4 Mousa Al-abbadi. Ola Al-juneidi. Abdul-rahman Ibrahim
|
|
|
- Alexis Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 Mousa Al-abbadi Ola Al-juneidi Abdul-rahman Ibrahim
2 Cervical Cancer We previously talked about human papilloma virus (HPV). There are almost 140 serotypes of HPV so far. Certain serotypes (14 of them) cause precursor lesions (high grade lesions). These lesions can progress to carcinoma in situ(cis) and then invasive cervical carcinoma. The most common serotypes that are associated with high grade lesions (which later on cause cervical carcinoma) are 16 and 18, others include 31, 33, 54, etc. The molecular testing for HPV that is done now (in addition to PAP smear whether done together or separately) is for 16, 18 and non-16,18; i.e. the machine tells you if the sample is 16 positive, 18 positive or non-16,18 positive (the sample can be 16 and 18 positive). Natural history 60% of low grade lesions regress and 30% persist. Out of all low grade lesions 10% will probably transform into high grade lesions. However, it is not HPV6 and 11 (that are associated with low grade lesions) that cause high grade lesion; associated high grade serotypes are present in addition to these low grade serotypes. When you look at the Pap smear you will find low grade and high grade serotypes at the same time (in the same sample) and it is marked high grade. 30% of high grade lesions regress and 60% persist. Chronic persistent infection with high grade serotypes is what causes high grade CIN and then cervical carcinoma (10% of high grade lesions). Once we detect a high grade lesion in a Pap smear, a colposcopy must be done where a special microscope is used to examine the cervix and vagina (more intensive than pap). [See picture next page] 1 P a g e
3 1 4 1 this is how a normal cervix looks like; the mucosa is white and shiny with no lesions. 2 low grade lesions appear whitish and slightly elevated 3 high grade lesions 4 cancer 2 3 HGSIL Detection An experienced colposcopist knows very well from where the biopsy should be taken. A definitive management is not done until there is a tissue diagnosis. If the biopsy was wrongly taken from normal tissue, lesions will be missed. It is very important to know exactly from where to take the biopsy to have an accurate tissue diagnosis. The issue here is to detect early cancers. In 40s and 50s, cervical cancer was 2 nd cause of cancer death but now it is the 13 th or 14 th cause of cancer death because of the success of the Pap smear, the best screening test in the history of cancer screening. The inventor of Pap smear, George Papanicolaou, struggled for years to convince people that you can detect cancer cells by looking at morphology of cells (cytology). To help in taking the biopsy from the right place Acetic acid test or Lugol's solution test are done. They put a substance on the cervix and take the biopsy from the place that didn't take this substance up. There are other techniques which help the colposcopist to know from where to take the biopsy. If the Pap smear was termed high grade but the biopsy from colposcopy turned out to be negative we should look at the Pap smear again. If it was confirmed to be high grade (high grade cells where found), we should believe it (not the colposcopy) because it samples/scrapes more area. The colposcopist must have missed the lesions (the biopsy was not done correctly). This could be because the lesion is in the T-zone and the T-zone is somewhat up. 2 P a g e
4 The location of the T-zone differs depending on age, reproductive and sexual history. In a virgin female before menarche T-zone is up. With the menstrual cycle, it becomes somewhat lower. After marriage (with intercourse) it becomes even lower. That's why in colposcopy or vaginal examination you can see the nice red columnar epithelium. But after delivery it becomes up again so in a 55 year old female (postmenopausal) you need to take the sample from higher places to sample T-zone. There are a lot of technical issues but you need to remember that when the Pap smear is true you believe it. Treatment of high grade lesions or early invasive cancer Cone excision: The treatment was previously done using cone excision procedure. In this procedure, a big amount of ecto- and endo-cervix was removed which will include the T-zone. The excision is cone-shaped with a base externally (exocervical margin) and an apex towards inside (endocervical margin). The removed tissue is then examined to make sure we removed the lesion and to see if the endocervical margin is clear or not and inform the doctor with the result. This procedure is big and it is associated with morbidity and complications (like cervical incompetence and frequent abortions). LEEP procedure: Nowadays, we do a simpler procedure which is LEEP excision (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure). The concept is the same but here we use a wire or blazer which results in smaller cone with less morbidity and complications. Nowadays, Cone excision is only done in rare occasions where there is microinvasion and a bigger piece is needed out. 3 P a g e
