The Gastrointestinal System
|
|
|
- Brendan Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Gastrointestinal System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain key terms related to the body 3. Explain the structure and function of the gastrointestinal system 4. Discuss changes in the gastrointestinal system due to aging 5. List normal qualities of stool and identify signs and symptoms to report about stool 6. List factors affecting bowel elimination and describe how to promote normal bowel elimination 7. Discuss common disorders of the gastrointestinal system 8. Discuss how enemas are given 9. Demonstrate how to collect a stool specimen 10. Explain occult blood testing 11. Define the term ostomy and identify the difference between colostomy and ileostomy 12. Explain guidelines for assisting with bowel retraining Supplemental Tools transparency 15-1 the gastrointestinal system transparency 15-2 factors affecting bowel elimination handout 15-1 suppositories handout 15-2: ileostomy care chapter 15: exam Assignments textbook reading, pp workbook exercises, pp Overview of Teaching Strategies This chapter introduces the students to the terms related to the body and the ten body systems. The concept of homeostasis is also introduced. The structure and function of the gastrointestinal system is briefly explained, and normal changes of the gastrointestinal system due to aging are described. The normal changes of aging for each body system should be emphasized so that students are better able to recognize abnormal changes. This chapter describes the process of bowel elimination and describes normal qualities of stool. Emphasis should be placed on the importance of regular bowel movements for maintaining health in elderly people. Students will learn signs and symptoms about stool that should be reported to the nurse. Factors affecting bowel elimination are described. Stress that the NA has an important role in promotion of bowel elimination for his or her residents. Common disorders of the gastrointestinal system are described in this chapter. It may be a good idea to have students make flash cards for these disorders and those described in the other body systems chapters. An important component of this chapter is the emphasis on providing plenty of privacy for all elimination and support for residents who have ostomies or are incontinent. Ask students to think about what it would feel like if they could not control their bowels and had to rely on others for assistance with elimination. 1. Define important words in this chapter textbook pp workbook p. 89
2 102 Pronounce and define each of the key terms listed in the Learning Objective on pages Explain key terms related to the body textbook p. 272 workbook p. 89 Biology Anatomy Physiology Cells Tissues Organs Body systems Homeostasis Pathophysiology Review the ten systems that make up the human body: Gastrointestinal or digestive Urinary Reproductive Integumentary or skin Circulatory or cardiovascular Respiratory Musculoskeletal Nervous Endocrine Immune and lymphatic 3. Explain the structure and function of the gastrointestinal system textbook pp workbook pp Gastrointestinal tract Peristalsis Chyme Duodenum Absorption Feces Electrolytes Colon Defecation Ingestion Digestion Elimination Display Transparency 15-1 the gastrointestinal system Discuss the following points: Digestion prepares food for absorption into cells. Elimination is expelling solid wastes. Review the functions of the gastrointestinal system: Ingestion of food and fluids Digestion of food Absorption of nutrients Elimination of waste products from food/fluids 4. Discuss changes in the gastrointestinal system due to aging textbook p. 274 workbook p. 90 Review normal changes of aging: Ability to taste decreases. Process of digestion takes longer and is less efficient. Body waste moves more slowly through the intestines, causing more frequent constipation. Difficulty chewing and swallowing may occur. Absorption of vitamins and minerals decreases. Production of saliva and digestive fluids decreases.
