Content. Course (LV 21246): Fr. 12:00-14:00 16 Lectures
|
|
|
- Briana Harris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Content Course (LV 21246): Fr. 12:00-14:00 16 Lectures Content 1: Overview Occurrence of carbohydrates in nature Glycopolymers and glycoconjugates Carbohydrates in animals Carbohydrates in bacteria and fungi Carbohydrates in plants 2: Carbohydrate synthesis and analysis Synthesis of complex oligosaccharides Synthesis of rare carbohydrates Carbohydrates as key building blocks in the total synthesis of natural products Analysis and characterization of carbohydrates by NMR, MS and other analytical methods
2 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
3 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
4 Enzymes
5 Proteases - Proteases catalyze the hydrolysis of amide bonds in peptides and proteins. - Proteases are used in industry (e.g. laundry detergents, bread improvers), medicine and as a basic biological research tool. - Serine, threonine and cysteine proteases use a nucleophilic residue in a (usually in a catalytic triad).
6 JM Berg, JL Tymockzo, L Stryer, Biochemistry 6th Ed. Catalytic Triade in Proteases
7 Glycocalix - The glycocalix consists of the carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins and glycolipids and covers the surface of cells Rutledge et al., Nature Rev. Neph. 2010, 361.
8 Common Classes of Animal Glycans Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 1, Figure 6
9 Carbohydrate-Modifying Enzymes Glycosyltransferases Enzyme + Glycosidases Enzyme + H 2 O + Other carbohydrate modifying enzymes (e.g. Epimerases) Enzyme
10 Synthesis of Sugar Nucleotides Enzymatic synthesis of sugar nucleotides Enzyme Glycosyltransferase Examples of activated sugar nucleotides UDP-Glucose GDP-Fucose CMP-Neuraminic acid
11 Chemical Synthesis of Sugar Nucleotides Chemical synthesis of sugar monophosphates Chemical synthesis of sugar nucleotides Field et al., Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 1172.
12 Biosynthesis and Interconversion of Monosaccharides Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 4, Figure 1
13 Carbohydrate-Modifying Enzymes Glycosyltransferases Enzyme + Glycosidases Enzyme + H 2 O +
14 Enzymatic Mechanism in Glycosyl Transfer and Hydrolysis Glycosyltransferases + Enzyme Glycosidases Enzyme + H 2 O +
15 Mechanism of Retaining Glycosyltransferases
16 Catalytic site of Bovine β1-4 Galactosyltransferase Inverting glycosyltransferase Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 5, Figure 8
17 Mechanism of Inverting and Retaining Glycosidases Retaining Transition state Inverting Kren et al., Trends in Biotechnology 2009, 199.
18 Glycosidase Inhibitors
19 Tom Wennekes, UBC Neuraminidase
20 Carbohydrate-Modifying Enzymes Glycosyltransferases Enzyme + Glycosidases Enzyme + H 2 O + Other carbohydrate modifying enzymes (e.g. Epimerases) Enzyme
21 Biosynthesis of UDP-Apiose and dtdp-dihydrostreptose Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 4 Figure 3
22 Nomenclature of the Consortium of Functional Glycomics
23 Common Classes of Animal Glycans (Glycoproteins) Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 1, Figure 6
24 Protein Glycosylation - There are two types of protein glycosylation: N-glycosylation and O-glycosylation
25 - The three main types of N-glycans N-Glycans
26 N-Glycans - Different species have different types of N-glycans
27 Animal Cell
28 Synthesis of Dolichol-P-P-GlcNAc 2 Man 9 Glc 3 Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 8, Figure 3
29 Processing and Maturation of an N-Glycan Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 8, Figure 4
30 Consensus Sequence for N-Glycosylation
31 Protein Glycosylation - There are two main types of protein glycosylation: N-glycosylation and O-glycosylation
32 Trends in Microbiology, Volume 20, Issue 1, 2012, 30. O-Glycans
33 Blood Group Antigens
34 Animal Cell
35 Biosynthesis of Core 1 and 2 O-GalNAc Glycans Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 9, Figure 3
36 Mucin 1 Glycosylation
37 Common Classes of Animal Glycans (GAGs) Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 1, Figure 6
38 Occurrence of Proteoglycans
39 Occurrence of Proteoglycans (Extracellular Matrix) Proteoglycan Collagen Hyaluronic acid
40 Biosynthesis of Heparan Sulfate Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 16, Figure 7
41 Common Classes of Animal Glycans (Glycolipids) Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 1, Figure 6
42 Glycolipids Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 10, Figure 1
43 Biosynthesis of Glycosphingolipids Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 10, Figure 2
44 Biosynthesis of Glycosphingolipids
45 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