5 Invasive cervical carcinoma Most of cervical carcinomas are squamous (75%), a small proportion is mixed adeno and squamous which are called adenosquamous carcinomas (20%) and the rest are small cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Almost all of them are HPV-associated even adenocarcinomas. The incidence of cervical carcinoma has roughly plateaued because we reached the maximum saturation in terms of early detection. However, it is now believed that the incidence of adenocarcinomas of cervix is going up because there are no specific standards for the examination and detection of adenocarcinomas compared with squamous carcinomas. Small cell carcinoma (neuroendocrine carcinoma) of the cervix is a very bad disease just like SCC of lung. They are very aggressive; they are small cells that can easily reach blood stream and metastasize. At the time of diagnosis you assume the patient has metastasis. Actually, SCCs of any organ (prostate, lung, cervix, etc.) are aggressive and fatal, they are considered as leukemia; i.e. there is no point of resection and they are treated by chemotherapy. Squamous CC peak at age 45 (10-15 years after the initial exposure to HPV). Initial exposure usually is when females start sexual activity (according to culture).* **Nowadays, invasive cervical carcinoma is often seen in unscreened women. We should not see invasive cervical carcinoma because we have successful screening by Pap smear; lesions are detected and treated early. Most of the cases of invasive cervical carcinomas that we see now are in unscreened women (because of Ignorance, sometimes have multiple partners, prostitutes). They present with vaginal bleeding, leukorrhea and dyspareunia. As we said, biopsy is always needed to confirm diagnosis and examine depth of invasion (above or below 3mm) before planning treatment. Depth of invasion in any epithelial or mucosal cancer (vaginal, vulvar, etc.) dictates staging. Grading and depth of invasion are important predictors of stage and prognosis, that's why we need a proper and deep biopsy. Cancer cells then usually spread to pelvic lymph nodes. *remember: the development of cervical carcinoma from HPV usually needs years of persistent long-term infection. 4 P a g e
6 In the 80's and during surgery on a patient with invasive cervical carcinoma (while under anesthesia), surgeons would send lymph nodes to pathologists for frozen sections to see whether cancer has spread to lymph nodes or not. If it has not spread (negative) they proceed with radical hysterectomy. If it was positive (cancer has spread) they stop (don't do radical hysterectomy) because we add morbidity without any benefit; they are only treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Nowadays, in situ and early invasive cancer can be treated with simple hysterectomy. Otherwise, radical surgery is needed. Some are treated either with radiotherapy alone or with radiotherapy followed by radical hysterectomy. Risk factors for invasion: smoking, HIV, alcohol. 00:00-15:00 HPV vaccines: quadrivalent (HPV 6, 11, 16, 18) and more (divalent and 9-valent); are promising preventive measures. They are not part of our national program but it is available. It is given at the age of 9 and repeated after 1 and 3 months. Diseases of the endometrium Endometrial pathology is very common. Uterine Pathology 1. Endometritis whether acute (neutrophilic) or chronic (plasma cells). Acute endometritis is not very important because endometrium is a dynamic cyclical functional organ. So, if there is superficial inflammation in the endometrium it will shed and clear up by itself. On the other hand, chronic endometritis is very important. It is not an easy diagnosis and it is commonly associated with what we call chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (usually multiple organisms: N.gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis, etc.). Chronic endometritis is histologically characterized by the presence of plasma cells in the endometrium (1 or 2 cells are enough for diagnosis, usually there is more). 2. TB: The other chronic inflammatory condition of the endometrium is granulomatous endometritis caused by tuberculosis in endemic countries or immunocompromised patients. Usually you don't see TB endometritis alone; it is usually associated with 5 P a g e
