severity and impact on HRQOL, respectively. 36 Although no specific questionnaires are endorsed by professional societies in the US, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends the use of: The international consultation on incontinence questionnaire (ICIQ) The Bristol female lower urinary tract symptoms questionnaire (BFLUTS) The incontinence quality of life questionnaire (I-QOL) The stress and urge incontinence and quality of life questionnaire (SUIQQ) The urinary incontinence severity score (UISS) The stress-related leak, emptying ability, anatomy, protection, inhibition, quality of life, mobility and mental status quality of life index (SEAPI-QMM) The incontinence severity index (ISI) The king s health questionnaire (KHQ). 35 A systematic review by the symptom and quality of life committee of the International Consultation on confirms the use of these questionnaires, all with a grade A recommendation. 37 Bladder diary A bladder diary can be useful for quantifying symptoms and recording the number and type of episodes of urinary incontinence, and these diaries are recommended by both the AUA and the Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) A bladder diary will also record the voiding times and exact voided volumes (recorded by a hat placed in the toilet). 40 NICE guidelines also recommend the use of bladder diaries in the initial assessment of women with urinary incontinence or overactive bladder syndrome. 35 Women should complete the diary for a minimum of three days to cover variations in their daily activities, although a two day diary may be more feasible for patients to complete. 35 However, bladder diaries are not always needed when the severity and type of urinary incontinence are readily ascertained from the history. Physical examination Pelvic examination will identify the presence of associated pelvic organ prolapse, as well as a woman s ability to initiate voluntary contraction of her pelvic floor muscles (the Kegel exercise). 34 The ability to contract the pelvic floor muscles should be confirmed on pelvic examination before initiating pelvic floor muscle training for treatment. 35 This can be done by asking the patient to squeeze her vaginal muscles around the examining finger. A cough stress test with a comfortably full bladder will identify the presence of stress urinary incontinence in most cases. The stress test is performed by asking the patient whose bladder is comfortably full to cough in the supine or lithotomy position. The test is positive if clinical stress leakage defined as involuntary leakage from the urethra synchronous with effort or physical exertion, or on sneezing or coughing is observed. 2 If leakage is not seen on a supine stress test, it may be repeated in the standing position. However, this test is limited, because 34% of women with genuine stress incontinence have a negative stress test at the time of evaluation. 41 It is also important to identify lower extremity edema (to determine possible sources of polyuria in a patient with nocturia) and overall cognitive status, and to perform a neurologic examination. Urine analysis should be performed in all patients to assess for microhematuria, glucose, protein, leucocytes, and nitrites, and to rule out infection as an acute cause. 35 When indicated, a urine culture is performed. Uroflow (measured flow rate), commonly performed in urologists and urogynecologists offices, is useful only for women with signs of voiding dysfunction. 34 Measurement of post-void residual volume, by ultrasound or catheterization, will assess a patient s ability to empty the bladder, and should be performed in women presenting with voiding difficulty or recurrent urinary tract infection. Cystometry Patients with uncomplicated stress or urgency urinary incontinence generally do not require cystometry before starting conservative treatment, including drugs, unless they have microhematuria or other complicating f actors, such as previous incontinence surgery or recurrent urinary tract infections. A multicenter randomized non-inferiority trial of 630 women showed no benefit of performing urodynamics over office evaluation alone in patients with straightforward stress incontinence before sling surgery. 42 Treatment was successful in 76.9% of the urodynamic testing group versus 77.2% of the office evaluation group, with a non-inferiority margin of 11%. 42 Treatment success was defined as a 70% or more reduction in the baseline score of the urogenital distress inventory and a patient global impression of improvement response of much better or very much better at 12 months. 42 However, women with a history of antiincontinence surgery, planned surgery for pelvic organ prolapse, urge predominant incontinence, and neurologic disease were excluded, which limits the generalizability of the study results to patients with more complex needs. A second multicenter diagnostic cohort non-inferiority randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 126 women with urodynamic findings discordant with clinical assessment randomized women to immediate surgery or tailored treatment based on urodynamics. 43 It concluded that urodynamics should not be routinely used before midurethral sling surgery because immediate surgery was non-inferior to treatment based on urodynamic findings, with non-inferiority defined as less than a five point difference on the urogenital distress inventory. 43 Urodynamics should not be performed in women with untreated symptoms or urgency incontinence who have no evidence of neurologic disease or voiding dysfunction. 34 AUA/SUFU guidelines discourage the use of urodynamics in the initial workup of the uncomplicated patient. 38 However, it is often helpful in patients with 28 6 December 2014 the bmj