46 Last Week - The glycocalix is a layer composed of oligo- and polysaccharides that surrounds all cells. - The oligo- and polysaccharides are synthesized by the action of carbohydrate-modifying enzymes (glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, epimerases, etc.). - Glycosyltransferases catalyze the reaction of sugar nucleotide donors (eg UDP-glucose) with glycosyl acceptors. - Glycosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds. - There are different types of oligo- and polysaccharides attached to proteins: N-glycans, O-glycans and glycosaminoglycans (proteoglycans). - N-Glycans are always attached to an asparagine of the protein backbone via a GlcNAc monosaccharide and O-Glycans to serine or threonine via a GalNAc. - N-Glycans are attached to proteins in the endoplasmatic reticulum as a conserved precursor (from lipid-conjugate) and further elaborated in the Golgi apparatus. O- Glycans are attached and elaborated in the Golgi (also glycans of glycolipids)
47 Last Week Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 13, Figure 1
48 Common Classes of Animal Glycans (GPI-Anchors) Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 1, Figure 6
49 GPI-Anchored Proteins
50 GPI-Anchored Proteins
51 Biosynthesis of GPI-Anchored Proteins
52 Bacteria
53 Bacteria
54 Bacteria - A pilus is a hairlike appendage found on the surface of many bacteria. Pili are primarily composed of oligomeric pilin proteins and important for the attachment of bacteria to host cells. - The bacterial flagellum is made up of the protein flagellin. They are helical filaments, each with a rotary motor at its base which can turn clockwise or counterclockwise. The rotary motor provides bacterial mobility.
55 Bacterial Adhesion Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 39, Figure 3
56 Bacteria Gram-negative Gram-positive
57 Gram-negative Bacteria
58 Cell wall of Gram-Negative Bacteria Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 20, Figure 1
59 Exemplary LPS-Structure
60 Biosynthesis of LPS
61 Capsular Polysaccharides
62 Biosynthesis of Capsular Polysaccharides Bentley SD, Aanensen DM, Mavroidi A, Saunders D, et al. (2006) Genetic Analysis of the Capsular Biosynthetic Locus from All 90 Pneumococcal Serotypes. PLoS Genet 2(3): e31. doi: /journal.pgen
63 Gram-positive Bacteria
64 Cell Wall of Gram-positive Bacteria Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 20, Figure 2
65 van Heijenoort J Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011;75: Structure of Peptidoglycan
66 Biosynthesis of Peptidoglycan Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 20, Figure 4
67 Antibiotic Vancomycin
68 Inhibition of Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis by Antibiotics
69 Griffey R H et al. PNAS 1999;96: Aminoglycosides
70 Aminoglycoside Mode of Action - Aminoglycosides are active against gram-negative bacteria - Aminoglycosides bind to RNA in the Ribosome and inhibit protein synthesis
71 Fungal Cell Wall Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 21, Figure 1
72 Biosynthesis of Fungal Cell Walls
73 O-Glycans in Fungi Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 21, Figure 3
74 Plant Cell Wall
75 Cellulose Microfibrils
76 Biosynthesis of Cellulose Bashline L et al. Ann Bot 2014;aob.mcu040 The Author Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Annals of Botany Company. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com
77 Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis
78 Xylan Biosynthesis Glucuronoarabinoxylan UDP-GlcA UDP-Xyl UDP-Ara
79 Harholt et al., Plant Physiol Pectin
80 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
81 Glycolysis
82 Glycolysis
83 Glycolysis Overall reaction Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 P i + NAD + 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + NADH Reaction sequence
84 Glycolysis
85 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
86 Enzymatic Synthesis of Oligosaccharides
87 Expression of Proteins in Bacteria Affinity purification: His-Tag:
88 Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycopeptides
89 Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycopeptides
90 Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycopeptides
91 Enzymatic Synthesis of N-Glycans Isolierung aus Eigelb Asn Sialidase Asn
92 Enzymatic Synthesis of N-Glycans
93 Purification by Size-Exclusion Chromatography
94 Enzymatic Synthesis of O-Glycans
95 Enzymatic Synthesis of O-Glycans
96 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
97 Last Week - While in vertebrates only 9 different monosaccharides are present, bacterial glycans contain many different and also rare monosaccharides. - Bacteria can be devided into two classes: gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. - Characteristic for gram-positive bacteria is a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall. Characteristic for gram-negative bacteria is an outer coat composed of lipopolysaccharide - The enzymatic machinery for glycan synthesis can be used for preparative oligosaccharide synthesis. Usually glcosyltransferases and glycosidases are employed to produce the oligosaccharide of choice. - The enzymatic reactions for elongation of glycans are performed by mixing the oligosaccharide acceptor with the respective sugar nucleotide donor and the glycosyltransferase in buffer. - The products of the enzymatic reactions can be purified either by reversed-phase HPLC or by size-exclusion chromatography.