3 List normal qualities of stool and identify signs and symptoms to report about stool textbook p. 274 workbook p. 90 Bowel elimination Discuss normal bowel elimination: Stool is normally brown, soft, moist, and formed. No pain with passing stool There should not be blood, pus, mucus, or worms in the stool Review signs and symptoms to report about stool: Bloody or abnormally-colored stool Hard, dry stools Diarrhea Constipation Pain with bowel movements Blood, pus, mucus, or discharge in stool Fecal incontinence 6. List factors affecting bowel elimination and describe how to promote normal bowel elimination textbook pp workbook pp Fracture pan Portable commode Display Transparency 15-2 factors affecting bowel elimination Discuss the factors listed on the transparency: Growth and development Psychological factors Diet Fluid intake Physical activity and exercise Personal habits Medications Demonstrate each of the following procedures, including all of the numbered steps in your demonstration: Assisting a resident with use of a bedpan Assisting a male resident with a urinal Helping a resident use a portable commode Have the students return each demonstration. Procedure checklists are located at the back of the 7. Discuss common disorders of the gastrointestinal system textbook pp workbook pp Heartburn Review the following points about heartburn: Cause: weakening of the sphincter muscle which joins the esophagus and the stomach Symptoms: burning feeling in the esophagus, chest pain, bitter taste in the mouth, feeling of food coming back up into the throat or the mouth Pain usually occurs directly after a meal and may worsen when person is lying down. Treatment: medication, change in diet or sleep position Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Review the following points about GERD: Cause: liquid contents of the stomach back up into the esophagus; can inflame and damage lining of the esophagus and cause bleeding, ulcers, or difficulty swallowing Symptoms: frequent heartburn, chest pain, hoarseness in the morning, difficulty swallowing,
4 104 tightness in the throat, coughing, foul-smelling breath Possible causes: hiatal hernia, weak lower esophageal sphincter, slow digestion, diets high in acidic and spicy foods, obesity, smoking, alcohol use Treatment: stopping smoking and drinking alcohol; losing weight; wearing loose-fitting clothing; serving frequent, small meals throughout the day; serving last meal of the day three to four hours before bedtime; sitting up for at least two to three hours after eating; elevation of the head of the bed; and using extra pillows Review the following points about ulcers: Raw sores in the stomach or small intestine Cause: excessive acid Symptoms: dull or burning pain after eating, belching, vomiting Treatment: antacids and medications, change in diet Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and cigarette use Ulcerative colitis Review the following points about ulcerative colitis: Symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramping, rectal bleeding, poor appetite, fever, weight loss Can cause intestinal bleeding and death, if not treated Medication can help symptoms but do not cure it. Treatment may include an ostomy. Crohn s disease Review the following points about Crohn s disease: Causes the wall of the intestines to become inflamed Symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, joint pain Medication can help symptoms but do not cure it Treatment may include an ostomy Diverticulosis Diverticulitis Review the following points about diverticulosis and diverticulitis: Diverticulosis causes sac-like pouches to develop in weakened areas of the intestinal wall. Some people with diverticulosis will develop diverticulitis, or inflammation inside the pouchings. Cause: low-fiber diet Treatment: rest, medications, special diets, surgery Define the following terms: Flatulence Malabsorption Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Review the following points about flatulence: Presence of excessive air in the digestive tract Causes: high fiber foods, intolerance of foods, swallowing air when eating, antibiotics, malabsorption, IBS May be relieved by positioning, rectal tube Define the following terms: Constipation Enema Suppository Optional Distribute Handout 15-1 suppositories If regulations require you to teach this procedure, distribute the handout and discuss how to safely administer a suppository. Review the following points about constipation: Inability to eliminate stool, or the infrequent, difficult and often painful elimination of a hard, dry stool Causes: changes of aging, poor diet, lack of exercise, decrease in fluid intake, medication, disease, or ignoring urge to eliminate Signs include abdominal swelling, gas, irritability Treatment: increasing fiber, physical activity, and medication
5 105 Diarrhea Review the following points about diarrhea: It is the frequent elimination of liquid or semiliquid feces. Causes: infections, microorganisms, irritating foods, medication Treatment: medication, change of diet Fecal incontinence Review the following points about fecal incontinence: It is an inability to control the bowels. Causes: muscle and nerve damage, disorders of the spinal cord or anus, fecal impaction, constipation, tumors Treatment: changes in diet, medication, bowel training, surgery Fecal impaction Review the following points about fecal impaction: Buildup of dry, hardened feces in the rectum Signs include: no stool for several days, cramping, abdominal and rectal pain, abdominal swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Nurse or doctor will break mass into fragments. Can be fatal if complete bowel obstruction occurs Hemorrhoids Review the following points about hemorrhoids: Enlarged veins in the rectum Causes: constipation, obesity, pregnancy, diarrhea, overuse of enemas and laxatives, straining during bowel movements Symptoms: rectal itching, burning, pain, and bleeding Treatment: changes in diet, surgery 8. Discuss how enemas are given textbook pp workbook p. 92 Review different types of enemas: Tap water enema Soapsuds enema Saline enema Commercial enema Tell students that residents must be in Sims position to receive an enema. Emphasize that an enema should be stopped immediately if the resident complains of pain or if the NA feels resistance. This must be reported to the nurse. If your facility allows, demonstrate each of the following procedures, including all of the numbered steps in your demonstration: Giving a cleansing enema Giving a commercial enema Have the students return the demonstration. Procedure checklists are located at the end of the Emphasize that these procedures should only be performed if allowed by the facility and if the NA is trained to perform the procedure. 9. Demonstrate how to collect a stool specimen textbook pp workbook p. 92 Specimen Discuss these points about stool specimens: Stool is tested for blood, pathogens, and other things. Stool must be warm if being tested for ova and parasites. Urine or tissue in a stool sample can ruin the sample. Demonstrate the procedure: Collecting a stool specimen. Include all of the numbered steps in your demonstration.
