Sex differentiation to puberty. Introduction
|
|
|
- Kerry Loraine Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ex to puberty exual in general: chromosomal, gonadal and phenotypic sex, endocrine control of phenotypic, role of testicular hormones in male development, disorders of sexual 30 Hypothalamic sexual : sexual dimorphic areas, androgenized female model, olfactory placode and GnRH migration, development and maturation of female HPG axis as intro to puberty and to adult cyclicity Puberty: definition, hypothesis, role of GnRH and other systems, diseases Introduction repro and its story lines & Page 1
2 Introduction ex Neuroendo control egg sperm genetic sex external features gonadal sex phenotypic sex internal urogenital system external secondary genitalia sex charachteristics FH-LH secretion CN genetic sex established at conception governs development of gonadal sex sex behavior Introduction ex Neuroendo control The undifferentiated state has a bipotential gonad and both Mullerian and Wolffian systems Page 2
3 Introduction ex Neuroendo control The bipotential gonad can give origin to an ovary (cortex, default) or to a testis (medulla) Introduction ex Neuroendo control The bipotential gonad can give origin to an ovary (cortex, default) or to a testis (medulla) Page 3
4 ex and Gonadal Differentiation ex Neuroendo control undifferent gonad cortex --> ovary medulla --> testis female pattern is default unless testis-determining factor (TDF), a transcription factor of the RY gene (sex-determining region of Y gene), is present The bipotential gonad can give origin to an ovary (cortex, default) or to a testis (medulla) ex and Gonadal Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Development of the testes and ovaries from common precursors in the genital ridges. RY, (the sex-determining region of the Y chromosome), is the gene expressed only in cells that develop into ertoli cells. In the absence of RY these cells develop into follicle cells. ertoli cells express OX 9 and other transcription factors and the autocrine factor FGF9 (fibroblast growth factor 9) that lead to and multiplication of ertoli cells. nclosure of the primordial germ cells by ertoli cells to form the primitive spermatic cords and unequivocal recognition of the primitive gonads as testes occurs as early as the seventh week. ubsequent recruitment of mesenchymal cells and their into Leydig cells takes place in response to the secreted factors DHH (desert hedgehog) and PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor). Newly differentiated ertoli cells also secrete AMH (antimüllerian hormone) and inhibin. The first primordial follicles do not appear in the primitive ovary until the eleventh week. The bipotential gonad can give origin to an ovary (cortex, default) or to a testis (medulla) Page 4
5 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Development of the male and female internal genitalia. Normal development of the male and female reproductive tracts. Tissues destined to form male tract are in blue; tissues that develop into female tract are in pink. Bilateral castration of either male or female embryos results in development of the female pattern. arly unilateral castration of male embryos results in development of the normal male duct system on the side with the remaining gonad, but female development on the contralateral side. This pattern develops because both testosterone and antimüllerian hormone act as paracrine factors. Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control female pattern is default unless TDF, a transcription factor of the RY gene, is present Page 5
6 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control TDF of RY gene as master switch for downstream genes embryo without Y develops as female embryo with multiple X + 1Y = male XX injected with RY gene ---> male RY turns indifferent genital ridge into medullary development of testis, testosterone production, male phenotype RY gene is normally present in males but its locus was deduced from XX individuals with testis development that inherited 40kb Y chromosome (n=4) gain of function mutations in genes downstream might explain testis in XX female pattern is default unless TDF, a transcription factor of the RY gene, is present Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control steroid receptors, ligand- dependent transcription factors, bind unique HR in the promoter of specific target genes orphan receptors, which have been cloned by homology, have no known ligands but appear to be mediators of adult endocrine function and organogenesis F-1 = Ad4BP is one of these receptors. It resembles the Drosophila Ftz-F1, which regulates the developmental homobox gene fushi tarazu (for paired body components) F-1 transcripts are found in steroid-producing organs, in ertoli cells, in pituitary gonadotrope, and in the VMN during formation of bipotential gonad, sexual (sexually dimorphic pattern), and in the adult gonad expressed in developing gonadotropes prior to expression of alpha and ß subunits of LH & FH, but not in GnRH neurons F-1 knockout mice die of corticoid insufficiency (volume depletion, low corticosterone, high ACTH), have female external & internal genitalia regardless of chromosomal sex, do not express LH & FH, and do not have the VMN a proposed homeostatic relay center involved in metabolic and reproductive control female pattern is default unless TDF, a transcription factor of the RY gene, is present Page 6