98 Enzymatic Synthesis of Carbohydrates Expression of recombinant enzyme in bacteria, yeast, or mammalian cell lines Purification by affinity chromatography Enzymatic synthesis (sugar 1-phosphate + UTP) Chemical synthesis (sugar 1-phosphate + activated UMP) Enzymatic synthesis Chemical synthesis Isolation and purification
99 Enzymatic Synthesis of Carbohydrates
100 Chemo-Enzymatic Synthesis of Asymmetrical N-Glycans Wang et al., Science 2013, 341,
101 Chemo-Enzymatic Synthesis of Asymmetric N-Glycans Wang et al., Science 2013, 341,
102 Biosynthesis of Capsular Polysaccharides Bentley SD, Aanensen DM, Mavroidi A, Saunders D, et al. (2006) Genetic Analysis of the Capsular Biosynthetic Locus from All 90 Pneumococcal Serotypes. PLoS Genet 2(3): e31. doi: /journal.pgen
103 Enzymatic Synthesis of a Bacterial Antigen nature chemical biology vol 6 june
104 Occurrence of Proteoglycans
105 Biosynthesis of Heparan Sulfate Essentials of Glycobiology Second Edition Chapter 16, Figure 7
106 Enzymatic Sulfation of Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharides
107 Glycosynthases
108 Glycosynthases Enzymatic synthesis of Xylo-oligosaccharides Enzymatic synthesis of Xyloglucan-oligosaccharides
109 Enzymatic Synthesis of Polysaccharides
110 Sialic acid
111 Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, Sialic acid
112 Overview: Enzymatic Oligosaccharide Synthesis
113 Content 3: Enzymatic reactions with carbohydrates Biosynthesis of carbohydrates Glycolysis Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides (application of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases) Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering 4: General methods in Glycobiology Evaluation of carbohydrate-protein interactions using carbohydrate microarrays, ELISA, SPR, and STD-NMR 5: Carbohydrates in Immunology Lectins and anti-carbohydrate antibodies Carbohydrate-based vaccines
114 Molecular Imaging
115 Metabolic Glycan Engineering
116 Design and synthesis of Cu-free click chemistry reagents Baskin J M et al. PNAS 2007;104:
117 Metabolic labeling with Azide-Modified Monosaccharides
118 Metabolic Labeling of Sialic Acid
119 Metabolic Labeling of Cells
120 Metabolic Labeling in Zebrafish Laughlin S T, and Bertozzi C R PNAS 2009;106:12-17
121 Metabolic Labeling of Bacterial Polysaccharides Yi W et al. PNAS 2009;106:
122 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1 5 Metabolic Labeling of Bacterial Polysaccharides
123 Metabolic Labeling of Plant Polysaccharides
What sort of Science is Glycoscience? (Introductory lecture)
 Glycosciences: Glycobiology & Glycochemistry e-learning course What sort of Science is Glycoscience? (Introductory lecture) Paula Videira Faculdade de Ciências Médicas Nova University, Lisbon Portugal
Glycosciences: Glycobiology & Glycochemistry e-learning course What sort of Science is Glycoscience? (Introductory lecture) Paula Videira Faculdade de Ciências Médicas Nova University, Lisbon Portugal
Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates. Bacterial Cell Walls
 Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
189,311, , ,561, ,639, ,679, Ch13; , Carbohydrates
 Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units
 Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains a ketone functionality
 RCT Chapter 7 Aldoses and Ketoses; Representative monosaccharides. (a)two trioses, an aldose and a ketose. The carbonyl group in each is shaded. An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains
RCT Chapter 7 Aldoses and Ketoses; Representative monosaccharides. (a)two trioses, an aldose and a ketose. The carbonyl group in each is shaded. An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains
Abdullah zurayqat. Bahaa Najjar. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Abdullah zurayqat Bahaa Najjar Mamoun Ahram Polysaccharides Polysaccharides Definition and Structure [Greek poly = many; sacchar = sugar] are complex carbohydrates, composed of 10 to up to several thousand
9 Abdullah zurayqat Bahaa Najjar Mamoun Ahram Polysaccharides Polysaccharides Definition and Structure [Greek poly = many; sacchar = sugar] are complex carbohydrates, composed of 10 to up to several thousand
Glycoproteins and Mucins. B.Sopko
 Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Biosynthesis of N and O Glycans
 TechNote #TNGL101 Biosynthesis of N and O Glycans These suggestions and data are based on information we believe to be reliable. They are offered in good faith, but without guarantee, as conditions and
TechNote #TNGL101 Biosynthesis of N and O Glycans These suggestions and data are based on information we believe to be reliable. They are offered in good faith, but without guarantee, as conditions and
Chapter 11. Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins.
