Burra Gokhru; Gokshura; Puncture Vine; Small Caltrops
|
|
|
- Anthony Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROTOCIN (PROTODIOSCIN) Introduction Botanical name/species Common name Division Class Order Family Available Parts used Tribulus Terrestris Burra Gokhru; Gokshura; Puncture Vine; Small Caltrops Magnoliophyta Magnoliopsida Zygophillales Zygophyllaceae India, Eastern Europe & China Leaves, Roots, Fruit, Stem Tribulus terrestris is a weed that grows around the world and is commonly known as Puncture Vine. It is a botanical that has been used for hundreds of years in Europe for hormone insufficiency in men and women. It is widely believed that Tribulus is the closest and strongest natural herbal alternative to synthetic hormones. (Although Tribulus grows in many parts of the world including India, China and Bulgaria, all Tribulus is not created equal. Studies that were conducted at the University of Mississippi for NutraStar, Inc. conclusively proved that Bulgarian Tribulus included significantly more steroidal saponins than plants found in other areas. The aerial portion of the plant including the fruit contains pharmacologically active metabolites such as phytosteroids, flavonoids, alkaloids and glycosides. However it is the Protodioscin as well as other steroidal saponins that are believed to actually elevate the level of several hormones in the human body. Protodioscin which classified as a furostanol saponin, is the active ingredient of the plant extract of Tribulus terrestris L. Tribulus terrestris (also known as puncture vine), a member of the Zygophyllaceae family, is an annual herb found in many tropical and moderate areas of the world, including the US and Mexico, the Mediterranean region, and throughout Asia. Its health and medicinal effects to three groups of active Phytochemicals: A- Dioscin, protodioscin, diosgenin and similar. These substances stimulate sexual performance and may be useful for treating a variety of sexual disorders, they help to regulate sexual energy levels and sexual strength by increasing the percentage of free available testosterone levels for men and they even effect pregnenolone, progesterone and estrogen. The hormone balancing abilities of Tribulus Terrestris in the bodies of women makes this herb possibly useful for aiding in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome and menopausal syndrome. Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 1 of 18
2 B- Sterols such as betasitosterols or stigma. These chemical compounds help to protect the prostate gland from swelling and in combination with the X steroidal saponins, may help to protect the prostate from cancer. C- Proprietary steroidal saponins currently referred by medical researchers and physicians as X steroidal saponins. These X steroidal saponins have the ability to influence the entire immune system of the body. They have been shown to have antibacterial and anti-viral effects. Due to the effects of these substances it is now believed that Tribulus Terrestris may be used both internally and externally as a treatment for herpes, and virus infections such as influenza and the common cold. Most of all, steroidal saponins have been identified as the bioactive constituents responsible for the anabolic and aphrodisiac effects, these saponins (of which protodioscin is the primary) enable the body to produce more testosterone by raising the levels of the Leuteinizing Hormone (LH), which a hormone released normally by the pituitary gland helps to maintain testosterone production. As the LH increases, so testosterone increases. These effects have been shown in both animal and human clinical trials. Protocin, delivers the highest levels of Protodioscin per dose of any product on the market. Recent blood tests of people using (Tribistol )for 4 weeks show tremendous increases in all hormone categories including Testosterone, LH and FSH. In addition, individuals reported subjective feedback of increased libido and overall well-being on the product. Further, no adverse effects were reported either through the blood tests or the individuals related to liver functions or any other side effects. Macroscopic characteristics: Fruit pedicellate, globose, possessing five woody wedges shaped cocci, covered with two pairs of short stiff spines, one pair larger than the other. Tips of spines almost meet in pairs together forming pentagonal framework around the fruit. Outer surface of the schizocarp is rough. Odor faintly aromatic and slightly acrid in taste. Photochemistry: Studies on the constituents of the Aerial parts of Tribulus terrestris led to the isolation of five new steroidal saponins (terrestrosin A-E), (25R,S)-5 alpha-spirostan-3 beta-ol-3 -Obeta-D-galactopyranosyl (1-2)-beta-D- glucopyranosyl (1-4)-beta-D-galactopyranoside, (25R,S)-5 alpha-spirostan-3 beta-ol-3-o-beta-d-glucopyranosyl (1-4)-[alpha-Lrhamnopyranosyl (1-2)]-beta-D-galactopyranoside, (25R,S)-5 alpha-spirostan-12-on-3 beta-ol-3-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl (1-2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-4)-beta-Dgalactopyranoside, hecogenin 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl)1-2)-[beta-D- Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 2 of 18
