Kisspeptin, its Localization and Physiological Functions in Primates: A Review
|
|
|
- Melvyn Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World Journal of Zoology 10 (2): , 2015 ISSN IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: /idosi.wjz Kisspeptin, its Localization and Physiological Functions in Primates: A Review Ghulam Nabi, Hazir Muhammad, Sardar Ali and Sami Ullah 1 Department of Animal Sciences, Laboratory Reproductive Neuro-Endocrinolgy, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan 2 Department of Biotechnology, University of Malakand, Pakistan 3 Department of Microbiology, KUST, Pakistan 4 Department of Zoology, Islamia College University of Peshawar, Pakistan Abstract: Neuropeptide kisspeptin is considered a key regulator of reproductive system and a gate keeper of puberty. It expresses in a wide range of animal species both in the brain and other parts of the body. It is encoded by KISS1 gene and acts through GPR54 receptor. Kisspeptin has a wide range of physiological functions in the body. Inactivating or precocious activating mutations of either KISS1 or KISS1R gene can leads to serious health consequences. This review focuses on the brief introduction, localization and various physiological functions of kisspeptin in mammals. Key words: Kisspeptin Kiss1 Neuropeptide Puberty INTRODUCTION [13], neuromodulation [14-15], muscular contraction [16] and cardio-excitatory function [17-19]. Neuropeptide kisspeptin is a key regulator of Immunocytochemistry has shown the expression of reproductive system. Kisspeptin is encoded by a these peptides in vertebrates like amphibians, fishes metastasis suppressor gene called KISS1 [1]. Kisspeptin and birds [20]. In mammals RF-amide has a pivotal role in is found in human plasma andits concentration increases neuroendocrine functions [20-22]. during gestation [2]. Kisspeptin acts as a tumor Kisspeptin-54, -14, -13 and -10 (indicating the number metastasis suppressor [3].It contains 145-amino acids and of amino acids) are the members of kisspeptin family. belongs to RF-amide family of neuropeptides [1, 3-5]. All these are encoded by KISS1 gene. The precursor KISS1 is present on long arm of chromosome1 at the molecule called preprokisspeptin is enzymatically split position of 1q32. KISS1 gene manufactures a 145- amino into smaller naturally active C-terminal amide group in acids precursor molecule. A 54-amino acids kisspeptin post-translational changes resulting into kisspeptins. (kisspeptin-54), the product of proteolytic processof All the kisspeptin family members possess equal efficacy precursor molecule, is crucial for mammalian puberty and and affinity for kisspeptin receptor. This is because all the fertility. Lack of KISS1 or kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R) members possess a C terminal decapeptide which is genes causes hypogonadotropichypogonadism in essential for binding and provocation of kisspeptin humans and rodents [6]. Further cleavage of kisspeptin-54 receptor [3-5]. Kisspeptin carried out its function via a leads to the synthesis of kisspeptin-14, -13 and -10. They receptor called G- protein couple receptor (GPR54) or are differentiated by peptide length [7-10]. AXOR12 [3, 5]. In rat brain tissues an orphan G-protein The RF-amide neuropeptides terminate in -Arg-Phe- couple receptor (GPR54) was recognized for kisspeptin NH2motif [11]. RF-amides were first recognized in [23]. Latter researches identified kisspeptin receptors in Mollusca s. Latter on it was found also in other other species [24]. According to the rules of nomenclature vertebrates that peptides containing RF-amide motif at committee, International Union of Basic and Clinical their C-terminus were present [12]. RF-amide in Pharmacology (NC-IUPHAR) suggests the abbreviation, invertebrates has many functions such as locomotion KISS1R for kisspeptin receptor and KISS1 for the peptide. Corresponding Author: Ghulam Nabi, Department of Animal Sciences, Laboratory Reproductive Neuro-endocrinolgy, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan. Mob:
2 Gene names should be italicized and consistent with the Human Genome Organization (HUGO), KISS1 to the peptide gene and KISSIR to the receptor gene, with lower case letter used for nonhuman species [24-25]. Kisspeptin Distribution: Using specific antibodies, cdna and RNA probes against kisspeptin, it was found that kisspeptin cells were present in the arcuate (ARC), preoptic area (POA) and median eminence (ME) of humans [26-27] and rhesus monkey, while bed nucleus of the striaterminalis (BNST) only in rhesus monkey [28-29]. In mouse these cells were located in the ARC, POA, rostral periventricular region of the third ventricle (RP3V), dorsal medial nucleus of hypothalamus (DMH), medial amygdala and BNST [30-31]. In rats, kisspeptin cells were localized to ARC, RP3V, ventro medial hypothalamus (VMH), medial amygdala and BNST [32-33]. In hamsters only in the ARC and RP3V [34], while in the guinea pig, kisspeptin cells were distributed in ARC, RP3V and DMH [35]. Similarly kisspeptin cells also expressed in the ARC, POA, DMH and VMH of sheep [36], goat (except DMH and VMH) [37] and horse (except VMH) [38]. In the mouse kisspeptin cells are also present in the neocortex, insular cortex, piriform cortex and lateral septum [30-31]. Similarly, in sheep kisspeptin cells are located in intermediate and caudal periventricular area [35]. On the other hand, kisspeptin fibers are also expressed in the ARC and POA of human [27], rhesus monkey [28], rat [32], mouse [31], hamster [39], guinea pig [35], sheep [40,41], goat [37] and horse [38]. In human beside ARC and POA, kisspeptin fibers are also expressed in RP3V, external and internal median eminence, PVN, VMH, DMH and lateral septum [27]. In rats kisspeptins existence has been observed in various parts of spinal cord and medulla oblongata suggesting, its role in controlling autonomic and sensory functions [42]. Kisspeptin expression is also present in human ganglionic cells and rat superior cervical ganglia [43]. Kisspeptin is also highly expressed in numerous peripheral regions including, placenta of rat and human [44], pituitary, small intestine, thymus, spleen, lung, stomach, kidney, liver, adrenal gland, vessels, adipose tissue [1, 4-5, 45-47] ovary [48], testis [3], pancreas [49], endothelial cells of the aorta, coronary artery and umbilical vein [50]. In mammals major population of kisspeptin cells have been observed in different areas of hypothalamus [51]. In rodents entire kisspeptin cells are present in rostral-caudal region of hypothalamus [52-53]. In sheep and monkeys, kisspeptin cells are frequently localized to caudal and middle region [40, 54]. Kisspeptin Receptor Distribution: Kisspeptin receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor. It belongs to the sub-family of Gq/11 proteins [4,5]. In human the KISSIR is confined to chromosomal site 19p13.3 [3]. Its mrna expressions are found in medial basal hypothalamus (MBH), POA, ARC, hypothalamus, medial amygdala, locus coeruleus, thalamus, substantial nigra, cingulate gyrus and anterior pituitary gland [4]. KISS1R is also expressed in testes especially in seminiferous tubules, round spermatocytes, Sertoli cells and spermatids but absent in Leydig cells, suggesting a role of kisspeptin in spermatogenesis via paracrine/autocrine action [55]. In human mature spermatozoa, kisspeptin and its receptors are located on equatorial section, neck region and slightly in mid- piece [56-58]. Kisspeptin Gene Regulation: Kisspeptin gene is mainly regulated by testosterone and estradiol feedback effects. Kisspeptin neurons in rodents are limited to anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) and ARC. Kiss1 gene expression in the ARC is suppressed by estradiol. In female and male mice kiss1mrna level is reduced by administering estradiol [59-60]. Similarly in female rats the level of Kiss1mRNA in ARC is negatively regulated by treating with progesterone and estradiol [53]. In the AVPV and ARC of female rat and mice, all kiss1 neurons express ERá [53, 61]. Ovarectomy in sheep stimulates the expression of kiss1 mrna and this effect is prevented by replacing estradiol [41, 62]. ERá and androgen receptor (AR) mediate negative feedback regulation of the kiss1gene in ARC of male mouse [60]. In male hypothalamus kiss1 mrna expression is regulated by testosterone. In castrated mice, testosterone treatment inhibits the rise of ARC kiss1 mrna. The expression of kiss1 mrna in AVPV is reduces by castration but is stimulated by testosterone [59]. In male AVPV and ARC most of the kisspeptin neurons co-express AR and ERá [59, 63]. In addition to gonadal steroids, some other hormones also influence kiss1 gene expression. Leptin stimulates the kisspeptin neurons of ARC nucleus. It has been reported that the expression of ARC kiss1 is low in male mice having no active leptin gene. On the other hand expression is restored partially by treating mice with leptin [53]. The expression of leptin receptor in AVPV kiss1 neuron is not observed however, in ARC it constitutes about forty two percent [53]. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) unlike leptin has no effects on ARC kiss1 gene but stimulates the expression of AVPV kiss1 gene [64]. In female rat, ghrelin increases the expression of ARC and AVPV kiss1gene but its receptor on kisspeptin neuron is 95
3 not reported [65]. In mice both of AVPV and ARC p a t i e n t s s u f f e r i n g f r o m kisspeptin neurons express melanocortin4 receptor idiophatichypogonadotropichypogonadism (IHH) [9, 81]. indicating some role in the regulations of kisspeptin A number of etiological factors were reported for IHH neurons [61]. such as, inactivating mutations in GnRH receptor genes, fibroblast growth factor receptor and Kal1 [82-83] but Mechanism of Action of Kisspeptin: Kisspeptin form a interestingly they account for sporadic and a subset of composite when binds to its G-protein coupled receptors, familial forms of IHH, indicating the correspondence of activating a series of cellular pathways. All this leads to other causative factors. In GPR54 gene, homozygous activations of phospholipase C (PLC-â) by releasing deletion of 155 nucleotides at the intron 4 exon 5 [81], intracellular calcium stores. After kisspeptin receptor substitution of homozygous Leu146Ser and heterozygous activations, other intracellular pathways includes mutations of X399Arg and Arg331X were responsible for accumulations of inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate, hydrolysis sporadic or familial form of IHH [9]. Similarly heterozygous of phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate, release of missense mutations at Arg297Leu and Cys223Arg [83] arachidonic acid and phosphorylation of extracellular and the homozygous insertion ( insC) were signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated reported as causative factors for IHH [84]. GPR54 gene protein kinases (MAPK) [4, 48] calcineurin and nuclear null mutations in mice were found to be a complete factor-kappa B (NF-kB) [48]. phenocopy of human patients, suggesting that GPR54 has a very indispensable role in mammalian reproduction Functions of Kisspeptin: Historically kisspeptin was [9, 85]. recognized as anti-metastatic in melanoma cells [3]. Later on, kisspeptin anti-metastatic activity was also reported CONCLUSION in the samples of thyroid cancer [66], hepatocellular cancer [67], bladder [68], stomach [69], esophagus [70], Kisspeptin regulates various physiological functions pancreatic [71], prostate [71], ovaries [72], breast [73] and in the body but most importantly it is considered as a lung cancer [74]. Kisspeptin also stimulates oxytocin central regulator of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) release [4]. In placenta, kisspeptin physiologically axis. Deactivating mutation of KISS1 or KISS1R leads to regulates trophoblast invasion [44]. Kisspeptin in delay puberty, IHH and fertility problems while activating hippocampus affects neural transmission, suggesting a mutations can cause precocious puberty which in case of role in neurogenesis and epilepsy [75]. On the basis of human lead to various social and biological problems. indirect evidence, kisspeptin role as a nociception and Further, therapeutic use of the kisspeptin and its visceral regulators has been suggested [76]. In human, antagonist against a wide range of the reproductive kisspeptin and its receptors were expressed in umbilical problems is not clear. vein, aorta and coronary artery and played a role as vasoconstrictor [50]. In mouse and human heart, REFERENCES kisspeptin increases intracellular calcium concentration, operating as a cardiovascular transmitter [77]. In mouse 1. Lee, J.H., M.E. Miele, D.J. Hicks, K.K. Phillips, and human pancreas, kisspeptin enhances insulin J.M. Trent, B.E. Weissman and D.R. Welch, secretion [49]. Similarly in rats, intravenous administration KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma of kisspeptin-10 increases insulin level [78]. KISS1 metastasis suppressor gene. Journal of National neurons in the hypothalamus are involved in conveying Cancer Institute, 88: metabolic information to the GnRH neurons that control 2. Horikoshi, Y., H. Matsumoto, Y. Takatsu, T. Ohtaki, reproductive axis [79]. Kisspeptin through autocrine or C. Kitada, S. Usuki and M. Fujino, Dramatical paracrine mechanisms may have a role in modulation of elevation of plasma metastin concentrations in the sympathetic function [43]. KISS1R is detected in human pregnancy: metastin as a novel placentahuman Leydig cells and also in human sperm and its direct derived hormone in humans. Journal of Clinical and intra-testicular action has been determined [80]. Endocrinology Metabolism, 88: Ohtaki, T., Y. Shintani, S. Honda, H. Matsumoto, Kisspeptin and Reproduction: The essential role of A. Hori, K. Kanehashi, Y. Terao, S. Kumano, Y. kisspeptin and GPR54 in the control of reproduction Takatsu et al., 2001 Metastasis suppressor gene evolved late in During that time, two independents KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-proteinresearch group observed loss of function mutations in coupled receptor. Nature, 411:
