Testis /10/2019. Please submit all questions concerning the webinar content through the Q&A panel.
|
|
|
- Evan Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Testis NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES 1 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning the webinar content through the Q&A panel. If you have participants watching this webinar at your site, please collect their names and s We will be distributing a Q&A document in about one week. This document will fully answer questions asked during the webinar and will contain any corrections that we may discover after the webinar. 2 NAACCR Webinar Series 1
2 Fabulous Prizes 3 Guest Speakers Louanne Currence, RHIT, CTR Denise Harrison, BS, CTR 4 NAACCR Webinar Series 2
3 Agenda Anatomy Solid Tumor Rules Staging AJCC Summary Stage EOD SSDI 5 TESTICULAR CANCER Where the Boys Are Louanne Currence, RHIT, CTR Denise Harrison, BS, CTR NAACCR Webinar Series 3
4 Case Study #1: Workup 42 yr old male noticed palpable Lt testicular mass. CXR, CT scan abd/pelvis, and screening serum testicular cancer tests negative. Sonogram: mult. areas hypoechoic heterogeneity; overall diameter 2.5 cm; appearance suspicious for malignancy Pre-op markers: AFP 2 ng/ml (normal 0 9); BHCG < 2 miu/ml (normal < 2); LDH 197 units/l (normal ). 7 Case Study #1: CAP Checklist SPECIMEN TYPE: radical orchiectomy SPECIMEN LATERALITY: Left TUMOR FOCALITY: Unifocal TUMOR SIZE: 1.8 cm in greatest dimension of tumor MACROSCOPIC EXTENT OF TUMOR: Confined to testes HISTOLOGIC TYPE: Seminoma, classic type SPERMATIC CORD: Uninvolved by tumor MICROSCOPIC TUMOR EXTENSION: None identified LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION: Absent PATHOLOGIC STAGING: Primary tumor: pt1a, tumor limited to testes Regional lymph nodes: pnx 8 NAACCR Webinar Series 4
5 Case Study #1: Post-Op Post-op lab markers: per urologist not required since they were negative prior to surgery. POSTOP RAD ONC CONSULTATION: Here to discuss treatment options; given his disease stage, we discussed recurrence potential of ~15 to 20%; discussed alternatives of observation alone, adjuvant radiation therapy, or single-agent carboplatinum. Postop adjuvant RT: 22.5GY peri-aortic lymph nodes, 18MV photons 9 Case Study #2: Workup Here for scrotal swelling; mass on Lt side has grown in size and is painful; hx of hernial repair and varicocele repair at age 14. Sonogram: 8.1 cm Lt testicular mass concerning for malignancy Pre-op Labs: AFP 4.7 ng/ml (normal 0 8); BHCG: 51.48mIU/mL (< 5000 miu/ml); LDH 1447 IU/L ( IU/L) 10 NAACCR Webinar Series 5
6 Case Study #2: CAP Checklist SPECIMEN TYPE: radical orchiectomy SPECIMEN LATERALITY: Left TUMOR FOCALITY: Multifocal (two foci of 5 cm and 2.7cm) TUMOR SIZE: 5 cm and 2.7 cm in greatest dimension of tumors MICROSCOPIC EXTENT OF TUMOR: Confined to the testis HISTOLOGIC TYPE: Mixed germ cell tumor: Embryonal carcinoma (85%), Seminoma (10%, Yolk sac tumor (5%) MARGINS: Spermatic cord margin and other margins: Uninvolved by tumor MICROSCOPIC TUMOR EXTENSION: Not identified LYMPH-VASCULAR INVASION: Indeterminate (see comment) 11 Case Study #2: continued PATHOLOGIC STAGING TNM descriptors: m(multiple) Primary tumor: pt1(m): Tumor limited to the testis and epididymis without definitive vascular/lymphatic invasion Regional lymph nodes: pnx: Cannot be assessed (no nodes submitted or found) SERUM TUMOR MARKERS: At least S1 AFP 4.7 ng/ml (normal 0 8); BHCG: 51.48mIU/mL (< 5000 miu/ml); LDH 1447 IU/L ( IU/L ) POST-OP LABS: AFP 3.2 ng/ml (normal 0 8); BHCG < 2.39 miu/ml (normal 0 1); LDH 412 IU/L (normal IU/L) 12 NAACCR Webinar Series 6
7 Case Study #3: Workup 34 year old male in E.R. with large very firm testicular tumor about 9 cm in size, consistent with possible malignancy by exam and ultrasound. Pre-op labs: AFP = 83 (H), BHCG 3 miu/ml (normal 0 5); LDH 293 u/l (normal ) 13 Case Study #3: CAP Checklist SPECIMEN TYPE: radical orchiectomy SPECIMEN LATERALITY: Left TUMOR FOCALITY: Unifocal TUMOR SIZE: 9.5 x 7.9 x 6.4 cm MICROSCOPIC EXTENT OF TUMOR: Confined to the testis HISTOLOGIC TYPE: Teratoma (90%) and yolk sac tumor (10%) with focal rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation MARGINS Spermatic cord margin: Uninvolved by tumor Other margins: Uninvolved by tumor LYMPH-VASCULAR INVASION: Present PATHOLOGIC STAGING Primary tumor: pt2 Regional lymph nodes: pnx 14 NAACCR Webinar Series 7
8 Case Study #3: Post-op Post-op CT Abd/Pel: prominent 3.3 cm para-aortic and 1.3 cm aortocaval LNs concerning for metastatic dz; Additional Rt retrocrural LN, 1.6 cm subcarinal/paraesophageal LN, soft tissue nodule in periphery of RLL and nodular area of pleural thickening in medial aspect Lt lung base suspicious for additional areas of metastatic dz Post-op markers: AFP = 193 (H), LDH = 201 (normal), BhCG not repeated 15 Case Study #3: Post-op, continued Med onc Consult: Good risk, nonseminomatous, Lt testicular mixed germ cell carcinoma. Plan: 3 cycles of BEP (Bleomycin, Etoposide, Cisplatin) after he heals from surgery followed by excision of metastatic tissue in 3-stage 6/19/XX: chemo started 9/27/XX: Mediastinal LND and removal of pulmonary mets 11/19/XX: Rt RPLND: 0/4 periaortic, 1/7 interaortocaval LNs 2/12/YY: Lt RPLND: 3/5 paracaval LNs in 8.8 cm mass 16 NAACCR Webinar Series 8
9 Testicular Cancer Facts 1% of all male cancer About 8,000 new cases a year 390 deaths per year Most common cancer ages Usually white males, especially Scandinavian 1-3% bilateral 90% curable even in late stage 17 SEER Data 18 NAACCR Webinar Series 9
10 Risk Factors Cryptorchidism Congenital abnormalities Testes, penis, or kidneys Inguinal hernia History of testicular cancer Family history (father, brother) Genetics: TGCT1 found 19 Incidence Rate by Race (U.S.A.) RACE/ETHNICITY White Black Asian/Pacific Island Amer Indian/Alaskan Hispanic RATE 6.8 per 100,000 men 1.54 per 100,000 men 2.2 per 100,000 men 5.4 per 100,000 men 5.1 per 100,000 men NCI s SEER Cancer Statistics Review NAACCR Webinar Series 10
11 Screening Not recommended Good survival rate, even at later stage Not cost-effective Testicular Self-Exam After shower Roll both Check epididymis 21 Symptoms Painless lump or swelling Pain or discomfort Enlargement, funny feeling Heaviness in scrotum Dull ache in back, groin, or abdomen Fluid collection in scrotum Enlargement/tenderness breasts 22 NAACCR Webinar Series 11
12 Topography Codes C62.0 Undescended C62.1 Descended C62.9 Testis NOS Unknown if descended 23 Vocabulary Leydig cells secrete testosterone Sertoli cells nurse or mother cells; nourish the developing sperm cells through the process of spermatogenesis Tunica albuginea dense capsule around each testis; inhibits direct extension of tumor Rete (ree' tee) testis network of efferent ducts Epididymis storage vessel for sperm; long, coiled tube external to testis Vas (ductus) deferens muscular extension of epididymis which carries sperm to urethra 24 NAACCR Webinar Series 12
13 25 Testicle and Epididymis, Surface SEER Training Modules, Testicular Cancer. U. S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. November 27, 2018 < 26 NAACCR Webinar Series 13
14 2015 Pearson Education, Inc, November tcrc.acor.org 27, 2018,< 27 Covering Layers of Testicle From lecture by Dr Isha Jaiswal 28 NAACCR Webinar Series 14
15 Descent of Testis Lymphatics Follow Abdominal cavity Inguinal canal Scrotum From lecture by Dr Isha Jaiswal NAACCR Webinar Series 15
16 Workup Tumor markers pre-op LDH, AFP, HCG Ultrasound Biopsy (not usually of testicle to avoid scrotal contamination) Chest x-ray and other radiology for staging 31 MP/H Rules Other Sites Rule M8 Tumors on both sides (right and left) of a site listed in Table 1 are multiple primaries. (C62 YES) Rule M10 Tumors diagnosed more than one (1) year apart are multiple primaries. Rule M17 Tumors with ICD-O-3 histology codes that are different at the first (xxxx), second (xxxx) or third (xxxx) number are multiple primaries. 32 NAACCR Webinar Series 16