7 tubal TB (TB salpingitis). That's because tubal TB spreads to endometrium and sometimes ovaries. Remember: - The primary target of TB is the lungs and lymph nodes. Extra-pulmonary sites include fallopian tubes and endometrium. - Immunocompromised states leads to reactivation of latent TB. In our region we still see TB and it is sometimes a cause of infertility because of associated nodules and sclerosis of fallopian tubes that lead to abnormal motility. While investigating infertility you sometimes discover tubal TB. The hallmark of TB infection is necrotizing granulomatous inflammation (granulomas with central necrosis). Wherever you see necrotizing granulomatous inflammation you have to rule out TB especially in endemic areas. 3. Retained POC (products of conception) and IUCD (Intrauterine Contraceptive Device) associated Retained POC are commonly seen either after delivery or abortion. Females who use IUCD (or IUD) are at a higher risk to develop chronic endometritis. IUCD is a foreign body and can cause endometritis in some people. Once chronic endometritis has developed on top of IUCD, IUCD has to be removed. All the previous pathologies are benign. The most common signs and symptoms of endometrial pathology include systemic signs of inflammation (like fever), abdominal pain and menstrual abnormalities. Diagnosis is usually by taking a biopsy. Treatment is by antibiotics or removal of IUCD and POC (according to the pathology). Diseases of the myometrium The 2 common diseases of the myometrium are adenomyosis and leiomyoma (or fibroid). Leiomyomas are discussed in the next lecture. Adenomyosis: Endometrial tissue deep in myometrium. 15:00-26:00 6 P a g e
8 When we section the uterus (we usually take from anterior and posterior), we must see mucosa, submucosa with endometrial glands, myometrium and finally serosa. If you see benign endometrial glands deep in the myometrium this is adenomyosis. These glands are functional most of the time, so they will undergo the same changes that occur in the endometrium during the menstrual cycle (i.e. they have bleeding, shedding ). This leads to abdominal pain. Patients with adenomyosis have abdominal pain especially with cycles (cyclical pain, before or during menses). It is said that adenomyosis is associated with higher incidence of infertility because of adhesions (the uterus is not functioning well for proper implantation). When extensive it causes menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea and pelvic pain (especially before menses). Sometimes high resolution ultrasound examination of the uterus shows abnormal myometrium. It can co-exist with endometriosis. When glands are outside the serosa (outside the uterus) it is called endometriosis. Adenomyosis and endometriosis are probably the same pathology but they differ in location. In adenomyosis the glands are in the myometrium (inside the uterus) and in endometriosis the glands are outside the uterus. Endometriosis: Endometrial glands and stroma outside uterus. It can be anywhere but common locations are ovaries, pouch of Douglas, uterine ligaments, cervix, tubes and rectovaginal septum. However, it has been diagnosed everywhere; in lungs, peritoneum, umbilicus, heart, etc. It could be multifocal. When a patient presents with chronic abdominal pain a laparoscopy is done to see what's wrong. They might find red spots on the ovary or peritoneum for example. They then take a biopsy to rule out endometriosis. When pathologists examine the biopsy, they see endometrial glands and stroma and sometimes hemosiderin-laden macrophages. This is an evidence of previous functionality of these glands with each cycle. With each cycle, there is bleeding that leads to deposition of iron which is then phagocytosed by macrophages. 7 P a g e
9 The 3 hallmarks of endometriosis anywhere are benign endometrial glands, stroma and hemosiderin-laden macrophages. Theories: Several theories were proposed to explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis 1) Regurgitation (favored): during menstrual cycle, shed tissue should go out through the vagina. Instead, it goes up the tube and into the ovary, uterine ligaments and peritoneal cavity (retrograde). It seeds there and gets its blood supply and becomes functional. This is the most accepted theory in the pathogenesis of endometriosis because it explains most cases of endometriosis which are around or near the uterus. 2) Benign metastases: endometrial glands and stroma travels through lymphatics or blood to distant organs (brain, lungs, etc.) and lives there. 3) Metaplasia: For example, mullerian epithelium of the tube turns into endometrial glands with stroma around them. 26:00-36:00 4) Extra-uterine stem cell differentiation: Stem cells are everywhere, they are undifferentiated cells. Abnormal environment around these cells might drive its differentiation toward benign endometrial tissue. This figure illustrates the regurgitation theory of endometriosis. A lot of research suggests that there are mediators which enhance the presence of endometriosis. Regurgitation and implantation of glands is not easy; it needs mediators like COX1, COX2, PGE2, etc. to make those endometrial glands that gets implanted outside the uterus survive and form endometriosis. 8 P a g e