7 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control female pattern is default unless TDF, a transcription factor of the RY gene, is present Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control AMH Antimüllerian hormone (AMH) signaling pathway. AMH binds to its specific primary receptor (II), which then forms a heterodimer with and phosphorylates the secondary signal transducing subunit (I). The activated receptor complex then catalyzes phosphorylation of mad proteins on serine and threonine residues causing them to bind mad 4, which carries them into the nucleus where transcription of specific genes results in expression of an apoptotic program and resorption of the müllerian duct cells. Mullerian system regress in males (AMH) through apoptotic mechanisms (suicide) Page 7
8 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Anomalies in male development due to single gene mutations. A.- Normal production of AMH, T and 5-DHT results in regression of female internal organs and the development of internal and external male organs. B.- Absence or defect in RY leads to ovarian agenesis and normal development of female internal and external genitalia and absence of male characteristics. C.- AMH absence leads to develop-ment of both male and female internal genitalia and normal male external genitalia except that in some cases the presence of the female organs interferes with normal testicular descent into the scrotum. D.- Absence of 17-hydroxylase or the androgen receptor results in an individual without an internal male or female reproductive tract, and with female external genitalia..- Absence of 5-dehydrogenase II results in normal development of male internal organs, except prostate, and normal regression of female internal sex organs. The external organs may be overtly female or ambiguous. Mullerian system regress in males (AMH) through apoptotic mechanisms (suicide) Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control gonocytes from yolk sac move to gut and seed undifferentiated gonad: male / medulla, female / cortex gonadal anlagen is visible at 4 weeks gestation, testis at 7 weeks (if the Y gene is present) and the ovary at weeks in females apoptosis of Wolffian system in males anti-mullerian hormone (AMH), a member of the TGFß family of peptides female genitalia in the absence of Y male genitalia is dependent of androgen production by the testis. Timing, effect of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in XX testosterone, critical period, hypothalamic sexual and reproductive cycles In the absence of testis development the genetic program stimulates development of an ovary Page 8
9 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control T DHT 5a-reductase nucleus diff. male ext. genitalia (penis & scrotum) T nucleus diff. male int. genitals & 2nd sex charact. T 2 aromatase nucleus diff. male hypoth. (tonic vs phasic LH) chromosomal sex: and the role of RY, such as in the Klinefelter s (XXY) and in Turner s (XO) syndromes gonadal sex: when chromosomal sex is normal but gonadal is abnormal (pure gonadal disgenesis) genital fold & tubercle genital swelling phenotypic sex: can be ambiguous or in disagreement with chromosomal and with gonadal sex (pseudohermaphroditism) T induces of the internal genitalia and DHT that of the external genitalia Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Metabolism of testosterone. Most of the testosterone (T) secreted each day is degraded in the liver and other tissues by reduction of the A ring, oxidation of the 17 hydroxyl group, and conjugation with polar substituents. Conversion to 5- DHT takes place in target cells catalyzed mainly by the type II dehydrogenase and in nontarget cells mainly but not exclusively by the type I dehydrogenase. Aromatization of T to 2 may occur directly or after conversion to androstenedione. Note that 5- DHT cannot be aromatized or reconverted to T. T in presence of 5a-reductase generates DHT and in presence of aromatase generates 2 Page 9
10 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Action of testosterone. Testosterone (T) enters target cell and binds to its nuclear androgen receptor (AR) either directly or after it is converted to 5-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The thickness of the arrows reflects the quantitative importance of each reaction. The hormone receptor complex binds DNA along with a variety of cell-specific nuclear regulatory proteins to induce formation of the RNA that encodes the proteins that express effects of the hormone. Not shown: T may also bind to membrane receptors & initiate rapid ionic changes that may reinforce its genomic effects. T may also produce rapid changes in camp production through binding of the sex hormone binding globulin (HBG) to surface receptors. T and DHT are steroids and their mechanism of action involve intracellular receptors Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Action of testosterone. Testosterone (T) enters target cell and binds to its nuclear androgen receptor (AR) either directly or after it is converted to 5-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The thickness of the arrows reflects the quantitative importance of each reaction. The hormone receptor complex binds DNA along with a variety of cell-specific nuclear regulatory proteins to induce formation of the RNA that encodes the proteins that express effects of the hormone. Not shown: T may also bind to membrane receptors & initiate rapid ionic changes that may reinforce its genomic effects. T may also produce rapid changes in camp production through binding of the sex hormone binding globulin (HBG) to surface receptors. T and DHT are steroids and their mechanism of action involve intracellular receptors Page 10