4 4. Kotani, M., M. Detheux, A. Vandenbogaerde, 12. Chartrel, N., C. Dujardin, J. Leprince, L. Desrues, D. Communi, J.M. Vanderwinden, P.E. Le, S. Brezillon, M.C. Tonon, E. Cellier, T. Jouenne, G. Simonnet and R. Tyldesley, N. Suarez-Huerta, F. Vandeput, H. Vaudry, Isolation, characterization and C. Blanpain, S.N. Schiffmann, G. Vassart and distribution of a novel neuropeptide, Rana-RFamide M. Parmentier, The metastasis suppressor (R-RFa) in the brain of the European green frog gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural Ranaesculenta. Journal of Comparative Neurology, ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled 448: receptor GPR54. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 13. Nelson, L.S., M.L. Rosoff and C. Li, Disruption 276: of a neuropeptide gene, flp-1, causes multiple 5. Muir, A.I., L. Chamberlain, N.A. Elshourbagy, behavioural defects in Caenorhabditiselegans. D. Michalovich, D.J. Moore, A. Calamari, Science, 281: P.G. Szekeres, H.M. Sarau, J.K. Chambers, 14. Cottrell, G.A., L.P. Schot and G.J. Dockray, P. Murdock, K. Steplewski, U. Shabon, J.E. Miller, Identification and probable role of a single neuron S.E. Middleton, J.G. Darker, C.G. Larminie, S. Wilson, containing the neuropeptide Helix FMRF-amide. D.J. Bergsma, P. Emson, R. Faull, K.L. Philpott and Nature, 304: D.C. Harrison, AXOR12, a novel human G 15. Askwith, C.C., C.C. Cheng, M. Ikuma, C. Benson, protein-coupled receptor, activated by the M.P. Price and M.J. Welsh, Neuropeptide FF peptide KiSS-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, and FMRF amide potentiate acid-evoked currents 276: from sensory neurons and proton-gateddeg/ena C 6. Terasawa, E., K.A. Guerriero and T.M. Plant, channels. Neurons, 26: kisspeptin and puberty in mammals. In: Kauffman, AS 16. Bowman, J.W., A.R. Friedman, A.D. Thompson, and Smith, JT (eds). Kisspeptin Signaling in A.K. Ichhpurani, M.F. Kellman, N. Marks, A.G. Maule Reproductive Biology. Advance in Experimental and T.G. Geary, Structure-activity relationships Medical Biololgy, 784: of KNEFI RFamide (AF1), a nematode FMRFamide- 7. West, A., P.J. Vojta and D.R. Welch, related peptide, on Ascarissuum muscle. Peptides, Chromosome localization and genomic structure of 17: the KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor gene (KISS1). 17. Koch, G., M.L. Chen, R. Sharla and R.H. Walker, Genomics, 54: The actions of neuroactive peptides on the isolated 8. Clements, M.K, T.P. McDonald, R. Wang, G. Xie, heart of the giant African snail (Achatinafulica). B.F. O Dowd, S.R. George, C.P. Austin and Q. Liu, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiol., 106: FMRFamide-related neuropeptides are agonists 18. Lesser, W. and M.J. Greenberg, Cardiac of the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPR54. regulation by endogenous small cardioactive BiochemBiophys Res Commun, 284: peptides and FMRF-amide-related peptides in the 9. Seminara, S.B., S. Messager, E.E. Chatzidaki, snail Helix aspersa. Journal of Experimental Biology, R.R. Thresher, J.S. Acierno, J.K. Shagoury, Y. Bo- 178: Abbas, W. Kuohung, K.M. Schwinof, A.G. Hendrick, 19. Sakai, T., H. Satake, H. Minakata and M. Takeda, D. Zahn, J. Dixon, U.B. Kaiser, S.A. Slaugenhaupt, Characterization of crustacean cardio active J.F. Gusella, S. O Rahilly, M.B. Carlton, W.F. Crowley, peptide as a novel insect mid gut factor: S.A. Aparicio and W.H. Colledge, The GPR54 isolation, localization and stimulation of a- gene as a regulator of puberty. New England Journal amylase activity and gut contraction. Endocrinology, of Medicine, 349: : Tena-Sempere, M., Kisspeptins and the 20. Chartrel, N., F. Bruzzone, J. Leprince, H. Tollemer, metabolic control of reproduction: physiologic roles Y. Anouar, J.C. Do-Rego, I. Ségalas-Milazzo, and physiopathological implications. Annal of L. Guilhaudis, P. Cosette, T. Jouenne, G. Simonnet, Endocrinology, 71: M. Vallarino, J.C. Beauvillain, J. Costentin and 11. Dockray, G.J., The expanding family of RF H. Vaudry, Structure and functions of the novel amides peptides and their effects on feeding hypothalamic RFamide neuropeptides R-RFa and behavior. Experimental Physiology, 89(3): RFa in vertebrates. Peptides, 27:
5 21. Fukusumi, S., R. Fujii and S. Hinuma, Recent 30. Clarkson, J. and A.E. Herbison, Postnatal advances in mammalian RFamide peptides: the discovery and functional analyses of PrRP, RFRPs development of kisspeptin neurons in mouse hypothalamus; sexual dimorphism and projections to and QRFP. Peptides, 27: gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. 22. Tsutsui, K., G.E. Bentley, L.J. Kriegsfeld, T. Osugi, J.Y. Seong and H. Vaudry, Discovery and evolutionary history of gonadotrophin-inhibitory hormone and kisspeptin: new key neuropeptides Endocrinology, 147: Clarkson, J., X.D. detassigny, W.H. Colledge, A. Caraty and A.E. Herbison, 2009 Distribution of kisspeptin neurones in the adult female mouse brain. controlling reproduction. Journal of Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 21: Neuroendocrinology, 22: Lee, D.K., T. Nguyen, G.P. O'Neill, R. Cheng, Y. Liu, A.D. Howard, N. Coulombe, C.P. Tan, A.T. Tang- Nguyen, S.R. George and B.F. O'Dowd, Discovery of a receptor related to the galanin 32. Adachi, S., S. Yamada, Y. Takatsu, H. Matsui, M. Kinoshita, K. Takase, H. Matsui and K. Maeda, Involvement of anteroventral periventricular metastin/kisspeptin neurons in estrogen positive feedback action on luteinizing hormone release in receptors. FEBS Letter, 446: female rats. Journal of Reproduction and 24. Gottsch, M.L., D.K. Clifton and R.A. Steiner, Development, 53(2): From KISS1 to kisspeptins: A historical perspective 33. Kim, J., S.J. Semaan, D.K. Clifton, R.A. Steiner, and suggested nomenclature. Peptides, 30: 4-9. S. Dhamija and A.S. Kauffman, Regulation of 25. Kirby, H.R., J.M. Janet, H.C. William and Kiss1 expression by sex steroids in the amygdala of P.D. Anthony, International Union of Basic and the rat and mouse. Endocrinology, 152: Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVII. Kisspeptin receptor 34. Mason, A.O., T.J. Greives, M.A.L. Scotti, J. Levine, S. Frommeyer, E.D. Ketterson, G.E. Demas