4 Wide angle glaucoma Frail, elderly Beta 3 agonist UUI Urgency Urinary Lifestyle interventions Reduce fluids, caffeine, carbonated drinks SUI Stress Urinary Timed voiding Reduce BMI to below 25 Manage constipation Pharmacology Anticholinergics oxybutynin trospium tolterodine solifenacin fesoterodine darifenacin propiverine (UK only) Poor efficacy or side effects myrbetriq 2 or more treatments failed? Yes No Minimally invasive techniques OnabotulinumtoxinA injection Sacral neuromodulation Pelvic floor muscle training Surgery Reformulate as patch / gel or change drug Posterior tibial nerve stimulation Injectable bulking agents Burch colposuspension Poor surgical candidate / averse to surgery Fascial slings Midurethral synthetic slings In UK? pessiaries Duloxetine Treatment options available for urinary incontinence in women. For full details of drug treatments for urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome, treatment of drug refractory urgency urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome, and treatment of stress incontinence, see the full version of the review on thebmj.com. mixed symptoms who could benefit from further specific delineation of the cause of their urinary incontinence. Cystometry is also useful before starting more invasive treatment for drug refractory overactive bladder syndrome. NICE guidelines advocate the use of filling and voiding cystometry in women with suspected detrusor overactivity, voiding dysfunction, anterior prolapse, or in those who have had surgery for stress incontinence. 35 If the diagnosis is still unclear, video urodynamics can be considered. 35 Many specialists prefer video urodynamics as part of routine urodynamics because it provides important anatomic information about the appearance of the bladder and bladder neck (often open in women with stress urinary incontinence). Initial management Urinary incontinence can successfully be managed initially at the primary care level in most patients. Referral to a specialist is usually indicated when conservative measures fail to improve symptoms. Specialists include No Yes urologists and gynecologists with experience in treating urinary incontinence. The figure shows the available treatment options. Lifestyle interventions Women with all types of urinary incontinence can be advised to decrease their intake of fluids, caffeine, and carbonated drinks. 44 Women are taught, by both the media and the medical establishment, that it is necessary and optimal to drink eight glasses of water daily. Many women do not understand that the recommended six to eight glasses (240 ml each) of water a day includes the water present in food, which contributes substantially to overall total fluid intake. 45 Hence, re-education is appropriate for women with symptoms of overactive bladder syndrome who admit to excessive fluid intake, unless otherwise medically indicated. Further behavioral modification includes timed voiding, with a goal of reducing voiding frequency to every two to three hours. Women who are unable to wait this long begin by voiding at a set interval (such as an hour) and then increase the time interval by minutes each week until the desired interval is reached. 46 According to both AUA/SUFU and NICE guidelines, women with urgency or mixed urinary incontinence should be offered bladder training as a first line treatment. Constipation should be managed and avoided because this contributes to urinary incontinence and voiding dysfunction. 47 Women with a body mass index greater than 25 should be advised to lose weight if they present with new or worsening symptoms, 34 because weight loss significantly reduces symptoms of urinary incontinence. 48 A randomized trial of weight loss versus no intervention in 347 obese women with 10 or more episodes of urinary incontinence a week found a 65% reduction in stress urinary incontinence in the weight loss group versus 47% in controls at 12 months (P<0.001). 48 Pelvic floor muscle training Pelvic floor muscle training consists of strengthening the muscles of the pelvic floor (to reduce stress urinary incontinence) and contracting them in isolation to inhibit detrusor contractions (and reduce urgency urinary incontinence). More commonly known as Kegel exercises, these should be done several times a day and need to be performed consistently over time for benefit to be sustained. A systematic review of patients with urgency, stress, and mixed incontinence found that pelvic floor muscle training was more effective than placebo or no treatment at all and should be included as first line management for urinary incontinence. 49 AUA/SUFU guidelines recommend pelvic floor muscle training as a first line treatment for overactive bladder syndrome. 38 NICE guidelines recommend offering a trial of pelvic floor muscle training for three months, with eight contractions being performed three times a day, as first line treatment for women with both stress and mixed urinary incontinence. 35 In a study of 22 women with pure stress incontinence, 32% were cured after three months. 50 the bmj 6 December
