Clinical Diagnosis. your PR.i.VATES.
|
|
|
- Vanessa Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 your PR.i.VATES Clinical Diagnosis What is an orchidectomy? What to expect after orchidectomy Results and Confirmed Diagnosis What is the lymphatic system?
2 CONTENTS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Contents Introduction 3 Methods of diagnosis 4 What are lymph nodes? 6 Surgery 7 After surgery 9 Tips 11 Male pelvic anatomy 12 Clinical staging 13 Types of testicular cancer 14 The TNM system 14 Stage 1 17 Stage 2 18 Stage 3 19 The MDT Process 20 Localised testicular cancer 21 Non localised testicular cancer 23 Tips 24
3 Diagnosis An ultrasound scan is extremely accurate at diagnosing testicular cancer and if a man is suspected of having it, a referral will be made to a hospital specialist called a urologist. If there is a strong suspicion that testicular cancer is present then a decision will be made to surgically remove the affected testicle. This decision will not be taken lightly but will be in a man s best interest. No one will want to wait around and see what happens; surgery to remove the testicle (orchidectomy) will usually be the only time that a definite cancer diagnosis can be verified or ruled out. A number of other tests are also likely to be carried out to identify any cancer that may have potentially spread beyond the testicle to other parts of the body. Please see below.
4 METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Methods of Diagnosis 1. Blood Tests Some testicular cancers produce chemicals, which are released into the bloodstream. These chemicals, called tumour markers, are alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (BHCG) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). They may be abnormal in the presence of particular types of testicular cancer. For instance AFP and HCG can be raised in the presence of a particular type of testicular cancer called non seminoma. They can also be used to measure the effect of treatment such as an orchidectomy, in reducing cancer activity and they may be repeated after orchidectomy at hours if they were abnormal beforehand. Blood tests to measure kidney and liver function will also usually be requested. Occasionally if the specific blood tests for testicular cancer are very raised or abnormal or there is obvious evidence that testicular cancer is present and has spread to other areas of the body, a referral may be made to an oncologist (cancer specialist) to see if treatment such as chemotherapy should be given before surgery (orchidectomy).
5 METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS 2. Chest X-ray This can identify any cancer which may have already spread to the lungs. 3. Pregnancy test A pregnancy test can identify BHCG, however this can also be present for other reasons which are not caused by testicular cancer. 4. Computerised Tomography (CT) Scan A CT scan is performed to check for any potential sign that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body; lungs or lymph glands in the abdomen (see below). The scan takes a series of x-rays, which are fed into a computer to build up a three-dimensional image of the inside of the body and takes from 10 to 30 minutes to perform. A special drink or an injection of a dye into a vein which helps show areas of the body more clearly will usually be given. This may cause a warm sensation for a few minutes. The scan is painless, but involves lying still for minutes.
6 WHAT ARE LYMPH NODES? CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS What are lymph nodes? The human body is covered by a special type of drainage system called the lymphatic system. This system is responsible for transporting excess fluid from the organs and tissues of the body in a fluid called lymph. Lymph fluid will contain various types of cells and substances that are no longer needed. The lymph fluid will be transported through the lymphatic drainage system and pass through small nodules or nodes that act as filters which are responsible for filtering out these unwanted substances. Cancerous cells which break off from the an organ which has cancer can also travel along this route and become trapped at the lymph nodes where they can then accumulate and infiltrate a different area of the body.
7 SURGERY CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Surgery (orchidectomy) Orchidectomy (unilateral) is the surgical removal of one testicle and is usually performed very quickly after a suspected diagnosis of testicular cancer. It is a simple procedure which may take about half an hour to perform and will usually be carried out as a day case procedure under general anaesthetic. During this surgery a small incision is made into the groin region on the affected side and the testicle is removed from above. The scrotum will not be cut. A prosthetic (artificial) testicle can be inserted in place of the cancerous testicle. Men may also be offered the possibility of sperm storage before surgery.
8 SURGERY CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Some possible problems may include: Falsey or not? The doctor may discuss the insertion of a false (prosthetic) ball to take the place of the old one. These are silicone implants that can be inflated with salt water. They come in various sizes and can make men feel whole again. They can give a very good cosmetic result and be of great psychological value but some men may experience problems with them in the longer term. Once inserted the neck of the scrotum is closed with stitches to prevent the prosthesis from moving back up to the groin. Men who are unsure of whether they want an implant or not can have the procedure performed at a later date if they wish. Scar tissue forming around the implant inside the scrotum. This can sometimes cause a thick fibrous growth of tissue which may in turn cause discomfort or give rise to worry that a second cancer has appeared. The overall cosmetic result may vary. Rupture of the implant can rarely occur due to vigorous activities such as contact sport, cycling or physical contact including sexual intercourse. Sometimes the implant may move out of its original position. Surgery can cause small spots of calcium in the testicle to appear usually some years following surgery. Although they are harmless they can sometimes be confused with the type of calcium deposits (microlithiasis), which may rarely cause testicular cancer. A prosthetic testicle will not react to temperature like a normal one and will stay the same size.