17 Number of Primaries Case 1: Orchiectomy path states unifocal Case 2: Orchiectomy path states multifocal (two foci) Case 3: Orchiectomy path states unifocal 33 Number of Primaries Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 1 per M2: single tumor = single primary 1 per M18: rules M3-M17 do not apply, therefore single primary 1 per M2: single tumor = single primary 34 NAACCR Webinar Series 17
18 Rule H5, H16, H30 Table 2 Column 1: Required Histo Column 2: Combined w/histo Column 3: Combination Term Column 4: Code Teratoma Embryonal carcinoma Teratocarcinoma 9081 Teratoma & one or more of histologies in Col 2 Seminoma Yolk sac tumor Mixed germ cell tumor 9085 Choriocarcinoma Teratoma Seminoma Embryonal Choriocarcinoma combined w/other germ cell elements Histology Case 1: Seminoma, classic type Case 2: Mixed germ cell tumor Embryonal carcinoma (85%) Seminoma (10%) Yolk sac tumor (5%) Case 3: Teratoma (90%) and yolk sac tumor (10%) with focal rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation 36 NAACCR Webinar Series 18
19 Histology Case 1 Case 2 Case /3 Seminoma 9085/3 Mixed germ cell tumor 9085/3 Mixed germ cell tumor 37 Germ Cell Tumors CIS Seminoma Seminoma with syncytiotropholastic cells Spermatocytic tumor (formerly spermatocytic seminoma) Embryonal carcinoma Yolk sac tumor Teratoma Choriocarcinoma 38 NAACCR Webinar Series 19
20 Seminoma 75% stage I 4-5 th decade at diagnosis Mets to LNs Negative AFP (for pure seminoma) medstat.med.utah.edu 39 Nonseminomatous Germ Cell Tumors Embryonal Yolk Sac Choriocarcinoma Teratoma Age 30s Children Children 25-30s Adults 20-30s Pure 2% Children Rare (poor prognosis) 5% Mixed Usually Adults Usually Usually Mets Liver, RLNs, lung Liver Lung, liver, brain AFP (+) focal (+) (-) (-) hcg (-) (-) (+) (>100K miu/ml) (-) CEA (-) 40 NAACCR Webinar Series 20
21 Nongerminal Tumors Sex Cord Stromal Tumors Leydig cell Median age 60 yrs Rarely metastasize Sx: Endocrine abnormalities Sertoli cell Any age Only 10% malignant Granulosa cell Juvenile - benign Adult - rare 41 Nongerminal Tumors, cont. Gonadoblastomas Mixed germ cell & sex cord tumor Occurs in undescended Bilateral 30% Benign BUT path should be reviewed for malignant germ cell Lymphomas & leukemias Late manifestation of disseminated disease Common in children with ALL 42 NAACCR Webinar Series 21
22 Others Rhabdomyosarcoma Most common sarcoma in children Can originate in testicle Metastatic 2.5% men Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Usually mediastinal, retroperitoneal, or pineal May have CIS in testicle if retroperitoneal 43 Grade Time Frame Guidelines Grade Clinical Info during clinical time frame Usually bx or FNA Before any treatment Grade Post-Therapy Info from resected tumor POST neoadjuvant Grade Pathological Info from resected tumor UNLESS clinical grade is higher/worse Resection must meet AJCC criteria for cancer site 44 NAACCR Webinar Series 22
23 Grade Clinical Guidelines Microscopic exam is done (FNA, biopsy, needle core biopsy, etc.) Cannot be BLANK Assign highest grade from primary tumor during clinical time frame Code 9 (unknown) when: Grade not documented Clinical staging N/A Grade checked N/A on CAP Protocol If only 1 grade available, and unknown grade time frame, assign to grade clinical 45 Grade Pathological Guidelines Surgical resection done MUST not be BLANK Assign highest grade from PRIMARY tumor Use clinical grade when resection performed and: Clinical grade is higher No grade documented No residual tumor Bx T4/Bx LN: eligible for path stage in AJCC, cannot use for grade path because NO resection 46 NAACCR Webinar Series 23
24 Grade Pathological Guidelines Code 9 (unk) when: Grade not documented (and no clinical grade) No resection of primary site Neoadjuvant therapy done (see Post-Tx Grade) Clinical case only Only one grade documented and can t tell if clinical or pathological (put in clinical) Grade checked N/A on CAP Protocol 47 Grade Post-Therapy Guidelines Leave BLANK when: No neoadjuvant therapy Clinical or pathological case only Only one grade and can t tell which one code to clinical Assign highest grade from resected primary AFTER neoadjuvant therapy Code 9 (unk) when surgical resection performed post neoadjuvant treatment, and: Grade from primary not documented No residual tumor Grade checked N/A on CAP Protocol 48 NAACCR Webinar Series 24
25 Grade ID Table 98 Code Description A Well differentiated B Moderately differentiated C Poorl differentiated D Undifferentiated, anaplastic 9 Grade cannot be assessed; Unknown Note: No grade items on CAP Protocol forms/instructions 49 Grade Fields Cases 1-3 : Clinical no microscopic examination Pathological no grade provided Post-Therapy no neoadjuvant treatment 50 NAACCR Webinar Series 25
26 Grade Fields Clinical Pathological Post Therapy Case Blank Case Blank Case Blank 51 Timing for Tumor Size Clinical Size (SEER) Largest size in mm Before ANY treatment starts OR Within 4 months diagnosis date if no treatment (incl observation, supportive care) OR To date of cancer progression if happens before 4-month window Pathological Size (SEER) Largest size in mm of primary tumor that has been resected (including after neoadjuvant therapy) as part of the first definitive treatment TS Summary Best TS prior to neoadjuvant therapy (Path size when surgery is first treatment) Surgical size = Clinical size 52 NAACCR Webinar Series 26
27 Recording Tumor Size Code Tumor Size Description 000 No mass/tumor found mm or < 1 mm Exact size in mm (2 mm to 988 mm) mm 990 Microscopic focus or foci only and no size focus given 999 Unknown; size not stated; not documented in patient record; size tumor cannot be assessed; not applicable 53 Tumor Size fields Case 1: Sonogram: mult. areas hypoechoic heterogeneity; overall diameter 2.5 cm; appearance suspicious for malignancy Path: 1.8 cm in greatest dimension of tumor; additional dimensions 1.6 x 1.4 cm Case 2: Sonogam: 8.1 cm mass. Path: Main tumor mass: 5 c cm; additional tumor nodule: 2.7 cm Case 3: H&P: large very firm testicular tumor about 9 cm in size, consistent with possible malignancy by exam and ultrasound. Path: 9.5 x 7.9 x 6.4 cm 54 NAACCR Webinar Series 27
28 Tumor Size Fields Clinical Pathological Summary Case Case Case Lymphovascular Invasion Record from path report or physician statement Any primary tumor specimen: biopsy or resection Code 0 for in situ Code 8 for benign, borderline brain and CNS Special instructions (use the table) for pts treated with neoadjuvant therapy 56 NAACCR Webinar Series 28
29 Lymphovascular Invasion, cont. Code 1 (LVI NOS) when: LVI or one of its synonyms is present Synonyms (not an exhaustive list) Angiolymphatic invasion Blood vessel invasion Lymph vascular emboli Lymphatic invasion Lymphovascular invasion Vascular invasion 57 Lymphovascular Invasion, cont. Code 8 Code 9 Lymphoma No micro exam of primary tumor tissue HemeRetic Primary site specimen is Cytology or FNA Plasma Cell Myeloma Schemas other than Penis and Testis IF the registry is not collecting LVI (standard setter does not require it) Bx is very small tissue sample Not possible to determine LVI Pathologists states specimen insufficient to determine LVI LVI not mentioned in path rpt Primary site unknown 58 NAACCR Webinar Series 29
30 Lymphovascular Invasion Codes 0 LVI not present, not identified (includes in situ) 1 LVI present/identified, NOS 2 Lymphatic & small vessel invasion only (L) 3 Venous (large vessel) invasion only (V) 4 BOTH lymphatic & small vessel AND venous large vessel invasion 8 Not Applicable 9 Presence of LVI unknown CAP Protocol choices: Not identified, Present, Cannot be determined 59 Lymphovascular Invasion Case 1: LVI absent Case 2: LVI indeterminate Case 3: LVI present 60 NAACCR Webinar Series 30
31 Lymphovascular Invasion Case 1: Case 2: Case 3: SUMMARY STAGE NAACCR Webinar Series 31