10 Endometriosis clinically It appears as red spots in laparoscopy. During laparoscopy, a biopsy is taken to be examined under the microscope and to look for evidence of endometriosis. In ovaries, it sometimes results in cysts that fill with blood with each cycle. Old blood is called chocolate blood and the cysts are called chocolate cysts or endometriotic cysts. When the cysts are opened we see blood, and under the microscope we see endometrial glands and stroma. Any ovarian cyst might be sent to pathologists as frozen section to rule out malignancy. Some people say that endometriosis is more common in the high socio-economic class. You can read about the relation between the two. Gross features Gross appearance of an opened ovarian chocolate cyst Intraoperative appearance of endometriosis on the surface of the small bowel A surgeon opens the abdomen of a patient with abdominal pain and finds red spots on the small bowel. A frozen section is ordered to make sure it is not malignancy. 9 P a g e
11 Microscopic features When examined histologically: You can see endometrial glands and stroma. The brown material is hemosiderin-laden macrophages. Sometimes we don't see epithelium or glands and we only see abundant hemosiderin-laden macrophages which raises the diagnosis of but does not confirm endometriosis (we are not 100% sure). Usually when we examine any tissue, we make several cuts at different levels. So, if something didn't appear in the same slide it might appear in the next. So if we look at more levels we might find the glands. Signs and symptoms depend on distribution, location and quantity. - The most common signs and symptoms are severe dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain bleeding and adhesions. This is because most cases involve organs around the uterus. - Massive endometriosis on the ovaries and fallopian tubes leads to scarring of tubes and ovaries, cyclical abdominal pain and discomfort and infertility. - If in lungs, patients might present with bloody plural effusion. - If it is rectal painful defecation - uterine and bladder serosa dyspareunia and dysuria It affects 10% of women in reproductive age and 50% of infertile women. Endometriosis is claimed to be responsible for many cases of infertility because of resultant adhesions. 10 P a g e
12 Treatment is not easy; there are many algorithms on how to treat it. It is surgical and/or medical. Some people might need to surgically remove the involved organ. Because COX2 and PGE2 are involved in the implantation and growth of endometriosis anywhere, anti-cox2 and PGE2 can be used to treat endometriosis. However, there is no full agreement about the best way to treat endometriosis. Endometriosis is not an easy disease to treat. 36:00-45:00 THE END GOOD LUCK 11 P a g e
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد
 Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
What Causes Cervical Cancer? Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Definition Endometriosis is the presence of functioning endometrial tissue outside the cavity of the uterus.
 Dept. of Obstetrics t and Gynecology Faculty of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Endometriosis Definition Endometriosis is the presence of functioning endometrial tissue outside the cavity of the
Dept. of Obstetrics t and Gynecology Faculty of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Endometriosis Definition Endometriosis is the presence of functioning endometrial tissue outside the cavity of the
Done by khozama jehad. Neoplasia of the cervix
 Done by khozama jehad Neoplasia of the cervix An overview of cervical neoplasia very import. Most tumors of the cervix are of epithelial origin and are caused by oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus
Done by khozama jehad Neoplasia of the cervix An overview of cervical neoplasia very import. Most tumors of the cervix are of epithelial origin and are caused by oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003 Images removed due to copyright reasons.
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003 Images removed due to copyright reasons.
Cervical Conization. 1
 Cervical Conization www.zohrehyousefi.com 1 Cone Biopsy is a surgical procedure with removal of a cone shaped portion of the cervix The extent of involvement of epithelium on the ectocervix has been clearly
Cervical Conization www.zohrehyousefi.com 1 Cone Biopsy is a surgical procedure with removal of a cone shaped portion of the cervix The extent of involvement of epithelium on the ectocervix has been clearly
CERVIX. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb.
 CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Reproductive System Disorders
 Reproductive System Disorders Overview Male Infertility Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Prostate Cancer Female Infertility Endometriosis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Ovarian Cysts Cancer Breast Cervical Uterine
Reproductive System Disorders Overview Male Infertility Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Prostate Cancer Female Infertility Endometriosis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Ovarian Cysts Cancer Breast Cervical Uterine
Gynecological Cancers
 Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
The many faces of Endometriosis
 The many faces of Endometriosis Beryl Benacerraf M.D Harvard Medical School What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is defined as the presence of normal endometrial tissue occurring outside of the endometrial
The many faces of Endometriosis Beryl Benacerraf M.D Harvard Medical School What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is defined as the presence of normal endometrial tissue occurring outside of the endometrial
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
CPC on Cervical Pathology
 CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
ADENOMYOSIS CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN ADENOMYOSIS: PATHOLOGY ADENOMYOSIS
 CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Freedom of Information
 ND ref. FOI/16/309 Freedom of Information Thank you for your 19/10/16 request for the following information: Under the Freedom of Information Act, please could you fill out the following Freedom of Information
ND ref. FOI/16/309 Freedom of Information Thank you for your 19/10/16 request for the following information: Under the Freedom of Information Act, please could you fill out the following Freedom of Information
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi. Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat. Ahmad Al-Tarefe
 5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Female Reproduc.ve System. Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D.
 Female Reproduc.ve System Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D. Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Uterus Ovaries Breast Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Cervical carcinoma Cervical Carcinoma Once the most
Female Reproduc.ve System Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D. Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Uterus Ovaries Breast Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Cervical carcinoma Cervical Carcinoma Once the most
Endometriosis. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Endometriosis What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition whereby the lining
Endometriosis What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition whereby the lining
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers
 Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011
 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011 This talk What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease? Why it is important How it is spread Diagnosis Treatment Prevention What is PID? Inflammation
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011 This talk What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease? Why it is important How it is spread Diagnosis Treatment Prevention What is PID? Inflammation
6 Week Course Agenda. Today s Agenda. Ovarian Cancer: Risk Factors. Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention
 6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
Pelvic Pain: Overlooked
 EDUCATION EXHIBIT 3 Pelvic Pain: Overlooked and Underdiagnosed Gynecologic Conditions 1 CME FEATURE See accompanying test at http:// www.rsna.org /education /rg_cme.html LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR TEST 1
EDUCATION EXHIBIT 3 Pelvic Pain: Overlooked and Underdiagnosed Gynecologic Conditions 1 CME FEATURE See accompanying test at http:// www.rsna.org /education /rg_cme.html LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR TEST 1
Female Reproduc.ve System. Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D.
 Female Reproduc.ve System Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D. Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Uterus Ovaries Breast Cervical Carcinoma Once the most common cancer in women now not even in top 10. Decrease due
Female Reproduc.ve System Kris.ne Kra7s, M.D. Female Reproduc.ve System Outline Cervix Uterus Ovaries Breast Cervical Carcinoma Once the most common cancer in women now not even in top 10. Decrease due
Endometriosis. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary
 Endometriosis What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a common condition in young women. It's chronic, painful, and it often progressively gets worse over the time. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary Normally,
Endometriosis What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a common condition in young women. It's chronic, painful, and it often progressively gets worse over the time. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary Normally,
Cervical cancer presentation
 Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
 Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines Tim Kremer, MD Ralph Anderson, MD 1 Objectives Describe the natural history of HPV particularly as it relates
Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines Tim Kremer, MD Ralph Anderson, MD 1 Objectives Describe the natural history of HPV particularly as it relates
Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis
 Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference PCOS vs Endometriosis Ovaries play an important role in the reproduction and the maintenance of the female body. They
Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference PCOS vs Endometriosis Ovaries play an important role in the reproduction and the maintenance of the female body. They
Cervical Cancer : Pap smear
 Taking a PAP SMEAR Cervical Cancer : Pap smear George N Papanicolaou introduced cervical cytology in clinical practice in 1940 In 1945, PAP smear was endorsed by American cancer society as an effective
Taking a PAP SMEAR Cervical Cancer : Pap smear George N Papanicolaou introduced cervical cytology in clinical practice in 1940 In 1945, PAP smear was endorsed by American cancer society as an effective
Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis
 Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: Know the clinicopathologic features of endometriosis with special emphasis on: definition,
Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: Know the clinicopathologic features of endometriosis with special emphasis on: definition,
What is Cervical Cancer?