9 AFTER SURGERY CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS After surgery Dressing & Stitches Washing Clothing Pain Returning to Work There will be a dressing covering the incision site on the groin. This can usually be removed 24 hours after the operation. The stitches (sutures) in the wound will usually be dissolvable but may take some weeks to fully disappear. Men can have a bath or shower, normally after 24 hours, but it is important not to rub soap on the wound area. The wound should be dried by gently patting it with a clean towel/gauze pad. The groin and scrotal area can feel bruised and swollen after the operation. It is advisable to wear close fitting underwear, such as briefs or Y fronts or a scrotal support rather than boxer shorts. This will help the bruising settle. Painkillers which may have been prescribed should be taken on a regular basis, (not just when pain is felt) for the first 48 hours until comfortable. Always read the instructions to ensure they are administered correctly. Often simple paracetamol combined with an antiinflammatory medication (such as ibuprofen) are effective at reducing discomfort. Although this is a minor operation, it is important to take things easy for the first week. Men should be able to return to work within a few weeks. However if they are going to be reviewed in an outpatient clinic or referred to an oncologist for further treatment; it may be a good idea to await for these arrangements to be made before returning to work as further time off may be needed.
10 AFTER SURGERY CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Infection Physical Activity Sexual Activity Sexual performance Occasionally a collection of blood may form under the surgical wound (haematoma) or the wound may become infected. Men should seek medical advice if they think there may be infection. It is sometimes useful to phone the unit that performed the operation or contact a GP. It is important to avoid heavy lifting and or strenuous exercise for the first few weeks. Men should only start driving when they are able to do an emergency stop without hesitation. Sexual activity can begin again after two weeks as long as it is not uncomfortable. Having an orchidectomy should not affect a man s ability to have an erection, but the psychological stress associated with a potential diagnosis of cancer may affect performance. Men should be given a follow up appointment within a few weeks of orchidectomy to see a hospital specialist (oncologist) where the results of the operation will be discussed along with the need for any further recommended treatment. About 5% of men with testicular cancer may also have pre-cancerous or cancerous cells in the opposite testicle. If this is suspected a biopsy of the opposite (contralateral) testicle may be taken at the same time as the orchidectomy.
11 Tips Key workers & professionals Men who are diagnosed or suspected of having testicular cancer will usually be given the details of a urology specialist nurse or Key worker who will act as their point of contact during and after treatment and who can provide them with relevant information and advice. They will usually also have access to other medical professionals who may be involved in a man s care and may be able to liaise with them if there are any problems. Sick certificates Although the hospital where a man has been treated can issue you a sick certificate to cover stay in hospital they will not be able to provide a long term sick certificate. This will need to be obtained from a G.P. Timeframes Once a diagnosis of testicular cancer is suspected things will begin to move very quickly; surgery will be booked and scans arranged usually within a twoweek period. Men should try and plan ahead and involve all of their family so that they can help with any arrangements that need to be made while having treatment (childcare, work etc.). Time off work Men will need to take time off work during and after treatment. It is advisable to keep any correspondence/ letters and contact details of the health professionals involved or procedures performed as proof of treatment in case an employer wants evidence. It may also be a good idea to talk to a human resources department if available and inform them of the situation.
12 CLINICAL STAGING CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Spine Lymph nodes Bladder Pubic bone Seminal vesicle Prostate Urethra Rectum Penis Vas deferens Epididymis Scrotum Male pelvic anatomy
13 CLINICAL STAGING CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Clinical Staging Seminoma The most common type of testicular cancer is called a seminoma, a slow progressing type of cancer that does not usually spread to other areas of the body. This type of cancer is more common in men between the ages of 25-55, with a peak age of 35 years old. A rarer type of testicular cancer is called a nonseminomatous germ cell tumour (NSGCT). It used to be called a teratoma. This tends to affect men between the ages of 15-35, with a peak age of 25 years old. Non-Seminoma Both of these tumours are also known as germ cell tumours. About 95% of testicular cancers will be germ cell cancers. Germ in this term means seed and refers to the sperm making process. Other tumours (mixed cell tumours) may contain elements of both types of the above. Other rarer, non-germ cell tumours (Sertoli, Leydig) account for only a small percentage of testicular cancers. In addition 4% of men with lymphoma, usually over the age of 50 years may also have similar symptoms to testicular cancer with testicular swelling.
