Chromosomes of Human Endometrium
|
|
|
- Emil Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
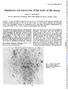
1 J. med. Genet. (1967). 4, 91. Chromosomes of Human Endometrium C. ELIZABETH BOWEY and A. I. SPRIGGS From Clinical Cytology Laboratory, Churchill Hospital, Oxford Evidence is gradually accumulating about acquired somatic chromosome anomalies, particularly those of neoplasms. Unfortunately, control observations are almost entirely lacking. It is generally assumed that all the tissues of the body consist of cells with the normal karyotype as it is seen in cultured lymphocytes or fibroblasts, but this has not yet been shown to be the case. Even bone-marrow, which is rich in dividing cells, has not been the subject of extensive control observations to see how frequently there is a visible departure from the normal karyotype. The present paper is a brief account of the findings in preparations of the chromosomes of human endometrial cells entering mitosis in vivo, where the tissue is histologically normal. Endometrium was chosen as the only accessible normal solid tissue with a sufficiently high mitotic rate. Material and Methods Endometrial curettings were obtained from the operating theatre. As soon as the material was removed it was placed by the surgeon in a solution consisting of one part of human AB serum (inactivated by heating at 60 C. for 30 minutes) and four parts of tissue culture medium 199 (Glaxo). It was processed within an hour of collection, or rarely two. When the material arrived in the laboratory it was teased out with sharp-pointed forceps to separate epithelial cells from stroma, and the solid fragments were removed. The cell suspension was pipetted into a universal container and colcemid (Ciba) added to a final concentration of 1 mg./100 ml. It was incubated at 370 C. for 2 hours, with the object of improving chromosome contraction (it is not believed that any cells are found in metaphase which have not already begun division in vivo). The supernatant fluid was then replaced by 0.9% sodium citrate, and the suspension incubated for a further 10 minutes. It was then centrifuged'again ( minutes at about 70 rpm), and the deposit fixed with freshly madeup acetic acid-methanol (1:2). In a few cases the curettings were teased directly in 099% sodium citrate, Received January 9, incubated at 37 C. for 10 minutes, centrifuged, and fixed in acetic-methanol. Spreading was by either of two methods: (1) (Cases 1-12 and 18-22) Material was left in fixative for several hours, centrifuged ( min. at 1100 rpm) and resuspended in 0% acetic acid and left in the deepfreeze (-20 C.) overnight. Slides were cleaned by flooding with acetone and then water, and dried by wiping with tissue. A drop of cell suspension was then placed on the slide and gently warmed over a flame, allowing the drop to move over the glass surface until dry. (2) (Cases 13-17) Material was stored overnight in acetic acid-methanol (1:3) at room temperature and the fixative changed several times before use. Slides were cleaned by flooding with acetone and then rinsed with cold tap water. A drop of cell suspension was squirted onto the slide and the same side gently flamed to burn off the alcohol and completely dried by waving in air. Slides were stained with 1% lacto-acetic orcein (Harleco) and mounted permanently in Euparal. Altogether 8 samples were processed, but only 22 could be used; the remainder showed few or no adequately displayed metaphases. Samples were accepted from various times in the menstrual cycle, and in some of the cases this was irregular. None of them, however, showed any morphological abnormality other than simple hyperplasia, either in sections or in Papanicolaoustained smears from the curettage specimen. Chromosomes of cells in metaphase were counted under the microscope, drawings being made either freehand or using a Wild drawing tube. Forty-six cells were analysed from photographs; this was particularly done whenever an abnormality was suspected, and (apart from chromosome loss) none was recorded unless it could be verified in this way. Results Fig. 1 shows an apparently normal cell from Case 2; it illustrates the best quality of chromosome spreading achieved with this method. Table I shows the whole material giving the distribution of chromosome counts. Many cells were not included because they were obviously broken and incomplete, but it has to be admitted that this 91
2 92 Bowey and Spriggs J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 June Downloaded from *X oi <.. H. -..;.- : ;rr :.. :.-: -f.i :. : R FIG. 1. Above, a normal cell in metaphase from a direct preparation of human endometrium (Case 2). Below, the chromosomes of the same cell arranged as a karyotype. judgement is very unreliable and the real extent of cell breakage is unknown. Doubtful counts are not included. Histograms of the chromosome counts from 12 cases are given in Fig. 2. It will be seen that there is a large scatter of values to the left of 46, and the question arises whether the loss of chromosomes is random or not. Table II gives the Patau groups of the missing chromosomes from 41 cells in which this could be decided with reasonable certainty. There seems to be a preferential loss of the E group chromosomes (16-18), which is difficult to explain by postulating any bias in the analysis. Of the cells with 46 chromosomes, 1 were analysed. Only one showed a clear abnormality. It came from Case 3, and had an acentric fragment in place of a chromosome. One other cell, from Case 11, appeared to have a deletion of the long on 22 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 Chromosomes of Human Endometnum TABLE I DISTRIBUTION OF CHROMOSOME COUNTS ON 279 CELLS FROM 22 ENDOMETRIAL SAMPLES Chromosome Counts Case Age Day II IHistology and Comments No. (yr.) of < Cycle Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium Early secretory endometrium Early secretory endometrium 40 1 Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium, hypertrophic; amputation of cervix for