and nomenclature, distribution and functions. L.J. Kriegsfeld, Suppression of kisspeptin Pharmacology Review, 62: expression and gonadotropic axis sensitivity 26. Rometo, A.M., S.J. Krajewski, M.L. Voytko and following exposure to inhibitory day lengths in N.E. Rance, Hypertrophy and increased female Siberian hamsters. Hormone Behavior, kisspeptin gene expression in the hypothalamic 52: infundibular nucleus of postmenopausal women and 35. Bosch, M.A., C.H. Xue and O.K. Ronnekleiv, ovariectomized monkeys. Journal of Clinical Kisspeptin expression in guinea pig Endocrinology and Metabolism, 92: hypothalamus:effects of 17 beta-estradiol. Journal of 27. Hrabovszky, E., P. Ciofi, B. Vida, M.C. Horvath, Comprative Neurology, 520: E. Keller, A. Caraty, S.R. Bloom, M.A. Ghatei, 36. Ansel, L., M. Bolborea, A.H. Bentsen, P. Klosen, W.S. Dhillo, Z. Liposits and I. Kallo, The J.D. Mikkelsen and V. Simonneaux, kisspeptin system of the human hypothalamus: Differential regulation of Kiss1 expression by sexual dimorphism and relationship with melatonin and gonadal hormones in male and female gonadotropin releasing hormone and neurokininb Syrian hamsters. Journal of Biological Rhythms, neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 25(2): : Wakabayashi, Y., T. Nakada, K. Murata, S. Ohkura, 28. Ramaswamy, S., K.A. Guerriero, R.B. Gibbs and K. Mogi, V.M. Navarro, D.K. Clifton, Y. Mori, T.M. Plant, Structural interactions between H. Tsukamura, K. Maeda, R.A. Steiner and kisspeptin and GnRH neurons in the mediobasal H. Okamura, Neurokinin B and dynorphin A in hypothalamus of the male rhesus monkey kisspeptin neurons of the arcuate nucleus participate (Macacamulatta) as revealed by double in generation of periodic oscillation of neural activity immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. driving pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone Endocrinology, 149: Ramaswamy, S., S.B. Seminara, B. Ali, P. Ciofi, N.A. Amin and T.M. Plant, Neurokinin B stimulates GnRH release in the male monkey secretion in the goat. Journal of Neuroscience, 30: Decourt, C., Y. Tillet, A. Caraty, I. Franceschini and C. Briant, Kisspeptin immunoreactive neurons (Macaccamulatta) and is colocalized with in the equine hypothalamus interactions with GnRH kisspeptin in the arcuate nucleus. Endocrinology, 151: neuronal system. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 36:
6 39. Yeo, S.H. and A.E. Herbison, Projections of 49. Hauge-evans, A.C., C.C. Richardson, H.M. Milne, arcuate nucleus and rostral periventricular kisspeptin neurons in the adult female mouse brain. Endocrinology, 152 : Goodman, R.L., M.N. Lehman, J.T. Smith, L.M. Coolen, C.V.R. De Oliveira, M.R. Jafarzadehshirazi, A. Pereira, J. Iqbal, A. Caraty, P. Ciofi and I.J. Clarke, Kisspeptin neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the ewe express both dynorphin A and neurokinin B. Endocrinology, 148: Smith, JT Kisspeptin signaling in the brain: steroid regulation in the rodent and ewe. Brain Research Review, 57: Dun, S.L., G.C. Brailoiua, A. Parsons, J. Yang, Q. Zeng, X. Chen, J.K. Chang and N.J. Duna, Metastin-like immunoreactivity in the rat medulla oblongata and spinal cord. Neuroscience Letter, 335: Porzionato, A., G. Fenu, M. Ruciñski, V. Macchi, A. Montella, M.M. Costantino, K. Ludwik and R. De Caro, KISS1and KISS1R expression in the human and rat carotid body and superior cervical ganglion. European Journal of Histochemistrey, 55: Bilban, M., N. Ghaffari-Tabrizi, E. Hintermann, S. Bauer, S. Molzer, C. Zoratti and R. Malli, Kisspeptin-10, a KiSS-1/metastin derived decapeptide, is a physiological invasion inhibitor of primary human trophoblasts. Journal of Cell Science, 117: Nakamura, Y., S. Aoki, Y. Xing, H. Sasano and W.E. Rainey, Metastin stimulates aldosterone synthesis in human adrenal cells. Reproductive Science, 14: Brown, R.E., S.A. Imran and M. Wilkinson, KiSS-1 mrna in adipose tissue is regulated by sex hormones and food intake. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 281: Silvestre, R.A., E.M. Egido, R. Hernández and J. Marco, Kisspeptin-13 inhibits insulin secretion without affecting glucagon or somatostatin release: study in the perfused rat pancreas. Journal of Endocrinology, 196: Castellano, J.M., V.M. Navarro, R. Fernández- Fernández, J.P. Castaño, M.M. Malagón, E. Aguilar, C. Dieguez, P. Magni, L. Pinilla and M. Tena-Sempere, Ontogeny and mechanisms of action for the stimulatory effect of kisspeptin on gonadotropinreleasing hormone system of the rat. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, : M.R. Christie, SJ. Persaud and PM. Jones, A role for kisspeptin in islets function. Diabetologia, 49: Mead, J., J. Maguire, R.E. Kuc and A.P. Davenport, Kisspeptin sare novel potent vasoconstrictors in humans, with a discrete localization of their receptor, G protein-coupled receptor 54, to atherosclerosis-prone vessels. Endocrinology, 148: Lehman, M.N., L.M. Coolen and R.L. Goodman, Mini review: kisspeptin/neurokininbs/ dynorphin (KNDy) cells of the arcuate nucleus: a central node in the control of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion. Endocrinology, 151: Gottsch, M.L., M.J. Cunningham, J.T. Smith, S.M. Popa, B.V. Acohido, W.F. Crowley, S. Seminara, DK. Clifton and RA. Steiner, A role of kisspeptins in the regulation of gonadotropin secretion In the mouse. Endocrinology, 145: Smith, J.T., S.M. Popa, D.K. Clifton, G.E. Hoffman and R.A. Steiner, Kiss1 neurons in the forebrain as central processors for generating the preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge. Journal of Neuroscience, 26: Ramaswamy, S., R.B. Gibbs and T.M. Plant, Studies of the localisation of kisspeptin within the pituitary of the.rhesus monkey (Macacamulatta) and the effect of kisspeptin on the release of nongonadotropic pituitary hormones. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 21: Tariq, A.R., M. Shahab, I.J. Clarke, A. Pereira, J.T. Smith, S.H. Khan, J. Sultan, S. Javed and T. Anwar, Kiss1 and kiss1 receptor expression in the rhesus monkey testis: a possible local regulator of testicular function. Cent Eur J Biol8: Suarez, S.S, B. Marquez, T.P. Harris and J.C. Schimenti, Different regulatory systems operate in the mid piece and principal piece of the mammalian sperm flagellum. SocReprodFertilSuppl 65: BeduAddo, K., S. Costello, C. Harper, G. Machado- Oliveira, L. Lefievre, C. Ford, C. Barratt and S. Publicover, Mobilisation of stored calcium in the neck region of human sperm a mechanism for regulation of flagellar activity. International Journal of Developmental Biology, 52:
7 58. Publicover, S.J., L.C. Giojalas, M.E. Teves, G.S. de 68. Sanchez-Carbayo, M., T.J. Belbin, K. Scotlandi, Oliveira, A.A. Garcia, C.L. Barratt and C.V. Harper, Ca2+ signalling in the control of motility and guidance in mammalian sperm. Frontier Bioscience, 13: Smith, J.T., M.J. Cunningham, E.F. Rissman, D.F. Clifton and R.A. Steiner 2005 a Regulation of Kiss1 gene expression in the brain of the female mouse. Endocrinology 146: Smith, J.T., H.M. Dungan, E.A. Stoll, M.L. Gottsch, R.E. Braun, S.M. Eacker, D.K. Clifton and R.A. Steiner, 2005 b. Differential regulation of KiSS-1 mrna expression by sex steroids in the brain of the male mouse. Endocrinology, 146: Cravo, R.M., L.O. Margatho, S. Osborne-Lawrence, J. DonatoJr, S. Atkin, A.L. Bookout, S. Rovinsky, R. Frazão, C.E. Lee, L. Gautron, J.M. Zigman and C.F. Elias, Characterization of Kiss1 neurons using transgenic mouse models. Neuroscience, 173: Smith, J.T., C.M. Clay, A. Caraty and I.J. Clarke, KiSS-1 messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the hypothalamus of the ewe is regulated by sex steroids and season. Endocrinology, 148: Clarkson, J., S. Shamas, S. Mallinson and A.E. Herbison, Gonadal steroid induction of kisspeptin peptide expression in the rostral periventricular area of the third ventricle during postnatal development in the male mouse. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 24: Hiney, J.K., V.K. Srivastava, M.D. Pine and D.W. Les, Insulin-like growth factor-i activates KiSS-1 gene expression in the brain of the prepubertal female rat. Endocrinology, 150: Forbes, S., X.F. Li, J. Kinsey-Jones and K. O' Byrne, Effects of ghrelin on Kisspeptin mrna expression in the hypothalamic medial preoptic area and pulsatile luteinising hormone secretion in the female rat. Neuroscience Letter, 460: Ringel, M.D., E. Hardy, V.J. Bernet, H.B. Burch, F. Schuppert, K.D. Burman and M. Saji, Metastin receptor is overexpressed in papillary thyroid cancer and activates MAP kinase in thyroid cancer cells. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 87(5): Ikeguchi, M., Y. Hirooka and N. Kaibara, Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis for KISS-1 and orphan ag-proteincoupled receptor (hot7t175) gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 129: M. Prystowsky, N. Baldini, G. Childs and C. Cordon- Cardo, Expression profiling ofosteosarcoma cells transfected with MDR1 and NEO genes: regulation of cell adhesion, apoptosis and tumor suppression-related genes. Laboratory Investigation, 83: Dhar, D.K., H. Naora, H. Kubota, R. Maruyama, H. Yoshimura, Y. Tonomoto, M. Tachibana, T. Ono, H. Otani and N. Nagasue, Down regulation of KiSS-1 expression is responsible for tumor invasionand worse prognosis in gastric carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 111: Ikeguchi, M., K. Yamaguchi and N. Kaibara, Clinical significance of the loss of KISS-1 and orphan G-protein-coupled receptor (hot7t175) gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 10: Masui, T., R. Doi, T. Mori, E. Toyoda, M. Koizumi, K. Kami, D. Ito, S.C. Peiper, J.R. Broach, S. Oishi, A. Niida, N. Fujii and M. Imamura, Metastin and its variant forms suppress migration of pancreatic cancer cells. BiochemBiophys Res Commun, 315: Zhang, S.L., Y. Yu, T. Jiang, B. Lin and H. Gao, Expression and significance of KiSS-1 and its receptor GPR54 mrna in epithelial ovarian cancer. Zhonghua Fu Chan KeZaZhi, 40: Stark, A.M., K. Tongers, N. Maass, H.M. Mehdorn and J. Held-Feindt, Reduced metastasissuppressor.gene mrna-expression inbreast cancer brain metastases. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 131: Zohrabian, V.M., H. Nandu, N. Gulati, G. Khitrov, C. Zhao, A. Mohan, J. Demattia, A. Braun, K. Das, R. Murali and M. Jhanwar-Uniyal, Gene expression profiling of metastatic brain cancer. Oncology Report, 18: Arai, A.C., Y.F. Xia, E. Suzuki, M. Kessler, O. Civelli and H.P. Nothacker, Cancer metastasissuppressing peptide metastinupregulates excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal dentategranule cells. Journal of Neurophysiology, 94(5): Brailoiu, G.C., S.L. Dun, M. Oshawa, D. Yin, J. Yang, J.K. Chang, E. Brailoiu and N.J. Dun, KiSS-1 expression and metastin-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 481:
8 77. Kirby, H., E. Mead, J. Maguire, S. Pitkin, 82. Iovane, A., C. Aumas and N. de Roux, New W.H. Colledge, X. d Anglemont de Tassigny and insights in the genetics of isolated A.P. Davenport, Kisspeptins as hypogonadotropichypogonadism. European Journal inotropicagents in human and mouse heart. Proc. of Endocrinology, 151: Physiol. Soc., 11: Semple, R.K., J.C. Achermann, J. Ellery, I.S. Farooqi, 78. Bowe, J.E., A.J. King, J.S. Kinsey-Jones, V.L. Foot, F.E. Karet, R.G. Stanhope, S. O'rahilly and X.F. Li, K.T. O Byrne, S.J. Persaud and P.M. Jones, S.A. Aparicio, Two novel missense mutations Kisspeptin stimulation of insulin secretion: in G protein coupled receptor 54 in a patient with mechanisms of action in mouse islets and rats. hypogonadotropichypogonadism. Journal of Clinical Diabetologia, 52(5): Endocrinology and Metabolism, 90: Roa, J., E. Aguilar, C. Dieguez, L. Pinilla and M. Tena- 84. Lanfranco, F., J. Gromoll, E.S. Von, E.M. Herding, Sempere, New frontiers in kisspeptin/ E. Nieschlag and M. Simoni, Role of sequence GPR54 physiology as fundamental gatekeepers of variations of the GnRH receptor and G proteinreproductive function. Frontier Neuroendocrinology, coupled receptor 54 gene in male idiopathic 29: hypogonadotropichypogonadism. European Journal 80. Irfan, S., J. Ehmcke, F. Wahab, M. Shahab and of Endocrinology, 153: S. Schlatt, Intratesticular action of 85. Funes, S., J.A. Hedrick, G. Vassileva, L. Markowitz, kisspeptin in rhesus monkey (Macacamulatta). S. Abbondanzo, A. Golovko, S. Yang, F.J. Monsma Andrologia, 46(6): and E.L. Gustafson, The KiSS-1 receptor GPR deroux, N., E. Genin, J.C. Carel, F. Matsuda, is essential for the development of the murine J.L. Chaussain and E. Milgrom, reproductive system. BiochemBiophys Res. Hypogonadotropichypogonadism due to loss of Commun., 312: function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. PNAS USA, 100:
KISSPEPTIN AND GNIH CONTROL OF GNRH IN FEMALE MAMMALS
 KISSPEPTIN AND GNIH CONTROL OF GNRH IN FEMALE MAMMALS M.J. Zamiri Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran mjzamiri@gmail.com Introduction Since the discovery
KISSPEPTIN AND GNIH CONTROL OF GNRH IN FEMALE MAMMALS M.J. Zamiri Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran mjzamiri@gmail.com Introduction Since the discovery
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELSA) investigation for Human Kisspeptin and progesterone Levels in female having regular menstrual cycle
 Original Article Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELSA) investigation for Human Kisspeptin and progesterone Levels in female having regular menstrual cycle * MSc, PhD Fac Med Baghdad 2011; Vol. 53, No.