14 TYPES OF TESTICULAR CANCER CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Types of Testicular Cancer Lymphoma 5% Germ Cell 95% Rare <1% Seminoma 45% Mixed 15% Non-Seminoma 5% The type of testicular cancer that is present will be diagnosed when the results of the removed testicle have been analysed in the laboratory. This analysis will be able to differentiate between the various types of testicular cancer and in combination with the blood tests and scans that have been performed, can be used to give an accurate picture of the extent of testicular cancer. This is known as a clinical stage and can be described using a medical method of categorising the extent of cancer called the TNM system, where: T stands for tumour size (given a value of 1-4 indicating how big it is. N stands for affected (positive) lymph nodes. M stands for metastases
15 THE TNM SYSTEM CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS The TNM System T stands for tumour size (given a value of 1-4 indicating how big it is. TIS T1 T2 T3 T4 (testicular carcinoma insitu). Cancer cells are within the testes but they have not invaded the surrounding testicular tissue Tumour confined to testicle and epididymis Tumour has begun to infiltrate the blood vessels or lymph nodes close to the testicle Tumour has grown as far as the spermatic cord and possibly blood vessels and lymph nodes Tumour has invaded the scrotum. T 1 T 2 Scrotal wall Cancer Testis Tunica vaginals T3 T4
16 THE TNM SYSTEM CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS N stands for affected (positive) lymph nodes. N0 N1 N2 N3 Lymph nodes do not contain cancer cells Lymph nodes are smaller than 2cm wide At least one lymph node is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm wide At least one affected lymph node is bigger than 5cm M stands for metastases Metastases are deposits of cancer which form as a result of the primary cancer travelling to other organs in the body or bones. They are sometimes referred to as secondaries.testicular cancer which has spread from its primary site in this way tends to be deposited in the lungs, liver or brain. M0 M1a M1b There is no evidence that the cancer has spread to other organs The cancer has spread to the lungs or distant lymph nodes furthest away from the testicle. Organs such as the liver or brain have been affected. A further way of categorising testicular cancer is to split it into 3 stages (see below). The results of tumour markers can also be added to either of these systems to predict possible treatment success. This is denoted as S where S stands for Serum markers. S0 Tumour marker levels within normal limits S1 LDH < 1.5 X Normal and HCG < 5,000 and AFP < 1,000 S2 LDH X Normal or HCG 5,000-50,000 or AFP 1,000-10,000 S3 LDH > 10 X Normal or HCG > 50,000 or AFP > 10,000
17 STAGE 1 CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS T 1-4 N 0 M 0 Stage 1 This is the earliest stage of testicular cancer The cancer is contained within the testicle and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs
18 STAGE 2 CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS T 1-4 N 1-3 M 0 Stage 2 The cancer cells have spread into nearby lymph nodes in the abdomen or pelvis. This is further split into sub stages 2A, 2B and 2C. Stage 2A - lymph nodes are all smaller than 2cm Stage 2B - lymph nodes are between 2cm and 5cm Stage 2C - at least one lymph node is bigger than 5cm
19 STAGE 3 CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS T 1-4 N 1-3 M 1 Stage 3 This can be split into 3A, 3B and 3C. Stage 3A - cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or lungs Stage 3B - cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant lymph nodes and lungs and there is a moderately high marker level Stage 3C - can be the same as stage 3B but you have a very high marker level or your cancer has spread to another body organ, such as the liver or brain
20 THE MDT PROCESS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS The MDT Process An MDT will consist of a group of medical experts including urologists, oncologists, radiologists (X-ray specialists) and other healthcare professionals. When the results of the orchidectomy (type of cancer present), blood tests and scans are known they will be reviewed at a Multi Disciplinary Team Meeting (MDT). The MDT team will then come up with a consensus opinion as to what if any, further treatment is needed. This will then be explained to men when they attend a follow up clinic appointment. Any decision made by this team will reflect their experience in dealing with similar cases to and will be based on the latest medical research and techniques. The recommendation or outcome of the meeting will be in a man s best interest. Some hospitals will have nurses who specialise in testicular cancer (germ cell tumour nurse specialists) who will be able to guide men through their treatment or answer any specific questions they may have. They may also know of local support groups for men with testicular cancer which men may find helpful.
21 LOCALISED TESTICULAR CANCER CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Localised testicular cancer Early stage seminoma or non-seminoma which is confined to the testicle with no evidence of spread outside of it can usually be treated with a policy of surveillance. This means regular CT scans and blood tests will be performed to detect any recurrence. Should testicular cancer reoccur then chemotherapy will be given and the chances are that a man will be cured. However some men may find that they want to get on with their lives and not keep returning for scans as frequently as surveillance requires. In this situation a limited dose of chemotherapy can be given after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer returning. Chemotherapy is the use of anticancer (cytotoxic) drugs to destroy cancer cells. It works by disrupting the growth of cancer cells as they circulate in the blood. If men opt for up front chemotherapy it will usually be a one off dose which may take around 1-2 hours to administer. Men may feel tired and suffer some minor side effects for a few weeks after.
22 Traditionally radiotherapy has been used to treat the lymph nodes at the back of the abdomen which may still harbour some testicular cancer for seminoma. This treatment will usually involve around 21 days of treatment every day, 5 days a week for around 10 minutes a day. Again the oncologist will discuss this treatment. It is not used for nonseminoma. Some studies have indicated that radiotherapy may increase the chance of a second cancer occurring many years after treatment. Both chemotherapy and radiotherapy (for seminoma) are as successful as each other in curing early testicular cancer. After having treatment for testicular cancer, men will be reviewed on a regular basis with visits to clinic every 6-8 weeks. These visits will gradually become less but men will still need to be monitored for around 10 years. Most testicular cancer that reoccurs does so within 2 years of treatment. Only 5% reoccur after this. Men will of course need to regularly perform testicular self-examination of their remaining testicle.
