Degree of twisting and duration of symptoms are prognostic factors of testis salvage during episodes of testicular torsion
|
|
|
- Geraldine Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Degree of twisting and duration of symptoms are prognostic factors of testis salvage during episodes of testicular torsion Adam S. Howe 1,2, Vinaya Vasudevan 2, Michael Kongnyuy 1, Kevin Rychik 1, Lisa A. Thomas 3, Maria Matuskova 4, Steven C. Friedman 2, Jordan S. Gitlin 1,2, Edward F. Reda 1,2, Lane S. Palmer 1,2 1 Department of Urology, Winthrop University Hospital, Mineola, NY, USA; 2 Division of Pediatric Urology, 3 Department of Pediatrics, Cohen Children s Medical Center of NY, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, New Hyde Park, NY, USA; 4 Department of Mathematics, Engineering, and Computer Science, LaGuardia Community College, Long Island City, NY, USA Contributions: (I) Conception and design: AS Howe, LS Palmer, JS Gitlin; (II) Administrative support: None; (III) Provision of study material or patients: None; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: AH Howe, K Rychik, SC Friedman, EF Reda, JS Gitlin, LS Palmer; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: V Vasudevan, M Kongnyuy, M Matuskova, LS Palmer; (VI): Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Adam S. Howe, MD. 488 Broadway, Apt. #515, Albany, NY 12207, USA. adamo.howe@gmail.com. Background: Testicular torsion is surgical emergency. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of testicular torsion is essential for testicular viability. At surgical exploration, the spermatic cord is seen twisted a variable number of times around its longitudinal axis. There is scant data regarding the degree of twisting and its association with testis outcomes. The purpose of our study is to explore how the degree of torsion factors into testicular outcome using follow-up data. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the records of adolescent males who presented with testicular torsion to our institution, looking at duration of pain symptoms, degree of torsion documented in the operative note, procedure performed (orchiopexy versus orchiectomy), and follow-up clinic data for whether testicular atrophy after orchiopexy was present. A non-salvageable testis was defined as orchiectomy or atrophy. Receiver operator characteristics (ROC), multivariate, and logistic regression analyses were performed to determine the probability of a non-salvageable torsed testis based on time and degree of twisting. Results: Eighty-one patients met our study criteria, with 55 testes deemed viable and 26 non-salvageable. We found a 25.7% atrophy rate after orchiopexy. Cut-off values of 8.5 h and 495 degrees of torsion would provide sensitivities of 73% and 53%, respectively, with specificity of 80% for both. Only duration and age were correlated with the risk of non-salvage on multivariate analysis. Logistic regression generated linear probability formulas of 4 + (3 hours) and 7 + (0.05 degrees) in calculating the probability of non-salvage with strong correlation. Conclusions: We were able to derive separate formulas to determine the viability of the torsed testis based on symptom duration and degrees of twisting. Fifteen h of symptoms and 860 degrees of torsion gives testes a 50% salvage rate. Interestingly, we also found that about 1 out of every 4 testes undergoes atrophy after orchiopexy. Keywords: Testicular torsion; twist; degrees; pediatrics; statistics Submitted Sep 02, Accepted for publication Sep 14, doi: /tau View this article at:
2 1160 Howe et al. Time and twist degree in testis torsion Introduction Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency affecting 1 in 4,000 boys below the age of 25, and accounting for up to 25% of acute scrotal disease in pediatrics (1). Although testicular torsion can occur at any age, it is most commonly seen in the adolescent population. Testicular torsion is defined as a twisting of the spermatic cord along a longitudinal axis, with resultant ischemia due to compromised blood flow to the testicle. Clinically, testicular torsion presents with an acute onset of scrotal pain, followed by scrotal swelling, nausea and vomiting. A high-riding testis in a transverse lie is often found on physical examination. These findings, in association with an absent cremasteric reflex, are highly suggestive of testicular torsion. The goal in managing testicular torsion is organ salvage. In order to maximize the chances of testicular survival, prompt diagnosis and treatment of testicular torsion is essential. Parameters associated with testis viability include duration of symptoms and the sonographic echotexture of the testis. Non-surgical management by way of manual detorsion can be attempted, however, its success rate is not known. Manual detorsion is not a definitive treatment option and complete detorsion may not be achieved depending on the degree of twist; testicular ischemia may persist. In addition, testicle may still be at risk for torsion in the future. Shortcomings of manual detorsion can be addressed with surgical exploration which is the gold standard in the management of suspected testicular torsion. During surgical exploration, if the testicle appears viable, an orchiopexy is generally performed. On the contrary, if the testicle appears to be necrotic and dead, an orchiectomy will be the next step. While testicles undergoing orchiopexy are considered viable at the time of surgery, they are often found to undergo atrophy upon follow up. In fact, Lian et al. concluded that half of patients with testicular torsion who undergo salvage surgery ultimately go on to develop testicular atrophy (2). Although studies have looked at factors predicting testicular viability during surgical exploration, there is far less literature on what predicts testicular atrophy following orchiopexy and thus the true salvage rates. It is well documented that there is a 4 to 8 h window of time from the onset of symptoms to surgery that is needed in order to save a torsed testicle (3). Delays in seeking medical care result in higher chances of needing an orchiectomy, as well as the potential burden of impaired fertility. Ramachandra et al. demonstrated through multivariate analysis of the factors associated with testicular salvage, that duration of symptoms of less than 6 h was a significant predictor of testicular salvage. They found that the median duration of pain was significantly longer in patients who underwent orchiectomy versus orchidopexy. Similar findings were seen with respect to time to operating room from initial presentation. They concluded that time to presentation is in fact the most important factor in determining salvageability of the testicle in testicular torsion. If surgical exploration is delayed, testicular atrophy will occur by 6 to 8 h, with necrosis ensuing within 8 to 10 h of initial presentation. Salvage rates of over 90% are seen when surgical exploration is performed within 6 h of the onset of symptoms, decreasing to 50% when symptoms last beyond 12 h. The chance of testicular salvage is less than 10%, when symptoms have been present for over 24 h (4). At surgical exploration, the spermatic cord is seen twisted a variable number of times around its longitudinal axis. There is scant data regarding the degree of twisting found at surgical exploration and its association with testis outcomes. Animal models have demonstrated a relationship between various testicular outcomes and degrees of twisting in the spermatic cord (5-8). In humans, Filho et al. demonstrated that the degree of testicular rotation has a multiplicative effect on the role of presentation delay in testicular torsion. Greater degree of testicular rotation is seen in patients undergoing orchidectomy vs. orchiopexy. However, testicular atrophy rates at follow-up were not measured (9). The purpose of our study is to further explore how the degree of torsion factors into testicular outcome. It is hypothesized that the greater number of twists of the spermatic cord would offer more obstruction of the vasculature and thus a lower salvage rate based on immediate intraoperative findings (orchiectomy) along with delayed atrophy of the testicle at follow-up. Methods Data collection After obtaining institutional review board approval, we reviewed the records of 229 adolescent males who presented with testicular torsion to our institution using ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes for testicular torsion ( and N44.00, respectively) and CPT codes for testis detorsion with contralateral fixation or orchiectomy (54600 or 54520, respectively). We reviewed patient charts to obtain demographics, descriptive information, clinical presentation