3 xylopyranosyl(1-3)]-beta-d-glucopyranosyl(1-4)-beta-d-galactopyranoside and (25R,S)- 5 alpha-spirostane-2 alpha, 3 beta-diol-3- O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl(1-2)-beta-Dglucopyranosyl(1-4)-beta-D- galactopyranoside, together with five known steroidal saponins, desgalactotigonin, F-gitonin, desglucolanatigonin, gitonin and tigogenin 3-Obeta-D- xylopyranosyl)1-2)-[beta-d-xylopyranosyl)1-3)]-beta-d-glucopyranosyl)1-4 )- [alpha-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1-2)]-beta-d-galactopyranoside. The structures of the new saponins were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analyses, including twodimensional NMR techniques, and chemical reactions. The alkaloid, Harman, has been reported from the herb, and harmine from the seeds of the plant. The plant contains Saponins, which on hydrolysis, yield steroidal sapogenins diosgenin, gitogenin, chlorogenin(m.p ), ruscogenin and 25 D-spirosta-3,5-diene. Kaempferol, Kaempferol-3-glucoside, Kaempferol-3-rutinoside, and a new flavanoid tribuloside (C 30 H 26 O 13 ; m.p ) have also been isolated from the leaves and fruits. Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Protodioscin Protodioscin is the active ingredient of the plant extract of Tribulus terrestris L., and is produced by Phytotech extracts pvt Ltd. Protodioscin is classified as a furostanol saponin, and is present in the extract at no less than 45% of the total weight. The chemical structure of this compound is shown below in Figure 1. The chemical structure of protodioscin, the active ingredient of Tribulus terrestris L. extract. Protodioscin is physically characterized as a bitter-tasting amorphous powder, with a yellow-brown color. It is soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, but not soluble in chloroform. Mechanism of Protodioscin Protodioscin acts by stimulating the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which plays a role in the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (Viktorof et al. 1994). In addition, protodioscin also stimulates the hypothalamus secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH), but not of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Protodioscin is shown to Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 3 of 18
4 increase the density of the Leydig, but not that of the Sertoli cells, and to improve the level of spermatogonia and to increase the production of spermatocytes and spermatids without changing the diameter of the seminiferous tubules. Physically, protodioscin treatment results in increased male fertility and sexual functions. In respect to improving fertility, protodioscin increases the level of spermatogenesis by stimulating the Sertoli and germinal cells, resulting in the increased production of sperms. In this process, protodioscin improves the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which in turn stimulates the production of Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) in the Sertoli cells. Increased ABP production results in increased formation of DHT-ABP complex, which stimulates spermatogenesis in the germinal cells. Another fraction of the DHT- ABP complex is transported to the epididymis, which increases the efficiency of the maturation of spermatozoa into fertile sperms. In respect to increasing sexual functions, protodioscin works by increasing the conversion of testosterone into the potent DHT (shown in the figure below). In addition to the increase in sexual drive or libido, DHT also stimulates erythropoiesis or production of red blood cells, and muscle developments, thus contributing to the improvement of blood circulation as well as the oxygen transport systems. Importantly, regular use of protodioscin has also been shown to increase the duration of penile erection and improve ejaculation in males. PROTOCIN (PROTODIOSCIN) Testosterone Dihydrotestosteron Erythropiosis + Muscle Development Increase in Hemoglobin Level Increase in Oxygen Transport Optimal Health Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 4 of 18 Increase in Sexual Functions
5 The mechanism of protodioscin's action. Protodioscin increases the production of serum testosterone and the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. Dihydrotestosterone, in turn enhances erythropoiesis and muscle development. More erythropoiesis or production of red blood cell increases the hemoglobin level, which results in better oxygen transport throughout the body, resulting in a more optimal health. Both increased production of testosterone contribute to the increase in sexual functions, especially the increase in sex drive and better health. PROTOCIN (Protodioscin 10%) - Total FUROSTANOLIC SAPONIN 80% and 10% PROTODIOSCIN Physical properties Appearance Smell Color Taste Plant part used Greenish brown to brown powder; hygroscopic in nature. Characteristic odor Greenish brown to pale brown powder Bitter Fruit Identification Identification To comply with the standard by Thin Layer Chromatography Purity Loss on Drying Not more than 10.0% Solubility Not less than 85.0% -Water solubles -Alcohol solubles Not less than 70.0% Ash contents Not more than 20.0% Arsenic Not more than 1 ppm Heavy metals Not more than 20 ppm Lead Not more than 10 ppm Assay -Content of Total saponins Not less than 80.0% -Content of protodioscin Not less than 10.0% Microbial count Total microbial count Yeast and Molds E.coli and Salmonella Not more than 1000 cfu/g Not more than 100 cfu/g Should be absent Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 5 of 18
6 PROTOCIN (Protodioscin 20%) - Total FUROSTANOLIC SAPONIN 60% and 20% PROTODIOSCIN Physical properties Appearance Smell Color Taste Plant part used Greenish brown to brown powder; hygroscopic in nature. Characteristic odor Greenish brown to pale brown powder Bitter Fruit Identification Identification To comply with the standard by Thin Layer Chromatography Purity Loss on Drying Not more than 10.0% Solubility Not less than 85.0% -Water solubles -Alcohol solubles Not less than 70.0% Ash contents Not more than 20.0% Arsenic Not more than 1 ppm Heavy metals Not more than 20 ppm Lead Not more than 10 ppm Assay -Content of Total saponins Not less than 60.0% -Content of protodioscin Not less than 20.0% Microbial count Total microbial count Yeast and Molds E.coli and Salmonella Not more than 1000 cfu/g Not more than 100 cfu/g Should be absent Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 6 of 18
7 PROTOCIN (Protodioscin 30%) - Total FUROSTANOLIC SAPONIN 50% and 30% PROTODIOSCIN Physical properties Appearance Smell Color Taste Plant part used Greenish brown to brown powder; hygroscopic in nature. Characteristic odor Greenish brown to pale brown powder Bitter Fruit Identification Identification To comply with the standard by Thin Layer Chromatography Purity Loss on Drying Not more than 10.0% Solubility Not less than 85.0% -Water solubles -Alcohol solubles Not less than 70.0% Ash contents Not more than 20.0% Arsenic Not more than 1 ppm Heavy metals Not more than 20 ppm Lead Not more than 10 ppm Assay -Content of Total saponins Not less than 50.0% -Content of protodioscin Not less than 30.0% Microbial count Total microbial count Yeast and Molds E.coli and Salmonella Not more than 1000 cfu/g Not more than 100 cfu/g Should be absent Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 7 of 18
