Pelvis Perineum MCQs. Block 1.1. A. Urinary bladder. B. Rectum. C. Reproductive organs. D. The thigh
|
|
|
- Barrie Long
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pelvis Perineum MCQs Block The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The coccygeus B. The levator ani C. The external urethral sphincter D. The internal urethral sphincter E. The obturator internus 2. The peritoneum of the recto-uterine pouch (cul-de-sac of Douglas) passes over the following structures: A. Fundus of uterus B. Posterior vaginal wall C. Anterior wall of the rectal ampulla D. Fundus of urinary bladder E. Anterior wall of anal canal 3. The parietal pelvic fascia lines the inner aspect of the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The piriformis C. The coccygeus D. The levator ani E. The obturator externus 4. The branches of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery supply the following structures: 1 A. Urinary bladder B. Rectum C. Reproductive organs D. The thigh E. The liver 5.* The iliolumbar vein usually drains into the following vein: A. Common iliac B. Internal iliac C. Obturator D. Portal E. Gonadal 6. The four primary groups of lymph nodes receiving lymph drainage from pelvic organs include: A. External iliac lymph nodes B. Internal iliac lymph nodes C. Sacral lymph nodes D. Common iliac E. Celiac 7.* The ganglion impar (coccygeal ganglion) is formed by convergence of the following paired structure: A. Sacral sympathetic trunks B. Obturator nerves C. Sacral parasympathetic trunks D. Pudendal nerves E. Coccygeal nerves 8. The major portions of the urinary bladder include:
2 A. Apex B. Fundus C. Body D. Neck E. Isthmus 9. The parts of the male urethra include: A. Intramural part B. Prostatic urethra C. Intermediate part D. Spongy urethra E. Cavernous urethra 10. The ejaculatory ducts arise by the union of the ducts of the following structures: A. Seminal glands B. Ductus deferentes C. Epididymes D. Ureters E. Urethra 11. The parts of the uterine tubes include: A. Infundibulum B. Ampulla C. Isthmus D. Uterine part E. Cervix 12. The lymph node groups involved in lymphatic drainage of structures of pelvis and perineum include: A. Lumbar B. Inferior mesenteric C. Common iliac D. Superficial inguinal E. Celiac 13. The male urogenital triangle includes: A. External genitalia B. Perineal muscles C. Internal genitalia D. Levator ani muscle E. External anal sphincter 14.* The pelvic cavity is continuous with the abdominal cavity at the level of: A. The pelvic inlet B. The obturator membrane C. The obturator fascia D. The pelvic diaphragm E. The diaphragm 15. The attachments of the coccygeus muscle include: A. Ischial spine B. Inferior end of sacrum and coccyx C. Walls of prostate or vagina D. Tendinous arch of obturator fascia E. Ischial spine 16. The proximal attachment of the levator ani muscle includes: 2
3 A. Body of pubis B. Tendinous arch of obturator fascia C. Ischial spine D. Ischial tuberosity E. Perineal body 17. The distal attachment of the levator ani muscle includes: A. Perineal body B. Coccyx C. Anococcygeal ligament D. Walls of prostate and vagina E. Ischial spine 18. The levator ani includes the following muscles: A. Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus D. Piriformis E. Coccygeus 19. The tendinous arch of pelvic fascia has the following parts: A. The puboprostatic ligament B. The pubovesical ligament C. The sacrogenital ligament D. The broad ligament E. The mesometrium 20. The paracolpium connects the following structures: A. The visceral fascia of the vagina B. The tendinous arch of the pelvic fascia C. The peritoneum of the vagina D. The inguinal canal E. The pubic symphysis 21. The anococcygeal body is a ligament connecting the following structures: A. Anus B. Coccyx C. Tendinous arch of levator ani D. Urogenital hiatus E. Obturator fascia 22.* The pararectal fossae are the lateral extensions of the following peritoneal pouch: A. Recto-uterine B. Hepatorenal C. Omental bursa D. Subphrenic E. Vesico-uterine 23. The following elements are inclosed within the broad ligaments: A. Uterine tubes B. Ovaries C. Ligaments of the ovaries D. Round ligaments of the uterus E. Bulbs of vestibule 3