3 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 6, No 6 December (duration of pain), imaging (scrotal ultrasound), intraoperative findings (degree of spermatic cord twisting), and if orchiopexy or orchiectomy was performed. Most testes which remained dark-colored even after detorsion were removed, however, this was largely determined by the surgeons' judgement for the possibility of testicular recovery with an orchiopexy procedure. Finally, follow-up clinic notes were reviewed for the presence of postoperative testicular atrophy after orchiopexy (defined as a >20% difference in volume when compared to the contralateral testis based on obvious physical examination findings, orchidometry, or sonographic measurements, depending on the clinician s preference). We excluded patients without documentation of both the number of twists and duration of symptoms, those with intermittent pain upon presentation, symptom onset over 24 h from presentation (due to the assumption that there is a low risk of salvage after this time), boys under 11 years old (as assessment of the spermatic vessels along with symptomatology is more difficult and unreliable in smaller patients) or over 18 years old, and patients with less than one month follow-up (as testicular examination and measurements are misleading this early after surgery due to postoperative edema and inflammation). Testicular outcome was defined as viable (orchiopexy with adequate growth at the last clinic followup) or non-salvageable (orchiectomy or orchiopexy with subsequent atrophy). Data analysis Descriptive data including age, laterality of the affected testicle, degrees of torsion, median time to surgery, intervention, and outcome were collected and analyzed using SPSS statistical analysis software platform (IBM SPSS, Version 22.0, IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA, 2013). Chi-Square analysis was applied to categorical data and Wilcoxon rank/kruskal-wallis nonparametric test or t-test was used for comparison of continuous data where this was deemed appropriate. A receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine the sensitivity and specificity of the degree of testicular twist for determining the risk of a non-salvageable testis based on orchiectomy or atrophy after orchiopexy. Time to intervention was analyzed in an identical fashion. Youden s index, which comes without bias, was used for cut-offs for threshold time and degree to maximize specificity, as we wanted to determine testes that would be viable and to not remove them unnecessarily. Multivariate analysis was then used to predict testicular viability adjusting for the patient s age, degree of twist, and time until intervention. Probability of non-salvage Logistic regression analysis was then performed using the SAS JMP statistical analysis software platform (JMP, Version 13.1, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA, 2016) to determine the predictive value of duration of pain and degree of twists for the probability of a non-salvageable testis at the time of surgical exploration. This was then used to estimate the probability of non-salvage for each patient based upon either the duration of pain or degree of twisting alone, with linear probability formulas generated for each variable. Results Descriptive data Eighty-one patients met our inclusion criteria, with a mean age of 14.3 years (median 14; range, years) and mean follow-up of 8.0 months (range, 1 48 months) of those who had orchiopexy. Forty-four (54%) torsions were left-sided and 37 were on the right side. Fifty-five (68%) testes were deemed viable at follow-up after orchiopexy, and 26 testes were non-salvageable [7 (8.6%) underwent orchiectomy and 19 had atrophy at follow-up after orchiopexy]. Interestingly, we saw a 25.7% atrophy rate after orchiopexy in our cohort (Table 1). For viable testes versus non-salvageable testes, the mean duration of pain or symptoms was 6.2 (range, 1 21) versus 13.4 h (range, 3 24 h), while mean degree of twisting seen in the torsion at exploration was 375 (range, 90 1,800) versus 529 (range, 180 1,080) degrees (Table 2). Predictors of testicular non-salvage On univariate logistic regression analysis, increased time to intervention (P<0.0001) and the degree of torsion in excess of 360 degrees (P<0.019) were significantly associated with orchiectomy or atrophy. A non-parametric Wilcoxon rank/ Kruskal-Wallis analysis confirmed that non-salvageable testicles tended to have significantly higher degrees of twisting when compared to their viable counterparts (P=0.002). An ROC analysis was performed and a threshold time to intervention of 8.5 h [area under the curve (AUC) 0.762, with 95% confidence intervals (CI): ] would provide a 73% sensitivity and 80% specificity for the
4 1162 Howe et al. Time and twist degree in testis torsion prediction of testicular non-salvage (Figure 1A). Also, a cutoff value of 495 degrees of torsion would provide a 53% sensitivity and 80% specificity for predicting non-salvage (AUC 0.711, 95% CI: ) (Figure 1B). A multivariate analysis including age, degree of testicular twist, and time until intervention revealed that only patient age and time to intervention were correlated with the risk of a non-salvageable testis (Table 3). Probability of non-salvage formula Table 1 Descriptive data for entire cohort Variable Data Median age [range], years 14 [11 17] Testicle involved, n (%) Left 44 (54.3) Right 37 (45.7) Degree of torsion, n (%), ( ) (33.3) (44.4) (22.3) Median time to surgery [range], h 6 [1 24] Intervention, n (%) Orchiopexy 74 (91.4) Orchiectomy 7 (8.6) Testicular outcome, n (%) Viable 55 (67.9) Non-salvageable (orchiectomy or atrophic) 26 (32.1) Logistic regression analysis determined that the degree of twist and duration of pain were predictive of non-salvage on nominal logistic multivariate analysis (P<0.0140, P<0.0006). A bivariate fit of probability of non-salvage based on duration of pain (r 2 =0.91) and degree of twist (r 2 =0.99) were then used, separately to estimate the probability of nonsalvage. Each variable was then used to generate a linear probability formula, which was as follows: % probability of non-salvage = 4 + 3x [1] % probability of non-salvage = y [2] where x was equivalent to the duration of pain in hours (P<0.001) and y was equivalent to degree of testicular twist. Overall, a 50% chance of testicular non-salvage would be coincident with 15 h of testicular pain (Figure 2A), while an 860-degree twist (Figure 2B) would coincide with a 50% chance of non-salvage (P<0.001). When both duration and degree were combined, we found a poor correlation coefficient (r 2 =0.2) and were unfortunately unable to derive a probability formula combining the variables. Table 2 Comparison of continuous data for viable and non-salvageable testes Variable Viable testes Non-salvageable testes (orchiectomy or atrophic) OR (95% CI) P value Median age [range], years 15 [11 17] 14 [12 16] 1.3 ( ) 0.06 Testicle involved, n (%) Left 32 (58.2) 12 (46.2) Ref Right 23 (41.8) 14 (53.8) 0.6 ( ) Median time to intervention [range]*, h 5 [1 21] 12.5 [3 24] 0.1 ( ) < Median degree of torsion [range]*, ( ) 360 [90 1,800] 540 [180 1,080] 0.1 ( ) 0.06 Degree of torsion ( ) (43.6) 3 (11.5) Ref (41.8) 13 (50.0) 0.9 ( ) (14.5) 10 (38.5) 1.4 ( ) *, continuous variable with interquartile range reported. Univariate logistic regression assessing variable prediction of testicular viability. The P values in italic form mean significance (P<0.05). Ref, 1.0.