carcinoma in situ Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium, hypertrophic Secretory endometrium Early secretory endometrium Curettage after avulsion of fibroid polyp of cervix Non-secretory endometrium Non-secretory endometrium, hypertrophic Non-secretory endometrium, hypertrophic; simple endometrial polyp Non-secretory endometrium; postmenopausal Decidua Early secretory endometrium; small, ll endometrial polyp Non-secretory endometrium : 1 1 Non-secretory endometrium Total ,o arms of a No. 17 or 18 chromosome, but the quality of the metaphase was not quite good enough to allow this to be recorded with certainty. Discussion Until 196 the methods in use for displaying human chromosomes were so unsatisfactory that the results are only of historical interest. In 1947 Barigozzi reported that squashed cells from normal endometrium had 48 chromosomes, then believed to be the normal human number. Timonen (190) examined the chromosomes of endometrium from 41 patients not suffering from cancer. His specimens were fixed, Feulgen-stained, and squashed, and examined under phase-contrast. He found chromosome counts varying from 4-104, with the main peak at 21-2 and a lower one at These results were challenged by Sachs (194), who performed counts on 0 human endometrial cells and found no variations from the supposed normal diploid number. A scatter around a diploid peak was found by Walker and Boothroyd (194), while Manna (194) observed many values below the diploid mode but hardly any above. After the introduction of hypotonic pre-treatment and the discovery of the correct chromosome number of man, it was found that cultured normal cells from various organs showed a high constancy, with hardly any aberrations except for random chromosome loss (Levan and Biesele, 198; Tjio and Puck, 198; Petursson and Fogh, 1963; Court Brown, Buckton, Jacobs, Tough, Kuenssberg, and Knox, 1966). Observations on direct preparations were less satisfactory, as the new techniques did not give a high success rate with suspensions made from most solid tissues. Ford (1964) has analysed the sources of error, and given reasons for believing that cells in vivo have an even higher chromosome constancy than cells in culture. Human endometrium was examined by Takemura (1960), and of the 109 cells examined from five normal samples, 1 %/ were found to have 46 TABLE II CLASSIFICATION OF 86 MISSING CHROMOSOMES FROM 41 HYPODIPLOID CELLS I1 23 B!C+Xa D F G No.ofchromosomes Observed o Expected Note: 'Expected' values are calculated from the proportions of the different chromosome groups present in the normal female set. 93
4 Ca se 3 Case 6 I Case 2 Case -z - * Li 0 - Case 18 Case 20 1~~~~~~~~~ z L 1 10 Case Case 13 ic,- Case 7 Case I I U] rc,.a. 7-sJ r-.- LUC in 3N 4 u 463o4c 4o Number of chromosomes Okg Iv.sel FIG. 2. Distribution of chromosome counts in direct preparations from 12 different samples of endometrium obtained by curettage. Counts below 30 have been ignored. Note the marked scatter to the left of 46, and the absence of hyperdiploid cells. chromosomes. There was a scatter above as well as below this level. Wakonig-Vaartaja (1963) made counts on 428 cells from 16 patients, and 910% were found to have 46 chromosomes. Cells with less than 46 chromosomes amounted to 80%, and 10% had cells were analysed and 'the only variation from the normal karyotype was the presence of a few chromosomal deletions in 3 cells from one patient with endometrial hyperplasia'; the hyperdiploid cells do not appear to have been analysed. Cultures of normal human endometrium have been examined by Hughes and Csermely (196) with rather surprising results. Out of 232 mitoses 0 Bowey and Spriggs studied, only 79 (32%) had the normal number of 46 chromosomes. There was a scatter of values not only beneath 46, but to a considerable extent above; for instance, 24 cells out of 449 were found with counts between 49 and 8 (Hughes and Csermely, 1966). The number with 47 is not given, because they are classified in this paper along with diploid cells in the group These authors present several photographic karyotypes of normal or hypodiploid cells but none with supernumerary chromosomes. Our findings resemble those of Hughes and Csermely in the high frequency of random chromosome loss, but not at all in the matter of cells with supernumerary chromosomes. The simplest explanation for the occurrence of a substantial number of hyperdiploid cells in other series is that cells have been included which do not have the chromosomes displayed well enough for a really exact count, as well perhaps as the presence of acentric fragments counted as chromosomes. An additional explanation of the difference between our findings and Hughes and Csermely's is that aneuploidy may develop in culture to an extent not observed in vivo. Because of technical difficulties, we do not believe that the last word has been said on this question, and in particular we need to know whether the hypodiploid cells found in such large numbers are really present in the living endometrium, and, if they are, what is the mechanism of chromosome loss. Assuming that chromosome loss is due in some way to the technical procedure, the findings in our series support Ford's (1964) view that there is hardly any departure from diploidy and that spurious counts explain some of the variation recorded. Summary Direct preparations were made to examine the chromosomes of non-malignant human endometrium. Out of 8 samples, 22 furnished metaphases which were suitable for chromosome counting. Whenever possible a karyotype analysis was also done. The modal chromosome number was 46 but there was a large scatter of values to the left due to chromosome loss. Cells with more than 46 chromosomes were not encountered, and those with 46 chromosomes had apparently normal karyotypes. This work was supported by the British Empire Cancer Campaign. The authors are very grateful to Mr. J. A. Stallworthy and his staff in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Churchill Hospital, for supplying the samples of endometrium.
