Ethiopian patients and a brief review
|
|
|
- Ariel Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Postgraduate Medical Journal (November 1979) 55, Testicular feminization syndrome: a report of three Ethiopian patients and a brief review EDEMARIAM TSEGA M.D., D.C.M.T.(L), F.R.C.P.(C) Summary The clinical features of 3 Ethiopian patients presenting with the complete syndrome of testicular feminization are descrilbed. All 3 were seen because of primary amenorrhoea. At laparotomy, one patient had testes located intra-abdominally, a second lodged in the inguinal canals and a third as masses in the labia majora. Also, one of these patients had bilateral inguinal herniae, a usual feature of this syndrome. Since the incidence of malignancy is high among individuals with undescended testes, they were removed in 2 patients. In the third patient, however, the testes were not removed because of delay in development of secondary sex characteristics. The literature on testicular feminization is also briefly reviewed. Introduction The syndrome of testicular feminization, as originally described by Morris (1953), is characterized by a phenotypic female with typical female body build, well developed breasts, scanty or absent pubic and axillary hair, a small vagina ending in a cul-de-sac, absence of internal female structures and presence of testes intra-abdominally, in the inguinal canal or in the labia majora. Such patients are chromatin negative and have XY karyotypes. Genetically, therefore, they are males. The condition is transmitted as sex-linked recessive or a sex-limited autosomal dominant mutant gene. Thus, in an affected family, all of the females are normal while half of the males may be expected to be reared as females. The testes of the affected males produce Miillerianinhibiting factor during fetal life resulting in absence of internal female structures (Jones and Wilkins, 1961). In spite of normal blood levels of testosterone and urinary 17-ketosteroids, male secondary sexual characteristics fail to develop at adolescence. The production of a normal level of testosterone for males, a failure to respond to exogenous testosterone and a variable level of oestrogen, low for normal female but usually high for normal male, suggest BELAI Department of Internal Medicine, Black Lion Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Addis Ababa University DAMTEW M.D. that the basic lesion in testicular feminization is abnormality in the response of target tissues to androgens (Morris and Mahesh, 1963; French et al., 1966; Chan and O'Malley, 1976) leaving the oestrogen unopposed for breast development and the appearance of other female secondary characteristics. Patients with the complete syndrome of testicular feminization have a normal or small clitoris. There are some patients, however, with clitoral enlargement and unpredictable secondary sex characteristics. It has been suggested that patients with an enlarged clitoris should be differentiated from the complete form as 'incomplete', 'partial' or 'genitalia ambiguous' (Teter and Boczkowski, 1966). In this communication 3 cases of testicular feminization in Ethiopians are presented and the literature is briefly reviewed. Case I A 20-year-old patient was seen with complaints of amenorrhoea and infertility. She had always been identified as a female since childhood. She claimed a normal sexual relationship with her husband whom she had married 3 years previously. The only disappointment had been infertility. She is the fourth child of a normal family. Two of the siblings are male and one, who could not be traced, is female. Physical examination revealed a tall, slender girl with a feminine voice and body build. There was strabismus but colour vision was normal. The neck was not webbed. The thyroid gland was not enlarged. The breasts were well developed with wide areolae and small nipples. Axillary as well as the suprapubic hair was absent. The labia majora were prominent and each labium contained a firm eliptical, non-tender and freely mobile mass measuring 4x 7 cm. The clitoris and labia minora were small and the vagina was a short pouch ending in a /79/ $ The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine
2 cul-de-sac and without palpable or visible cervix (Fig. 1). FIG. 1. Case 1 showing well developed breasts with wide areolae but small nipples; absence of suprapubic hair, a mass in each labium majora, small clitoris and labia minora. The buccal smear was negative for sex chromatin. Karyotyping and hormones could not be determined. At laparotomy, no uterus or related gonadal tissues were found. However, there were testes, one on either side of the labia majora and associated with indirect inguinal herniae. Both testes were removed and the herniae repaired. She was discharged on stilboestrol and was lost to follow-up. Case 2 A 19-year-old student was admitted to hospital because of amenorrhoea and poor development of secondary sex characteristics. The patient grew up as a 'female' and was always healthy. Both parents are alive and well. The mother had her menarche at a late age 12 years after marriage. The patient has 2 brothers and 2 sisters. Both sisters are known to have a normal menstrual history. Physical examination revealed infantile breast 845 and absence of axillary and pubic hair. The labia were small and the vagina was very shallow (only about 2 cm long) ending in a cul-de-sac. There was no inguinal or labial mass. The rest of the physical examination was normal. At laparotomy, the uterus was absent and 2 gonads were found intra-abdominally. A biopsy taken from the right gonad showed it was malformed with disorganized tubules. There was no spermatogenesis and Leydig cells were not conspicuous. Connective tissue cells were chromatin negative (Fig. 2). Karyotyping and hormone levels were not determined. The patient was lost to follow-up. Case 3 A 19-year-old girl was admitted to hospital with a complaint of bilateral swelling in the groins since childhood. She had never menstruated but had a satisfactory sexual relationship with her boy friend. She had 2 brothers, and one sister who is <6 years old Ṗhysical examination revealed a slender, tall and well developed girl. Colour vision was intact. There was no webbing of the neck. The thyroid gland was not enlarged and there was no lymphadenopathy. The breasts were big with wide areolae and small nipples. The respiratory and cardiovascular systems were normal. There was no hepatomegaly. There was an oval, freely mobile and non-tender mass measuring 2 x 3 cm located on each side of the symphysis pubis. There was no inguinal hernia. Axillary and pubic hair was absent. The vulva revealed a small clitoris and labia minora. The vagina was very short ending in a cul-de-sac. There was no palpable cervix or uterus. The buccal smear showed absence of sex chromatin. Hormone levels and karyotype were not determined. At laparotomy, no uterus or other female gonadal tissues could be found. The 2 inguinal masses were removed. Macroscopically, both masses were covered with adipose tissue and the cut surface showed seminiferous tubules. Microscopically, the seminiferous tubules were atrophic and there were Sertoli cell 'adenomas'. There was no spermatogenesis (Fig. 3). The patient was informed that she would never menstruate and should not expect children. She was discharged on oral stilboestrol 1'5 mg daily. After being lost to follow-up for nearly 30 months, during which time she had stopped taking stilboestrol, she complained that she had lost half of the volume of her breasts. There was no other secondary sex characteristic change. She was restarted on oral stilboestrol 1-5 mg daily and seems to be pleased with the result of her treatment 6 months later.
3 846 ~,.... :, & F^ X. < : 'i' ~ * t ::.. :..'::!,,% :~...v ''".. *.,,,*,*. * ".".....: 4.1.,,.,, ;.:;:~...,.p :::..:.:..d i'.....'~.,2 '!::.~... ~,.,~:.*''i?' t~ e'<.. b. ~ s. X * ::o * S'",, " *,' I;...?,,'.;:.~.*...' "."I i :. ':," I'. 4..!~.- :.. ':~. vjj?.:' :.;.v!4 U:'f' FIG. 2. Case 2. Testicular tubules with masses of luteal cells between them and the capsule and without spermatogenesis (x 160). *:i.~~l i:, *: *: -l~ri$ '..f. ii'm.'::tm.,.,'w'i:- '.,s. -* rr: 1 a ~~L~-Q I)~ FIG. 3. Case 3. Testicular tubules show Sertoli cells only. There is no spermatogenesis. The edge of Sertoli cell 'adenoma' is on the left (x 280)..