5 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 6, No 6 December A 1.0 ROC curve B 1.0 ROC curve Sensitivity 0.4 Sensitivity specificity 1-specificity Diagonal segments are produce by ties. Diagonal segments are produce by ties. Figure 1 Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve for predicting the risk of a non-salvageable testis. (A) Duration of pain (hours); (B) degree of twisting. A B 0.7 Prob Death Prob[0] Figure 2 Bivariate fit of probability of a non-salvageable testis based on (A) duration of pain in hours, % probability of non-salvage = 4 + 3x (where x = duration of pain in hours); and (B) degree of twisting, % probability of non-salvage = y (where y = twisting of spermatic cord in degrees) Duration of pain (hr) Twist (degrees) 0.2 Table 3 Multivariate analysis for risks of a non-salvageable testis Variable OR (95% CI) P value Age (years) 0.1 ( ) 0.04 Degrees of twist ( ) 0.1 ( ) 0.07 Time to intervention (h) 8.3 ( ) <0.01 The P values in italic form mean significance. Discussion While the current data regarding the degree of twisting in the spermatic cord s effects on ultimate testicular outcomes in emergent cases of testicular torsion in humans are limited, animal studies addressing this topic have been performed. In 1986, Cosentino s team performed studies on rats to first examine the effects of duration of symptoms
6 1164 Howe et al. Time and twist degree in testis torsion of testicular torsion. The degree of twisting was fixed at 720 for all rats with duration of symptoms ranging from 0 12 h and found poor histologic findings and fertility rates after a period of recovery starting at 3 h of torsion, as well as markedly decreased fertility rates at 9 h (10). Later, Lee s group started the investigation into the degree of twisting in testicular torsion by creating torsion in five anesthetized dogs and measuring blood flow blood flow by color Doppler sonography at serial increasing degrees of twisting. They found undetectable flows starting at 450 in all but one dog, who s flow became undetectable at 540 (5). Other studies have used contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rabbits showing mild drops in perfusion starting at 360 with significantly decreased blood flow starting at 540 (6,7). Heindel s group decided to look at fertility rates after a period of recovery from various degrees of torsion in rats, reporting significantly decreased fertility starting at 720 of torsion, however, they did not measure 540 twisting between the measurements (8). Filho et al. recently reviewed their records of 117 patients with testis torsion, and found a correlation in time (median of 8.4 h in the orchiopexy group) and degree of torsion in the orchiopexy group. Orchiectomy rates increased starting at 540, in which duration of symptoms became more relevant in testis survival rates seen between 6 and 12 h. Testes were salvaged in all patients less than 360 and removed in all patients over 1,080 of twisting (9). Based on this study combined with prior animal research, it appears that somewhere between of twisting during testicular torsion lies the point where significant occlusion to arterial flow occurs with risk of damage to the testicle. While Filho's was the first study in humans giving a close look into the degree of torsion, we are unsure of the ultimate outcome of the testis based on this study as performance of orchiopexy at surgery was used as the positive outcome instead of using follow-up data via physical examination with or without orchidometry or sonographic measuring. We are well aware that many testes undergo atrophy even after detorsion and orchiopexy (2). While lesser degrees of torsion may bring back appreciable perfusion to the testicle, along with the surgeons decision to attempt testis salvage based on the possible chance for recovery of testicular function and withholding orchiectomy until it is necessitated, many testicles undergo significant atrophy after being followed long term in the clinic setting. Our study included follow-up data in an attempt to further investigate the significance in the relationship between the degree of twisting in the prognosis of the testis during episodes of testicular torsion. Interestingly our data showed that about 25% of testes undergo atrophy after orchiopexy is performed. While the significance of an atrophied testis is questionable, it is nevertheless compromised in function, and this is clinically relevant and helpful in counseling patients to expectations on how well the testis will grow after a torsion episode if an orchiopexy is performed. Duration of symptoms appeared to be the primary predictor of outcomes. We agree with previous studies that duration of symptoms greater than 6 8 h are at higher risk for testicular demise. While immediate return of blood flow to the testicle can occur after detorsion, the inevitable effects of ischemia can have lasting effects on the viability of a testis. This was seen in our data as the nonsalvageable testis rate more than doubled the orchiectomy rate due to a high number of atrophic testes seen at followup evaluation. We were also able to determine the clinical significance of the degree of twisting (separate from the duration of pain as the degree of twist did not significantly contribute to derive a formula which combined both variables) in ultimate testis viability during episodes of testicular torsion in the pediatric population, despite a low sensitivity on ROC analysis. When there is greater than one twist (more than 360 degrees) seen in the spermatic cord at scrotal exploration, there is a higher risk of non-salvage for the testis based on our data. Our study is also the first to derive separate formulas for duration and degree of twisting to determine the probability of a non-salvageable testis during torsion episodes. This probability can be calculated by our formulas, 4 + (3 duration in hours) and 7 + (0.05 degree of twisting). The clinical significance of these formulas can be helpful in patients counseling perioperatively and monitoring these testes during follow-up. For example, a testis that is twisted 360 degrees for 6 h will have a 25% and 22% chance of non-salvage based on degree and duration, respectively. However, the role these formulas play into the decision on whether to perform an orchiopexy versus orchiectomy at time of surgery largely depend on clinical judgement, the philosophy of the urologist in the management of a testis with equivocal viability, along with other intraoperative findings. It is likely that multiple factors including immunologic responses and fluid dynamics are at play in testicular injury during torsion that we cannot appropriately measure in humans with modern science. The later can be appreciated by Bernoulli s principle, which states that an increase in
