Patient Information Department of Urology 36/Info_04_11
|
|
|
- Egbert Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
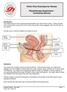
1 Patient Information Department of Urology 36/Info_04_11 : Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency) and without much warning (urgency), associated with leakage of urine (urge incontinence); not being able to start to pass urine immediately (hesitancy), and a decrease in the force of the stream. This may also be associated with having to pass urine more frequently at night. Sometimes after prostate surgery there can be leakage of urine during physical activity or when coughing or sneezing; this is stress incontinence. Men can also experience leakage of urine after finishing voiding and then on walking away from the toilet (post-micturition dribble). What is normal? The kidneys are continuously filtering blood to produce urine, which is stored in the bladder. The bladder will hold mls of urine, and an urge to pass urine is normally felt when the bladder is half full, thus giving time to reach the toilet. For various reasons, this message may become blurred or your bladder may contract to empty without warning, not allowing time to reach the toilet. At the base of the bladder is the prostate gland, which circles the water pipe (urethra). In men over the age of 60, it is quite common for this gland to become enlarged and give rise to the above urinary symptoms. It is important for you to have consulted your GP regarding this so that he can examine the prostate gland. Going to the toilet up to 8 times in 24 hours, with one of these occurring at night is considered normal. There are several strategies that can be employed to control symptoms of urgency and frequency. Page 1 of 9
2 Lifestyle advice Fluid Management A daily fluid intake of litres is recommended. This is approximately 5-7 mugs. Caffeine tends to act as an irritant to the bladder it is recommended that caffeine free products are tried. These are widely available. Substitute caffeinated drinks with water or fruit squashes. Caffeine is found in tea, coffee, chocolate, high-energy drinks like Red Bull and Lucozade, Coca-cola and cocoa. If you drink large quantities of caffeinated drinks you should cut down gradually over a fortnight to reduce withdrawal effects. Large volumes of fluid within a short period of time and fizzy drinks can cause rapid filling of the bladder leading to frequency and urgency. Drinks should be spaced evenly through the day. If you cut down on fluids to try to control frequency, this means urine will become more concentrated and will irritate the bladder more. You will also be more prone to constipation, which will exacerbate bladder symptoms. Ideally urine should be a light straw colour. Very dark and strong smelling urine may mean it is too concentrated, and you should drink a bit more. If urine is very pale with no smell, then you may be drinking too much. During hot weather, air travel, after exercising and during sickness you will need to drink more. The table below indicates some of the fluids and foods which can irritate the bladder. Good Water Decaffeinated drinks Squashes and cordials Possible irritants Caffeinated drinks Fizzy drinks Grapefruit juice Alcohol Spicy foods Stronger brands of tea and coffee contain more caffeine and tannins Cranberry juice should be limited to 400mls a day, and should be avoided if you have been diagnosed with interstitial cystitis or prescribed Warfarin. Drug Management A number of medications can be prescribed by your GP to help control urgency and urge incontinence, and to treat prostate disease. You can discuss these with your GP. Taking a prescribed diuretic (water tablet) will cause you to go to the toilet more frequently than normal a few hours after you have taken it. It is important for your health that you continue to take prescribed medications, so if you find it is causing you great difficulty you should consult your GP. Page 2 of 9
3 A number of common drugs and remedies can also contribute to bladder symptoms. You should seek advice from your Pharmacist, GP or Continence Nurse. Bad Habits Going to the toilet just-in-case Straining to empty your bladder or bowel Good tips Give your bladder time to empty properly. If you feel you are not emptying completely, make sure you have fully emptied by waiting a few seconds and then try to empty more. If you are troubled by getting up to empty your bladder during the night, do not drink directly before you go to bed. If you wake up thirsty during the night, have a few sips of water. Bladder retraining This is a process whereby you train your bladder to hold a greater volume of urine. Bladder training is a way of teaching your bladder how to hold more urine and cut back on the number of times you need to pass urine (frequency). It also helps to stop urine leaking when you experience urgency (the sudden, uncontrollable need to pass water). It is used to treat an overactive or unstable bladder which is responsible for the symptoms you are experiencing. If you have this condition the bladder contracts before you are ready to go to the toilet and this can happen especially if you get into the habit of going just in case, as the bladder learns to hold a small amount. Instead of your bladder controlling you, you must learn to control your bladder. When you feel the urge to pass water, tell yourself that you are not going to. Try to distract yourself for five to fifteen minutes from the time you get the first urge (use whatever method best distracts you). If you do this for a week, every time you want to pass water, you should find that by the end of the week the urge to urinate is delayed. During the next week do the same thing and delay passing urine by a further five to fifteen minutes; by doing this your bladder will learn to hold on more, and your symptoms will reduce. Please be persistent and remember that your bladder is like any other muscle in the body and may require a few months training in order to reach its full potential. Page 3 of 9
