Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthetic on "Glossina"
|
|
|
- Camron Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthetic on "Glossina" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moloo, S.K. / Kutuza, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: Persistenter Link: Nutzungsbedingungen Die ETH-Bibliothek ist Anbieterin der digitalisierten Zeitschriften. Sie besitzt keine Urheberrechte an den Inhalten der Zeitschriften. Die Rechte liegen in der Regel bei den Herausgebern. Die auf der Plattform e-periodica veröffentlichten Dokumente stehen für nicht-kommerzielle Zwecke in Lehre und Forschung sowie für die private Nutzung frei zur Verfügung. Einzelne Dateien oder Ausdrucke aus diesem Angebot können zusammen mit diesen Nutzungsbedingungen und den korrekten Herkunftsbezeichnungen weitergegeben werden. Das Veröffentlichen von Bildern in Print- und Online-Publikationen ist nur mit vorheriger Genehmigung der Rechteinhaber erlaubt. Die systematische Speicherung von Teilen des elektronischen Angebots auf anderen Servern bedarf ebenfalls des schriftlichen Einverständnisses der Rechteinhaber. Haftungsausschluss Alle Angaben erfolgen ohne Gewähr für Vollständigkeit oder Richtigkeit. Es wird keine Haftung übernommen für Schäden durch die Verwendung von Informationen aus diesem Online-Angebot oder durch das Fehlen von Informationen. Dies gilt auch für Inhalte Dritter, die über dieses Angebot zugänglich sind. Ein Dienst der ETH-Bibliothek ETH Zürich, Rämistrasse 101, 8092 Zürich, Schweiz,
2 East African Trypanosomiasis Research Organization, P.O. Box 96, Tororo, Uganda Effects of Carbon Dioxide Anaesthetic on Glossina S. K. Moloo * and S. B. Kutuza Abstract Exposure of 2 day old virgin females of Glossina fuscipes fuscipes, G. palli dipes, G. brevipalpis, and G. morsitans centralis to carbon dioxide anaesthesia for 15 sec has the effect of suppressing their subsequent insemination frequency. This insemination-inhibitory effect of the gas is more pronounced in G. f. fuscipes and G. pallidipes than in G. brevipalpis and G. m. centralis. In G. f. fuscipes the adverse effect on insemination persists, albeit to a lesser degree, at least up to 72 hr. Carbon dioxide anaesthesia also reduces the insemination capability of G.f.fuscipes males; this effect, however, is less marked than in females. Exposure of wild non-teneral G. f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes, G. brevipalpis, and 3 day old G. m. centralis to the gas for 30 min causes some mortality during anaesthesia, which increases with increasing exposure period. G. m. centralis is most tolerant to the lethal effect of the gas within the min exposure periods. Wild females of G.f. fuscipes and G. pallidipes seem to be more sensitive to carbon dioxide in this respect than males. In view of these adverse effects produced by carbon dioxide anaesthesia, its use on tsetse is not to be recommended. Introduction Of the various immobilizing agents, carbon dioxide has been by far the most widely used anaesthetic for ease in the handling of insects. However, an in creasing number of investigators have found that this anaesthetic produces un desirable side effects in many insects (McCrady & Sulerud, 1964; Henneberry & Kishaba, 1967; Crystal, 1967; Hooper, 1970; White et al., 1970; Perron et al., 1972). In a study on functions of the male accessory glands of G.f. fuscipes Machado, preliminary experiments revealed that carbon dioxide anaesthesia was unsatisfactory as it resulted in reduced insemination frequency (Moloo, 1972). The present paper is concerned with further work on the effects of this anaesthetic on G.f.fuscipes, G. pallidipes Aust., G. brevipalpis Newst. and G. m. centralis Machado. Materials and Methods G.f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes and G. brevipalpis were caught from the South Busoga fly-belt of Uganda. The non-teneral wild or their offspring were used in the present study. G. m. centralis puparia were collected near Singida in Tanzania, and dispatched to EATRO, Uganda, in expanded polystyrene boxes (Kernaghan & Nash, 1964). Flies and puparia were kept in an insectarium * Present address: Tsetse Research Laboratory, Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Bristol, Langford, Bristol BS18 7 DU.
3 160 Ada Trop. XXXII, 2, Miscellanea maintained at 25 C, 80 /o r.h., and under a daily photoperiod of 12 hr subdued natural light. Flies were fed daily on live oxen. Those oxen which were used to feed wild were examined regularly for trypanosomes by the haematocrit centrifugation technique of Woo (1970), and when diagnosed positive were eliminated and treated. Emerging (0-24 hr old) were separated daily by sex to ensure virginity. Unless otherwise stated, 3 day old females were mated singly with 10 day old males, and the pairs left together for 24 hr. Flies were placed either singly or in groups in a specially constructed glass chamber connected to a cylinder of commercial pressurized carbon dioxide. To ensure immediate exposure of to carbon dioxide, the gas was first released through the bottom 1-cm diameter inlet opening of the 30 x 30 x 10-cm chamber for 30 sec with the same size outlet opening in the top lid left open. At the end of this period, the experimental fly/ in a Geigy cage were rapidly placed in the chamber and, with the top lid closed, a steady flow of the gas was continued for the required period at room temperature. The methods specific to particular experiments are described under appropriate sections. Experiments and results Insemination frequency Two day old virgin females of G. f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes, G. brevipalpis and G. m. centralis were exposed singly to carbon dioxide for 15 sec. Similar females of each species served as untreated controls. The anaesthetized flics of all four species recovered within I min. Twenty-four hours subsequent to the treatment all the were mated with untreated males and then the females were dis sected, and their spermathecae were examined under a phase-contrast microscope to determine insemination. Although pairing of the sexes occurred, insemination frequency of the treated was lower compared with their respective controls (Table I). The degree of insemination inhibitory effect, however, varied among the four species; insemination rates among treated insects of 8.9 %>, 6.6 %>, 41.4 %> and 79.9% of control values being recorded for G. f. fuscipes, G. palli dipes, G. brevipalpis and G. m. centralis, respectively. Table I. Insemination frequency in four species of virgin female Glossina sub jected to carbon dioxide anaesthesia and mated 24 hr later with normal males Species Treatment Number of Insemination frequency /o G. f. fuscipes G. pallidipes G. brevipalpis G. m. centralis
4 Moloo & Kiitiiza, Effects of Carbon Dioxide Anaesthetic 161 Table II. Duration of insemination inhibitory effect of carbon dioxide anaesthesia upon virgin female G. f. fuscipes mated with normal males Treatment Interval after anaesthesia when mated h Number of Insemination frequency To investigate the duration of this effect in G. f. fuscipes. 2 day old virgin females were exposed to carbon dioxide for 15 sec, and after varying periods were mated with 10 day old untreated virgin males. Table II shows that the inhibitory effect of this anaesthetic on insemination rate was approximately the same up to 48 hr after exposure, and the effect persisted, albeit to a relatively lesser extent, at least for 72 hr. Since G. f. fuscipes was originally selected for the study of functions of the male accessory glands, and since in the females of this species the adverse effect of carbon dioxide was markedly high, the effect of this anaesthetic on the in semination capability of the males was also investigated. Eighty 9 day old virgin males were individually exposed to the gas for 15 sec, and 24 hr later were mated with 3 day old untreated virgin females. Forty contemporary males served as untreated controls. The insemination frequency of the experimental was 52.5 /o as against 85.0 /o for the untreated controls. Toxicity Having established that carbon dioxide anaesthesia produces an inseminationinhibitory effect, an attempt was made to determine if this immobilizing agent is toxic to tsetse. Wild non-teneral males and females of G. f. fuscipes, G. palli dipes, G. brevipalpis, and 3 day old G. m. centralis were exposed to the gas for varying period from 10 to 300 min. Those which died during the exposure were scored: those which came to activity following the exposure were not scored even though some of these survived for only a short period. The mortality of all four tsetse species increased with increasing exposure period (Table III). Also, the recovery period of survivors increased with in creasing exposure to carbon dioxide. In all four species bloating of the abdomen with gas occurred in most of the during exposure particularly for exposures longer than 10 min. This bloating subsided shortly after were removed from the influence of the anaesthetic. The majorit\ of which recovered after exposure of 120 min and longer seemed lethargic and either died soon afterwards