4 Discussion Since the first description of 82 cases by Morris in 1953, over 350 patients with testicular feminization had been reported by 1966 (Morris, 1953; Morris and Mahesh, 1963; Teter and Boczkowski, 1966). Out of 265 cases of primary amenorrhoea seen in an obstetrics and gynaecology clinic in Warsaw, Poland, during a period of 12 years, 7 were noted to be cases of testicular feminization (Teter and Boczkowski, 1966). Therefore, this condition, although uncommon, is not very rare. However, so far as the authors know, there are no reports of the syndrome from the African continent. The incidence of inguinal herniae is high among these patients. In nearly 50%4 of the reported cases, herniae and inguinal gonads have been described (Morris and Mahesh, 1963). The reason for the failure of the closure of the inguinal ring is probably the lack of androgen effect. Case 1 had bilateral inguinal herniae and gonads in the labia majora. Since inguinal herniae are significantly less common in young girls than in boys, girls presenting with primary amenorrhoea and inguinal herniae must be suspected of having the syndrome of testicular feminization, especially if the axillary and pubic hair is scanty or absent, the vagina is small and the uterus cannot be palpated. Another curious but not uncommon finding among these patients is colour blindness, the cause of which is unknown. None of the 3 patients described in this paper is colour blind. Case 1 and 3 presented with female phenotype, well developed secondary sex characteristics and satisfactory sexual relationship with their partners. Both were chromatin negative. The external genitalia were of the adult female type but with short vagina, small clitoris and labia minora. The axillary and pubic hair were absent. The breasts were fully developed with wide areolae but small nipples. The uterus was absent and the testes were removed from the labia majora (Case 1) and inguinal canals (Case 3). Case 2, who is also phenotypically female but not married, presented with much less developed breasts, and an infantile vagina as well as total absence of pubic and axillary hair. The sex chromatin was negative. The uterus was absent and the gonads were located intra-abdominally. It appears that there was a delay in the development of secondary sex characteristics in this particular patient. The syndrome of testicular feminization is genetically transmitted through the maternal line affecting only genetic males. Observations on pedigrees of previously reported cases suggest a sex-linked recessive or a sex-limited autosomal dominant mutant gene as a transmitter of this condition. Late menarche and decreased pubic 847 and axillary hair have been noted in mothers, grandmothers, aunts and sisters of patients with testicular feminization (Morris and Mahesh, 1963). The phenotypic expression in about 50%O of genetic males, with negative sex chromatin and XY chromosome, is a result of lack of androgen effect on target tissues. In fetal life, the Wolfflan duct system fails to develop because of androgen insensitivity and the external genitalia fail to develop along male lines because of absent response to androgens (Jost, 1958). Although androgenic steroids do not appear to inhibit the development of the Mullerian system, the absence of Miillerian derivatives (ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus) in the syndrome of testicular feminization is best explained by a Miillerian-inhibiting factor originating from the testes. Again, at puberty, absence of development of male secondary sex characteristics in the complete syndiome is a result of lack of androgen effect. Administration of large doses of androgen to these patients does not produce virilization or change in the secondary sex characteristics. This is not entirely true in the 'incomplete' form (Morris and Mahesh, 1963). After castration, there is a tendency for ketosteroid and oestrogen levels to fall resulting in a decrease in vaginal cornification and some changes in secondary sex characteristics. This is best exemplified by Case 3 who complained that she had lost 505/s of the size of her breasts after stopping her stilboestrol for 30 months. The anatomical location of the testes in these cases varies from individual to individual. The 3 cases presented here revealed the 3 possible sites: In Case 1 the testes were located in the labia majora, in Case 2, it was intra-abdominal while in Case 3 it was in the inguinal canals. The incidence of malignancy (usually as germinomas, tubular adenomas, Sertoli cell tumours or cysts) in these organs after the age of 30 years is about 22%y (Morris and Mahesh, 1963; Manuel, Katayana and Jones, 1976; Richardson and Robboy, 1977). Therefore, after the full development of secondary sex characteristics, removal of the testes with oestrogen replacement therapy is indicated. Cases 1 and 3 were discharged on an oestrogen preparation after castration but follow-up, as is always the case in Ethiopa, was unsuccessful. Case 2 was also lost to follow-up for nearly 2 years. Considering the cultural and educational backgrounds of these patients, no attempt was made to announce their true sex; however, they were informed that they would never menstruate and hence should not expect children. References CHAN, L. & MALLEY, B.W. (1976) Mechanism of action of the sex steroid hormones. New England Journal ofmedicine, 294, 1322.
