We face continuing challenges for the. A Novel Composite Sling for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence. First Clinical Experience
|
|
|
- Joy Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article 63 A Novel Composite Sling for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence First Clinical Experience Arnaldo F. Trabucco, MD, FACS,* Jeffrey Blitstein, MD and Richard Chang, MD* Abstract Objectives: The purpose of this study was to test the effectiveness of a mesh that was designed for the surgical correction of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using a new surgical synthetic composite sling. The sling was designed to prevent the inherent complications of chronic retention and urethral erosion, associated with traditional synthetic polypropylene slings and to provide the urologic surgeon with a minimally invasive userfriendly approach. Methods: 40 patients with urethral hypermobility SUI were treated with this sling. The sling, composed of both absorbable and nonabsorbable components, is implanted using a modified Stamey approach. Follow-up was performed retrospectively. Follow-up was for months, with a mean 48.4 months. Results: 39 patients (97.5%) operated on had cure of incontinence. Irritative voiding symptoms improved in all patients. No morbidity or complications were seen. Conclusion: The preliminary results indicate that this approach is safe, effective, and well tolerated compared with other available surgical materials and techniques. This procedure is minimally invasive, easily reproducible, and can be performed as a short- stay surgical procedure using materials that are found in any operating room. Key Words: incontinence, tension-free sling, pubovaginal sling, polypropylene, T Sling, stress urinary incontinence. (J Pelvic Med Surg 2004;10:63 70) We face continuing challenges for the optimal form of treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Long-term outcome studies have revealed disappointing results for percutaneous needle suspensions and other sling substitutes secondary to the recurrence of urethral hypermobility or creation of urethral obstruction. 1 The pubovaginal sling procedure is an established, reliable technique for correcting Type 3 (intrinsic sphincter deficiency, ISD) SUI, and Type 2 SUI with coexisting ISD. 2 Recently, the pubovaginal sling procedure has been popularized and used as a primary modality to treat all forms of SUI including urethral hypermobility (Type 1 and 2) in the female patient. 3 Weakness of the urethropelvic ligament (UPL) (endocervical and periurethral fascia) with its attachments to the arcus tendinous and urethra correlates with urethral hypermobility and SUI. This anatomic defect is a herniation of the pelvic contents. Anatomic corrective surgery has addressed these issues in the past with suboptimal long-term results without the use of autologous or prosthetic sling material. 2,4,5,6,7 Many procedures have been used to attempt to resupport the UPL. If one were to reconstruct the fascia, one could potentially correct all forms of SUI secondary to urethral hypermobility. Complications of urethral sling procedures using a synthetic prosthesis have been reported: urethral obstruction, urinary retention, mesh erosion, extrusion, infection and nerve entrapment. 8,9 A novel sling was designed to eliminate these inherent complications. The main objective of this operation is to address all anatomic concerns using a modified Stamey approach. It is also designed to prevent the inherent complications seen with prosthetic Manuscript received March 23, 2003; accepted April 12, From the *Department of Urology, Saint Vincent Catholic Medical Centers - Brooklyn and Queens, St Johns Queens Hospital Division, Elmhurst, New York; and the Department of Urology, SUNY Downstate Medical School, Brooklyn, New York. Presented June 22, 2001, Milan, Italy, XXIII International Congress of the European Hernia Society Reprints: Arnaldo F. Trabucco, MD, FACS, 1549 N. Meadows Ct., Columbus, Indiana dt@institute-md.com. Copyright 2004 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ISSN: /04/ DOI: /01.spv b9
2 64 Trabucco et al FIGURE 1. The outer portions of the T Sling are composed of PP while the central portion is composed of monofilament absorbable PDO material. material positioned underneath the urethra and bladder neck. MATERIALS AND METHODS Surgical Material The tension-free sling (T Sling) is a mesh composed of 2 different materials. The 2 lateral aspects of the mesh are composed of a 2cm-width monofilament nonabsorbable polypropylene (PP) mesh with a 1-cm center absorbable monofilament of polydioxanone (PDO). The sling was prepared and length tapered by hand for each patient intraoperatively by measuring the distance between the arcus tendinous (Fig. 1). All surgical materials were FDA and CE approved in this study. Patient Evaluation Thirty female patients who underwent this surgical procedure were retrospectively studied. All patients had been educated preoperatively as to the potential risks and complications including potential (early or late) failure prior to the operation. All patients that chose to undergo this procedure had consented preoperatively and reported herein (Table 1). All patients elected for the T Sling procedure were confirmed to have stress Type 1, Type 2 - SUI diagnosed by complete history and physical examination, and cotton swab test. Patients with ISD (Type 3), were not tested prior to surgery. A Valsalva leak point pressure was not routinely measured on all patients and thus is not available for analysis. All patients had a urinary questionnaire, 24- hour voiding diary, pad test, post void residual volumes (before and after surgery). Preoperative evaluation also included urine analysis, Marshall test, uroflow evaluation, cystoscopy, IVP, urodynamics and vaginoscopy (rule out the possibility of associated