 What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical cancer starts in a woman's cervix, the lower narrow part of the uterus. The uterus holds the growing fetus during pregnancy. The cervix connects the lower part of the
What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical cancer starts in a woman's cervix, the lower narrow part of the uterus. The uterus holds the growing fetus during pregnancy. The cervix connects the lower part of the
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Oppgave: MED5600_OPPGAVE04_V18_ORD
 Side 23 av 63 Oppgave: MED5600_OPPGAVE04_V18_ORD Del 1: Sofie, 38 years, para1, comes to your office complaining about dyspareunia and spotting she has recently observed on several occasions, unrelated
Side 23 av 63 Oppgave: MED5600_OPPGAVE04_V18_ORD Del 1: Sofie, 38 years, para1, comes to your office complaining about dyspareunia and spotting she has recently observed on several occasions, unrelated
Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Sarah Burton. Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru
 Sarah Burton Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru Gynaecological Cancers Cervical Cancers Risk factors Presentation Early sexual activity Multiple sexual partners Smoking Human Papiloma
Sarah Burton Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru Gynaecological Cancers Cervical Cancers Risk factors Presentation Early sexual activity Multiple sexual partners Smoking Human Papiloma
Major tips: The importance of early detection: Hx, risk factors
 Cancer Chapter 3 Introduction Cancer ranks 2nd to cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of death in the Gaza Strip. Death rate increased from 10.3% in 2007 to 13.6 in 2012. Some related factors :
Cancer Chapter 3 Introduction Cancer ranks 2nd to cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of death in the Gaza Strip. Death rate increased from 10.3% in 2007 to 13.6 in 2012. Some related factors :
Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive
 CANCER CERVIX Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive leison by PAP Smears. Etiology: Age - 2 peaks
CANCER CERVIX Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive leison by PAP Smears. Etiology: Age - 2 peaks
Pelvic Pain. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two
 Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans.
 Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
ENDOMETRIOSIS WITH LYMPHATIC SPREAD P. Narmadha 1, P. Viswanathan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, U. Manohar 4, Lavanya Kumari 5
 ENDOMETRIOSIS WITH LYMPHATIC SPREAD P. Narmadha 1, P. Viswanathan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, U. Manohar 4, Lavanya Kumari 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. Narmadha, P. Viswanathan, Rehana Tippoo, U. Manohar, Lavanya
ENDOMETRIOSIS WITH LYMPHATIC SPREAD P. Narmadha 1, P. Viswanathan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, U. Manohar 4, Lavanya Kumari 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. Narmadha, P. Viswanathan, Rehana Tippoo, U. Manohar, Lavanya
Question Bank III - BHMS
 Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
Pap test results FOR WOMEN WITH AN ABNORMAL PAP TEST
 Pap test results FOR WOMEN WITH AN ABNORMAL PAP TEST Introduction This booklet provides women with information about abnormal Pap test results. Many women feel anxious or worried when they are told their
Pap test results FOR WOMEN WITH AN ABNORMAL PAP TEST Introduction This booklet provides women with information about abnormal Pap test results. Many women feel anxious or worried when they are told their
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Your Colposcopy Visit
 Introduction Welcome to the colposcopy clinic. This booklet tells you about. The colposcopy examination.. Tests that are done in the colposcopy clinic.. What these tests look for Take a few minutes to
Introduction Welcome to the colposcopy clinic. This booklet tells you about. The colposcopy examination.. Tests that are done in the colposcopy clinic.. What these tests look for Take a few minutes to
Mousa. Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh. Nizar Alkhlaifat
 6 Mousa Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh Nizar Alkhlaifat P a g e 1 This sheet written based on record 13 on website Cover slide( 95-117 ) No need to go back to slide FALLOPIAN TUBE PATHOLOGY In general fallopian
6 Mousa Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh Nizar Alkhlaifat P a g e 1 This sheet written based on record 13 on website Cover slide( 95-117 ) No need to go back to slide FALLOPIAN TUBE PATHOLOGY In general fallopian
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Gynaecological Malignancies
 Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine. Speaker Disclosure:
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Speaker Disclosure: Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine. Controversies in Women s Health
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
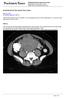 May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
Cervical Cancer 3/25/2019. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
 Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Chronic Pelvic Pain. AP099, December 2010
 AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
Management of Gynae Problems in Primary Care David Griffiths FRCOG The Great Western Hospital Swindon. A brief overview
 Management of Gynae Problems in Primary Care David Griffiths FRCOG The Great Western Hospital Swindon A brief overview Pelvic Pain Challenge to the physician In UK 1 Million sufferers 20% of all gynae
