Nordic consensus on treatment of undescended testes
|
|
|
- Emerald Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Pædiatrica ISSN REVIEW ARTICLE Nordic consensus on treatment of undescended testes E. Martin Ritzén 1, A Bergh 2, R Bjerknes 3, P Christiansen 4, D Cortes 4,5, SE Haugen 6,NJörgensen 7, C Kollin 1, S Lindahl 8,GLäckgren 9, KM Main 7, A Nordenskjöld 1, E Rajpert-De Meyts 7,OSöder 1, S Taskinen 10, A Thorsson 11, J Thorup 5, J Toppari 12, H Virtanen 12 1.Department of Woman and Child Health, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden 2.Department of Pathology, University of Umeå, Umeå, Sweden 3.Department of Paediatrics, Haukeland University Hospital, Bergen, Norway 4.Department of Paediatrics, Glostrup University Hospital, Glostrup, Denmark 5.Department of Paediatric Surgery, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark 6.Section for Paediatric Surgery, St. Olav Hospital, Trondheim, Norway 7.Department of Growth and Reproduction, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark 8.Department of Anaesthesiology, Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden 9.Department of Paediatric Surgery, Akademiska Barnsjukhuset, Uppsala, Sweden 10.Hospital for Children and Adolescents, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland 11.Children s Hospital, Landspitali University Hospital, Reykjavik, Iceland 12.Departments of Paediatrics and Physiology, University of Turku, Turku, Finland Keywords Cryptorchidism, human, surgery, treatment, undescended testes Correspondence Prof. Martin Ritzén, Paediatric Endocrinology Unit, Karolinska Hospital Q2:08, Stockholm, Sweden. Tel: Fax: Martin.Ritzen@ki.se Received 20 October 2006; accepted 30 November 2006 DOI: /j x Abstract Aim: To reach consensus among specialists from the Nordic countries on the present state-of-the-art in treatment of undescended testicles. Methods: A group of specialists in testicular physiology, paediatric surgery/urology, endocrinology, andrology, pathology and anaesthesiology from all the Nordic countries met for two days. Before the meeting, reviews of the literature had been prepared by the participants. Recommendations: The group came to the following unanimous conclusions: (1) In general, hormonal treatment is not recommended, considering the poor immediate results and the possible long term adverse effects on spermatogenesis. Thus, surgery is to be preferred. (2) Orchiopexy should be done between 6 and 12 months of age, or upon diagnosis, if that occurs later. (3) Orchiopexy before age one year should only be done at centres with both paediatric surgeons/urologists and paediatric anaesthesiologists. (4) If a testis is found to be undescended at any age after 6 months, the patient should be referred for surgery to paediatric rather than general surgeons/urologists if the boy is less than one year old or if he has bilateral or non-palpable testes, or if he has got relapse of cryptorchidism. INTRODUCTION The optimal mode of treatment of undescended testes has been a matter of debate for decades. The problems in reaching consensus in the scientific community largely depends on the very long follow-up needed, from diagnosis and treatment in the neonate or in early childhood until full testicular function in adulthood. Randomized controlled studies are still lacking, comparing different modalities with each other until adulthood. However, over the last few years, thanks to research in the Nordic countries and elsewhere, enough data have been accumulated to allow preliminary conclusions on many of the most controversial issues. Therefore, a group of clinical scientists from the five Nordic countries decided to meet and define the present state of knowledge. This report is the condensed result of this meeting, where full consensus was reached. Five different literature reviews were also prepared, before the meeting. These are published as separate articles in this issue. The following invited participants were unable to attend, but have read and approved the text: L Dunkel, Department of Paediatrics, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland; NE Skakkebaek, Department of Growth and Reproduction, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark. The participants in the meeting that was held on August 22 24, 2006, in Sigtuna, Sweden, included experts in the field of testicular physiology, paediatric surgery, paediatric urology, paediatric endocrinology, andrology, pathology and anaesthesiology. PATHOGENESIS AND FUNCTIONAL CONSEQUENCES OF TESTICULAR MALDESCENT Normal testicular descent in humans requires the formation of a testis from an indifferent gonad, close to the kidney, at about 7 weeks of gestation. The descent of the testis into the scrotum starts with the transabdominal phase that lasts until week 15. The subsequent inguinoscrotal phase is completed by week 35. Numerous genetic and hormonal factors are involved in the regulation of normal testicular descent, but not all have been shown to be of relevance in the pathogenesis of human maldescent. The transabdominal phase is dependent on insulin-like peptide 3 (INSL3) and its receptor LGR8, whereas the inguinoscrotal phase is highly dependent on normal androgen production and action (reviewed in Ref. 1). In childhood, a secondary ascent of the testis from the scrotum may occur, the aetiology and consequences of which are yet unclear. This secondary 638 C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
2 Ritzén et al. Consensus on treatment of undescended testes ascent ( aquired cryptorchidism ) may explain why the accumulated orchiopexy rates are often higher than prevalence rates of congenital cryptorchidism in the same populations (2 4). Endocrine and genetic disorders can cause maldescent of the testis, but in the majority of cases no distinct aetiology can be determined. Any disturbance of normal testicular differentiation and function may compromise its normal descent. In unilateral cryptorchidism, the retained testis is most often smaller than its scrotal counterpart already at birth, suggesting prenatal testicular maldevelopment (5). In addition, changes caused by the malposition itself (e.g. increased testicular temperature) can add further damage. The more severe the testicular dysgenesis, the more severe the cryptorchidism. For example, individuals with gonadal dysgenesis frequently present with high intra-abdominal testes. Such patients often present with abnormal karyotype, e.g. 45X/46XY mosaicism. Mutations/polymorphisms of the gene for INSL3 and its receptor LGR8 seem to be rare causes of cryptorchidism in boys, even in studies of familial cryptorchidism (6). Insufficient androgen action, e.g. in the case of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, impaired Leydig cell function or androgen receptor mutations, is often associated with congenital cryptorchidism, as are malformations of the caudal body segment, such as spina bifida. There is also emerging suspicions that life style factors, such as maternal smoking during pregnancy (7) and environmental factors, such as endocrine disrupting chemicals (8,9) may contribute to some cases of undescended testis. Impairment of spermatogenesis is the major problem in undescended testes. Untreated bilateral cryptorchidism leads to azoospermia, which is possibly ameliorated by treatment. Treated unilateral cryptorchidism is not reported to affect fertility, although also in these patients sperm count is reduced (reviewed by 10,11). There is evidence that the age at orchiopexy matters for semen quality in adulthood, as the loss of germ cells becomes more pronounced the older the child is at surgery (12). In adult men, impaired spermatogenesis is often reflected by high FSH and low inhibin B. It is yet unresolved whether also Leydig cell function is compromised. Cryptorchidism is associated with a 4 5-fold higher risk of testicular cancer. These observations strongly indicate that in most cases cryptorchidism is caused by a primary testicular maldevelopment that occurred already in utero. However, testicular function deteriorates further if the testis is left in a position above the scrotum. DIAGNOSIS OF UNDESCENDED TESTIS The clearest classification system divides undescended testis into non-palpable and palpable testes. However, the latter need a more precise definition. We suggest the following criteria, using the middle of the testis as a reference for each position: (1) Suprascrotal including inguinal and non-palpable testes. (2) Upper portion of the scrotum or (3) Lower