4 24. In the male, the ureteric fold is formed as the peritoneum passes up and over the following structures: A. Ureter B. Ductus deferens C. Seminal vesicle D. Internal iliac vessels E. Ejaculatory duct 25. The male reproductive organs in contact with the peritoneum are: A. Seminal glands B. Ampulla of ductus deferens C. Testis D. Prostate E. Bulb of penis 26. The loose areolar (fatty) tissue in the subperitoneal endopelvic fascia can be explored through blunt dissection, therefore representing potential spaces, as follows: A. Retropubic space B. Prevesical space C. Retrorectal space D. Presacral space E. Retroperitoneal space 27. The hypogastric sheath gives passage to the following elements: A. Vessels to pelvic viscera B. Nerves to pelvic viscera C. Ureters D. Ductus deferens 28. The hypogastric sheath divides into the following laminae (layers): A. Lateral ligament of the bladder B. Lateral rectal ligament C. Rectovesical septum D. Cardinal ligament E. Broad ligament 29. The rectosacral (lateral sacral) ligaments divide the pelvirectal space into the following spaces: A. Rectouterine B. Rectovesical C. Retrorectal D. Pararectal E. Paracolpium 30. The pubic branch of the obturator artery ascends on the pelvic surface of the pubis to anastomose with the following: A. The pubic branch of the obturator artery from the other side B. The pubic branch of the inferior epigastric artery, a branch of the external iliac artery C. The pubic branch of the inferior epigastric artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery D. The pubic branch of the inferior epigastric artery, a branch of the common iliac artery E. The pubic branch of the umbilical artery 31.* The inferior vesical artery occurs only in males, being replaced in females by the following artery: 4
5 A. Vaginal B. Uterine C. Ovarian D. Middle rectal E. Internal pudendal 32.* The uterine artery is the homolog of the following artery in male: A. Artery of the ductus deferens B. Inferior vesical artery C. Internal pudendal artery D. Lateral sacral artery E. Dorsal artery of penis 33. The following arteries have their origin in the posterior division of the internal iliac: A. Gonadal arteries B. Inferior gluteal C. Superior gluteal D. Iliolumbar E. Lateral sacral 34. On reaching the side of the cervix, the uterine artery divides into the following branches: A. Vaginal B. Ascending C. Inferior vesical D. Tubal E. Ovarian 35. In males, the ureter lies to the ductus deferens and enters the urinary bladder just to the seminal gland. A. Posterolateral B. Superior C. Anteromedial D. Inferior E. Medial 36. In females, the ureter is crossed by the uterine artery and then to the fornix of the vagina before entering the urinary bladder. A. Superiorly B. Lateral C. Inferiorly D. Posterior E. Anterior 37. The pelvic parts of the ureter is supplied by the following arteries: A. Common iliac B. Internal iliac C. Ovarian D. Uterine E. Middle rectal 38. The urinary bladder, according to its content and the state of neighbouring viscera, varies in the following respects: A. Size B. Shape C. Position 5
6 D. Relationships E. Innervation 39. The potential retropubic space (of Retzius) separates the following structures: A. Pubic bones B. Urinary bladder C. Uterus D. Rectum E. Urethra 40. The following parts of the urinary bladder meet at the neck of the bladder: A. Fundus B. Inferolateral surfaces C. Apex D. Body E. External urethral orifice 41. In males, the fundus of the urinary bladder is separated from the rectum by the following structures: A. Rectovesical septum B. Seminal glands C. Ampullae of ductus deferentes D. Superior anterior wall of vagina E. Pubic symphysis 42. The three urinary systems developped from mesodermal tissue include: A. Pronephros B. Mesonephros 6 C. Metanephros D. Cloacal folds E. Urogenital sinus 43. The mesonephros is characterized by the following: A. The excretory units B. The mesonephric or Wolffianduct C. The metanephros D. The ureteric bud E. Forms in the cervical region, is vestigial 44. The ureteric bud gives rise to the following structures: A. Ureter B. Renal pelvis C. Calyces D. Excretory units (nephrons) E. The urinary bladder 45. During the 4th to 7th weeks of development, the cloaca is subdivided into the following structures: A. Urogenital sinus B. Anal canal C. Mesonephros D. Pronephros E. Hind gut 46. The urogenital sinus differentiates into the following structures: A. Urinary bladder B. Prostatic urethra