23 NON-LOCALISED TESTICULAR CANCER CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS Non Localised testicular cancer Testicular cancer tends to spread to the lymph nodes in the abdomen and to other areas of the body such as the lungs. Other more serious organs, to which the cancer can spread, include the liver and brain. If there is evidence of testicular cancer which has spread to these or other areas then a course of chemotherapy treatment will be recommended. (See Chemotherapy Information Sheet). Testicular cancer that has spread to the lungs liver or brain is still testicular cancer and not a separate cancer. Recent research has shown that 96% of men diagnosed with testicular cancer at any stage will be alive 10 years after treatment.
24 Recovery Tips Men may feel tired or exhausted following treatment for testicular cancer and should take this into account when considering going back to work or a busy lifestyle. Family & Friends It may also take family and friends time to adjust to long term changes in a man s health so do not be surprised if they are acting a bit strange or distant. Having children Although there is no definite evidence that radiotherapy or chemotherapy can affect children that are fathered after treatment it is usually advisable for you to use contraception for 6-12 months afterwards.
25
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Radical Orchidectomy. Department of Urology. Patient Information
 Radical Orchidectomy Department of Urology 2 Patient Information This leaflet answers some of the questions people ask about a radical orchidectomy operation. If any further questions are raised after
Radical Orchidectomy Department of Urology 2 Patient Information This leaflet answers some of the questions people ask about a radical orchidectomy operation. If any further questions are raised after
Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained
 The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre Pan Glasgow Urology / Oncology Patient Information Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre 1053 Great Western Road, Glasgow
The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre Pan Glasgow Urology / Oncology Patient Information Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre 1053 Great Western Road, Glasgow
Suspected testicular cancer
 Suspected testicular cancer Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Your consultant has informed you that you may have testicular cancer. This leaflet gives the facts about your condition
Suspected testicular cancer Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Your consultant has informed you that you may have testicular cancer. This leaflet gives the facts about your condition
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
The testicle is made up of groups of specialised cells and has two main functions: to produce sperm to produce the male hormone, testosterone.
 Radical Orchidectomy This leaflet answers questions many people ask about a radical orchidectomy operation. If any further questions are raised from reading this information, please speak to a member of
Radical Orchidectomy This leaflet answers questions many people ask about a radical orchidectomy operation. If any further questions are raised from reading this information, please speak to a member of
Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND)
 Acute Services Division Information for patients about Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Introduction This booklet gives you information about surgery to remove the residual lymph nodes at the
Acute Services Division Information for patients about Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Introduction This booklet gives you information about surgery to remove the residual lymph nodes at the
Having a vasectomy Urology department
 Having a vasectomy Urology department 01935 384 345 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Vasectomy is the permanent method of contraception for men. It is safe, simple and effective. What is vasectomy? Vasectomy is a
Having a vasectomy Urology department 01935 384 345 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Vasectomy is the permanent method of contraception for men. It is safe, simple and effective. What is vasectomy? Vasectomy is a
What you need to know about having a vasectomy
 University Teaching Trust What you need to know about having a vasectomy Urology Hope Building 0161 206 5380 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. What is a vasectomy? A vasectomy is
University Teaching Trust What you need to know about having a vasectomy Urology Hope Building 0161 206 5380 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. What is a vasectomy? A vasectomy is
Treatment for testicular cancer Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support Treatment for testicular cancer Contents Sperm banking Surgery Surveillance policy Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Information reviewed by In almost all cases an orchidectomy
13 11 20 Information and support Treatment for testicular cancer Contents Sperm banking Surgery Surveillance policy Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Information reviewed by In almost all cases an orchidectomy
Removal of Epididymal Cyst Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Removal of Epididymal Cyst Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is an Epididymal Cyst? Epididymal cysts or as they are sometimes known spermatocele are cysts of the head of the epididymis that
Removal of Epididymal Cyst Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is an Epididymal Cyst? Epididymal cysts or as they are sometimes known spermatocele are cysts of the head of the epididymis that
Mr Sanjeev Sarin MS FRCS. Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet
 Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet The aim of this information sheet is to ensure that you understand the nature of the treatment you wish to undertake. Please read it carefully and discuss any
Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet The aim of this information sheet is to ensure that you understand the nature of the treatment you wish to undertake. Please read it carefully and discuss any
Cardiff MRCS OSCE Courses Testicular Cancer
 Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
NO-SCALPEL VASECTOMY
 Dr William Lynch MRCGP MICGP Vasectomist & GP Surgeon FREEPHONE 1800 313 595 NO-SCALPEL VASECTOMY An affordable and permanent method of family planning for men. Advantages: Less Discomfort One small opening
Dr William Lynch MRCGP MICGP Vasectomist & GP Surgeon FREEPHONE 1800 313 595 NO-SCALPEL VASECTOMY An affordable and permanent method of family planning for men. Advantages: Less Discomfort One small opening
Radiotherapy to the pelvis. (bladder, prostate, rectum)
 Radiotherapy to the pelvis (bladder, prostate, rectum) General advice Everyone having radiotherapy is different. Your treatment is specific to you and so is the way you react to treatment. If you are worried
Radiotherapy to the pelvis (bladder, prostate, rectum) General advice Everyone having radiotherapy is different. Your treatment is specific to you and so is the way you react to treatment. If you are worried
 Although rare compared to other cancers, testicular cancer most commonly affects young men between the ages of 15 and 45. Over 2,400 cases of testicular cancer will be diagnosed each year. The information
Although rare compared to other cancers, testicular cancer most commonly affects young men between the ages of 15 and 45. Over 2,400 cases of testicular cancer will be diagnosed each year. The information
Testicular Cancer. What is testicular cancer? What are the symptoms? Patient Information. Risk factors for testicular cancer.