portion of the scrotum. If a testis spontaneously assumes a suprascrotal position and cannot be pulled down into the scrotum, it is diagnosed as an undescended testis, which needs treatment. The borderline cases, often called retractile testes, present the most difficult diagnostic dilemma. If the testis is in a suprascrotal position and can be pulled down to the upper scrotum, but does not remain there after exhausting the cremasteric activity, it is also defined as an undescended testis, and needs treatment. If it remains in the upper or lower scrotal position after the traction is released, the current recommendation is that these testes should not be subject to treatment. However, the patient should be followed at least once a year, due to the markedly increased risk of later ascent. Since some retractile testes may show a gradual histological deterioration and a reduction in volume, compared to the contralateral testis, treatment may be considered (13). In some rare cases, ectopic testes can be femoral or perineal and should be regarded and managed as undescended testes. In general, the position of the testes may change during childhood. Boys should get repeated examinations of the testicular position during childhood at the stipulated physical examinations done in child health care. Especially the boys with undescended testes at birth, with spontaneous descent during the first months of age, are at high risk of later reascent. RESULTS AND POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS OF TREATMENT Two principally different approaches to treatment of undescended testes have been used for many years: Surgery (orchiopexy) and hormonal treatment. The results of orchiopexy and the two modes of hormonal treatment (human gonadotropic hormone, hcg, gonadotropin releasing hormone, (hcg) GnRH, LHRH) will be shortly reviewed below. Surgical treatment The success rate of operative treatment, defined as a scrotal position of the testis, without atrophy, is related to the type of undescended testis (palpable and non-palpable), the choice of operative procedure and the age at the time of surgery. It is generally accepted that the possible surgical failures such as postoperative testicular atrophy and recurrent cryptorchidism cannot be estimated until follow-up at least one year postoperatively. In the analysis of 64 articles including 8425 undescended testicles, the anatomical success rate, in expert hands, varied between 74% for abdominal and 92% for testes located beyond the external ring (14). In the past decade, the corresponding success of orchiopexy for inguinal testes has been reported to be >95%. For abdominal testes, the reported success for orchiopexy has been >85 90% in most series with single stage orchiopexy or two stage Fowler-Stephens orchiopexy, both with open surgical or laparoscopic technique (15). However, having a palpable testis in the scrotum does not assure normal function. Normal function would entail normal hormone production and normal spermatogenesis. Generally, adult men with persistent bilateral C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
3 Consensus on treatment of undescended testes Ritzén et al. cryptorchidism have azoospermia, whereas after operation in childhood about 28% of patients with bilateral cryptorchidism have at least 20 millions sperms/ml of the ejaculate. In unilateral cases the dependency on proper treatment is not that strong, since about 50% of men with persistent unilateral cryptorchidism have at least 20 millions sperms/ml. as compared to about 70% after orchiopexy. Surgery significantly improved sperm count in uni- and bilateral cases, even if most patients in this study underwent orchiopexy after 2 years of age (12). The impact of orchiopexy on Sertoli cell function may be reflected by postoperative levels of serum inhibin B. In adulthood, higher levels of inhibin B were found in men who underwent orchiopexy before 2 years of age than in men with surgery at higher age (16). Orchiopexy in late childhood appears to be associated to impaired Leydig cell function in adulthood (17,18). The side-effects of surgery include pain, haematoma, infection, and the risk of anaesthetic complications. Testicular atrophy and damage of the vas deferens may also occur in rare cases, especially when performing surgery a second time (reviewed by Ref. 15). Hormonal treatment We found three meta-analyses of randomised trials concerning the effect of hormonal treatment on testicular descent (19 21). Most of the studies using hcg or LHRH show overall efficacy of about 20%, less if retractile testes were excluded. The efficacy depends on the initial position of the testes. The lower the position of the testis, the higher the rate of descent. However, after hormonal treatment, up to 25% of the testes reascend to a suprascrotal position later on (21). Hormonal treatment following orchiopexy has been proposed to have beneficial effects on sperm count (22,23). These findings need confirmation by other groups before being incorporated into clinical practice. Reported side effects of hormonal treatment include repeated pain at the injection site, growth of the penis, pubic hair, pain in the groin, erection pain, behavioural problems, temporary inflammatory changes in the testes, germ cell apoptosis and, importantly, reduction in the number of germ cells and the size of the testes in adulthood (24,25). The adverse effects of hormonal treatment may be agedependent, most harm being caused at 1 3 years of age (26). PREFERRED METHODS FOR TREATMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES Considering the efficacy and the possible side effects of the different treatment modalities described above, we find surgery to be the primary choice for most patients. The efficacy of hormonal treatment is poor, and several potential side effects after hcg-treatment in childhood have been described, including acute inflammatory changes in the testis and reduced testicular volume in adulthood. Despite these concerns, in rare special cases of undescended testes, hormonal treatment might be considered. We have not found enough evidence for a beneficial effect of hormonal treatment before or after surgery. RECOMMENDED SURGICAL TREATMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES Palpable undescended testes Today, the surgical therapy for the palpable undescended testis is orchiopexy with creation of a subdartos pouch. Transverse groin incision should be made over the internal ring. The external oblique aponeurosis is usually incised laterally from the external ring in the direction of its fibers, avoiding injury to the ilioinguinal nerve. Once located, the testis and spermatic cord are freed and notification of testis size, position and abnormalities should be done. The testis and hernia sac are dissected from the canal. Retroperitoneal dissection through the internal ring may provide additional cord length for the testis to reach the scrotum. A subdartos pouch is created (27). The Bianchi single high scrotal incision technique for orchiopexy in boys with palpable undescended testes distal to the external inguinal ring is an optional technique for many surgeons. The retroperitoneal dissection is however crucial for the success of both surgical procedures. Bilateral cases can be done in a one-stage procedure. Unilateral non-palpable undescended testis When the testis is non-palpable, diagnostic laparoscopy through an umbilical port is useful for determining which surgical approach should be taken. The operative procedure is chosen according to pathoanatomical findings related to the testis and vessels and to the surgeons preferences. Bilateral non-palpable undescended testes If both testes are missing and/or ambiguity of the sex assignment of the patient is raised, the patient is referred to the paediatric endocrinology unit immediately after birth for diagnostic work-up. Later laparoscopy is performed to determine surgical therapy in the same manner as for unilateral, nonpalpable undescended testes. Diagnostic ultrasound investigation has no value for management of the testis. Operation should preferentially be done at one side at a time in order to evaluate the operative result before proceeding to the contralateral side. Thus, in case of postoperative atrophy there is a possibility do minimal surgery on the other side, aiming at bringing the contralateral initially non-operated testis to a palpable position. Although spermatogenesis in this still suprascrotal testis may be compromised, it will hopefully have preserved hormonal production. Testicular biopsy Paediatric testicular biopsy during orchiopexy should only be performed in case of ambiguous genitalia, chromosomal disorders or as a part of clinical studies. OPTIMAL AGE FOR TREATMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES The optimal age for treatment should consider the final (adult) results on both spermatogenesis and hormone production, as well as risk for tumours. 640 C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