32 SEER Summary Stage In situ, Intraepithelial, noninvasive Germ cell neoplasia in situ Intratubular germ cell neoplasia 1 Localized only (localized, NOS) WITHOUT or UNKNOWN lymphovascular invasion Body of testis Rete testis Surface implants (surface of tunica vaginalis) Tunica albuginea Tunica vaginalis involved Tunica, NOS 63 SEER Summary Stage 2018, cont. 2 Regional by direct extension only WITH lymphovascular invasion Tumor limited to testis (including rete testis invasion) WITH or WITHOUT lymphovascular invasion Dartos muscle, ipsilateral Epididymis Hilar soft tissue Mediastinum (of testis) Scrotum, ipsilateral Spermatic cord, ipsilateral Vas deferens Visceral mesothelial layer 64 NAACCR Webinar Series 32
33 SEER Summary Stage 2018, cont. 3 Regional lymph node(s) involved only WITH or WITHOUT previous scrotal or inguinal surgery Aortic, NOS Lateral (lumbar) Para-aortic Periaortic Preaortic Retroaortic Pericaval, NOS Interaortocaval Paracaval Precaval Retrocaval Retroperitoneal, NOS Spermatic vein Regional LN(s), NOS; LN(s), NOS 65 SEER Summary Stage 2018, cont. 3 Regional lymph node(s) involved only WITH previous scrotal or inguinal surgery External iliac Inguinal node(s), NOS Deep, NOS Node of Cloquet or Rosenmuller (highest deep inguinal) Superficial (femoral) Pelvic, NOS 4 Regional by BOTH direct extension AND regional lymph node(s) involved (Codes 2 + 3) 66 NAACCR Webinar Series 33
34 SEER Summary Stage 2018, cont. 7 Distant site(s) (including further contiguous extension) Adrenal (suprarenal gland) Kidney Penis Retroperitoneum Scrotum, contralateral Testis, bilateral Ulceration of scrotum Distant metastasis, NOS Carcinomatosis Distant metastasis WITH or WITHOUT distant lymph node(s) 67 SEER Summary Stage 2018, cont. 7 Distant lymph node(s), cont. Deep, NOS Node of Cloquet or Rosenmuller (highest deep inguinal) Superficial (femoral) Pelvic, NOS Lymph nodes WITHOUT previous scrotal or inguinal surgery or UNKNOWN if previous scrotal or inguinal surgery External iliac Inguinal nodes, NOS 68 NAACCR Webinar Series 34
35 Summary Stage 2018 Case 1: Confined to testes; LVI absent Case 2: Confined to testes; LVI indeterminate Case 3: Confined to testes; LVI present: post-op scans show involved RLNs (para-aortic and aortocaval), as well as mets to distant LNs (retrocrural and subcarinal/paraesophageal) and bilateral lung mets 69 Summary Stage 2018 Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 1 Limited to testis w/o LVI 1 Limited to testis; indeterminate LVI 7 Distant mets 70 NAACCR Webinar Series 35
36 Extent of Disease EOD Primary Tumor Code Description In situ, intraepithelial, noninvasive Intra articular germ cell neoplasia Germ cell neoplasia in situ FOR PURE SEMINOMAS ONLY Tumor < 3 cm, limited to the testis W/O LVI or unknown if LVI FOR PURE SEMINOMAS ONLY Tumor 3 cm, limited to the testis W/O LVI or unknown if LVI Note: radical orchiectomy required for codes 100, 200, 400, and NAACCR Webinar Series 36
37 EOD Primary Tumor, cont. Tumor limited to testis W/O LVI or unknown if LVI Body of testis Tunica albuginea 200 Rete testis Tunica vaginalis involved Surface implants (surface of Tunica, NOS tunica vaginalis) Confined to testis, NOS Localized, NOS 300 Tumor limited to testis (including rete testis invasion) W/ LVI Epididymis Hilar soft tissue 400 Mediastinum (of testis) Visceral mesothelial layer 73 EOD Primary Tumor, cont. Spermatic cord, ipsilateral 500 Vas deferens Dartos muscle, ipsilateral 600 Scrotum, ipsilateral Penis Scrotum, contralateral 700 Ulceration of scrotum Further contiguous extension 800 No evidence of primary tumor Unknown extension; Primary tumor cannot be assessed; Not 999 documented in patient record; Death Certificate Only 74 NAACCR Webinar Series 37
38 EOD Regional Nodes Aortic, NOS Lateral (lumbar) Para-aortic Periaortic Preaortic Retroaortic Pericaval, NOS Interaortocaval Paracaval Precaval Retrocaval Retroperitoneal below the diaphragm or NOS Spermatic vein 75 EOD Regional Nodes Lymph nodes WITH previous scrotal or inguinal surgery External iliac Inguinal nodes, NOS Deep, NOS Node of Cloquet or Rosenmuller (highest deep inguinal) Superficial (femoral) Pelvic Note: Involvement of inguinal, pelvic, or external iliac LNs WITHOUT or unknown if previous scrotal or inguinal surgery prior to presentation of the testis tumor is coded in EOD Mets as distant lymph node involvement. 76 NAACCR Webinar Series 38
39 EOD Regional Nodes 000 CLINICAL or PATHOLOGICAL: No RLN involvement 100 CLINICAL ONLY: Metastasis in LN(s), all < 2 cm 200 PATHOLOGICAL ONLY: : Metastasis in LN(s), all < 2 cm 300 CLINICAL ONLY: Metastasis lymph node(s), 2 to 5 cm (inclusive) 400 PATHOLOGICAL ONLY: Metastasis lymph node(s), 2 to 5 cm (inclusive) 500 PATHOLOGICAL ONLY: ENE present 600 CLINICAL or PATHOLOGICAL: Metastasis in a LN > 5 cm Regional lymph node(s), NOS 800 Lymph node(s), NOS Unknown; regional lymph node(s) not stated Regional lymph node(s) cannot be assessed 999 Not documented in patient record Death Certificate Only 77 EOD Mets Code Description No distant metastasis 00 Unknown if distant metastasis Distant LN(s) W/O or UNKNOWN if previous scrotal or inguinal surgery 10 External iliac Pelvic, NOS Distant LN(s) W/O or UNKNOWN if previous scrotal or inguinal surgery Inguinal, NOS Deep, NOS 30 Node of Cloquet or Rosenmuller Superficial (femoral) (highest deep inguinal) Distant lymph node(s), NOS Retroperitoneal specified as above the diaphragm 50 Lung WITH or WITHOUT distant lymph nodes Other distant site(s) W/ or W/O/ distant LN(s) and/or lung 60 Carcinomatosis 70 Distant metastasis, NOS 99 Death Certificate Only 78 NAACCR Webinar Series 39
40 EOD Fields Case 1: Pure seminoma confined to testes; LVI absent; CT abdomen/pelvis negative Case 2: Mixed germ cell tumor confined to testes; LVI indeterminate Case 3: Mixed germ cell tumor confined to testes; LVI present: post-op scans show involved RLNs (3.3 cm para-aortic and 1.3 cmaortocaval), as well as mets to distant LNs (retrocrural and subcarinal/paraesophageal) and bilateral lung mets; path showed 8.8 cm paracaval LN mass 79 EOD Fields Primary Regional Mets Tumor Nodes 100 Case Case Case NAACCR Webinar Series 40
41 Survival 81 TNM Staging NAACCR Webinar Series 41
42 Changes from the 7 th Edition Seminomas use TS 3 cm cut point Invasion of epididymis and hilar soft tissue have changed T definition Spermatic cord involvement could be categorized in T or M, depending on route of involvement Review TNM Staging forms 83 CAP Testis Protocol Summary of Changes (3/2018) Version errata Size of largest metastatic deposit MODIFIED unit of measure from mm to cm Tumor extension MODIFIED Tumor invades through tunica albuginea and perforates tunica vaginalis (mesothelium) Primary tumor MODIFIED pt3: Tumor directly invades spermatic cord soft tissue with or without lymphovascular invasion 84 NAACCR Webinar Series 42
43 Additional Notes (from TNM Supplement for 7 th ed. TNM staging) pt2: includes invasion of cremaster muscle, cremaster fascia, testicular portion of internal/external spermatic fascia (i.e. invasion scrotum w/o skin) pt3: invading spermatic cord means direct invasion. Invasion lymph or blood vessels = vessels lined by endothelium. Includes invasion plexus pampiniformis or invasion perihilar fat pt4: invasion subcutis or cutis of scrotum 85 More Notes (TNM Supplement for 7 th ed TNM staging) Tis can be diagnosed in case of testis biopsy with intratubular germ cell neoplasia (carcinoma in situ) T4 can be diagnosed if scrotum invasion is confirmed by biopsy 86 NAACCR Webinar Series 43
44 N Categories Very important to check patient history of surgeries (looking for abdominal or inguinal surgeries) Separate tables for clinical and pathological N cn based on size of involved LN; 2 and 5 cm cut points pn based on Size of involved LN: 2 and 5 cm cut points Number of involved LNs: 5 is cut point 87 M Categories M1 subdivided to distinguish between distant nodal or lung mets and mets to other viscera 88 NAACCR Webinar Series 44