 Chapter 11 Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins. Carbohydrates Fuels Structural components Coating of cells Part of extracellular matrix
Chapter 11 Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins. Carbohydrates Fuels Structural components Coating of cells Part of extracellular matrix
Session Date Instructors Topic
 Session Date Instructors Topic Lect CC 1/11 Tiemeyer/Wells Introduction and course overview 1/13 Wells Carbohydrate structures monosaccharides and the glycosidic bond 1/18 Bar-Peled Nucleotide sugar donors
Session Date Instructors Topic Lect CC 1/11 Tiemeyer/Wells Introduction and course overview 1/13 Wells Carbohydrate structures monosaccharides and the glycosidic bond 1/18 Bar-Peled Nucleotide sugar donors
Glycobiology 8130, 18/1/2005 Spring 2005
 Glycobiology 8130, 18/1/2005 Spring 2005 Nucleotide-sugar donors. Maor Bar-Peled, CCRC; Plant Biology Peled@ccrc.uga.edu ISTRY 1906 arden and Young- discovered that yeast fermented with sugar accumulate
Glycobiology 8130, 18/1/2005 Spring 2005 Nucleotide-sugar donors. Maor Bar-Peled, CCRC; Plant Biology Peled@ccrc.uga.edu ISTRY 1906 arden and Young- discovered that yeast fermented with sugar accumulate
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, and Glycoproteins
 Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, and Glycoproteins Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy I. OVERVIEW OF GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS
Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, and Glycoproteins Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy I. OVERVIEW OF GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Determination of a Second Substitution, [alpha]-glycerophosphate, Common to C311 Pilins
![Determination of a Second Substitution, [alpha]-glycerophosphate, Common to C311 Pilins Determination of a Second Substitution, [alpha]-glycerophosphate, Common to C311 Pilins](/thumbs/82/86025176.jpg) Non-S-Layer Glycoproteins: A Review Introduction p. 1 Flagellar Glycoproteins p. 2 Bacteria p. 2 Archaeal Flagella p. 5 Glycosylated Flagellar Proteins: What Are the Sugar Chains For? p. 7 Glycoproteins
Non-S-Layer Glycoproteins: A Review Introduction p. 1 Flagellar Glycoproteins p. 2 Bacteria p. 2 Archaeal Flagella p. 5 Glycosylated Flagellar Proteins: What Are the Sugar Chains For? p. 7 Glycoproteins
All cells are assembled from four building blocks: nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates or GLYCANS.
 All cells are assembled from four building blocks: nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates or GLYCANS. Glycans are biopolymers characterized by a significant diversity responsible for many biological
All cells are assembled from four building blocks: nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates or GLYCANS. Glycans are biopolymers characterized by a significant diversity responsible for many biological
Nucleotide-activated sugars
 2 Donor substrates Monosaccharides are chemically inert molecules, thus they need to be activated to high-energy donor substrates for glycosyltransferase reactions. Typically, phosphate is used as reactive
2 Donor substrates Monosaccharides are chemically inert molecules, thus they need to be activated to high-energy donor substrates for glycosyltransferase reactions. Typically, phosphate is used as reactive
The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group
 The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group Sugars attached to glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surfaces of red blood cells determine the blood group termed A, B, and O. The A and B antigens
The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group Sugars attached to glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surfaces of red blood cells determine the blood group termed A, B, and O. The A and B antigens
189,311, , ,561, ,639, ,679, Ch13; , Carbohydrates. Oligosaccharides: Determination of Sequence
 Lecture (2//7) Reading: Chs4,6,8,0,4,6,7,8; 28-29, 89,,77-80,555-557,56,62-622,69,662-66,679, 69-694 Ch; 497-50, 507-54 Problems: Ch (text); 5,6,9,0,22,24 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 4 Ch7 (study-guide:
Lecture (2//7) Reading: Chs4,6,8,0,4,6,7,8; 28-29, 89,,77-80,555-557,56,62-622,69,662-66,679, 69-694 Ch; 497-50, 507-54 Problems: Ch (text); 5,6,9,0,22,24 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 4 Ch7 (study-guide:
Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1)
 14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
i. II. Alpha-L-Ribose Aldose i. III. Beta-D-Mannose Aldose i. IV. Beta-L-Fructose Ketose
 BMB170, Fall 2017 Problem Set 5: Carbohydrates Due: 12/01/2017 by 5pm, as PDF. OH: 11/30, 3:00-5:00PM, Broad Café Please email questions and PDF files to Jingzhou Wang (jingzhou@caltech.edu) Problem 1:
BMB170, Fall 2017 Problem Set 5: Carbohydrates Due: 12/01/2017 by 5pm, as PDF. OH: 11/30, 3:00-5:00PM, Broad Café Please email questions and PDF files to Jingzhou Wang (jingzhou@caltech.edu) Problem 1:
4. If a GT uses a one-step mechanism it is retaining or inverting? 5. Name: Gal GlcNAc Neu5Gc Xyl GlcA
 Primer 1. The 4-epimer of Glucose once it is 2-N-acetylated is called? 2. If the SNFG shape of a monosaccharide is a diamond it is an? 3. Which of the 11 common mammalian monosaccharides is: a) a pentose?