8 Method of analysis Appearance: Identification: Greenish brown colored powder, with characteristic odor. The Rf value of the spot obtained from sample should be comparable with that of Standard Loss on drying: Not more than 10.0 % Determine on IR moisture balance at 105 o C Water solubles: Not less than 85.0 % Weigh accurately about 1 g of the extract. Add 100 ml of water. Stir for one hour and filter through Whatman filter paper No. 41. Dry the paper at 105 C to a constant weight. Calculation: Wt of the residue x x 100 Wt of the sample taken Alcohol solubles: Not less than 70.0 % Weigh accurately about 1 g of the extract. Add 100 ml of alcohol. Stir for one hour and filter through Whatman filter paper No. 41. Dry the paper at 105 C to a constant weight. Calculation: Wt of the residue x x 100 Wt of the sample taken Ash content: Not less than 20.0 % Weigh accurately about 1 g of the extract in a weighed platinum / silica crucible. Incinerate at 400 C till it is charred. Add 100 ml of water. Stir for one hour and filter through Whatman filter paper No. 41. Dry the paper at 105 C to a constant weight. Calculation: Wt of the residue x x 100 Wt of the sample taken Assay: Not less than 60.0 % Total FUROSTANOLIC SAPONIN and 30% PROTODIOSCIN Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 8 of 18
9 Content of Steroidal sapogenins by Gravimetric method: 1. Weigh accurately about 5 gm. sample into a 250 ml glass joint conical flask. 2. Add about 50 ml of the 90% w/v alcohol and reflux for half an hour, cool. 3. Decant the aqu. Alcohol into another 250 ml beaker. 4. Repeat this process 3 times. The final extraction of the alcohol layer should not be colored. 5. Collect the aqu. Alcohol together and evaporate the solvent till the sample volume is about 5 ml. 6. Treat the concentrate with petroleum ether 60-80, 25 ml, by reflux for half an hour. Cool and remove solvent by decantation. 7. Now treat the soft extract as per step 6 with 25 ml of chloroform and followed by 25 ml of Ethyl acetate. 8. Discard the solvents after cooling. 9. Dissolve the soft extract (after three extractions cited above) in 25ml methanol, filter. Concentrate the methanolic extract to 5ml. 10. Add methanolic extract drop by drop with constant stirring to 250ml Acetone to precipitate Glycosides. 11. Filter the precipitate in a pre weighed G4 crucible. 12. Dry the crucible to a constant weight at From the weight calculate the content of sapogenins. Content of protodioscin by HPLC: PHARMACOLOGY: The active components of the plant Tribulus terrestris L. extract are non-steroid saponins of the furostanol type, termed protodioscin. A pronounced stimulating effect on the spermatogenesis is observed after the preparation is administered orally to sexually mature rats. Increased numbers of spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids and mature spermatozoa in the testes has been observed without widening of the diameter of the seminiferous tubules. In parallel, increased number of Sertoli cells is observed in a volume unit from rat testes. Oral administration stimulates the mitotic activity of spermatogonia in mature rats. Oral administration of the preparation leads to intensification of spermatogenesis and enhancement of the quality of spermatozoa in sexually mature rats. The percentage of motile spermatozoa increases, the characteristics of their motility improve, prolonging the period of their viability at the same time. Given orally to swine, protodioscin stimulates their sexual behavior. The clinical trials of the preparation have also confirmed the experimental data. Protodioscin, administered to male subjects with disorders in the spermiogram, due to varicocele, increases the volume of ejaculated sperm by 1-2 ml, increases Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 9 of 18
10 spermatozoid concentration by 30 million/ml, increases the percentage of motile spermatozoa by 30%. The preparation has a marked effect on the motility of spermatozoa in case of oligoasthenozoospermia, as revealed by the study of its therapeutic properties in men. The mean number of motile spermatozoa in the group studied was 29% prior to the study, and later it reached up to 36.6%. The motility rate of the spermatozoa prior to the treatment was 1.95 mm/sec and 3.76 mm/sec post treatment. Of definite interest is the treatment of patients with unilateral and bilateral hypotrophy of the testes, combined with disorders of the spermiogram. The libido was enhanced after a 60-day protodioscin treatment and the characteristics of the spermiogram were improved. Recovery and enhanced libido were observed in patients with primary and secondary hypogonadism after administration, as well as prolonged erection. Both experimental and clinical studies reveal that protodioscin is not toxic and induces no adverse effects. Clinical investigations on a total of 212 males with disorders of sexual functions confirmed experimental data pointing at a pronounced stimulating effect on these sexual functions by the new phytochemical preparation of Tribulus terrestris extract. Administered in average daily doses of 1.5 g in the course of 30 to 40 days, it restores and improves libido sexualis in all forms of impotentia coeundi. Studies on the acute, subchronic and chronic toxicities of protodioscin, the active ingredient of Tribulus terrestris extract, determined that the compound is to be classified as a practically non-toxic substances. The harmlessness of the preparation deserves particular attention. No data about toxic manifestations were established under experimental conditions with acute, subchronic and chronic toxicities (behavioral, hematological, biochemical, functional and morphological studies). No data were established concerning carcinogenic and teratogenic effect. The combined action of the preparation (stimulation of the sexual behavior and spermatogenesis) and the absence of adverse effects characterize the preparation as an original agent for the treatment of males with disorders in the sexual functions. Clinical application: Trials of Tribulus terrestris (protodioscin) on oligo-zoospermia N. Moeloek, A. Adimoelja, T. Tanojo, and W. Pangkahila Proceedings of the VIth National Congress and IIIrd International Symposium on New Perspectives of Andrology on Human Reproduction National Congress of Indonesian Association of Andrologs. Scientific Meeting VI in Manado (1994 Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 10 of 18