45 TNM Fields Case 1: 1.8 cm Pure seminoma confined to testes; LVI absent. CT abdomen/pelvis negative Case 2: 5 cm and 2.7 cm mixed germ cell tumors confined to testes; LVI indeterminate Case 3: 9.5 cm mixed germ cell tumor confined to testes; LVI present: post-op scans show involved RLNs (para-aortic and aortocaval), as well as mets to distant LNs (retrocrural and subcarinal/paraesophageal) and bilateral lung mets 89 Clinical AJCC TNM Categories T N M Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 ctx cn0 cm0 ctx cnx cm0 ctx cnx cm0 90 NAACCR Webinar Series 45
46 Pathological AJCC TNM Categories T N M Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 pt1a pnx cm0 pt1(m) pnx cm0 pt2 pnx cm1a 91 Tumor Markers Pre-op markers May suggest histo types of tumor (Example: seminomas do not produce AFP) May be used by urologists to request further path specimens Used for clinical group stage Post-op markers Residual? If markers do not return to normal in appropriate time, discuss adjuvant therapy (chemo, RT) Recurrence? After normal labs then markers start rising Used for pathological stage 92 NAACCR Webinar Series 46
47 Recording Lab Values when less than or greater than are used Record the lab value as one less than stated when a value is reported as less than X. Example 1: PSA stated as < 5. Record 4.9 Example 2: hcg lab value resulting findings of <1. Record 0.9 Example 3: ER Percent Positive stated as < 60%. Record 059 (59%) Record the value as one more than stated when value is reported as more than X. Example 1: CEA stated as > 7. Record 7.1 Example 2: PR Percent Positive > 75%. Record 076 (76%) Per General Instructions (updated with Version 1.5 January 2019) 93 Serum Markers (S) - Notes Code S per MD; MD statement takes priority over any S value determined by available lab values or calculated by vendor software For AFP: 1 ug/l = 1 ng/ml = 0.83 IU/mL Code clinical S prior to any treatment Code pathological S post-orchiectomy If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest post-orchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy All 3 lab values are needed for S0-S1. Only 1 elevated test is needed to assign S2-S3. If any individual test is N/A and none of the available tests meets the S2-S3 criterion for that test, assign code 9 (SX). 94 NAACCR Webinar Series 47
48 Serum Markers (S) Clinical and Pathological Code Description 0 S0: Marker study levels within normal levels 1 S1: At least one of these values is elevated AND LDH less than 1.5 x N* AND hcg (miu/l) less than 5,000 AND AFP (ng/ml) less than 1,000 2 S2: LDH 1.5 x N* to 10 x N* OR hcg (miu/l) 5,000 to 50,000 OR AFP (ng/ml) 1,000 to 10,000 3 S3: Only one elevated test is needed LDH greater than 10 x N* OR hcg (miu/ml) greater than 50,000 OR AFP (ng/ml) greater than 10,000 9 SX: Not documented in medical record S Category Clinical not assessed or unknown if assessed 95 Serum Markers (S) Fields Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 AFP Pre 2 ng/ml ( 0 9) 4.7 ng/ml (0 8) 83 (H) Post Not repeated 3.2 ng/ml (0 8) 193 (H) BhCG Pre < 2 miu/ml (< 2) miu/ml (< 5000 miu/ml) 3 miu/ml (0 5) Post Not repeated < 2.39 miu/ml (0 1) Not repeated LDH Pre 197 units/l ( ) LDH 1447 IU/L ( ) 293 u/l ( ) Post Not repeated LDH 412 IU/L ( ) 201 (normal) 96 NAACCR Webinar Series 48
49 Serum Markers (S) Clinical and Pathological Clinical Pathological Case (use pre-orchi markers) Case Case (use post orchi AFP and LDH with pre orchi HCG 97 SSDI: AFP Pre-Orchiectomy Lab Value MD statement when no other info available Record highest AFP lab value prior to orchiectomy or systemic treatment ug/l = ng/ml 1 ng/ml = 0.83 IU/mL (to be added to version 1.5) Use same lab value for pre-orchiectomy lab value and range Level should return to normal < 35 days after surgery False + with liver diseases 98 NAACCR Webinar Series 49
50 AFP Conversion from IU/mL to ng/ml Per the Canswer Forum 11/1/18 This will be added to the SSDI manual for the 2019 update. From the ADVIA Centaur Assay Manual for AFP: The system reports AFP results in ng/ml (common units) or IU/mL (SI units), depending on the units defined when setting up the assay. The conversion formula is 1 ng/ml = 0.83 IU/mL. To calculate ng from IU/mL, divide the value for IU by IU/mL: 10/0.83 = ng/ml; 5 IU/mL: 5/0.83 = 6.02 ng/ml 99 SSDI: AFP Pre-Orchiectomy Lab Value Code Description nanograms/milliliter (ng/ml) ,999.9 ng/ml XXXXX.1 100,000 ng/ml or greater XXXXX.7 Test ordered, results not in chart XXXXX.8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case XXXXX.9 Not documented in medical record AFP Pre Orchiectomy not assessed or unknown if assessed 100 NAACCR Webinar Series 50
51 SSDI: AFP Post-Orchiectomy Lab Value MD statement when no other info available Record highest AFP lab value after orchiectomy but prior to adjuvant treatment If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest postorchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy ug/l = ng/ml 1 ng/ml = 0.83 IU/mL (to be added to version 1.5) Use same lab value for post-orchiectomy lab value and range 101 SSDI: AFP Post-Orchiectomy Lab Value Code Description nanograms/milliliter (ng/ml) ,999.9 ng/ml XXXXX.1 100,000 ng/ml or greater XXXXX.7 Test ordered, results not in chart XXXXX.8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case XXXXX.9 Not documented in medical record AFP Post Orchiectomy not assessed or unknown if assessed 102 NAACCR Webinar Series 51
52 SSDI: AFP Pre-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest AFP prior to orchiectomy or systemic treatment ug/l = ng/ml (1 ng/ml = 0.83 IU/mL) Use same lab value for pre-orchiectomy lab value and rang 103 SSDI: AFP Pre-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Above normal and less than 1,000 nanograms/milliliter (ng/ml) 2 1,000 10,000 ng/ml 3 Greater than 10,000 ng/ml 4 Pre Orchiectomy alpha fetoprotein (AFP) stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record AFP Pre Orchiectomy Range not assessed or unknown if assessed 104 NAACCR Webinar Series 52
53 SSDI: AFP Post-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest AFP after orchiectomy but prior to adjuvant treatment If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest postorchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy ug/l = ng/ml Use same lab value for pre-orchiectomy lab value and range 105 SSDI: AFP Post-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Above normal and less than 1,000 nanograms/milliliter (ng/ml) 2 1,000 10,000 ng/ml 3 Greater than 10,000 ng/ml 4 Post Orchiectomy alpha fetoprotein (AFP) stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record AFP Post Orchiectomy Range not assessed or unknown if assessed 106 NAACCR Webinar Series 53
54 Serum Markers Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 AFP Pre 2 ng/ml ( 0 9) 4.7 ng/ml (0 8) 83 (H) Post Not repeated 3.2 ng/ml (0 8) 193 (H) BhCG Pre < 2 miu/ml (< 2) miu/ml (< 5000 miu/ml) 3 miu/ml (0 5) Post Not repeated < 2.39 miu/ml (0 1) Not repeated LDH Pre 197 units/l ( ) LDH 1447 IU/L ( ) 293 u/l ( ) Post Not repeated LDH 412 IU/L ( ) 201 (normal) 107 SSDI: AFP Pre and Post Orchiectomy Fields Pre-Orchiectomy Post-Orchiectomy Value Range Value Range Case XXXXX.9 9 Case Case NAACCR Webinar Series 54
55 Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Not detectable in healthy males (produced during pregnancy) 90% of level every 21 days should be noted during chemo If not, residual? Drug resistance? False + from low testosterone or marijuana use Elevated in chorioca (100%), embryonal (60%), teratoca (55%) 109 SSDI: hcg Pre-Orchiectomy Lab Value MD statement when no other info available Record highest hcg prior to orchiectomy systemic treatment IU/L = miu/ml Use same lab value for pre-orchiectomy lab value and range 110 NAACCR Webinar Series 55