Primer 1. The 4-epimer of Glucose once it is 2-N-acetylated is called? 2. If the SNFG shape of a monosaccharide is a diamond it is an? 3. Which of the 11 common mammalian monosaccharides is: a) a pentose?
-can be classified by the number of sugars that constitute the molecules: -how to differentiate between glucose and galactose?
 Carbohydrates (Also called: saccharides) -can be classified by the number of sugars that constitute the molecules: 1- monosaccharides: -General formula: (CH2O)n -Contain one sugar molecule -Contain two
Carbohydrates (Also called: saccharides) -can be classified by the number of sugars that constitute the molecules: 1- monosaccharides: -General formula: (CH2O)n -Contain one sugar molecule -Contain two
DEPARTMENT: Chemistry
 CODE: CHEM-236 TITLE: Biochemistry Institute: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: Upon completion of this course the student will be able to recognize and draw the structure and state the nature
CODE: CHEM-236 TITLE: Biochemistry Institute: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: Upon completion of this course the student will be able to recognize and draw the structure and state the nature
Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life
 Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life Classification Serve as energy stores, fuels, and metabolic intermediates
Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life Classification Serve as energy stores, fuels, and metabolic intermediates
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Carbohydrates. Learning Objective
 , one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
, one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Stability of polysaccharides against degradation and the techniques used to assess their molecular integrity
 Stability of polysaccharides against degradation and the techniques used to assess their molecular integrity Stability studies of polysaccharides turned out to be of huge practical importance. They improved
Stability of polysaccharides against degradation and the techniques used to assess their molecular integrity Stability studies of polysaccharides turned out to be of huge practical importance. They improved
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T MOL.911. Cell Engineering. u
 1 W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T MOL.911 Cell Engineering u www.tugraz.at MOL.911 Molecular Biotechnology I 2 Cell Engineering General strategies: Knock out of specific genes - Gene
1 W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T MOL.911 Cell Engineering u www.tugraz.at MOL.911 Molecular Biotechnology I 2 Cell Engineering General strategies: Knock out of specific genes - Gene
Protein regulation Protein motion
 Lecture 13 Protein regulation Protein motion Antoine van Oijen BCMP201 Spring 2008 04/02 Section IV 04/09 Hands-on methods session / PS 4 due 1 Today s lecture 1) Mechanisms of protein regulation 2) Molecular
Lecture 13 Protein regulation Protein motion Antoine van Oijen BCMP201 Spring 2008 04/02 Section IV 04/09 Hands-on methods session / PS 4 due 1 Today s lecture 1) Mechanisms of protein regulation 2) Molecular
Mechanisms of Enzymes
 Mechanisms of Enzymes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy How enzymes work * Chemical reactions have an energy
Mechanisms of Enzymes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy How enzymes work * Chemical reactions have an energy
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology CARBOHYDRATE CHEMISTRY. By Hussein Abdelaziz
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology CARBOHYDRATE CHEMISTRY 2 By Hussein Abdelaziz Disaccharides Disaccharides consist of two sugars joined by an O-glycosidic bond. The most abundant disaccharides
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology CARBOHYDRATE CHEMISTRY 2 By Hussein Abdelaziz Disaccharides Disaccharides consist of two sugars joined by an O-glycosidic bond. The most abundant disaccharides
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college
 A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O
 BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
Chemical and biological approaches to glycoprotein synthesis Roslyn M Bill and Sabine L Flitsch2
 Crosstalk 145 Chemical and biological approaches to glycoprotein synthesis Roslyn M Bill and Sabine L Flitsch2 Protein glycosylation is a common posttranslational modification that produces glycoproteins
Crosstalk 145 Chemical and biological approaches to glycoprotein synthesis Roslyn M Bill and Sabine L Flitsch2 Protein glycosylation is a common posttranslational modification that produces glycoproteins
51 Demetria M. Dickinson, Jian Liu, and Robert J. Linhardt
 Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Heparins 51 Demetria M. Dickinson, Jian Liu, and Robert J. Linhardt Contents Introduction... 420 Principles... 420 Synthetic Methods... 421 Strategy... 421 Acceptors... 421
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Heparins 51 Demetria M. Dickinson, Jian Liu, and Robert J. Linhardt Contents Introduction... 420 Principles... 420 Synthetic Methods... 421 Strategy... 421 Acceptors... 421
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet
 Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist
 Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Chapter 10. 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation)
 Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Sheet #8 Dr. Nafeth Abu-Tarboush
 1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
Chapter 1. Chemistry of Life - Advanced TABLE 1.2: title
 Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. Ser/Thr. Ser/Thr. Ser/Thr. Ser/Thr. Ser/Thr. Asn. Asn. Asn. Asn. Asn. Asn
 A. B. C. D. E. F. "3 "3!4!3 Ser/Thr "3!4!3!4 Asn Asn Ser/Thr Asn!3!6 Ser/Thr G. H. I. J. K.!3 Ser/Thr Ser/Thr 4 4 2 2 6 3 6 Asn Asn Asn Glycosidases and Glycosyltransferases Introduction to Inverting/Retaining
A. B. C. D. E. F. "3 "3!4!3 Ser/Thr "3!4!3!4 Asn Asn Ser/Thr Asn!3!6 Ser/Thr G. H. I. J. K.!3 Ser/Thr Ser/Thr 4 4 2 2 6 3 6 Asn Asn Asn Glycosidases and Glycosyltransferases Introduction to Inverting/Retaining
UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES
 UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES OUTLINE 4.1. Introduction. 4.2. Classification. 4.3. Monosaccharides. Classification. Stereoisomers. Cyclic structures. Reducing sugars. Sugar derivatives 4.4. Oligosaccharides. Disaccharides.
UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES OUTLINE 4.1. Introduction. 4.2. Classification. 4.3. Monosaccharides. Classification. Stereoisomers. Cyclic structures. Reducing sugars. Sugar derivatives 4.4. Oligosaccharides. Disaccharides.
An Introduction to Carbohydrates
 An Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Monosaccharides also known as simple sugars, are the simplest carbohydrates containing
An Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Monosaccharides also known as simple sugars, are the simplest carbohydrates containing
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
GLYCAN STRUCTURES, CLUES TO THE ORIGIN OF SACCHARIDES
 GLYCAN STRUCTURES, CLUES TO THE ORIGIN OF SACCHARIDES Jun Hirabayashi Department of Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Teikyo University Sagamiko, Kanagawa 199-0195, Japan Tel: 0426-85-3741
GLYCAN STRUCTURES, CLUES TO THE ORIGIN OF SACCHARIDES Jun Hirabayashi Department of Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Teikyo University Sagamiko, Kanagawa 199-0195, Japan Tel: 0426-85-3741
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function
 Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
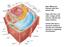 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function
 Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
The pentose phosphate pathway
 The pentose phosphate pathway Metabolism of fructose and galactose The uronic acid pathway The synthesis of amino sugars and glycosyl donors in glycoprotein synthesis Biochemistry I Lecture 5 2008 (J.S.)
The pentose phosphate pathway Metabolism of fructose and galactose The uronic acid pathway The synthesis of amino sugars and glycosyl donors in glycoprotein synthesis Biochemistry I Lecture 5 2008 (J.S.)