4 Ritzén et al. Consensus on treatment of undescended testes Spermatogenesis Few studies have assessed semen quality in relation to age at orchiopexy. Due to the variable previous treatment regimens, the age range at treatment is usually higher than in current recommendations. Orchiopexy in bilateral cryptorchidism led to a normal sperm count in 76% of the men if surgery was performed between 10 months and 3 years of age, compared to 26% (9 51%) following surgery between 4 and 14 years of age (28,29). These findings are supported by several animal studies demonstrating that earlier intervention preserves spermatogenesis and fertility. Animal studies cannot be translated directly into human medicine to determine optimal timing of operation, but a recent prospective randomised study shows that orchiopexy at age 9 months results in significantly larger testicular volume at age 4 years compared to orchiopexy at 3 years of age (30). Whether this difference will sustain until adulthood and result in improved spermatogenesis must await longer follow-up. Testicular endocrine function Whether or not early orchiopexy influences the altered endocrine function of the testis in adulthood remains unresolved. In bilateral cases the parents should also be advised, that the patient should undergo examination in early adolescence, to ensure normal pubertal masculinisation. Testicular cancer It remains to established whether orchiopexy at an early age, e.g. before 2 years of age, will decrease the risk of testicular cancer. The parents should be informed that the boy has an elevated risk of testicular cancer after puberty. Psychological aspects To our knowledge there are no specific studies addressing the impact of age of orchiopexy on the psychological outcome of cryptorchid patients. Although studies on the age of surgery of genitals in general suggest that operation should be avoided between 2 and 6 years of age (31), there are to our knowledge no documented psychological sequelae after orchiopexy at any age, provided that the parents and the child have been adequately informed about the procedure, and that general anaesthesia has been used. Furthermore, our recommendation is that surgery for congenital cryptorchidism should be performed before 1 year of age, if possible. Conclusions regarding age at operation Thus, there are no hard data on the optimal age of orchiopexy although many recent findings suggest that early intervention (<1 years of age) is most beneficial. Given the high rate of spontaneous descent during the first months of life, surgery of undescended testes diagnosed at birth should probably not be performed before 6 months of age. FACILITIES AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED FOR SURGICAL TREATMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES Ideally, all cases of undescended testes should be operated on by paediatric surgeons or paediatric urologists. However, in most countries and for the time being this is not realistic, but at least three minimal requirements have to be met to ensure patients safety: 1. Operation of congenital cryptorchidism at the recommended age of 6 12 months should be performed by paediatric surgeons or paediatric urologists. 2. All bilateral cases, non-palpable testes and re-do cases, irrespective of age, should also be performed by paediatric surgeons or paediatric urologists. 3. Paediatric anaesthesiologic expertise is required when operation is performed before the age of 1 year. When the boy is referred at a later age, palpable unilaterally undescended testes may be operated on by general surgeons and urologists with special interest and experience (31,32). PAEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA FOR INFANT ORCHIOPEXY Today the anaesthetic risk, even during infancy, is low (33 35). Patel and Hannalah have also demonstrated that outpatient surgery in infants and children is safe (36). These issues on patient safety are all statements from major centres with specialized paediatric anaesthesia services. The reasoning rests on the notion that the increased complexity in younger children, particularly under the age of 12 months, is more safely handled by an experienced paediatric anaesthesiologist than by an experienced general anaesthesiologist who is relatively inexperienced in paediatric anaesthesia and who usually performs in an environment that is not entirely dedicated to paediatrics. Some areas of paediatric surgery could be characterized as chirurgia minor. Anaesthesia minor does, however, not exist. The complication rate in infants is first comparable to the one that is found in patients 75 years and older (37). Hence, surgery in infants requires the anaesthetic to be administered at a medical centre with a specialized service for paediatric anaesthesia. Therefore, in the planning of surgery for un-descended testicles at the age of 6 12 months, the current patient safety records require that the anaesthesia must be carried out by specialists. Since this type of surgery is fairly common, proposed changes in guidelines and routines for surgical treatment of un-descended testicles, such as these, also ask for changes in patient flows putting higher quantitative and financial demands on paediatric centres. A compromise with regard to the requirement of specialist treatment is not to be recommended and will have an impact on patient safety. SUMMARY: SUGGESTED ROUTINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES AT THE PAEDIATRIC UNIT (See Fig. 1.) After diagnosis of congenital cryptorchidism in a newborn boy, he should be referred to a paediatric C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
5 Consensus on treatment of undescended testes Ritzén et al. Boys with undescended testes Undescended palpable testis, age >6 months Bilaterally nonpalpable testes Unilaterally nonpalpable testes Can be pulled into scrotum, remains there after traction is released Can be pulled into scrotum, but returns at once upon release. Refer for op. at 6-12 months 2 Cannot be pulled into scrotum. Refer for op. at 6-12 months 2 If combined with hypospadias or micropenis, refer immediately to DSD team 1 If penis is normal, refer for op. at 6-12 months 2 Refer for operation at 6-12 months 2 Retractile testis. Follow-up annually to detect later ascent Figure 1 Schematic representation of a decision tree that can be used for management of boys with undescended testes. See also text, for a more detailed discussion. surgeon/urologist not later than at 6 months of age. If the testis by then has descended into the scrotum, or if it is classified as retractile, the parents should be advised that annual follow-up will be needed throughout childhood, since there is a very significant risk for reascent. If the testis is not descended by 6 months of age the paediatric surgeon/urologist schedules orchiopexy before one year of age. If a testis is found to be undescended at any age after 6 months, the patient should be referred for surgery to paediatric surgeons/urologists if the boy is less than one year old or if he has bilateral or non-palpable testes, or if he has got relapse of cryptorchidism. Unilateral cases >1 year old may also be operated by other competent surgeons. 1 A DSD team should include experts with experience of management of children born with undetermined sex, including endocrinology, urology, gynaecology, medical genetics and child psychiatry. 2 Orchiopexy should ideally be made between 6 and 12 months of age. If the testis is found to be undescended at an older age, the boy should be referred as soon as the diagnosis is made. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The financial support by The Acta Paediatrica Foundation and The Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care is gratefully acknowledged. References 1. Hutson JM, Hasthorpe S. Testicular descent and cryptorchidism: the state of the art in J Pediatr Surg 2005; 40: John Radcliffe Hospital Cryptorchidism Study Group. Cryptorchidism: a prospective study of 7500 consecutive male births, Arch Dis Child 1992; 67: Toppari J, Kaleva M, Virtanen HE. Trends in the incidence of cryptorchidism and hypospadias, and methodological limitations of registry-based data. Hum Reprod Update 2001; 7: Thorup J, Cortes D. The incidence of maldescended testes in Denmark. Pediatr Surg Int 1990; 5: Kollin C, Hesser U, Ritzen EM, Karpe B. Testicular growth from birth to two years of age, and the effect of orchidopexy at age nine months: a randomized, controlled study. Acta Paediatr 2006; 95: C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