5 848 Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 November Downloaded from FRENCH, F.S., VANWYK, J.J., BEGGETT, B., EASTERLING, W.E., TALBERT, L.M., JOHNSTON, F.R., FORCHIELLI, E. & DEY, A.C. (1966) Further evidence of a target organ defect in the syndrome of testicular feminization. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology, 26, 493. JONES, H.W. & WILKINS, L. (1961) Gynecological operations in 94 patients with intersexuality. Implications concerning the endocrine theory of sexual differentiation. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 82, JOST, A. (1958) In: Hermaphroditism, Genital Anomalies and Related Disorders, p. 15, by H.W. Jones Jr and W. Wilkins, Williarns & Wilkins Co., Baltimore. MANUEL, M., KATAYAMA, K.P. & JONES Jr, H.W. (1976) The age of occurrence of gonadal tumor in intersex patients with a Y chromosome. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 124, 293. MORRIS, J.M. (1953) The syndrome of testicular feminization in male pseudohermaphrodites. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 65, MORRIS, J.M. & MAHESH, V.B. (1963) Further observations on the syndrome, 'testicular feminization'. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 87, 731. RICHARDSON, G.S. & ROBBOX, S.J. (1977) Pelvic mass in a 53-year-old woman with primary amenorrhea. New England Journal of Medicine, 296, 439. TETER, J. & BOCZKOWSKI, K. (1966) Testicular feminization with and without clitoral enlargement. American Joutrnal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 94, 813. on 29 June 2018 by guest. Protected
Testicular feminization. The features of this syndrome in its typical form are these (Fig. 1): (1) Female bodily configuration.
 Personal Practice Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 595. The XY Female Child C. J. DEWHURST From the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Queen Charlotte's Maternity Hospital, and Chelsea
Personal Practice Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 595. The XY Female Child C. J. DEWHURST From the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Queen Charlotte's Maternity Hospital, and Chelsea
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood
 When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD)
 Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype.
 INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract. Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim
 Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
AND TREATMENT OF HERMAPHRODITISM*
 THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HERMAPHRODITISM* BY C. C. WINKEL SMITH From the Paediatric Surgical Department, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION OCTOBER 8, 1959)
THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HERMAPHRODITISM* BY C. C. WINKEL SMITH From the Paediatric Surgical Department, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION OCTOBER 8, 1959)
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine
 International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 326535, 19 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.326535 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 Ahmet Ay, Aybala Agac Ay, Ozan Turgut,
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 326535, 19 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.326535 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 Ahmet Ay, Aybala Agac Ay, Ozan Turgut,
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda
 1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
Sexual Development. 6 Stages of Development
 6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA. Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK. Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
Disordered Sex Differentiation Mixed gonadal dysgenesis Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Mixed gonadal dysgenesis
 Disordered Sex Differentiation DSD has superceded intersex in describing genital anomalies in childhood DSD results from hormonal imbalances due to (i) abnormal genetic status, (ii) enzyme defects, or
Disordered Sex Differentiation DSD has superceded intersex in describing genital anomalies in childhood DSD results from hormonal imbalances due to (i) abnormal genetic status, (ii) enzyme defects, or
Martin Ritzén. bioscience explained Vol 7 No 2. Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within
 Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
Martin Ritzén Professor emeritus, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Girl or boy: What guides gender development and how can this be a problem within sport? Introduction During the 2009 athletics
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Downloaded from amuj.arakmu.ac.ir at 22: on Thursday June 21st 2018 FSH.
 * Downloaded from amuj.arakmu.ac.ir at 22:26 +0430 on Thursday June 21st 2018 CT Email: mjamilian@yahoo.com * X 1 - T F: Testicular feminization. TF T F xy TSH immature testicular tissue CT TF patients
* Downloaded from amuj.arakmu.ac.ir at 22:26 +0430 on Thursday June 21st 2018 CT Email: mjamilian@yahoo.com * X 1 - T F: Testicular feminization. TF T F xy TSH immature testicular tissue CT TF patients
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
Disclosure. Session Objectives. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation.