11 Tribulus terrestris L. is a natural, non-hormonal herbal preparation. This trial focuses on determining the effect of this preparation on the fertility of men with oligozoospermia. A three-centered study in Indonesia (the cities of Jakarta, Surabaya, and Denpasar) include 45 subjects. Thirty six of these men compose the experimental group, and are administered Tribulus terrestris L. (Libilov), whereas 9 are given placebo (control group). The study includes analyses of three phases: - Before treatment - During treatment (9 weeks) - After treatment (3 weeks after treatment) Effect of protodioscin (Tribulus terrestris) on the well-being and sexual response of men with diabetes mellitus K.M. Arsyad Medical Biology Division of Andrology, University of Sriwijaya, Indonesia (1997) We conducted this trial to study the effect of Tribulus terrestris (protodioscin) supplement on the sense of well-being and sexual response of men suffering from diabetes mellitus. 30 men between the ages of 40 to 55 years were divided into two 15- men groups. The experimental and control groups were given Tribulus terrestris extract (Libilov tablets, 250mg) and placebo pills 3 times per day for 30 days, respectively. Both groups were not statistically different in age, body weight and fasting sugar levels. Our results showed that Tribulus supplement is able to improve the sense of well being and sexual response of diabetic subjects. We found improvement in sex drive, erection, ejaculation and orgasm in the treated group and no improvement in these parameters in the control group. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease which prevalence tends to increase steadily irrespective of social and economic status (1). Clinical symptoms of DM include symptoms related to the pancreatic compensation stages, including polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria, and an increase in body weight. If left untreated, these symptoms could lead to nausea and diabetic coma. Other symptoms include that of the pancreatic decompensation stages and other chronic symptoms, such as asthenia, anorexia, hyperesthesia, blurred vision, myalgia, athralgia and a decrease in sexual drive. Diabetes could also be complicated by vasculopathy and neuropathy, or both. Furthermore, sexual dysfunctions in diabetic men are often diagnosed as erectile dysfunction, disorders in ejaculation and decreased libido. These sexual dysfunctions often occur before DM is diagnosed (2). Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 11 of 18
12 Sexual dysfunctions in diabetic men are caused by (3,4,5): 1. Disturbance in hormone productions Reduction in blood vessels causes the subsequent reduction in blood flow to the testes tissues, leading to degeneration of these tissues and reduction in androgen production. Coupled with decreased hormone production in other glandular tissues, the decrease in total androgen levels is responsible for the decrease in libido. 2. Impaired erection The destruction of blood vessels increases blood viscosity and abnormally affects the nervous system. This often results in impotence or disturbance in achieving erection. 3. Impaired ejaculation Impairment in achieving ejaculation is most often caused by the destruction of the nervous system in vesica urinaria. 4. Impaired orgasm Impairment in achieving orgasm is caused by the failure of fulfilling the appropriate sexual response phase. The active ingredient in Tribulus terrestris extract, called protodioscin, has been reported to increase the level of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the bloodstream. DHEA is a hormone involved in the immune system and has been attributed to be responsible in improving the general sense of well-being. It has been hypothesized that DHEA functions by improving the integrity and functions of cellular membranes, including those of the endothelial cells in the penile corpus cavernosum and other blood vessels (6,7). Treatment with Tribulus terrestris extract (Libilov ) at one tablet three times daily for 10 days has been reported to increase the DHEA level in diabetic and non-diabetic male subjects diagnosed with erectile dysfunction (8). Protodioscin increases the secretion of LH, but not that of FSH. Protodioscin has been shown to increase the density of the Sertoli cells, without changing the density of the Leydig cells; and to increase the number of spermatogonia, spematocytes and spermatids without affecting the diameter of the seminiferous tubules. This clinical study was designed to determine the effect of protodioscin on the sense of well-being and the sexual response of men diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. Aphrodisiac properties of Tribulus terrestris extract (protodioscin) in normal and castrated rats A. Gauthaman, P.G. Adaikan, R.N. Prasad National University of Singapore, National University Hospital, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Singapore Life Sci 2002 Aug 9; 71(12): Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 12 of 18