7 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 6, No 6 December speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure, such that there is a conservation of energy (11). The theorem is utilized mostly in cardiovascular research, where studies looking at hemodynamics in stenotic arterial lesions have been able to derive a validated simplified formula: 4 (maximum velocity, m/s) 2 = pressure drop, mmhg (12). When fluid moves from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure, such as is in detorsion, more pressure is behind the fluid and this gives a net force and accelerates the fluid. This can result in pressurerelated damage to the testis upon return of flow to further insult the oxidative damage produced with ischemia from prolonged torsion. Therefore, a patient's blood pressure, plasma density, elasticity of the vasculature, and the length along the spermatic cord in which the torsion involves can all potentially play roles in effecting reperfusion dynamics, and thus testicular viability. The limitations of the study are its retrospective nature and the relatively low number of patients with more than one month of follow-up as well as the degree of twisting dictated in the operative notes. Also, while our study was able to determine clinically helpful formulas using degree of twisting and duration of pain for testicular prognosis, we were unable to combine these variables into one formula to give one definitive probability of non-salvage. While more studies in humans are needed to truly determine the clinical relevance of twisting degree in relation to prognosis of testicular torsion, we must also look to other areas of torsion pathology to better enhance our knowledge in this common emergency room presentation in children. Conclusions The viability of the torsed testis can be determined by the duration of symptoms along with degree of twisting, with 15 h of symptom duration and 860 degrees of torsion leading to a 50% probability of non-salvage. Twenty-five percent of testes undergo atrophy after orchiopexy, which proves the concept of reperfusion injury having delayed and lasting effects on testis viability. Further studies are need to accurately characterize the significance of twisting degree in relation to time and prognosis during testicular torsion. Acknowledgements We would like to thank Kaitlin Kosinsky in the Department of Urology at Winthrop University Hospital in Mineola, NY, USA for her research coordination in this study. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: LS Palmer is a speaker for Laborie. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: We obtained ethical approval to conduct this research by the institutional review board (IRB ID# ). Informed consent is not required due to the retrospective nature of this study. References 1. Lemini R, Guanà R, Tommasoni N, et al. Predictivity of Clinical Findings and Doppler Ultrasound in Pediatric Acute Scrotum. Urol J 2016;13: Lian BS, Ong CC, Chiang LW, et al. Factors Predicting Testicular Atrophy after Testicular Salvage following Torsion. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2016;26: Mansbach JM, Forbes P, Peters C. Testicular torsion and risk factors for orchiectomy. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005;159: Ramachandra P, Palazzi KL, Holmes NM, et al. Factors influencing rate of testicular salvage in acute testicular torsion at a tertiary pediatric center. West J Emerg Med 2015;16: Lee FT Jr, Winter DB, Madsen FA, et al. Conventional color Doppler velocity sonography versus color Doppler energy sonography for the diagnosis of acute experimental torsion of the spermatic cord. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996;167: Paltiel HJ, Estrada CR Jr, Alomari AI, et al. Multi-planar dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound assessment of blood flow in a rabbit model of testicular torsion. Ultrasound Med Biol 2014;40: Paltiel HJ, Padua HM, Gargollo PC, et al. Contrastenhanced, real-time volumetric ultrasound imaging of tissue perfusion: preliminary results in a rabbit model of testicular torsion. Phys Med Biol 2011;56: Heindel RM, Pakyz RE, Reinking LN, et al. The effect of various degrees of unilateral spermatic cord torsion on fertility in the rat. J Urol 1990;144: Dias AC Filho, Alves JR, Buson H Filho, et al. The Amount of spermatic cord rotation magnifies the timerelated orchidectomy risk in intravaginal testicular torsion. Int Braz J Urol 2016;42: Cosentino MJ, Nishida M, Rabinowitz R, et al. Histopathology of prepubertal rat testes subjected to various durations of spermatic cord torsion. J Androl
8 1166 Howe et al. Time and twist degree in testis torsion 1986;7: Babinsky H. How do wings work? Phys Educ 2003;38: Faccenda F, Usui Y, Spencer MP. Doppler measurement of the pressure drop caused by arterial stenosis: an experimental study: a case report. Angiology 1985;36: Cite this article as: Howe AS, Vasudevan V, Kongnyuy M, Rychik K, Thomas LA, Matuskova M, Friedman SC, Gitlin JS, Reda EF, Palmer LS. Degree of twisting and duration of symptoms are prognostic factors of testis salvage during episodes of testicular torsion. Transl Androl Urol 2017;6(6): doi: /tau
Ultrasonic Evaluation of Heterogeneity Levels in Normal and Torsed Testes
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (EECSS 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 13-14, 2015 Paper No. 297 Ultrasonic Evaluation of Heterogeneity Levels in
Proceedings of the World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (EECSS 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 13-14, 2015 Paper No. 297 Ultrasonic Evaluation of Heterogeneity Levels in
Dr Prashant Jain. Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital
 Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center
 Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Testicular Torsion. Pediatric Testicular Torsion: Demographics of National Orchiopexy Versus Orchiectomy Rates
 Testicular Torsion Pediatric Testicular Torsion: Demographics of National Orchiopexy Versus Orchiectomy Rates Nicholas G. Cost,* Nicol C. Bush, Theodore D. Barber, Rong Huang and Linda A. Baker From the
Testicular Torsion Pediatric Testicular Torsion: Demographics of National Orchiopexy Versus Orchiectomy Rates Nicholas G. Cost,* Nicol C. Bush, Theodore D. Barber, Rong Huang and Linda A. Baker From the
Management of the Acute Scrotum in a District General Hospital: 10-Year Experience
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 281 286 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.37 Management of the Acute Scrotum in a District General Hospital: 10-Year Experience Lukas
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 281 286 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.37 Management of the Acute Scrotum in a District General Hospital: 10-Year Experience Lukas
The amount of spermatic cord rotation magnifies the timerelated orchidectomy risk in Intravaginal testicular torsion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (6): 1210-1219, November - December, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0166 The amount of spermatic cord rotation magnifies the timerelated orchidectomy risk in Intravaginal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (6): 1210-1219, November - December, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0166 The amount of spermatic cord rotation magnifies the timerelated orchidectomy risk in Intravaginal
Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound. Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound
 Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh
 Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
Factors Influencing Rate of Testicular Salvage in Acute Testicular Torsion at a Tertiary Pediatric Center