pathology). Preand postoperative evaluations of patients were determined by diapers, voiding diaries and objective demonstration on physical examination. A standard questionnaire was used for fol- TABLE 1. Preoperative Patient Data Treated With T Sling No. pts. with SUI 40 Mean duration of symptoms prior to surgery (1 15 y) 6.2 y Mean patient age (35 78 y) y No. pts. with irritative voiding symptoms (urgency and frequency) 12 No. pts. with atrophic vaginitis 12 No. pts. total abdominal hysterectomy bilateral oophorectomy 5 No. prior total abdominal hysterectomy 5 No. prior vaginal hysterectomy 12 No. parity by vaginal delivery (35), caesarian section (4) 39 No. pts. with family history of stress urinary incontinence 21 No. pts. with prior SUI procedures 22 (Kelly 16, Vesica 1, Gittes 2, Pereyra 1, Stamey 2) No. pts. postmenopause 19 No. pts. with uterine prolapse 2 No. pts. with cystocele (grade I 5, II 10, III 14, IV 3) 32 No. pts. with Enterocele Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
3 low-up (see Appendix). 10 IVSX (frequency and urgency) were determined by subjective evaluation and voiding diary. Postoperative evaluation was conducted at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months and every 6 months and yearly. Patients satisfaction was addressed by subjective (modified Urogenital Distress Inventory form) and objective evaluation (see Appendix). 10 Cure was defined as no loss of urine due to stress or urge incontinence, objectively by 24-hour diary and pad test, and subjectively by the patient feeling cured. Failure was defined as poor objective results with the subjective feelings by the patient that the surgery had failed. Improvement was defined as not having achieved the results of cure. 11 Preoperative antibiotics were administered to all patients. Novel Composite Sling for SUI Surgical Procedure The T Sling procedure consists of 2 surgically implanted meshes connected by a Polybutester suture. A modified Stamey approach was used for the transvaginal suspension. The vaginal mucosa is incised (3-4cm) longitudinally at the level of the bladder neck. Sharp dissection is performed to expose the inferior surface of the urethra and lateral pelvic sidewalls. Blunt finger dissection is used to develop the existing plane inferior to the endopelvic fascia, confirming the deficiency of the structural integrity of the UPL up to the arcus tendinous. If a concomitant cystocele is present, this is repaired first. The T Sling is trimmed to 2cm more than the distance between the arcus tendinous so that it can be placed under the UPL in a tension-free fashion from one arcus tendinous to the other. A single 1-2cm suprapubic incision is made. Sharp dissection is performed from the fibro-fatty tissue down to the anterior rectus fascia at the level of the linea Alba insertion to the pubic bone. A spinal needle is used to inject 100 ml sterile water in the space of Retzius allowing the fluid to dissect a plane between the pubic bone and bladder. A Stamey needle is passed behind the pubic bone after penetrating the anterior rectus fascia at its inferior insertion near the pubic bone. The needle is first passed para-urethral and is then positioned medial to the arcus tendinous and passed into the vaginal incision. One pass is used for this maneuver. A 0 Polybutester suture is laced 1cm medial to the ends of the PP mesh. The sutures are then introduced into the eye of the Stamey needle and are then drawn upward. The center of the T Sling is aligned under the urethral-vesical junction to lie flat on either side from one arcus tendinous to the other with flat apposition underneath the destroyed or deficient UPL. Both sutures are delivered through the same puncture site to prevent any potential for nerve entrapment. Cystoscopy is then performed to assess for a bladder perforation and the urinary bladder is filled with fluid. At the termination of the procedure, the second smaller (1 2cm) PP mesh is then placed in the anterior suprapubic incision with the sutures placed through the holes of the mesh on both sides. The mesh is then placed to lie flat over the linea Alba. Both sides are performed in an identical fashion. Excess vaginal mucosa due to a concomitant cystocele is trimmed. The vaginal mucosa is then closed with a running continuous interlocking stitch with 2 0 absorbable sutures before tying the sutures (Fig. 2). Before tying the suprapubic sutures a provoked Valsalva cough test while under spinal or epidural anesthesia is performed. The surgeon then determines the minimal assessment of tension on tying the sutures to maintain continence. Alternatively, if the patient is under general anesthesia, the sutures are tied with a cotton swab in the urethra allowing for an approximate 15-degree deflection upward by tying the sutures under minimal tension. The suprapubic incision is closed with 4 0 absorbable suture and Steri strips applied. Vaginal packing coated with antibiotic ointment is placed for 12 hours. A Foley catheter is inserted to leg bag urinary drainage for 3 7 days. 65