7 C. Membranous urethra D. Upper portion of vagina E. Genital tubercle 47. Testosterone produced in the testes stimulates development of the mesonephric ducts to form the following structures: A. Epididymis B. Vas deferens C. Ejaculatory duct D. Efferent ducts E. Genital tubercles 48. During the indifferent stage of development, the genital system includes the following ducts: A. Mesonephric ducts B. Paramesonephric ducts C. Efferent ducts D. Vas deferens E. Uterine tube 49. Estrogens regulate development of the paramesonephric ducts which form the following: A. Uterine tube B. Uterus C. Cervix D. Upper portion of vagina E. Clitoris 50. The indifferent stage of the external genitalia features the following structures: A. Genital tubercle 7 B. Genital swellings C. Cloacal folds D. Scrotal swellings E. Clitoris 51.* In females, the genital tubercle forms the following structure: A. Clitoris B. Labia majora C. Labia minora D. Cervix 52.* In females, the genital tubercle forms the following structure: A. Clitoris B. Labia majora C. Labia minora D. Cervix 53.* In females, the urethral folds form the following structure: A. Clitoris B. Labia majora C. Labia minora D. Cervix 54.* In females, the urethral folds form the following structure:
8 A. Clitoris B. Labia majora C. Labia minora D. Cervix 55.* In females, the genital swellings form the following structure: A. Clitoris B. Labia majora C. Labia minora D. Cervix 56. The following structures are at the angles of the trigone of the urinary bladder: A. Ureteric orifices B. Internal urethral orifice C. Internal urethral sphincter D. Uvula of the urinary bladder E. Apex of the bladder 57. The urinary bladder bed is formed by the following structures: A. Pubic bones B. Fascia covering the levator ani muscle C. Fascia covering the superior obturator internus muscle D. Superior anterior wall of vagina E. Trigone of the bladder 58. The arterial supply of the urniary bladder features the following vessels: A. Superior vesical arteries B. Inferior vesical arteries C. Vaginal arteries D. Obturator arteries E. Superior gluteal 59. For descriptive purposes, the male urethra is divided into the following parts: A. Intramural B. Prostatic C. Intermediate D. Spongy E. Cavernous 60. The location of the female external urethral orifice includes: A. Vestibule of vagina B. Anterior to the vaginal orifice C. Posterior to the anal orifice D. Inferior to the internal urethral orifice E. Anterior to the pubic syphysis 61.* The teniae coli of the sigmoid colon spread to form a continuous layer of smooth muscle at the level of: A. Rectosigmoid junction B. Duodenojejunal junction C. Sigmoid mesocolon D. Internal anal sphincter 8
9 E. External anal sphincter 62. The essential elements of maintaining fecal continence include: A. The angle of the anorectal flexure of the anal canal B. The ability of the rectal ampulla to relax C. The angle of the sacral flexure of the rectum D. The lateral flexures of the rectum E. The rectosigmoid junction 63. The arteries of the rectum and their origins include: A. The inferior rectal arteries, arising from the internal pudendal arteries B. The superior rectal artery, continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery C. The middle rectal arteries, arising from the anterior divisions of the internal iliac artery D. The anterior rectal arteries, arising from the external pudendal arteries E. The middle rectal arteries, arising from the superior divisions of the obturator artery 64. The parts of the rectal venous plexus include: A. The internal rectal venous plexus deep to the mucosa of the anorectal junction B. The external rectal venous plexus external to the muscular wall C. The external rectal venous plexus deep to the peritoneum D. The internal rectal venous plexus just deep to the skin E. The