DEVELOPMENTAL AND BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF IMIDACLOPRID ON CHICK EMBRYOS
|
|
|
- Dina Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Anat. Sciences, 22(2): Dec. 2014, Original Article DEVELOPMENTAL AND BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF IMIDACLOPRID ON CHICK EMBRYOS Muktyaz Hussein*, Vishram Singh**, Prerna Gupta***, Birendra Yadav****, A.K.Singh* *Department of Anatomy, Govt. Medical College Ambedkar Nagar. **Department of Anatomy, Santosh Medical College Ghaziabad ***Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Lucknow ****Department of Physiology, Govt. Medical College Ambedkar Nagar ABSTRACT Introduction: Environmental pollution is a worldwide problem in a modern society. The extensive uses of pesticides are widely used to enhance the crop production and other bene ts and have raised concerns about potential adverse effects on the environment, human health and nontarget animals. Imidacloprid is one of the major representatives of the new generation of neonicotinoid insecticides derived from nicotine isolated from the tobacco plant. Imidacloprid is a widely applied pesticide due to their higher af nity for insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, it acts on nervous system. Worldwide, it is considered to be one of the insecticides used in the largest volume. Methods: Present study was carried out in the department of Anatomy Govt. Medical College, Ambedkar Nagar and Santosh Medical College Ghaziabad U.P. on 270 fertile eggs of white leghorn chicken obtained from government poultry farm after taking permission from animal ethical committee. Chicken eggs exposed to Imidacloprid with doses of 12.5µg, 25µg, and 50µg in a volume of 12.5µl, 25µl and 50µl respectively and control same as test group. The embryos were terminated on 21st day, egg shell broken with a scalpel and embryos removed. Biochemical and developmental changes observed and recorded. Results: The results show that experimental group had comparatively more cases of developmental changes, growth retardation resulting into failure of retraction of yolk sac, limbs defects, and Ectopia Viscerale and biochemical changes as compared to controls. Conclusion: Imidacloprid exposure increases the risks of developmental defects and biochemical parameters alterations with increasing embryonic age. Comparatively higher doses proved more toxic and also caused many developmental defects in chick embryos. Keywords: Imidacloprid, chick embryos, developmental and biochemical effects. INTRODUCTION Imidacloprid (IMI) is one of the major representatives of the new generation of neonicotinoid insecticide have outstanding potency and systemic action for crop protection against piercing-sucking pests, and they are highly effective for ea control. It is one of the fastest sold insecticides across the world because of its high selective toxicity in insects and apparent safety in humans. It was patented for the rst time in 1985 by Bayer and was placed on the market in Imidacloprid is a systemic chloro-nicitnyl insecticide. It was the rst member of a new family, the neonicotinoids, and is chemically related to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agaonists nicotine and epibatidine. Imidacloprid was discovered in 1984 at Nihon Bayer Agrochem in Japan by screening novel synthetic compounds for a high af nity to the insect nicotinic AChRs receptors, but with low toxicity to 1 vertebrate species reported by Kagabu. Imidacloprid interacts with the acetylcholine receptor, which is 2 widely conserved across species. Environmental Pollution, when considered in its broadest context, is a by-product of human activities and its signi cance is in what ways it affects directly or indirectly the living population. In the past few years the agricultural production has been enormously enhanced by the use of many synthetic pesticides. Although, their application is based on selective toxicity for certain organisms yet it has resulted in serious effects on many non-target organisms as well. The use of pesticides has created a type of chemical environment which is proving harmful to the living systems. Global pesticide use is increasing, particularly in third world countries. India uses approximately 85,000 tons of pesticides per annum and an 8% increase in pesticide use is expected every year. As the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) de ned, pesticide is any substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest, including vectors of human or animal disease or weed which can cause harm during or otherwise interfering with the production, processing, storage, transport or marketing of food, agricultural commodities, wood and wood products or 3 animal feedstuffs. The current study was designed to study the developmental and biochemical effects of imidacloprid on chick embryos. Address for Correspondence: Dr Muktyaz Hussein Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy, Govt. Medical College Ambedkar Nagar, U.P. India. muktyazmukky@gmail.com Contact No:
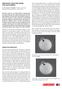
2 Muktyaz Hussein, Vishram Singh, Prerna Gupta, Birendra Yadav, A.K.Singh MATERIALS AND METHODS The present study was designed to assess the effect of Imidacloprid on chick embryos in the department of Anatomy Govt. Medical College, Ambedkar Nagar and Santosh Medical College Ghaziabad U.P. on 270 fertile eggs of white leghorn chicken weighing between 40 to 50 gm obtained from the government poultry farm after taking permission from animal ethical committee. Eggs from stock known to be nutritionally healthy were taken. Eggs were rst candled in the order to discard the defective ones and to outline the exact location of the air cell with a pencil. All the eggs were thoroughly washed with soap water solution and incubated immediately in standard electrical digital incubator with their broad end up where the chorioallantoic membrane is situated. The thermostat of the incubator will be set at temperature of 38 C in a humidity inside the chamber will be maintain at percent with no additional CO2 or O2 and the eggs were tilted three times a day. Method for Injection of Imidacloprid in chick embryos on 2nd day: Eggs will be candled on 2nd day to discard unfertilized eggs prior to injection. Eggs were divided into three groups A, B and C. Each group has 45 eggs each. Control same as test group treated with same volume of normal saline, whereas test group A, B and C were exposed to Imidacloprid with doses of 12.5µg, 25µg and 50 µg in a volume of 12.5µl, 25µl and 50µl respectively on 2nd day of incubation. The solutions were taken in a tuberculin syringe. The broad end of the egg was wiped with a sterile gauze pad moistened with 70 percent alcohol solutions. A hole was drilled in eggshell in the centre of the surface over the air cell with a sterile needle; care was taken not to damage the shell membranes with point of drill. This is to avoid contact of air with the egg membrane. The needle was inserted horizontally into the air cell. The needle was wiped with a sterile gauze pad between each injection and hole of the shell was sealed with Candle melted wax. After injection of drug, eggs were again kept for incubation at 38 C temperature. The embryos were terminated and eggs removed from the incubator on 21st day, the egg shell were broken with a scalpel and the embryos were removed. The number of live and dead embryos was noted. Parameters namely crown rump length; size and weight of the embryos and the hardness of the tissue were measured. The embryos to be secri ed and blood collected from the heart. Blood sample collected into a clot promoting vaccutainers and allowed to clot for 3 to 4 hours later centrifuged at 20k rpm for 10 minutes, serum was separated into tubes. Biochemical parameter namely blood urea, Serum creatinine, Serum total protein, and Serum Albumin and Serum uric acid done in biochemistry lab using standard methods using semiautomatic biochemical analyzer by employing standard biochemical kits. The dissection of chick embryo was done to observe the developmental changes and skeletal anomalies were carefully observed and photographs. Obtained data were analyzed statically. RESULTS T h e c h i c k e m b r y o w e r e e x a m i n e d f o r developmental abnormalities and we observed Failure of Retraction of Yolk sac ( gure 2, 3,4 and 6), Growth Retardation ( gure 2, 3,5 and 6), Limbs deformities ( gure 4), Head Enlargement ( gure 5), Ectopia Viscerale ( gure 6) and Scanty feathers ( gure 5) shown in table 1. Imidacloprid caused developmental delays or smaller embryos. The effects of imidacloprid on growth retardation overall statistically signi cant for embryos at 25µg and 50µg levels. Imidacloprid had a signi cant adverse effects on embryo failure of retraction of yolk 13