56 SSDI: hcg Pre-Orchiectomy Lab Value Code Description milli-international Units/milliliter (miu/ml) ,999.9 miu/ml XXXXX.1 100,000 miu/ml or greater XXXXX.7 Test ordered, results not in chart XXXXX.8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case XXXXX.9 Not documented in medical record hcg Pre-Orchiectomy Lab Value not assessed or unknown if assessed 111 SSDI: hcg Post-Orchiectomy Lab Value MD statement when no other info available Record highest hcg after orchiectomy but prior to adjuvant treatment If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest postorchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy IU/L = miu/ml Use same lab value for post-orchiectomy lab value and range 112 NAACCR Webinar Series 56
57 SSDI: hcg Post-Orchiectomy Lab Value Code Description milli-international Units/milliliter (miu/ml) ,999.9 miu/ml XXXXX.1 100,000 miu/ml or greater XXXXX.7 Test ordered, results not in chart XXXXX.8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case XXXXX.9 Not documented in medical record hcg Post-Orchiectomy Lab Value not assessed or unknown if assessed 113 SSDI: hcg Pre-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest hcg prior to orchiectomy or systemic treatment IU/L = miu/ml Use same lab value for pre-orchiectomy lab value and range 114 NAACCR Webinar Series 57
58 SSDI: hcg Pre-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Above normal and less than 5,000 milli International Units/milliliter (miu/ml) 2 5,000 50,000 miu/ml 3 Greater than 50,000 miu/ml 4 Pre orchiectomy human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg) stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record hcg Pre Orchiectomy range not assessed or unknown if assessed 115 SSDI: hcg Post-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest hcg after orchiectomy but prior to adjuvant treatment If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest postorchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy IU/L = miu/ml Use same lab value for post-orchiectomy lab value and range 116 NAACCR Webinar Series 58
59 SSDI: hcg Post-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Above normal and less than 5,000 milli International Units/milliliter (miu/ml) 2 5,000 50,000 miu/ml 3 Greater than 50,000 miu/ml 4 Pre orchiectomy human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg) stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record hcg Post Orchiectomy range not assessed or unknown if assessed 117 HCG Fields Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 AFP Pre 2 ng/ml ( 0 9) 4.7 ng/ml (0 8) 83 (H) Post Not repeated 3.2 ng/ml (0 8) 193 (H) BhCG Pre < 2 miu/ml (< 2) miu/ml (< 5000 miu/ml) 3 miu/ml (0 5) Post Not repeated < 2.39 miu/ml (0 1) Not repeated LDH Pre 197 units/l ( ) LDH 1447 IU/L ( ) 293 u/l ( ) Post Not repeated LDH 412 IU/L ( ) 201 (normal) 118 NAACCR Webinar Series 59
60 SSDI: hcg Pre and Post Orchiectomy Fields Pre-Orchiectomy Post-Orchiectomy Value Range Value Range Case XXXXX.9 9 Case Case XXXXX Histo & Tumor Markers TYPE FREQ % AFP % HCG % Germ cell Seminoma Non-sem germ Embryonal Teratocarcinoma Teratoma Choriocarcinoma Yolk sac < NAACCR Webinar Series 60
61 SSDI: LDH Pre-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest LDH prior to orchiectomy or systemic treatment Test indicates some type of tissue damage called nonspecific marker in 8 th ed. AJCC Elevated in 50% patients Any tumor can elevate LDH 121 LDH Elevation Causes Hemolytic anemia Pernicious anemia Infections Sepsis Intestinal or lung infarction Acute kidney disease Acute liver disease Acute muscle injury Pancreatitis Bone fractures Testicular cancer, lymphoma, OR other cancers Strenuous exercise Increased platelet count 122 NAACCR Webinar Series 61
62 SSDI: LDH Pre-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Less than 1.5 x N (Less than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal for LDH) to 10 x N (Between 1.5 and 10 times the upper limit of normal for LDH) 3 Greater than 10 x N 4 Pre Orchiectomy LDH range stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record LDH Pre Orchiectomy Range not assessed or unknown if assessed 123 SSDI: LDH Post-Orchiectomy Range MD statement when no other info available Record range of highest LDH after orchiectomy but prior to adjuvant treatment If post-orchiectomy remains elevated, use lowest postorchiectomy value prior to adjuvant therapy LDH is least specific of the 3 tumor markers for testicular cancer; magnitude of LDH elevation directly correlates with testis tumor burden If pre-orchiectomy LDH was normal, post-orchiectomy LDH may not be performed: use code NAACCR Webinar Series 62
63 SSDI: LDH Post-Orchiectomy Range Code Description 0 Within normal limits 1 Less than 1.5 x N (Less than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal for LDH) to 10 x N (Between 1.5 and 10 times the upper limit of normal for LDH) 3 Greater than 10 x N 4 Post Orchiectomy LDH range stated to be elevated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case 9 Not documented in medical record LDH Post Orchiectomy Range not assessed or unknown if assessed 125 LDH Fields Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 AFP Pre 2 ng/ml ( 0 9) 4.7 ng/ml (0 8) 83 (H) Post Not repeated 3.2 ng/ml (0 8) 193 (H) BhCG Pre < 2 miu/ml (< 2) miu/ml (< 5000 miu/ml) 3 miu/ml (0 5) Post Not repeated < 2.39 miu/ml (0 1) Not repeated LDH Pre 197 units/l ( ) LDH 1447 IU/L ( ) 293 u/l ( ) Post Not repeated LDH 412 IU/L ( ) 201 (normal) 126 NAACCR Webinar Series 63
64 SSDI: LDH Pre and Post Orchiectomy Fields Pre Post Case 1 Case 2 Case AJCC Prognostic Stage Group Clinical Pathological Post Therapy Case Blank Case Blank Case 3 99 IIIA Blank 128 NAACCR Webinar Series 64
65 TREATMENT Landmark Advancements in Testicular CA 1937 hcg found in male urine CA patients 1940s Seminomas radiosensitive 1960 Actinomycin-D chemo in advanced CA 1965 Cisplatin found 1974 PVB regimen (cisplatin, vinblastine, bleo) 1980s nerve-sparing RPLND 1987 BEP replaces PVB 1989 BEP down to 3 cycles 130 NAACCR Webinar Series 65
66 Orchiectomy Surgery Codes 12 Local destruction NOS (no path) 20 Local/partial excision 30 Orchi WITHOUT spermatic cord 40 Orchi WITH cord or NOS if cord 80 Orchi NOS 132 NAACCR Webinar Series 66
67 until the fat tenor sings Doctor watches: Markers CT scans to decide whether Chemo RT for LN Observe only Takes approx. 3 mos to decide if adjuvant tx 133 Surveillance? (sample) Year One: Tumor markers & CXR q 2 mo; CT q 3 mos Year Two: Tumor markers & CXR q 2 mo; CT q 4 mos Years 3-5: Tumor markers, CXR, CT q 6 mos After Year 5: Tumor markers, CXR q year 134 NAACCR Webinar Series 67
68 Retroperitoneal LN Dissection Clin Stage Modified Nerve-Spare Full Bilateral I Optional Recom Not Recom IIA Optional Recom Not Recom IIB Recommended Possible Possible IIC Not Recom Possible Recom 135 Treatment Considerations Implants Silicone (firmer?) Saline (softer, more $) Sperm Banking 136 NAACCR Webinar Series 68
69 NCCN Treatment: Seminoma Stage 1 RT to retroperitoneal and ipsilateral inguinal nodes OR Surveillance Stage 2A Stage 2B, 2C RT to retroperitoneal and inguinal nodes, possibly with mediastinal and supraclavicular nodes OR chemo Platinum-based combination chemotherapy or RT, as in IIA Stage 3 Platinum-based combination chemotherapy, possibly with resection of residual mass 137 NCCN Treatment: NON-Seminoma Stage 1A Stage IB Stage 2A Stage 2B, 2C Stage 3 Surveillance OR nerve-spare RPLND Nerve spare RPLND OR chemo OR surveillance (T2 only) RPLND OR chemo Chemotherapy OR RPLND Chemo +/- RPLND 138 NAACCR Webinar Series 69
70 Tx Decision Tree Clinical Oncology, 3 rd Edition, 2004, Elsevier 139 First-Line Chemo (per NCI 2018) Bleomycin Cisplatin Cosmegen (dactinomycin) Etoposide phosphate Ifosfamide Vinblastine sulfate BEP (bleo, etop, cispl) JEB (carbo, etop, bleo) PEB (cispl, etop, bleo) VeIP (velban, ifos, cispl) VIP (etop, ifos, cispl) 140 NAACCR Webinar Series 70