11 Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Action of testosterone. Testosterone (T) enters target cell and binds to its nuclear androgen receptor (AR) either directly or after it is converted to 5-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The thickness of the arrows reflects the quantitative importance of each reaction. The hormone receptor complex binds DNA along with a variety of cell-specific nuclear regulatory proteins to induce formation of the RNA that encodes the proteins that express effects of the hormone. Not shown: T may also bind to membrane receptors & initiate rapid ionic changes that may reinforce its genomic effects. T may also produce rapid changes in camp production through binding of the sex hormone binding globulin (HBG) to surface receptors. T and DHT are steroids and their mechanism of action involve intracellular receptors Phenotypic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control ndocrine pathologies include hypofunction and hyperfunction of primary or secondary origin Page 11
12 ex Differentiation and Development Disorders ex Neuroendo control Turner syndrome patients (XO) usually have short stature and delay puberty ex Differentiation and Development Disorders ex Neuroendo control beware of single bars Complete testicular feminization (XY, AR mutation)) and an undervirilized male Page 12
13 ex Differentiation and Development Disorders ex Virilization fetal adrenal steroidogenesis defects Neuroendo control 3ßH-steroid dehydrogenase partial (top) and complete deficiency in male (top) and (below) virilization in genetic in female (below) females with 21 H deficiency Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism before and after treatment with T cypionate ex Differentiation and Development Disorders ex Neuroendo control Page 13
14 Hypothalamic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Male hypothalamic is caused by T to 2 aromatization in sexual dimorphic areas Hypothalamic Differentiation ex GnRH neurons GnRH GnRH Neuroendo control Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Page 14
15 Hypothalamic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Hypothalamic Differentiation ex Neuroendo control embriology, neonatal androgenization, POA, 2 positive feedback, 2 vs in androgenized rats, pituitary deafferentation, transplant, HHA, M, glia and portal vessels, maturation of the HPG axis GnRH neuroanatomy, migration, Kallman syndrome, hypogonadal mouse, sex behavior, H. burtoni, GnRH agonist / antagonists olfactory placode sexual dimorphic areas tonic vs phasic LH control the preovulatory surge of GnRH & LH Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Page 15
16 Neuroendocrinology of Puberty ex Neuroendo control Puberty as a process and its relationship to the theoretical control the onset of puberty as an example of the hypothalamic maturation of the theoretical neural components of a feedback system controlling pulsatile GnRH release and reproduction "ability to carry a fetus to terminus" and "temporal maturational process" as components in the definition of female puberty and in their relationship with the black boxes of the control system Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Phenotypic changes at puberty ex Neuroendo control Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Page 16
17 Functional changes at puberty ex Neuroendo control infantile uterus responds to steroids well before the onset of puberty (assays and ideopathic precocious puberty) neonatal ovary has autonomous follicular growth and responds to gonadotrophins during infantile period (has steroid output) neonatal anterior pituitary responds as an adult pituitary when transplanted to adult hypox rats (neonatal AP to their mothers) the CN negative and positive feedbacks of 2 on LH and FH are not present in the infantile period, but they become progresively active during the prepubertal period ( - and + FB approaches) Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Hormonal change at puberty ex Neuroendo control LH GH Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Page 17
18 Theories on puberty onset ex Neuroendo control while dynamic AP-ovarian relationship are operative before puberty, its onset results from the elaboration of sufficient hormones it is brought about by removal of inhibitory inputs to gonadotropins (reseting of the gonadostat) it is caused by stimulation of facilitatory inputs on gonadotropin secretion (increase in central drive), rather than by gonadostat resetting puberty onset is the climax of a cascade of developmental changes occurring harmoniously during reproductive immaturity the cascade of events preceding puberty is elicited by hypothalamic "timekeeping" genes (homeotic genes), which activate a central drive neurogenic mechanism Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Theories on puberty onset ex GnRH Neuroendo control GnRH GnRH GnRH GnRH Female hypothalamic, the default program, includes 2 s ability to induce ovulation Page 18