3 Developmental And Biochemical Effects of Imidacloprid On Chick Embryos sac although the control group has also shown the failure of retraction of yolk sac but the difference is statistically signi cant (p>0.001). The lethal effects and malformations induced by Imidacloprid in chick embryo we found dead embryos in test A group 8(17.7%), B group 10(22.2%) and C group 13(28.8%) shown in table 2. In control we observed in A group all chick embryo were live, B group 2(4.4%) and C group 3(6.6%) embryos found dead shown in table 2. The mortality rate was 3.7% in control group and 22.9% in test group, this difference was statistically signi cant (p>0.05). Photograph:1 shows Imidacloprid exposed chick embryos with developmental abnormalities failure of retraction of yolk sac ( g.2, 3, 5), growth retardation ( g.2, 3, 5and 6), Limbs deformities ( g. 4), Head Enlargement ( g.5), Ectopia Viscerale ( g.6) and Scanty feathers ( g.5) and control (C) is normal ( g.1). The present biochemical study was conducted to evaluate the serum biochemical alterations induced by imidacloprid in chick embryos. The biochemical analysis showed a signi cant (P< 0.001) increase in blood urea in groups B and C; and serum creatinine in group B in comparison to control. Serum AST was signi cantly higher (p<0.001) in groups A, B and C; and serum ALT was also signi cantly higher (p<0.001) in group B and C in comparison to control. The biochemical effects of Imidacloprid on chick embryos serum parameter, namely blood urea, S.creatinine, S.total protein, S.Albumin, AST and ALT are shown in table no.3 to 8 and the corresponding box plots. 14
4 Muktyaz Hussein, Vishram Singh, Prerna Gupta, Birendra Yadav, A.K.Singh DISCUSSION Animal studies are important because, in some instances, they have shed light on mechanisms of teratogenicity and because when such an agent causes similar patterns of anomalies in several species, human teratogens should also be suspected. For obvious reasons no studies of teratogenicity are conducted during embryogenesis of humans. Imidacloprid is a neurotoxin that is selectively toxic to insects relative to vertebrates and most non-insect invertebrates. Imidacloprid is a neonicotinoid insecticide which produces neurotoxicity through binding or partial binding to speci c areas of the nicotinic acetylcholine r e c e p t o r. A c e t y l c h o l i n e i s a n i m p o r t a n t neurotransmitter in both insects and mammals; it is released at the nerve synapse in response to a membrane depolarization which is the hallmark of nerve transmission. In mammals, the primary effects following acute high-dose oral exposure to imidacloprid are mortality, transient cholinergic effects (dizziness, apathy, locomotor effects, labored breathing) and transient growth retardation. It acts as an agonist at the postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nachr) in insects, Tomizawa 4 Casida (2005). Exposures to high doses may be associated with degenerative changes in the testes, thymus, bone marrow and pancreas. Cardiovascular and hematological effects have also been observed at higher doses. Animal studies are important because, in some instances, they have shed light on mechanisms of teratogenicity and because when such an agent causes similar patterns of anomalies in several species, human teratogens should also be suspected. Akhtar et al. studied on exposure to various environmental chemicals especially pesticides during developmental 5 period is liable to give rise to congenital defects. One recent study by Capowiez et al. presents very interesting data. The study was about the effect of neonicotinoids on the behavior of two earthworm 6 species. Epidemiological studies have shown neurobehavioral and cognitive de cits and increased susceptibility to disease in offspring at various developmental stages, all associated with maternal exposure to neurotoxic chemicals during pregnancy 7 Jacobson & Jacobson (2002). P. E. Natekar et al. observed malformations in Methotrexate treated group of chick embryo were stunted growth, break deformities, limb deformities, scanty feathers, short 8 wings and ectopia vescerale. In 90 days oral toxicity study with imidacloprid in 15
5 Developmental And Biochemical Effects of Imidacloprid On Chick Embryos female rats at the concentration of 20 mg/kg/day evidenced decreased activity of acetyl choline esterase (AchE) in brain, spontaneous locomotor activity, histopathologically cerebellum of brain showed degenerative changes in purkinji cells and loss of 9 granules in granular layer studied by Bhardwaj et al. Recently imidacloprid has raised concern because of reports of egg shell thinning; reduced egg production and hatching time which are considered as signs of pos- 10 sible endocrine disruption (Berny et al., (1999) and 11 Matsuda et al., (2001). A speci c concern about imidacloprid is that it may cause similar developmental defects as the known teratogen nicotine. For developmental studies, chicken embryos are a model organism because they are inexpensive, easy to control with dosing, sensitive to toxins, and are vertebrates reported by Ejaz and Woong 12 (2006). Increased use of chemical pesticides has resulted in contamination of the environment and many associated long-term effects on human health, ranging from short-term impacts such as headaches and nausea to chronic impacts such as cancer, 13 reproductive harm, and endocrine disruption. In view of the large-scale use of imidacloprid and the scarcity 14 of Indian literature, it is essential to assess the present environmental load of imidacloprid residues in different food commodities because imidacloprid is a 15,16 toxic chemical. In mammals, the primary effects following acute high-dose oral exposure to imidacloprid are mortality, transient cholinergic effects (dizziness, apathy, locomotor effects, labored breathing) and transient growth retardation. Balani et al. (2011) evaluated the toxic effects of oral administration of imidacloprid in male white leg horn chicken at 1.25, 1.67 and 2.5mg/kg b. wt for 28 days and noticed an increase in ALT, no change in AST, serum total protein, total 17 globulins, total albumin and serum creatinine levels. The increased levels of ALT and AST could be due to degeneration and necrosis of hepatocytes, which attributes an increased permeability of cell membrane that results in release of transaminases into the blood stream. H. kaur Toor, et al., (2013) reported that Imidacloprid induced biochemical alterations in liver 18 also found in female albino rats. Chronic exposure to imidacloprid also induces in ammation and oxidative stress in the liver and central nervous system of rats (V.Duzguner, S. 19 Erdogan, 2012). Hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were studied in layer chickens following single acute doses of 55 mg/kg bw and 139 mg/kg bw of CPF and Imidacloprid, respectively. The cholinergic signs in CPF intoxicated chickens were in agreement with those reported in chickens intoxicated with CPF and other 20 organophosphate insecticides (Lumeij, 1997) and 2 1 Mohammad, (2007). However, there is less information about the mechanism of the action of imidacloprid in chickens. Increase in serum creatinine levels might be due to failure of glomerular ltration process induced by imidacloprid toxicity to kidney. Decreased total protein levels were in accordance with 22 observations of (Siddiqui et al., 2007) and it may be attributed to imidacloprid induced hepato toxicity which was also evident from elevated serum ALT and AST activities. CONCLUSION In the light of present study, it can be concluded that the imidacloprid is a potential teratogenic compound and therefore its use should be limited. Results show that experimental group had comparatively more cases of growth retardation resulting into failure of retraction of yolk sac, head enlargement and ectopia viscerale as compared to the controls. Comparatively higher doses proved more toxic and also caused many developmental defects on chick embryos. Biochemical analysis can provide valuable information for monitoring the health conditions of chick embryos. Biochemical analyses in the current study revealed that exposure to imidacloprid in chick embryo resulted in signi cantly higher values of blood urea (P< 0.001) at higher doses (Group B & C), serum creatinine (P< 0.001) in Group B, serum AST signi cantly higher (p<0.001) at all doses (Groups A, B, C) and serum AST (p<0.001) at higher doses (Groups B & C). The current study concludes that that exposure to Imidacloprid is associated with Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in chick embryos. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I express my gratitude to Dr. Arvind Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, department of Com.Medicine, Dr Manoj Gupta, Assistant professor, department of pathology and Dr Ajay Kumar Singh, Lecturer, department of biochemistry, Govt. Medical College Ambedkar Nagar U.P. India., for suggesting the research problem, statistical analysis, constant encouragement and valuable guidance. I also thankful to my wife Nigar Hussain for the strength and help. REFERENCES 1. Kagabu S; Chloronicotinyl insecticides discovery, application and future prospective. Rev Toxicol., 1997; 1:
6 Muktyaz Hussein, Vishram Singh, Prerna Gupta, Birendra Yadav, A.K.Singh 2. Seifert J, Stollberg J; Antagonism of a neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid at neuromuscular receptors. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2005; 20: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations International Code of Conduct on the Distribution and Use of Pesticides (2002). 4. Tomizawa, M., Lee, D. L. and Casida, J. E. Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: Mechanisms of selective action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005; 45: Akhtar N, Srivastava MK, Raizada RB; Transplacental disposition and teratogenic effects of chlorpyrifos in rats. J Toxicol Sci., 2006; 31(5): Caposiez Y, Berard A; Assessment of the effects of imidacloprid on the behavior of two earthworm s p e c i e s ( A p o r r e c t o d e a n o c t u r n a a n d Allolobophora icterica) using 2D terraria. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2006, 64: Jacobson, J. L., and Jacobson, S. W. Association of prenatal exposure to environmental contaminants with intellectual functions in childhood. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol.2002; 40: Natekar PE, F. DeSouza FM; experimental induction of teratogenic effect in chick embryos. Anatomica Karnataka, 2012; 6(3): Bhardwaj S, Srivastava MK, Upasana K, Srivastava LP; A 90 days oral toxicity of imidacloprid in female rats morphological, mbiochemical& histopathological evaluation. Food and chemical toxicology, 2010; 48(5): Berny, P J., Florence, B., Bernadette, V., Videmann, T.B. Evaluation of the toxicity of imidacloprid in wild birds. A new high performance thin layer chromatography method for the analysis of liver and crop samples in suspected poisoning cases. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Related Technol. 1999; 22, Matsuda, K., Buckingham, S D., Kleier, D., Rauh, J J., Grauso, M., Satelle, D B., Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001; 22, Ejaz S, Woong LC. Diminished embryonic movements of developing embryo by direct exposure of side stream whole smoke solutions. Archives of Toxicology 2006; 80: Chen C, Qian Y, Chen Q, Tao C, Li C, Li Y. Evaluation of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from Xiamen, China. Food Control 2011; 22: Arora S. Analysis of insecticides in okra and brinjal from IPM and non-ipm elds. Environ Monit Assess 2009; 151: Kapoor U, Srivastava MK, Bhardwaj S, Srivastava LP. Effect of imidacloprid on Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in female rats. J Toxicol Sci 2010; 35: Tomizawa M, Casida JE Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to speci city of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu Rev Entomol 48: Balani T., Agarwal S. and Thaker A. M. Haematological and biochemical changes due to short-term oral administration of imidacloprid. Toxicology International, (2011); 18: H.Kaur, G.K.Sangha, K.S.Khere. Imidacloprid induced histological and biochemical alterations in liver of female albino rats. Pesticide Biochemistry and physiology, 105(2013); 1; V. Duzguner, S. Erdogan. Acute oxidant and in ammatory effects of imidacloprid on the mammalian central nervous system. Pestic. Biochem Physiol., 97 (2010); Lumeij, J. T. (1997): Avian clinical biochemistry. In: Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, Kaneko, J. J., J. W. Harvey, M. L. Bruss, eds. 5th ed. Academic Press. pp Mohammad, f. K., y. M. Al-badrany, m. M. Aljobory (2008): Acute toxicity and cholinesterase inhibition in chicks dosed orally with organophosphate insecticides. Arhiv Za higijenu rada i toksikologiju 59, Siddiqui A., Choudhary M., Goriya H. V., Bhavsar S. K. and Thaker A. M. (2007). Evaluation of immunotoxic effect of short-term administration of quinalphos and imidacloprid in white leghorn cockerels. Toxicology international, 14 (1), p
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Muktyaz Hussein.
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(1A):67-72 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(1A):67-72 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Body Weight and Malformations in Relation to Pesticide Embryotoxicity
 International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 12, Number 4 (2016) pp. 811-816 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Body Weight and Malformations in Relation to Pesticide
International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 12, Number 4 (2016) pp. 811-816 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Body Weight and Malformations in Relation to Pesticide
Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos
 Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos Amy Langevin Independent Research Project Bio254- Developmental Biology November 28, 2007 Introduction Thousands of mothers
Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos Amy Langevin Independent Research Project Bio254- Developmental Biology November 28, 2007 Introduction Thousands of mothers
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
Avian encephalomyelitis (AE) Epidemic tremor. Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ.