13 Tribulus terrestris (TT) has long been used in traditional Chinese and Indian systems of medicine for the treatment of various ailments and is popularly claimed to improve sexual functions in man. Sexual behavior and intracavernous pressure (ICP) were studied in both normal and castrated rats to further understand the role of TT containing protodioscin (PTN) as an aphrodisiac. Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into five groups of 8 each that included distilled water treated (normal and castrated), testosterone treated (normal and castrated, 10 mg/kg body weight, subcutaneously, biweekly) and TT treated (castrated, 5 mg/kg body weight, orally once daily). Decreases in body weight, prostate weight and ICP were observed among the castrated groups of rats compared to the intact group. There was an overall reduction in the sexual behavior parameters in the castrated groups of rats as reflected by decrease in mount and intromission frequencies (MF and IF) and increase in mount, intromission, ejaculation latencies (ML, IL, EL) as well as post-ejaculatory interval (PEI). Compared to the castrated control, treatment of castrated rats (with either testosterone or TT extract) showed increase in prostate weight and ICP that were statistically significant. There was also a mild to moderate improvement of the sexual behavior parameters as evidenced by increase in MF and IFl; decrease in ML, IL and PEI. These results were statistically significant. It is concluded that TT extracts appear to possess aphrodisiac activity probably due to an androgen increasing property of TT (observed in our earlier study on primates). Tribulus terrestris (protodioscin) increases men's sex drive W. Pangkahila Reproductive Medicine Faculty, University of Denpasar, Indonesia Proceedings of the Xth National Congress on New Perspectives of Andrology on Human Reproduction National Congress of Indonesian Association of Andrologs 10th Scientific Meeting in Denpasar(1993) Male erectile dysfunctions are composed of the dysfunctions of libido, erection, ejaculation and orgasm. One medical approach to solve this problem is the use of natural medicine, i.e. the use of compounds derived from natural sources rather than those of synthetic origins. Here, we conduct a clinical trial to test the efficacy of Libilov's protodioscin, a natural compound derived from the extract of a medicinal plant Tribulus terrestris. In this test, we study the sex drive, erection, ejaculation and orgasm of 53 married men diagnosed with sexual dysfunctions. These men were given Libilov at 3 x 2 tablets per day for 3 months. We report that statistical analyses suggest significant improvement in sex drive in the majority of our trial constituents, without any evidence of adverse effects. Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 13 of 18
14 Tribulus terrestris (protodioscin) in the treatment of male infertility with idiopathic oligoasthenoterato-zoospermia A Adimoelja, L Setiawan, and T Djojotananjo Academic Hospital Dr. Soetomo and Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia in First International Conference of Medical Plants for Reproductive Medicine in Taipei, Taiwan (1995) Tribulus terrestris L (TTL) extract is a natural remedy that has been successfully tested clinically for its use in the treatment of idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (OTA). Here, we conducted a double blind study of 45 infertile, married men with OTA. 36 men were treated with 500 mg purified TTL (Libilov) 3 times daily for 3 months. Composing the controlled group, 9 men were given placebo (sugar pills) for the same period of time. Spouses of 8 of the men in the treated group successfully achieved pregnancies after treatment of their husbands, whereas no pregnancies occurred in the spouses of the men in the control group. An improvement in the sperm morphology, including that observed under conventional phase contrast microscopy as well as improvements in acrosome morphology and reaction, seemed to account for the increased fertility after treatment. In addition, TTL was also shown to increase the level of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and might also contributed to the activation of cell membrane receptors and the production of weak androgens. These, in turn, might additionally improve fertility by increasing the level of spermatogenesis. Effect of protodioscin on the quantity and quality of sperms from males with moderate idiopathic oligozoospermia K.M. Arsyad Medical Biology Division of Andrology, University of Sriwijaya, Indonesia (1996) Medika 22 (8): (1996) This study was conducted to assess the effectiveness of a certain dosage and period of administration of Libilov (protodioscin) on sperm quality and quantity in men with moderate idiopathic oligozoospermia. This study also evaluated protodioscin's effect on libido, erection, ejaculation and orgasm. Lastly, We also determined the length of time that the beneficial effects of the treatment lasted after administration of the preparation was stopped. Our result showed that oral Libilov treatment with the dose of 3 x 2 tablets per day for 60 days could: - increase sperm quantity and quality in men diagnosed with moderate idiopathic oligozoospermia - restore and enhance libido, erection, ejaculation, and orgasm of sexual intercourse, as compared to before the treatment. This result was obtained in more than 80% of the treated patients. Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 14 of 18
15 Protodioscin from herbal plant Tribulus terrestris L improves the male sexual functions, probably via DHEA Adimoelja and P. Ganeshan Adaikan Airlangga University, Indonesia and National University of Singapore in 6th Biennial Asian-Pacific Meeting on Impotence in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (1997) Int. J. Impotence Research v9, supp 1 (1997) An interesting correlation of dehydroepiandrosterone-sulphate (DHEA-S) level with the incident of low sex drive and higher occurrence of impotence was discovered in studies with patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. To test further the relationship between DHEA-S and erectile dysfunction (ED), we conducted a clinical trial of 30 non-diabetic men with ED, 30 non-diabetic men without ED and 15 diabetic men with ED. These men are given extract of Tribulus terrestris (Libilov) at 3 x 250 mg / day for 3 weeks. The DHEA-S levels, as well as other blood and liver parameters were evaluated. We found a significant increase of DHEA-S levels in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects after treatment, and a significant increase in the frequency of successful intercourse by 60% in both the