 Original Research Factors Influencing Rate of Testicular Salvage in Acute Testicular Torsion at a Tertiary Pediatric Center Puneeta Ramachandra, MD* Kerrin L. Palazzi, MPH Nicholas M. Holmes, MD Sarah
Original Research Factors Influencing Rate of Testicular Salvage in Acute Testicular Torsion at a Tertiary Pediatric Center Puneeta Ramachandra, MD* Kerrin L. Palazzi, MPH Nicholas M. Holmes, MD Sarah
Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0)
 Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0) Clinical Director Signed Name... Mr C. Hendrickse.. Date 14/10/2011.. Meta Data Guideline Title: Guidelines for the Management of
Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0) Clinical Director Signed Name... Mr C. Hendrickse.. Date 14/10/2011.. Meta Data Guideline Title: Guidelines for the Management of
Testicular Torsion: A Perspective from the Middle East
 Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2004;13:255 259 DOI: 10.1159/000079523 Received: June 22, 2003 Revised: October 6, 2003 Testicular Torsion: A Perspective from the Middle East A.A. Al-Hunayan A.M. Hanafy
Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2004;13:255 259 DOI: 10.1159/000079523 Received: June 22, 2003 Revised: October 6, 2003 Testicular Torsion: A Perspective from the Middle East A.A. Al-Hunayan A.M. Hanafy
Predictive Parameters of Testicular Salvage of Pediatric Testicular Torsion: A 6-Year Experience of a Single Center
 Original Article ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.14777/uti.2016.11.1.25 Urogenit Tract Infect 2016;11(1):25-29 Predictive Parameters of Testicular Salvage of Pediatric
Original Article ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.14777/uti.2016.11.1.25 Urogenit Tract Infect 2016;11(1):25-29 Predictive Parameters of Testicular Salvage of Pediatric
Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis
 www.kjurology.org DOI:1.4111/kju.21.51.2.16 Laparoscopy/Robotics Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis Jongwon Kim, Gyeong Eun Min 1, Kun Suk Kim Department of Urology, University of Ulsan College
www.kjurology.org DOI:1.4111/kju.21.51.2.16 Laparoscopy/Robotics Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis Jongwon Kim, Gyeong Eun Min 1, Kun Suk Kim Department of Urology, University of Ulsan College
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings
 The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
Role of Spectral Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Partial Testicular Torsion
 ase Series Role of Spectral Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Partial Testicular Torsion Scott assar, MD, Shweta hatt, MD, Harriet J. Paltiel, MD, Vikram S. Dogra, MD Objective. The purpose of this
ase Series Role of Spectral Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Partial Testicular Torsion Scott assar, MD, Shweta hatt, MD, Harriet J. Paltiel, MD, Vikram S. Dogra, MD Objective. The purpose of this
Testicular Torsion in Children: A 20-Year Retrospective Study in a Single Institution
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 362 368 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.39 Testicular Torsion in Children: A 20-Year Retrospective Study in a Single Institution Chao
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 362 368 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.39 Testicular Torsion in Children: A 20-Year Retrospective Study in a Single Institution Chao
RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY
 RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY Isabel Roca Vall d'hebron Hospital General Servei de Medicina Nuclear TESTICULAR SCINTIGRAPHY ACUTE TESTICULAR PAIN Differential Diagnosis
RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY Isabel Roca Vall d'hebron Hospital General Servei de Medicina Nuclear TESTICULAR SCINTIGRAPHY ACUTE TESTICULAR PAIN Differential Diagnosis
Importance of the testicular torsion in the male infertility. A. Rusz, Gy. Papp Military Hospital-State Health Centre (ÁEK) EAA Centre
 Importance of the testicular torsion in the male infertility A. Rusz, Gy. Papp Military Hospital-State Health Centre (ÁEK) EAA Centre Budapest, Hungary Acute scrotum Torsion of the testis Torsion of the
Importance of the testicular torsion in the male infertility A. Rusz, Gy. Papp Military Hospital-State Health Centre (ÁEK) EAA Centre Budapest, Hungary Acute scrotum Torsion of the testis Torsion of the
Managing testicular torsion time is of the essence
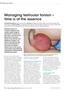 Managing testicular torsion time is of the essence Christopher Bastianpillai, Urology Clinical Fellow; Kate Ryan, Foundation Year Doctor, Whipps Cross University Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust; James
Managing testicular torsion time is of the essence Christopher Bastianpillai, Urology Clinical Fellow; Kate Ryan, Foundation Year Doctor, Whipps Cross University Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust; James
The acute scrotum the two most difficult US problems. Simon Freeman Derriford Hospital, Plymouth. UK
 The acute scrotum the two most difficult US problems Simon Freeman Derriford Hospital, Plymouth. UK simonfreeman@nhs.net The Acute Scrotum 1. Ischaemia 1. Spermatic cord torsion 2. Torsion of a testicular
The acute scrotum the two most difficult US problems Simon Freeman Derriford Hospital, Plymouth. UK simonfreeman@nhs.net The Acute Scrotum 1. Ischaemia 1. Spermatic cord torsion 2. Torsion of a testicular
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum. AUA update series 2016 volume 35. By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr.
 Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract -
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
TESTICULAR TORSION IS A
 ARTICLE Testicular Torsion and Risk Factors for Orchiectomy Jonathan M. Mansbach, MD; Peter Forbes, MA; Craig Peters, MD Objective: To determine risk factors for testicular loss due to testicular torsion.
ARTICLE Testicular Torsion and Risk Factors for Orchiectomy Jonathan M. Mansbach, MD; Peter Forbes, MA; Craig Peters, MD Objective: To determine risk factors for testicular loss due to testicular torsion.
The case. I m smiling because it hurts
 Brad Sobolewski, MD The case A 7 year old boy has been referred to the ED because his privates hurt The pain has been present for 2 days It is worse when he jumps up and down There is no history of trauma,
Brad Sobolewski, MD The case A 7 year old boy has been referred to the ED because his privates hurt The pain has been present for 2 days It is worse when he jumps up and down There is no history of trauma,
Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective Descriptive Study
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 878509, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/878509 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 878509, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/878509 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective
Basic Biostatistics. Chapter 1. Content
 Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Badness in Babies. Samuel Reid, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Minnesota
 Badness in Babies Samuel Reid, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Minnesota Case 8 day-old infant transported by EMS with a twelve hour history of vomiting and increasingly poor responsiveness.