Original Article Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELSA) investigation for Human Kisspeptin and progesterone Levels in female having regular menstrual cycle * MSc, PhD Fac Med Baghdad 2011; Vol. 53, No.
The role of KiSS-1 in the regulation of puberty in higher primates
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2006) 155 S11 S16 ISSN 0804-4643 The role of KiSS-1 in the regulation of puberty in higher primates Tony M Plant Department of Cell Biology and Physiology and Obstetrics,
European Journal of Endocrinology (2006) 155 S11 S16 ISSN 0804-4643 The role of KiSS-1 in the regulation of puberty in higher primates Tony M Plant Department of Cell Biology and Physiology and Obstetrics,
Current Highlights The role of kisspeptin signalling in control of reproduction in genetically similar species
 Current Highlights The role of kisspeptin signalling in control of reproduction in genetically similar species Amir Babiker (1), Adnan Al Shaikh (2) (1) King Saud University Medical City and King Saud
Current Highlights The role of kisspeptin signalling in control of reproduction in genetically similar species Amir Babiker (1), Adnan Al Shaikh (2) (1) King Saud University Medical City and King Saud
Serum Kisspeptin Levels in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.7.927 J Korean Med Sci 2011; 26: 927-931 Serum Kisspeptin Levels in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty Young Jun Rhie 1,2, Kee Hyoung Lee
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.7.927 J Korean Med Sci 2011; 26: 927-931 Serum Kisspeptin Levels in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty Young Jun Rhie 1,2, Kee Hyoung Lee
Evidence that estrogen mediates the positive feedback effect on GnRH
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 3(3): 244-248, 2009 ISSN 1995-0756 2009, American-Eurasian Network for Scientific Information 244 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened
Advances in Environmental Biology, 3(3): 244-248, 2009 ISSN 1995-0756 2009, American-Eurasian Network for Scientific Information 244 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened
Thiruvarur Dist.,Tamilnadu, India.
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 12, Issue 5 Ver. VI (Sep. - Oct.2016), PP 14-19 www.iosrjournals.org A Mathematical Weibull model for desensitization
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 12, Issue 5 Ver. VI (Sep. - Oct.2016), PP 14-19 www.iosrjournals.org A Mathematical Weibull model for desensitization
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Hot Topics in Translational Endocrinology Endocrine Research
 JCEM ONLINE Hot Topics in Translational Endocrinology Endocrine Research The Effects of Kisspeptin-10 on Reproductive Hormone Release Show Sexual Dimorphism in Humans Channa N. Jayasena, Gurjinder M. K.
JCEM ONLINE Hot Topics in Translational Endocrinology Endocrine Research The Effects of Kisspeptin-10 on Reproductive Hormone Release Show Sexual Dimorphism in Humans Channa N. Jayasena, Gurjinder M. K.
/06/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 147(5): Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: /en
 0013-7227/06/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 147(5):2122 2126 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1550 Continuous Human Metastin 45 54 Infusion Desensitizes G Protein-Coupled
0013-7227/06/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 147(5):2122 2126 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1550 Continuous Human Metastin 45 54 Infusion Desensitizes G Protein-Coupled
Immunohistochemical Expression of KISS-1 Protein and KISS-1R in Breast Cancer
 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (3-4) Sofia 2018 Morphology Immunohistochemical Expression
Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (3-4) Sofia 2018 Morphology Immunohistochemical Expression
Kisspeptin and other neuropeptides. New opportunities for reproductive endocrinology Nobel Laureates. Richard A Anderson
 Kisspeptin and other neuropeptides Higher centres Timing of puberty Stress New opportunities for reproductive endocrinology E2 +ve E2 -ve Richard A Anderson Obstetrics and Gynaecology University of Edinburgh
Kisspeptin and other neuropeptides Higher centres Timing of puberty Stress New opportunities for reproductive endocrinology E2 +ve E2 -ve Richard A Anderson Obstetrics and Gynaecology University of Edinburgh
Mystic Effects of Kisspeptin in Reproduction of Livestock
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 07 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.251
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 07 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.251
Plasma metastin levels are negatively correlated with insulin resistance and free androgens in women with polycystic ovary syndrome
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Plasma metastin levels are negatively correlated with insulin resistance and free androgens in women with polycystic ovary syndrome Dimitrios Panidis, Ph.D., a David Rousso, M.D.,
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Plasma metastin levels are negatively correlated with insulin resistance and free androgens in women with polycystic ovary syndrome Dimitrios Panidis, Ph.D., a David Rousso, M.D.,
Emerging ideas about kisspeptin GPR54 signaling in the neuroendocrine regulation of reproduction
 Review TRENDS in Neurosciences Vol.30 No.10 Emerging ideas about kisspeptin GPR54 signaling in the neuroendocrine regulation of reproduction Alexander S. Kauffman 1, Donald K Clifton 2 and Robert A. Steiner
Review TRENDS in Neurosciences Vol.30 No.10 Emerging ideas about kisspeptin GPR54 signaling in the neuroendocrine regulation of reproduction Alexander S. Kauffman 1, Donald K Clifton 2 and Robert A. Steiner
PITUITARY GONADOTROPINS LH and FSH are structurally
 0013-7227/05/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 146(9):3917 3925 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2005 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0337 Changes in Hypothalamic KiSS-1 System and Restoration of Pubertal
0013-7227/05/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 146(9):3917 3925 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2005 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0337 Changes in Hypothalamic KiSS-1 System and Restoration of Pubertal
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVII. Kisspeptin Receptor Nomenclature, Distribution, and Function
 0031-6997/10/6204-565 578$20.00 PHARMACOLOGICAL REVIEWS Vol. 62, No. 4 Copyright 2010 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2774/3624006 Pharmacol Rev 62:565 578, 2010
0031-6997/10/6204-565 578$20.00 PHARMACOLOGICAL REVIEWS Vol. 62, No. 4 Copyright 2010 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2774/3624006 Pharmacol Rev 62:565 578, 2010
Evaluation of the Hypothalamic Kisspeptin System Throughout the Estrous Cycle and During the Attainment of Puberty in Gilts
 South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Theses and Dissertations 2016 Evaluation of the Hypothalamic Kisspeptin System
South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Theses and Dissertations 2016 Evaluation of the Hypothalamic Kisspeptin System
Sex differences in the regulation of Kiss1/NKB neurons in juvenile
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297: E1212 E1221, 2009. First published September 15, 2009; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00461.2009. Sex differences in the regulation of Kiss1/NKB neurons in juvenile mice: implications