5 162 Ada Trop. XXXII, 2, Miscellanea Table III. Mortality rate of four species of Glossina subjected to carbon dioxide anaesthesia for varying periods Exposure period min. G.f. fuscipes G. pallidipes G.,brevipalpis G. m. centrali: malles females males fem ales ma les females maies females N M N M N M N M N M N M N M N M N number exposed M» /o mortality or were found dead on the following day. The toxic effect of carbon dioxide anaesthesia was in general greater in females than in males of G. f. fuscipes and G. pallidipes. In the other two species, however, no such trend was detected. Table III also shows that for exposure periods up to 90 min G. m. centralis were less sensitive to the toxic effect of the gas compared with the other three tsetse species; longer exposure periods induced high mortality in all four species. Longevity and reproductive performance Since en exposure period of 15 sec to carbon dioxide has been used at the EATRO laboratory to immobilize wild as well as laboratory reared tsetse for Table IV. Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthesia on the reproductive performance of wild females of G. f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes and G. brevipalpis Species Treatment No. of No. of abor- tions Mean survival after test (days) No. of normal pupae Normal pupae/ female Pupae Mean weight (mg) G. /. fuscipes Ü ±1.1 G. pallidipes ± Ü G. brevipalpis ±
6 Moloo & Kiitiiza, Effects of Carbon Dioxide Anaesthetic 163 Table V. Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthesia on the longevity and reproductive performance of G. /. fuscipes Treatment Males Females No. of Mean longevity (days) No. of Mean Pupae longevity (days) No. Mean produced weight (mg) t ±1.3 experimental manipulation, the effects of this technique on the longevity and reproductive performance of Glossina were investigated as follows: (i) Wild females of G. f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes and G. brevipalpis were each divided in two groups. One group of each species was anaesthetized in batches of up to 25 while the other group served as control. Results (Table IV) showed that exposure of these to carbon dioxide anaesthetic for 15 sec produced no demonstrable effect on longevity or on reproductive performance. Nevertheless, the used in this experiment were wild and hence differed in their chronological as well as physiological age. Thus it is not possible to state with certainty that the anaesthesia had no effect. (ii) Forty 4 day old males of G. /. fuscipes were divided into two equal groups; the of one group were anaesthetized individually while those of the other served as control. In another experiment, 4 day old mated females were used and the experiment was conducted in the same way. Again, the results (Table V) showed that the anaesthetic produced no effect on longevity or on reproductive performance. Discussion It has been demonstrated that short exposure of the cabbage looper moth, Trichoplusia ni (Hubner) to carbon dioxide reduces mating for 24 hr (Henneberry & Kishaba, 1967). The present study shows that exposure of 2 day old virgin females of G.f. fuscipes, G. pallidipes, G. brevipalpis and G. m. centralis to carbon dioxide for as short a period as 15 sec has the effect of suppressing their subsequent insemination frequency. Whether this adverse effect on insemina tion is carbon dioxide specific or due to anoxia cannot be stated on the basis of the present experiments. The insemination-inhibitory effect of carbon dioxide anaesthesia is more pronounced in G.f. fuscipes and G. pallidipes than in G. brevipalpis and G. m. centralis, and suggests that there are interspecific differ ences in the sensitivity of tsetse to this gas. In G. f. fuscipes females the inhibi tion persists, albeit to a lesser degree, for at least 72 hr. However, since insemina tion rate increases as the period between exposure and mating is increased, it would seem that the adverse effect of carbon dioxide anaesthesia is not permanent. Carbon dioxide as an anaesthetic also reduces the insemination capability of G. /. fuscipes males, although to a lesser extent compared with its effect on
7 164 Acta Trop. XXXII, 2, Miscellanea females. It is noteworthy that exposure of G. m. morsitans Westwood (G. m. orientalis Vanderplank) males to carbon dioxide for 4-5 min does not affect their insemination capability (Birkenmeyer & Dame, 1970), again indicating interspecific differences in the sensitity of tsetse to this anaesthetic. The present study also demonstrates a toxic effect of carbon dioxide anaesthe sia. Exposure of wild non-teneral G. /. fuscipes, G. pallidipes, G. brevipalpis, and 3 day old G. m. centralis to the gas for 30 min causes some mortality which increases with increasing exposure period. Although all recovered some of these died not long after recovery following 10 min exposure, while for 150 min exposure and longer most which recovered died during the following 24 hr. The relatively greater tolerance to the toxic effects of carbon dioxide in the min exposure periods of G. m. centralis compared with the other three species could be attributed to the following factors, operating either singly or in combination: (i) the G. m. centralis adults used were younger than the wild of the other three species, in which case greater sensitivity to carbon dioxide with increasing age must be postulated; (ii) the G. m. centralis adults emerged from pupae under laboratory conditions whereas wild were handled many times during the period between catching and setting up the experiment; hence the latter were possibly weaker; (iii) G. m. centralis is inherently more tolerant to carbon dioxide anaesthesia and/or anoxia. Birkenmeyer & Dame (1970) found that exposure of newly emerged (0-24 hr old) G. m. morsitans to carbon dioxide for min does not affect their longevity. These authors reported that young (0-24 hr old) exposed for 30 min to this gas had increased survival, whereas exposure of older (2 day old) resulted in the reduction of survival of the males and not the females. How ever, in our experiments exposure of 3 day old G. m. centralis for the same period resulted in some mortality of the females alone. In the case of wild G. /. fuscipes and G. pallidipes, females seemed more sensitive to carbon dioxide anaesthesia within the min exposure periods than males; no such trend between the sexes was observed in the other two tsetse species. Toxic effects of carbon dioxide have been described for other insects. For example, L'Héritier (1948, 1958) found that certain Drosophila strains were unable to recover after a 30 sec exposure to carbon dioxide, and showed that such sensitivity was due to sigma virus. Virus-like particles have been observed in tsetse tissues (Jenni. 1973; Jenni & Steiger, 1977), but whether such particles are responsible for the sensitivity of their hosts to carbon dioxide is unknown. An enhanced mor tality due to carbon dioxide anaesthesia was reported in the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata (Wied) (Sherman. 1953), and also in the Mexican fruit fly, Anastrepha ludens (Loew) (Lopez & Balock, 1970). Perron et al. (1972) found that min exposure to carbon dioxide resulted in high mortality of the 0-3 hr old Drosophila melanogaster Meig., but no such toxic effect was observed in older than 3 hr. Also, 0-3 hr old females were more sensitive to the gas than males. Although the four species of Glossina studied show different reactions to carbon dioxide anaesthesia insofar as the degree of sensitivity is concerned, all four species are adversely affected by the gas. Hence the use of this anaesthetic on tsetse is not to be recommended. Acknowledgement We wish to thank Dr. P. A. Langley for helpful comments on the manuscript, and the Director of EATRO for permission to publish this paper.