5 REFERENCES Barigozzi, C. (1947). Les chromosomes humains dans quelques etats pathologiques. Arch. Klaus-Stift. Vererb.-Forsch., 22, 342. Court Brown, W. M., Buckton, K. E., Jacobs, P. A., Tough, I. M., Kuenssberg, E. V., and Knox, J. D. E. (1966). Chromosome Studies on Adults. Eugenics Lab. Memoir XLII. London. Ford, C. E. (1964). Selection pressure in mammalian cell populations. In Cytogenetics of Cells in Culture, ed. R. J. C. Harris. Academic Press, New York and London. Hughes, E. C., and Csermely, T. V. (196). Chromosome constitution of human endometrium. Amer. J'. Obstet. Gynec., 93, , and- (1966). Chromosomal constitution of human endometrium. Nature (Lond.), 209, 326. Levan, A., and Biesele, J. J. (198). Role of chromosomes in cancerogenesis as studied in serial tissue culture of mammalian cells. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 71, Chromosomes of Human Endometrium 9 Manna, G. K. (194). Chromosome number of human endometrium. Nature (Lond.), 173, 271. Petursson, G., and Fogh, J. (1963). The chromosomes of primary human amnion cells and FL cells. Cancer Res., 23, Sachs, L. (194). The chromosome constancy of the normal mammalian uterus. Heredity, 8, 117. Takemura, T. (1960). Chromosome survey of normal human endometrium and endometrial carcinoma. 7. Jap. obstet. gynaec. Soc., 7, 300. Timonen, S. (190). Mitosis in normal endometrium and genital cancer. Acta obstet. gynec. scand., 31, suppl. 2. Tjio, J. H., and Puck, T. T. (198). The somatic chromosomes of man. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.), 44, Wakonig-Vaartaja, R. (1963). Chromosomes in gynaecological malignant tumours. Aust. N.Z.7. Obstet. Gynaec., 3, 170. Walker, B. E., and Boothroyd, E. R. (194). Chromosome numbers in somatic tissues of mouse and man. Genetics, 39,210. J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 June Downloaded from on 22 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human
 Jap. Jour. Genet. Vol. 38, No. 2, 106-112 (1963) Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human Leukocytes in vitrol) Akio AWA, Yasushi OHNUKI, and C. M. POMERAT Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University,
Jap. Jour. Genet. Vol. 38, No. 2, 106-112 (1963) Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human Leukocytes in vitrol) Akio AWA, Yasushi OHNUKI, and C. M. POMERAT Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University,
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical.
 Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE
 KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE TOSHIO KASUYA The chromosomes of the Mammalia have been studied for a long period, and many species of mammals except those belonging to the Lemures, Proboscidea, Hyracoidea and
KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE TOSHIO KASUYA The chromosomes of the Mammalia have been studied for a long period, and many species of mammals except those belonging to the Lemures, Proboscidea, Hyracoidea and
THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 673-68 (97) 673 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS U. BREGULA,* G. KLEIN Department of Tumor Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 8, 673-68 (97) 673 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS U. BREGULA,* G. KLEIN Department of Tumor Biology,
Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova
 Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova II. Delayed Ovulation and Chromosome Anomalies ROY L. BUTCHER, PH.D., and N. W. FUGO, PH.D., M.D. THE CAUSES of abortion and birth defects are undoubtedly multiple and
Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova II. Delayed Ovulation and Chromosome Anomalies ROY L. BUTCHER, PH.D., and N. W. FUGO, PH.D., M.D. THE CAUSES of abortion and birth defects are undoubtedly multiple and
CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA
 528 CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ ASCITES TUAIOUR AFTER TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR- INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA E. MAYHEW* AND E. M. F. ROE From
528 CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ ASCITES TUAIOUR AFTER TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR- INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA E. MAYHEW* AND E. M. F. ROE From
Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4. Introduction. This kit contains the following materials:
 CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellserv.org Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4 Introduction Each somatic cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. During the interphase stage of the
CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellserv.org Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4 Introduction Each somatic cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. During the interphase stage of the
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
OBSERVING MITOSIS. Purpose. Preparing the cells. Interpreting what you see on your cell preparation. Salters-Nuffield Advanced Biology Resources
 Activity 3.9 Student Sheet OBSERVING MITOSIS Purpose To prepare some slides of actively dividing plant tissue. To observe the stages of the cell cycle in living tissue. To determine the duration of the
Activity 3.9 Student Sheet OBSERVING MITOSIS Purpose To prepare some slides of actively dividing plant tissue. To observe the stages of the cell cycle in living tissue. To determine the duration of the
Karyology. Preparation and study of karyotypes is part of Cytogenetics.
 Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
CHROMOSOME STUDIES IN 12 SOLID TUMOURS FROM CHILDREN
 40 CHROMOSOME STUDIES IN SOLID TUMOURS FROM CHILDREN D. COX From the *Department of Morbid Anatomy, Institute of Child Health and Ho8pital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London. W.C.I. Received
40 CHROMOSOME STUDIES IN SOLID TUMOURS FROM CHILDREN D. COX From the *Department of Morbid Anatomy, Institute of Child Health and Ho8pital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London. W.C.I. Received
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D.
 Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia
 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
Pericentric inversion of chromosome 1: frequency and possible association with cancer
 Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 19: 180-184 (1977) BRIEF REPORT Pericentric inversion of chromosome 1: frequency and possible association with cancer N.B. Atkin and M.C. Baker Department of Cancer Research. Mount
Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 19: 180-184 (1977) BRIEF REPORT Pericentric inversion of chromosome 1: frequency and possible association with cancer N.B. Atkin and M.C. Baker Department of Cancer Research. Mount
Significance of Endometrial Cells in Cervicovaginal Smears
 ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 7,No. 6 Copyright 1977, Institute for Clinical Science Cervicovaginal Smears BERNARD GONDOS, M.D. and EILEEN B. KING, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 7,No. 6 Copyright 1977, Institute for Clinical Science Cervicovaginal Smears BERNARD GONDOS, M.D. and EILEEN B. KING, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN
 Policy # MI\TECH\11\v01 Page 1 of 6 Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN Latex particles coated
Policy # MI\TECH\11\v01 Page 1 of 6 Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN Latex particles coated
Late-replicating X Chromosome
 J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, I07. The Relative Length and Arm Ratio of the Human Late-replicating X Chromosome AUDREY BISHOP, MARGARET LEESE, and C. E. BLANK From the Centre for Human Genetics, United Sheffield
J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, I07. The Relative Length and Arm Ratio of the Human Late-replicating X Chromosome AUDREY BISHOP, MARGARET LEESE, and C. E. BLANK From the Centre for Human Genetics, United Sheffield
TEACHER/LECTURER GUIDE
 TEACHER/LECTURER GUIDE Type and purpose of activity This experiment can be used to: provide evidence for assessment of Outcome 3 (For advice on marking Outcome 3 report, please contact the SAPS Scotland
TEACHER/LECTURER GUIDE Type and purpose of activity This experiment can be used to: provide evidence for assessment of Outcome 3 (For advice on marking Outcome 3 report, please contact the SAPS Scotland
Comparative effects of colchicine, 8-hydroxyquinoline and paradichlorobenzene on arm ratio of mitotic chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
Pollen Slide Mounting Protocol
 Pollen Slide Mounting Protocol Materials: Syn-Matrix mounting medium Microcentrifuge Microscope slides Slide coverslips (18mm x 18mm) Coverslip podium (see Figure 1) Capillary tubes Dissecting microscope
Pollen Slide Mounting Protocol Materials: Syn-Matrix mounting medium Microcentrifuge Microscope slides Slide coverslips (18mm x 18mm) Coverslip podium (see Figure 1) Capillary tubes Dissecting microscope
BIL Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data
 BIL 151 - Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data You and your teammates have chosen to examine the outcome of treating a rapidly dividing tissue (onion root tip) with a substance that either promotes
BIL 151 - Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data You and your teammates have chosen to examine the outcome of treating a rapidly dividing tissue (onion root tip) with a substance that either promotes
Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014
 Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014 Chris Wragg Head of Oncology Genomics, BGL BGL Bristol Genetics Laboratory (BGL) CPA accredited Genetics laboratory serving a core population of 4-5million
Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014 Chris Wragg Head of Oncology Genomics, BGL BGL Bristol Genetics Laboratory (BGL) CPA accredited Genetics laboratory serving a core population of 4-5million
NUCLEAR ABNORMALITIES RESULTING FROM INHIBITION OF MITOSIS BY COLCHICINE AND OTHER SUBSTANCES '
 NUCLEAR ABNORMALITIES RESULTING FROM INHIBITION OF MITOSIS BY COLCHICINE AND OTHER SUBSTANCES ' AUSTIN M. BRUES AND ELIZABETH B. JACKSON (From the Medicul Lnborutorif~ of the Collis P. Iiz4ntingtolz M~moricil
NUCLEAR ABNORMALITIES RESULTING FROM INHIBITION OF MITOSIS BY COLCHICINE AND OTHER SUBSTANCES ' AUSTIN M. BRUES AND ELIZABETH B. JACKSON (From the Medicul Lnborutorif~ of the Collis P. Iiz4ntingtolz M~moricil
Radiation Research Society is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Radiation Research.
