Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
|
|
|
- Allison Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
2 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4 Normal bowel emptying.5 Causes of constipation.6 Anatomical...6 Functional..8 Complications of being constipated 9 Tests for investigating constipation...10 History and Physical Examination 10 Special investigations..11 Treatment for constipation.12 Medications 12 4 F s (fibre, fluid, fitness and feet). 14 Biofeedback 15 Surgery 15 Glossary.16 GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 2
3 Role of the large intestine The large intestine (also known as the colon) is responsible for transforming waste into semi solid stools for excretion. It does this by absorbing fluid from the waste as it moves through. Stool consistency can vary between hard lumps to loose / mushy depending on how long the stools have been in the large intestine and how much water has been reabsorbed from them. Ideally, stools should be formed into soft, smooth sausage shapes which are comfortable to pass. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 3
4 Mass movements in the large intestine The descending colon and the rectum are the storage tank at the end of the large intestine Normally the rectum is relatively empty, although some stool enters the rectum regularly However, most stool arrives all at once in the rectum as a result of mass movements, which happen from time to time, especially before the need to go to the toilet is experienced These mass movements are major waves of pressure which are capable of moving the stool through the whole length of the colon, like toothpaste being squeezed along a tube. What causes these mass movements? Food arriving in the stomach when you eat a meal sets off a pressure wave in the colon a few minutes later. This is why people often need to empty the bowel, sometimes urgently, soon after eating. This is also why, for many people, the bowel is relatively quiet at night The first meal of the day, along with the physical activity of getting ready in the morning, stimulates contractions in the colon and mass movements. Thus many people experience the urge to evacuate their bowels shortly after breakfast. The rate of movement through the digestive system is highly variable. Depending on what you have eaten, food USUALLY takes an average of 1-3 days to be processed. 90% of this time is spent in the colon. Normal bowel function varies between different people Some people move their bowels 3 times a day while others move their bowels once every 3 days. Anything in between this is normal. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 4
5 Normal bowel emptying When stool enters the rectum, the internal anal sphincter muscle automatically relaxes to open up the anal canal. This allows stool to enter the upper anal canal. Here, very sensitive nerve cells figure out whether there is wind, diarrhoea or normal stool present. Most people know that stool is in the rectum without really having to think about it. The external anal sphincter is a much thicker ring of muscle wrapping around the outside of the internal anal sphincter. We have voluntary control of this muscle this means that you can deliberately squeeze / use this muscle, just like you could with a muscle in the arm or leg. If a normal stool is sensed and it is NOT convenient for you to find a toilet at that time, you can DELAY bowel emptying by squeezing the external anal sphincter. Stool will be pushed back up and out of the anal canal. Most people do this without even thinking about it. Thus the urge to empty the bowel is resisted and will wear off. The external sphincter can relax, and stool will not enter the anal canal again until the next mass movement action. When this occurs, you will feel another urge to empty your bowels. These urges will continue at intervals until the bowel is emptied. Continually resisting the urge to empty your bowel or ignoring the urge to empty the bowel can lead to constipation. This is because the stool is forced to spend a longer amount of time in the colon, allowing more fluid to be reabsorbed. The stool will become harder and more difficult to pass. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 5
6 Causes of constipation Constipation can be caused by anatomical or functional problems. 1. Anatomical problems where the bowel muscles, surrounding structure or the nerves supplying the bowel are responsible for symptoms Rectocoele This condition is most commonly found in women who have had a baby by vaginal delivery OR women who have strained repeatedly because of heavy lifting and constipation. Strain causes the rectovaginal septum (the wall between the rectum and the vagina) to bulge forwards, down into the vagina. This bulge is called a rectal prolapse. Stool can get trapped in the bulge, resulting in a feeling of incomplete emptying Rectovaginal septum (wall) Hirschsprung s disease This is a very rare condition where the lower part of the bowel lacks the proper nerve supply required to propel stools along. It is usually diagnosed in babies soon after birth. Patients are constipated with huge distension (stretching) of the sigmoid colon. Sigmoid colon Collapsed rectum GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 6
7 Megacolon or megarectum This is a rare group of conditions where the colon is abnormally dilated These conditions can be inherited (passed down through families) or acquired (spontaneously occurring in someone with no family history). Patients will have constipation and soiling as liquid faeces leaks past the main impacted mass of faeces peristalsis Nerve disease / injury Nerve problems will cause problems with defaecation, especially constipation. E.g. spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson s disease, stroke, Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo obstruction Visceral myopathy and visceral neuropathy These are extremely rare conditions where problems with intrinsic gut muscles and nerves cause a generalised disturbance of gut function. Patients may experience abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation and bladder problems KEY Layers of gut wall Nerves supplying gut GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 7