 46, XY Female: A Case of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (CAIS) MICHELLE MCLOUGHLINMSN, CRNP, CPNP-AC THE CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND DIABETES Disclosure
46, XY Female: A Case of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (CAIS) MICHELLE MCLOUGHLINMSN, CRNP, CPNP-AC THE CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND DIABETES Disclosure
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
2. Which male target tissues respond to testosterone, and which require dihydrotestosterone?
 308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Case Report Intra-Abdominal Testicular Seminoma in a Woman with Testicular Feminization Syndrome
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2011, Article ID 592124, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/592124 Case Report Intra-Abdominal Testicular Seminoma in a Woman with Testicular Feminization Syndrome Darshana D. Rasalkar,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2011, Article ID 592124, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/592124 Case Report Intra-Abdominal Testicular Seminoma in a Woman with Testicular Feminization Syndrome Darshana D. Rasalkar,
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION
 Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Intersex is a group of conditions where there is a discrepancy between the external genitals and the internal genitals (the testes and ovaries).
 Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA BY Dr Numair Ali sheikh FCPS PGT I Department Of Pediatrics BBH RWP AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA Children born with ambiguous genitalia may be subdivided in to
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA BY Dr Numair Ali sheikh FCPS PGT I Department Of Pediatrics BBH RWP AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA Children born with ambiguous genitalia may be subdivided in to
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Laura Stewart, MD, FRCPC Clinical Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Endocrinology University of British Columbia
 Precocious Puberty Laura Stewart, MD, FRCPC Clinical Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Endocrinology University of British Columbia Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Laura Stewart No relationships with
Precocious Puberty Laura Stewart, MD, FRCPC Clinical Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Endocrinology University of British Columbia Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Laura Stewart No relationships with
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
OVOTESTIS Background Pathophysiology
 OVOTESTIS Background Ovotestis refers to the histology of a gonad that contains both ovarian follicles and testicular tubular elements. Such gonads are found exclusively in people with ovotesticular disorder
OVOTESTIS Background Ovotestis refers to the histology of a gonad that contains both ovarian follicles and testicular tubular elements. Such gonads are found exclusively in people with ovotesticular disorder
Androgen insensitivity revealed by surgery in elderly identical twins
 Gynecol Surg (2009) 6:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s10397-009-0512-4 CASE REPORT Androgen insensitivity revealed by surgery in elderly identical twins Serge Landen & Sebastian Doniga & Peter Bollars & Veronique
Gynecol Surg (2009) 6:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s10397-009-0512-4 CASE REPORT Androgen insensitivity revealed by surgery in elderly identical twins Serge Landen & Sebastian Doniga & Peter Bollars & Veronique
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Female with 46, XY karyotype
 Case Report Obstet Gynecol Sci 2017;60(4):378-382 https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.4.378 pissn 2287-8572 eissn 2287-8580 Female with 46, XY karyotype Eun Jung Jung 1, Do Hwa Im 1, Yong Hee Park 1, Jung
Case Report Obstet Gynecol Sci 2017;60(4):378-382 https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.4.378 pissn 2287-8572 eissn 2287-8580 Female with 46, XY karyotype Eun Jung Jung 1, Do Hwa Im 1, Yong Hee Park 1, Jung
The Female Reproductive System
 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO
 JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 43, No. 4: 289-298 (1968) A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO Received May 9, 1968 Zoological Institute, Hokkaido
JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 43, No. 4: 289-298 (1968) A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO Received May 9, 1968 Zoological Institute, Hokkaido
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Development of the urogenital system
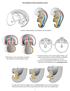 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
considered, who identify themselves with the female gender, the generic pronoun used throughout the book is she. 4 th Sex
 44 Glossary 3rd Gender/Sex, Akwa, Ali, Aravani, Aruvani Chhakka, Eunuch, Hijra, Jogappa, Khusra, Khasuaa, Kinnar, Kojja, Maada, Mukhannathun, Napunsakudu, Other Sex, Pavaiyaa, Thirunangai, Transgender
44 Glossary 3rd Gender/Sex, Akwa, Ali, Aravani, Aruvani Chhakka, Eunuch, Hijra, Jogappa, Khusra, Khasuaa, Kinnar, Kojja, Maada, Mukhannathun, Napunsakudu, Other Sex, Pavaiyaa, Thirunangai, Transgender
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
46,XY Female: SRY and AR Basis: Genotype & Phenotype Correlation
 Original Article Indian Journal of Genetics and Molecular Research 53 Volume 1 Number 2, July - December 2012 46,XY Female: SRY and AR Basis: Genotype & Phenotype Correlation Amudha S.*, MSc; Sayee Rajangam**,
Original Article Indian Journal of Genetics and Molecular Research 53 Volume 1 Number 2, July - December 2012 46,XY Female: SRY and AR Basis: Genotype & Phenotype Correlation Amudha S.*, MSc; Sayee Rajangam**,
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex
 Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female.
 Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female. Disorders of sex development (DSD); True hermaphrodite;
Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female. Disorders of sex development (DSD); True hermaphrodite;
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Controversies in the Management of Ambiguous Genitalia
 A4 Controversies in the Management of Ambiguous Genitalia Jorge J. Daaboul, MD Medical Director Florida Center for Pediatric Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Orlando, FL The speaker has signed a
A4 Controversies in the Management of Ambiguous Genitalia Jorge J. Daaboul, MD Medical Director Florida Center for Pediatric Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Orlando, FL The speaker has signed a
normally developed. Copenhagen, Denmark (Prof. dr. med. Dyre Trolle) By Krzysztof Boczkowski, John Philip
 Endocrine Department (Doc. dr. med. J. Teter) First Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medical Academy in Warsaw, Poland (Prof. dr. med. T. Bulski) and University Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Endocrine Department (Doc. dr. med. J. Teter) First Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medical Academy in Warsaw, Poland (Prof. dr. med. T. Bulski) and University Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
MANAGEMENT AND REPORT OF A CASE OF INTERSEX. By N. JOHN WILDE, D.D.S., M.D., JUAN J. TUR, M.D. and FRED W. BIEKER, M.D.
 MANAGEMENT AND REPORT OF A CASE OF INTERSEX By N. JOHN WILDE, D.D.S., M.D., JUAN J. TUR, M.D. and FRED W. BIEKER, M.D. Fresno, California, U.S.A. DURING man's embryological development, the analogues of
MANAGEMENT AND REPORT OF A CASE OF INTERSEX By N. JOHN WILDE, D.D.S., M.D., JUAN J. TUR, M.D. and FRED W. BIEKER, M.D. Fresno, California, U.S.A. DURING man's embryological development, the analogues of
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Class VIII Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence Science
 Question 1: What is the term used for secretions of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body? Hormones are chemical substances which are secreted by endocrine glands. They are
Question 1: What is the term used for secretions of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body? Hormones are chemical substances which are secreted by endocrine glands. They are
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10):
 Title46XX male; report of case OKUYAMA, Akihiko; KONDO, Nobuyuki; Author(s) NAKAMURA, Masahiro; SONODA, Takao; Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10): 1539-1542 Issue Date 1986-10 URL
Title46XX male; report of case OKUYAMA, Akihiko; KONDO, Nobuyuki; Author(s) NAKAMURA, Masahiro; SONODA, Takao; Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10): 1539-1542 Issue Date 1986-10 URL
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Management of gonads in DSD
 Management of gonads in DSD Martine Cools, paediatric endocrinologist, Katja Wolffenbuttel and Piet Hoebeke, paediatric urologists, all at University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Sten Drop, paediatric endocrinologist
Management of gonads in DSD Martine Cools, paediatric endocrinologist, Katja Wolffenbuttel and Piet Hoebeke, paediatric urologists, all at University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Sten Drop, paediatric endocrinologist
Professor, Prasad Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India. ABSTRACT. Online Access and Article Informtaion
 Original Research Article Disorders of Sexual Differentiation: A study on the Incidence and Types of Female Pseudo Hermaphrodites J.Radhika * 1, C.Bhuvaneswari 2, Arudyuti Chowdhury 3. *1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Disorders of Sexual Differentiation: A study on the Incidence and Types of Female Pseudo Hermaphrodites J.Radhika * 1, C.Bhuvaneswari 2, Arudyuti Chowdhury 3. *1 Associate Professor,
Goals. Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview. Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology
 Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Why Sex??? Advantages: It limits harmful mutations Asexual: all offspring get all mutations. Sexual: There is a random distribution of mutations.