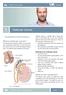 Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
Information for Patients. Testicular Cancer. English
 Information for Patients Testicular Cancer English Table of contents What is testicular cancer?... 3 What are the symptoms?... 3 How is testicular cancer diagnosed?... 3 What is staging?... 4 Stages of
Information for Patients Testicular Cancer English Table of contents What is testicular cancer?... 3 What are the symptoms?... 3 How is testicular cancer diagnosed?... 3 What is staging?... 4 Stages of
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation
 Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation This fact sheet aims to provide information about why and when a testicular biopsy or aspiration might be offered, what it involves and
Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation This fact sheet aims to provide information about why and when a testicular biopsy or aspiration might be offered, what it involves and
Use of fiducial markers in the treatment of prostate cancer with radiotherapy
 in the treatment of prostate cancer with radiotherapy Information for patients This leaflet explains: Introduction... 2 The prostate and fiducial markers... 2 When and how the markers are used... 2 Medication
in the treatment of prostate cancer with radiotherapy Information for patients This leaflet explains: Introduction... 2 The prostate and fiducial markers... 2 When and how the markers are used... 2 Medication
About your Hernia Operation
 Patient Information About your Hernia Operation Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you should
Patient Information About your Hernia Operation Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you should
Surgery. In this fact sheet. Surgery: English
 Surgery: English Surgery This information is about surgery (having an operation). Any words that are underlined are explained in the glossary at the end. Many people with cancer will have surgery as part
Surgery: English Surgery This information is about surgery (having an operation). Any words that are underlined are explained in the glossary at the end. Many people with cancer will have surgery as part
Hernia surgery in adults
 Page 1 of 9 Hernia surgery in adults Introduction This leaflet will give you information about having hernia surgery. It also answers some of the commonly asked questions and outlines some of the risks
Page 1 of 9 Hernia surgery in adults Introduction This leaflet will give you information about having hernia surgery. It also answers some of the commonly asked questions and outlines some of the risks
What is a hydrocele? It is a swelling caused by a build-up of fluid in the fluid sac surrounding the testicle. It is very common.
 Repair of hydrocele Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been recommended to have a procedure to repair a hydrocele. It gives information on what
Repair of hydrocele Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been recommended to have a procedure to repair a hydrocele. It gives information on what
Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS)
 Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS) What is the prostate gland? The prostate is a small gland the size of a walnut. It is found at the base of the bladder and surrounds the urethra (water pipe).
Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS) What is the prostate gland? The prostate is a small gland the size of a walnut. It is found at the base of the bladder and surrounds the urethra (water pipe).
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Wide Local Excision. Gynae-oncology
 Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Wide Local Excision Gynae-oncology We put our patients first by working as one team; leading and listening, and striving for the best. Together, we make the difference. Patient
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Wide Local Excision Gynae-oncology We put our patients first by working as one team; leading and listening, and striving for the best. Together, we make the difference. Patient
Department of Surgery. Glansectomy Surgery for cancer of the penis
 Department of Surgery Glansectomy Surgery for cancer of the penis This information is for men who need surgery to remove the end of the penis (glansectomy) because of cancer of the penis. What is a glansectomy?
Department of Surgery Glansectomy Surgery for cancer of the penis This information is for men who need surgery to remove the end of the penis (glansectomy) because of cancer of the penis. What is a glansectomy?
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
 Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Every year in the UK over 50,000 men will be diagnosed with a male-specific cancer: prostate, testicular or penile.
 Every year in the UK over 50,000 men will be diagnosed with a male-specific cancer: prostate, testicular or penile. This leaflet offers information on the three cancers from signs and symptoms, risk factors
Every year in the UK over 50,000 men will be diagnosed with a male-specific cancer: prostate, testicular or penile. This leaflet offers information on the three cancers from signs and symptoms, risk factors
Male Cancer. Awareness, diagnosis and treatment. Revised 4th Edition
 Male Cancer Awareness, diagnosis and treatment Revised 4th Edition 2 Every year in the UK over 50,000 men will be diagnosed with a male-specific cancer: prostate, testicular or penile. This leaflet offers
Male Cancer Awareness, diagnosis and treatment Revised 4th Edition 2 Every year in the UK over 50,000 men will be diagnosed with a male-specific cancer: prostate, testicular or penile. This leaflet offers
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Testicular Cancer
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Testicular Cancer Information for patients This leaflet aims to help you have a better understanding of your diagnosis of testicular cancer. There are two main
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Testicular Cancer Information for patients This leaflet aims to help you have a better understanding of your diagnosis of testicular cancer. There are two main
What does the procedure involve? What are the alternatives to this procedure? What should I expect before the procedure?...