4 Deferment techniques helping you to hold on Rushing to the toilet will not help. You can tighten your pelvic floor muscles to help calm your bladder when the feeling of urgency develops, this will enable you to hold on for longer. Sitting or standing still when you get this urge will help you to concentrate on tightening your pelvic floor muscles. Pelvic floor exercises Your pelvic floor muscles The pelvic floor muscles form a hammock underneath your pelvis to provide support and control the bladder and bowel. The muscles attach to the pubic bone at the front, then span backwards to the coccyx (tailbone) behind. The openings to your bladder and your bowel both pass through the pelvic floor muscle. What does the pelvic floor do? It supports your pelvic organs and abdominal contents, especially when standing or on exertion. It supports the bladder to help stop leaking. The muscles need to work gently at all times and be able to work harder when you cough and sneeze to avoid leaking. When muscles are not working effectively you may suffer from urinary incontinence. It is used to control wind and for holding on with your bowels. Why should I exercise my pelvic floor muscles? The sphincter muscles around the bladder neck may be damaged by prostate surgery, so the pelvic floor muscles become an important way of regaining Page 4 of 9
5 continence. You can also contract your pelvic floor muscles after emptying your bladder to prevent post-micturition dribble. To do this pelvic floor muscles need to be exercised. The exercise programme will help to maintain and /or improve their strength. The Exercise Programme A pelvic floor contraction is performed by closing and drawing up you front and back passages. Imagine you are trying to stop yourself from passing wind and at the same time try to stop the flow of urine. The feeling is one of squeeze and lift. You can do this lying, sitting or standing. You can see if you are contracting the correct muscles by standing in front of a mirror and if you are contracting the correct muscle you will see the penis and testicles lift. Start gently and stop if it hurts. DON T Pull in your tummy muscles excessively Squeeze your legs together Tighten your buttocks You should aim to perform at least 10 contractions of the muscles, up to 6 times during the day, everyday. Muscles only develop when you challenge them to work harder than normal. This will be different for everyone. There are many other ways of exercising the pelvic floor muscles. Develop a habit of bracing your pelvic floor muscles gently during everyday activities (lifting, carrying and during strenuous exercise) and particularly during any task which might challenge the bladder or put pressure through the pelvis. Do not exercise using the pelvic floor muscles to stop and start the flow of urine as it may interfere with normal bladder emptying. Tips for a healthy pelvic floor To relieve the load on your pelvic floor, aim for an acceptable weight for your height and build. Being overweight [a BMI over 29] has been proven to have a negative impact on symptoms of stress incontinence. There are many ways of losing weight; your GP should be able to guide you as to the most suitable method for you. Lifting puts extra strain on the pelvic floor. If you do need to lift a heavy object remember to tighten your pelvic floor before you lift, and hold it tight until you have lowered the load. Page 5 of 9
6 Smoking - research suggests that smokers are more likely to experience urinary incontinence and this is due to the excessive strain that repetitive coughing puts on the pelvic floor. If you do smoke and would like support to stop smoking contact: CAMQUIT Cambridgeshire Stopping Smoking Service Or visit NHS Smoking helpline Avoiding Constipation Many people find symptoms are worse if they are constipated. As the bladder and bowel are next to each other, a full bowel will affect bladder function. To keep a healthy bowel, eat a balanced diet, which includes both soluble fibre (oats, barley, berries and fruit) and insoluble fibre (wheat-based foods, cereal, vegetables and nuts). Eat regular meals. You should go to the toilet to empty your bowel when you feel the need, as delaying may lead to constipation. Adequate fluid intake of litres will also help. For further advice and information contact: Bladder and Bowel Foundation Local Continence Advisory Service or Who can I contact for more help or information? Oncology Nurses Uro-Oncology Nurse Specialist Bladder cancer Nurse Practitioner (haematuria, chemotherapy & BCG) Prostate cancer Nurse Practitioner or or bleep Surgical Care Practitioner or or bleep Non-Oncology Nurses Urology Nurse Practitioner (incontinence, urodynamics, catheter patients) or Page 6 of 9