6 106 Have the students return the demonstration. Procedure checklists are located at the end of the 10. Explain occult blood testing textbook pp workbook p. 92 Occult Discuss the fact that blood in the stool may be a sign of a serious problem, such as cancer. The Hemoccult test is one test that checks for occult blood. If in a facility and staff performs this test, demonstrate the procedure: Testing a stool specimen for occult blood. Include all of the numbered steps in your demonstration. Have the students return the demonstration. Procedure checklists are located at the end of the 11. Define the term ostomy and identify the difference between colostomy and ileostomy textbook pp workbook p. 93 Ostomy Stoma Colostomy Ileostomy Ureterostomy Urostomy Point out the body locations of the types of openings and why the care of the skin and the stoma are very important. Discuss and show different types of commercially sold ostomy appliances and equipment. Point out which types are most appropriate for certain ostomies. Emphasize that some residents are embarrassed about having an ostomy and promoting privacy is very important. Review the guidelines for ostomy care: Follow Standard and/or Transmission-Based Precautions. Provide good skin care and hygiene. Remove ostomy appliances carefully. Before removing appliance, allow a little air out of the bag. Observe contents of bag. Empty, clean, and replace the ostomy bag whenever stool is eliminated. Assist residents to wash hands. Observe for skin irritation, rashes, swelling or bleeding around stoma. Use skin barriers as ordered. Make sure bottom of appliance/bag is securely clamped before applying to stoma. Make sure bag is attached securely before completing care and before residents go out or receive visitors. Be supportive, empathetic, and caring. Demonstrate the procedure: Caring for an ostomy. Include all of the numbered steps in your demonstration. Have the students return the demonstration. Procedure checklists are located at the end of the Optional Distribute Handout 15-2 ileostomy care Distribute this handout if you want to include more information on ileostomy care. Go over all of the numbered steps.
7 Explain guidelines for assisting with bowel retraining textbook pp workbook p. 93 Discuss how NAs may assist in bowel retraining, including: Explain the schedule to the resident. Follow the schedule. Follow Standard Precautions. Wear gloves. Observe resident s elimination habits. Keep a record of elimination. Offer bedpan or trip to the bathroom at specific times each day. Answer call lights promptly. Provide privacy. Do not rush resident. Help with perineal care. Encourage fluids and proper diet. Dispose of wastes properly. Praise attempts and successes in controlling bowels. Never show frustration or anger. Discuss with students how to keep a positive attitude when assisting residents who are going through bowel retraining and have accidents. Ask students how they would feel if they were unable to control elimination. Create empathy for residents. Chapter Review Exam distribute chapter 15: exam (appendix c, pp ) Allow students enough time to finish the test. See Appendix D for answers to the chapter exams. Answers to Chapter Review in Textbook 1. Anatomy is the study of body structure. Physiology is the study of how body parts function. Cells are the basic structural unit of all organisms. Tissues are groups of cells that perform similar tasks. Organs are structural units in the human body that perform specific functions. Body systems are groups of organs that perform specific functions in the human body. Homeostasis is the condition in which all of the body s systems are balanced and are working at their best. 2. Peristalsis is muscular contractions that push food from the stomach toward the esophagus. 3. Feces is solid body waste excreted through the anus from the large intestine. 4. Ingestion of food, digestion of food, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of waste products from food/fluids 5. Answers include: Ability to taste decreases. Process of digestion takes longer and is less efficient. Body waste moves more slowly through the intestines, causing more frequent constipation. Difficulty chewing and swallowing may occur. Absorption of vitamins and minerals decreases. Production of saliva and digestive fluids decreases. 6. Brown in color; soft; moist; and formed 7. Answers include: abnormally colored stool; hard, dry stool; liquid stool; constipation; pain when having a bowel movement; blood, pus, mucus or discharge in stool; or fecal incontinence 8. Answers include: Growth and development: Encourage fluids and nutritious meals. Encourage regular activity and exercise. Provide good oral care. Make sure dentures are clean and fit properly. Psychological factors: Provide privacy and allow plenty of time for elimination. Leave the call light in reach. Respond to call lights and toileting requests immediately. Listen to residents if they want to talk. Diet: Encourage nutritious meals. Increase fiber intake. Decrease fatty and sugary foods. Use dietary supplements as ordered. Fluid intake: Encourage fluid intake. Remind residents to drink often. Make sure pitcher and water are in reach and light enough to lift. Assist with fluid intake as needed.