8 Moloo & Kutuza, Effects of Carbon Dioxide Anaesthetic 165 References Birkenmeyer, D. R. & Dame, D. A. (1970). Effects of carbon dioxide and nitrogen on Glossina morsitans orientalis Vanderplank. - Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, Crystal, M. M. (1967). Carbon dioxide anaesthesia of untreated and chemosterilant-treated screw-worm, Cochliomyia hominivorax (Coquerel). - J. med. Ent. 4, Henneberry, T. J. & Kishaba, A. N. (1967). Mating and oviposition of the cabbage looper in the laboratory. - J. econ. Ent. 60, Hooper, G. H. S. (1970). Use of carbon dioxide, nitrogen and cold to immobilize adults of the Mediterranean fruit fly. - J. econ. Ent. 63, Jenni, L. (1973). Viruslike particles in a strain of Glossina morsitans centralis, Machado Trans, roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 67, 295. Jenni, L. & Steiger, R. (1974). Viruslike particles of Glossina fuscipes fuscipes Newst Acta trop. 31, Kernaghan, R. J. & Nash, T. A. M. (1964). A technique for the despatch of pupae of Glossina and other insects by air from the tropics. - Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 58, L'Héritier, P. (1948). Sensitivity to C02 in Drosophila. A review. - Heredity 2, L'Héritier, P. (1958). A hereditary virus of Drosophila. - Adv. Virus Res. 5, Lopez, D. F. & Balock, J. W. (1970). Mortality of the Mexican fruit fly from carbon dioxide generated in buried mangoes and oranges. - J. econ. Ent. 63, McCrady, W. B. & Sulerud, R. L. (1964). Delayed recovery from carbon dioxide in Drosophila melanogaster. - Genetics 50, Moloo, S. K. (1972). Effect of carbon dioxide narcosis on the mating behaviour of Glossina. - Trans, roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 66, 307. Perron, J. M., Huot, L., Corrivault, G.-W. & Chawla, S. S. (1972). Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthesia on Drosophila melanogaster. - J. Insect Physiol. 18, Sherman, M. (1953). Effects of carbon dioxide on fruit in Hawaii. - J. econ. Ent. 46, & Onsager, J. A. (1970). Effects of CO,, chilling White, L. D., Hutt, R. B. and staining on codling moths to be used for sterile uses. - J. econ. Ent. 63, Woo, P. K. T. (1970). The haematocrit centrifuge technique for the diagnosis of African trypanosomiasis. - Acta trop. 27,
Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti"
 Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti" Autor(en): Geering, K. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 27.07.2018 Persistenter Link:
Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti" Autor(en): Geering, K. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 27.07.2018 Persistenter Link:
Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis"
 Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis" Autor(en): Zeledón, R. / Soto, R. / González, G. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis" Autor(en): Zeledón, R. / Soto, R. / González, G. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee
 Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee Autor(en): Layton, Laurence L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen Wissenschaften
Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee Autor(en): Layton, Laurence L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen Wissenschaften
The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology
 The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology Autor(en): Lea, Arden O. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt
The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology Autor(en): Lea, Arden O. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt
Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania
 Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mbwambo, H.A. / Mella, P.N.P. / Lekaki, K.A. Article
Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mbwambo, H.A. / Mella, P.N.P. / Lekaki, K.A. Article
Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"]
![Conclusions [for Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien] Conclusions [for Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien]](/thumbs/81/83890744.jpg) Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"] Autor(en): Diczfalusy, E. / Lunenfeld, B. / Ferin, J. Objekttyp: Postface Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie
Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"] Autor(en): Diczfalusy, E. / Lunenfeld, B. / Ferin, J. Objekttyp: Postface Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie
Freud and the "School of Helmholtz"
 Freud and the "School of Helmholtz" Autor(en): Cranefield, Paul F. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1-2 PDF erstellt
Freud and the "School of Helmholtz" Autor(en): Cranefield, Paul F. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1-2 PDF erstellt
Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report
 Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report Autor(en): Bouvet, J.P. / Thérizol, Madeleine / Auquier, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (977)
Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report Autor(en): Bouvet, J.P. / Thérizol, Madeleine / Auquier, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (977)
The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis
 The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Partono, F. / Purnomo / Oemijati, Sri Article Zeitschrift:
The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Partono, F. / Purnomo / Oemijati, Sri Article Zeitschrift:
The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria
 The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ejezie, G.C. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am: 19.07.2018 Persistenter
The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ejezie, G.C. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am: 19.07.2018 Persistenter
Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery
 Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vinke, B. / Donker, A.J.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am:
Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vinke, B. / Donker, A.J.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am:
Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin
 Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin Autor(en): Objekttyp: Imperato, Pascal James / Fofana, Benitieni / Sow, Ousmane Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin Autor(en): Objekttyp: Imperato, Pascal James / Fofana, Benitieni / Sow, Ousmane Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review
 Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ikede, B.O. / Elhassan, Elizabeth / Akpavie, S.O. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 1 PDF
Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ikede, B.O. / Elhassan, Elizabeth / Akpavie, S.O. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 1 PDF
Autor(en): Snow, W.F. / Tarimo, S.A. / Staak, C. Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4. PDF erstellt am:
 The feeding habits of the tsetse, "Glossina pallidipes" Austen on the south Kenya coast, in the context of its host range and trypanosome infection rates in other parts of East Africa Autor(en): Snow,
The feeding habits of the tsetse, "Glossina pallidipes" Austen on the south Kenya coast, in the context of its host range and trypanosome infection rates in other parts of East Africa Autor(en): Snow,
Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox
 Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox Autor(en): Objekttyp: Jezek, Z. / Szczeniowski, M. / Paluku, K.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am: 18.7.218 Persistenter
Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox Autor(en): Objekttyp: Jezek, Z. / Szczeniowski, M. / Paluku, K.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am: 18.7.218 Persistenter
Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities
 Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ottesen, E.A. / Mendell, Nancy R. / MacQueen, J. Marilyn Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ottesen, E.A. / Mendell, Nancy R. / MacQueen, J. Marilyn Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection
 Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection Autor(en): Objekttyp: Adeiga, A.A. / Ade-Serrano, M.A. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 40 (1983) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 26.10.2017 Persistenter
Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection Autor(en): Objekttyp: Adeiga, A.A. / Ade-Serrano, M.A. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 40 (1983) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 26.10.2017 Persistenter
Palynology of a bumble-bee nest
 Palynology of a bumble-bee nest Autor(en): Objekttyp: Faegri, Knut Article Zeitschrift: Veröffentlichungen des Geobotanischen Institutes der Eidg. Tech. Hochschule, Stiftung Rübel, in Zürich Band (Jahr):
Palynology of a bumble-bee nest Autor(en): Objekttyp: Faegri, Knut Article Zeitschrift: Veröffentlichungen des Geobotanischen Institutes der Eidg. Tech. Hochschule, Stiftung Rübel, in Zürich Band (Jahr):
Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters
 Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters Autor(en): Objekttyp: Rajasekariah, G.R. / Deb, B.N. / Dhage, K.R. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 42 (985) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am:
Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters Autor(en): Objekttyp: Rajasekariah, G.R. / Deb, B.N. / Dhage, K.R. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 42 (985) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am:
Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N. / Dietrich, F.M. Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 4. PDF erstellt am:
 Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis outside endemic areas : use of histamine release from basophils by schistosomal antigens and radioallergosorbent test Autor(en): Objekttyp: Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N.
Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis outside endemic areas : use of histamine release from basophils by schistosomal antigens and radioallergosorbent test Autor(en): Objekttyp: Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N.
Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae"
 Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mukkada, A.J. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (1977) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 03.10.2018 Persistenter
Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mukkada, A.J. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (1977) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 03.10.2018 Persistenter
Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males
 Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mani, Erwin / Wildbolz, Theodor / Riggenbach,
Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mani, Erwin / Wildbolz, Theodor / Riggenbach,
Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice
 Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vickery, A.C. / Nayar, J.K. / Albertine, K.H. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vickery, A.C. / Nayar, J.K. / Albertine, K.H. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever
 Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever Autor(en): Walker, D.H. / Staiti, A. / Mansueto, S. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 43 (1986) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am:
Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever Autor(en): Walker, D.H. / Staiti, A. / Mansueto, S. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 43 (1986) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am:
"Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets
 "Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets Autor(en): Objekttyp: Flavell, D.J. / Pattanapanyasat, K. / Lucas, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
"Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets Autor(en): Objekttyp: Flavell, D.J. / Pattanapanyasat, K. / Lucas, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation
 Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation Autor(en): Objekttyp: Cameron, E. Alan Article Zeitschrift: Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft = Bulletin de la
Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation Autor(en): Objekttyp: Cameron, E. Alan Article Zeitschrift: Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft = Bulletin de la
Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis
 Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Lambert, Paul Henri / Casali, Paolo / Nydegger, Urs Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen
Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Lambert, Paul Henri / Casali, Paolo / Nydegger, Urs Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen
Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions
 Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions Autor(en): Dayer, Jean-Michel / Goldring, Steven R. / Robinson, Dwight R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions Autor(en): Dayer, Jean-Michel / Goldring, Steven R. / Robinson, Dwight R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics. Peter Van den Bossche
 Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics Peter Van den Bossche Climate change & animal health Climate change in Africa: Temperature Rainfall Variability Climate change & animal
Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics Peter Van den Bossche Climate change & animal health Climate change in Africa: Temperature Rainfall Variability Climate change & animal
of Dacus dorsalis1 and Ceratitis capitata1'2'3
 Vol. XXII, No. 2, Sept. 1976 335 Gamma Irradiation Effect on the Flight Mill Performance of Dacus dorsalis1 and Ceratitis capitata1'2'3 J.L. Sharp4 and D.L. Chambers4 DEPARTMENT OF ENTOMOLOGY, UNIVERSITY
Vol. XXII, No. 2, Sept. 1976 335 Gamma Irradiation Effect on the Flight Mill Performance of Dacus dorsalis1 and Ceratitis capitata1'2'3 J.L. Sharp4 and D.L. Chambers4 DEPARTMENT OF ENTOMOLOGY, UNIVERSITY
Hybridization Asymmetries in Tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae): Role of Maternally Inherited Factors and the Tsetse Genome
 ARTICLE Hybridization Asymmetries in Tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae): Role of Maternally Inherited Factors and the Tsetse Genome R. H. GOODING Department of Biological Sciences, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
ARTICLE Hybridization Asymmetries in Tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae): Role of Maternally Inherited Factors and the Tsetse Genome R. H. GOODING Department of Biological Sciences, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie"
 Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie" Autor(en): Weiner, Dora B. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal
Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie" Autor(en): Weiner, Dora B. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal
Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland)
 Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moosmann, Yves / Brossard, Michel / Raeber, Pierre-Alain Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin de la Société
Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moosmann, Yves / Brossard, Michel / Raeber, Pierre-Alain Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin de la Société
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY
![[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY](/thumbs/91/107443416.jpg) [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark
 www.ssoar.info The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Arbeitspapier
www.ssoar.info The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Arbeitspapier
Effects of Increasing Dosages of Gamma Irradiation on
 Vol. XXI, No. 2, December, 1972 257 Effects of Increasing Dosages of Gamma Irradiation on Wingbeat Frequencies of Dacus dorsalis Hendel Males and Females at Different Age Levels1 John L. Sharp2 UNIVERSITY
Vol. XXI, No. 2, December, 1972 257 Effects of Increasing Dosages of Gamma Irradiation on Wingbeat Frequencies of Dacus dorsalis Hendel Males and Females at Different Age Levels1 John L. Sharp2 UNIVERSITY
Sperm Precedence of Irradiated Mediterranean Fruit Fly Males (Diptera: Tephritidae)
 SPERM PROC. HAWAIIAN PRECEDENCE ENTOMOL. IN CERATITIS SOC. (2003) CAPITATA 36:47 59 47 Sperm Precedence of Irradiated Mediterranean Fruit Fly Males (Diptera: Tephritidae) Stephan G. Lee, Susan D. McCombs,
SPERM PROC. HAWAIIAN PRECEDENCE ENTOMOL. IN CERATITIS SOC. (2003) CAPITATA 36:47 59 47 Sperm Precedence of Irradiated Mediterranean Fruit Fly Males (Diptera: Tephritidae) Stephan G. Lee, Susan D. McCombs,
AIC. Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602 wangen bei dübendorf
 AIP services phone: +41 (0) 43 931 61 68 fax: +41 (0) 43 931 61 59 AFTN: LSSAYOYX aip@skyguide.ch AIC Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602
AIP services phone: +41 (0) 43 931 61 68 fax: +41 (0) 43 931 61 59 AFTN: LSSAYOYX aip@skyguide.ch AIC Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602
Morphological changes in human schistosomiasis and certain analogies in ancient Egyptian sculpture
 Morphological changes in human schistosomiasis and certain analogies in ancient Egyptian sculpture Autor(en): Hoeppli, R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 30 (1973) Heft 1-2 PDF
Morphological changes in human schistosomiasis and certain analogies in ancient Egyptian sculpture Autor(en): Hoeppli, R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 30 (1973) Heft 1-2 PDF
COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE
 J. Exp. BM. (1965), 4*. 373-378 3-73 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE BY K. G. DAVEY Institute of Parasitology,
J. Exp. BM. (1965), 4*. 373-378 3-73 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE BY K. G. DAVEY Institute of Parasitology,
Water, air and light : Arnold Rikli ( )
 Water, air and light : Arnold Rikli (1823-1906) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Zupanic-Slavec, Zvonka / Toplak, Cirila Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band
Water, air and light : Arnold Rikli (1823-1906) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Zupanic-Slavec, Zvonka / Toplak, Cirila Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band
DDT poisoning in the pomace fly, Drosophila melanog aster Meigen. One experiment was on the development of several strains of flies under
 Some Laboratory Experiments on Resistance of the Pomace Fly to DDT Poisoning Philip W. Berg, Purdue University Introduction During 1951 the author carried out two experiments on resistance to DDT poisoning
Some Laboratory Experiments on Resistance of the Pomace Fly to DDT Poisoning Philip W. Berg, Purdue University Introduction During 1951 the author carried out two experiments on resistance to DDT poisoning
Comparison of specific and relative alanine and aspartate aminotransferases of "Trypanosoma brucei" subgroup trypanosomes
 Comparison of specific and relative alanine and aspartate aminotransferases of "Trypanosoma brucei" subgroup trypanosomes Autor(en): Steiger, R. / Krassner, S.M. / Jenni, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
Comparison of specific and relative alanine and aspartate aminotransferases of "Trypanosoma brucei" subgroup trypanosomes Autor(en): Steiger, R. / Krassner, S.M. / Jenni, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf
 ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 Ã 1.1 The olive fly, Bactrocera oleae... 4 Ã 1.2 Medfly transformation... 4 Ã 1.3 Field
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 Ã 1.1 The olive fly, Bactrocera oleae... 4 Ã 1.2 Medfly transformation... 4 Ã 1.3 Field
Entomology Unit FAO/IAEA Agriculture & Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf
 Entomology Unit FAO/IAEA Agriculture & Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...3 1.1 A New Medfly Genetic Sexing Strain and Chromosome Inversions...4 1.2 Field Cages for
Entomology Unit FAO/IAEA Agriculture & Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...3 1.1 A New Medfly Genetic Sexing Strain and Chromosome Inversions...4 1.2 Field Cages for
Rearing Fopius arisanus (Sonan) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in Mediterranean Fruit Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae)
 Rearing Proc. Hawaiian Fopius Entomol. arisanus in Soc. Medfly (2007) 39:121 126 121 Rearing Fopius arisanus (Sonan) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in Mediterranean Fruit Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Ernest J.
Rearing Proc. Hawaiian Fopius Entomol. arisanus in Soc. Medfly (2007) 39:121 126 121 Rearing Fopius arisanus (Sonan) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in Mediterranean Fruit Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Ernest J.
61A the flies were mass-mated in half-pint culture bottles containing the usual
 VOL. 43, 1957 ZOOLOGY: HILDRETH AND CARSON 175 for each W the canonical function on IF is analytic on (W);, it follows that the canonical function on 5Y is analytic everywhere on D u e. Clearly also the
VOL. 43, 1957 ZOOLOGY: HILDRETH AND CARSON 175 for each W the canonical function on IF is analytic on (W);, it follows that the canonical function on 5Y is analytic everywhere on D u e. Clearly also the
L.A. Buscarlet'; Beatrice Aminian-; and Chaza Bali!