7 Patient Advice & Liaison Centre (PALS) Telephone +44 (0) or (0) or PatientLine *801 (from patient bedside telephones only) E mail pals@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Mail PALS, Box No 53 Addenbrooke's Hospital Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 2QQ Chaplaincy and Multi-Faith Community Telephone +44 (0) E mail derek.fraser@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Mail The Chaplaincy, Box No 105 Addenbrooke's Hospital Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 2QQ MINICOM System ("type" system for the hard of hearing) Telephone +44 (0) Access Office (travel, parking & security information) Telephone +44 (0) Other information This leaflet contains guidelines and advice from professional bodies, together with information about the prescription of drugs. All NHS hospitals have local arrangements with their Primary Care Trusts (PCTs) about which medicines can be used. As a result, some drugs mentioned cannot be prescribed by local hospitals. Treatment of patients will be planned with the Consultant responsible for care, taking into account those drugs which are or are not available at the local hospital and what is appropriate for optimum patient care. Healthcare professionals are advised to check prescribing arrangements with their local hospital or PCT. Page 7 of 9
8 How can I get information in alternative formats? Please ask if you require this information in other languages, large print or audio format: or patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Polish Informacje te można otrzymać w innych językach, w wersji dużym drukiem lub audio. Zamówienia prosimy składać pod numerem: lub wysyłając patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Portuguese Se precisar desta informação num outro idioma, em impressão de letras grandes ou formato áudio por favor telefone para o ou envie uma mensagem para: patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Russian Cantonese Turkish Если вам требуется эта информация на другом языке, крупным шрифтом или в аудиоформате, пожалуйста, обращайтесь по телефону или на вебсайт patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk 若你需要此信息的其他語言版本 大字體版或音頻格式, 請致電 或發郵件到 :patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Bu bilgiyi diger dillerde veya büyük baskılı ya da sesli formatta isterseniz lütfen su numaradan kontak kurun: veya asagıdaki adrese e-posta gönderin: patient.information@addenbrookes.nhs.uk Bengali Page 8 of 9
9 Addenbrooke s is smoke-free. You cannot smoke anywhere on the site. Smoking increases the severity of some urological diseases and increases the risk of post-operative complications. For advice on quitting, contact your GP or the NHS smoking helpline free on Document history Author(s) Nikesh Thiruchelvam (on behalf of the Continence Sustainable Healthcare Partnership and the Consultant Urologists). Minor modification from the Cambridgeshire Community Services NHS Trust leaflet: Male Bladder Health Department Department of Urology, Box No 43 Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hills Road Cambridge, CB2 2QQ Contact number Fax number Dept website First published Jan 2011 Review date April 2011 (next review April 2014) File name Male LUTS Version number 5.0 Ref 35/Info_04_11 Page 9 of 9
Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises
 MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
Patient Information Department of Urology 26/Info_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 26/Info_04_14 : frequently-asked questions What is the pelvic floor and why does it become weak? The pelvic floor is a complex layer of muscles and ligaments which
Patient Information Department of Urology 26/Info_04_14 : frequently-asked questions What is the pelvic floor and why does it become weak? The pelvic floor is a complex layer of muscles and ligaments which
Patient Information Department of Urology 15/Info_04_11. Viagra, Cialis or Levitra treatment for erectile dysfunction: frequently-asked questions
 Patient Information Department of Urology 15/Info_04_11 Viagra, Cialis or Levitra treatment for erectile dysfunction: frequently-asked questions What are these drugs? Viagra (Sildenafil), and the newer
Patient Information Department of Urology 15/Info_04_11 Viagra, Cialis or Levitra treatment for erectile dysfunction: frequently-asked questions What are these drugs? Viagra (Sildenafil), and the newer
Patient Information Department of Urology 11/Info_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 11/Info_04_11 Advice to patients requesting PSA (prostate-specific antigen) measurement: frequently-asked questions What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer
Patient Information Department of Urology 11/Info_04_11 Advice to patients requesting PSA (prostate-specific antigen) measurement: frequently-asked questions What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer
Patient Information Department of Urology 27/Urol_04_09. Pelvic floor exercises in men: frequentlyasked
 Patient Information Department of Urology 27/Urol_04_09 : frequentlyasked questions What is the pelvic floor and why does it become weak? Many men experience a variety of problems with their urinary system
Patient Information Department of Urology 27/Urol_04_09 : frequentlyasked questions What is the pelvic floor and why does it become weak? Many men experience a variety of problems with their urinary system
Patient Information Department of Urology 05/Info_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 05/Info_04_11 : frequently-asked questions How much do I need to drink? Drinking enough fluid is the most important aspect of preventing stone formation and will
Patient Information Department of Urology 05/Info_04_11 : frequently-asked questions How much do I need to drink? Drinking enough fluid is the most important aspect of preventing stone formation and will
Patient Information Department of Urology 100/Urol_04_11. Intravesical epirubicin chemotherapy: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 100/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 100/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 82/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 82/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 82/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 114/Urol_04_11. Videourodynamics (or pressure tests on the bladder): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 114/Urol_04_11 Videourodynamics (or pressure tests on the bladder): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 114/Urol_04_11 Videourodynamics (or pressure tests on the bladder): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 75/Urol_04_11. Fixation of a retractile testis: procedurespecific