8 2. Functional problems where the bowel is healthy but not working properly Medications Constipation is common side effects of a wide variety of prescribed and over the counter medications. These include pain killers (especially opioids, antacids containing aluminium and calcium, calcium channel blockers (for blood pressure), anti-parkinson drugs, antispasmodics, antidepressants, iron supplements, diuretics (fluid tablet), Using laxatives regularly for a long period of time can reduce your bowel s movements Pregnancy and after childbirth During pregnancy, changes in hormone levels cause the gut to slow down. Also, as the uterus grows, there is the additional factor of the extra volume in the pelvis. New mothers may find that they cannot respond to the urge to open their bowels. Following an operation - Constipation after surgery is related to several factors 1. The general anaesthetic and painkillers given during / after surgery can slow down the bowel 2. manipulation of the bowel during intestinal surgery can temporarily but significantly reduce bowel movements 3. the pain after an abdominal operation may be too painful for you to try pushing 4. some major pelvic operations can damage the pelvic nerves, interrupting defaecation reflexes Eating disorders Failing to eat regularly causes irregular bowel actions. These patients often fail to recover gut function even after eating habits are normalised. Lifestyle Changes in life routine like aging or travel can affect bowel movements Lack of fibre in the diet, low fluid intake or lack of physical activity may contribute. Ignoring the urge People sometimes feel unable to open their bowels at school or in the workplace or feel that their lives are too busy to attempt regular bowel opening. If people constantly put off bowel motions then over the years, the gastrointestinal tract gradually slows down and they become constipated. Psychological disturbances Having experienced major traumatic life events can place you at risk for constipation. Patients who have experienced sexual or physical abuse often have in-coordination between the rectum and the anus as well as slowing down of gut transit. As the rectum tries to contract to squeeze the stool out, the anus contracts to retain it Fear of pain People might experience pain during defaecation due to problems like haemorrhoids or fissures (split in the anal lining). Fear of experiencing this pain can cause patients to resist the urge to empty their bowels, and constipation can result GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 8
9 Complications of being constipated Common features associated with constipation include abdominal bloating and discomfort, tired, easily fatigued, pain and vomiting. It is uncommon for young or fit people to get serious complications from constipation. However, elderly or malnourished people may develop serious complications. Serious complications of being constipated 1. Faecal impaction when a solid ball of stool builds up in the rectum. This can present diarrhoea as liquid stool leaks out around the ball of obstructing stool. This is most commonly seen in patients with poor mobility who are taking multiple medications 2. Stool perforation (exceptionally rare!) when hard stool sits in the colon for so long that it wears through the wall and makes a perforation (hole) requiring surgical therapy 3. Rectal prolapse rectum comes down and out of the back passage. This is a complication of constipation / a weak pelvic floor / advanced age or malnutrition Note Haemorrhoids are NOT a complication of constipation. However, sitting on the toilet for long periods of time as well as straining can aggravate haemorrhoids. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 9
10 Tests for investigating constipation Which investigations you and your doctor decide on will depend on your symptoms, family history and age. Medical history The doctor may ask you to describe your constipation, particularly how long you have been constipated, how often your bowel movements are, consistency of stools, presence of blood and your bowel habits. A record of eating habits, medication, and level of physical activity or exercise will also help the doctor determine the cause of constipation. The clinical definition of constipation is any two of the following symptoms for at least 12 weeks* in the previous 12 months. straining during bowel motions lumpy or hard stool sensation of incomplete evacuation sensation of anorectal blockage / obstruction fewer than three bowel movements per week * The 12 weeks do not need to be consecutive. Physical examination This may include a digital rectal examination, where a gloved, lubricated finger is used to evaluate the tone of the anal sphincter and also detect tenderness, obstruction and blood. In some cases, blood and thyroid tests might be necessary to look for thyroid disease and serum calcium, OR to rule out inflammatory, endocrine, metabolic and other systemic disorders which may be causing your constipation. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 10