diabetic and non-diabetic groups with or without ED. Tribulus terrestris L (TTL) is a herbal plant native to Bulgaria and China that has a long history as a powerful aphrodisiac and as a traditional medicine for treating male infertility (1,6). Recently, a chemical compound isolated from TTL called protodioscin (2) has been identified, purified and standardized as a phytochemical agent. In a multi-center, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind clinical trial, protodioscin proved to be an effective form of treatment for male infertility (2,6,7). It is known that sufficient dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the epididymis is necessary for the maturation process of spermatozoa (5). Furthermore, it has been speculated that in some idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia, male infertility is due to the low concentration of DHEA in the epididymis. In another clinical trial protodioscin is proved to increase the serum DHEA level of infertile men, without any change in the level of testosterone and other androgens. It is also shown that liver and kidney functions do not change significantly by protodioscin (1,2,6,7). The study concludes that protodioscin in TTL could be the precursor of DHEA in patients with low serum level of this hormone. As TTL has been known for its aphrodisiac quality, speculations have been made that its mechanism of action involves the conversion of protodioscin to DHEA. In turn, DHEA may increase cell membrane integrity and functions (3,4), thereby resulting in better sexual performance and the general feeling of well-being. Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 15 of 18
16 Recommended uses: 1. Muscle Mass 2. Aphrodisiac 3. Spermatorrhoea 4. Oligospermoea 5. Impotence 6. Diseases of genital complaints 7. Calculus affection 8. Gout 9. Urolithiatic 10. diuretic. Recommended intake A number of clinical trials on human subjects recommend the dosage of Tribulus as below mg of standardized extract containing 30%, once daily provides remarkable clinical effects. No adverse effects to the central nervous or cardiovascular systems were noted in any of the clinical studies: no toxicity and no deviations in blood count occurred. No known negative effects presently found when Tribulus is used as a dietary supplement of the above dosage. Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 16 of 18
17 References: 1.Viktorov,E.Bozadjieva,M.Protich,etal. Higher Medical Institute; Medical Academy Institute of Endocrinology, Gerontology and Geriatrics; Medical Academy Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Bulgaria IIMS Therapeutic Focus (1994) 2.Gaby AR (1993). DHEA: The hormone that "does it all". Holistic Medicine. pp Hafez ESE and Prasad MRN (1976). Functional aspects of the epididymis. In Human Semen and Fertility Regulation in Men. Pp ESE Hafez editor. The CV Mosby Company, St. Louis. 3.Moeloek N, Adimoelja A, Tanojo T, Pangkahila W (1994). Trials of Tribulus terrestris on oligozoospermia. Proceedings of the VIth National Congress and IIIrd International Symposium on New Perspectives on Andrology in Human Reproduction. National Congress of Indonesian Association of Andrology (PANDI) in Manado, Indonesia. 4.Adimoelja, A. (1996) Sex Therapy in Asia. 4th Asian Conference of Sexology in Taipei, Taiwan. 5.Adimoelja, A., Suryaatmadja, S., Setiawan, L., and Tanojo, T. (1997) Protodioscin, the main active component in Tribulus terrestris L. may improve sperm function in subfertile males and increase the frequency of successful intercourse in men with erectile dysfunctions. VII National congress of Andrology in Bandung,Indonesia. 6.Dyner, T.S., et al. (1993) An open label dose escalation trial of oral DHEA tolerance and pharmacokinetics in patients with HIV-disease. J. AIDS 6(5): Gaby, A.R. (1993) DHEA: The hormone that "does it all". Holistic Medicine Viktorov, I., D. Kaloyanov, Al. Lilov, L. Zlatanova, V. Kasabov. Clinical investigation on Tribestan in males with disorders in the sexual function MBI, 1982 (in print) 9.Gyulemetova, R., M. Tomova, M. Simova, P. Pangarova, S. Peeva. On Tribestan standardization. Die Pharmatie, 1982, 37,4. 10.Gendjev, Z. Studies on Tribestan carcinogenicity. Scientific-technical Report, Vankov, S. On Tribestan pharmacology. Scientific-technical Report, Dikova, N., V. Ognyanova. Pharmacokinetic studies on Tribestan. Anniversary Scientific Session '35 Years Chemical Pharmaceutical Research Institute' Sofia, March 22-23, Ilieva, Z. Embryotoxic and Teratological studies on Tribestan. Scientific-technical Report, 1981 Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 17 of 18
18 14.Koumanov, F., E. Bozadjieva, M. Andreeva, E. Platonova, V. Ankov. Clinical trial of Tribestan. Exper. 15. Steinberger, E. Hormonal control of mammalian spermatogenesis. Physiol. Rev Tomova, M., R. Gyulemetova. Steroid saponin and Steroidsapogenine VI. Furostanol bisglykosid aus Tribulus ferrestris L., Planta medica, , Rowe P.J., Comhaire F.H., Hargreave T.B., and Mellows H.J. World Health Organization manual for the standardized investigation and diagnosis of the infertile couple. WHO, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993). 18.Susilo W. Impotence, causes and pharmacological solutions. Seminar in Solving Impotence in Semarang, Indonesia (1994). 19.Viktorof I., Bozadjieva E., Protich M., et al. Pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, toxicological and clinical studies on protodioscin. IIMS Therapeutic Focus Vol 2 (1994). 20.Watterauer U. Anatomy of the penis and physiology of erection. In Sexology. Eicher W., and Kockott G. editors. Pp Springer-verlag Berlin, Heidelberg (1988). Copyright 2008 Phytotech-Optigen Page 18 of 18
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
TESTOSTERONE DEFINITION
 DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
FIGURE The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis.
 Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act
 Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
Immunohistochemical Study of Leydig Cells in the Testicular Interstitial Tissue of Rats Treated with Tribulus Terrestris Using P450scc.