4 66 Trabucco et al TABLE 2. Postoperative Evaluations- T Sling No. pts. cystocele repair 26 No. pts. enterocele repair 8 No. pts. vaginal hysterectomy 2 Complications (intraoperative/ 0 postoperative) Mean hospital stay (20 48 h) 24 h Mean follow-up interval (15 59 mo) 30.2 mo No. pts. satisfied with surgical 40 results No. pts. cured (dry) of incontinence 39 No. pts. partial improvement (not 1 100% dry) No. pts. persistent irritative voiding 2 symptoms No. pts. receiving regional 38 anesthesia No. pts. receiving general 2 anesthesia No. pts. with pain after 7 d 0 No. pts. with de-novo irritative 0 voiding symptoms FIGURE 2. the edges of the mesh are positioned in a proper anatomical position under the inferior surface of the periurethral fascia by pulling up the T Sling via the sutures from the anterior abdominal incision via the Stamey needle Lippincott Williams & Wilkins RESULTS All terms and definitions used in this study were in accordance with the International Continence Society. 12 All patients had successful outcomes as measured by the lack of SUI with a cured 97.5% success ranging from months follow-up (Table 2). One patient (with severe atrophic vaginitis) had marked improvement (not cured surgically) after 15 months, from 22 to 1 pad per day. This patient wears occasional pads now with estrogen topical cream. Ten of the 12 patients with preoperative IVSX symptoms had resolution of their symptoms at 1 8 months with one improvement prior to the development of adult onset diabetes mellitus. Follow-up was 100% at 59 months and 92.5% at 70 months. The operating time of the procedure was approximately 30 minutes for each patient. This was calculated after surgical repair of the cystocele. Estimated intraoperative blood loss was ml. Epidural or spinal anesthesia was performed on 38 patients. Two patients undergoing a concomitant vaginal hysterectomy were placed under general anesthesia. All patients were seen in the office for evaluation of post void residual, pain, diary, pad test and physical examination at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and yearly (until 2003 where follow-up was then conducted with a mailed questionnaire) with follow-up for months, mean 48.4 months. All patients voided spontaneously and no new onset urge incontinence was noted. Partial retention occurred in 1 patient, post void residual volume 300 ml, with a concomitant hysterectomy, which resolved with a Foley catheter insertion for a total period of 2 weeks. This patient had preoperative retention with 900 ml post void urinary volume. Average hospital stay was hours. No patient complained of pain on the seven-day postoperative visit or subsequent visits. All patients stated that their lifestyles had improved dramatically. DISCUSSION In patients with pelvic prolapse, the defective regenerative fibroblastic founda-
5 Novel Composite Sling for SUI tion in these patients may not be adequate to establish a sufficient connective tissue fascial support structure. Reports have documented an increased collagenase, elastase activity, type III collagen synthesis, and fibroblast generation interval, leading to an overall decreased fascial support structure inherent (possibly genetic) resulting in stress urinary incontinence. 13,14 Many types of allogenic, xenogeneic and synthetic materials have been used in an effort to provide readily available and reliable sling material without the additional morbidity and operative time associated with fascia harvesting. Synthetic materials are easy to store, readily available and avoid the harvesting procedure of an autograft. Designing the ideal synthetic material to replace autogenous fascia continues to be a challenge. The synthetic material should provide a nonantigenic framework that is gradually interlaced or replaced by host fibroplasia resulting in a strong stable aponeurotic structure. 15 Many synthetic biomaterials have failed clinical trials. Some major problems have been pain, fragmentation, extrusion, erosions, early loss of tensile strength, shrinkage, and low tolerance to infections. Polypropylene has become the most commonly used biomaterial for the repair of abdominal wall hernias by general surgeons. This provides a durable framework for the in-growth of collagen and has a high tolerance to infection. Reports of large numbers of patients (inguinal hernia surgery) with long-term follow-up results have been excellent. However, its use in the lower urinary tract can create complications when improperly placed. Polypropylene can be safely used in the treatment of SUI. 16 When placed into the body a fibroblastic reaction is produced that is immediate and allows the material to remain in place. Numerous reports have also indicated 20 30% shrinkage in length and pore size of Marlex mesh (flat) within a twelve-month interval. 17,18 A mesh placed in a 3-dimensional shape may shrink up to 75 80%. Due to the weave, pore size and consistency, an increased shrinkage rate for prolene and other flat PP weaves is postulated where comparative studies are presently lacking. 19,20 Using less quantities of mesh, not more, reduces the possibility of complications. We believe it is not the mesh, per se, that causes complications or recurrences after implantation. Its how, why, how much and where the prosthetic material is implanted under the urinary tract that may cause complications during its shrinkage period. We believe that nonabsorbable meshes should not be placed against any abdominal or pelvic visceral organ including the bladder or urethra if possible. Polypropylene is best used in a tensionfree fashion with flat apposition to the tissue. Any form of tension or movement on tissues will impede proper tissue healing with normal collagen fibril ingrowth and healing. Many new variations of the PP have been made which do not address issues such as obstruction, erosion and shrinkage. 21,22,23 In theory, when PP mesh is used as a continuous sling for SUI, any Valsalva maneuver will induce intermittent hydrostatic pressure from the abdominal-pelvic contents onto this nonmovable, nonexpanding material. The mesh will also tend to curl acting as a nonexpandable rigid circular bridge. Over time, a mesh will shrink contributing to an increase in pressure on the urethra or contiguous organs. This can translate into an increased resistance during the shrinkage of the mesh. Previous reports of retention and urethral erosion have been documented with the use of PP when used directly under the urethra. 24 This continuous pressure can eventually translate into an erosive process. Eventual migration of the mesh material will penetrate the urethra or even bladder neck or possibly result in urinary retention. 25 This may be more prevalent in obese and COPD patients. Complications of retention and urethral erosion may require a secondary surgical (urethrolysis) procedure. 26 Surgically implanting PP away from the urethra in a tension-free fashion may preserve the urethral vascular supply and mucosal seal. By incorporating absorbable material 67