Badness in Babies Samuel Reid, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Minnesota Case 8 day-old infant transported by EMS with a twelve hour history of vomiting and increasingly poor responsiveness.
Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion.
 LAPAROSCOPIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ORCHIDOPEXY MEDICAL JOURNAL Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion. Saad Dakhil F ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: With the use of diagnostic laparoscopy widely accepted
LAPAROSCOPIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ORCHIDOPEXY MEDICAL JOURNAL Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion. Saad Dakhil F ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: With the use of diagnostic laparoscopy widely accepted
Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain
 Bang Med J Khulna 2017; 50 : 26-30 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain G Salahuddin 1, SMZ Nayeem 2, SM Hossain 3, S Parvin 4, MM Hossain
Bang Med J Khulna 2017; 50 : 26-30 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain G Salahuddin 1, SMZ Nayeem 2, SM Hossain 3, S Parvin 4, MM Hossain
THE incidence of stroke after noncardiac surgery
 Lack of Association between Carotid Artery Stenosis and Stroke or Myocardial Injury after Noncardiac Surgery in High-risk Patients ABSTRACT Background: Whether carotid artery stenosis predicts stroke after
Lack of Association between Carotid Artery Stenosis and Stroke or Myocardial Injury after Noncardiac Surgery in High-risk Patients ABSTRACT Background: Whether carotid artery stenosis predicts stroke after
Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer
 Bladder Cancer 3 (2017) 45 49 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160068 IOS Press Research Report 45 Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer Richard S. Matulewicz a,b,, John Oliver DeLancey
Bladder Cancer 3 (2017) 45 49 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160068 IOS Press Research Report 45 Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer Richard S. Matulewicz a,b,, John Oliver DeLancey
Neonatal testicular torsion after cesarean section with spinal anesthesia: a presentation of two cases
 Case Report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 160-166 Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 22:32 IRST on Tuesday October 30th 2018 Neonatal testicular torsion
Case Report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 160-166 Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 22:32 IRST on Tuesday October 30th 2018 Neonatal testicular torsion
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
Levothyroxine replacement dosage determination after thyroidectomy
 The American Journal of Surgery (2013) 205, 360-364 Midwest Surgical Association Levothyroxine replacement dosage determination after thyroidectomy Judy Jin, M.D. a, Matthew T. Allemang, M.D. b, Christopher
The American Journal of Surgery (2013) 205, 360-364 Midwest Surgical Association Levothyroxine replacement dosage determination after thyroidectomy Judy Jin, M.D. a, Matthew T. Allemang, M.D. b, Christopher
Time to improvement in semen parameters after microsurgical varicocelectomy in men with severe oligospermia
 Time to improvement in semen parameters after microsurgical varicocelectomy in men with severe oligospermia Thomas A. Masterson; Aubrey B. Greer; Ranjith Ramasamy University of Miami, Miami, FL, United
Time to improvement in semen parameters after microsurgical varicocelectomy in men with severe oligospermia Thomas A. Masterson; Aubrey B. Greer; Ranjith Ramasamy University of Miami, Miami, FL, United
Common Problems in Urology
 Common Problems in Urology 1. Renal Colic Outline 2. Urinary Retention 3. Acute Scrotum Supanut Lumbiganon, MD. Renal colic The most common urologic emergency O Sudden increase of pressure in the urinary
Common Problems in Urology 1. Renal Colic Outline 2. Urinary Retention 3. Acute Scrotum Supanut Lumbiganon, MD. Renal colic The most common urologic emergency O Sudden increase of pressure in the urinary
CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS
 CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS RISK FACTORS IN THE EMERGENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE RENAL FAILURE, IMPACT OF TREATMENT WITH ACE INHIBITORS Scientific
CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS RISK FACTORS IN THE EMERGENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE RENAL FAILURE, IMPACT OF TREATMENT WITH ACE INHIBITORS Scientific
Biostats Final Project Fall 2002 Dr. Chang Claire Pothier, Michael O'Connor, Carrie Longano, Jodi Zimmerman - CSU
 Biostats Final Project Fall 2002 Dr. Chang Claire Pothier, Michael O'Connor, Carrie Longano, Jodi Zimmerman - CSU Prevalence and Probability of Diabetes in Patients Referred for Stress Testing in Northeast
Biostats Final Project Fall 2002 Dr. Chang Claire Pothier, Michael O'Connor, Carrie Longano, Jodi Zimmerman - CSU Prevalence and Probability of Diabetes in Patients Referred for Stress Testing in Northeast
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
The use of assisted reproductive technology before male factor infertility evaluation
 Original Article The use of assisted reproductive technology before male factor infertility evaluation Madhur Nayan 1, Nahid Punjani 2, Ethan Grober 1, Kirk Lo 1,3,4, Keith Jarvi 1,3,4 1 Division of Urology,
Original Article The use of assisted reproductive technology before male factor infertility evaluation Madhur Nayan 1, Nahid Punjani 2, Ethan Grober 1, Kirk Lo 1,3,4, Keith Jarvi 1,3,4 1 Division of Urology,
Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes
 Brief Report Page 1 of 5 Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes Marcelo Trivi, Ruth Henquin, Juan Costabel, Diego Conde Cardiovascular Institute of Buenos
Brief Report Page 1 of 5 Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes Marcelo Trivi, Ruth Henquin, Juan Costabel, Diego Conde Cardiovascular Institute of Buenos
Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan
 Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan Weill Cornell Medicine, New York (Qatar campus) Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar Disclosure Statement I have no relationships with commercial interests
Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan Weill Cornell Medicine, New York (Qatar campus) Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar Disclosure Statement I have no relationships with commercial interests
Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Malignant Breast Masses Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 4-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad
 ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
Lecture Outline. Biost 590: Statistical Consulting. Stages of Scientific Studies. Scientific Method
 Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
Alex Lam, HMS III. September The Acute Scrotum. Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD. Gillian Lieberman, MD
 September 2002 The Acute Scrotum Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III DDx: : Acute Scrotal Pain & Enlargement PAIN Inflammatory disorder Testicular torsion Testicular infarction Testicular abscess
September 2002 The Acute Scrotum Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III DDx: : Acute Scrotal Pain & Enlargement PAIN Inflammatory disorder Testicular torsion Testicular infarction Testicular abscess
Evaluation of the role of varicocelectomy including external spermatic vein ligation in patients with scrotal pain
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdApril 2005124484488Original ArticleRole of varicocelectomy for paink Karademir et al. International