6 Ritzén et al. Consensus on treatment of undescended testes 6. Bogatcheva NV, Agoulnik AI. INSL3/LGR8 role in testicular descent and cryptorchidism. Reprod Biomed Online 2005; 10: Thorup J, Cortes D, Petersen BL. The incidence of bilateral cryptorchidism is increased and the fertility potential is reduced in sons born to mothers who have smoked during pregnancy. J Urol 2006; 176: Damgaard IN, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J, Virtanen HE, Shen H, Schramm KW, et al. Persistent pesticides in human breast milk and cryptorchidism. Environ Health Perspect 2006; 114: Swan SH, Main KM, Liu F, Stewart SL, Kruse RL, Calafat AM, et al. Decrease in anogenital distance among male infants with prenatal phthalate exposure. Environ Health Perspect 2005; 113: Lee PA. Fertility after cryptorchidism: epidemiology and other outcome studies. Urology 2005; 66: Virtanen HE, Cortes D, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Ritzen M, Nordenskjöld A, Skakkebaek NE, et al. Development and descent of the testis and cryptorchidism. Acta Paediatr in press. 12. Virtanen HE, Bjerknes R, Cortes D, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Thorsson A, Thorup J, et al. Cryptorchidism: classification, prevalence and long-term consequences. Acta Paediatr in press. 13. Ito H, Kataumi Z, Yanagi S, Kawamura K, Sumiya H, Fuse H, et al. Changes in the volume and histology of retractile testes in prepubertal boys. Int J Androl 1986; 9: Docimo SG. The results of surgical therapy for cryptorchidism: a literature review and analysis. J Urol 1995; 154: Taran I, Elder JS. Results of orchiopexy for the undescended testis. World J Urol 2006; 24: Coughlin MT, Bellinger MF, Lee PA. Age at unilateral orchiopexy: effect on hormone levels and sperm count in adulthood. J Urol 1999; 162: 986 8; discussion Lee PA, Coughlin MT. Leydig cell function after cryptorchidism: evidence of the beneficial result of early surgery. J Urol 2002; 167: Andersson AM, Jørgensen N, Frydelund-Larsen L, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek NE. Impaired Leydig cell function in infertile men: a study of 357 idiopathic infertile men and 318 proven fertile controls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: Pyörälä S, Huttunen NP, Uhari M. A review and meta-analysis of hormonal treatment of cryptorchidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995; 80: Henna MR, Del Nero RG, Sampaio CZ, Atallah AN, Schettini ST, Castro AA, et al. Hormonal cryptorchidism therapy: systematic review with metanalysis of randomized clinical trials. Pediatr Surg Int 2004; 20: Ong C, Hasthorpe S, Hutson JM. Germ cell development in the descended and cryptorchid testis and the effects of hormonal manipulation. Pediatr Surg Int 2005; 21: Hadziselimovic F, Herzog B. Treatment with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue after successful orchiopexy markedly improves the chance of fertility later in life. J Urol 1997; 158: Huff DS, Snyder HM, 3rd, Rusnack SL, Zderic SA, Carr MC, Canning DA. Hormonal therapy for the subfertility of cryptorchidism. Horm Res 2001; 55: Hjertkvist M, Lackgren G, Ploen L, Bergh A. Does HCG treatment induce inflammation-like changes in undescended testes in boys? J Pediatr Surg 1993; 28: Dunkel L, Taskinen S, Hovatta O, Tilly JL, Wikstrom S. Germ cell apoptosis after treatment of cryptorchidism with human chorionic gonadotropin is associated with impaired reproductive function in the adult. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: Cortes D, Thorup J, Visfeldt J. Hormonal treatment may harm the germ cells in 1 to 3-year-old boys with cryptorchidism. J Urol 2000; 163: Wallan EM, Shortliffe LMD. Undescended testis and testicular tumors. In:M. J. Ashcraft KW, Sharp RJ, Sigalet DL, Snyder CL, editors. Pediatric surgery. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, London, New York: WB Saunders Company, Taskinen S, Hovatta O, Wikstrom S. Early treatment of cryptorchidism, semen quality and testicular endocrinology. J Urol 1996; 156: Engeler DS, Hosli PO, John H, Bannwart F, Sulser T, Amin MB, et al. Early orchiopexy: prepubertal intratubular germ cell neoplasia and fertility outcome. Urology 2000; 56: Kollin C, Karpe B, Granholm K, Hesser U, Ritzén EM. Surgical treatment of undescended testes. Testicular growth after randomization to orchidopexy at 9 months or 3 years of age. J Urology 2007, in press. 31. Kass E, Kogan SJ, Manley C, Wacksman JA, Klykylo WM, Meza A, et al. Timing of elective surgery on the genitalia of male children with particular reference to the risks, benefits, and psychological effects of surgery and anesthesia. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics 1996; 97: Arul GS, Spicer RD. Where should paediatric surgery be performed? Arch Dis Child 1998; 79: 65 70; discussion Mayhew JF, Guiness WS. Cardiac arrest due to anesthesia in children. JAMA 1986; 256: Roy WL, Lerman J. Laryngospasm in paediatric anaesthesia. Can J Anaesth 1988; 35: Tiret L, Nivoche Y, Hatton F, Desmonts JM, Vourc h G. Complications related to anaesthesia in infants and children. A prospective survey of anaesthetics. Br J Anaesth 1988; 61: Patel RI, Hannallah RS. Anesthetic complications following pediatric ambulatory surgery: a 3-yr study. Anesthesiology 1988; 69: Nilsson K, Larsson L-E. Anestesi till barn. In:Halldin M.A.B. and Lindahl S.G.E., editors Anestesi. 2nd ed. Stockholm: Liber AB, 2005 (in Swedish). C 2007 The Author(s)/Journal Compilation C 2007 Foundation Acta Pædiatrica/Acta Pædiatrica , pp
7
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 9, September ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 9, September-2017 1031 Undescended Testicle Surgical Repair procedures, efficiency and outcomes, Review Authors: Nawal Swailem
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 9, September-2017 1031 Undescended Testicle Surgical Repair procedures, efficiency and outcomes, Review Authors: Nawal Swailem
Maldescended testis in Adults. Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Undescended testis varying presentation - Clinical research study
 Original Research Article Undescended testis varying presentation - Clinical research study S. C. Naren Kumar 1*, Bharathidasan 2, G. Ambujam 3 1 Postgraduate, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head
Original Research Article Undescended testis varying presentation - Clinical research study S. C. Naren Kumar 1*, Bharathidasan 2, G. Ambujam 3 1 Postgraduate, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head
Chapter 4.2. Acquired undescended testis: putting the pieces together. WWM Hack J Goede LM van der Voort-Doedens RW Meijer K Sijstermans
 Chapter 4.2 Acquired undescended testis: putting the pieces together WWM Hack J Goede LM van der Voort-Doedens RW Meijer K Sijstermans Int J Androl; 2011 Jun 9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01155.x. [Epub
Chapter 4.2 Acquired undescended testis: putting the pieces together WWM Hack J Goede LM van der Voort-Doedens RW Meijer K Sijstermans Int J Androl; 2011 Jun 9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01155.x. [Epub
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract -
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
Neoadjuvant human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hcg) therapy may improve the position of undescended testis: a preliminary report
 224 Original Paper PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Neoadjuvant human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hcg) therapy may improve the position of undescended testis: a preliminary report Piotr Kucharski, Jerzy Niedzielski Department
224 Original Paper PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Neoadjuvant human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hcg) therapy may improve the position of undescended testis: a preliminary report Piotr Kucharski, Jerzy Niedzielski Department
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Personal Practice. Cryptorchidism: What s New?