 Immunohistochemical Study of Leydig Cells in the Testicular Interstitial Tissue of Rats Treated with Tribulus Terrestris Using P450scc. Issam T. Abdul-Wahaab*,Malak A. Al-Yawer*,Fadhil A. Al Khafaji* ABSTRACT:
Immunohistochemical Study of Leydig Cells in the Testicular Interstitial Tissue of Rats Treated with Tribulus Terrestris Using P450scc. Issam T. Abdul-Wahaab*,Malak A. Al-Yawer*,Fadhil A. Al Khafaji* ABSTRACT:
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
First you must understand what is needed for becoming pregnant?
 What is infertility? Infertility means difficulty in becoming pregnant without using contraception. First you must understand what is needed for becoming pregnant? Ovum from the woman to combine with a
What is infertility? Infertility means difficulty in becoming pregnant without using contraception. First you must understand what is needed for becoming pregnant? Ovum from the woman to combine with a
Physiologic Anatomy of the Male Sexual Organs
 Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease. Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist
 Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist Disturbances in sexual function are a common feature of chronic renal failure. Sexual dysfunction is inversely associated with
Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist Disturbances in sexual function are a common feature of chronic renal failure. Sexual dysfunction is inversely associated with
Natural Herbal Extracts Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma Longifolia)
 Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma Longifolia) Male Menopause (Andropause): The reduction of male sex hormones When age increasing, the male s hormones i.e. Testosterone and Dehydroepiandrosterone will gradually decreasing
Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma Longifolia) Male Menopause (Andropause): The reduction of male sex hormones When age increasing, the male s hormones i.e. Testosterone and Dehydroepiandrosterone will gradually decreasing
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
Good pharmacopoeial practices: Chapter on monographs on herbal medicines
 Annex 7 Good pharmacopoeial practices: Chapter on monographs on herbal medicines Background Following the fiftieth meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations,
Annex 7 Good pharmacopoeial practices: Chapter on monographs on herbal medicines Background Following the fiftieth meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations,
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Health Canada Approval Number: NPN: Dr. J s Formulas: Dr. J. Horny OX-XS
 Health Canada Approval Number: NPN: 800 58191 1 Dr. J s Formulas: DR. J S FORMULAS: J. stands for the first letter of the formulator s first name. Dr. Jalal is a nutritionist by qualification. In 1981,
Health Canada Approval Number: NPN: 800 58191 1 Dr. J s Formulas: DR. J S FORMULAS: J. stands for the first letter of the formulator s first name. Dr. Jalal is a nutritionist by qualification. In 1981,
Tribulus terrestris Linn.: A review article
 Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 5(16), pp. 3601-3605, 18 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jmpr ISSN 1996-0875 2011 Academic Journals Review Tribulus terrestris
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 5(16), pp. 3601-3605, 18 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jmpr ISSN 1996-0875 2011 Academic Journals Review Tribulus terrestris
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
A. K. EYONG AND V. B. BRAIDE
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES VOL 8, NO. 1&2, 2009: 23-30 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1596-2911 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com EFFECTS
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES VOL 8, NO. 1&2, 2009: 23-30 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1596-2911 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com EFFECTS
Product Introduction
 Product Introduction 康達生命科學有限公司 Contek Life Science Co., Ltd. Red Algae Peptide Hydrolysate-EDpeptide The Next Generations of Erectile Dysfunction Cure Introduction of small peptides Erectile dysfunction
Product Introduction 康達生命科學有限公司 Contek Life Science Co., Ltd. Red Algae Peptide Hydrolysate-EDpeptide The Next Generations of Erectile Dysfunction Cure Introduction of small peptides Erectile dysfunction
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Reproduction. Liang Huawei( 梁华为 )
 Reproduction Liang Huawei( 梁华为 ) E-mail: liang.huawei@yahoo.com.cn Reproduction Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced. An individual does not need the system
Reproduction Liang Huawei( 梁华为 ) E-mail: liang.huawei@yahoo.com.cn Reproduction Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced. An individual does not need the system
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Tongkat Ali.
 Tongkat Ali www.powertongkatali.com Tongkat Ali Tongkat Ali is a very potent herbal product in South East Asia. It has been used by the locals for centuries to improve male s vitality and virility. Page
Tongkat Ali www.powertongkatali.com Tongkat Ali Tongkat Ali is a very potent herbal product in South East Asia. It has been used by the locals for centuries to improve male s vitality and virility. Page
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS
 MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW
 A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Male Reproductive System. Figure 80-1 Copyright 2011 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
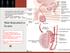 Male reprodctive system anatomy: briefly: composed of testis and external genetilia, the testis seminefrous tubules with space for spermatogenesis...the path is from the epidedimys-->vas defans-->prostatic
Male reprodctive system anatomy: briefly: composed of testis and external genetilia, the testis seminefrous tubules with space for spermatogenesis...the path is from the epidedimys-->vas defans-->prostatic
Male Reproductive System
 Male Hormone Issues The Ideal Male What describes a healthy male? Happy guy, well-muscled, good sex drive, focused brain This is what a guy can expect with the right level of testosterone Low testosterone?
Male Hormone Issues The Ideal Male What describes a healthy male? Happy guy, well-muscled, good sex drive, focused brain This is what a guy can expect with the right level of testosterone Low testosterone?