Chemical Biology of Protein O-Glycosylation
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Chemistry & Biochemistry Graduate Theses & Dissertations Chemistry & Biochemistry Spring 1-1-2016 Chemical Biology of Protein O-Glycosylation Patrick Chaffey
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Chemistry & Biochemistry Graduate Theses & Dissertations Chemistry & Biochemistry Spring 1-1-2016 Chemical Biology of Protein O-Glycosylation Patrick Chaffey
biological mechanisms Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis Bacillus anthracis vaccine development
 http://www.microbio.uab.edu/ Bacteriology at UAB Streptococcus pneumoniae Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bacillus anthracis Mycoplasma biological mechanisms virulence factors pathogenesis vaccine development
http://www.microbio.uab.edu/ Bacteriology at UAB Streptococcus pneumoniae Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bacillus anthracis Mycoplasma biological mechanisms virulence factors pathogenesis vaccine development
A. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule. B. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Bacterial Cell Structures. Stijn van der Veen
 Bacterial Cell Structures Stijn van der Veen How do I know what bacterium makes my patient ill? Bacterial species can be differentiated by: Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures)
Bacterial Cell Structures Stijn van der Veen How do I know what bacterium makes my patient ill? Bacterial species can be differentiated by: Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures)
ME 411 / ME 511. Biological Frameworks for Engineers
 ME 411 / ME 511 Biological Frameworks for Engineers Class Organization HW 1 due on Friday HW 2 available online Grad project available online What are Cells? Sea Urchin Mouse Seaweed Robert Hooke Prokaryotic
ME 411 / ME 511 Biological Frameworks for Engineers Class Organization HW 1 due on Friday HW 2 available online Grad project available online What are Cells? Sea Urchin Mouse Seaweed Robert Hooke Prokaryotic
Glycans linked to lipids and lipid precursors
 Glycobiology BCMB 8130 Clinical Correlations! -sign up for 1st and 2nd choice (1/2)! *********************************! Glycosylation in Diabetes! O-Mannosylation in Human Pathophysiology! Glycoconjugate
Glycobiology BCMB 8130 Clinical Correlations! -sign up for 1st and 2nd choice (1/2)! *********************************! Glycosylation in Diabetes! O-Mannosylation in Human Pathophysiology! Glycoconjugate
Chemical Composition of the Cell. B. Balen
 Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
An Introduction to Carbohydrates
 An Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Monosaccharides also known as simple sugars, are the simplest carbohydrates containing
An Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Monosaccharides also known as simple sugars, are the simplest carbohydrates containing
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Glycobiology
 Examination Candidate Number: This paper has two parts: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 3 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Glycobiology Time allowed: 2 hours Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: This paper has two parts: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 3 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Glycobiology Time allowed: 2 hours Total marks available
Ch. 9 - Carbohydrates & Glycobiology. 3 major size classes. Carbon atoms attached to -OH groups often chiral centers. Monosaccharides & Disaccharides
 Ch. 9 - Carbohydrates & Glycobiology Mono- and disaccharid es (simple su gar s) Oligosacc har ides (inf orm ationa l molecu les) Polysaccharides (ergy stores, cell structures) Glycoconjuga tes Proteoglycans
Ch. 9 - Carbohydrates & Glycobiology Mono- and disaccharid es (simple su gar s) Oligosacc har ides (inf orm ationa l molecu les) Polysaccharides (ergy stores, cell structures) Glycoconjuga tes Proteoglycans
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE
 DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2012-13 BC 3200 STRUCTURE & CATALYSIS INSTRUCTOR: Philip Johnson PHONE: 780-539-2863 OFFICE: J224 E-MAIL: PJohnson@gprc.ab.ca OFFICE HOURS: Mondays 1000-1120
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2012-13 BC 3200 STRUCTURE & CATALYSIS INSTRUCTOR: Philip Johnson PHONE: 780-539-2863 OFFICE: J224 E-MAIL: PJohnson@gprc.ab.ca OFFICE HOURS: Mondays 1000-1120
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Carbohydrate Chemistry
 Carbohydrate Chemistry edited by Geert-Jan Boons University of Birmingham Birmingham UK m BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Weinheim New York * Tokyo Melbourne Madras
Carbohydrate Chemistry edited by Geert-Jan Boons University of Birmingham Birmingham UK m BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hall London Weinheim New York * Tokyo Melbourne Madras
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM
 CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Molecules
 Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
Review of Biochemistry
 Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Carbohydrates. What are they? What do cells do with carbs? Where do carbs come from? O) n. Formula = (CH 2
 Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
3. When he discovered enzymes in 1897, Eduard Buchner was investigating the causes of. disease antisepsis spontaneous generation fermentation
 Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
LIVING SYSTEMS APPEAR COMPLEX BUT THERE IS AN UNDERLYING SIMPLICITY AND ELEGANCE:
 CHM333 LECTURE 1: 8/26/09 FALL 2009 Professor Christine Hrycyna What is Biochemistry? Simplest definition: Chemistry of the living cell Uses basic laws of chemistry, biology and physics to explain processes
CHM333 LECTURE 1: 8/26/09 FALL 2009 Professor Christine Hrycyna What is Biochemistry? Simplest definition: Chemistry of the living cell Uses basic laws of chemistry, biology and physics to explain processes
Carbohydrates- Chapter 10
 Carbohydrates are the major recognition molecules in many cellcell interaction events in nature Varki (2007) Nature 446, 1023-1029 Fig. 10.26 Lymphocytes adhering to lymph node Fig. 10.17 Carbohydrates-
Carbohydrates are the major recognition molecules in many cellcell interaction events in nature Varki (2007) Nature 446, 1023-1029 Fig. 10.26 Lymphocytes adhering to lymph node Fig. 10.17 Carbohydrates-
Contents. Contributors...xi. Preface...xv. 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1
 Contents Contributors...xi Preface...xv 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure... 2 1.2.1 Molecular Structure... 2 1.2.2 Hydrogen Bonding...
