ANSC/FSTC 607 Biochemistry and Physiology of Muscle as a Food PRIMARY, SECONDARY, AND TERTIARY MYOTUBES
|
|
|
- Chad Moody
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANSC/FSTC 607 Biochemistry and Physiology of Muscle as a Food PRIMARY, SECONDARY, AND TERTIARY MYOTUBES I. Satellite Cells A. Proliferative, myoblastic cells that lie in invaginations in the sarcolemma B. Can be stimulated to proliferate by muscle growth or damage C. Can be isolated for cell culture 1. Proliferate like immortalized premyoblasts 2. Express myofibrillar proteins 3. Fuse to form new myotubes. Developing limb bud. Satellite cells are involved in the formation of primary and secondary myotubes during fetal development. Premyoblasts from somites close to the point of limb formation migrate to a point just under the ectoderm. Myoblasts fuse to form myotubes, aligning Satellite cell hyperplasia. The total number of muscle nuclei increases during postnatal growth. Nuclei increase at a faster rate than total cytoplasm (sarcoplasm), indicating that satellite cell hyperplasia exceeds myofiber hypertrophy. 1
2 with developing limb bones. II. Satellite cells and muscle fiber repair A. Proliferation increases greatly when the muscle is damaged. 1. Satellite cells migrate to damaged area. 2. Secretion of mitogenic factors by damaged muscle stimulates migration. 3. Satellite cells (now called myoblasts by some authors) fuse to form new myotubes. Damaged muscle fiber Satellite cells Skeletal muscle fibers from rat soleus muscle. A satellite cell (SC) is shown between the external lamina (EL) and sarcolemma (SL). Note the paler myonucleus (MN) in the top micrograph. Regenerating myotube (MT). A myotube formed after the muscle was damaged. The myotube with a central nucleus is shown adjacent to three myoblasts (MB). The external lamina (EL) from an originally minced muscle fiber appears to be completely surrounding the myotube and myoblasts. 2
3 III. Changes in fiber number A. Species-specific 1. Virtually no increase in myofiber number in animals born relatively developed. a. Cattle b. Hares 2. Measureable conversion of myotubes to myofibers early postnatally in animals born relatively undeveloped. a. Pigs b. Rabbits (domesticated) B. Mechanism 1. In all species, primary myotubes develop prenatally (late embryo and early fetal periods). 2. Secondary myotubes develop primarily prenatally (late gestation) and early postnatally in some species. a. Use primary myotube as template. b. Split away from primary myotube because of contraction. c. Are innervated by the same motoneuron as the primary myotube. 3
4 IV. Primary and secondary myotubes A. Primary myotubes: progenitors of 10% of myofibers in adults. 1. From CMRI and CMRII myoblasts. 2. These myoblasts disappear once secondary myotube formation begins. B. Secondary myotubes 1. Formed with primary myotubes as templates. 2. Formed with secondary myotubes as templates ("tertiary"). 3. From CMRIII myoblasts. a. Require functional innervation for proliferation. b. Disappear in denervated muscle. 4
5 V. Myofibril assembly A. Stress fiber model 1. A combination of nonmuscle (nm) and muscle-specific myofibrillar proteins aggregate immediately under the sarcolemma of the developing myofiber. 2. Muscle-type myofibrillar proteins and thick filaments are added adjacent to the stress fiber structure, using the original structure as a template. 3. The myofibril separates from the sarcolemma, and is added to the pool of myofibrils. 4. Sarcomere length does not increase in length as the myofibril develops. 5
6 B. Premyofibril model 1. A premyofibril containing only nonmuscle proteins forms under the sarcolemma. 2. This detaches from sarcolemma and serves as the template for the developing myofibril. 3. Nonmuscle proteins are gradually replaced with muscle-type myofibrillar proteins. 4. There is a lengthening of the sarcomere, which does not occur in the stress fiber model. 6
7 VI. Acquisition of fiber type-specific myofibrillar proteins A. Type I 1. From primary myotubes (type I emb ). 2. From secondary myotubes if they are surrounded by type I myofibers. 3. Denervation of a slow-twitch muscle: a. Primary myotubes remain as type I. b. Secondary myotubes convert to type II. B. Type II 1. From type II emb myotubes. 2. From secondary myotubes? Muscle type Gene family Slow Fast Myosin heavy chain S F 2A, F 2B, F 2X, F2 EO, F SF Alkaline myosin light chain 1 SA, 1 SB 1 F, 3 F Regulatory myosin light chain 2 S, 2 S 2 F Actin (not fiber-specific) a SK a SK Tropomyosin S F Troponin C S F Troponin I S F Troponin T S F C. Acquisition of MHC isoforms during embryonic, fetal, and postnatal growth 1. Embryonic and fetal isoforms are expressed during the development of early myofibrils. a. Primary myotubes begin as type I myotubes, and later some primary myotubes differentiate into type II myotubes. b. Secondary myotubes are programmed to develop into type II myofibers. 2. The embryonic MHC isoforms are replaced by fetal isoforms. 3. Fetal MHC isoforms are replaced by adult isoforms as more myofibrils are added to the growing myofibers. 7
8 8 Primary, secondary & tertiary myotubes
9 Primary myotubes Secondary myotubes soleus only embryonic embryonic embryonic neonatal embryonic embryonic neonatal neonatal slow embryonic embryonic embryonic slow neonatal neonatal slow slow slow F 2A F 2B F 2X slow F 2A F 2B F 2X 9
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Genes and Human Behaviour: Analysing Mouse Models of Williams-Beuren Syndrome