71 Survival Stage Seminoma Non- Seminoma Overall Stage I 99% 98% 98% Stage II 95% 95% 95% Stage III 90% 76% 78% All Stages 96% 141 Side Effects Post Treatment Secondary malignant neoplasms (AML, bladder, kidney, pancreas, rectal, thyroid) Pulmonary (especially if bleomycin) Cardiovascular toxicity Neurotoxicity Ototoxicity Nephrotoxicity Hypogonadism Fertility issues 142 NAACCR Webinar Series 71
72 Follow-Up Most recurrences within first 3 years Q 2-3 mos year 1 Then q 3-6 mos year 2 Then q 6 mos til year 5 May include PE, lab markers, CXR, CT abd/pel 143 MD-IQ Quiz (NCI PDQ Information) Q1: Which of the following statements about testicular cancer is most accurate? A. It most often develops in elderly men B. Most testicular cancers are somatic cell tumors C. It is highly treatable and usually curable Q2: Which of the following types is associated with an elevated level of alphafetoprotein (AFP) in testicular cancer? A. Seminomas B. Nonseminomas 144 NAACCR Webinar Series 72
73 MD-IQ Quiz Q3: Which of the following testicular subtypes are considered nonseminomas? A. Embryonal carcinomas B. Teratomas C. Yolk sac tumors D. Choriocarcinomas E. All of the above Q4: True or False: Men with nonseminomatous primary tumors appear to have a lower risk of developing subsequent contralateral testis tumors than men with seminomas A. True B. False 145 MD-IQ Quiz Q5: Which of the following is the procedure of choice to diagnose and treat a malignant testicular mass? A. Trans-scrotal biopsy B. Biopsy of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes C. Radical inguinal orchiectomy with initial high ligation of the spermatic cord MD-IQ Quiz Editors (imn-newsletters@flmdiq.com) 146 NAACCR Webinar Series 73
74 Testis /10/2019 Slogans/Campaigns Get a Grip! Eyes down, check your balls Bollocks to cancer Balls in my court Cancer stole my left Nut So long Mr Right Check your bag Let s give the boys a hand 147 Fabulous Prize Winners NAACCR Webinar Series 74
75 Coming UP Collecting Cancer Data: Colon 02/07/2019 Abstracting and Coding Boot Camp 03/07/2019 CE Certificate Quiz/Survey Phrase Link NAACCR Webinar Series 75
Testicular Malignancies /8/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2/3/11. Collecting Cancer Data: NAACCR Webinar Series 1. Agenda. Fabulous Prizes
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis February 3, 2011 NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series Agenda Coding moment Race/Hispanic origin Overview Collaborative Stage Treatment Exercises Fabulous Prizes NAACCR 2010-2011
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis February 3, 2011 NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series Agenda Coding moment Race/Hispanic origin Overview Collaborative Stage Treatment Exercises Fabulous Prizes NAACCR 2010-2011
Quiz 1. Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios.
 Quiz 1 Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios. 1. 62 year old Brazilian female Race 1 Race 2 Spanish/Hispanic Origin 2. 43 year old Asian male born in Japan Race 1
Quiz 1 Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios. 1. 62 year old Brazilian female Race 1 Race 2 Spanish/Hispanic Origin 2. 43 year old Asian male born in Japan Race 1
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 38 (Text updated March 2005) P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro Introduction Compared with other types of cancer
38 (Text updated March 2005) P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro Introduction Compared with other types of cancer
Exercise. Discharge Summary
 Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Testis. Protocol applies to all malignant germ cell and malignant sex cord-stromal tumors of the testis, exclusive of paratesticular malignancies.
 Testis Protocol applies to all malignant germ cell and malignant sex cord-stromal tumors of the testis, exclusive of paratesticular malignancies. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC
Testis Protocol applies to all malignant germ cell and malignant sex cord-stromal tumors of the testis, exclusive of paratesticular malignancies. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2018) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna (Vice-chair), N. Nicolai,
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2018) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna (Vice-chair), N. Nicolai,
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2015) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2015) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULR CNCER (Limited text update March 2017) P. lbers (Chair), W. lbrecht, F. lgaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi,. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Introduction
EU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULR CNCER (Limited text update March 2017) P. lbers (Chair), W. lbrecht, F. lgaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi,. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Introduction
STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
Testicular germ cell tumors
 Testicular germ cell tumors Introduction Most common solid tumor in young adult men with 3 6 new cases/100,000 men/year. They acc ount for 1.5% of male malignancies and 5% of urological tumors. Bilateral
Testicular germ cell tumors Introduction Most common solid tumor in young adult men with 3 6 new cases/100,000 men/year. They acc ount for 1.5% of male malignancies and 5% of urological tumors. Bilateral
*OPERATIVE PROCEDURE. Serum tumour markers within normal limits S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN
 Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
4/10/2018. SEER EOD and Summary Stage. Overview KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING. What is SEER EOD? Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines
 SEER EOD and Summary Stage KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING Overview What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets SEER Summary Stage 2018 Site Specific
SEER EOD and Summary Stage KCR 2018 SPRING TRAINING Overview What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets SEER Summary Stage 2018 Site Specific
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Lung /4/18. Please submit all questions concerning the webinar content through the Q&A panel.
 Lung NAACCR 2018 2019 WEBINAR SERIES 1 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning the webinar content through the Q&A panel. If you have participants watching this webinar at your site, please collect
Lung NAACCR 2018 2019 WEBINAR SERIES 1 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning the webinar content through the Q&A panel. If you have participants watching this webinar at your site, please collect
Cardiff MRCS OSCE Courses Testicular Cancer
 Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
TESTICULAR CANCER Updated March 2016 by Dr. Safiya Karim (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Toronto)
 TESTICULAR CANCER Updated March 2016 by Dr. Safiya Karim (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Toronto) Reviewed by Dr. Aaron Hansen (Staff Medical Oncologist, University of Toronto) DISCLAIMER:
TESTICULAR CANCER Updated March 2016 by Dr. Safiya Karim (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Toronto) Reviewed by Dr. Aaron Hansen (Staff Medical Oncologist, University of Toronto) DISCLAIMER:
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
-The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
Fellow GU Lecture Series, Testicular Cancer. Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018
 Fellow GU Lecture Series, 2018 Testicular Cancer Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018 Rare cancer worldwide, approximately 1% of all male cancers There is a large difference among ethnic/racial groups. Rates
Fellow GU Lecture Series, 2018 Testicular Cancer Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018 Rare cancer worldwide, approximately 1% of all male cancers There is a large difference among ethnic/racial groups. Rates
SEER Summary Stage Still Here!
 SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Fellow GU Lecture Series, Testicular Cancer. Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018
 Fellow GU Lecture Series, 2018 Testicular Cancer Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018 Rare cancer worldwide, approximately 1% of all male cancers There is a large difference among ethnic/racial groups. Rates
Fellow GU Lecture Series, 2018 Testicular Cancer Asit Paul, MD, PhD 02/06/2018 Rare cancer worldwide, approximately 1% of all male cancers There is a large difference among ethnic/racial groups. Rates
Interactive Staging Bee
 Interactive Staging Bee ROBIN BILLET, MA, CTR GA/SC REGIONAL CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 6, 2018? Clinical Staging includes any information obtained about the extent of cancer obtained before initiation of treatment
Interactive Staging Bee ROBIN BILLET, MA, CTR GA/SC REGIONAL CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 6, 2018? Clinical Staging includes any information obtained about the extent of cancer obtained before initiation of treatment
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES. Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES
 BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
Testicular Cancer. J. Richard Auman, MD. James J. Stark, MD. Jerry Singer, MD. September 19, 2008
 Testicular Cancer J. Richard Auman, MD James J. Stark, MD Jerry Singer, MD September 19, 2008 Testicular Cancer From mystery to far-advanced disease: a remarkable case Case Presentation. 23 y. o. male
Testicular Cancer J. Richard Auman, MD James J. Stark, MD Jerry Singer, MD September 19, 2008 Testicular Cancer From mystery to far-advanced disease: a remarkable case Case Presentation. 23 y. o. male
NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
Male Genital Cancers in the US in Frequency of Types
 Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 European Association of Urology GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro UPDATE MARCH
European Association of Urology GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro UPDATE MARCH
ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 4 SURGERY CASE REPORTS ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT Ș. Iacob 1, R. Vrînceanu 2,3, B.
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 4 SURGERY CASE REPORTS ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT Ș. Iacob 1, R. Vrînceanu 2,3, B.
Male genital tract tumors. SiCA. Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital.
 Male genital tract tumors Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital. adenocarcinoma Prostate Cancer most common male cancer in western countries more detected in
Male genital tract tumors Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital. adenocarcinoma Prostate Cancer most common male cancer in western countries more detected in
Guidelines on Testicular Cancer
 Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna European Association of Urology 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna European Association of Urology 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Thyroid and Adrenal Gland
 Thyroid and Adrenal Gland NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 12/1/11 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Thyroid and Adrenal Gland NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 12/1/11 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Major Rule Changes. Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging
 AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Major Rule Changes Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving patient
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Major Rule Changes Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving patient
STAGE CATEGORY DEFINITIONS
 CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery TX Tis Tis (DCIS) Tis (LCIS) Tis (Paget s) T1 T1mi T1a T1b T1c a b c
CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery TX Tis Tis (DCIS) Tis (LCIS) Tis (Paget s) T1 T1mi T1a T1b T1c a b c
6. Cervical Lymph Nodes and Unknown Primary Tumors of the Head and Neck
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Testicular Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a person's life, normal cells
What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a person's life, normal cells
Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Breast
 Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Breast Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. No materials in this presentation may be repurposed in print or online without the express written
Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Breast Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. No materials in this presentation may be repurposed in print or online without the express written
Histology Coding ANSWERS
 Histology Coding ANSWERS 1.) Biopsy of a right thyroid nodule reveals papillary carcinoma. What is the ICD-O-3 code? a. 8050/3 - Papillary carcinoma b. 8260/3 - Papillary adenocarcinoma Rationale/comment:
Histology Coding ANSWERS 1.) Biopsy of a right thyroid nodule reveals papillary carcinoma. What is the ICD-O-3 code? a. 8050/3 - Papillary carcinoma b. 8260/3 - Papillary adenocarcinoma Rationale/comment:
47. Melanoma of the Skin
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013
 EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
This form may provide more data elements than required for collection by standard setters such as NCI SEER, CDC NPCR, and CoC NCDB.
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
NICaN Testicular Germ Cell Tumours SACT protocols
 Reference No: Title: Author(s) Ownership: Approval by: Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Germ Cell Tumours Dr Audrey Fenton Consultant Medical Oncologist, Dr Vicky Coyle Consultant Medical
Reference No: Title: Author(s) Ownership: Approval by: Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Germ Cell Tumours Dr Audrey Fenton Consultant Medical Oncologist, Dr Vicky Coyle Consultant Medical
MCR: MANAGEMENT OF 2018 CHANGES. By: Maricarmen Traverso-Ortiz MPH, CGG, CTR
 MCR: MANAGEMENT OF 2018 CHANGES By: Maricarmen Traverso-Ortiz MPH, CGG, CTR LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss a summary of the new changes for 2018 Overview of how the Maryland Cancer Registry is managing and
MCR: MANAGEMENT OF 2018 CHANGES By: Maricarmen Traverso-Ortiz MPH, CGG, CTR LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss a summary of the new changes for 2018 Overview of how the Maryland Cancer Registry is managing and
46. Merkel Cell Carcinoma
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care?
 Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care? Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Professor and Director of Surgical Pathology The Methodist Hospital, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Houston,
Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care? Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Professor and Director of Surgical Pathology The Methodist Hospital, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Houston,
Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Bladder, Renal Pelvis, and Ureter 5/2/13. NAACCR Webinar Series
 Collecting Cancer Data Bladder & Renal Pelvis NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data Bladder & Renal Pelvis NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
SEER EOD AND SUMMARY STAGE ABSTRACTORS TRAINING
 SEER EOD AND SUMMARY STAGE ABSTRACTORS TRAINING OVERVIEW What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets Site Specific Data Items (SSDI) SEER Summary
SEER EOD AND SUMMARY STAGE ABSTRACTORS TRAINING OVERVIEW What is SEER EOD Ambiguous Terminology General Guidelines EOD Primary Tumor EOD Regional Nodes EOD Mets Site Specific Data Items (SSDI) SEER Summary
Interactive Discussion of Part I CS Coding Instructions: Working the Cases
 Interactive Discussion of Part I CS Coding Instructions: Working the Cases April Fritz, RHIT, CTR Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Jennifer Ruhl, RHIT, CCS, CTR This presentation was supported by the Cooperative
Interactive Discussion of Part I CS Coding Instructions: Working the Cases April Fritz, RHIT, CTR Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Jennifer Ruhl, RHIT, CCS, CTR This presentation was supported by the Cooperative
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_in_the_treatment_of_germ_cell_tumor
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_in_the_treatment_of_germ_cell_tumor
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast. Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017
 Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understanding of Breast TNM staging Identify clinical
Completing the Puzzle AJCC TNM Staging Breast Nicole Catlett, CTR 2017 Kentucky Cancer Registry Fall Conference, September 21 & 22, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understanding of Breast TNM staging Identify clinical
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
This form may provide more data elements than required for collection by standard setters such as NCI SEER, CDC NPCR, and CoC NCDB.
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14%
 Distribution ib ti of Cancers in Children under 15 years Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14% Neuroblastoma 9% Other 5% Liver 1% Retinoblastoma 3% Bone and STS 15% CNS 20% Wilms' 8% 30-40% Mortality Germ Cell Tumours
Distribution ib ti of Cancers in Children under 15 years Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14% Neuroblastoma 9% Other 5% Liver 1% Retinoblastoma 3% Bone and STS 15% CNS 20% Wilms' 8% 30-40% Mortality Germ Cell Tumours
2018 Grade PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR OCTOBER 11, 2018
 1 2018 Grade PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR ADAMOM@MAIL.NIH.GOV OCTOBER 11, 2018 2 Acknowledgements Donna Hansen, CCR Jennifer Ruhl, NCI SEER Introduction 3 Histologic Type vs. Grade Credit: Dr. Kay Washington
1 2018 Grade PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR ADAMOM@MAIL.NIH.GOV OCTOBER 11, 2018 2 Acknowledgements Donna Hansen, CCR Jennifer Ruhl, NCI SEER Introduction 3 Histologic Type vs. Grade Credit: Dr. Kay Washington
Ovarian Tumors. Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 Ovarian Tumors Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Case 13yo female with abdominal pain Ultrasound shows huge ovarian mass Surgeon
Ovarian Tumors Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Case 13yo female with abdominal pain Ultrasound shows huge ovarian mass Surgeon
You Want ME to Stage that Case???