19 Puberty-related Pathologies ex Neuroendo control 7 year old boy, central precocious puberty 2ary to neurofibromatosis, unaffected twin Puberty-related Pathologies ex Neuroendo control 5 year old 2 year old Precocious puberty central ideopathic (girl) & 2nd to congenital adrenal hyperplasia (boy) Page 19
Sex Differentiation. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Reproduction. Introduction
 Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
Menstrual Cycle. Last example of how a circle works. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Sexual Development. 6 Stages of Development
 6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17)
 Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span 9/22/99
 Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
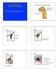 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
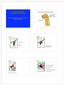 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Please Take Seats by Gender as Shown Leave Three Seats Empty in the Middle
 Please Take Seats by Gender as Shown Leave Three Seats Empty in the Middle Women Men Sexual Differentiation & Development Neal G. Simon, Ph.D. Professor Dept. of Biological Sciences Signaling Cascade &
Please Take Seats by Gender as Shown Leave Three Seats Empty in the Middle Women Men Sexual Differentiation & Development Neal G. Simon, Ph.D. Professor Dept. of Biological Sciences Signaling Cascade &
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs
 Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: SEX HORMONES PART 1 An Overview What are steroid hormones? Steroid
1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: SEX HORMONES PART 1 An Overview What are steroid hormones? Steroid
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Reproductive cyclicity 19. Introduction. Page 1. repro and its story lines. Male repro: a simpler way of control
 Reproductive cyclicity 19 Male repro: a simpler way of control Menstrual cycles: ovary / uterine anatomy and cell types, follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, cyclicity Race events: removal of P4
Reproductive cyclicity 19 Male repro: a simpler way of control Menstrual cycles: ovary / uterine anatomy and cell types, follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, cyclicity Race events: removal of P4
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems!
 Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype.
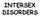 INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
Mohammad Sha ban. Basheq Jehad. Hamzah Nakhleh
 11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
Sexual Differentiation. Physiological Psychology PSYC370 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D. Sexual Differentiation. Sexual Differentiation (continued)
 Physiological Psychology PSYC370 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D. Sexual Differentiation Sexual Differentiation Reproductive behavior constitute the most important category of social behavior, Ú because without
Physiological Psychology PSYC370 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D. Sexual Differentiation Sexual Differentiation Reproductive behavior constitute the most important category of social behavior, Ú because without
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
DAX1, testes development role 7, 8 DFFRY, spermatogenesis role 49 DMRT genes, male sex differentiation role 15
 Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
Development of the female Reproductive System. Dr. Susheela Rani
 Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
2. Which of the following factors does not contribute to ion selectivity?
 General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Development of the Genital System
 Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood
 When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline. 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing Effects of Sex Hormones in Utero and Anomalies
 Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female.
 The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female. Dr. Tamatha Barbeau, Dept. of Biology Guest Lecture for Gender 200 March 2017 Objectives: 1. Sex vs. Gender defined. 2. Biological sex based on inheritance
The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female. Dr. Tamatha Barbeau, Dept. of Biology Guest Lecture for Gender 200 March 2017 Objectives: 1. Sex vs. Gender defined. 2. Biological sex based on inheritance
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
DEVELOPMENT (DSD) 1 4 DISORDERS OF SEX
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5)
 IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
Reproduction. AMH Anti-Müllerian Hormone. Analyte Information
 Reproduction AMH Anti-Müllerian Hormone Analyte Information - 1-2011-01-11 AMH Anti-Müllerian Hormone Introduction Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein dimer composed of two 72 kda monomers 1.
Reproduction AMH Anti-Müllerian Hormone Analyte Information - 1-2011-01-11 AMH Anti-Müllerian Hormone Introduction Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein dimer composed of two 72 kda monomers 1.