 Personal Practice Cryptorchidism: What s New? Anup Mohta Undescended testis (UDT), also known as cryptorchidism, is defined as a condition in which testis cannot be made to reach the bottom of the scrotum.
Personal Practice Cryptorchidism: What s New? Anup Mohta Undescended testis (UDT), also known as cryptorchidism, is defined as a condition in which testis cannot be made to reach the bottom of the scrotum.
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion
 Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Management of gonads in DSD
 Management of gonads in DSD Martine Cools, paediatric endocrinologist, Katja Wolffenbuttel and Piet Hoebeke, paediatric urologists, all at University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Sten Drop, paediatric endocrinologist
Management of gonads in DSD Martine Cools, paediatric endocrinologist, Katja Wolffenbuttel and Piet Hoebeke, paediatric urologists, all at University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Sten Drop, paediatric endocrinologist
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2
 MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
Your article is protected by copyright and all rights are held exclusively by Springer- Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. This e-offprint is for personal use
 1 23 Your article is protected by copyright and all rights are held exclusively by Springer- Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. This e-offprint is for personal use only and shall not be selfarchived in electronic
1 23 Your article is protected by copyright and all rights are held exclusively by Springer- Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. This e-offprint is for personal use only and shall not be selfarchived in electronic
The Developing Testis. Physiology and Pathophysiology
 The Developing Testis. Physiology and Pathophysiology Endocrine Development Vol. 5 Series Editor Martin O. Savage London The Developing Testis Physiology and Pathophysiology Volume Editor Olle Söder Stockholm
The Developing Testis. Physiology and Pathophysiology Endocrine Development Vol. 5 Series Editor Martin O. Savage London The Developing Testis Physiology and Pathophysiology Volume Editor Olle Söder Stockholm
Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.9.649 Pediatric Urology Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis Jae Jun Bae, Bum Soo Kim, Sung Kwang Chung Department of Urology, Kyungpook National
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.9.649 Pediatric Urology Long-Term Outcomes of Retractile Testis Jae Jun Bae, Bum Soo Kim, Sung Kwang Chung Department of Urology, Kyungpook National
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective Descriptive Study
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 878509, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/878509 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 878509, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/878509 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Management of Intra-Abdominal Testis: 5-Year Single-Centre Experience A Retrospective
Undescended Testicle
 What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
Prevalence and Pathological Features of Cryptorchidism among Iranian Children in Yazd Province, Central Iran
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 7615-7621) Prevalence and Pathological Features of Cryptorchidism among Iranian Children in Yazd Province, Central Iran Abdolhamid Amooei 1, *Saeid Kargar
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 7615-7621) Prevalence and Pathological Features of Cryptorchidism among Iranian Children in Yazd Province, Central Iran Abdolhamid Amooei 1, *Saeid Kargar
Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis
 www.kjurology.org DOI:1.4111/kju.21.51.2.16 Laparoscopy/Robotics Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis Jongwon Kim, Gyeong Eun Min 1, Kun Suk Kim Department of Urology, University of Ulsan College
www.kjurology.org DOI:1.4111/kju.21.51.2.16 Laparoscopy/Robotics Laparoscopic Orchiopexy for a Nonpalpable Testis Jongwon Kim, Gyeong Eun Min 1, Kun Suk Kim Department of Urology, University of Ulsan College
Epidemiology, Classification and Management of Undescended Testes: Does Medication Have Value in its Treatment?
 J Clin Res Pediatr En docrinol 2013;5(2):65-72 DO I: 10.4274/Jcrpe.883 Review Epidemiology, Classification and Management of Undescended Testes: Does Medication Have Value in its Treatment? Ayhan Abacı,
J Clin Res Pediatr En docrinol 2013;5(2):65-72 DO I: 10.4274/Jcrpe.883 Review Epidemiology, Classification and Management of Undescended Testes: Does Medication Have Value in its Treatment? Ayhan Abacı,
Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testicle
 Acta chir belg, 2005, 105, 662-666 Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testicle N. Satar, Y. Bayazıt, Ş. Doran Çukurova University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Urology, Balcalı Hospital,
Acta chir belg, 2005, 105, 662-666 Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testicle N. Satar, Y. Bayazıt, Ş. Doran Çukurova University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Urology, Balcalı Hospital,
PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA
 PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA Dr. Abdulrahman A. Al-Bassam, FRCS(Ed) Assistant Professor & Consultant Paediatric Surgeon King Khalid University Hospital
PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA Dr. Abdulrahman A. Al-Bassam, FRCS(Ed) Assistant Professor & Consultant Paediatric Surgeon King Khalid University Hospital
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, A. (2014). Testing the undescended testis General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, A. (2014). Testing the undescended testis General
Single Scrotal Incision Orchiopexy for Children with Palpable Low-Lying Undescended Testis: Early Outcome of a Prospective Randomized Controlled Study
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/0.4/kju.20.52.9.637 Pediatric Urology Single Scrotal Incision Orchiopexy for Children with Palpable LowLying Undescended Testis: Early Outcome of a Prospective Randomized
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/0.4/kju.20.52.9.637 Pediatric Urology Single Scrotal Incision Orchiopexy for Children with Palpable LowLying Undescended Testis: Early Outcome of a Prospective Randomized
Comparison of penile length at 6 24 months between children with unilateral cryptorchidism and a healthy normal cohort
 Original Article - Pediatric Urology Investig Clin Urol 2018;59:55-60. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Comparison of penile length at 6 24 months between children with unilateral cryptorchidism and a healthy
Original Article - Pediatric Urology Investig Clin Urol 2018;59:55-60. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Comparison of penile length at 6 24 months between children with unilateral cryptorchidism and a healthy