 Patient Information Department of Urology 75/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 75/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 39/Urol_04_11. Surgery for a congenital hydrocele/hernia: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 39/Urol_04_11 Surgery for a congenital hydrocele/hernia: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 39/Urol_04_11 Surgery for a congenital hydrocele/hernia: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 116/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 116/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 116/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 38/Urol_04_11. Orchidopexy (bringing down of an undescended testis): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 38/Urol_04_11 Orchidopexy (bringing down of an undescended testis): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 38/Urol_04_11 Orchidopexy (bringing down of an undescended testis): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 08/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 08/Urol_04_11 Sperm retrieval from vas deferens or epididymis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 08/Urol_04_11 Sperm retrieval from vas deferens or epididymis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_11. Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_11 Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_11 Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 14/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 14/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 14/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 102/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 102/Urol_04_11 Mitrofanoff procedure (catheterisable urinary stoma): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 102/Urol_04_11 Mitrofanoff procedure (catheterisable urinary stoma): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_11. Surgical repair of injury to the penis: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 21/Urol_04_11. Bladder tumour resection: procedurespecific
 Patient Information Department of Urology 21/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 21/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 104/Urol_04_11. Holmium laser bladder neck incision: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 104/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 104/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 106/Urol_04_11. Laparotomy to remove a large retroperitoneal mass: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 106/Urol_04_11 Laparotomy to remove a large retroperitoneal mass: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 106/Urol_04_11 Laparotomy to remove a large retroperitoneal mass: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_14 Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 111/Urol_04_14 Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 23/Urol_04_11
 Patient Information Department of Urology 23/Urol_04_11 Transurethral resection of the prostate (for cancer): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 23/Urol_04_11 Transurethral resection of the prostate (for cancer): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_11. Ureterolysis for retroperitoneal fibrosis: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 34/Urol_04_11. Open reconstruction of the kidney pelvis: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 34/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 34/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 77/Urol_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 77/Urol_04_14 Penile injections for impotence: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from
Patient Information Department of Urology 77/Urol_04_14 Penile injections for impotence: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from
Patient Information Department of Urology 22/Urol_04_11. Transurethral resection of the prostate (for benign disease): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 22/Urol_04_11 Transurethral resection of the prostate (for benign disease): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This
Patient Information Department of Urology 22/Urol_04_11 Transurethral resection of the prostate (for benign disease): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This
Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_14 Surgical repair of injury to the penis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 86/Urol_04_14 Surgical repair of injury to the penis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 109/Urol_04_11. Distal urethroplasty: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 109/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 109/Urol_04_11 : procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British
Patient Information Department of Urology 54/Urol_04_11. Radical removal of the kidney: procedurespecific
 Patient Information Department of Urology 54/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 54/Urol_04_11 : procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