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdApril 2005124484488Original ArticleRole of varicocelectomy for paink Karademir et al. International
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion
 Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Predictive Models. Michael W. Kattan, Ph.D. Department of Quantitative Health Sciences and Glickman Urologic and Kidney Institute
 Predictive Models Michael W. Kattan, Ph.D. Department of Quantitative Health Sciences and Glickman Urologic and Kidney Institute Treatment for clinically localized prostate cancer Trade off: Substantial
Predictive Models Michael W. Kattan, Ph.D. Department of Quantitative Health Sciences and Glickman Urologic and Kidney Institute Treatment for clinically localized prostate cancer Trade off: Substantial
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test
 Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
Effect of female partner age on pregnancy rates after vasectomy reversal
 MALE FACTOR Effect of female partner age on pregnancy rates after vasectomy reversal Edward R. Gerrard, Jr., M.D., a Jay I. Sandlow, b Robert A. Oster, Ph.D., c John R. Burns, M.D., a Lyndon C. Box, M.D.,
MALE FACTOR Effect of female partner age on pregnancy rates after vasectomy reversal Edward R. Gerrard, Jr., M.D., a Jay I. Sandlow, b Robert A. Oster, Ph.D., c John R. Burns, M.D., a Lyndon C. Box, M.D.,
Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.9.649 Pediatric Urology Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis Jae Jun Bae, Bum Soo Kim, Sung Kwang Chung Department of Urology, Kyungpook National
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.9.649 Pediatric Urology Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis Jae Jun Bae, Bum Soo Kim, Sung Kwang Chung Department of Urology, Kyungpook National
isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS
 isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS S E C O N D! E D I T I O N (and sex, drugs and rock V roll) A N D Y F I E L D Publications London o Thousand Oaks New Delhi CONTENTS Preface How To Use This Book Acknowledgements
isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS S E C O N D! E D I T I O N (and sex, drugs and rock V roll) A N D Y F I E L D Publications London o Thousand Oaks New Delhi CONTENTS Preface How To Use This Book Acknowledgements
Prepubertal Testicular Teratomas and Epidermoid Cysts
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prepubertal Testicular Teratomas and Epidermoid Cysts Comparison of Clinical and Sonographic Features Min-Yung Chang, MD, Hyun Joo Shin, MD, Hyun Gi Kim, MD, Myung-Joon Kim, MD, PhD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prepubertal Testicular Teratomas and Epidermoid Cysts Comparison of Clinical and Sonographic Features Min-Yung Chang, MD, Hyun Joo Shin, MD, Hyun Gi Kim, MD, Myung-Joon Kim, MD, PhD,
Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication for Repeat Metastasectomy
 Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS
 COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF ACUTE SCROTUM
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 100: 196 201, 2011 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF ACUTE SCROTUM E. Mäkelä 1, T. Lahdes-Vasama 1, P. Ryymin 2, V. Kähärä 2, J. Suvanto 2, M. Kangasniemi 3, A. Kaipia 4 1 Paediatric
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 100: 196 201, 2011 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF ACUTE SCROTUM E. Mäkelä 1, T. Lahdes-Vasama 1, P. Ryymin 2, V. Kähärä 2, J. Suvanto 2, M. Kangasniemi 3, A. Kaipia 4 1 Paediatric
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES. Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES
 BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
Undescended Testicle
 What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection
 Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Research Article The Effect of Erythropoietin on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury after Testicular Torsion/Detorsion: A Randomized Experimental Study
 ISRN Urology Volume 213, Article ID 35139, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/35139 Research Article The Effect of Erythropoietin on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury after Testicular Torsion/Detorsion: A
ISRN Urology Volume 213, Article ID 35139, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/35139 Research Article The Effect of Erythropoietin on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury after Testicular Torsion/Detorsion: A
Statistical analysis DIANA SAPLACAN 2017 * SLIDES ADAPTED BASED ON LECTURE NOTES BY ALMA LEORA CULEN
 Statistical analysis DIANA SAPLACAN 2017 * SLIDES ADAPTED BASED ON LECTURE NOTES BY ALMA LEORA CULEN Vs. 2 Background 3 There are different types of research methods to study behaviour: Descriptive: observations,
Statistical analysis DIANA SAPLACAN 2017 * SLIDES ADAPTED BASED ON LECTURE NOTES BY ALMA LEORA CULEN Vs. 2 Background 3 There are different types of research methods to study behaviour: Descriptive: observations,
All Men are created. (more or less) Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA
 Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
This article is the second in a series in which I
 COMMON STATISTICAL ERRORS EVEN YOU CAN FIND* PART 2: ERRORS IN MULTIVARIATE ANALYSES AND IN INTERPRETING DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GROUPS Tom Lang, MA Tom Lang Communications This article is the second in a
COMMON STATISTICAL ERRORS EVEN YOU CAN FIND* PART 2: ERRORS IN MULTIVARIATE ANALYSES AND IN INTERPRETING DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GROUPS Tom Lang, MA Tom Lang Communications This article is the second in a
Early experience of laparoscopic varicocelectomy in College
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-2, 32-36 Original Article Early experience of laparoscopic varicocelectomy in College of Medical Sciences, Teaching Hospital, Bhartpur,, Nepal
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-2, 32-36 Original Article Early experience of laparoscopic varicocelectomy in College of Medical Sciences, Teaching Hospital, Bhartpur,, Nepal
How to describe bivariate data
 Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions
 Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions Instructions to fill the table: When no element can be added under one or more heading, include the mention: O Not applicable when an
Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions Instructions to fill the table: When no element can be added under one or more heading, include the mention: O Not applicable when an
Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy
 Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Baldisserotto; Porto Alegre/BR Acceptance testing,
Doppler Ultrasound findings in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Baldisserotto; Porto Alegre/BR Acceptance testing,
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2
 MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling
 Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Chapter 1: Introduction... 1
 From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
Abstract ESC Pisa
 Abstract ESC 82441 Maximal left ventricular mass-to-power output: A novel index to assess left ventricular performance and to predict outcome in patients with advanced heart failure FL. Dini 1, D. Mele
Abstract ESC 82441 Maximal left ventricular mass-to-power output: A novel index to assess left ventricular performance and to predict outcome in patients with advanced heart failure FL. Dini 1, D. Mele
Statistics as a Tool. A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations.