 Persistent Chromosome Aberrations in Irradiated Human Subjects Author(s): M. A. Bender and P. C. Gooch Reviewed work(s): Source: Radiation Research, Vol. 16, No. 1 (Jan., 1962), pp. 44-53 Published by:
Persistent Chromosome Aberrations in Irradiated Human Subjects Author(s): M. A. Bender and P. C. Gooch Reviewed work(s): Source: Radiation Research, Vol. 16, No. 1 (Jan., 1962), pp. 44-53 Published by:
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
TOSIHIDE H. YOSIDA, KYOKO OHARA, AND LLOYD W. LAW*
 JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 42, No. 5: 339-347 (1967) CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS. XVI. KARYOLOGICAL STUDIES ON SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT SUBLINES OF THE MOUSE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA,
JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 42, No. 5: 339-347 (1967) CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS. XVI. KARYOLOGICAL STUDIES ON SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT SUBLINES OF THE MOUSE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA,
A Photographic Representation of Mitosis and Meiosis in the Male of Rattus norvegicus
 422 Cytologia 23 A Photographic Representation of Mitosis and Meiosis in the Male of Rattus norvegicus S. Ohno, W. D. Kaplan and R. Kinosita Department of Cytology and Genetics, Medical Research Institute,
422 Cytologia 23 A Photographic Representation of Mitosis and Meiosis in the Male of Rattus norvegicus S. Ohno, W. D. Kaplan and R. Kinosita Department of Cytology and Genetics, Medical Research Institute,
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
Cytological Studies in Six Species of Pill-Millipedes (Diplopoda-Myriapoda)
 Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 Cytological Studies in
Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 Cytological Studies in
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease. By S. BRADBURY
 Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Sperm Survival in Women. Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases
 Sperm Survival in Women Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases Boris B. Rubenstein, M.D., Ph.D.; Hermann Strauss, M.D.; Maurice L. Lazarus, M.D., and Henry Hankin, M.D. THE DURATION of
Sperm Survival in Women Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases Boris B. Rubenstein, M.D., Ph.D.; Hermann Strauss, M.D.; Maurice L. Lazarus, M.D., and Henry Hankin, M.D. THE DURATION of
Eretmapodites quinquevittatus Theobald 1
 Mosquito Systematics Vol. 15(4) 1983 325 Mitotic Chromosomes of the Mosquito Eretmapodites quinquevittatus Theobald 1 W. Keith Hartberg and William H. Faircloth Institute of Arthropodology and Parasitology
Mosquito Systematics Vol. 15(4) 1983 325 Mitotic Chromosomes of the Mosquito Eretmapodites quinquevittatus Theobald 1 W. Keith Hartberg and William H. Faircloth Institute of Arthropodology and Parasitology
Karyotype analysis of teratocarcinomas and embryoid bodies of C3H mice
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol., pp. 77-, 77 77 Printed in Great Britain Karyotype analysis of teratocarcinomas and embryoid bodies of CH mice By S. A. ILES AND E. P. EVANS From the Department of Zoology
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol., pp. 77-, 77 77 Printed in Great Britain Karyotype analysis of teratocarcinomas and embryoid bodies of CH mice By S. A. ILES AND E. P. EVANS From the Department of Zoology
CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS
 J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 222. CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS BY M. M. BODDINGTON From the Department of Pathology, Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION DECEMBER 19,
J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 222. CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS BY M. M. BODDINGTON From the Department of Pathology, Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION DECEMBER 19,
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH CLINICAL LABORATORY EVALUATION PROGRAM. Crosswalk of Proposed Revisions to Cytogenetics Standards
 2014 Standard 2014 Guidance 2016 Standard 2016 Guidance Cytogenetics Standard 1 (CG S1) The laboratory shall request clinical information necessary for proper initiation of test procedures and interpretation
2014 Standard 2014 Guidance 2016 Standard 2016 Guidance Cytogenetics Standard 1 (CG S1) The laboratory shall request clinical information necessary for proper initiation of test procedures and interpretation
ANOMALIES, IN TUMOURS OF FEMALES
 40 TRIPLE SEX CHROMATIN, AND OTHER SEX CHROMATIN ANOMALIES, IN TUMOURS OF FEMALES N. B. ATKIN From the Department of Cancer Research, Mount Vernon Hospital. Northwood, Middlesex Received for publication
40 TRIPLE SEX CHROMATIN, AND OTHER SEX CHROMATIN ANOMALIES, IN TUMOURS OF FEMALES N. B. ATKIN From the Department of Cancer Research, Mount Vernon Hospital. Northwood, Middlesex Received for publication
CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY TO ENCEPHALITOGENIC FACTOR (MMI TEST) IN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL DYSPLASIA AND CARCINOMA
 Br. J. Cancer (1978) 38, 396 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY TO ENCEPHALITOGENIC FACTOR (MMI TEST) IN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL DYSPLASIA AND CARCINOMA IN SITU: THE EFFECTS OF SERUM D. J. FLAVELL*l, A. SINGER2 AND C.
Br. J. Cancer (1978) 38, 396 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY TO ENCEPHALITOGENIC FACTOR (MMI TEST) IN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL DYSPLASIA AND CARCINOMA IN SITU: THE EFFECTS OF SERUM D. J. FLAVELL*l, A. SINGER2 AND C.
Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code
 P ford residence southampton, ny Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code Jun 24, 2014. Billable Medical Code for Malignant Neoplasm of Corpus Uteri, Except Isthmus Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim:
P ford residence southampton, ny Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code Jun 24, 2014. Billable Medical Code for Malignant Neoplasm of Corpus Uteri, Except Isthmus Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim:
LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
 6 November 2014 EMA/CVMP/VICH/526/2000 Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
6 November 2014 EMA/CVMP/VICH/526/2000 Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa
 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Within the last decade, histologic grading has become widely accepted as a powerful indicator
Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Within the last decade, histologic grading has become widely accepted as a powerful indicator
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1
 Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Received, June 29, 1904; accepted for publication
 THE AMEBICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1964 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 42, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. CARCINOMA IN SITU OF THE ENDOMETRIUM ISABELLE A. BUEHL, M.D., PRANK VELLIOS, M.D.,
THE AMEBICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1964 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 42, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. CARCINOMA IN SITU OF THE ENDOMETRIUM ISABELLE A. BUEHL, M.D., PRANK VELLIOS, M.D.,
IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS
 IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS A. Introduction Influenza A, Influenza B and RSV are responsible for serious respiratory
IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS A. Introduction Influenza A, Influenza B and RSV are responsible for serious respiratory
Differences in Human Spermatozoa
 Differences in Human Spermatozoa Landrum B. Shettles, M.D. RECENT OBSERVATIONS show that thin, dried, unstained smears of human spermatozoa viewed through the dry objectives of the phase-contrast microscope
Differences in Human Spermatozoa Landrum B. Shettles, M.D. RECENT OBSERVATIONS show that thin, dried, unstained smears of human spermatozoa viewed through the dry objectives of the phase-contrast microscope
THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA
 J. Cell Sci. 18, 19-25(1975) 29 Printed in Great Britain THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA G.E.MARKS John Innes Institute, Colney Lane, Norwich, NR4 7 UH, England SUMMARY The centromere
J. Cell Sci. 18, 19-25(1975) 29 Printed in Great Britain THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA G.E.MARKS John Innes Institute, Colney Lane, Norwich, NR4 7 UH, England SUMMARY The centromere
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1. ed by cytotoxicity tests. Cells from leukemia without thymus involvement
 [Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
[Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
[GANN, 52, ; September, 1961]
![[GANN, 52, ; September, 1961] [GANN, 52, ; September, 1961]](/thumbs/87/97250948.jpg) [GANN, 52, 257-264; September, 1961] CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS, VII. KARYOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF SPONTA- NEOUS AND INDUCED LEUKEMIAS IN MICE1)2) YOSHINORI KURITA and TOSIHIDE H.
[GANN, 52, 257-264; September, 1961] CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS, VII. KARYOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF SPONTA- NEOUS AND INDUCED LEUKEMIAS IN MICE1)2) YOSHINORI KURITA and TOSIHIDE H.
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
THE BRITISH JOURN OF VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE TRANSMISSIBLE VENEREAL TUMOUR OF THE DOG
 Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report
 Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report Date Published: 05/19/2008 Page One 1. Lesson Plan Title: Cell Division and Mitosis 2. Subject Area: Living Environment 3. Topic(s): Mitosis 4. Suggested Grade
Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report Date Published: 05/19/2008 Page One 1. Lesson Plan Title: Cell Division and Mitosis 2. Subject Area: Living Environment 3. Topic(s): Mitosis 4. Suggested Grade
Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements
 CONWAY REGIONAL HEALTH SYSTEM CLINICAL LABORATORY Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements POLICY: Tissue or body fluids, etc. removed or collected during any procedure for purposes of Pathologist examination
CONWAY REGIONAL HEALTH SYSTEM CLINICAL LABORATORY Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements POLICY: Tissue or body fluids, etc. removed or collected during any procedure for purposes of Pathologist examination
NINDS Repository Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Handling Protocols (Matrigel and mtesr Media)
 General Guidelines for Handling Human ipsc cells ipsc are cryopreserved in plastic cryovials and shipped on dry ice. If storing the ipsc before thawing, store in liquid nitrogen vapor. Storage directly
General Guidelines for Handling Human ipsc cells ipsc are cryopreserved in plastic cryovials and shipped on dry ice. If storing the ipsc before thawing, store in liquid nitrogen vapor. Storage directly
THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION VI. HYBRIDS BETWEEN DIFFERENT TUMOUR CELLS
 y. Cell Sci. 1, 189-198 (197) 189 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION VI. HYBRIDS BETWEEN DIFFERENT TUMOUR CELLS F. WIENER, G. KLEIN Department of Tumour Biology, Karolivska
y. Cell Sci. 1, 189-198 (197) 189 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION VI. HYBRIDS BETWEEN DIFFERENT TUMOUR CELLS F. WIENER, G. KLEIN Department of Tumour Biology, Karolivska
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man
 Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
UTERINE LESIONS ASSOCIATED WITH FIBROMYOMA*
 UTERINE LESIONS ASSOCIATED WITH FIBROMYOMA* F. W. LIGHT, JR. From the Department of Pathology, St. John's Hospital, Springfield, Illinois Fibromyoma of the uterus is recognized as one of the commonest
UTERINE LESIONS ASSOCIATED WITH FIBROMYOMA* F. W. LIGHT, JR. From the Department of Pathology, St. John's Hospital, Springfield, Illinois Fibromyoma of the uterus is recognized as one of the commonest
1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the method for conducting analysis for semen and sperm in forensic casework.