Contents Contributors...xi Preface...xv 1 Configurations, Structures and Morphologies of Cellulose... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure... 2 1.2.1 Molecular Structure... 2 1.2.2 Hydrogen Bonding...
Chemical Energy. Valencia College
 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. R 2 GlcNAcβ1 4GlcNAcβ1 Asn
 GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
Structural features. Figure 2 Chirality of glyceraldehyde compared to the internal symmetry of the ketotriose dihydroxyacetone.
 1 Structural features As defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry glycans are structures of multiple monosaccharides linked through glycosidic bonds. The terms sugar and saccharide
1 Structural features As defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry glycans are structures of multiple monosaccharides linked through glycosidic bonds. The terms sugar and saccharide
Module 1. Introduction. Microbial Physiology
 Module 1 Introduction to Microbial Physiology Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGY Page 2 Last time * Discussed the central dogma of molecular biology * Look at, in detail, the process of replication,
Module 1 Introduction to Microbial Physiology Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGY Page 2 Last time * Discussed the central dogma of molecular biology * Look at, in detail, the process of replication,
Biological Sciences B. CHEM. ENGG. Part 1. Chemicals of life: Water, Amino acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids. Dr. Ratnesh Jain
 Biological Sciences B. CHEM. ENGG. Part 1. Chemicals of life: Water, Amino acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids Dr. Ratnesh Jain The Foundations Content Cellular Foundations Chemical Foundations Physical Foundations
Biological Sciences B. CHEM. ENGG. Part 1. Chemicals of life: Water, Amino acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids Dr. Ratnesh Jain The Foundations Content Cellular Foundations Chemical Foundations Physical Foundations
Carbohydrates. Prof. Ramune Morkuniene
 Carbohydrates Prof. Ramune Morkuniene Topics Monosaccharides and their derivatives Disaccharides. Lactose intolerance Carbohydrate sweeteners. Artificial sweeteners Blood type and monosaccharides Important
Carbohydrates Prof. Ramune Morkuniene Topics Monosaccharides and their derivatives Disaccharides. Lactose intolerance Carbohydrate sweeteners. Artificial sweeteners Blood type and monosaccharides Important
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
ILOs. 10/10/2016 Maha Fathy 2
 ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Tarek Khrisat
 1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
TRANSPORT PROCESSES. 1b. moving proteins into membranes and organelles
 1b. moving proteins into membranes and organelles SLIDE 1 A typical mammalian cell contains up to 10,000 different kinds of proteins. The vast majority of these proteins are synthesized by cytosolic ribosomes,
1b. moving proteins into membranes and organelles SLIDE 1 A typical mammalian cell contains up to 10,000 different kinds of proteins. The vast majority of these proteins are synthesized by cytosolic ribosomes,
Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11
 Name: Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11 Total: 100 points Be sure to include units where appropriate. Show all calculations. There are 5 pages and 11 questions. 1.(20pts)A. If ph = 4.6, [H + ] =
Name: Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11 Total: 100 points Be sure to include units where appropriate. Show all calculations. There are 5 pages and 11 questions. 1.(20pts)A. If ph = 4.6, [H + ] =
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz )
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins
 Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
Office number.
 The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacy Program: Pharmacy Academic Year/ Fall Semester: 2014/15 BIOCHEMISTRY 2 [1203253] Credit hours 3 Level 2 nd
The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacy Program: Pharmacy Academic Year/ Fall Semester: 2014/15 BIOCHEMISTRY 2 [1203253] Credit hours 3 Level 2 nd
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