 EFFECT OF IRRADIATION AND EXPOSURE TO NITROGEN ON MORTALITY OF ADULTS OF TRIBOLIUMCONFUSUMJ. Du V. L.A. Buscarlet'; Beatrice Aminian-; and Chaza Bali! ICentre d'etude Nucleatre de Cadarache, Saint Paullez
EFFECT OF IRRADIATION AND EXPOSURE TO NITROGEN ON MORTALITY OF ADULTS OF TRIBOLIUMCONFUSUMJ. Du V. L.A. Buscarlet'; Beatrice Aminian-; and Chaza Bali! ICentre d'etude Nucleatre de Cadarache, Saint Paullez
Study on the Survival and Reproductive Performance of Sterile Male Glossina pallidipes
 International Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2016; 4(3): 13-21 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbse doi: 10.11648/j.ijbse.20160403.11 ISSN: 2376-7227 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7235 (Online)
International Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2016; 4(3): 13-21 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbse doi: 10.11648/j.ijbse.20160403.11 ISSN: 2376-7227 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7235 (Online)
DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI
 f. exp. Biol. (1975). 63, 381-390 381 ^t*a 6 figures Printed in Great Britain DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI BY J. D. GEE* University of Cambridge, Department of Zoology, Downing Street, Cambridge
f. exp. Biol. (1975). 63, 381-390 381 ^t*a 6 figures Printed in Great Britain DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI BY J. D. GEE* University of Cambridge, Department of Zoology, Downing Street, Cambridge
F the mating activity and fertility in Ilrosophilo melanogaster. NovITSKY
 HERE 51-5 MATING AND FERTILITY PATTERN OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER MALES EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT T E M PARATUR ES By INGERID KVELLAND INSTITUTE OF GENERAL GENETICS, UNIVERSITY OF OSLO, BLINDERN, NORWAY (Received
HERE 51-5 MATING AND FERTILITY PATTERN OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER MALES EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT T E M PARATUR ES By INGERID KVELLAND INSTITUTE OF GENERAL GENETICS, UNIVERSITY OF OSLO, BLINDERN, NORWAY (Received
Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats. Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer
 1 Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer 2 Presentation overview Background to the study Challenges Why it s not as simple as fitting a trend line through data
1 Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer 2 Presentation overview Background to the study Challenges Why it s not as simple as fitting a trend line through data
Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta State, Nigeria
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
SD4. SD 4 Anfang Monoblockventile P. Position 1. Position 0 (45.5) Position
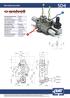 SD 4 nfang SD4 Nominale Durchflussmenge 45 l/min Max. rbeitsdruck 5 bar Max. Druck am nschluss 5 bar Interne Leckage () zu bei p=bar und 4 C 3 cm3/min Hydraulikflüssigkeit Mineralöl Öltemperatur mit NR
SD 4 nfang SD4 Nominale Durchflussmenge 45 l/min Max. rbeitsdruck 5 bar Max. Druck am nschluss 5 bar Interne Leckage () zu bei p=bar und 4 C 3 cm3/min Hydraulikflüssigkeit Mineralöl Öltemperatur mit NR
Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR
 Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR 32 nd International Scientific Council for Trypanosomiasis Research and Control (ISCTRC), September
Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR 32 nd International Scientific Council for Trypanosomiasis Research and Control (ISCTRC), September
Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis
 Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 3 Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis Tsetse colonies at ILRAD Some research results Tsetse characteristics
Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 3 Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis Tsetse colonies at ILRAD Some research results Tsetse characteristics
Aufklärung Nr. 9: Hepatitis A Englisch / English
 On protective immunization against hepatitis A Hepatitis A is an acute liver inflammation, which is caused by infection with the hepatitis A virus (HAV). This pathogen is excreted in the stool of an infected
On protective immunization against hepatitis A Hepatitis A is an acute liver inflammation, which is caused by infection with the hepatitis A virus (HAV). This pathogen is excreted in the stool of an infected
Trypanosomiasis. By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy
 Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Are experimental economists prone to framing effects? A natural field experiment Gächter, Simon; Orzen, Henrik; Renner, Elke; Starmer, Chris
 www.ssoar.info Are experimental economists prone to framing effects? A natural field experiment Gächter, Simon; Orzen, Henrik; Renner, Elke; Starmer, Chris Postprint / Postprint Zeitschriftenartikel /
www.ssoar.info Are experimental economists prone to framing effects? A natural field experiment Gächter, Simon; Orzen, Henrik; Renner, Elke; Starmer, Chris Postprint / Postprint Zeitschriftenartikel /
The effect of light exposure on Drosophila melanogaster survival
 The effect of light exposure on Drosophila melanogaster survival Grace M. Chen, Caroline M. Kim, Steve Lee, Elsie Ng ABSTRACT The purpose of our study was to observe how exposure to light affects the survival
The effect of light exposure on Drosophila melanogaster survival Grace M. Chen, Caroline M. Kim, Steve Lee, Elsie Ng ABSTRACT The purpose of our study was to observe how exposure to light affects the survival
German Collegiate Programming Contest
 German Collegiate Programming Contest GCPC Jury gcpc@nwerc.eu 2. Juli 2011 GCPC Jury German Collegiate Programming Contest 2. Juli 2011 1 / 23 jury sample solutions Problem min. LOC max. LOC Faculty Dividing