 Reproduction Why sex??? Why Sex??? Asexual reproduction is quicker, easier, and produces more offspring per individual. Bacteria do it. Dandelions do it. Unisexual whiptail lizards do it. With sexual reproduction
Reproduction Why sex??? Why Sex??? Asexual reproduction is quicker, easier, and produces more offspring per individual. Bacteria do it. Dandelions do it. Unisexual whiptail lizards do it. With sexual reproduction
Maldescended testis in Adults. Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
-There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex. In women, the sex chromosomes are XX. In men, the sex chromosomes are XY.
 111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs
 Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
IB 140 Midterm #2 March 23 rd, 2007
 IB 140 Midterm #2 March 23 rd, 2007 Student Name Student ID Number 1. Which answer is false about X chromosomes? a. A Barr body is formed when one X chromosome in female diploid cell shuts down b. only
IB 140 Midterm #2 March 23 rd, 2007 Student Name Student ID Number 1. Which answer is false about X chromosomes? a. A Barr body is formed when one X chromosome in female diploid cell shuts down b. only
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery
 C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery Drop use of hermaphrodite and derivatives 1 in 15,000 live births Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Mixed Gonadal
C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery Drop use of hermaphrodite and derivatives 1 in 15,000 live births Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Mixed Gonadal
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Leydig cell hypofunction resulting in male pseudohermaphroditism*
 FERmlTY AND STERILlTY Copyright" 1982 The American Fertility Society Vol. 37, No.6, May 1982 Printed in U.S.A. Leydig cell hypofunction resulting in male pseudohermaphroditism* Peter A. Lee, M.D., Ph.D.t+1I
FERmlTY AND STERILlTY Copyright" 1982 The American Fertility Society Vol. 37, No.6, May 1982 Printed in U.S.A. Leydig cell hypofunction resulting in male pseudohermaphroditism* Peter A. Lee, M.D., Ph.D.t+1I
Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome in Three Generations of Indian Pedigree
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-015-0736-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome in Three Generations of Indian Pedigree Bibhas Kar 1 Subbiah Sivamani 1 Shankar Kundavi 2 Thankam Rama Varma 2 Received:
DOI 10.1007/s13224-015-0736-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome in Three Generations of Indian Pedigree Bibhas Kar 1 Subbiah Sivamani 1 Shankar Kundavi 2 Thankam Rama Varma 2 Received:
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Year Five. God loves me in my changing and development. 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5
 Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
DEVELOPMENT (DSD) 1 4 DISORDERS OF SEX
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections. David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017
 Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017 Primary Amenorrhea No menses by age 13-14 WITHOUT BREAST DEVELOPMENT No menses by age 15-16 WITH BREAST DEVELOPMENT
Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017 Primary Amenorrhea No menses by age 13-14 WITHOUT BREAST DEVELOPMENT No menses by age 15-16 WITH BREAST DEVELOPMENT
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Case Report Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome in Adults
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 158484, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/158484 Case Report Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Complete
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 158484, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/158484 Case Report Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Complete
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline. 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing Effects of Sex Hormones in Utero and Anomalies
 Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
Lecture 15 (Nov 16 th ): Hormones and Sexual Behavior Lecture Outline 1) Organs / Glands / Hormonal Communication 2) Sex Hormones: Male vs. Female 3) Genetic Gender (XX, XY) 4) Gender Phenotype : Organizing
Adolescent Menstrual Problem in a Form of Primary Amenorrhoea-A Challenge to Gynaecologist
 Advances in Biological Research 5 (5): 255-259, 2011 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2011 Adolescent Menstrual Problem in a Form of Primary Amenorrhoea-A Challenge to Gynaecologist 1 2 Sabyasachi Ray,
Advances in Biological Research 5 (5): 255-259, 2011 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2011 Adolescent Menstrual Problem in a Form of Primary Amenorrhoea-A Challenge to Gynaecologist 1 2 Sabyasachi Ray,
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5)
 IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
 Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