 This leaflet explains: What does the procedure involve?... 2 What are the alternatives to this procedure?... 2 What should I expect before the procedure?... 2 What happens during the procedure?... 2 What
This leaflet explains: What does the procedure involve?... 2 What are the alternatives to this procedure?... 2 What should I expect before the procedure?... 2 What happens during the procedure?... 2 What
Having a Testicular (Varicocele) Embolisation
 Having a Testicular (Varicocele) Embolisation Information for patients What is a Varicocele? What is a Varicocele? A varicocele is an abnormality of the veins that take blood away from the testicle. A
Having a Testicular (Varicocele) Embolisation Information for patients What is a Varicocele? What is a Varicocele? A varicocele is an abnormality of the veins that take blood away from the testicle. A
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram
 Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
Your guide to Wide Local Excision
 Your guide to Wide Local Excision This leaflet has been produced to provide you with information about your breast surgery and aims to answer any questions that you might have. If you have any further
Your guide to Wide Local Excision This leaflet has been produced to provide you with information about your breast surgery and aims to answer any questions that you might have. If you have any further
INFORMATION ON MALE STERILISATION. Vasectomy
 INFORMATION ON MALE STERILISATION Vasectomy Please read this leaflet before your operation. Keep it in a safe place, as you may need the information later. Solent Vasectomy Service Sexual Health Service
INFORMATION ON MALE STERILISATION Vasectomy Please read this leaflet before your operation. Keep it in a safe place, as you may need the information later. Solent Vasectomy Service Sexual Health Service
What are Varicoceles?
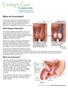 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
Testicular Malignancies /8/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Repair of Hydrocele. Patient Information. Day Surgery. Ward 3, Leigh Infirmary
 Repair of Hydrocele Patient Information Day Surgery Ward 3, Leigh Infirmary Author ID: LS Leaflet Number: SW3.002 Version: 5 Name of Leaflet: Repair of Hydrocele Date Produced: August 2017 Review Date:
Repair of Hydrocele Patient Information Day Surgery Ward 3, Leigh Infirmary Author ID: LS Leaflet Number: SW3.002 Version: 5 Name of Leaflet: Repair of Hydrocele Date Produced: August 2017 Review Date:
Varicoceles can cause various problems, including subfertility.
 This leaflet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you or those who care for you may have about percutaneous abscess drainage. It is not meant to replace the consultation between you and
This leaflet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you or those who care for you may have about percutaneous abscess drainage. It is not meant to replace the consultation between you and
Sentinel lymph node biopsy and wide local excision
 How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
Groin dissection. Information for patients This leaflet describes the removal of lymph nodes in the groin
 How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Laparoscopy Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who are having a procedure called a laparoscopy. It explains what the operation involves, why it is
Laparoscopy Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who are having a procedure called a laparoscopy. It explains what the operation involves, why it is
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP)
 Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
REVERSAL OF VASECTOMY INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
 The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk INFORMATION
The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk INFORMATION
Thoracic outlet syndrome and cervical or first rib removal. Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute
 Thoracic outlet syndrome and cervical or first rib removal Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute page 2 of 12 You have been diagnosed with having thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). This information
Thoracic outlet syndrome and cervical or first rib removal Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute page 2 of 12 You have been diagnosed with having thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). This information
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
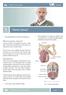 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Treatment Centre Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy What is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy? You need this operation because stones have collected in your gallbladder (the area where a small amount of bile is
Treatment Centre Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy What is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy? You need this operation because stones have collected in your gallbladder (the area where a small amount of bile is
B02 Mastectomy. Expires end of November Write questions or notes here:
 Practice Locations: St John of God Consulting Suites, 117 Anstruther Road, Mandurah Suite 50, Murdoch Medical Centre, 100 Murdoch Drive, Murdoch Tel: 08 6333 2800 Web: saudhamza.com.au B02 Mastectomy Expires
Practice Locations: St John of God Consulting Suites, 117 Anstruther Road, Mandurah Suite 50, Murdoch Medical Centre, 100 Murdoch Drive, Murdoch Tel: 08 6333 2800 Web: saudhamza.com.au B02 Mastectomy Expires
Having a Hydrocele Repair (adult)
 Having a Hydrocele Repair (adult) Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Department of Urology The York Hospital, Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel: 01904
Having a Hydrocele Repair (adult) Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Department of Urology The York Hospital, Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel: 01904
Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour
 Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour Department of Urology 2 Patient Information Contents Where is the bladder and what does it do? 3 What is non invasive cancer of the bladder? 4 How is bladder
Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour Department of Urology 2 Patient Information Contents Where is the bladder and what does it do? 3 What is non invasive cancer of the bladder? 4 How is bladder
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients
 Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients i What is a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND)? You have probably already undergone surgery and treatment
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients i What is a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND)? You have probably already undergone surgery and treatment
Hernia Operations. What is a hernia? What does the operation involve? What are the benefits of an operation?