German Collegiate Programming Contest GCPC Jury gcpc@nwerc.eu 2. Juli 2011 GCPC Jury German Collegiate Programming Contest 2. Juli 2011 1 / 23 jury sample solutions Problem min. LOC max. LOC Faculty Dividing
Sterile insect technique From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 7 Sterile insect technique From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The sterile insect technique (SIT) [1][2] is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects
Page 1 of 7 Sterile insect technique From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The sterile insect technique (SIT) [1][2] is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects
A comparison between factor analysis and smallest space analysis of the comprehensive scoring system of the Rorschach Cohen, Arie
 www.ssoar.info A comparison between factor analysis and smallest space analysis of the comprehensive scoring system of the Rorschach Cohen, Arie Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Sammelwerksbeitrag
www.ssoar.info A comparison between factor analysis and smallest space analysis of the comprehensive scoring system of the Rorschach Cohen, Arie Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Sammelwerksbeitrag
Mass rearing lepidoptera with persistent baculovirus infections. Insect population dynamics are impacted by lethal and chronic infections
 Mass rearing lepidoptera with persistent baculovirus infections Helen Hesketh & Rosie Hails Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) Wallingford, UK Natural Environment
Mass rearing lepidoptera with persistent baculovirus infections Helen Hesketh & Rosie Hails Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) Wallingford, UK Natural Environment
Mating affects egg maturation in Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae)
 June, 24 Journal of Vector Ecology 135 Mating affects egg maturation in Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae) Marc J. Klowden and Richard C. Russell Division of Entomology, University of Idaho,
June, 24 Journal of Vector Ecology 135 Mating affects egg maturation in Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae) Marc J. Klowden and Richard C. Russell Division of Entomology, University of Idaho,
Title of the Co-ordinated Research Project: Improving Sterile Male Performance in Fruit Fly Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) Programmes
 CRP No. 1327 (D41020) CRP Evaluation Report Research Contracts System Title of the Co-ordinated Research Project: Improving Sterile Male Performance in Fruit Fly Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) Programmes
CRP No. 1327 (D41020) CRP Evaluation Report Research Contracts System Title of the Co-ordinated Research Project: Improving Sterile Male Performance in Fruit Fly Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) Programmes
Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Ergotherapie
 Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Ergotherapie Ressourcen zur Evidenzbasierung in den Gesundheitsfachberufen Nutzerspezifische Cochrane Reviews Juli bis September 2018 Die Cochrane Deutschland Stiftung
Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Ergotherapie Ressourcen zur Evidenzbasierung in den Gesundheitsfachberufen Nutzerspezifische Cochrane Reviews Juli bis September 2018 Die Cochrane Deutschland Stiftung
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf
 ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Cryopreservation Techniques for Medfly Embryos 4 1.2 Liquid Diet for Medfly Genetic
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Seibersdorf Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Cryopreservation Techniques for Medfly Embryos 4 1.2 Liquid Diet for Medfly Genetic
Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 35(3). p105-
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Treatment of Wolbachia pipientis In Hydrochloride and the Change of Cyt Nagasaki Strain of Culex pipiens mo Suenaga, Osamu Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Treatment of Wolbachia pipientis In Hydrochloride and the Change of Cyt Nagasaki Strain of Culex pipiens mo Suenaga, Osamu Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine
321Kochen.tv Display/Video Video Video 7TV Video Video Video Video. 90 Min
 321Kochen.tv http://www.321kochen.tv/ / 7 http://www.7tv.de/ 90 Min http://www.90min.com/de Autoplenum http://www.autoplenum.de/ http://www.12autowerkstatt.de/ http://www.12gebrauchtwagen.de/ http://www.12neuwagen.de/
321Kochen.tv http://www.321kochen.tv/ / 7 http://www.7tv.de/ 90 Min http://www.90min.com/de Autoplenum http://www.autoplenum.de/ http://www.12autowerkstatt.de/ http://www.12gebrauchtwagen.de/ http://www.12neuwagen.de/
SEX RATIO MANIPULATION BY THE PARASITOID WASP MUSCIDIFURAX RAPTOR IN RESPONSE TO HOST SIZE
 This is an electronic version of an article published as Seidl, S.E. and B.H. King. 1993. Sex ratio response to host size in the parasitoid wasp Muscidifurax raptor. Evolution 47:1876-1882. SEX RATIO MANIPULATION
This is an electronic version of an article published as Seidl, S.E. and B.H. King. 1993. Sex ratio response to host size in the parasitoid wasp Muscidifurax raptor. Evolution 47:1876-1882. SEX RATIO MANIPULATION
licarsisalis, and its Adaptability for Laboratory Tests1
 Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 533 Colonization of the Grass Webworm, Herpetogramma licarsisalis, and its Adaptability for Laboratory Tests1 H. Tashiro2 COLLEGE OF TROPICAL AGRICULTURE, UNIVERSITY OF
Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 533 Colonization of the Grass Webworm, Herpetogramma licarsisalis, and its Adaptability for Laboratory Tests1 H. Tashiro2 COLLEGE OF TROPICAL AGRICULTURE, UNIVERSITY OF
Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster
 Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster Genetics: Fall 2012 Joshua Hanau Introduction: An experiment was performed in order to determine the presence and degree of gene linkage in Drosophila Melanogaster.