Management of undescended testis may be improved with educational updates and new transferring model
 Yi et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:58 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-018-0499-4 RESEARCH Open Access Management of undescended testis may be improved with educational updates and new transferring
Yi et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018) 44:58 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-018-0499-4 RESEARCH Open Access Management of undescended testis may be improved with educational updates and new transferring
Different surgical findings in congenital and acquired undescended testes
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Different surgical findings in congenital and acquired undescended testes Jocelyn van Brakel, Gert R. Dohle, Sabine M.P.F. de Muinck Keizer-Schrama * and Frans W. Hazebroek Urology,
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Different surgical findings in congenital and acquired undescended testes Jocelyn van Brakel, Gert R. Dohle, Sabine M.P.F. de Muinck Keizer-Schrama * and Frans W. Hazebroek Urology,
Role of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Hormone in Undescended Testis a Prospective Study in 100 Children
 Role of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Hormone in Undescended Testis a Prospective Study in 100 Children BA CHEECHAK 1 MY WANI 2 A HUSSAIN 3 G HASSAN 4 This is a prospective study of 100 children (122
Role of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Hormone in Undescended Testis a Prospective Study in 100 Children BA CHEECHAK 1 MY WANI 2 A HUSSAIN 3 G HASSAN 4 This is a prospective study of 100 children (122
Cryptorchidism and its impact on male fertility: a state of art review of current literature. Case 1
 CASE REPORT Cryptorchidism and its impact on male fertility: a state of art review of current literature Eric Chung, MBBS, FRACS; Gerald B. Brock, MD, FRCSC Division of Urology, University of Western Ontario,
CASE REPORT Cryptorchidism and its impact on male fertility: a state of art review of current literature Eric Chung, MBBS, FRACS; Gerald B. Brock, MD, FRCSC Division of Urology, University of Western Ontario,
Commissioning guide:
 2014 Commissioning guide: Paediatric orchidopexy for undescended testis Funded by Sponsoring Organisation: British Association of Paediatric Surgeons Date of evidence search: February 2014 Date of publication:
2014 Commissioning guide: Paediatric orchidopexy for undescended testis Funded by Sponsoring Organisation: British Association of Paediatric Surgeons Date of evidence search: February 2014 Date of publication:
Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Cryptorchidism in Adults: A Single Center Experience
 pissn: 8748 / eissn: 87469 World J Mens Health 4 August (): 5 http://dx.doi.org/.554/wjmh.4... Original Article Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Cryptorchidism in Adults: A Single Center Experience
pissn: 8748 / eissn: 87469 World J Mens Health 4 August (): 5 http://dx.doi.org/.554/wjmh.4... Original Article Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Cryptorchidism in Adults: A Single Center Experience
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole
 The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole A SHAH 1 AV SHAH 2 Of the various modalities for management of impalpable undescended testis, the use of laparoscopy or keyhole surgery is being widely
The Impalpable Testicle Peeping Through the Key Hole A SHAH 1 AV SHAH 2 Of the various modalities for management of impalpable undescended testis, the use of laparoscopy or keyhole surgery is being widely
Different aspects of congenital undescended testis
 Different aspects of congenital undescended testis chapter : DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF CONGENITAL UNDESCENDED TESTIS Synopsis: In this chapter the surgical aspects of congenital undescended testis, as found
Different aspects of congenital undescended testis chapter : DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF CONGENITAL UNDESCENDED TESTIS Synopsis: In this chapter the surgical aspects of congenital undescended testis, as found
Laparoscopic Management of Cryptorchidism in Adults
 European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 453 457 Laparoscopy Laparoscopic Management of Cryptorchidism in Adults R. Kucheria, A. Sahai, T.A. Sami, B. Challacombe, H. Godbole, M.S. Khan, P. Dasgupta*
European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 453 457 Laparoscopy Laparoscopic Management of Cryptorchidism in Adults R. Kucheria, A. Sahai, T.A. Sami, B. Challacombe, H. Godbole, M.S. Khan, P. Dasgupta*
16:30-18:30 WS #52: Paediatric Forum (120mins - not repeated)
 Dr Kate Gibson Clinical Geneticist Genetic Health Service NZ, Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch Dr Antony Bedggood Ophthalmologist Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch
Dr Kate Gibson Clinical Geneticist Genetic Health Service NZ, Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch Dr Antony Bedggood Ophthalmologist Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch
American Urological Association (AUA) Guideline
 1 Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2014 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article. 2014 by the American Urological
1 Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2014 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article. 2014 by the American Urological
Review Article Single Port Laparoscopic Orchidopexy in Children Using Surgical Glove Port and Conventional Rigid Instruments
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS PAEDIATRICS Review Article Single Port Laparoscopic Orchidopexy in Children Using Surgical Glove Port and Conventional Rigid Instruments BEN DHAOU Mahdi 1, CHTOUROU Rahma 1 *, JALLOULI
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS PAEDIATRICS Review Article Single Port Laparoscopic Orchidopexy in Children Using Surgical Glove Port and Conventional Rigid Instruments BEN DHAOU Mahdi 1, CHTOUROU Rahma 1 *, JALLOULI
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing
 Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
DEVELOPMENT (DSD) 1 4 DISORDERS OF SEX
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele
 Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
Age at Surgery for Undescended Testis and Risk of Testicular Cancer
 original article Age at Surgery for Undescended Testis and Risk of Testicular Cancer Andreas Pettersson, M.D., Lorenzo Richiardi, M.D., Ph.D., Agneta Nordenskjold, M.D., Ph.D., Magnus Kaijser, M.D., Ph.D.,
original article Age at Surgery for Undescended Testis and Risk of Testicular Cancer Andreas Pettersson, M.D., Lorenzo Richiardi, M.D., Ph.D., Agneta Nordenskjold, M.D., Ph.D., Magnus Kaijser, M.D., Ph.D.,
Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion.
 LAPAROSCOPIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ORCHIDOPEXY MEDICAL JOURNAL Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion. Saad Dakhil F ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: With the use of diagnostic laparoscopy widely accepted
LAPAROSCOPIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ORCHIDOPEXY MEDICAL JOURNAL Laparoscopic Orchidopexy: Current Surgical Opinion. Saad Dakhil F ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: With the use of diagnostic laparoscopy widely accepted
Descent of the Testis
 Descent of the Testis John M. Hutson Jørgen M. Thorup Spencer W. Beasley Descent of the Testis Second Edition John M. Hutson Royal Children s Hospital University of Melbourne Parkville, Victoria Australia
Descent of the Testis John M. Hutson Jørgen M. Thorup Spencer W. Beasley Descent of the Testis Second Edition John M. Hutson Royal Children s Hospital University of Melbourne Parkville, Victoria Australia
U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon,
 Delayed Treatment of Cryptorchidisnt with Subsequent Infertility L. STUART SCOTT, M.D., CH.M., F.R.C.S. (EDIN.), F.R.C.S. (GLAsc.) U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon, inevitably
Delayed Treatment of Cryptorchidisnt with Subsequent Infertility L. STUART SCOTT, M.D., CH.M., F.R.C.S. (EDIN.), F.R.C.S. (GLAsc.) U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon, inevitably
DAX1, testes development role 7, 8 DFFRY, spermatogenesis role 49 DMRT genes, male sex differentiation role 15
 Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
What s not! Imaging i.e CT scan, Sonography to localize testes. Find testes with imaging= surgery/orchiopexy
 What s Hot and What s Not in Pediatric Urology Undescended Testes Laurence Baskin, UCSF Children s Hospital Early Surgery MRI in UDT Obesity to localize Testes Bilateral Disease Non-Palpable Testes Refer
What s Hot and What s Not in Pediatric Urology Undescended Testes Laurence Baskin, UCSF Children s Hospital Early Surgery MRI in UDT Obesity to localize Testes Bilateral Disease Non-Palpable Testes Refer
Surgical Presentations in Children
 From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Surgery and Anesthesia
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Timing of Elective Surgery on the Genitalia of Male Children With Particular Reference to the Risks, Benefits, and Psychological Effects of Surgery and Anesthesia Section
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Timing of Elective Surgery on the Genitalia of Male Children With Particular Reference to the Risks, Benefits, and Psychological Effects of Surgery and Anesthesia Section
Management of undescended testes: European Association of Urology/European Society for Paediatric Urology Guidelines
 Accepted Manuscript Management of undescended testes: European Association of Urology/European Society for Paediatric Urology Guidelines Christian Radmayr, Hasan S. Dogan, Piet Hoebeke, Radim Kocvara,
Accepted Manuscript Management of undescended testes: European Association of Urology/European Society for Paediatric Urology Guidelines Christian Radmayr, Hasan S. Dogan, Piet Hoebeke, Radim Kocvara,
Current management of non-palpable testes: a literature review and clinical results
 Review Article Current management of non-palpable testes: a literature review and clinical results Ximena Sepúlveda 1, Pedro-José López Egaña 2,3,4 1 Department of Pediatric Surgery, University of Valparaíso,
Review Article Current management of non-palpable testes: a literature review and clinical results Ximena Sepúlveda 1, Pedro-José López Egaña 2,3,4 1 Department of Pediatric Surgery, University of Valparaíso,
Interventions for undescended testes in children(protocol)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Interventions for undescended testes in children(protocol) Deshpande AV, Michail P, Smith GH Deshpande AV, Michail P, Smith GH. Interventions for undescended testes
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Interventions for undescended testes in children(protocol) Deshpande AV, Michail P, Smith GH Deshpande AV, Michail P, Smith GH. Interventions for undescended testes
Disclosure. Session Objectives. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation.
 46, XY Female: A Case of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (CAIS) MICHELLE MCLOUGHLINMSN, CRNP, CPNP-AC THE CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND DIABETES Disclosure
46, XY Female: A Case of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (CAIS) MICHELLE MCLOUGHLINMSN, CRNP, CPNP-AC THE CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND DIABETES Disclosure
Natural history and long-term testicular growth of acquired undescended testis after spontaneous descent or pubertal orchidopexy
 Chapter 4.1 Natural history and long-term testicular growth of acquired undescended testis after spontaneous descent or pubertal orchidopexy WWM Hack LM van der Voort-Doedens J Goede JM van Dijk RW Meijer
Chapter 4.1 Natural history and long-term testicular growth of acquired undescended testis after spontaneous descent or pubertal orchidopexy WWM Hack LM van der Voort-Doedens J Goede JM van Dijk RW Meijer
Use of Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testis in Children
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2009;14:172-176 Use of Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testis in Children PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, BPY WONG, WK KWOK, KKW LIU Abstract Key words Purpose: To
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2009;14:172-176 Use of Laparoscopy in the Management of Impalpable Testis in Children PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, BPY WONG, WK KWOK, KKW LIU Abstract Key words Purpose: To
Sensitive and vulnerable risks groups in relation to chemical risk assessment and management
 International Research and Research Training Centre Sensitive and vulnerable risks groups in relation to chemical risk assessment and management Niels E. Skakkebaek Department of Growth and Reproduction
International Research and Research Training Centre Sensitive and vulnerable risks groups in relation to chemical risk assessment and management Niels E. Skakkebaek Department of Growth and Reproduction
Semen Quality in Infertile Men with a History of Unilateral Cryptorchidism
 Journal of Reproduction & Contraception (2004) 15 (3):139-143 Semen Quality in Infertile Men with a History of Unilateral Cryptorchidism P. Tzvetkova 1, Wei-Jie ZHU 2, D. Tzvetkov 3 1. Department of Immunoneuroendocrinology,
Journal of Reproduction & Contraception (2004) 15 (3):139-143 Semen Quality in Infertile Men with a History of Unilateral Cryptorchidism P. Tzvetkova 1, Wei-Jie ZHU 2, D. Tzvetkov 3 1. Department of Immunoneuroendocrinology,
Single scrotal incision orchiopexy - a systematic review
 REVIEW Article Vol. 39 (3): 305-311, May - June, 2013 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.03.02 Single incision orchiopexy - a systematic review Hugo Fabiano Fernandes Novaes, José Abraão Carneiro Neto,
REVIEW Article Vol. 39 (3): 305-311, May - June, 2013 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.03.02 Single incision orchiopexy - a systematic review Hugo Fabiano Fernandes Novaes, José Abraão Carneiro Neto,
Surgical Sperm Retrieval
 Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Information for Patients Surgical Sperm Retrieval About one man in a hundred produces no sperm (10-15% of all sub fertile men) - a condition known
Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Information for Patients Surgical Sperm Retrieval About one man in a hundred produces no sperm (10-15% of all sub fertile men) - a condition known
Laparoscopy for the management of impalpable testis Basem El-Nabulsi *, Samer Karadsheh, Mohmad Dajja, Wasim Mofleh and Mohmad Zaid Abu Risha
 bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Basem El-Nabulsi *, Samer Karadsheh, Mohmad Dajja, Wasim Mofleh and Mohmad Zaid Abu Risha Abstract Background: Cryptorchidism is encountered in 21% of preterm infants, 2-4% of all full
bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Basem El-Nabulsi *, Samer Karadsheh, Mohmad Dajja, Wasim Mofleh and Mohmad Zaid Abu Risha Abstract Background: Cryptorchidism is encountered in 21% of preterm infants, 2-4% of all full
Information for Patients. Male infertility. English
 Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism
 Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism Frank Hinman, Jr., M.D. THE RESULTS of orchiopexy are disappointing. Is it that the surgical procedure is faulty, or can the defect be in the patient or in
Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism Frank Hinman, Jr., M.D. THE RESULTS of orchiopexy are disappointing. Is it that the surgical procedure is faulty, or can the defect be in the patient or in
/03/ /0 Vol. 170, , December, 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY
 0022-5347/03/1706-2396/0 Vol. 170, 2396 2401, December, 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000095793.04232.d8 Review Article
0022-5347/03/1706-2396/0 Vol. 170, 2396 2401, December, 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000095793.04232.d8 Review Article
Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10):
 Title46XX male; report of case OKUYAMA, Akihiko; KONDO, Nobuyuki; Author(s) NAKAMURA, Masahiro; SONODA, Takao; Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10): 1539-1542 Issue Date 1986-10 URL
Title46XX male; report of case OKUYAMA, Akihiko; KONDO, Nobuyuki; Author(s) NAKAMURA, Masahiro; SONODA, Takao; Yutaka; SAKAMOTO, Hiromi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1986), 32(10): 1539-1542 Issue Date 1986-10 URL
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood
 When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Reasons for Delayed Orchiopexies in a Korean Tertiary Care Hospital
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.1.69 Original Article - Pediatric Urology http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.1.69&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-1-17 Reasons
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.1.69 Original Article - Pediatric Urology http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.1.69&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-1-17 Reasons
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except
 1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
Abstract. Introduction. RBMOnline - Vol 19. No Reproductive BioMedicine Online; on web 12 October 2009
 RBMOnline - Vol 19. No 6. 2009 778 783 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/4178 on web 12 October 2009 Article Does age at orchidopexy impact on the results of testicular sperm extraction?