11 Special investigations These are usually reserved for people with severe symptoms, for those with sudden changes in number and consistency of bowel movements or blood in the stool and for older adults. Colonic investigations These look for anatomical causes for your symptoms. They are usually safe, with an extremely small risk of damage to your bowel. 1. Endoscopy involves using an internal telescope called an endoscope to inspect the bowel. This could be a colonoscopy (looking at the colon) or flexible sigmoidoscopy (looking at the sigmoid colon (S shaped part)) 2. Barium enema X ray since the bowelnormally does not show up well on X ray, a chalky liquid called barium sulfate is introduced into your colon through a tube in your rectum. This barium fills your colon and an X ray is taken, showing bowel shape, position and if there are blockages Anorectal physiological testing this test is only rarely indicated in patients with constipation. Some parts of the test are: 1. anorectal manometry A probe with a balloon at the end is inserted into the anus to measure anal sphincter muscle tone and contractions 2. balloon expulsion tests the balloon is now filled with 50 ml of air, and the patient is asked to expel the balloon. Inability to do so after 4 minutes may indicate a decrease in bowel function 3. electromyography to check the pelvic nerves and their innervations of the anal sphincter muscles and the pelvic floor muscles 4. nerve stimulation tests an electrode is used to stimulate the nerve and measure conduction to the anal muscles Colorectal transit studies assess speed of faecal passage through the bowel. You will be asked to swallow some capsules containing tiny markers which show up on X ray. You will then maintain a high fibre diet, and come back to the clinic to have X rays taken at 24, 48 and 72 hours. The distribution of the markers will show whether your transit is normal or slow. Defaecating proctography a special paste is inserted into the rectum. The patient is asked to evacuate their bowels and an X ray is taken while this is happening. The test looks at completeness of stool elimination, anorectal abnormalities and rectal muscle contraction and relaxation. Dynamic MRI defaecography a jelly is inserted into the rectum. MRI studies are taken of the anorectal area as you relax and as you bear down. These images show the anatomy of the rectum in relation to surrounding structures. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 11
12 Treatment for constipation 1. Medications 2. 4 F s (fibre, fluid, fitness and feet) 3. Biofeedback 4. Surgery 1. Medications Prescription If you are taking any medications, these should be reviewed by a health professional to see if they are contributing to your constipation. If possible, try to remove the constipating medication. Do I need to take medication for my constipation? If necessary, try using a fibre supplement such as fybogel. If really necessary, possible try suppositories or mini enemas to help regularise the bowels. Remember, it is best only to use these as an aid to getting into a regular routine, rather than relying on them long term. Laxatives It is common for patients to come to clinic and say I tried this laxative and it worked well at the beginning but then it stopped working. Then they try another laxative and another and another. However, long term laxative use will make the bowel less and less responsive. Laxatives should only be used by 1. Patients who have only very occasional episodes of constipation 2. Patients who need laxatives to counteract a short term constipating medication 3. Patients who need to avoid straining on the toilet (e.g. angina sufferers) 4. Patients who are in hospital or are severely ill 5. Patients with an anal condition which needs soft stools for the healing period (e.g. anal fissures) 6. Patients undergoing a radiological or surgical procedure GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 12
13 Fact or myth? 1. Long term laxative use permanently damages the bowel MYTH - There is no convincing evidence that this is true. However, the more you take laxatives, the less likely it is that your bowel will work on its own. 2. Once I start taking laxatives, I can never stop MYTH - Your bowel will have decreased activity while you are on laxatives. However, if you stop and give your bowel time, it will start working on its own again. This may take quite some time. 3. Laxatives can stain the bowel FACT - Some laxatives like Sienna can stain the bowel, and can be seen on colonoscopy. Just because sienna is natural does not mean it is good for you. 4. Laxatives cause bowel cancer MYTH- There is no significant evidence which supports this idea. Nonetheless, laxatives should not be considered harmless. 5. Laxatives cause loss of minerals FACT This loss of minerals can, in the long term, cause imbalances in the body s chemistry especially in older people or people who are unwell. Suppositories (mini enema) These must be inserted into the rectum for maximum effect. They act by causing contraction of the rectum, softening the stool in the rectum and by causing the bowel higher up to contract. While the idea of inserting an enema or suppository may not appeal to all, gloves are easy to buy, and there are several important advantages 1. More predictable in timing of bowel motion than laxatives 2. Less likely to cause diarrhoea than laxatives 3. Encourage a more regular bowel action, especially if taken at the same time on regular days 4. Since they act locally, they are generally well tolerated with few side effects GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 13
14 5. They act more rapidly than laxatives taken by mouth 2. The 4 F s FIBRE The daily recommended intake of fibre is 30 grams Fibre is found in cereals, grains, legumes, fruit, vegetables and salad 2.5g 6.2g 1.6g 3.1g 1.8g 3g 0.9g 8.1g 4.1g 2g 0.5g FLUIDS 1.5g 3.8g Drink at least 2L of fluid each day (8-10 cups) These include water (tap, bottled, mineral, soda and tonic) as well as milk, juice, cordial, soups,, herbal tea and decaffeinated tea / coffee 0.4g 2g FITNESS Exercise is important for maintaining good bowel function Walking is the best; try to keep your body moving GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 14
15 FEET The correct sitting position gives you the best angle to relax your muscles and do a complete motion 1. Feet on stool with knees higher than hips 2. Lean forwards, keeping your back straight 3. Elbows on knees 3. Biofeedback This is a bowel retraining program run by therapists who are usually specialist nurses or physiotherapists. There are usually 4 to 5 one-on-one sessions where the health professional will review things like: 1. Diet advice 2. Toileting habits and access to acceptable facilities 3. Correcting sitting position 4. Exercises to retrain muscles and nerves to coordinate and produce a satisfactory effort to empty the bowel SITTING SQUATTING 4. Surgery This is only required in a very small minority of patients, usually those with anatomical problems. o E.g. women who have a rectocoele may need surgery o Rectal prolapses sometimes require an operation. Removing all or part of the colon to improve bowel function often has a poor result. Approximately 10% of patients who have part of the colon removed will end up with a stoma (where the bowel is brought out to the skin, and GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 15