Linkage Mapping in Drosophila Melanogaster Genetics: Fall 2012 Joshua Hanau Introduction: An experiment was performed in order to determine the presence and degree of gene linkage in Drosophila Melanogaster.
Impact of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Virus Infection on the Mating Success of Male Glossina pallidipes: Consequences for the Sterile Insect Technique
 Impact of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Virus Infection on the Mating Success of Male Glossina pallidipes: Consequences for the Sterile Insect Technique Gratian N. Mutika 1, Carmen Marin 1, Andrew G. Parker
Impact of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Virus Infection on the Mating Success of Male Glossina pallidipes: Consequences for the Sterile Insect Technique Gratian N. Mutika 1, Carmen Marin 1, Andrew G. Parker
A New Eye Mutant, apricot, of the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis
 Vol. 31, December 31,1992 165 A New Eye Mutant, apricot, of the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae), and its Mating Preference RATANA PORAMARCOM1 - ABSTRACT. Genetic
Vol. 31, December 31,1992 165 A New Eye Mutant, apricot, of the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae), and its Mating Preference RATANA PORAMARCOM1 - ABSTRACT. Genetic
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT ANNUAL REPORT 2005
 ENTOMOLOGY UNIT ANNUAL REPORT 2005 International Atomic Energy Agency FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Agency s Laboratories, Seibersdorf - 1 - Table of Contents 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY...
ENTOMOLOGY UNIT ANNUAL REPORT 2005 International Atomic Energy Agency FAO/IAEA Agriculture and Biotechnology Laboratory Agency s Laboratories, Seibersdorf - 1 - Table of Contents 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY...
Female mating failure and the failure of mating in sterile insect programs
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Publications from USDA-ARS / UNL Faculty U.S. Department of Agriculture: Agricultural Research Service, Lincoln, Nebraska
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Publications from USDA-ARS / UNL Faculty U.S. Department of Agriculture: Agricultural Research Service, Lincoln, Nebraska
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Competitive mating in Drosophila melanogaster Citation for published version: Sharp, PM 1982, 'Competitive mating in Drosophila melanogaster' Genetics Research, vol 40, no.
Edinburgh Research Explorer Competitive mating in Drosophila melanogaster Citation for published version: Sharp, PM 1982, 'Competitive mating in Drosophila melanogaster' Genetics Research, vol 40, no.
Rezension: Timothy A. Brown, 2006: Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research Schmidt, Peter
 www.ssoar.info Rezension: Timothy A. Brown, 2006: Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research Schmidt, Peter Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Rezension / review Zur Verfügung gestellt
www.ssoar.info Rezension: Timothy A. Brown, 2006: Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research Schmidt, Peter Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Rezension / review Zur Verfügung gestellt
Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly
 1 Section 1 Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly 1.1. Introduction The objective of this section is to provide essential information for the subsequent two sections, which give guidelines for conducting
1 Section 1 Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly 1.1. Introduction The objective of this section is to provide essential information for the subsequent two sections, which give guidelines for conducting
Examination of wild mammals as a potential reservoir for "T. rhodesiense"
 Exmintion of wild mmmls s potentil reservoir for "T. rhodesiense" Objekttyp: Chpter Zeitschrift: Act Tropic Bnd (Jhr): 28 (1971) Heft 3 PDF erstellt m: 27.6.218 Nutzungsbedingungen Die ETH-Bibliothek ist
Exmintion of wild mmmls s potentil reservoir for "T. rhodesiense" Objekttyp: Chpter Zeitschrift: Act Tropic Bnd (Jhr): 28 (1971) Heft 3 PDF erstellt m: 27.6.218 Nutzungsbedingungen Die ETH-Bibliothek ist
inside the insectary were 23.5±1.2 and 25.7±0.1oC and 74.5±0.4 and
 Vol. XXII, No., August, 75 37 Flight Mill and Stroboscopic Studies of Oriental Fruit Flies and Melon Flies, Including Observations of Mediterranean Fruit Flies'» 3- J. L. Sharp,5 Derrell L. Chambers,6
Vol. XXII, No., August, 75 37 Flight Mill and Stroboscopic Studies of Oriental Fruit Flies and Melon Flies, Including Observations of Mediterranean Fruit Flies'» 3- J. L. Sharp,5 Derrell L. Chambers,6
(Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a Larval. (Diptera: Tephritidae)
 Vol. 29, November 30,1989 41 Insectary Production of Biosteres tryoni (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a Larval Parasitoid of Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae) MOHSEN M. RAMADAN,1
Vol. 29, November 30,1989 41 Insectary Production of Biosteres tryoni (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a Larval Parasitoid of Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae) MOHSEN M. RAMADAN,1
Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome
 Page 1 of 6 Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome Adly M. M. Abd-Alla, Henry M. Kariithi, Abdul
Page 1 of 6 Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome Adly M. M. Abd-Alla, Henry M. Kariithi, Abdul
Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome
 Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome Adly M. M. Abd-Alla 1 *., Henry M. Kariithi 1,2., Abdul Hasim
Managing Hytrosavirus Infections in Glossina pallidipes Colonies: Feeding Regime Affects the Prevalence of Salivary Gland Hypertrophy Syndrome Adly M. M. Abd-Alla 1 *., Henry M. Kariithi 1,2., Abdul Hasim
1. Introduction 1.1 SCOPE
 1 1. Introduction 1.1 SCOPE This guidance represents the recommendations, reached by consensus of an international group of experts, on the standard procedures for the packing, shipping, holding and release
1 1. Introduction 1.1 SCOPE This guidance represents the recommendations, reached by consensus of an international group of experts, on the standard procedures for the packing, shipping, holding and release
Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Extraction of the Diffusible Substances Concerned. Kenneth V. Thimann, and G. W. Beadle
 Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Extraction of the Diffusible Substances Concerned Kenneth V. Thimann, and G. W. Beadle PNAS 1937;23;143-146 doi:10.1073/pnas.23.3.143 This information is current
Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Extraction of the Diffusible Substances Concerned Kenneth V. Thimann, and G. W. Beadle PNAS 1937;23;143-146 doi:10.1073/pnas.23.3.143 This information is current
Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives
 Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives Mike Lehane Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine Total Papers Published 44 new papers published with
Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives Mike Lehane Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine Total Papers Published 44 new papers published with
Aymeé Michel de Arévalo Phytosterol enrichment in vegetable oil by high pressure processing
 Berichte aus der Verfahrenstechnik Aymeé Michel de Arévalo Phytosterol enrichment in vegetable oil by high pressure processing Shaker Verlag Aachen 2009 Bibliographic information published by the Deutsche
Berichte aus der Verfahrenstechnik Aymeé Michel de Arévalo Phytosterol enrichment in vegetable oil by high pressure processing Shaker Verlag Aachen 2009 Bibliographic information published by the Deutsche
University of Groningen. Molecular mechanisms of synaptic plasticity Nijholt, Ingrid
 University of Groningen Molecular mechanisms of synaptic plasticity Nijholt, Ingrid IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Molecular mechanisms of synaptic plasticity Nijholt, Ingrid IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
GUIDELINES FOR AUTHORS CAMERA-READY MANUSCRIPTS (Instructions, layout and examples) TITLE OF ARTICLE
 GUIDELINES FOR AUTHORS CAMERA-READY MANUSCRIPTS (Instructions, layout and examples) The font size should be 8 pts. TITLE OF ARTICLE AUTHOR NAME(S) Author Affiliation(s) SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION These instructions
GUIDELINES FOR AUTHORS CAMERA-READY MANUSCRIPTS (Instructions, layout and examples) The font size should be 8 pts. TITLE OF ARTICLE AUTHOR NAME(S) Author Affiliation(s) SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION These instructions
Standard Operating Procedures for Preparing and Handling Sterile Male Tsetse flies for Release
 Standard Operating Procedures for Preparing and Handling Sterile Male Tsetse flies for Release Edited by: Rafa Argiles-Herrero and Stephen G. A. Leak 2016 Page 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 4 2. Feeding
Standard Operating Procedures for Preparing and Handling Sterile Male Tsetse flies for Release Edited by: Rafa Argiles-Herrero and Stephen G. A. Leak 2016 Page 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 4 2. Feeding
INDUCTION OF DOMINANT LETHAL MUTATIONS IN INSECT OOCYTES AND SPERM BY GAMMA RAYS AND AN ALKYLATING AGENT: DOSE-RESPONSE AND JOINT ACTION STUDIES
 INDUCTION OF DOMINANT LETHAL MUTATIONS IN INSECT OOCYTES AND SPERM BY GAMMA RAYS AND AN ALKYLATING AGENT: DOSE-RESPONSE AND JOINT ACTION STUDIES LEO E. LACHANCE' AND MAXWELL M. CRYSTAL Entomology Research
INDUCTION OF DOMINANT LETHAL MUTATIONS IN INSECT OOCYTES AND SPERM BY GAMMA RAYS AND AN ALKYLATING AGENT: DOSE-RESPONSE AND JOINT ACTION STUDIES LEO E. LACHANCE' AND MAXWELL M. CRYSTAL Entomology Research
guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH
 1 ISSN 1810-0708 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES 1 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines
1 ISSN 1810-0708 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES 1 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines
econstor Make Your Publications Visible.
 econstor Make Your Publications Visible. A Service of Wirtschaft Centre zbwleibniz-informationszentrum Economics Desmet, Pieter; Engel, Christoph Working Paper People are conditional rule followers Preprints
econstor Make Your Publications Visible. A Service of Wirtschaft Centre zbwleibniz-informationszentrum Economics Desmet, Pieter; Engel, Christoph Working Paper People are conditional rule followers Preprints
Lab 7 Heredity. Is there a fly in here?
 Lab 7 Heredity Is there a fly in here? Note: This lab is another old lab from the previous manual, however you ll need to write it into your lab notebooks as an informal report (not a packet). The Background
Lab 7 Heredity Is there a fly in here? Note: This lab is another old lab from the previous manual, however you ll need to write it into your lab notebooks as an informal report (not a packet). The Background
Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Physiotherapie
 Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Physiotherapie Ressourcen zur Evidenzbasierung in den Gesundheitsfachberufen Nutzerspezifische Cochrane Reviews Juli bis September 2018 Die Cochrane Deutschland Stiftung
Cochrane Reviews für den Fachbereich Physiotherapie Ressourcen zur Evidenzbasierung in den Gesundheitsfachberufen Nutzerspezifische Cochrane Reviews Juli bis September 2018 Die Cochrane Deutschland Stiftung
Morphological method for sexing anopheline larvae
 J Vector Borne Dis 44, December 2007, pp. 245 249 Morphological method for sexing anopheline larvae S.N. Emami a, H. Vatandoost a, M.A. Oshaghi a, F. Mohtarami a, E. Javadian a & A. Raeisi b a Department
J Vector Borne Dis 44, December 2007, pp. 245 249 Morphological method for sexing anopheline larvae S.N. Emami a, H. Vatandoost a, M.A. Oshaghi a, F. Mohtarami a, E. Javadian a & A. Raeisi b a Department
Aufklärung Nr. 27: Pneumokokken (Konjugat) Englisch / English
 On protective immunization against pneumococcal diseases in infants/small children with conjugate vaccine Pneumococcal infections are caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. There are more than 90
On protective immunization against pneumococcal diseases in infants/small children with conjugate vaccine Pneumococcal infections are caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. There are more than 90