Patient Information Department of Urology 44/Urol_04_14. Open removal of stone from the ureter: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 44/Urol_04_14 Open removal of stone from the ureter: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 44/Urol_04_14 Open removal of stone from the ureter: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 110/Urol_04_14. Transrectal prostatic ultrasound and transperineal biopsy: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 110/Urol_04_14 Transrectal prostatic ultrasound and transperineal biopsy: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 110/Urol_04_14 Transrectal prostatic ultrasound and transperineal biopsy: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_14. Ureterolysis for retroperitoneal fibrosis: procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_14 Ureterolysis for retroperitoneal fibrosis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 43/Urol_04_14 Ureterolysis for retroperitoneal fibrosis: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice
Patient Information Department of Urology 107/Urol_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 107/Urol_04_14 Reconstruction of the ureter (refashioning of drainage of urine to the bladder after scarring or damage to the ureter): procedure-specific information
Patient Information Department of Urology 107/Urol_04_14 Reconstruction of the ureter (refashioning of drainage of urine to the bladder after scarring or damage to the ureter): procedure-specific information
Patient Information Department of Urology 72/Urol_04_14. Cryoablation of renal tumour: procedurespecific
 Patient Information Department of Urology 72/Urol_04_14 Cryoablation of renal tumour: procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus
Patient Information Department of Urology 72/Urol_04_14 Cryoablation of renal tumour: procedurespecific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from consensus
Patient Information Department of Urology 60/Urol_04_14. Radical removal of the testis (± silicone implant): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 60/Urol_04_14 Radical removal of the testis (± silicone implant): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 60/Urol_04_14 Radical removal of the testis (± silicone implant): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes
Patient Information Department of Urology 47/Urol_04_14
 Patient Information Department of Urology 47/Urol_04_14 Enlargement of the bladder using a segment of bowel: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 47/Urol_04_14 Enlargement of the bladder using a segment of bowel: procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 62/Urol_04_14. Retroperitoneal excision of abdominal lymph nodes (RPLND): procedure-specific information
 Patient Information Department of Urology 62/Urol_04_14 Retroperitoneal excision of abdominal lymph nodes (RPLND): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Patient Information Department of Urology 62/Urol_04_14 Retroperitoneal excision of abdominal lymph nodes (RPLND): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet
Keep high, stay dry. Pelvic floor exercises for men
 Keep high, stay dry Pelvic floor exercises for men What is the pelvic floor? Layers of muscle stretch like a hammock from your pubic bone in the front to the bottom of your backbone (see diagram). These
Keep high, stay dry Pelvic floor exercises for men What is the pelvic floor? Layers of muscle stretch like a hammock from your pubic bone in the front to the bottom of your backbone (see diagram). These
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles. Information for men
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder
 www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help
 Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Pelvic Floor Muscle exercises and Bladder advice
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Pelvic Floor Muscle exercises and Bladder advice Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health This leaflet aims to explain about your pelvic floor muscles,
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Pelvic Floor Muscle exercises and Bladder advice Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health This leaflet aims to explain about your pelvic floor muscles,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for
 A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Incontinence and Bladder Problems in Women
 Physiotherapy Department Incontinence and Bladder Problems in Women Patient Information Leaflet Many women have a bladder problem at some time in their lives. It is a common complaint and is not restricted
Physiotherapy Department Incontinence and Bladder Problems in Women Patient Information Leaflet Many women have a bladder problem at some time in their lives. It is a common complaint and is not restricted
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Your pelvic floor muscles
 Continence office Ballochmyle Suite, University Hospital Ayr Telephone 019 177 Your pelvic floor muscles Advice and exercise for women Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa
Continence office Ballochmyle Suite, University Hospital Ayr Telephone 019 177 Your pelvic floor muscles Advice and exercise for women Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
Pelvic floor exercises for men
 Information for men This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. Your GP or healthcare professional has advised
Information for men This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. Your GP or healthcare professional has advised
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING FOR WOMEN STRONG PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES MEAN GOOD BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL WHAT ARE THE PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES?