external rectal venous plexus just deep to the mucosa of the anorectal junction The male internal genital organs include: A. Testes B. Epididymides C. Ductus deferentes D. Seminal glands E. Scrotum 66. The male internal genital organs include the following: A. Bulbo-urethral glands B. Prostate C. Ejaculatory ducts D. Scrotum E. Penis 67. The course of the ductus deferens include: A. Begins in the tail of epididymes B. Ascends posterior to testis C. Ascends medial to epididymis D. Penetrates the anterior abdominal wall via the inguinal canal E. Ends by joining the cystic duct to form the ejaculatory duct 68. The ampulla of the ductus deferens has the following relations: A. Posterior to the urinary bladder B. Medial to the ureter C. Medial to the seminal gland D. Lateral to the testis on the same side E. Medial to the prostate
10 69. The relations of the seminal glands include: A. Superior to the prostate B. Posterior to the fundus of urinary bladder C. Anterior to the rectum D. Covered superiorly by peritoneum E. Anterior to the ureters 70. The arteries to the seminal glands derive from the following vessels: A. Inferior vesical artery B. Middle rectal artery C. Superior rectal artery D. Inferior mesenteric artery E. Superior vesical artery 71. The ejaculatory ducts arise by the union of the following structures: A. Ducts of seminal glands B. Ductus deferentes C. Urethra D. Ureters E. Prostate 73. The semen is a mixture of secretions produces by the following structures: A. Testes B. Seminal glands C. Prostate D. Bulbo-urethral glands E. Scrotum 74. The prostatic arteries are derived from the fllowing vessels: A. Inferior vesical arteries B. Internal pudendal arteries C. Middle rectal arteries D. Uterine arteries E. Testicular arteries 75. The relations of the bulbo-urethral glands include: A. Posterolateral to the intermediate part of urethra B. Embedded within the external urethral sphincter C. Posterolateral to the membranous part of urethra D. Embedded within the internal urethral sphincter E. Inferior to pelvic diaphragm 72. The main parts of the prostate include: A. Base B. Apex C. Anterior surface D. Posterior surface E. Neck 10
Pelvis MCQs. Block 1. B. Reproductive organs. C. The liver. D. Urinary bladder. 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: E.
 Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale. Category or Criterion. Rationale or Comments (1) (2) (3) (4)
 Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Urinary Bladder. Prof. Imran Qureshi
 Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics.
 NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Bony ypelvis. Composition: formed by coccyx, and their articulations Two portions
 Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal. Yes, with uterine artery (collateral circulation between abdominal +pelvic source)
 Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL
 ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Slide Read the tables it is about the difference between male & female pelvis.
 I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
Pelvic Angiogram - Male
 Pelvic Angiogram - Male Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Lateral sacral artery Iliolumbar artery Posterior trunk of internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery Internal pudendal artery External
Pelvic Angiogram - Male Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Lateral sacral artery Iliolumbar artery Posterior trunk of internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery Internal pudendal artery External
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Rama Nada. - Ensherah Mokheemer. - Ahmed salman. 1 P a g e
 - 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
- 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
The Female and Male External Genitalia. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia. Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
-15. -Alaa Albandi. -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib. 0 P a g e
 -15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
-15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2.