16 bowel contents is discharged into a regularly changed bag, rather than through the back passage.). This stoma is introduced because of incapacitating symptoms or as a result of the failure of previous surgery. Only a minority of patients have been found to have satisfactory health 5 years after such an operation. Glossary anal sphincter bowel habits continence defaecation incontinence faeces gastrointestinal tract peristalsis A ring of muscle closing off anal canal and allowing you to control WHEN you will defaecate, once faeces arrives in the rectum How often and where one has bowel motions Having voluntary control over urinary and faecal discharge The discharge of faeces from the rectum Inability to voluntarily control one s urinary and faecal discharge Once food is digested, it is transformed into a waste product called faeces to be expelled from the body The tube like organ connecting the mouth to the anus. Along this tract, food is broken down, digested, and converted to faeces to be expelled The muscular contraction / relaxation movements of the gastrointestinal tract which propels the food along the tube GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 16
Biofeedback Program. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
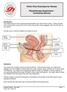
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Improving Your Bowel Function
 Improving Your Bowel Function EDUCATES, SUPPORTS AND PROMOTES SPECIALIST PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Glossary symptoms - a feeling of a physical change / bothersome change rectum/back passage - where stool / faeces
Improving Your Bowel Function EDUCATES, SUPPORTS AND PROMOTES SPECIALIST PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Glossary symptoms - a feeling of a physical change / bothersome change rectum/back passage - where stool / faeces
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Laparoscopic Ventral. Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR)
 Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR) Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital switchboard
Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR) Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital switchboard
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet. Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel
 Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse
 Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury
 Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
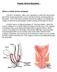 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
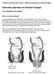 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS
 ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY. ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System
 PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
YOUR OPERATION EXPLAINED
 RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Pelvic organ prolapse. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Obstructive Defaecation
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Constipation. AL amyloidosis Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING FOR WOMEN STRONG PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES MEAN GOOD BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL WHAT ARE THE PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES?
 06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy
 Patient Information Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you
Patient Information Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you
Faecal incontinence. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Faecal incontinence Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine.. 3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Faecal incontinence Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine.. 3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Bright-red bleeding: If you have piles, you might see bright-red bleeding on the toilet paper, in the toilet bowl or on the surface of the faeces.
 What are haemorrhoids/piles? In the inner lining of the anus there are three haemorrhoidal cushions of tissue, which help to seal the anus and contribute to the control of the bowels (continence). Often,
What are haemorrhoids/piles? In the inner lining of the anus there are three haemorrhoidal cushions of tissue, which help to seal the anus and contribute to the control of the bowels (continence). Often,
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
AL amyloidosis Infosheet
 AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
What is a Colonoscopy?
 What is a Colonoscopy? A colonoscopy is a test to look inside your colon. A colonoscopy is done by a gastroenterologist, a doctor trained in looking at the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The main tool used
What is a Colonoscopy? A colonoscopy is a test to look inside your colon. A colonoscopy is done by a gastroenterologist, a doctor trained in looking at the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The main tool used
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems. Information for patients. Physiotherapy Department
 Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Simon Greenfield Consultant Gastroenterologist Spire Harpenden Hospital Pinehill Hospital, Hitchin QE2 Hospital, Welwyn Garden Lister Hospital, Stevenage
The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Simon Greenfield Consultant Gastroenterologist Spire Harpenden Hospital Pinehill Hospital, Hitchin QE2 Hospital, Welwyn Garden Lister Hospital, Stevenage
Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives. HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians.
 NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears
 Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Patient Information Leaflet. Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems
 Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Look Good Feel Good. after pregnancy. Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums
 Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Constipation. Disease Review
 bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
Bowel Management. Part One
 Bowel Management Part One Introduction Bowel Management in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury If you have a spinal cord injury (SCI) then a regular bowel management routine is vitally important, both physically
Bowel Management Part One Introduction Bowel Management in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury If you have a spinal cord injury (SCI) then a regular bowel management routine is vitally important, both physically
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Peristeen Anal Irrigation
 Peristeen Anal Irrigation Advice & Instructions Anal Irrigation Advice and Instructions for patients.indd 1 04/05/2011 11:29:28 Contents Introduction 3 History 3 The bowel system 4 Constipation 6 Faecal
Peristeen Anal Irrigation Advice & Instructions Anal Irrigation Advice and Instructions for patients.indd 1 04/05/2011 11:29:28 Contents Introduction 3 History 3 The bowel system 4 Constipation 6 Faecal
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Name: Date: Referring Provider: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary).
 Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
Physiotherapy advice following your third or fourth degree perineal tear
 Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
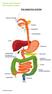 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
General Surgery. Haemorrhoids
 General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy
 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Constipation. What are the signs and symptoms of constipation? Less than three bowel movements per week. Pain or discomfort when opening your bowels
 Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
EXPECTING A BABY? SOME PREGNANT WOMEN CAN HAVE BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS. YOU CAN GET HELP. HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE A PROBLEM?
 11 BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS. When you are pregnant, you get a lot of advice from many people. One topic few people think about is bladder and bowel control problems during pregnancy and after
11 BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS. When you are pregnant, you get a lot of advice from many people. One topic few people think about is bladder and bowel control problems during pregnancy and after
Adult barium enema. X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing. What is a barium enema? Are there alternatives to Barium enema?
 Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
Constipation. Myeloma Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
Foreword. Bowel Management
 2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
Lower GI Series. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Lower GI Series National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a lower gastrointestinal (GI) series? A lower GI
Lower GI Series National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a lower gastrointestinal (GI) series? A lower GI
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES. Laparoscopic Colon Resection
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Colon Resection About Conventional
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Colon Resection About Conventional
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Managing your Bowels. Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System:
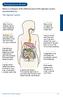 Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
To help you understand your operation, it is helpful to have a basic knowledge of how the body works (see Figure 1).
 Page 1 of 11 Anterior resection Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as an anterior resection. It explains what the procedure involves and also some of the common complications
Page 1 of 11 Anterior resection Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as an anterior resection. It explains what the procedure involves and also some of the common complications
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Stress. incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES.
 Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Constipation. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Your Bowel Operation Hartmanns Procedure
 Your Bowel Operation Hartmanns Procedure Introduction You are having an operation called Hartmanns Procedure and this booklet aims to help you to understand your condition and this operation. The nurses
Your Bowel Operation Hartmanns Procedure Introduction You are having an operation called Hartmanns Procedure and this booklet aims to help you to understand your condition and this operation. The nurses
X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Treating your prolapse
 Treating your prolapse This leaflet explains what a prolapse is, and how it can be treated and managed. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you. What is
Treating your prolapse This leaflet explains what a prolapse is, and how it can be treated and managed. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you. What is
Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence Introduction The muscles
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for anal incontinence Introduction The muscles
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE. Patient information Leaflet
 HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? Ease of Use: One Location: Reduced Cross-Infection: Focus on the Patient: Reduced Cost:
 Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? In our center, patients find that the process much more convenient, as well as more personal. Our center offers a relaxed environment with medical
Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? In our center, patients find that the process much more convenient, as well as more personal. Our center offers a relaxed environment with medical
Are you aware there are many different reasons for having irregular bowels? This chart is to help you get back into balance during and post detox.
 BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Pelvic Floor Muscles The pelvic floor muscles are a sling of muscles across the floor of the pelvis. The
Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Pelvic Floor Muscles The pelvic floor muscles are a sling of muscles across the floor of the pelvis. The
Capsule Endoscopy Preparation Instructions
 Capsule Endoscopy Preparation Instructions 1 day before your capsule endoscopy Prior to 2pm - Have your normal breakfast and a light lunch. After 2pm - You must have NO SOLID FOODS and only APPROVED clear
Capsule Endoscopy Preparation Instructions 1 day before your capsule endoscopy Prior to 2pm - Have your normal breakfast and a light lunch. After 2pm - You must have NO SOLID FOODS and only APPROVED clear