 Procedure for Semen and Sperm Analysis 1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the method for conducting analysis for semen and sperm in forensic casework. 2.0 Scope - This procedure applies to those Forensic
Procedure for Semen and Sperm Analysis 1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the method for conducting analysis for semen and sperm in forensic casework. 2.0 Scope - This procedure applies to those Forensic
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi. Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat. Ahmad Al-Tarefe
 5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
Cytology Update M Laing QEUH
 Cytology Update M Laing QEUH Age change to 25 to 65 Age 25 to 50 Three yearly smear invitation Age 50 to 65 Five yearly smear invitation Women on non routine screening will be invited up to age 70 OUTCOME
Cytology Update M Laing QEUH Age change to 25 to 65 Age 25 to 50 Three yearly smear invitation Age 50 to 65 Five yearly smear invitation Women on non routine screening will be invited up to age 70 OUTCOME
Perimenopausal Age Group (45-55yrs): For Early Detection And Treatment.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 9 Ver. 4 (September. 2018), PP 73-77 www.iosrjournals.org Perimenopausal Age Group (45-55yrs):
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 9 Ver. 4 (September. 2018), PP 73-77 www.iosrjournals.org Perimenopausal Age Group (45-55yrs):
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Human Induced Plutipotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Handling Protocols: Matrigel and mtesr/e8 Media
 General Guidelines for Handling Human ipsc cells ipsc are cryopreserved in plastic cryovials and shipped on dry ice. If storing the ipsc before thawing, store in liquid nitrogen vapor. Storage directly
General Guidelines for Handling Human ipsc cells ipsc are cryopreserved in plastic cryovials and shipped on dry ice. If storing the ipsc before thawing, store in liquid nitrogen vapor. Storage directly
LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER PART 1. NORMAL MITOSIS IN PLANTS FIGURE 1. DIAGRAMATIC GUIDE TO THE STAGES OF MITOSIS
 Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Squamous cell carcinoma ofthe body of the uterus
 J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 715 Squamous cell carcinoma ofthe body of the uterus HANNA BARNETT' From the Department of Pathology, South London Hospital for Women, Clapham, London SYNOPSIS A case of primary
J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 715 Squamous cell carcinoma ofthe body of the uterus HANNA BARNETT' From the Department of Pathology, South London Hospital for Women, Clapham, London SYNOPSIS A case of primary
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL TYPE IN CERVICAL CANCER'
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL TYPE IN CERVICAL CANCER' DANIEL G. MORTON, M.D. Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of California Medical School, San Francisco Among the factors which
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL TYPE IN CERVICAL CANCER' DANIEL G. MORTON, M.D. Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of California Medical School, San Francisco Among the factors which
Exploring Mitosis Lab IMPORTANT LEARNING OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
uterine cancer endometrial cancer
 2018 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code. Adenocarcinoma of endometrium ; Cancer of the. (mucous membrane that lines the endometrial cavity). ICD-10-CM C54.1 is grouped. Home ICD 9 Codes Endometrial Cancer ICD 9
2018 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code. Adenocarcinoma of endometrium ; Cancer of the. (mucous membrane that lines the endometrial cavity). ICD-10-CM C54.1 is grouped. Home ICD 9 Codes Endometrial Cancer ICD 9
Exploring Mitosis Lab IMPORTANT LEARNING OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION cell cycle interphase division (mitosis)
 Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
Chapter 10: Pap Test Results
 Chapter 10: Pap Test Results On completion of this section, the learner will be able to: 1. Identify how Pap test results are interpreted and the reasons for normal and abnormal results. 2. Describe the
Chapter 10: Pap Test Results On completion of this section, the learner will be able to: 1. Identify how Pap test results are interpreted and the reasons for normal and abnormal results. 2. Describe the
SAMPLE LITERATURE Please refer to included weblink for correct version. Morphology of Cancer Cells. Edvo-Kit #990. Experiment Objective:
 Edvo-Kit #990 Morphology of Cancer Cells Experiment Objective: 990 In this lab, students will explore the morphology of normal and cancerous cells by staining pre-fi xed cells with methylene blue and eosin.
Edvo-Kit #990 Morphology of Cancer Cells Experiment Objective: 990 In this lab, students will explore the morphology of normal and cancerous cells by staining pre-fi xed cells with methylene blue and eosin.
Thawing MEFs (Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs)
 1 FEEDER CULTURES The function of feeder cultures is to support the undifferentiated growth of hpsc. Typically primary fibroblasts are used for this purpose. We prepare our mouse feeder cells from ICR
1 FEEDER CULTURES The function of feeder cultures is to support the undifferentiated growth of hpsc. Typically primary fibroblasts are used for this purpose. We prepare our mouse feeder cells from ICR
CYTOLOGY: What every general practitioner should know ( and every future specialist)
 CYTOLOGY: What every general practitioner should know ( and every future specialist) 16 April 2014 Dr C Crause Pathologist and Senior Lecturer Department of Anatomical Pathology University of Pretoria/NHLS
CYTOLOGY: What every general practitioner should know ( and every future specialist) 16 April 2014 Dr C Crause Pathologist and Senior Lecturer Department of Anatomical Pathology University of Pretoria/NHLS
Preface to the Second Edition
 Preface to the Second Edition This second edition of Diagnosis of Endometrial Biopsies and Curettings: A Practical Approach follows a number of favorable comments we received about the first edition. As
Preface to the Second Edition This second edition of Diagnosis of Endometrial Biopsies and Curettings: A Practical Approach follows a number of favorable comments we received about the first edition. As
Squamous differentiation in carcinoma in situ of the
 J. clin. Path. (196), 20, Squamous differentiation in carcinoma in situ of the cervix uteri A cyto-histological correlation of malignant intraepithelial invasive carcinoma CHANDRA GRUBB AND IVAN JANOTA1
J. clin. Path. (196), 20, Squamous differentiation in carcinoma in situ of the cervix uteri A cyto-histological correlation of malignant intraepithelial invasive carcinoma CHANDRA GRUBB AND IVAN JANOTA1
A comparison of the effects of estrus cow. nuclear maturation of bovine oocytes
 A comparison of the effects of estrus cow serum and fetal calf serum on in vitro nuclear maturation of bovine oocytes J Spiropoulos, SE Long University of Bristol, School of Veterinary Science, Department
A comparison of the effects of estrus cow serum and fetal calf serum on in vitro nuclear maturation of bovine oocytes J Spiropoulos, SE Long University of Bristol, School of Veterinary Science, Department
Page # 1. Endometrium. Cellular Components. Anatomical Regions. Management of SIL Thomas C. Wright, Jr. Most common diseases:
 Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy
 Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy Patient Information Laparoscopy The laparoscope, a surgical instrument similar to a telescope, is inserted through a small incision (cut) in the belly button during laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy Patient Information Laparoscopy The laparoscope, a surgical instrument similar to a telescope, is inserted through a small incision (cut) in the belly button during laparoscopy.