 1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2. The extension of the vaginal lumen around the intravaginal part
1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2. The extension of the vaginal lumen around the intravaginal part
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space
 Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Perineum. Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان-
 -6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
-6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
Learning objectives. SGD on Functions of Testosterone. Class
 Learning objectives SGD on Functions of Testosterone Class 2016 14-1-2013 Discuss o Process of spermatogenesis. o Sex determination. o Process of maturation of sperms. o Physiology of mature sperms. Discuss
Learning objectives SGD on Functions of Testosterone Class 2016 14-1-2013 Discuss o Process of spermatogenesis. o Sex determination. o Process of maturation of sperms. o Physiology of mature sperms. Discuss
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra
 Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 1. Introduction I. 2. Lecturers I. 3. Timetable I. 4. Assessment I. 5. Study material II. 6. General information II.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن
 Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن إذا شئت سهال This work was done by: Alanoud Abuhaimed Dania Alkelabi Ghada Alothaim Jawaher Abanumy Rawan AlWadee Wejdan Alzeid Mohanad
Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن إذا شئت سهال This work was done by: Alanoud Abuhaimed Dania Alkelabi Ghada Alothaim Jawaher Abanumy Rawan AlWadee Wejdan Alzeid Mohanad
THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES
 THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES THE ABDOMINAL AORTA The abdominal aorta begins at the aor9c hiatus in the diaphragm at the level of the T12 vertebra and ends at the
THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES THE ABDOMINAL AORTA The abdominal aorta begins at the aor9c hiatus in the diaphragm at the level of the T12 vertebra and ends at the
Development of the urogenital system
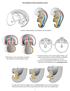 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The urinary system is composed of two kidneys,two ureters,urinary bladder and urethra The
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The urinary system is composed of two kidneys,two ureters,urinary bladder and urethra The
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
ischium Ischial tuberosities Sacrotuberous ligament The coccyx
 Perineum General lfeatures Region of below pelvic diaphragm A diamond shape space whose boundaries are those of the pelvic outlet Lower border of symphysis pubis Rami of pubis and ischium Ischial tuberosities
Perineum General lfeatures Region of below pelvic diaphragm A diamond shape space whose boundaries are those of the pelvic outlet Lower border of symphysis pubis Rami of pubis and ischium Ischial tuberosities
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Gross anatomy of the urinary system. Done by : razan krishan. slide in bold and book in green
 Gross anatomy of the urinary system Done by : razan krishan slide in bold and book in green Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and
Gross anatomy of the urinary system Done by : razan krishan slide in bold and book in green Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and
B) cervix of uterus C) vagina D) rectum. 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9
 Pelvis Practice Problems 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9 2. What number illustrates the cervix? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 8 C) 5 D) 6 3. Which of the following is
Pelvis Practice Problems 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9 2. What number illustrates the cervix? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 8 C) 5 D) 6 3. Which of the following is
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The urinary system is composed of two kidneys,two ureters,urinary bladder and urethra The
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The urinary system is composed of two kidneys,two ureters,urinary bladder and urethra The
TABLE OF CONTENTS A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT B. STUDY COMPONENT. Page. 1. Introduction I. 2. Lecturers I. 3. Timetable I. 4.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain
 Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain Yong-Chul Kim Department of anesthesia and pain medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine 1 Overview Anatomy Nerve innervation CPP by pathology CPP by
Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain Yong-Chul Kim Department of anesthesia and pain medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine 1 Overview Anatomy Nerve innervation CPP by pathology CPP by
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Cardiovascular Digestive. Endocrine Integumentary
 General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
The anatomy of the rectum and anal canal
 The anatomy of the rectum and anal canal Vishy Mahadevan Abstract Diseases of the rectum and anal canal, both benign and malignant, account for a very large part of colorectal surgical practice in the
The anatomy of the rectum and anal canal Vishy Mahadevan Abstract Diseases of the rectum and anal canal, both benign and malignant, account for a very large part of colorectal surgical practice in the
EMBRIOLOGY Intermediate Mesoderm. Becomes the suprarenal glands, gonads, kidneys and associated tubes and vasculature
 ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM EMBRIOLOGY Intermediate Mesoderm Becomes the suprarenal glands, gonads, kidneys and associated tubes and vasculature THE VULVA 1. Mons : a pad of
ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM EMBRIOLOGY Intermediate Mesoderm Becomes the suprarenal glands, gonads, kidneys and associated tubes and vasculature THE VULVA 1. Mons : a pad of
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 24
 primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Aniko Szabo Hill 1 of 12
 Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Male Reproductive System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Development of the urinary system
 Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Male genital system Learning Objectives 1. Identify External
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Male genital system Learning Objectives 1. Identify External
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. September 13, 2012 B C
 STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Urogenital System. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
 Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
 Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
Anatomy of Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES. Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga
 ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Objectives. Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble. Disclosures. Anatomy 101. Anterior Abdominal Wall. Arcuate Line. Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C)
 Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
The pelvis revisited: A pictorial review of normal anatomy and its correlation with MDCT images
 The pelvis revisited: A pictorial review of normal anatomy and its correlation with MDCT images Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-0356 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez,
The pelvis revisited: A pictorial review of normal anatomy and its correlation with MDCT images Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-0356 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez,
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