Management of Gynae Problems in Primary Care David Griffiths FRCOG The Great Western Hospital Swindon A brief overview Pelvic Pain Challenge to the physician In UK 1 Million sufferers 20% of all gynae
CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis
 CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis Anatomoclinical forms of endometriosis Definitions Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue containing both glands and stroma
CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis Anatomoclinical forms of endometriosis Definitions Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue containing both glands and stroma
If you do not have time for the entire presentation refer to the following table of contents. To navigate through the slides, right click on your
 Welcome This is an online version of a lecture given by Dr Keith Merritt on gyn cancers. Its purpose is to help women become more aware of early symptoms, risk factors, screening strategies and the importance
Welcome This is an online version of a lecture given by Dr Keith Merritt on gyn cancers. Its purpose is to help women become more aware of early symptoms, risk factors, screening strategies and the importance
Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH
 HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
Chapter 10: Pap Test Results
 Chapter 10: Pap Test Results On completion of this section, the learner will be able to: 1. Identify how Pap test results are interpreted and the reasons for normal and abnormal results. 2. Describe the
Chapter 10: Pap Test Results On completion of this section, the learner will be able to: 1. Identify how Pap test results are interpreted and the reasons for normal and abnormal results. 2. Describe the
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
A Rare Presentation of Endometriosis with Recurrent Massive Hemorrhagic Ascites which Can Mislead
 Case Report INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN'S HEALTH AND REPRODUCTION SCIENCES http://www.ijwhr.net A Rare Presentation of Endometriosis with Recurrent Massive Hemorrhagic Ascites which Can Mislead Article
Case Report INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WOMEN'S HEALTH AND REPRODUCTION SCIENCES http://www.ijwhr.net A Rare Presentation of Endometriosis with Recurrent Massive Hemorrhagic Ascites which Can Mislead Article
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Making Sense of Cervical Cancer Screening
 Making Sense of Cervical Cancer Screening New Guidelines published November 2012 Tammie Koehler DO, FACOG The incidence of cervical cancer in the US has decreased more than 50% in the past 30 years because
Making Sense of Cervical Cancer Screening New Guidelines published November 2012 Tammie Koehler DO, FACOG The incidence of cervical cancer in the US has decreased more than 50% in the past 30 years because
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates
 University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
and treating joins with the top of canal). at risk for cervical carcinomas, cervix.
 CERVICAL CANCER Worldwide, cervical cancer is twelfth most common and the fifth most deadly cancer in women. It affects about 16 per 100,000 women per year and kills about 9 per 100,000 per year. Cervical
CERVICAL CANCER Worldwide, cervical cancer is twelfth most common and the fifth most deadly cancer in women. It affects about 16 per 100,000 women per year and kills about 9 per 100,000 per year. Cervical
Endometriosis Information Leaflet
 Endometriosis Information Leaflet What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the womb (endometrium) is found outside the womb. About 1 out of 10 women of
Endometriosis Information Leaflet What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the womb (endometrium) is found outside the womb. About 1 out of 10 women of
Cervical Dysplasia and HPV
 Cervical Dysplasia and HPV J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse HPV Double stranded DNA virus The HPV infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes Highest risk
Cervical Dysplasia and HPV J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse HPV Double stranded DNA virus The HPV infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes Highest risk
Investigations and management of severe endometriosis
 Investigations and management of severe endometriosis Dr Jim Tsaltas Head of Gynaecological Endoscopy and Endometriosis Surgery Monash Health Monash University Dept of O&G Melbourne IVF Freemasons Hospital
Investigations and management of severe endometriosis Dr Jim Tsaltas Head of Gynaecological Endoscopy and Endometriosis Surgery Monash Health Monash University Dept of O&G Melbourne IVF Freemasons Hospital
Hysteroscopy. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Hysteroscopy What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 HYSTEROSCOPY AND DILATATION & CURETTAGE OF THE UTERUS Introduction I have
Hysteroscopy What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 HYSTEROSCOPY AND DILATATION & CURETTAGE OF THE UTERUS Introduction I have
Interactive Staging Bee
 Interactive Staging Bee ROBIN BILLET, MA, CTR GA/SC REGIONAL CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 6, 2018? Clinical Staging includes any information obtained about the extent of cancer obtained before initiation of treatment
Interactive Staging Bee ROBIN BILLET, MA, CTR GA/SC REGIONAL CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 6, 2018? Clinical Staging includes any information obtained about the extent of cancer obtained before initiation of treatment
Tissue Morcellation: Managing Risks to Drive Best Patient Outcomes
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Uterine Cervix. Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix.
 Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
University of Kentucky. Markey Cancer Center
 University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center Invasive Cancer of the Vagina and Urethra Fred Ueland, MD No matter what you accomplish in your life, the size of your funeral will still be determined by the
University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center Invasive Cancer of the Vagina and Urethra Fred Ueland, MD No matter what you accomplish in your life, the size of your funeral will still be determined by the
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way
 Women s Health Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way C50 - Malignant neoplasm of breast C50.0 Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola C50.01 - Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola, female C50.011 - Malignant
Women s Health Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way C50 - Malignant neoplasm of breast C50.0 Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola C50.01 - Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola, female C50.011 - Malignant
New Cancer Cases By Site Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3%
 Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
Gynaecology. Pelvic inflammatory disesase
 Gynaecology د.شيماءعبداألميرالجميلي Pelvic inflammatory disesase Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is usually the result of infection ascending from the endocervix causing endometritis, salpingitis, parametritis,
Gynaecology د.شيماءعبداألميرالجميلي Pelvic inflammatory disesase Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is usually the result of infection ascending from the endocervix causing endometritis, salpingitis, parametritis,
UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE
 UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Adenosarcoma with heterologous elements and stromal overgrowth o TAH, BSO, omentectomy, staging biopsies of cul-de-sac, bladder
UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Adenosarcoma with heterologous elements and stromal overgrowth o TAH, BSO, omentectomy, staging biopsies of cul-de-sac, bladder
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
The Pap Smear Test. The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Women s health promotion series
 The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series The Pap Smear Test Since the Pap smear test started to be used the number of cases of cervical cancer was greatly reduced.
The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series The Pap Smear Test Since the Pap smear test started to be used the number of cases of cervical cancer was greatly reduced.
What is a Pap Smear and What do the results mean? Maria E Daheri RN Cervical Nurse Case Harris Health System
 What is a Pap Smear and What do the results mean? Maria E Daheri RN Cervical Nurse Case Manager @ Harris Health System What is a Pap Smear and when is it recommended? Pap smear The Pap smear is a screening
What is a Pap Smear and What do the results mean? Maria E Daheri RN Cervical Nurse Case Manager @ Harris Health System What is a Pap Smear and when is it recommended? Pap smear The Pap smear is a screening
Cervical Cancer Prevention Month. January 2011 Morehouse College
 Cervical Cancer Prevention Month January 2011 Morehouse College What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical Cancer begins in the cervix (lower part of the womb, called the uterus). Cervical Cancer, at one point,
Cervical Cancer Prevention Month January 2011 Morehouse College What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical Cancer begins in the cervix (lower part of the womb, called the uterus). Cervical Cancer, at one point,
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS
 CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
Objectives. I have no financial interests in any product I will discuss today. Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines: Updates and Controversies
 Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines: Updates and Controversies I have no financial interests in any product I will discuss today. Jody Steinauer, MD, MAS University of California, San Francisco Objectives
Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines: Updates and Controversies I have no financial interests in any product I will discuss today. Jody Steinauer, MD, MAS University of California, San Francisco Objectives
HPV and Cervical Cancer, Screening and Prevention. John Ragsdale, MD July 12, 2018 CME Lecture Series
 HPV and Cervical Cancer, Screening and Prevention John Ragsdale, MD July 12, 2018 CME Lecture Series We have come a long Way Prevalence HPV in Young Adults in U.S HPV genotypes 55-60% of All cancers 20%
HPV and Cervical Cancer, Screening and Prevention John Ragsdale, MD July 12, 2018 CME Lecture Series We have come a long Way Prevalence HPV in Young Adults in U.S HPV genotypes 55-60% of All cancers 20%