5 FUTURE RESEARCH QUESTIONS What is the ideal treatment algorithm for patients in whom conservative management of overactive bladder syndrome has been unsuccessful? Should a patient be considered first for onabotulinumtoxina, tibial nerve stimulation, or sacral nerve modulation? Which patients will best respond to which types of treatment? What is the long term efficacy and safety of suburethral mini-slings and midurethral slings? In the era of mesh related complications, are midurethral slings still safe? What is the surgical outcome of repeat sling surgery after initial sling surgery has been ineffective? When properly performed, these exercises may be more effective than pharmacologic management. 51 An RCT of 197 women with urgency urinary incontinence randomized to behavioral treatment, oxybutynin, or placebo found an 80.7% reduction of urinary incontinence episodes with behavioral treatment versus a 68.5% reduction with drug treatment and a 39.4% reduction with placebo (P=0.04). 51 Looking ahead As healthcare systems seek increased value at a lower cost, urinary incontinence is an area where costs can be considerably reduced through minimizing the use of diagnostic testing. Quality of care indicators are a means to measure the care provided to women with urinary incontinence and can be used as an algorithm for the investigation and treatment of urinary incontinence, regardless of provider specialty. This method is useful for areas in which the level of evidence is limited. The application of these algorithms can improve incontinence care at the generalist level and thereby reduce the need for specialty care, while algorithms applied to specialist care can help reduce costly, and sometimes unnecessary, testing. Further research is needed to improve our understanding of the physiology underlying overactive bladder syndrome. In addition, the prevention of lower urinary tract symptoms is an exciting area of research that has the potential to reduce the burden of urinary incontinence. Urinary biomarkers are an ongoing area of research, and several clinical trials are under way to identify the role of urinary nerve growth factor, prostaglandin E2, ATP, and others as potential biomarkers for overactive bladder syndrome to identify at risk patients and predict responsiveness to treatment (see clinicaltrials.gov). Conclusion Urinary incontinence affects a large number of women and results in a substantial socioeconomic burden. Minimally invasive treatment measures can readily be initiated by primary care providers, with referral to a specialist when conservative management is not effective. Many minimally invasive and efficacious treatment options are available for both stress and urgency urinary incontinence. Despite the high rate of mesh related complications after vaginally placed mesh for prolapse, midurethral mesh slings for stress urinary incontinence have an acceptably low complication rate with durable efficacy. Newer treatments for overactive bladder syndrome and urgency urinary incontinence, including mirabegron and intravesical botulinum injection, have greatly changed the landscape of treatment, providing a wide range of treatment options to patients with overactive bladder syndrome that is refractory to tr aditional anticholinergic drugs. Contributors: Both authors helped plan, conduct, and report the work. JTA is guarantor. Competing interests: None declared. Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed. References are in the version on thebmj.com. ANSWERS TO ENDGAMES, p 36 For long answers go to the Education channel on thebmj.com ANATOMY QUIZ Anatomy of the brain: T2 weighted magnetic resonance image, axial section A: Right thalamus B: Right internal capsule C: Right lentiform nucleus D: Left head of caudate nucleus E: Left fornix F: Paired internal cerebral veins PICTURE QUIZ An abnormal chest radiograph 1 There is marked deviation of the trachea to the right, with a homogeneous opacity in the upper mediastinum. 2 It shows a large mass in the anterior mediastinum that seems to arise from the thyroid. 3 Teratoma, lymphoma, goitre, and thymoma. 4 Thyroid function tests and flow volume loops. Referral to the cardiothoracic team. STATISTICAL QUESTION Spearman s rank correlation coefficient Statement a is true, whereas b and c are false December 2014 the bmj
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline.