6 68 Trabucco et al shrinkage of the mesh may be potentially eliminated after 3 months postoperatively. Increased tension over time is prevalent with other surgical prosthesis when one uses a continuous conventional nonabsorbable mesh due to shrinkage. 27,28 In theory, the fibrosis reaction created by the 2 ends of PP allows for reconstituting the support of the periurethral fascia when placed from one arcus tendinous to the other. This now rebuilds the primary anatomic preoperative defect (UPL) by secondary intention (Figs. 3&4). Infection is reduced due to the inert properties of monofilament PP. Use of 1 puncture site on either side of the lower abdominal suprapubic area virtually eliminates any possibility of nerve entrapment and postoperative pain. FIGURE 3. SUI bladder before (top) showing loss of urethropelvic ligament support. Bottom (after T Sling insertion). The immediate fibroblastic reaction when inserted under the periurethral fascia acts as a support to the pelvic contents relieving the pressure off the urethra while simultaneously resuspending the bladder neck to its anatomical pubourethral position. CONCLUSION This report describes the use of a novel composite sling designed to reduce the complications seen with other synthetic slings. into the design of the sling, we have now introduced a preventive measure of escalating tension under the urethra. Once dissolved, this theoretically provides a tensionfree suspension sling (T Sling) around the urethra and supporting fascia while simultaneously avoiding any possible erosion. The design of the T Sling addresses these issues by the introduction of 2 types of material. The unique property of the T Sling is the central PDO portion of the prosthesis, which was designed to allow the central area to be absorbable. Assuming if 100 days are necessary for complete healing to occur postoperatively, one can understand the design of this sling. After 100 days, the central portion is dissolved by hydrolysis. The 2 nonabsorbable portions are detached from themselves rendering a true tension-free sling under the urinary tract. Any undue tension that may subsequently develop suburethrally due to 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins FIGURE 4. T Sling reconstitutes the primary defect of the urethropelvic ligament from 1 arcus tendinous to the other.
7 With the problems of chronic retention and urethral erosion associated with surgical synthetic prosthesis procedures for SUI, the T Sling could potentially eliminate intrinsic concerns and complications. The procedure is minimally invasive and results in a short hospital stay. The surgical procedure is technically simple and easily reproducible. This is the first study of the T Sling, containing 40 patients with a maximum follow-up of 70 months. There is no magic bullet for surgical treatment of SUI. The potential use in Type 3 SUI (ISD) needs to be evaluated separately in a prospective manner. Long-term studies of this procedure need to be conducted with large numbers in a prospective, randomized, controlled fashion to validate the promising findings of this novel surgical composite sling. REFERENCES 1. Clemens JQ, Stern JA, Bushman WA, et al. Long Term Results of the Stamey Bladder Neck Suspension: Direct Comparison with the Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz Procedure. J Urology. 1998;160: Blaivas JG, Jacobs BZ. Pubovaginal fascial sling for the treatment of complicated stress urinary incontinence. J Urology. 1991;145: Chaikin DC, Rosenthal J, Blaivas JG. Pubovaginal fascial sling for all types of stress incontinence: longterm analysis. J Urology. 1998;160: Cross CA, Cespedes DD, McGuire EJ. Our experience with pubovaginal slings in patients with stress urinary incontinence. J Urology. 1998;159: Zaragoza MR: Expanded indications for the pubovaginal sling: treatment of type 2 or 3 stress incontinence. J Urology. 1996;156: Tebyani N, Patel H, Yamaguchi R, et al. Percutaneous needle bladder neck suspension for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women: long-term results. J Urology. 2000;163: Kuo HC. Comparison of video urodynamic results after the pubovaginal sling procedure using rectus fascia and polypropylene mesh for stress urinary incontinence. J Urology. 2001;165: Kobashi KC, Dmochowski R, Mee SL, et al. Erosion of woven polyester pubovaginal sling. J Urology. 1999;162: Kuuva N, Nilsson C-G. A nationwide analysis of complications associated with the tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) procedure. Neurourol Urodyn. 2000;19: Uebersax JS, Wyman JF, Shumaker SA, et al. Short forms to assess life quality and symptom distress for urinary incontinence in women: the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Novel Composite Sling for SUI Distress Inventory. Neurourol Urodyn. 1995;14: Leach GE, Dmochowski RR, Appell RA, et al. Female stress urinary incontinence clinical guidelines panel summary report on surgical management of female stress incontinence. J Urology. 1997;158: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation subcommittee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21: Hom D, Desautel MG, Lumerman JH, et al. Pubovaginal sling using polypropylene mesh and vesica bone anchors. Urology. 1998;51: Klinge U, Zheng H, Si SY, et al. Altered collagen synthesis in transversalis of patients with inguinal hernia. Hernia. 1999: Berliner DS. Biomaterials in hernia repair. In: Nyhus LM, Condon RE, eds. Hernia, 3 rd Ed. Philadelphia: JB Lipcott Co.; 1989: Kuo HC. Anatomical and functional results of pubovaginal sling procedure using polypropylene mesh for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. J Urology. 