 Genes and Human Behaviour: Analysing Mouse Models of Williams-Beuren Syndrome Cross-eyed Long-sighted Middle ear inflammation SVAS angiogram Bladder diverticula in a 7 yr old boy ELN? Microdontia The craniofacial
Genes and Human Behaviour: Analysing Mouse Models of Williams-Beuren Syndrome Cross-eyed Long-sighted Middle ear inflammation SVAS angiogram Bladder diverticula in a 7 yr old boy ELN? Microdontia The craniofacial
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
ANSC/FSTC 607 Biochemistry and Physiology of Muscle as a Food INNERVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF MUSCLE
 ANSC/FSTC 607 Biochemistry and Physiology of Muscle as a Food INNERVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF MUSCLE I. Organization of the motor neuron and myofibers A. Motoneuron bifurcates into many branches (terminal
ANSC/FSTC 607 Biochemistry and Physiology of Muscle as a Food INNERVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF MUSCLE I. Organization of the motor neuron and myofibers A. Motoneuron bifurcates into many branches (terminal
The Cell Cycle M G2 G1 G0 S 1
 The Cell Cycle M G2 G1 G0 S 1 Cell Cycle G1 (Gap 1) 3 to 12 hours in length Respond to cues from the environment External cues Growth factors that signal the cell to stay in G1 or continue to through the
The Cell Cycle M G2 G1 G0 S 1 Cell Cycle G1 (Gap 1) 3 to 12 hours in length Respond to cues from the environment External cues Growth factors that signal the cell to stay in G1 or continue to through the
Nerve regeneration. Somatic nervous system
 Somatic nervous system Signals from CNS are sent to skeletal muscles. Final result is a muscle contraction. Motor neuron starts in CNS and its axon ends at a muscle cell. Alpha motor neuron Alpha motor
Somatic nervous system Signals from CNS are sent to skeletal muscles. Final result is a muscle contraction. Motor neuron starts in CNS and its axon ends at a muscle cell. Alpha motor neuron Alpha motor
Nerve meets muscle. Nerve regeneration. Somatic nervous system
 Somatic nervous system Signals from CNS are sent to skeletal muscles. Final result is a muscle contraction. Alpha motor neurons branch into several terminals (can be over 1000), each contacting a separate
Somatic nervous system Signals from CNS are sent to skeletal muscles. Final result is a muscle contraction. Alpha motor neurons branch into several terminals (can be over 1000), each contacting a separate
9/16/2009. Fast and slow twitch fibres. Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Chapter Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function
 Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
The organization of skeletal muscles. Excitation contraction coupling. Whole Skeletal Muscles contractions. Muscle Energetics
 Muscle and Movement The organization of skeletal muscles Excitation contraction coupling Whole Skeletal Muscles contractions Muscle Energetics The molecular bases of movement Muscular cells use molecular
Muscle and Movement The organization of skeletal muscles Excitation contraction coupling Whole Skeletal Muscles contractions Muscle Energetics The molecular bases of movement Muscular cells use molecular
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Lecture 9A. Muscle structure. Outline
 Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Ch 12 can be done in one lecture
 Ch 12 can be done in one lecture Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Chapter 12: Muscles Review muscle anatomy (esp. microanatomy of skeletal muscle) Terminology: sarcolemma t-tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch 12 can be done in one lecture Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Chapter 12: Muscles Review muscle anatomy (esp. microanatomy of skeletal muscle) Terminology: sarcolemma t-tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
#1 20. physiology. Muscle tissue 30/9/2015. Ahmad Adel Sallal. Mohammad Qudah
 # 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
# 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
 PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Development and Repair. Development: fusion of myoblasts. Repair: Satellite cells (S) 3 Types of Muscle
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Review Session Every Friday at 12:20 Muscle Tissue 3 Types of Muscle Function: Force generation Lab Practical Coming up! October 26 th, 27 th Muscle Tissue Striated Nonstriated Skeletal Smooth
ANNOUNCEMENTS Review Session Every Friday at 12:20 Muscle Tissue 3 Types of Muscle Function: Force generation Lab Practical Coming up! October 26 th, 27 th Muscle Tissue Striated Nonstriated Skeletal Smooth
Muscle Tissue. Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells. Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy
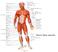 Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure
 Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Muscle Contraction A BIOCHEMICAL PERSPECTIVE
 Muscle Contraction A BIOCHEMICAL PERSPECTIVE This presentation was last edited Oct 2016, by Koni Stone, Professor of Chemistry California State University, Stanislaus Muscle cells! Myoblasts are large
Muscle Contraction A BIOCHEMICAL PERSPECTIVE This presentation was last edited Oct 2016, by Koni Stone, Professor of Chemistry California State University, Stanislaus Muscle cells! Myoblasts are large
Ch 12: Muscles sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere...
 Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle)
 Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle) What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal: morphology and functionality? Cardiac: morphology and functionality? Smooth: morphology and functionality? Skeletal
Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle) What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal: morphology and functionality? Cardiac: morphology and functionality? Smooth: morphology and functionality? Skeletal
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
3 muscle function_scr.notebook April 20, 2015
 the key to muscle function is an excitable membrane sarcolemma proteins on the sarcolemma allow muscle cells to communicate with other cells and the environment specific to muscle function is communication
the key to muscle function is an excitable membrane sarcolemma proteins on the sarcolemma allow muscle cells to communicate with other cells and the environment specific to muscle function is communication
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Muscle Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
Muscles and Animal Movement
 Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden
 Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
Animal Locomotion. Lots of ways to get around. What are the advantages of locomotion? Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Histology Lecture 14 Prof. Darwish Badran. Histology. Enjoy studying hard, but don't forget to get enough sleep :) 1 Author: J.K.
 Histology Enjoy studying hard, but don't forget to get enough sleep :) 1 Author: J.K. Rowling Shapes of Skeletal Muscles: Fig. 1 Circular muscles: Muscles mainly found in the face to control sphincters,
Histology Enjoy studying hard, but don't forget to get enough sleep :) 1 Author: J.K. Rowling Shapes of Skeletal Muscles: Fig. 1 Circular muscles: Muscles mainly found in the face to control sphincters,
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle Physiology. Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College
 Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
8 - Muscular System. Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
 8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle cells have unique characteristics which allow for body movement.
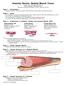 Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
11.2 Muscles and Movement
 11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: 2. A. Skeletal muscle tissue ("striated muscle tissue")
 1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
Muscular System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015
 Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015 Examples of Strength and Physique Athletes The Principle of Muscles The most important principle for muscles is the use it or
Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015 Examples of Strength and Physique Athletes The Principle of Muscles The most important principle for muscles is the use it or
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Tissue Outline. General Function of Muscle Tissue
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Topics Covered. General muscle structure non-muscle components, macro-structure, contractile elements, membrane components.
 1 Topics Covered General muscle structure non-muscle components, macro-structure, contractile elements, membrane components. Contractile function Contractile and regulatory proteins, force production.
1 Topics Covered General muscle structure non-muscle components, macro-structure, contractile elements, membrane components. Contractile function Contractile and regulatory proteins, force production.