 Hernia Operations Hernia Operations What is a hernia? The abdomen (the medical word for the tummy) contains many organs such as the liver spleen and intestines (the medical word for insides ) and these
Hernia Operations Hernia Operations What is a hernia? The abdomen (the medical word for the tummy) contains many organs such as the liver spleen and intestines (the medical word for insides ) and these
Patient Information. Prostate Tissue Ablation. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for
 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
NUPAS HAVING A VASECTOMY. T: T: (01) (Eire) Your guide to advice & information for vasectomy
 NUPAS national unplanned pregnancy advisory service HAVING A VASECTOMY Your guide to advice & information for vasectomy T: 0333 004 6666 T: (01) 874 0097 (Eire) 2-3 HAVING A VASECTOMY AFTERCARE HELPLINE
NUPAS national unplanned pregnancy advisory service HAVING A VASECTOMY Your guide to advice & information for vasectomy T: 0333 004 6666 T: (01) 874 0097 (Eire) 2-3 HAVING A VASECTOMY AFTERCARE HELPLINE
Mastectomy. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Mastectomy Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in this brochure
Mastectomy Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in this brochure
Providing patients with RAPID care (rapid access prostate Imaging and diagnostics) Urology
 Providing patients with RAPID care (rapid access prostate Imaging and diagnostics) Urology Providing patients with RAPID prostate diagnostic care We have launched a new initiative to make sure patients
Providing patients with RAPID care (rapid access prostate Imaging and diagnostics) Urology Providing patients with RAPID prostate diagnostic care We have launched a new initiative to make sure patients
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Imaging-assisted wide local excision Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to
Procedure Information Guide Imaging-assisted wide local excision Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to
Health Bites Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer. Normal breast
 Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Arch Angiography. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet has been prepared to tell you about arch angiography. It will explain what will happen during this procedure and we hope that it will answer some
Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet has been prepared to tell you about arch angiography. It will explain what will happen during this procedure and we hope that it will answer some
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer www.nscancercare.ca Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer www.nscancercare.ca Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Radiotherapy to your breast or chest wall
 Radiotherapy to your breast or chest wall The name of your consultant is: The radiographer who explained the treatment to you is: You can contact us on: What is radiotherapy? Radiotherapy treats cancer
Radiotherapy to your breast or chest wall The name of your consultant is: The radiographer who explained the treatment to you is: You can contact us on: What is radiotherapy? Radiotherapy treats cancer
Pre Vasectomy Consultation
 Pre Vasectomy Consultation Patient: Private/ GMS Date: D.o.B Tel. Occupation: GP: Number of children: Age of youngest child: General Health: Bleeding disorders: Medication: Allergies: Local Anaesthetics:
Pre Vasectomy Consultation Patient: Private/ GMS Date: D.o.B Tel. Occupation: GP: Number of children: Age of youngest child: General Health: Bleeding disorders: Medication: Allergies: Local Anaesthetics:
Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction The prostate is a small gland, which is found only in men. It is found at the base of the
Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction The prostate is a small gland, which is found only in men. It is found at the base of the
Information on Vasectomy Northwest Urological Clinic
 Information on Vasectomy Northwest Urological Clinic This handout is meant to give you information on the procedure of vasectomy, how to prepare for a vasectomy, what to expect during the vasectomy, what
Information on Vasectomy Northwest Urological Clinic This handout is meant to give you information on the procedure of vasectomy, how to prepare for a vasectomy, what to expect during the vasectomy, what
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma
 Squamous cell carcinoma Skin Oncology Team Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. It tells you what
Squamous cell carcinoma Skin Oncology Team Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. It tells you what
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Radiotherapy to the prostate
 Radiotherapy to the prostate Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 2 Preparation for planning and treatment... 2 Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) Service...
Radiotherapy to the prostate Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 2 Preparation for planning and treatment... 2 Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) Service...
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
Department of surgery
 Department of surgery Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) This information describes the operation to remove the residual lymph nodes at the back of the abdomen as part of your treatment for
Department of surgery Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) This information describes the operation to remove the residual lymph nodes at the back of the abdomen as part of your treatment for
Hernia Surgery in Adults
 Page 1 of 7 Hernia Surgery in Adults Introduction This leaflet provides information on hernias in the adult patient and the treatment options available. This leaflet is intended as a guide and is not a
Page 1 of 7 Hernia Surgery in Adults Introduction This leaflet provides information on hernias in the adult patient and the treatment options available. This leaflet is intended as a guide and is not a
ARTERIAL BYPASS GRAFTS IN THE LEG
 The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
Colposuspension operation
 Colposuspension operation This information explains: Overview... 1 Your admission date... 1 The operation... 2 The anaesthetic... 2 After the operation... 3 Problems... 3 Going home... 4 Getting back to
Colposuspension operation This information explains: Overview... 1 Your admission date... 1 The operation... 2 The anaesthetic... 2 After the operation... 3 Problems... 3 Going home... 4 Getting back to
Varicose Vein Surgery. Varicose Vein Surgery
 What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at
 GS12 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from:
GS12 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from:
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Uterine sarcoma. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy
 Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Having a nephrostomy tube inserted
 Having a nephrostomy tube inserted Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been advised to have a nephrostomy tube inserted. It includes information
Having a nephrostomy tube inserted Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been advised to have a nephrostomy tube inserted. It includes information
Nephrostomy Tube Urology Patient information Leaflet
 Nephrostomy Tube Urology Patient information Leaflet Page 1 Why do I need this procedure? Because there is a blockage that is preventing urine draining from the kidney down the tube (ureter) into the bladder.