2001;166: Amid PK. Classification of biomaterials and their related complications in abdominal wall hernia surgery. Hernia. 1997;1: Klinge U, Klosterhalfen B, Muller M, et al. Shrinking of polypropylene mesh in vivo: an experimental study in dogs. Eur J Surg. 1998;164: Schumpelick V, Arlt G, Schlachetzki A, et al. Chronic inguinal pain after transperitoneal mesh implantation. Case report of net shrinkage. Chirurg. 1997;68: Klinge U, Conze J, Klosterhalfen B, et al. Changes in abdominal wall mechanics after mesh implantation. Experimental changes in mesh stability. Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1996;381: Ulmsten U, Falconer C, Johnson P, et al. A multicenter study of tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) for surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 1998;9: Romanzi LJ, Blaivas JG. Protracted urinary retention necessitating urethrolysis following tensionfree vaginal tape surgery. J Urology. 1998;164: Comiter CV, Vasavada SP, Kavaler E, et al. The surgical treatment of female SUI: Making an intelligent choice. Contemporary Urology. 2000;4: Morgan JE, Farrow GA, Stewart FE. The Marlex sling operation for the treatment of recurrent stress urinary incontinence: A 16-year review. Am J Obst Gyn. 1985;15:151(2): McGuire EJ, O Connell HE. Pubovaginal slings. In: Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan ED, eds. Campbell s Urology. 7 th Ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1998: Sweat SD, Itano NB, Clemens JQ, et al. Polypropylene mesh tape for stress urinary incontinence: complications of urethral erosion and outlet obstruction. Urology. 2002;168:
8 70 Trabucco et al 27. Choe JM. Tension-free vaginal tape: Is it truly tension-free? J Urology. 2001;166: Haferkamp A, Steiner G, Müller SC, et al. Urethral erosion of tension-free vaginal tape. J Urology. 2002;167:250. APPENDIX 12 Modified Urogenital Distress Inventory form used to assess Quality of life The following questions were asked: Do you experience and if so how much are you bothered by: Frequent urination? Urine leakage related to the feeling of urgency? Urine leakage related to physical activity coughing or sneezing? If so how much urine leakage or pads are you using? Small amounts of urine leakage (drops)? Difficulty emptying the bladder? Pain or discomfort in the lower abdominal or genital area? How satisfied were you with the results of the operation? Do you have any of the symptoms that were present before the operation? If so please describe. Were there any complaints or symptoms that has adversely affected your life after the operation? If you were to grade the operative results on a scale of 1 10(where 10 is the best), what would you grade it? What terms would you describe the effects of the operation on your present quality of life? If it were only absolutely needed, would you undergo this operative procedure again? If you are sexually active what effect, has the operation had on your ability to have intercourse? 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Female Urology. The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh. Introduction ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE MINIMALLY INVASIVE SLING FOR FEMALE URINARY STRESS INCONTINENCE
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology SAFYRE TM - SLING FOR FEMALE SUI Vol. 29 (4): 353-359, July - August, 2003 SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology SAFYRE TM - SLING FOR FEMALE SUI Vol. 29 (4): 353-359, July - August, 2003 SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE
Urethrolysis; When, Why & How. M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati
 Urethrolysis; When, Why & How M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati Anatomy Urethra may be fixed to the pubic bone with dense scar tissue Goal of urethrolysis is to completely
Urethrolysis; When, Why & How M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati Anatomy Urethra may be fixed to the pubic bone with dense scar tissue Goal of urethrolysis is to completely
PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE FOR URETHRAL HYPERMOBILITY AND INTRINSIC SPHINCTERIC DEFICIENCY
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY RETENTION WITH A PUBOVAGINAL SLING
 Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (3): 275-280, May - June, 2001 A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY
Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (3): 275-280, May - June, 2001 A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY
Desara TV and Desara Blue TV
 Desara TV and Desara Blue TV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide Available Electronically M Manufactured
Desara TV and Desara Blue TV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide Available Electronically M Manufactured
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
 Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure M. Murphy, MD, M. H. Heit, MD, MSPH, L. Fouts, MD, C. A. Graham, MD, L. Blackwell, RN, and P. J. Culligan, MD OBJECTIVE:
Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure M. Murphy, MD, M. H. Heit, MD, MSPH, L. Fouts, MD, C. A. Graham, MD, L. Blackwell, RN, and P. J. Culligan, MD OBJECTIVE:
REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE
 REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE WITH RAZ SUSPENSION 17 VAGINAL INCISION AND DISSECTION Premarin cream application to the anterior vagina daily for 1 month before cystocele repair enriches the vasculature and
REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE WITH RAZ SUSPENSION 17 VAGINAL INCISION AND DISSECTION Premarin cream application to the anterior vagina daily for 1 month before cystocele repair enriches the vasculature and
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women. What YOU can do about it...