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297: E1212 E1221, 2009. First published September 15, 2009; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00461.2009. Sex differences in the regulation of Kiss1/NKB neurons in juvenile mice: implications
Syrian hamsters by promoting GnRH release
 Page 1 of 30 Reproduction Advance Publication first posted on 13 June 2011 as Manuscript REP-10-0313 Peripheral kisspeptin reverses short photoperiod-induced gonadal regression in Syrian hamsters by promoting
Page 1 of 30 Reproduction Advance Publication first posted on 13 June 2011 as Manuscript REP-10-0313 Peripheral kisspeptin reverses short photoperiod-induced gonadal regression in Syrian hamsters by promoting
Kisspeptin-54 Stimulates Gonadotropin Release Most Potently during the Preovulatory Phase of the Menstrual Cycle in Women
 0021-972X/07/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 92(10):3958 3966 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2007 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1116 Kisspeptin-54 Stimulates Gonadotropin
0021-972X/07/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 92(10):3958 3966 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2007 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1116 Kisspeptin-54 Stimulates Gonadotropin
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Ch 11: Endocrine System
 Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
MINI-REVIEW. Kisspeptins (KiSS-1): Essential Players in Suppressing Tumor Metastasis
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.11.6215 Kisspeptins (KiSS-1) as Supressors of Cancer Metastasis MINI-REVIEW Kisspeptins (KiSS-1): Essential Players in Suppressing Tumor Metastasis Venugopal
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.11.6215 Kisspeptins (KiSS-1) as Supressors of Cancer Metastasis MINI-REVIEW Kisspeptins (KiSS-1): Essential Players in Suppressing Tumor Metastasis Venugopal
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Hypothalamic Expression of KiSS1 and RFamide-related Peptide-3 mrnas during The Estrous Cycle of Rats
 Short Communication Hypothalamic Expression of KiSS1 and RFamide-related Peptide-3 mrnas during The Estrous Cycle of Rats Mohammad Saied Salehi, M.Sc. 1, Mohammad Reza Jafarzadeh Shirazi, Ph.D. 1, Mohammad
Short Communication Hypothalamic Expression of KiSS1 and RFamide-related Peptide-3 mrnas during The Estrous Cycle of Rats Mohammad Saied Salehi, M.Sc. 1, Mohammad Reza Jafarzadeh Shirazi, Ph.D. 1, Mohammad
The Role of Kisspeptin and KNDy Cells in the Reproductive Neuroendocrine System
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The Role of Kisspeptin and KNDy Cells in the Reproductive Neuroendocrine System Christina M. Merkley The
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The Role of Kisspeptin and KNDy Cells in the Reproductive Neuroendocrine System Christina M. Merkley The
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Kisspeptin and the Hypothalamic Control of Reproduction: Lessons from the Human
 Endocrinology. 2012 Nov; 153(11): 5130 5136. Published online 2012 Sep 26. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1429 PMCID: PMC3473216 Kisspeptin and the Hypothalamic Control of Reproduction: Lessons from the Human Jyothis
Endocrinology. 2012 Nov; 153(11): 5130 5136. Published online 2012 Sep 26. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1429 PMCID: PMC3473216 Kisspeptin and the Hypothalamic Control of Reproduction: Lessons from the Human Jyothis
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45. Intercellular communication. Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Signaling by local regulators 11/26/2017
 Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Summer 2012 Subject Lecture No. Lecturer Pages in the 11 th edition.
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Summer 2012 Subject Lecture No. Lecturer Pages in the 11 th edition.
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
8/26/13. Announcements
 Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Analysis of the association of the expression of KiSS-1 in colorectal cancer tissues with the pathology and prognosis
 3056 Analysis of the association of the expression of KiSS-1 in colorectal cancer tissues with the pathology and prognosis XINKAI HUO 1*, LEI ZHANG 2* and TAO LI 3 Departments of 1 Gastrointestinal Surgery,
3056 Analysis of the association of the expression of KiSS-1 in colorectal cancer tissues with the pathology and prognosis XINKAI HUO 1*, LEI ZHANG 2* and TAO LI 3 Departments of 1 Gastrointestinal Surgery,
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Downloaded from
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 81, 1216 1225 (2009) Published online before print 14 August 2009. DOI 10.1095/biolreprod.109.078311 Significance of Neonatal Testicular Sex Steroids to Defeminize Anteroventral
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 81, 1216 1225 (2009) Published online before print 14 August 2009. DOI 10.1095/biolreprod.109.078311 Significance of Neonatal Testicular Sex Steroids to Defeminize Anteroventral
Basal Serum Neurokinin B Levels in Differentiating Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty from Premature Thelarche
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.3817 J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol Basal Serum Neurokinin B Levels in Differentiating Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty from Premature Thelarche Mesut Parlak 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.3817 J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol Basal Serum Neurokinin B Levels in Differentiating Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty from Premature Thelarche Mesut Parlak 1,
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Hypothalamic Expression of KISS1 and Gonadotropin Inhibitory Hormone Genes During the Menstrual Cycle of a Non-Human Primate 1
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 83, 568 577 (2010) Published online before print 23 June 2010. DOI 10.1095/biolreprod.110.085407 Hypothalamic Expression of KISS1 and Gonadotropin Inhibitory Hormone Genes During
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 83, 568 577 (2010) Published online before print 23 June 2010. DOI 10.1095/biolreprod.110.085407 Hypothalamic Expression of KISS1 and Gonadotropin Inhibitory Hormone Genes During
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D.
 Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Implication of metastasis suppressor gene, Kiss-1 and its receptor Kiss-1R in colorectal cancer
 Ji et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:723 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Implication of metastasis suppressor gene, Kiss-1 and its receptor Kiss-1R in colorectal cancer Ke Ji 1, Lin Ye 1, Fiona Ruge 1, Rachel Hargest
Ji et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:723 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Implication of metastasis suppressor gene, Kiss-1 and its receptor Kiss-1R in colorectal cancer Ke Ji 1, Lin Ye 1, Fiona Ruge 1, Rachel Hargest
Expressions of HIF-1α and KISS-1 in patients with liver cancer and correlation analysis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4058-4063 Expressions of HIF-1α and KISS-1 in patients with liver cancer and correlation analysis W.-W. SONG 1, A.-P. GUI 2, W. LI 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4058-4063 Expressions of HIF-1α and KISS-1 in patients with liver cancer and correlation analysis W.-W. SONG 1, A.-P. GUI 2, W. LI 1,
Hypothalamus. Small, central, & essential.
 Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
KISS1 Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.8.1120 J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 1120-1125 KISS1 Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty Young-Jun Rhie, 1
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.8.1120 J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 1120-1125 KISS1 Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Girls with Central Precocious Puberty Young-Jun Rhie, 1
Kisspeptin and energy balance in reproduction. Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Human Biology, The University of Western Australia,
 Page 1 of 31 Reproduction Advance Publication first posted on 10 December 2013 as Manuscript REP-13-0509 Kisspeptin and energy balance in reproduction 5 Julie-Ann P. De Bond, Jeremy T. Smith School of
Page 1 of 31 Reproduction Advance Publication first posted on 10 December 2013 as Manuscript REP-13-0509 Kisspeptin and energy balance in reproduction 5 Julie-Ann P. De Bond, Jeremy T. Smith School of
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Kisspetins are products of the KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor
 REPRODUCTION-DEVELOPMENT Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Activates KiSS-1 Gene Expression in the Brain of the Prepubertal Female Rat Jill K. Hiney, Vinod K. Srivastava, Michelle D. Pine, and W. Les Dees Department
REPRODUCTION-DEVELOPMENT Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Activates KiSS-1 Gene Expression in the Brain of the Prepubertal Female Rat Jill K. Hiney, Vinod K. Srivastava, Michelle D. Pine, and W. Les Dees Department
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Experimental Physiology
 1522 Exp Physiol 98.11 (2013) pp 1522 1527 Symposium Report Use of genetic models of idiopathic hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism in mice and men to understand the mechanisms of disease Margaret F. Lippincott,CadenceTrue
1522 Exp Physiol 98.11 (2013) pp 1522 1527 Symposium Report Use of genetic models of idiopathic hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism in mice and men to understand the mechanisms of disease Margaret F. Lippincott,CadenceTrue
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Neuroendocrinol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 December 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 December ; 21(12): 1015 1023. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01926.x. Kisspeptin/Gpr54-independent GnRH activity
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 December ; 21(12): 1015 1023. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01926.x. Kisspeptin/Gpr54-independent GnRH activity
Endocrine system. General principle of endocrinology. Mode of hormone delivery to target. Mode of hormone delivery to target
 Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
BIOL 439: Endocrinology
 1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9)
 NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Endocrine Control. Chapter 35
 Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
Subject Index. hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis 158. Atherosclerosis, ghrelin role AVP, see Arginine vasopressin.
 Subject Index Acromegaly, somatostatin analog therapy dopamine agonist combination therapy 132 efficacy 132, 133 overview 130, 131 receptor subtype response 131, 132 SOM30 studies 131, 132 ACTH, see Adrenocorticotropic
Subject Index Acromegaly, somatostatin analog therapy dopamine agonist combination therapy 132 efficacy 132, 133 overview 130, 131 receptor subtype response 131, 132 SOM30 studies 131, 132 ACTH, see Adrenocorticotropic
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Reproductive FSH. Analyte Information
 Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction. Laura Gunter
 Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Natsumi Endo and Tomomi Tanaka *
 Endo and Tanaka BMC Research Notes 2014, 7:773 SHORT REPORT Open Access Effects of senktide, a neurokinin 3 receptor agonist, on luteinizing hormone secretion and follicular development in anestrous Shiba
Endo and Tanaka BMC Research Notes 2014, 7:773 SHORT REPORT Open Access Effects of senktide, a neurokinin 3 receptor agonist, on luteinizing hormone secretion and follicular development in anestrous Shiba
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology
 General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES:
 ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
ENDOCRINOLOGY COORDINATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES: -In a living organism there must be coordination of number of physiological activities taking place simultaneously such as: movement, respiration,
Energy Balance and Reproduction. BioScience in the 21st Century Candice M. Klingerman 03 October 2011
 Energy Balance and Reproduction BioScience in the 21st Century Candice M. Klingerman 03 October 2011 Outline Energy balance Sex and food in conflict Sex and ingestive behavior Motivation is more sensitive
Energy Balance and Reproduction BioScience in the 21st Century Candice M. Klingerman 03 October 2011 Outline Energy balance Sex and food in conflict Sex and ingestive behavior Motivation is more sensitive
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System
 Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Laith Abu Shekha. Omar Sami. Ebaa Alzayadneh
 24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Regulation of Kisspeptin-expressing neurons and stimulatory mode of action of Kisspeptin in Immortalized Hypothalamic Cell Models
 Regulation of Kisspeptin-expressing neurons and stimulatory mode of action of Kisspeptin in Immortalized Hypothalamic Cell Models Zoey Friedman A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for
Regulation of Kisspeptin-expressing neurons and stimulatory mode of action of Kisspeptin in Immortalized Hypothalamic Cell Models Zoey Friedman A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for
Lecture 11, 27 Sept 2005 Chapter 14 & 15. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 11, 27 Sept 2005 Chapter 14 & 15 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Lecture 11, 27 Sept 2005 Chapter 14 & 15 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Spermatogenesis. What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis?
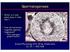 Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014
 Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014 G Protein Coupled Receptors Actually 4% of the human genome GPCR dysfunction contributes to some of the most prevalent human diseases GPCRs represent 60% of
Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014 G Protein Coupled Receptors Actually 4% of the human genome GPCR dysfunction contributes to some of the most prevalent human diseases GPCRs represent 60% of
The Missing Kiss of Life: Transcriptional Activity of the Metastasis Suppressor Gene KiSS1 in Early Breast Cancer
 The Missing Kiss of Life: Transcriptional Activity of the Metastasis Suppressor Gene KiSS1 in Early Breast Cancer L. KOSTADIMA, G. PENTHEROUDAKIS and N. PAVLIDIS Department of Medical Oncology, Ioannina
The Missing Kiss of Life: Transcriptional Activity of the Metastasis Suppressor Gene KiSS1 in Early Breast Cancer L. KOSTADIMA, G. PENTHEROUDAKIS and N. PAVLIDIS Department of Medical Oncology, Ioannina
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
KISSPEPTINS WERE originally identified as the products
 0013-7227/06/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 147(10):4852 4862 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0117 Expression of KiSS-1 in Rat Ovary: Putative Local Regulator of
0013-7227/06/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 147(10):4852 4862 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0117 Expression of KiSS-1 in Rat Ovary: Putative Local Regulator of
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho. REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5
 Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
The Endocrine System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris
 18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
Model Answer. M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology)
 Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works
 UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works Title Kisspeptin neurones do not directly signal to RRP-3 neurones but RRP-3 may directly modulate a subset of hypothalamic kisspeptin cells in mice
UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works Title Kisspeptin neurones do not directly signal to RRP-3 neurones but RRP-3 may directly modulate a subset of hypothalamic kisspeptin cells in mice