Nephrostomy Tube Urology Patient information Leaflet Page 1 Why do I need this procedure? Because there is a blockage that is preventing urine draining from the kidney down the tube (ureter) into the bladder.
If you have any further questions, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you.
 Having a laparoscopy This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a laparoscopy. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to hospital. If
Having a laparoscopy This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a laparoscopy. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to hospital. If
1 Prostate artery embolisation
 1 Prostate artery embolisation The following information about prostate artery embolisation (PAE) explains what is involved and the possible risks. It is not meant to be a substitute for informed discussion
1 Prostate artery embolisation The following information about prostate artery embolisation (PAE) explains what is involved and the possible risks. It is not meant to be a substitute for informed discussion
Scans in Neurofibromatosis
 Scans in Neurofibromatosis A scan creates an image or picture of internal organs of the body such as bone or soft tissue. Scans are used by doctors to help to identify the cause of your symptoms. Your
Scans in Neurofibromatosis A scan creates an image or picture of internal organs of the body such as bone or soft tissue. Scans are used by doctors to help to identify the cause of your symptoms. Your
STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE
 LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE HAVING A VASECTOMY A PATIENTS GUIDE TO HAVING A VASECTOMY AT LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE BARRACK ST. LOUGHREA CO. GALWAY PHONE/FAX: 091-841509 E-MAIL:lakeshoremedicalcentre@hotmail.com
LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE HAVING A VASECTOMY A PATIENTS GUIDE TO HAVING A VASECTOMY AT LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE LAKESHORE MEDICAL CENTRE BARRACK ST. LOUGHREA CO. GALWAY PHONE/FAX: 091-841509 E-MAIL:lakeshoremedicalcentre@hotmail.com
PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE)
 PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TEP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TEP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TEP) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
ADVICE TO PATIENTS REQUESTING PSA MEASUREMENT FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS
 The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
How Long To Heal After Vasectomy Reversal Can You Have Intercourse
 How Long To Heal After Vasectomy Reversal Can You Have Intercourse The recovery after vasectomy reversal is very important. If you can have help for a week, so that other person can do all the lifting,
How Long To Heal After Vasectomy Reversal Can You Have Intercourse The recovery after vasectomy reversal is very important. If you can have help for a week, so that other person can do all the lifting,
Transperineal Biopsy of the Prostate
 Transperineal Biopsy of the Prostate Department of Urology Patient Information What What is a is Prostate? a Prostate? The Prostate is an organ forming part of the male reproductive system. It is located
Transperineal Biopsy of the Prostate Department of Urology Patient Information What What is a is Prostate? a Prostate? The Prostate is an organ forming part of the male reproductive system. It is located
Instructions for Patients After:
 Form: D-5025 Instructions for Patients After: Hydrocelectomy Spermatocelectomy Epididyectomy Testicular biopsy Orchidectomy Varicocelectomy Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of yourself
Form: D-5025 Instructions for Patients After: Hydrocelectomy Spermatocelectomy Epididyectomy Testicular biopsy Orchidectomy Varicocelectomy Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of yourself
When should I ask my doctor about my fertility?
 Preserving Fertility for Men with Cancer Some cancers and their treatments can affect a man s ability to father a child (his fertility). These changes can last for a short time, or may be permanent. This
Preserving Fertility for Men with Cancer Some cancers and their treatments can affect a man s ability to father a child (his fertility). These changes can last for a short time, or may be permanent. This
No-Scalpel Vasectomy. Vasectomy
 No-Scalpel Vasectomy Vasectomy Once a man or a couple decides to not have more children, they usually consider permanent contraception. Vasectomy is a safe and very effective form of permanent birth control
No-Scalpel Vasectomy Vasectomy Once a man or a couple decides to not have more children, they usually consider permanent contraception. Vasectomy is a safe and very effective form of permanent birth control
Parent/Carer Information Leaflet
 Hydrocele repair Children s Ward Parent/Carer Information Leaflet Introduction Your doctor has recommended that your son has a hydrocele repair. This leaflet is for parents who are considering this operation
Hydrocele repair Children s Ward Parent/Carer Information Leaflet Introduction Your doctor has recommended that your son has a hydrocele repair. This leaflet is for parents who are considering this operation