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems
 Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
2 - male hormones/ female system
 2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
Aphrodisiac potentials of the aqueous extract of Fadogia agrestis (Schweinf. Ex Hiern) stem in male albino rats
 Asian J Androl 2005; 7 (4): 399 404 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2005.00052.x. Complementary Medicine. Aphrodisiac potentials of the aqueous extract of Fadogia agrestis (Schweinf. Ex Hiern) stem in male albino
Asian J Androl 2005; 7 (4): 399 404 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2005.00052.x. Complementary Medicine. Aphrodisiac potentials of the aqueous extract of Fadogia agrestis (Schweinf. Ex Hiern) stem in male albino
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Embryology 3. Spermatogenesis:
 Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE. result graph based on Luteal Phase. result graph based on Luteal Phase
 Patient Name: Patient DOB: Gender: Physician: Test Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE Grote, Mary Jane Batch Number: B6437 2/16/1954 Accession Number: N52281 F Date Received: 2/3/2015 Any Lab Test
Patient Name: Patient DOB: Gender: Physician: Test Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE Grote, Mary Jane Batch Number: B6437 2/16/1954 Accession Number: N52281 F Date Received: 2/3/2015 Any Lab Test
WinAge. (A product monograph) Jeevanjyoti Herbaceuticals HEALTH FOR ALL
 WinAge (A product monograph) Jeevanjyoti Herbaceuticals HEALTH FOR ALL NATURALLY Introduction Aging is an on going process of human being. As a biological phenomenon all the living tissues in the body
WinAge (A product monograph) Jeevanjyoti Herbaceuticals HEALTH FOR ALL NATURALLY Introduction Aging is an on going process of human being. As a biological phenomenon all the living tissues in the body
CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE. Cellulosum microcristallinum. Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0
 Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 Phthaloyl groups (C 8 H 5 O 3 ; M r 149.1): typically 30.0 per cent to 36.0 per cent (anhydrous and acid-free substance). Dissolve 1.000 g in 50 ml
Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 Phthaloyl groups (C 8 H 5 O 3 ; M r 149.1): typically 30.0 per cent to 36.0 per cent (anhydrous and acid-free substance). Dissolve 1.000 g in 50 ml
Alternative management of hypogonadism Tamoxifen. Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD Tor Vergata University of Rome ITALY
 Alternative management of hypogonadism Tamoxifen Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD Tor Vergata University of Rome ITALY eajannini@gmail.com What hypogonadism is? What hypogonadism is? It is an empty glass The two
Alternative management of hypogonadism Tamoxifen Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD Tor Vergata University of Rome ITALY eajannini@gmail.com What hypogonadism is? What hypogonadism is? It is an empty glass The two
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin); Novarel Pregnyl (chorionic gonadotropin); Ovidrel (choriogonadotropin alfa)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.08.09 Subject: HCG Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 19, 2015 HCG Powder, Novarel, Pregnyl, Ovidrel
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.08.09 Subject: HCG Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 19, 2015 HCG Powder, Novarel, Pregnyl, Ovidrel
B American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2017 J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. (2017) 28:2302Y2318 DOI: /s RESEARCH ARTICLE
 B American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2017 J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. (2017) 28:2302Y2318 DOI: 10.1007/s13361-017-1761-5 ESEACH ATICLE apid Characterization of Constituents in Tribulus terrestris from
B American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2017 J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. (2017) 28:2302Y2318 DOI: 10.1007/s13361-017-1761-5 ESEACH ATICLE apid Characterization of Constituents in Tribulus terrestris from
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
1200 mg 100 mg 250 mg 100 mg 100 mg 40 mg 750 mg 5 mg 400 mcg 3 mg
 +90 555 009 00 10 Contents; Arginine.... Lepidium (Lepidium meyenii).... Tribulus terrestris Epimedium (Epimedium sp.).. Opuntia ficus indica.. Ginseng (Panax ginseng) Vitamin C (L-askorbik asit). Zinc
+90 555 009 00 10 Contents; Arginine.... Lepidium (Lepidium meyenii).... Tribulus terrestris Epimedium (Epimedium sp.).. Opuntia ficus indica.. Ginseng (Panax ginseng) Vitamin C (L-askorbik asit). Zinc
Phytochemical Screening of Tubers and Leaf extracts of Sagittaria sagittifolial.:newsa (Arrowhead)
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 9, September 2017 431 Phytochemical Screening of Tubers and Leaf extracts of Sagittaria sagittifolial.:newsa (Arrowhead) Anita
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 9, September 2017 431 Phytochemical Screening of Tubers and Leaf extracts of Sagittaria sagittifolial.:newsa (Arrowhead) Anita
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Spermatogenesis. What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis?
 Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
The Effect of Oral Feeding of Tribulus terrestris L. on Sex Hormone and Gonadotropin Levels in Addicted Male Rats
 Original Article The Effect of Oral Feeding of Tribulus terrestris L. on Sex Hormone and Gonadotropin Levels in Addicted Male Rats Mohammad Hassan Ghosian Moghaddam, Ph.D. 1, Mohsen Khalili, Ph.D. 2, Maryam
Original Article The Effect of Oral Feeding of Tribulus terrestris L. on Sex Hormone and Gonadotropin Levels in Addicted Male Rats Mohammad Hassan Ghosian Moghaddam, Ph.D. 1, Mohsen Khalili, Ph.D. 2, Maryam
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS
 THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Does Zyrexin Really Work, And Will It Increase My Penis Size?
 Zyrexin Review Does Zyrexin Really Work, And Will It Increase My Penis Size? Today is a world of pharmaceutical advancements which gave rise to a lot of supplements that can evolve the human body s performance.
Zyrexin Review Does Zyrexin Really Work, And Will It Increase My Penis Size? Today is a world of pharmaceutical advancements which gave rise to a lot of supplements that can evolve the human body s performance.
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