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD)
 Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
Topics for this lecture: Sex determination Sexual differentiation Sex differences in behavior and CNS development. 1) organizational effects of
 Topics for this lecture: Sex determination Sexual differentiation Sex differences in behavior and CNS development. 1) organizational effects of gonadal steroids on CNS development 2) our model system:
Topics for this lecture: Sex determination Sexual differentiation Sex differences in behavior and CNS development. 1) organizational effects of gonadal steroids on CNS development 2) our model system:
Development of the urogenital system
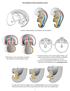 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
TESTOSTERONE DEFINITION
 DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
Why is my body not changing? Conflicts of interest. Overview 11/9/2015. None
 Why is my body not changing? Murthy Korada Pediatrician, Pediatric Endocrinologist Ridge Meadows Hospital Surrey Memorial Hospital None Conflicts of interest Overview Overview of normal pubertal timing
Why is my body not changing? Murthy Korada Pediatrician, Pediatric Endocrinologist Ridge Meadows Hospital Surrey Memorial Hospital None Conflicts of interest Overview Overview of normal pubertal timing
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Reproductive physiology
 Reproductive physiology Sex hormones: Androgens Estrogens Gestagens Learning objectives 86 (also 90) Sex Genetic sex Gonadal sex Phenotypic sex XY - XX chromosomes testes - ovaries external features Tha
Reproductive physiology Sex hormones: Androgens Estrogens Gestagens Learning objectives 86 (also 90) Sex Genetic sex Gonadal sex Phenotypic sex XY - XX chromosomes testes - ovaries external features Tha
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase
 Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Ch 11: Endocrine System
 Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
The reproductive system
 The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
Two important cells in female are the theca cells and the granulose cells. Granulosa cells are affected by the two gonadotropin hormones; FSH and LH.
 1 UGS physiology sheet #13 lecture 3 Dr.Saleem Khresha. Now we will start discussing the female reproductive system Ovarian Steroids Two important cells in female are the theca cells and the granulose
1 UGS physiology sheet #13 lecture 3 Dr.Saleem Khresha. Now we will start discussing the female reproductive system Ovarian Steroids Two important cells in female are the theca cells and the granulose
GENDER James Bier
 GENDER 2005-2008 James Bier Objectives 1. State the method of determining gender in several genetic systems. 2. List the three regions of the Y chromosome. 3. Describe the events that promote sexual development
GENDER 2005-2008 James Bier Objectives 1. State the method of determining gender in several genetic systems. 2. List the three regions of the Y chromosome. 3. Describe the events that promote sexual development
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system.
 Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
GONADAL FUNCTION: An Overview
 GONADAL FUNCTION: An Overview University of PNG School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry BMLS III & BDS IV VJ Temple 1 What are the Steroid hormones?
GONADAL FUNCTION: An Overview University of PNG School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry BMLS III & BDS IV VJ Temple 1 What are the Steroid hormones?
Goals. Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview. Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology
 Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Why Sex??? Advantages: It limits harmful mutations Asexual: all offspring get all mutations. Sexual: There is a random distribution of mutations.
 Reproduction Why sex??? Why Sex??? Asexual reproduction is quicker, easier, and produces more offspring per individual. Bacteria do it. Dandelions do it. Unisexual whiptail lizards do it. With sexual reproduction
Reproduction Why sex??? Why Sex??? Asexual reproduction is quicker, easier, and produces more offspring per individual. Bacteria do it. Dandelions do it. Unisexual whiptail lizards do it. With sexual reproduction
Model Answer. M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology)
 Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
SEX STERIOD HORMONES I: An Overview. University of PNG School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences PBL MBBS III VJ Temple
 SEX STERIOD HORMONES I: An Overview University of PNG School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences PBL MBBS III VJ Temple 1 What are the Steroid hormones? Hormones synthesized
SEX STERIOD HORMONES I: An Overview University of PNG School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences PBL MBBS III VJ Temple 1 What are the Steroid hormones? Hormones synthesized
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA. Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK. Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Intersex is a group of conditions where there is a discrepancy between the external genitals and the internal genitals (the testes and ovaries).
 Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive FSH. Analyte Information
 Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda
 1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
Maldescended testis in Adults. Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Reproduction Lecture Spring 2009
 Reproduction Lecture Spring 2009 Slide #2: The term gonads refer to the sex organs. In the male, these are the testes, and the in the female, the ovary. The produce sex cells, or gametes. The male gamete
Reproduction Lecture Spring 2009 Slide #2: The term gonads refer to the sex organs. In the male, these are the testes, and the in the female, the ovary. The produce sex cells, or gametes. The male gamete
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Puberty and Pubertal Disorders Part 3: Delayed Puberty
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Puberty and Pubertal Disorders Part 3: Delayed Puberty These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Puberty and Pubertal Disorders Part 3: Delayed Puberty These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Sexual Reproduction. For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species.
 Sex Determination Sexual Reproduction For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. Meiosis in the sexual organs of parents produces haploid
Sex Determination Sexual Reproduction For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. Meiosis in the sexual organs of parents produces haploid
Topic No. & Title: Topic 4 Biosynthesis and secretion of adrenal, ovarian and testicular hormones-factors influencing secretion
 [Academic Script] Biosynthesis and secretion of adrenal, ovarian and testicular hormones-factors influencing secretion Subject: Zoology Course: B.Sc. 2 nd Year Paper No. & Title: Z-203B Vertebrate Endocrinology
[Academic Script] Biosynthesis and secretion of adrenal, ovarian and testicular hormones-factors influencing secretion Subject: Zoology Course: B.Sc. 2 nd Year Paper No. & Title: Z-203B Vertebrate Endocrinology
Gender Dimorphism. Lecture 35
 Gender Dimorphism Lecture 35 1 Aspects of Gender Dimorphism Biological Sex Gender Identity Gender Role Sexual Orientation 2 The Human Genome National Geographic 3 Caster Semenya Gold Medal, 800m Race World
Gender Dimorphism Lecture 35 1 Aspects of Gender Dimorphism Biological Sex Gender Identity Gender Role Sexual Orientation 2 The Human Genome National Geographic 3 Caster Semenya Gold Medal, 800m Race World
Martin Ritzén. bioscience explained Vol 7 No 2. Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within
 Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
IN MOST species all aspects of reproduction are controlled
 0163-769X/99/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 20(5): 726 737 Copyright 1999 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. The Role of Androgens in Male Gender Role Behavior JEAN D. WILSON Department of Internal
0163-769X/99/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 20(5): 726 737 Copyright 1999 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. The Role of Androgens in Male Gender Role Behavior JEAN D. WILSON Department of Internal
HORMONES & REPRODUCTION OUTLINE
 1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION
 Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Sex chromosomes and sex determination
 Sex chromosomes and sex determination History (1) 1940-ties Alfred Jost embryo-surgical experiments on gonads gonadal sex; male gonadal sex presence of testes; female gonadal sex lack of testes. History
Sex chromosomes and sex determination History (1) 1940-ties Alfred Jost embryo-surgical experiments on gonads gonadal sex; male gonadal sex presence of testes; female gonadal sex lack of testes. History
HOMOSEXYALITY AS A CONSEQUENCE OF EPIGENETICALLY CANALIZED SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT. W.R.Rice, U.Freiberg, S.Gavrilets. December 2012
 HOMOSEXYALITY AS A CONSEQUENCE OF EPIGENETICALLY CANALIZED SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT W.R.Rice, U.Freiberg, S.Gavrilets December 2012 Used terms: Epi-marks means changes in chromatin structure that influence the
HOMOSEXYALITY AS A CONSEQUENCE OF EPIGENETICALLY CANALIZED SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT W.R.Rice, U.Freiberg, S.Gavrilets December 2012 Used terms: Epi-marks means changes in chromatin structure that influence the
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
BIOSYNTHESIS OF STEROID HORMONES
 BIOSYNTHESIS OF STEROID HORMONES Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI sw/steroidrepro/inter/08 1 STEROID HORMONES Progestins (21 C) Glucocorticoids (21 C) Mineralocorticoids
BIOSYNTHESIS OF STEROID HORMONES Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI sw/steroidrepro/inter/08 1 STEROID HORMONES Progestins (21 C) Glucocorticoids (21 C) Mineralocorticoids