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Content. Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management
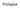 Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Urinary Incontinence. Lora Keeling and Byron Neale
 Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider
 Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 Assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence in women bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated
Assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence in women bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 61 Subject The management of female incontinence Date of decision May 2016 Date refreshed May 2017 Date of review May 2019 Introduction: GUIDANCE Urinary incontinence
Priorities Forum Statement Number 61 Subject The management of female incontinence Date of decision May 2016 Date refreshed May 2017 Date of review May 2019 Introduction: GUIDANCE Urinary incontinence
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Patient Information. Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms. pubic bone. urethra. scrotum. bladder. vaginal canal
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
SELF CARE IN URINARY INCONTINENCE
 O P I N I O N SelfCare 2011;2(6):160-166 Advancing the study&understanding of self-care JULIAN SPINKS General Practitioner, Medway Primary Care Trust ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence and its associated urinary
O P I N I O N SelfCare 2011;2(6):160-166 Advancing the study&understanding of self-care JULIAN SPINKS General Practitioner, Medway Primary Care Trust ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence and its associated urinary
Stress Incontinence. Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS
 Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Incontinence; Lets talk about it. Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery
 Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence. Urinary Incontinence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Compassionate and effective management
 IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
The Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome with Antimuscarinic Drugs
 The Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome with Antimuscarinic Drugs Author Version Date Consultation Date of Ratification By JPG Shaista Hussain Joint Formulary Pharmacist V2 16.09.2014 Homerton University
The Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome with Antimuscarinic Drugs Author Version Date Consultation Date of Ratification By JPG Shaista Hussain Joint Formulary Pharmacist V2 16.09.2014 Homerton University
Evaluation & Management of Overactive Bladder
 Evaluation & Management of Overactive Bladder Disclosures/Conflict of Interest/Bias I have no financial relationship with any of the companies that produce the products I m about to discuss I have no conflicts
Evaluation & Management of Overactive Bladder Disclosures/Conflict of Interest/Bias I have no financial relationship with any of the companies that produce the products I m about to discuss I have no conflicts
Urinary Incontinence. Vibhash Mishra Consultant Urological Surgeon Royal Free Hospital
 Urinary Incontinence Vibhash Mishra Consultant Urological Surgeon Royal Free Hospital Affects women of all ages Impacts physical, psychological & social wellbeing Impact on families & carers Costs the
Urinary Incontinence Vibhash Mishra Consultant Urological Surgeon Royal Free Hospital Affects women of all ages Impacts physical, psychological & social wellbeing Impact on families & carers Costs the
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems
 Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems You have scheduled an appointment for evaluation and treatment of a urogynecologic problem. Following, you will find a pelvic floor questionnaire
Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems You have scheduled an appointment for evaluation and treatment of a urogynecologic problem. Following, you will find a pelvic floor questionnaire
Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence
 Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence Arthur Mourtzinos, MD, MBA Co-Vice Chair, Institute of Urology Director, Continence Center Assistant Professor of Urology,
Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence Arthur Mourtzinos, MD, MBA Co-Vice Chair, Institute of Urology Director, Continence Center Assistant Professor of Urology,
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE. Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE 1 Guideline title Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 2 Guideline Contextualisation This is a contextualisation
BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE 1 Guideline title Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 2 Guideline Contextualisation This is a contextualisation
THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB)
 THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB) Passage of urine is caused by the bladder muscle contracting coordinated with the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, which is controlled by higher centers in the central
THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB) Passage of urine is caused by the bladder muscle contracting coordinated with the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, which is controlled by higher centers in the central
Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders
 Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders Dear Colleague: Multiple studies demonstrate that pelvic floor disorders urinary or fecal leakage occurring at an inappropriate time or place has a
Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders Dear Colleague: Multiple studies demonstrate that pelvic floor disorders urinary or fecal leakage occurring at an inappropriate time or place has a
URGE MOTOR INCONTINENCE
 URGE MOTOR INCONTINENCE URGE INCONTINENCE COMMONEST TYPE IN ELDERLY WOMEN Causes: 1 - Defects in CNS regulation Stroke Parkinson s disease Dementia (Alzheimer s and other types) Normopressure hydrocephalus
URGE MOTOR INCONTINENCE URGE INCONTINENCE COMMONEST TYPE IN ELDERLY WOMEN Causes: 1 - Defects in CNS regulation Stroke Parkinson s disease Dementia (Alzheimer s and other types) Normopressure hydrocephalus
Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None
 Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None Financial Disclosures Jeremiah McNamara, MD, OBGYN Boulder Women s Care 303-500-1947 Boulder Women s Care Agenda: Prolapse & Urinary Incontinence The Pelvic Floor
Latest Treatments for a Leaky Bladder None Financial Disclosures Jeremiah McNamara, MD, OBGYN Boulder Women s Care 303-500-1947 Boulder Women s Care Agenda: Prolapse & Urinary Incontinence The Pelvic Floor
Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia URODYNAMIC TESTING
 URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old. The International Continence Society has. In this article:
 Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors
 DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary Incontinence. Lee A. Jennings, MD, MSHS. Assistant Professor Reynolds Department of Geriatrics University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
 Urinary Incontinence Lee A. Jennings, MD, MSHS Assistant Professor Reynolds Department of Geriatrics University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Slides adapted from Alison Moore, MD, MPH University of
Urinary Incontinence Lee A. Jennings, MD, MSHS Assistant Professor Reynolds Department of Geriatrics University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Slides adapted from Alison Moore, MD, MPH University of
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Gina Clark Pacific University. Lauren Murphy Pacific University. Recommended Citation.
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION MIRABEGRON (Myrbetriq Astellas Pharma Canada Inc.) Indication: Overactive Bladder Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that mirabegron be listed
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION MIRABEGRON (Myrbetriq Astellas Pharma Canada Inc.) Indication: Overactive Bladder Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that mirabegron be listed
Overactive Bladder. When to see a doctor. Normal bladder function
 Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients
 Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
 URODYNAMICS Welcome to Chesapeake Urology s Urodynamics Services. Bladder control problems keep millions of people from enjoying a full life, but today, many treatments are available to help. To assist
URODYNAMICS Welcome to Chesapeake Urology s Urodynamics Services. Bladder control problems keep millions of people from enjoying a full life, but today, many treatments are available to help. To assist
Some people experience occasional, minor leaks of urine. Others wet their clothes frequently.
 Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having
Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Urinary Incontinence. Alison A Moore, MD, FACP
 Urinary Incontinence Alison A Moore, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine/Geriatric Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Department of Medicine, Division of Geriatrics Urinary Incontinence (UI) Involuntary
Urinary Incontinence Alison A Moore, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine/Geriatric Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Department of Medicine, Division of Geriatrics Urinary Incontinence (UI) Involuntary
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging
 Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Updates in the nonpharmacological. treatment on overactive bladder
 Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based
 Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based upon a medical history, and includes a focused physical exam (abdominal, neurological, pelvic in females and
Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based upon a medical history, and includes a focused physical exam (abdominal, neurological, pelvic in females and
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PTNS) TREATMENT FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY
 PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PTNS) TREATMENT FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Recommendation by: 1617v2a Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PTNS) TREATMENT FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Recommendation by: 1617v2a Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women. Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital
 Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Module 5 Management Of Urinary Incontinence
 Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Information for Patients. Urinary Incontinence. English
 Information for Patients Urinary Incontinence English Table of contents What is urinary incontinence?... 3 Causes of urinary incontinence... 3 Types of urinary incontinence... 3 Stress urinary incontinence...