 06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Pelvic floor exercises for women. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
Pelvic floor muscle exercises
 Lifestyle Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 31 Pelvic floor muscle exercises In this fact sheet: How do pelvic floor muscle exercises help with urinary problems? How do I do the exercises? More
Lifestyle Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 31 Pelvic floor muscle exercises In this fact sheet: How do pelvic floor muscle exercises help with urinary problems? How do I do the exercises? More
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Women and Men s Health Physiotherapy Pelvic floor exercises for men
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Women and Men s Health Physiotherapy Pelvic floor exercises for men Patient Information Pelvic floor exercises for men Your pelvic floor muscles help
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Women and Men s Health Physiotherapy Pelvic floor exercises for men Patient Information Pelvic floor exercises for men Your pelvic floor muscles help
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
Pelvic floor exercises for women. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for women This leaflet will provide you with information about
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for women This leaflet will provide you with information about
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Pelvic Floor Exercises for men
 PROSTATE INFORMATION SPOTLIGHT ON Pelvic Floor Exercises for men Introduction This leaflet gives you some information about pelvic floor exercises (PFE) and helps answer some of the questions you may have.
PROSTATE INFORMATION SPOTLIGHT ON Pelvic Floor Exercises for men Introduction This leaflet gives you some information about pelvic floor exercises (PFE) and helps answer some of the questions you may have.
Pelvic floor exercises for women. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Urodynamics Clinic. Patient Information
 Patient Information Urodynamics Clinic Author: Gynaecology Produced and designed by the Communications Team Issue date May 2017 - Review date May 2020 Version 3 Ref no. PILCOM1433 Urodynamics Clinic An
Patient Information Urodynamics Clinic Author: Gynaecology Produced and designed by the Communications Team Issue date May 2017 - Review date May 2020 Version 3 Ref no. PILCOM1433 Urodynamics Clinic An
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Pelvic Floor Muscles The pelvic floor muscles are a sling of muscles across the floor of the pelvis. The
Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Pelvic Floor Muscles The pelvic floor muscles are a sling of muscles across the floor of the pelvis. The
Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence Introduction The muscles
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence Introduction The muscles
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Urinary Incontinence? - gør dig ikke skakmat...
 Urinary Incontinence? - gør dig ikke skakmat... The International Continence Society (ICS) have defined urinary incontinence as invo- luntary loss of urine to such an extent that it constitutes a social
Urinary Incontinence? - gør dig ikke skakmat... The International Continence Society (ICS) have defined urinary incontinence as invo- luntary loss of urine to such an extent that it constitutes a social
opyright 2017 SAMPLE COPY Property of Hayward Bell Ltd Copyright 2017 Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone
 Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone This booklet could be your first positive step to a full and active life Contents 1. Introduction 2. A bladder 3. The most common problems 5. A bowel 6. Functional
Bladder and bowel conditions can affect anyone This booklet could be your first positive step to a full and active life Contents 1. Introduction 2. A bladder 3. The most common problems 5. A bowel 6. Functional
Exercises and advice following gynaecological surgery
 Exercises and advice following gynaecological surgery Bed mobility Immediately after your surgery, especially if you have had a general anaesthetic, you may not be able to move around as much as normal.