8 108 Physical activity and exercise: Increase daily exercise. Encourage regular walks and other activities that are allowed. Personal habits: Help residents to the bathroom at the best time for them. Use the bathroom resident prefers or get portable commode. Raise the head of the bed for residents using bedpan. Medications: Laxatives may be ordered. Report diarrhea or constipation to nurse promptly. 9. A fracture pan is used for small or thin people or those who cannot lift their buttocks onto a standard bedpan. 10. Position a standard bedpan so that the wider end is aligned with a resident s buttocks. Position a fracture pan with the handle toward the foot of the bed. 11. Portable commodes are used for people who can get out of bed but find it difficult to walk to the bathroom. 12. A resident with GERD should sit up for at least two to three hours after eating. 13. Medication and surgery 14. Answers include: high fiber foods, eating foods that a person cannot tolerate, swallowing air, antibiotics, malabsorption, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) 15. Answers include: increasing fiber in the diet and physical activity, and medications such as laxatives, enemas, or suppositories 16. Answers include: muscle and nerve damage, disorders of the spinal cord or anus, injuries to the anal muscles, fecal impactions, constipation, or tumors 17. Answers include: no stool for several days; cramping; abdominal or rectal pain; abdominal swelling; nausea; vomiting; seeping or oozing of liquid stool; increase in urination; inability to urinate; fever; or confusion or disorientation 1000 ml water with 5 ml of mild castile soap added. A saline enema has ml water with two teaspoons of salt added. A commercial enema has 120 ml solution and may have oil or other additives. 20. Sims position 21. Stop immediately 22. Not more than 12 inches 23. Tests must be done while the stool is still warm. 24. Urine or toilet paper 25. Hat 26. With a microscope or special chemical test 27. An ostomy is the surgical creation of an opening from an area inside the body to the outside. 28. Due to bowel disease such as diverticulitis or Crohn s disease, colon cancer, or trauma 29. A colostomy is a surgically-created opening into the large intestine to allow feces to be expelled. With a colostomy, stool may be semi-solid. An ileostomy is a surgically-created opening into the end of the small intestine, the ileum, to allow feces to be expelled. Stool will be liquid and may be irritating to the skin. 30. Answers include: Follow the plan consistently. Follow Standard Precautions. Observe residents elimination habits. Keep a record of elimination, including episodes of incontinence. Offer bedpan or trip to the bathroom at specific times each day. Answer call lights promptly. Provide privacy. Do not rush the resident. Help with perineal care as needed. Encourage fluids. Encourage proper diet. Dispose of wastes properly. Praise attempts and successes in controlling the bowels. Never show frustration or anger toward residents who are incontinent. 18. Answers include: excessive cleaning and wiping of the area, scented soaps 19. A tap water enema has ml water with nothing added. A soapsuds enema has 500-
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
F A M N O P R S ! D !
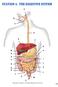 A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
Chapter 20. Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids
 Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Constipation. Self-study course
 Constipation Self-study course 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1. Define the term constipation 2. Explain three reasons why older adults are at greater risk for constipation
Constipation Self-study course 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1. Define the term constipation 2. Explain three reasons why older adults are at greater risk for constipation
Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Digestion. Absorption and Transport. Digestion. Digestion. (Chapter 3) Your GI tract is like a tube!
 Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
X-Plain Colostomy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Colostomy Reference Summary Introduction Diseases of the colon and intestines are common. When diseases of the intestines are treated with surgery, it sometimes results in a colostomy or an ileostomy.
X-Plain Colostomy Reference Summary Introduction Diseases of the colon and intestines are common. When diseases of the intestines are treated with surgery, it sometimes results in a colostomy or an ileostomy.
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Chapter 23. Nutrition Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain
 Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
Chapter 17. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery
 Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Docetaxel (Taxotere )
 Page 1 of 5 Docetaxel (Taxotere ) About This Drug Docetaxel is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white
Page 1 of 5 Docetaxel (Taxotere ) About This Drug Docetaxel is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Heartburn Overview. Causes & Risk Factors
 Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy
 Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. Overview of the gastrointestinal tract... 2 2. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2.1 What is a Jejeunostomy?...3
Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. Overview of the gastrointestinal tract... 2 2. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2.1 What is a Jejeunostomy?...3
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Methotrexate. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Section H Bladder and Bowel
 Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography)
 Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Trastuzumab (Herceptin )
 Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary Introduction Colon diseases are common. A sigmoidoscopy is a test that can help detect colon diseases. If your doctor recommends that you have a sigmoidoscopy, the
X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary Introduction Colon diseases are common. A sigmoidoscopy is a test that can help detect colon diseases. If your doctor recommends that you have a sigmoidoscopy, the
Colectomy. Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) Patient and Family Education
 Patient and Family Education Colectomy Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) A colectomy is a surgery that removes the colon, or large intestine. The colectomy
Patient and Family Education Colectomy Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) A colectomy is a surgery that removes the colon, or large intestine. The colectomy
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS
 UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS Structures 3.0 Objectives 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Conditions Affecting Digestive System 3.2.1 Chronic Liver Failure
UNIT3 INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH CONDITIONSIPROBLEMS RELATED TO DIGESTIVE AND URINARY ORGANS Structures 3.0 Objectives 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Conditions Affecting Digestive System 3.2.1 Chronic Liver Failure
64a Pathology: Digestive System!
 64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury
 Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Hemorrhoids. What are hemorrhoids? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Stoma Care Policy and Procedures
 Stoma Care Policy and Procedures Policy number 19.09 Approved by :CEO Version 1 Scheduled review date 28/3/2018 Created on 28/3/2017 POLICY STATEMENT Clients requiring management with the stoma will be
Stoma Care Policy and Procedures Policy number 19.09 Approved by :CEO Version 1 Scheduled review date 28/3/2018 Created on 28/3/2017 POLICY STATEMENT Clients requiring management with the stoma will be
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES. Laparoscopic Colon Resection
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Colon Resection About Conventional
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Colon Resection About Conventional
SPINAL CORD MEDICINE EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS FOR PATIENT AND FAMILY BOWEL MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING SPINAL CORD INJURY/IMPAIRMENT FRAZIER REHAB INSTITUTE
 SPINAL CORD MEDICINE EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS FOR PATIENT AND FAMILY BOWEL MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING SPINAL CORD INJURY/IMPAIRMENT FRAZIER REHAB INSTITUTE DISCLAIMER The information contained herein is intended
SPINAL CORD MEDICINE EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS FOR PATIENT AND FAMILY BOWEL MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING SPINAL CORD INJURY/IMPAIRMENT FRAZIER REHAB INSTITUTE DISCLAIMER The information contained herein is intended
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. PCV Treatment Chemotherapy for brain tumors DRAFT. PCV is a type of chemotherapy (chemo) treatment for brain
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
2. Have your symptoms affected your ability to carry out your daily activities? YES NO
 QUESTIONNAIRE Page 1 of 5 Date: Referring MD (Name, Address, Phone Number): Primary Care Physician (Name and Address, Phone Number): Reason for visit: 1. How long have you had symptoms? Describe your symptoms?
QUESTIONNAIRE Page 1 of 5 Date: Referring MD (Name, Address, Phone Number): Primary Care Physician (Name and Address, Phone Number): Reason for visit: 1. How long have you had symptoms? Describe your symptoms?