Information for Patients Urinary Incontinence English Table of contents What is urinary incontinence?... 3 Causes of urinary incontinence... 3 Types of urinary incontinence... 3 Stress urinary incontinence...
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Information for Patients. Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English
 Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
EVALUATION OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE: STATE-OF-THE-ART REVIEW
 EVALUATION OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE: STATE-OF-THE-ART REVIEW Dominic Lee, 1 *Philippe E. Zimmern 2 1. Department of Urology, St George Hospital, Kogarah, New South Wales, Australia 2. Department
EVALUATION OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE: STATE-OF-THE-ART REVIEW Dominic Lee, 1 *Philippe E. Zimmern 2 1. Department of Urology, St George Hospital, Kogarah, New South Wales, Australia 2. Department
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Urogynaecology & Prolapse. Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings
 + Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
+ Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
Geriatric Urinary Incontinence
 Geriatric Urinary Incontinence Neil M. Resnick, MD Thomas Detre Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Geriatric Medicine University of Pittsburgh/UPMC UI: The Problem Prevalence in elderly 33% Morbidity
Geriatric Urinary Incontinence Neil M. Resnick, MD Thomas Detre Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Geriatric Medicine University of Pittsburgh/UPMC UI: The Problem Prevalence in elderly 33% Morbidity
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary incontinence in women & men
 Urinary incontinence in women & men Dr. Blayne Welk Assistant Professor, Western University, London, ON, Canada Part 1: INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Urinary incontinence is common. About 1 in 4 young women, and
Urinary incontinence in women & men Dr. Blayne Welk Assistant Professor, Western University, London, ON, Canada Part 1: INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Urinary incontinence is common. About 1 in 4 young women, and
NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123
 Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults
 Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults Clinicians need to assess and manage co-existing co morbid conditions which are known to have an impact on continence
Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults Clinicians need to assess and manage co-existing co morbid conditions which are known to have an impact on continence
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Stress incontinence -- occurs during certain activities like coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercise.
 Urinary incontinence Definition Incontinence is the inability to control the passage of urine. This can range from an occasional leakage of urine, to a complete inability to hold any urine. The three main
Urinary incontinence Definition Incontinence is the inability to control the passage of urine. This can range from an occasional leakage of urine, to a complete inability to hold any urine. The three main
Dee E. Fenner, M.D. Chair and Furlong Professor of Women s Health Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Michigan.
 Management of Overactive Bladder Dee E. Fenner, M.D. Chair and Furlong Professor of Women s Health Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Michigan deef@umich.edu Disclosures NONE Objectives Review
Management of Overactive Bladder Dee E. Fenner, M.D. Chair and Furlong Professor of Women s Health Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Michigan deef@umich.edu Disclosures NONE Objectives Review
Top 10 Tips Bladder Control
 Top 10 Tips Bladder Control for Your Personal Guide to a Sensitive Bladder Dr. Mache Seibel Leading authority on women s wellness and menopause Message from Dr. Mache Seibel Thank you for downloading this
Top 10 Tips Bladder Control for Your Personal Guide to a Sensitive Bladder Dr. Mache Seibel Leading authority on women s wellness and menopause Message from Dr. Mache Seibel Thank you for downloading this
Supplement. Updated Literature Search for Pharmacologic Treatments for Urgency UI
 Supplement. Updated Literature Search for Pharmacologic Treatments for Urgency UI Authors: Tatyana A. Shamliyan, MD, MS Senior Director, Evidence-Based Medicine Quality Assurance Elsevier 1600 JFK Blvd,
Supplement. Updated Literature Search for Pharmacologic Treatments for Urgency UI Authors: Tatyana A. Shamliyan, MD, MS Senior Director, Evidence-Based Medicine Quality Assurance Elsevier 1600 JFK Blvd,
Continence Promotion in
 Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Millions of women experience involuntary loss of urine called urinary incontinence (UI). Some women may lose a few drops of urine while running or coughing. Others may feel a strong,
Urinary Incontinence Millions of women experience involuntary loss of urine called urinary incontinence (UI). Some women may lose a few drops of urine while running or coughing. Others may feel a strong,
Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT)
 Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