Experimental Neoplastic Formation in Embryonic Chick Brains
 Experimental Neoplastic Formation in Embryonic Chick Brains by BENGT KALLEN 1 From the Tornblad Institute of Comparative Embryology, Lund WITH TWO PLATES IN mammalian teratology, a malformation consisting
Experimental Neoplastic Formation in Embryonic Chick Brains by BENGT KALLEN 1 From the Tornblad Institute of Comparative Embryology, Lund WITH TWO PLATES IN mammalian teratology, a malformation consisting
MOTH DISSECTION GUIDE
 MOTH DISSECTION GUIDE GENITALIA EXAMINATION The beginner usually concentrates on the macro-moths (larger moths) as illustrated in Bernard Skinner or Paul Waring s moth guides. With the aid of these 'lepidopterist's
MOTH DISSECTION GUIDE GENITALIA EXAMINATION The beginner usually concentrates on the macro-moths (larger moths) as illustrated in Bernard Skinner or Paul Waring s moth guides. With the aid of these 'lepidopterist's
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma
 Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code
 Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code Gogamz Menu Cancer of the endometrium, adenocarcinoma ;. (mucous membrane that lines the endometrial cavity). ICD - 10 -CM C54.1 is grouped within. ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis
Endometrial adenocarcinoma icd 10 code Gogamz Menu Cancer of the endometrium, adenocarcinoma ;. (mucous membrane that lines the endometrial cavity). ICD - 10 -CM C54.1 is grouped within. ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 95. Chromosomal Abnormality, Megaloblastosis, and Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia P. E. CROSSEN, P. H. FITZGERALD, R. C. MENZIES, and L. A. BREHAUT From Cytogenetics
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 95. Chromosomal Abnormality, Megaloblastosis, and Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia P. E. CROSSEN, P. H. FITZGERALD, R. C. MENZIES, and L. A. BREHAUT From Cytogenetics
Chromosome pathology
 Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination. May 4, 2010
 Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination May 4, 2010 Examination Length = 3 hours Total Marks = 100 (7 questions) Total Pages = 8 (including cover sheet and 2 pages of prints)
Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination May 4, 2010 Examination Length = 3 hours Total Marks = 100 (7 questions) Total Pages = 8 (including cover sheet and 2 pages of prints)
One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans.
 Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
By H. BARNER and H. CHRISTIANSEN The Danish State Forestry's Tree Improvement Station Humlebaek, Denmark
 The Formation of Pollen, the Pollination Mechanism, and the Determination of the Most Favourable Time for Controlled Pollination in Pseudotsuga Menziesii By H. BARNER and H. CHRISTIANSEN The Danish State
The Formation of Pollen, the Pollination Mechanism, and the Determination of the Most Favourable Time for Controlled Pollination in Pseudotsuga Menziesii By H. BARNER and H. CHRISTIANSEN The Danish State
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL
 DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
connected grains in Trigonella foenum-graecum
 B-chromosomes, pollen germination in situ and connected grains in Trigonella foenum-graecum By Sheila JOSHI & Satendra S. RAGHUVANSHI Cytogenetic Laboratory, Department of Botany, Lucknow University, Lucknow,
B-chromosomes, pollen germination in situ and connected grains in Trigonella foenum-graecum By Sheila JOSHI & Satendra S. RAGHUVANSHI Cytogenetic Laboratory, Department of Botany, Lucknow University, Lucknow,
Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique and cytology smears among Sudanese patients
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 3/ June 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 3/ June 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique
Cervical Cancer Screening for the Primary Care Physician for Average Risk Individuals Clinical Practice Guidelines. June 2013
 Cervical Cancer Screening for the Primary Care Physician for Average Risk Individuals Clinical Practice Guidelines General Principles: Since its introduction in 1943, Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is widely
Cervical Cancer Screening for the Primary Care Physician for Average Risk Individuals Clinical Practice Guidelines General Principles: Since its introduction in 1943, Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is widely
The Gardner syndrome: increased tetraploidy in
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 52-56. The Gardner syndrome: increased tetraploidy in cultured skin fibroblast* B. SHANNON DANES Department of Medicine, Cornell University Medical College, New
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 52-56. The Gardner syndrome: increased tetraploidy in cultured skin fibroblast* B. SHANNON DANES Department of Medicine, Cornell University Medical College, New
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use
 Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