Exercises and advice following gynaecological surgery Bed mobility Immediately after your surgery, especially if you have had a general anaesthetic, you may not be able to move around as much as normal.
PHYSIOTHERAPY BEFORE AND AFTER PROSTATE CANCER SURGERY
 PHYSIOTHERAPY BEFORE AND AFTER PROSTATE CANCER SURGERY Urinary incontinence, or leakage, is to be expected after prostate surgery. It may be a mild problem, needing pads to manage it for only a few weeks,
PHYSIOTHERAPY BEFORE AND AFTER PROSTATE CANCER SURGERY Urinary incontinence, or leakage, is to be expected after prostate surgery. It may be a mild problem, needing pads to manage it for only a few weeks,
Patient Information Leaflet. Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel
 Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Page 1 of 5 Overactive Bladder Syndrome Overactive bladder syndrome is common. Symptoms include an urgent feeling to go to the toilet, going to the toilet frequently, and sometimes leaking urine before
Page 1 of 5 Overactive Bladder Syndrome Overactive bladder syndrome is common. Symptoms include an urgent feeling to go to the toilet, going to the toilet frequently, and sometimes leaking urine before
Post-operative advice for women following gynaecological surgery
 Post-operative advice for women following gynaecological surgery Information for patients from Women s Health This information leaflet has been compiled to help aid a good recovery after your surgery.
Post-operative advice for women following gynaecological surgery Information for patients from Women s Health This information leaflet has been compiled to help aid a good recovery after your surgery.
Intravesical Botox Injections
 Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
A Healthy Bladder. What to do if things go wrong.
 A Healthy Bladder What to do if things go wrong www.bladderandbowel.org Contents Introduction How the bladder works What can go wrong with the bladder? Keeping a healthy bladder What can be done to treat
A Healthy Bladder What to do if things go wrong www.bladderandbowel.org Contents Introduction How the bladder works What can go wrong with the bladder? Keeping a healthy bladder What can be done to treat
Urinary Incontinence. a problem for many
 Urinary Incontinence a problem for many This leaflet gives information on urinary incontinence and the problems arising from the various types of urinary incontinence. It also gives advice on how to relieve
Urinary Incontinence a problem for many This leaflet gives information on urinary incontinence and the problems arising from the various types of urinary incontinence. It also gives advice on how to relieve
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
Returning Home After Prostatectomy
 Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Post Natal Exercises
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Post Natal Exercises Taking care of yourself For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Scarborough Hospital: 01723 342259 Woodlands
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Post Natal Exercises Taking care of yourself For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Scarborough Hospital: 01723 342259 Woodlands
Intermittent Self-Catheterisation / Catheterisation Continence Advisory Service Community & Therapy Services North Lincolnshire
 Intermittent Self-Catheterisation / Catheterisation Continence Advisory Service Community & Therapy Services North Lincolnshire This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about Intermittent
Intermittent Self-Catheterisation / Catheterisation Continence Advisory Service Community & Therapy Services North Lincolnshire This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about Intermittent
Obstructive Defaecation
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
University College Hospital
 University College Hospital Having radiotherapy to the prostate: preparation for treatment Radiotherapy Department Patient information series No.56 If you would like this leaflet in another language or
University College Hospital Having radiotherapy to the prostate: preparation for treatment Radiotherapy Department Patient information series No.56 If you would like this leaflet in another language or
Continence and prostate
 Continence and prostate A guide for men undergoing prostate surgery p r o m o t i n g b l a d d e r a n d b o w e l h e a lt h Continence Foundation of Australia, 2012 This book is copyright. Apart from
Continence and prostate A guide for men undergoing prostate surgery p r o m o t i n g b l a d d e r a n d b o w e l h e a lt h Continence Foundation of Australia, 2012 This book is copyright. Apart from