 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Nine-year experience in sub-urethral prosthesis for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence
 Nine-year experience in sub-urethral prosthesis for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence Adrian Haşegan Department of Urology, Emergency County Hospital Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Abstract
Nine-year experience in sub-urethral prosthesis for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence Adrian Haşegan Department of Urology, Emergency County Hospital Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Abstract
A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
Desara and Desara Blue
 Desara and Desara Blue Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc.
Desara and Desara Blue Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc.
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence
 What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
Sep \8958 Appell Dmochowski.ppt LMF 1
 Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence. Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee, FICOG
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee,
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee,
Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
 J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence. Goals of presentation. Preoperative evaluation: Urodynamic Testing? Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D.
 Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
New Insights in the Surgical Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women
 New Insights in the Surgical Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women Gabriel Gillon MD Dept. of Urology Rabin Med. Cent. /Beilinson Incontinence and LUTS 25/6/2009 Symposium Ramat Aviv New Insights
New Insights in the Surgical Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women Gabriel Gillon MD Dept. of Urology Rabin Med. Cent. /Beilinson Incontinence and LUTS 25/6/2009 Symposium Ramat Aviv New Insights
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help?
 Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
UroToday International Journal. Volume 4 - June 2011
 UroToday International Journal Paulo Palma, 1 Cassio Riccetto, 1 Rodrigo Castro, 2 Sebastian Altuna, 3 Viviane Herrmann, 1 Ricardo Miyaoka 1 1 Division of Female Urology, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP),
UroToday International Journal Paulo Palma, 1 Cassio Riccetto, 1 Rodrigo Castro, 2 Sebastian Altuna, 3 Viviane Herrmann, 1 Ricardo Miyaoka 1 1 Division of Female Urology, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP),
Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence
 Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape
 Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.3.184 Voiding Dysfunction How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling Mahmoud
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.3.184 Voiding Dysfunction How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling Mahmoud
The incidence of mesh extrusion after vaginal incontinence and pelvic floor prolapse surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The incidence of mesh extrusion after vaginal incontinence and pelvic floor prolapse surgery Seth Cohen, Elizabeth Kavaler Department of Urology, Lenox Hill Hospital, USA Correspondence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The incidence of mesh extrusion after vaginal incontinence and pelvic floor prolapse surgery Seth Cohen, Elizabeth Kavaler Department of Urology, Lenox Hill Hospital, USA Correspondence:
When the suburethral sling was first
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY CHERYL IGLESIA, MD, AND MARIA PETTIT CANTER, MD Treating stress urinary incontinence with suburethral slings Recent modifications to suburethral sling procedures have brought them
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY CHERYL IGLESIA, MD, AND MARIA PETTIT CANTER, MD Treating stress urinary incontinence with suburethral slings Recent modifications to suburethral sling procedures have brought them
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Tension Free vaginal tape. Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD
 Tension Free vaginal tape Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD What is a TVT procedure? A TVT (Tension Free Vaginal Tape) procedure is an operation
Tension Free vaginal tape Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD What is a TVT procedure? A TVT (Tension Free Vaginal Tape) procedure is an operation
Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence Urology Grand Rounds April 6, 2005 Herman Christopher Kwan R4 A familiar case? 62 year old female initial presentation
Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence Urology Grand Rounds April 6, 2005 Herman Christopher Kwan R4 A familiar case? 62 year old female initial presentation
Comparison of bone-anchored male sling and collagen implant for the treatment of male incontinence
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience
 Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT)
 Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure urethra
 Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY
 INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
Seventeen years follow-up of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for female stress urinary incontinence
 Int Urogynecol J (2013) 24:1265 1269 DOI 10.1007/s00192-013-2090-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EDITORS CHOICE Seventeen years follow-up of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for female stress urinary incontinence
Int Urogynecol J (2013) 24:1265 1269 DOI 10.1007/s00192-013-2090-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EDITORS CHOICE Seventeen years follow-up of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for female stress urinary incontinence
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients
 Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015
 Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015 Disclosures I have none Objectives Identify the basic Anatomy and causes of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Examine office diagnosis
Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive & Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery 01/28/2015 Disclosures I have none Objectives Identify the basic Anatomy and causes of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Examine office diagnosis
Desara Blue OV D I. Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence. Instructions For Use
 Desara Blue OV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc. 5171 Clareton
Desara Blue OV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc. 5171 Clareton
Stop Coping. Start Living. Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy
 Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 3 million women in the United Kingdom have urinary
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 3 million women in the United Kingdom have urinary
Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence
 African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 1, 2011 1-5 Original article Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence M. Shoukry, M. Hassouna, A. AbdEl-Kerim and S. El-Salmy
African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 1, 2011 1-5 Original article Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence M. Shoukry, M. Hassouna, A. AbdEl-Kerim and S. El-Salmy
The Safety and Efficacy of a New Adjustable Single Incision Sling for Treatment of Female. Stress Urinary Incontinence Through 12-months of Follow-up
 Manuscript (Submit in MS Word; include Title Page and Abstract; Tables and Figures should NOT be included but attached separately) Runninghead: ALTIS SINGLE INCISION SLING The Safety and Efficacy of a
Manuscript (Submit in MS Word; include Title Page and Abstract; Tables and Figures should NOT be included but attached separately) Runninghead: ALTIS SINGLE INCISION SLING The Safety and Efficacy of a
Patient Information. Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence
 Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Brief involuntary urine loss associated with an increase in abdominal pressure. Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J.
 TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Since the initial description of tension-free vaginal. Double Tension Adjustments with Novel Modification on Tension-Free Vaginal Tape INTRODUCTION
 FEMALE UROLOGY Double Tension Adjustments with Novel Modification on Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Mahmoud Mustafa* Objective: To evaluate the results of novel modifications on tension- free vaginal tape (TVT)
FEMALE UROLOGY Double Tension Adjustments with Novel Modification on Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Mahmoud Mustafa* Objective: To evaluate the results of novel modifications on tension- free vaginal tape (TVT)
Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure for Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
INJ. Transvaginal Cystocele Repair by Purse-String Technique Reinforced with Three Simple Sutures: Surgical Technique and Results.
 Original Article Int Neurourol J 2012;16:144-148 pissn 2093-4777 eissn 2093-6931 International Neurourology Journal Transvaginal Cystocele Repair by Purse-String Technique Reinforced with Three Simple
Original Article Int Neurourol J 2012;16:144-148 pissn 2093-4777 eissn 2093-6931 International Neurourology Journal Transvaginal Cystocele Repair by Purse-String Technique Reinforced with Three Simple
Long-Term Durability of the Distal Urethral Polypropylene Sling for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: Minimum 11-Year Followup
 Long-Term Durability of the Distal Urethral Polypropylene Sling for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: Minimum 11-Year Followup Lisa Rogo-Gupta,*, Z. Chad Baxter, Ngoc-Bich Le, Shlomo Raz and
Long-Term Durability of the Distal Urethral Polypropylene Sling for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: Minimum 11-Year Followup Lisa Rogo-Gupta,*, Z. Chad Baxter, Ngoc-Bich Le, Shlomo Raz and
As more patients express reservations
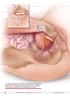 The autologous pubovaginal sling supports the proximal urethra and bladder neck to achieve continence by providing a direct compressive force on the urethra and bladder outlet, or by reestablishing a reinforcing
The autologous pubovaginal sling supports the proximal urethra and bladder neck to achieve continence by providing a direct compressive force on the urethra and bladder outlet, or by reestablishing a reinforcing
Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery
 Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery 吳銘斌醫師 (Ming-Ping Wu, M.D., Ph.D.) 奇美醫院婦產部婦女泌尿暨骨盆醫學科主任台北醫學大學醫學院婦產學科副教授成功大學醫學院臨床醫學所博士 Anti-incontinence surgery Bladder buttress operation: Kelly plication Needle
Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery 吳銘斌醫師 (Ming-Ping Wu, M.D., Ph.D.) 奇美醫院婦產部婦女泌尿暨骨盆醫學科主任台北醫學大學醫學院婦產學科副教授成功大學醫學院臨床醫學所博士 Anti-incontinence surgery Bladder buttress operation: Kelly plication Needle
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling
 I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
UroToday International Journal. Volume 4 - February 2011
 UroToday International Journal Scott Serels, 1 Sandy B Nosseir, 2 Lawrence R Lind, 2 Harvey A Winkler 2 1 Bladder Control Center of Norwalk and Section of Urogynecology, Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT,
UroToday International Journal Scott Serels, 1 Sandy B Nosseir, 2 Lawrence R Lind, 2 Harvey A Winkler 2 1 Bladder Control Center of Norwalk and Section of Urogynecology, Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT,
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.2.122 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence Hwa Su Lim, Jong Min Kim, Phil Hyun Song,
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.2.122 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence Hwa Su Lim, Jong Min Kim, Phil Hyun Song,
Tissue Reaction of the Rat Urinary Bladder to Synthetic Mesh Materials
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1046 1051 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.120 Tissue Reaction of the Rat Urinary Bladder to Synthetic Mesh Materials Gokhan Atis, Serdar
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1046 1051 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.120 Tissue Reaction of the Rat Urinary Bladder to Synthetic Mesh Materials Gokhan Atis, Serdar
Posterior intravaginal slingplasty for vault and uterovaginal prolapse: an initial experience
 Gynecol Surg (2006) 3: 88 92 DOI 10.1007/s10397-005-0168-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE R. Oliver. C. Dasgupta. A. Coker Posterior intravaginal slingplasty for vault and uterovaginal prolapse: an initial experience
Gynecol Surg (2006) 3: 88 92 DOI 10.1007/s10397-005-0168-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE R. Oliver. C. Dasgupta. A. Coker Posterior intravaginal slingplasty for vault and uterovaginal prolapse: an initial experience
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Prolapse & Stress Incontinence
 Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary Retention
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT
 URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
Sling procedures for urinary incontinence in women
 Update Article SLING PROCEDURES FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Z.G. KASSARDJIAN Sling procedures for urinary incontinence in women Z.G. KASSARDJIAN St.Elie Center, Antelias, Lebanon SUMMARY There are
Update Article SLING PROCEDURES FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Z.G. KASSARDJIAN Sling procedures for urinary incontinence in women Z.G. KASSARDJIAN St.Elie Center, Antelias, Lebanon SUMMARY There are
One Slim Needle One Incision. One Simple Solution for Stress Urinary Incontinence. The Difference is in the Data