RBMOnline - Vol 19. No 6. 2009 778 783 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/4178 on web 12 October 2009 Article Does age at orchidopexy impact on the results of testicular sperm extraction?
Laparoscopic Orchidopexy without Division of Spermatic Vessels using a Neoinguinal Canal Approach: A Single Center Experience
 WJOLS 10.5005/jp-journals-10007-1196 Laparoscopic Orchidopexy without Division of Spermatic Vessels using a Neoinguinal Canal Approach ORIGINAL ARTICLE Laparoscopic Orchidopexy without Division of Spermatic
WJOLS 10.5005/jp-journals-10007-1196 Laparoscopic Orchidopexy without Division of Spermatic Vessels using a Neoinguinal Canal Approach ORIGINAL ARTICLE Laparoscopic Orchidopexy without Division of Spermatic
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA. Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK. Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Sonographic localization of nonpalpable testis: Tracking the cord technique
 Abdominal and Pelvic Radiology Sonographic localization of nonpalpable testis: Tracking the cord technique S Boopathy Vijayaraghavan Sonoscan, Ultrasonic Scan Centre, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India Correspondence:
Abdominal and Pelvic Radiology Sonographic localization of nonpalpable testis: Tracking the cord technique S Boopathy Vijayaraghavan Sonoscan, Ultrasonic Scan Centre, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India Correspondence:
The Role of Testicular Volume in Adolescents With Varicocele: The Better Way and Time of Surgical Treatment
 The Role of Testicular Volume in Adolescents With Varicocele: The Better Way and Time of Surgical Treatment Claudio Spinelli, Martina Di Giacomo, Roberto Lo Piccolo, Alessandra Martin and Antonio Messineo
The Role of Testicular Volume in Adolescents With Varicocele: The Better Way and Time of Surgical Treatment Claudio Spinelli, Martina Di Giacomo, Roberto Lo Piccolo, Alessandra Martin and Antonio Messineo
Cancer and Fertility Ashley Munchel, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Maryland Medical Center
 Cancer and Fertility Ashley Munchel, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Maryland Medical Center Trends in Pediatric Cancer Incidence Rates by Site, Ages Birth to 19 Years, 1975 to 2010.
Cancer and Fertility Ashley Munchel, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Maryland Medical Center Trends in Pediatric Cancer Incidence Rates by Site, Ages Birth to 19 Years, 1975 to 2010.
Postnatal penile length and growth rate correlate to serum testosterone levels: a longitudinal study of 1962 normal boys
 European Journal of Endocrinology (00) 1 1 19 ISSN 080- CLINICAL STUDY Postnatal penile length and growth rate correlate to serum testosterone levels: a longitudinal study of 19 normal boys Malene Boas,
European Journal of Endocrinology (00) 1 1 19 ISSN 080- CLINICAL STUDY Postnatal penile length and growth rate correlate to serum testosterone levels: a longitudinal study of 19 normal boys Malene Boas,
Plasma testosterone response at 1 st and 4 th day after shortand long-term hcg stimulation test
 ---> The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 309-314 Original Plasma testosterone at 1 st and 4 th day after shortand long-term hcg stimulation test Pelin Adýyaman, Gönül Öcal, Merih Berberoðlu, Zehra
---> The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 309-314 Original Plasma testosterone at 1 st and 4 th day after shortand long-term hcg stimulation test Pelin Adýyaman, Gönül Öcal, Merih Berberoðlu, Zehra
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, A. (2014). Testing the undescended testis General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Testing the undescended testis de Vries, Annebeth Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, A. (2014). Testing the undescended testis General
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX
 DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
Paediatric Urology. EAU Guidelines on
 EAU Guidelines on Paediatric Urology S. Tekgül (Chair), H.S. Dogan, R. Kocvara, J.M. Nijman (Vice-chair), C. Radmayr, R. Stein Guidelines Associates: M.S. Silay, S. Undre, J. Quaedackers European Society
EAU Guidelines on Paediatric Urology S. Tekgül (Chair), H.S. Dogan, R. Kocvara, J.M. Nijman (Vice-chair), C. Radmayr, R. Stein Guidelines Associates: M.S. Silay, S. Undre, J. Quaedackers European Society
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL CRYPTORCHIDISM: A PRELIMINARY REPORT*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1970 by the Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 21, No. 11, November 1970 Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1970 by the Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 21, No. 11, November 1970 Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL
Undescended testis current trends and guidelines: a review of the literature
 State of the art paper Undescended testis current trends and guidelines: a review of the literature Jerzy K. Niedzielski 1, Elżbieta Oszukowska 2, Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer 3 1 Department of Pediatric
State of the art paper Undescended testis current trends and guidelines: a review of the literature Jerzy K. Niedzielski 1, Elżbieta Oszukowska 2, Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer 3 1 Department of Pediatric
Reproductive FSH. Analyte Information
 Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
What are Varicoceles?
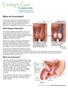 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
Cryptorchidism concordance in monozygotic and dizygotic twin brothers, full brothers, and half-brothers
 MALE FACTOR Cryptorchidism concordance in monozygotic and dizygotic twin brothers, full brothers, and half-brothers Morten Søndergaard Jensen, M.D., a,b Gunnar Toft, Ph.D., a Ane Marie Thulstrup, Ph.D.,
MALE FACTOR Cryptorchidism concordance in monozygotic and dizygotic twin brothers, full brothers, and half-brothers Morten Søndergaard Jensen, M.D., a,b Gunnar Toft, Ph.D., a Ane Marie Thulstrup, Ph.D.,
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM
 EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Limited text update March 2017) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Limited text update March 2017) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
Endocrine disrupters a role in human health?
 9 In: Endocrine Disrupters T. Grotmol, A. Bernhoft, G.S. Eriksen and T.P. Flaten, eds. Oslo: The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, 2006. Endocrine disrupters a role in human health? Erik Dybing
9 In: Endocrine Disrupters T. Grotmol, A. Bernhoft, G.S. Eriksen and T.P. Flaten, eds. Oslo: The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, 2006. Endocrine disrupters a role in human health? Erik Dybing
Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
Testosterone Therapy-Male Infertility
 Testosterone Therapy-Male Infertility Testosterone Therapy-Male Infertility Many men are prescribed testosterone for a variety of reasons. Low testosterone levels (Low T) with no symptoms, general symptoms
Testosterone Therapy-Male Infertility Testosterone Therapy-Male Infertility Many men are prescribed testosterone for a variety of reasons. Low testosterone levels (Low T) with no symptoms, general symptoms