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease
 Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Ragad Alhawi. Heba Kalbouneh
 13 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Heba Kalbouneh Motor unit: it s the muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, it s size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle
13 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Heba Kalbouneh Motor unit: it s the muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, it s size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle
Satellite cells. Muscle fiber growth. Muscle: factors affecting pre- and post-natal growth. Longitudinal: Radial ( girth):
 Satellite cells Muscle: factors affecting pre- and post-natal growth Animal Science 123 Animal Growth & Development R. D. Sainz Lecture 11 Unfused myoblasts adjacent to the sarcolemma Fuse with existing
Satellite cells Muscle: factors affecting pre- and post-natal growth Animal Science 123 Animal Growth & Development R. D. Sainz Lecture 11 Unfused myoblasts adjacent to the sarcolemma Fuse with existing
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue)
 Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue) General Structure of Muscle Cells (skeletal) several nuclei (skeletal muscle) skeletal muscles are formed when embryonic cells fuse together
Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue) General Structure of Muscle Cells (skeletal) several nuclei (skeletal muscle) skeletal muscles are formed when embryonic cells fuse together
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Musculoskeletal Systems. Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions
 Musculoskeletal Systems Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions Characteristics of all muscle Contractile: it shortens Excitable: receives & responds to electrical signals Extensible: stretches
Musculoskeletal Systems Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions Characteristics of all muscle Contractile: it shortens Excitable: receives & responds to electrical signals Extensible: stretches
AP Biology. Animal Locomotion. Muscles & Motor Locomotion. Why Do We Need All That ATP? Lots of ways to get around. Muscle
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscle tissue- part 2
 Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Most abundant tissue (600+)
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Most abundant tissue (600+) I. Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle 1) Function: motion; posture; body heat Excitable, Contract/Extend, Elastic 2) Structure A. Connective tissue:
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Most abundant tissue (600+) I. Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle 1) Function: motion; posture; body heat Excitable, Contract/Extend, Elastic 2) Structure A. Connective tissue:
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Physiological Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle
 Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contents I. Composition & structure of skeletal muscle II. Mechanics of Muscle Contraction III. Force production in muscle IV. Muscle remodeling V. Summary 2 Muscle types:
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contents I. Composition & structure of skeletal muscle II. Mechanics of Muscle Contraction III. Force production in muscle IV. Muscle remodeling V. Summary 2 Muscle types:
Muscular Tissue. Functions of Muscular Tissue. Types of Muscular Tissue. Skeletal Muscular Tissue. Properties of Muscular Tissue
 Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Nerve Cell (aka neuron)
 Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Skeletal Muscle. Connective tissue: Binding, support and insulation. Blood vessels
 Chapter 12 Muscle Physiology Outline o Skeletal Muscle Structure o The mechanism of Force Generation in Muscle o The mechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contraction o Skeletal Muscle Metabolism o Control of Skeletal
Chapter 12 Muscle Physiology Outline o Skeletal Muscle Structure o The mechanism of Force Generation in Muscle o The mechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contraction o Skeletal Muscle Metabolism o Control of Skeletal
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Muscle Cell Structure Muscle cells are specialized to contract. An individual muscle is actually a bundle of hundreds to thousands
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Muscle Cell Structure Muscle cells are specialized to contract. An individual muscle is actually a bundle of hundreds to thousands
DOWNLOAD PDF STRUCTURE AND REGULATION OF CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE THIN FILAMENTS
 Chapter 1 : ACTC1 - Wikipedia LARRY S. TOBACMAN STRUCTURE AND REGULATION OF CARDIAC AND The biological production of force and movement can be understood only when it is. Structure[ edit ] There are three
Chapter 1 : ACTC1 - Wikipedia LARRY S. TOBACMAN STRUCTURE AND REGULATION OF CARDIAC AND The biological production of force and movement can be understood only when it is. Structure[ edit ] There are three
Muscle Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 10-1 An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Learning Outcomes 10-1 Specify the functions of skeletal
10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 10-1 An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Learning Outcomes 10-1 Specify the functions of skeletal
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
10 - Muscular Contraction. Taft College Human Physiology
 10 - Muscular Contraction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular Contraction Sliding filament theory (Hanson and Huxley, 1954) These 2 investigators proposed that skeletal muscle shortens during contraction
10 - Muscular Contraction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular Contraction Sliding filament theory (Hanson and Huxley, 1954) These 2 investigators proposed that skeletal muscle shortens during contraction
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Warm-Up. 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
 Warm-Up 1. Based on what you know about Latin root words, what do you think these terms refer to? Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
Warm-Up 1. Based on what you know about Latin root words, what do you think these terms refer to? Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium 2. What structure connects muscle to bone?
SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY. Pathology of Muscle. Lecture 1. Paul Hanna Winter 2018
 SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY Pathology of Muscle Lecture 1 Paul Hanna Winter 2018 Normal Skeletal Muscle [For Information only] Muscle Development Neural tube Dermis Muscles of the body develop from myotome which
SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY Pathology of Muscle Lecture 1 Paul Hanna Winter 2018 Normal Skeletal Muscle [For Information only] Muscle Development Neural tube Dermis Muscles of the body develop from myotome which
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: Dem Bones Textbook p84-85, 88-99 61 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that you understand
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: Dem Bones Textbook p84-85, 88-99 61 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that you understand