 CONTINENCE SOLUTIONS One Slim Needle One Incision ordering information Description US International Order Number Order Number One Simple Solution for Stress Urinary Incontinence MiniArc Single-Incision
CONTINENCE SOLUTIONS One Slim Needle One Incision ordering information Description US International Order Number Order Number One Simple Solution for Stress Urinary Incontinence MiniArc Single-Incision
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach
 44 Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach John R. Miklos and Robert Moore Atlanta Urogynecology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Neeraj Kohli Harvard University, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A.
44 Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach John R. Miklos and Robert Moore Atlanta Urogynecology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Neeraj Kohli Harvard University, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A.
Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes
 LUTS (2012) 4, 120 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes Phil H. SONG, Chang H.
LUTS (2012) 4, 120 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes Phil H. SONG, Chang H.
Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence
 European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 362 366 Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence Long-Yau
European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 362 366 Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence Long-Yau
Technique Guide. Bard MK Hernia Repair. Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh SOFT TISSUE REPAIR. Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Midurethral Slings for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2006; Vol. 6, No. 3 Midurethral Slings for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence An Evidence Based Analysis February 2006 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry
Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2006; Vol. 6, No. 3 Midurethral Slings for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence An Evidence Based Analysis February 2006 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Surgery for stress incontinence:
 Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
Pan African Urological Surgeons Association. African Journal of Urology.
 African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents
 Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
Women s Health. Product innovation. Commitment. We are committed to you... and advancing the quality of your patient care.
 II Commitment We are committed to you... and advancing the quality of your patient care. Boston Scientific is always there for you, your physicians and your patients. We are anchored in our guiding principle
II Commitment We are committed to you... and advancing the quality of your patient care. Boston Scientific is always there for you, your physicians and your patients. We are anchored in our guiding principle
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Gökmen Sukgen, 1 Esra SaygJlJ YJlmaz, 2 and Eralp BaGer Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2016, Article ID 2906596, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2906596 Case Report Vaginal Hysterectomy with Anterior Four-Arm Mesh Implant Technique
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2016, Article ID 2906596, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2906596 Case Report Vaginal Hysterectomy with Anterior Four-Arm Mesh Implant Technique
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT!
 THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
The Suprapubic Arch Sling Procedure for Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A 5-Year Retrospective Study
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 897 901 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence The Suprapubic Arch Sling Procedure for Treatment of Stress Urinary
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 897 901 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence The Suprapubic Arch Sling Procedure for Treatment of Stress Urinary
To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of
 1 ABSTRACT: Objective: To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of urinary retention after mid-urethral sling surgery. Methods: Data registered in
1 ABSTRACT: Objective: To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of urinary retention after mid-urethral sling surgery. Methods: Data registered in
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
 Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA
 LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA Dr. A. Chrysostomou MD, FCOG (SA), Mmed (WITS) Senior Specialist,
LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA Dr. A. Chrysostomou MD, FCOG (SA), Mmed (WITS) Senior Specialist,
Carlos Errando-Smet Cristina Gutiérrez Ruiz Pedro Arañó Bertrán Humberto Villavicencio Mavrich 1 INTRODUCTION
 Received: 31 August 2017 Accepted: 4 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23444 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A re-adjustable sling for female recurrent stress incontinence and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency: Long-term
Received: 31 August 2017 Accepted: 4 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23444 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A re-adjustable sling for female recurrent stress incontinence and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency: Long-term
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