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD
 GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Caring for Your Ostomy Following Bowel Surgery
 ilearning about your health Caring for Your Ostomy Following Bowel Surgery www.cpmc.org/learning What is an Ostomy? An ostomy, usually either a colostomy or ileostomy, is a surgical procedure where the
ilearning about your health Caring for Your Ostomy Following Bowel Surgery www.cpmc.org/learning What is an Ostomy? An ostomy, usually either a colostomy or ileostomy, is a surgical procedure where the
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Colon Cancer Surgery
 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Limited Bowel Resection. Surgery for Crohn s Disease
 Limited Bowel Resection Surgery for Crohn s Disease What Is Crohn s Disease? Crohn s disease is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Crohn s disease occurs anywhere from the mouth
Limited Bowel Resection Surgery for Crohn s Disease What Is Crohn s Disease? Crohn s disease is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Crohn s disease occurs anywhere from the mouth
Rehabilitation and Restorative Care
 170 25 Rehabilitation and Restorative Care 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Discuss rehabilitation and restorative care 3. Describe the importance of promoting independence 4. Explain the complications
170 25 Rehabilitation and Restorative Care 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Discuss rehabilitation and restorative care 3. Describe the importance of promoting independence 4. Explain the complications
SURGERY LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
Name: Date: Referring Provider: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary).
 Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy
 The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy
 RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care
 Home Health Aide Training Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care Goal The goal of this module is to prepare participants to assist a home care client who has an ostomy. Time 7 hours and 30 minutes [1 hour
Home Health Aide Training Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care Goal The goal of this module is to prepare participants to assist a home care client who has an ostomy. Time 7 hours and 30 minutes [1 hour
Women s and Men s Health Intake Form Comprehensive Physical Therapy Center
 Name: (Last, First) DOB: Date: Age: Referring Physician: Next Physician Appointment: Today s visit: What is the main reason you came to the office today? When did it start? What treatments have you had
Name: (Last, First) DOB: Date: Age: Referring Physician: Next Physician Appointment: Today s visit: What is the main reason you came to the office today? When did it start? What treatments have you had
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Your Illness and Its Treatment
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Your Illness and Its Treatment What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease? Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Your digestive
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Your Illness and Its Treatment What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease? Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Your digestive
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Unit 2: Cells & Systems
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Unit 2: Cells & Systems CRACKER DIGESTION OBSERVATION Write down your observations: 1) What does it feel like initially (at the beginning)? 2) What does it feel like after 1 minutes in
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Unit 2: Cells & Systems CRACKER DIGESTION OBSERVATION Write down your observations: 1) What does it feel like initially (at the beginning)? 2) What does it feel like after 1 minutes in
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Continence Promotion. CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS
 Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Tapeworm Infection. Tapeworm
 Tapeworm Infection Introduction Tapeworm infection is caused by ingesting food or water that is contaminated with tapeworm eggs or larvae. Larvae are newly hatched tapeworms. A tapeworm may attach itself
Tapeworm Infection Introduction Tapeworm infection is caused by ingesting food or water that is contaminated with tapeworm eggs or larvae. Larvae are newly hatched tapeworms. A tapeworm may attach itself
What is a Colonoscopy?
 What is a Colonoscopy? A colonoscopy is a test to look inside your colon. A colonoscopy is done by a gastroenterologist, a doctor trained in looking at the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The main tool used
What is a Colonoscopy? A colonoscopy is a test to look inside your colon. A colonoscopy is done by a gastroenterologist, a doctor trained in looking at the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The main tool used
Digestion Assessment Scorecard
 Name Digestion Assessment Age Height Weight Based upon your health profile for the past 30 days, please select the appropriate number, from '0-3' on all questions (0 as least/never/no and 3 as most/always/yes).
Name Digestion Assessment Age Height Weight Based upon your health profile for the past 30 days, please select the appropriate number, from '0-3' on all questions (0 as least/never/no and 3 as most/always/yes).
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
COLORECTAL RESECTIONS
 COLORECTAL RESECTIONS What is a colorectal (bowel) resection? Surgery to remove a part of the large bowel is called a resection. Different parts of the colon require different operations and have different
COLORECTAL RESECTIONS What is a colorectal (bowel) resection? Surgery to remove a part of the large bowel is called a resection. Different parts of the colon require different operations and have different
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Information
 1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
General Surgery. Haemorrhoids
 General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