 You Want ME to Stage that Case??? Jayne Holubowsky, CTR, Director, Virginia Cancer Registry 2 nd DelMarVa-DC Regional Conference October 11, 2018 What s New in the AJCC 8 th Edition Objectives Explain
You Want ME to Stage that Case??? Jayne Holubowsky, CTR, Director, Virginia Cancer Registry 2 nd DelMarVa-DC Regional Conference October 11, 2018 What s New in the AJCC 8 th Edition Objectives Explain
A Practicum Approach to CS: GU Prostate, Testis, Bladder, Kidney, Renal Pelvis. Jennifer Ruhl, RHIT, CCS, CTR Janet Stengel, RHIA, CTR
 A Practicum Approach to CS: GU Prostate, Testis, Bladder, Kidney, Renal Pelvis Jennifer Ruhl, RHIT, CCS, CTR Janet Stengel, RHIA, CTR Survey Questions and Answers 250 Responses 2 Question #1 A gentleman
A Practicum Approach to CS: GU Prostate, Testis, Bladder, Kidney, Renal Pelvis Jennifer Ruhl, RHIT, CCS, CTR Janet Stengel, RHIA, CTR Survey Questions and Answers 250 Responses 2 Question #1 A gentleman
Introduction & Descriptors
 AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
2018 New Required Data Items for Hospitals
 2018 New Required Data Items for Hospitals The NJSCR is a population-based registry, mandated by state law, that collects data on all cancer cases diagnosed and/or treated in New Jersey since October 1,
2018 New Required Data Items for Hospitals The NJSCR is a population-based registry, mandated by state law, that collects data on all cancer cases diagnosed and/or treated in New Jersey since October 1,
Teratocarcinoma In A Young Boy- An Unusual Presentation
 Human Journals Case Report November 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Atia Zaka-ur-Rab et al. Teratocarcinoma In A Young Boy- An Unusual Presentation Keywords: Boy, Testicular Mass, Teratocarcinoma
Human Journals Case Report November 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Atia Zaka-ur-Rab et al. Teratocarcinoma In A Young Boy- An Unusual Presentation Keywords: Boy, Testicular Mass, Teratocarcinoma
Definition of Synoptic Reporting
 Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Running Title: Utility of HCG Washout in Cervical LND FNA
 AACE Clinical Case Reports Rapid Electronic Articles in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited,
AACE Clinical Case Reports Rapid Electronic Articles in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited,
Case Scenario 1 Worksheet. Primary Site C44.4 Morphology 8743/3 Laterality 0 Stage/ Prognostic Factors
 CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
11/21/13 CEA: 1.7 WNL
 Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
5/8/2014. AJCC Stage Introduction and General Rules. Acknowledgements* Introduction. Melissa Pearson, CTR North Carolina Central Cancer Registry
 AJCC Stage Introduction and General Rules Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
AJCC Stage Introduction and General Rules Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging. Introduction & Descriptors. Learning Objectives. This webinar is sponsored by
 AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
2018 Summary Stage PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR OCTOBER 11, 2018
 1 2018 Summary Stage PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR ADAMOM@MAIL.NIH.GOV OCTOBER 11, 2018 2 Acknowledgement Jennifer Ruhl, NCI SEER 3 Introduction 2018 SUMMARY STAGE 2018 Summary Stage 4 First update since 2001
1 2018 Summary Stage PEGGY ADAMO, RHIT, CTR ADAMOM@MAIL.NIH.GOV OCTOBER 11, 2018 2 Acknowledgement Jennifer Ruhl, NCI SEER 3 Introduction 2018 SUMMARY STAGE 2018 Summary Stage 4 First update since 2001
Kyle L. Ziegler, CTR. California Cancer Registry U.C. Davis Health System
 Kyle L. Ziegler, CTR California Cancer Registry U.C. Davis Health System Overview New Data Items Reportability Clarifications New Coding Rules Grade ICD-O-3 Changes Collaborative Stage v0205 2 New Data
Kyle L. Ziegler, CTR California Cancer Registry U.C. Davis Health System Overview New Data Items Reportability Clarifications New Coding Rules Grade ICD-O-3 Changes Collaborative Stage v0205 2 New Data
Testicular Cancer. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version December 8, NCCN.org.
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 2.2017 December 8, 2016 NCCN.org Continue Version 2.2017, 12/08/16 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2016, All rights
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 2.2017 December 8, 2016 NCCN.org Continue Version 2.2017, 12/08/16 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2016, All rights
Q&A. Overview. Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate. Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate 5/5/2011. NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series May 5, 2011 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel Overview NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series 1
Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series May 5, 2011 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel Overview NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series 1
Registrar s Guide to Chapter 1, AJCC Seventh Edition. Overview. Learning Objectives. Describe intent and purpose of AJCC staging
 Registrar s Guide to Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. This presentation was supported by the Cooperative Agreement Number DP13-1310 from The Centers for Disease Control
Registrar s Guide to Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. This presentation was supported by the Cooperative Agreement Number DP13-1310 from The Centers for Disease Control
EAU Guidelines on Testicular Cancer
 EAU Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Guidelines Associates: J.L.
EAU Guidelines on Testicular Cancer P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Guidelines Associates: J.L.
ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation *
 ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation * CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation 24842 12/11/2007: Q:
ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation * CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation 24842 12/11/2007: Q:
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging. Introduction & Descriptors. Learning Objectives. This webinar is sponsored by
 AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Introduction & Descriptors Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving
Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.31/ No. 2/2001 Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer AHMET ÖZET 1, ALİ AYDIN YAVUZ 1, MURAT BEYZADEOĞLU
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.31/ No. 2/2001 Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer AHMET ÖZET 1, ALİ AYDIN YAVUZ 1, MURAT BEYZADEOĞLU
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung
 Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
2018 IMPLEMENTATION UPDATE: WHAT S NEW IN STAGING FOR 2018?
 2018 IMPLEMENTATION UPDATE: WHAT S NEW IN STAGING FOR 2018? SESSION 2 10/20/17 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. A recording of today s session, the Q&A,
2018 IMPLEMENTATION UPDATE: WHAT S NEW IN STAGING FOR 2018? SESSION 2 10/20/17 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. A recording of today s session, the Q&A,
10. HPV-Mediated (p16+) Oropharyngeal Cancer
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
ESMO Consensus Empfehlungen 2017
 ESMO Consensus Empfehlungen 2017 What s old, what s new, what s missing? Jörg Beyer, Klinik für Onkologie Offenlegung Interessenskonflikte 1. Anstellungsverhältnis oder Führungsposition Keine 2. Beratungs-
ESMO Consensus Empfehlungen 2017 What s old, what s new, what s missing? Jörg Beyer, Klinik für Onkologie Offenlegung Interessenskonflikte 1. Anstellungsverhältnis oder Führungsposition Keine 2. Beratungs-
Stage 3c breast cancer survival rate
 Stage 3c breast cancer survival rate There are five main subtypes of ovarian carcinoma, of which high-grade serous carcinoma is the most common. [3]. Testicular cancer is generally found in young men.
Stage 3c breast cancer survival rate There are five main subtypes of ovarian carcinoma, of which high-grade serous carcinoma is the most common. [3]. Testicular cancer is generally found in young men.
CS Evaluation Fields. Outline of Presentation. Purpose of Evaluation Field. CSv2 Title of Presentation Jan 2011 Lecture Version: 1.
 CS Evaluation Fields Education and Training Team Collaborative Stage Data Collection System Version 02.03.02 (Effective date: 1/1/2011) Outline of Presentation Purpose AJCC TNM Classification Eval data
CS Evaluation Fields Education and Training Team Collaborative Stage Data Collection System Version 02.03.02 (Effective date: 1/1/2011) Outline of Presentation Purpose AJCC TNM Classification Eval data
Protocol for the Examination of Lymphadenectomy Specimens From Patients With Malignant Germ Cell and Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors of the Testis
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Malignant Germ Cell and Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors of the Testis Version: Testis 4.0.1.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Malignant Germ Cell and Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors of the Testis Version: Testis 4.0.1.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements
Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow. Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director
 Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director Tumor Marker - Definition Substances produced by cancer cells or other cells in response to cancer
Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director Tumor Marker - Definition Substances produced by cancer cells or other cells in response to cancer
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Q: How do you clinically code the N if the nodes are stated to be positive on mammogram/us or other imaging? No biopsy of nodes was done.
 Q&A Breast Webinar Q: One of my investigators is interested in knowing when Oncotype DX data collection was implemented. That data is collected in SSFs 22 and 23. I remember that the SSFs for breast were
Q&A Breast Webinar Q: One of my investigators is interested in knowing when Oncotype DX data collection was implemented. That data is collected in SSFs 22 and 23. I remember that the SSFs for breast were
Testicular Cancer. What is testicular cancer? What are the symptoms? Patient Information. Risk factors for testicular cancer.
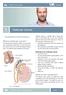 Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
Staging for Residents, Nurses, and Multidisciplinary Health Care Team
 Staging for Residents, Nurses, and Multidisciplinary Health Care Team Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. Learning Objectives Introduce the concept and history of stage
Staging for Residents, Nurses, and Multidisciplinary Health Care Team Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. Learning Objectives Introduce the concept and history of stage
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up
 Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