 Statistics as a Tool A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations. Descriptive Statistics Numerical facts or observations that are organized describe
Statistics as a Tool A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations. Descriptive Statistics Numerical facts or observations that are organized describe
Sonographic Appearance of the Epididymis in Pediatric Testicular Torsion
 Nussbaum Blask and Rushton Sonography of Testicular Torsion in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Anna R. Nussbaum Blask 1 H. Gil Rushton
Nussbaum Blask and Rushton Sonography of Testicular Torsion in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Anna R. Nussbaum Blask 1 H. Gil Rushton
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new
 Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria
 Article ID: WMC00807 ISSN 2046690 Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria Corresponding Author: Dr. Ahidjo Kawu, Consultant Surgeon, Dept of Orthopaedics, UATH, Gwagwalada Abuja
Article ID: WMC00807 ISSN 2046690 Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria Corresponding Author: Dr. Ahidjo Kawu, Consultant Surgeon, Dept of Orthopaedics, UATH, Gwagwalada Abuja
CAN WE PREDICT SURGERY FOR SCIATICA?
 7 CAN WE PREDICT SURGERY FOR SCIATICA? Improving prediction of inevitable surgery during non-surgical treatment of sciatica. Wilco C. Peul Ronald Brand Raph T.W.M. Thomeer Bart W. Koes Submitted for publication
7 CAN WE PREDICT SURGERY FOR SCIATICA? Improving prediction of inevitable surgery during non-surgical treatment of sciatica. Wilco C. Peul Ronald Brand Raph T.W.M. Thomeer Bart W. Koes Submitted for publication
Comparison of indocyanine green fluorescence and parathyroid autofluorescence imaging in the identification of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy
 Original Article Comparison of indocyanine green fluorescence and parathyroid autofluorescence imaging in the identification of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy Bora Kahramangil, Eren Berber Department
Original Article Comparison of indocyanine green fluorescence and parathyroid autofluorescence imaging in the identification of parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy Bora Kahramangil, Eren Berber Department
BEST PRACTICES FOR IMPLEMENTATION AND ANALYSIS OF PAIN SCALE PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN CLINICAL TRIALS
 BEST PRACTICES FOR IMPLEMENTATION AND ANALYSIS OF PAIN SCALE PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN CLINICAL TRIALS Nan Shao, Ph.D. Director, Biostatistics Premier Research Group, Limited and Mark Jaros, Ph.D. Senior
BEST PRACTICES FOR IMPLEMENTATION AND ANALYSIS OF PAIN SCALE PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN CLINICAL TRIALS Nan Shao, Ph.D. Director, Biostatistics Premier Research Group, Limited and Mark Jaros, Ph.D. Senior
Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men with Prostate Cancer
 Original Article Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men with Prostate Cancer Sunai Leewansangtong, Suchai Soontrapa, Chaiyong Nualyong, Sittiporn Srinualnad, Tawatchai Taweemonkongsap and Teerapon
Original Article Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men with Prostate Cancer Sunai Leewansangtong, Suchai Soontrapa, Chaiyong Nualyong, Sittiporn Srinualnad, Tawatchai Taweemonkongsap and Teerapon
List of Figures. List of Tables. Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
2.75: 84% 2.5: 80% 2.25: 78% 2: 74% 1.75: 70% 1.5: 66% 1.25: 64% 1.0: 60% 0.5: 50% 0.25: 25% 0: 0%
 Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
Local Anesthesia during Transrectal Prostate Biopsy
 Local Anesthesia during Transrectal Prostate Biopsy Awad A1-Kaabneh, MD*, Tareq Bisheh, MD ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine the effectiveness of the longer acting agent bupivacaine for periprostatic anesthesia
Local Anesthesia during Transrectal Prostate Biopsy Awad A1-Kaabneh, MD*, Tareq Bisheh, MD ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine the effectiveness of the longer acting agent bupivacaine for periprostatic anesthesia
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele
 Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
MET Mobile Emergency Triage
 MET Mobile Emergency Triage Saving Lives. Saving Dollars. Poznań University of Technology, Poland University of Ottawa, Canada CHEO (Childrens Hospital of Eastern Ontario), Canada What Triage Means? A
MET Mobile Emergency Triage Saving Lives. Saving Dollars. Poznań University of Technology, Poland University of Ottawa, Canada CHEO (Childrens Hospital of Eastern Ontario), Canada What Triage Means? A
The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole
 The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole A SHAH 1 AV SHAH 2 Of the various modalities for management of impalpable undescended testis, the use of laparoscopy or keyhole surgery is being widely
The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole A SHAH 1 AV SHAH 2 Of the various modalities for management of impalpable undescended testis, the use of laparoscopy or keyhole surgery is being widely
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering 786. Applied Biostatistics in Ergonomics Spring 2012 Kurt Beschorner
 Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering 786 Applied Biostatistics in Ergonomics Spring 2012 Kurt Beschorner Note: This syllabus is not finalized and is subject to change up until the start of the class.
Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering 786 Applied Biostatistics in Ergonomics Spring 2012 Kurt Beschorner Note: This syllabus is not finalized and is subject to change up until the start of the class.
@DrAshBowen. ll Pain: Solving mysteries of the male scrotum
 @DrAshBowen ll Pain: Solving mysteries of the male scrotum On the Docket Good Hydrocele Epididymal cysts Varicocele Bad Testis Cancer/Tumor Epididymitis/Orchitis STI Torsion UGLY Chronic Orchalgia Post
@DrAshBowen ll Pain: Solving mysteries of the male scrotum On the Docket Good Hydrocele Epididymal cysts Varicocele Bad Testis Cancer/Tumor Epididymitis/Orchitis STI Torsion UGLY Chronic Orchalgia Post
Overview. Goals of Interpretation. Methodology. Reasons to Read and Evaluate
 Overview Critical Literature Evaluation and Biostatistics Ahl Ashley N. Lewis, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Specialist, Drug Information UNC Hospitals Background Review of basic statistics Statistical tests Clinical
Overview Critical Literature Evaluation and Biostatistics Ahl Ashley N. Lewis, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Specialist, Drug Information UNC Hospitals Background Review of basic statistics Statistical tests Clinical
Carotid Imaging. Dr Andrew Farrall. Consultant Neuroradiologist
 20121123 SSCA http://www.neuroimage.co.uk/network Andrew Farrall Carotid Imaging Dr Andrew Farrall Consultant Neuroradiologist SFC Brain Imaging Research Centre (www.sbirc.ed.ac.uk), SINAPSE Collaboration
20121123 SSCA http://www.neuroimage.co.uk/network Andrew Farrall Carotid Imaging Dr Andrew Farrall Consultant Neuroradiologist SFC Brain Imaging Research Centre (www.sbirc.ed.ac.uk), SINAPSE Collaboration