 Avian encephalomyelitis (AE) Epidemic tremor Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ. Definition Avian encephalomyelitis (AE) is a viral infection affecting
Avian encephalomyelitis (AE) Epidemic tremor Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ. Definition Avian encephalomyelitis (AE) is a viral infection affecting
Haematological Alterations in Broilers Administered with Imidacloprid and Spinosad and Its Amelioration with Vitamin E and Silymarin
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 496-500 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.059
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 496-500 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.059
Cadmium-induced developmental defects in chick embryos and antioxidant effects of green tea
 2016; 2(5): 558-562 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(5): 558-562 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-03-2016 Accepted: 05-04-2016 Kshiteej Sode MSc student
2016; 2(5): 558-562 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(5): 558-562 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-03-2016 Accepted: 05-04-2016 Kshiteej Sode MSc student
Accelerating Embryonic Growth During Incubation Following Prolonged Egg Storage 2. Embryonic Growth and Metabolism 1
 Accelerating Embryonic Growth During Incubation Following Prolonged Egg Storage 2. Embryonic Growth and Metabolism 1 V. L. Christensen, 2 J. L. Grimes, M. J. Wineland, and G. S. Davis Department of Poultry
Accelerating Embryonic Growth During Incubation Following Prolonged Egg Storage 2. Embryonic Growth and Metabolism 1 V. L. Christensen, 2 J. L. Grimes, M. J. Wineland, and G. S. Davis Department of Poultry
EFFECTS OF SOME PESTICIDES ON THE EMBRYONIC STAGES OF CHICK
 EFFECTS OF SOME PESTICIDES ON THE EMBRYONIC STAGES OF CHICK Subrata Datta Department of Zoology, East Calcutta Girls College, Lake town Kolkata (INDIA) Received August 17, 2007 Accepted January 4, 2007
EFFECTS OF SOME PESTICIDES ON THE EMBRYONIC STAGES OF CHICK Subrata Datta Department of Zoology, East Calcutta Girls College, Lake town Kolkata (INDIA) Received August 17, 2007 Accepted January 4, 2007
A Case of Pesicide Poisoning
 STO-147 A Case of Pesicide Poisoning Part 1: A Case of Bed bugs Samantha noticed bug bites on her legs. She also found bug bites on her baby Carly s arms and neck. A few days later she discovered spots
STO-147 A Case of Pesicide Poisoning Part 1: A Case of Bed bugs Samantha noticed bug bites on her legs. She also found bug bites on her baby Carly s arms and neck. A few days later she discovered spots
What are pesticides? Children and pesticides A review of the evidence. Pesticide use - EU. Human s exposure routes. Page 1
 What are pesticides? Children and pesticides A review of the evidence Dr Roberto Bertollini World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Brussels, European Parliament March 7, 2007 Chemicals designed
What are pesticides? Children and pesticides A review of the evidence Dr Roberto Bertollini World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Brussels, European Parliament March 7, 2007 Chemicals designed
Pharmacology Autonomic Nervous System Lecture10
 Pharmacology Autonomic Nervous System Lecture10 Note : Most of the time in this lecture, the doctor was only reading from the slides, so I m going to write only the extra information he mentioned So Please
Pharmacology Autonomic Nervous System Lecture10 Note : Most of the time in this lecture, the doctor was only reading from the slides, so I m going to write only the extra information he mentioned So Please
A simple RP-HPLC method for determining imidacloprid residues in goat tissues.
 6 Biomedical Research 2016; 6 27 (1): 11-15 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A simple RP-HPLC method for determining imidacloprid residues in goat tissues. Gayatri Dewangan 1 *, Akhilesh Mishra 2, Tapan
6 Biomedical Research 2016; 6 27 (1): 11-15 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A simple RP-HPLC method for determining imidacloprid residues in goat tissues. Gayatri Dewangan 1 *, Akhilesh Mishra 2, Tapan
Histopathological Changes and Tissue Residue Deposition in Broiler Birds Following Profenofos Administration
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.023
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.023
Aflatoxin Effect On Health. Dr Subroto Mukherjee USAID/East Africa
 Aflatoxin Effect On Health Dr Subroto Mukherjee USAID/East Africa What is Toxin A toxin (from Ancient Greek: toxikon) is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms It simply means,
Aflatoxin Effect On Health Dr Subroto Mukherjee USAID/East Africa What is Toxin A toxin (from Ancient Greek: toxikon) is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms It simply means,
MEASURING FERTILITY & EARLY DEADS LEVELS PART 1
 MEASURING FERTILITY & EARLY DEADS LEVELS PART 1 Why measure fertility and early deads? An unfertilised egg cannot produce a chick. Flock fertility is governed by management of males and females on the
MEASURING FERTILITY & EARLY DEADS LEVELS PART 1 Why measure fertility and early deads? An unfertilised egg cannot produce a chick. Flock fertility is governed by management of males and females on the
Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals!
 Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals! Organic vegetables fare no better than non-organic ones in tests 2 out of 9 organic samples had pesticide residues and 5 contaminated by heavy metals Organic
Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals! Organic vegetables fare no better than non-organic ones in tests 2 out of 9 organic samples had pesticide residues and 5 contaminated by heavy metals Organic
Primary Isolation and Cultivation of Viruses
 Primary Isolation and Cultivation of Viruses Practical Medical Virology 450 MBIO 2017-18 01/10/2017 Amal Alghamdi Reham Alahmadi Dalia Alsrar 1 Diagnostic Virology Virus Isolation and Cultivation Viral
Primary Isolation and Cultivation of Viruses Practical Medical Virology 450 MBIO 2017-18 01/10/2017 Amal Alghamdi Reham Alahmadi Dalia Alsrar 1 Diagnostic Virology Virus Isolation and Cultivation Viral
The Effects 1. The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology
 The Effects 1 The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology The Effects 2 Abstract The aim of this experiment was
The Effects 1 The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology The Effects 2 Abstract The aim of this experiment was
Bayer Advanced Lawn Complete Insect Killer For Soil & Turf Ready-to-Spread Granules
 Bayer Advanced Lawn Complete Insect Killer For Soil & SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name Turf Ready-to-Spread Granules Chemical Name Common Name MSDS Number 2019 Chemical
Bayer Advanced Lawn Complete Insect Killer For Soil & SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name Turf Ready-to-Spread Granules Chemical Name Common Name MSDS Number 2019 Chemical
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 The Effects of Varying Amounts of Nicotine on the Development of Zebrafish Eggs Charlotte, Sydney Martins, Elyse Steingraeber Waukesha North High School ABSTRACT The purpose of the experiment was to see
The Effects of Varying Amounts of Nicotine on the Development of Zebrafish Eggs Charlotte, Sydney Martins, Elyse Steingraeber Waukesha North High School ABSTRACT The purpose of the experiment was to see
Avian Reo-virus infections. Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ.
 Avian Reo-virus infections Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ. Economic losses Increased mortality. Diminished weight gains, poor feed conversions.
Avian Reo-virus infections Dr./ Wafaa Abd El-ghany Assistant Professor of poultry dis., Fac. Vet. Med., Cairo Univ. Economic losses Increased mortality. Diminished weight gains, poor feed conversions.
A technique for introducing localized long-lasting implants in the chick embryo
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 39, pp. 261-266, 1977 261 Printed in Great Britain SHORT PAPERS A technique for introducing localized long-lasting implants in the chick embryo By MARIETA B. HEATON 1 From
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 39, pp. 261-266, 1977 261 Printed in Great Britain SHORT PAPERS A technique for introducing localized long-lasting implants in the chick embryo By MARIETA B. HEATON 1 From
BREAKOUT ANALYSIS GUIDE FOR HATCHERIES
 BREAKOUT ANALYSIS GUIDE FOR HATCHERIES By Dr. Joseph M. Mauldin, University of Georgia, Cooperative Extension Service, Athens, USA Breakout analyses are useful hatchery management procedures that provide
BREAKOUT ANALYSIS GUIDE FOR HATCHERIES By Dr. Joseph M. Mauldin, University of Georgia, Cooperative Extension Service, Athens, USA Breakout analyses are useful hatchery management procedures that provide
HAEMOBIOCHEMICAL PROFILE OF GOAT FOLLOWING SINGLE OR COMBINED APPLICATION OF FLUMETHRIN AND IMIDACLOPRID ON SKIN
 Explor Anim Exploratory Med Res, Animal and Medical Research, ISSN Vol.4, 2277-470X Issue (Print), 1, June, ISSN 2014 2319-247X (Online) Vol.4, Issue - 1, 2014, p. 48-56 Website: www.animalmedicalresearch.org
Explor Anim Exploratory Med Res, Animal and Medical Research, ISSN Vol.4, 2277-470X Issue (Print), 1, June, ISSN 2014 2319-247X (Online) Vol.4, Issue - 1, 2014, p. 48-56 Website: www.animalmedicalresearch.org
BITHOR DUAL ACTION. Dual mode of action. Non-repellent. Competitive. Long term INSECTICIDE
 bifenthrin imidacloprid THE SILENT ASSASSINS TWO DIFFERENT MODES OF ACTION COMBINE INTO THE UNSTOPPABLE Dual mode of action using the intensified effects of two actives with completely different properties
bifenthrin imidacloprid THE SILENT ASSASSINS TWO DIFFERENT MODES OF ACTION COMBINE INTO THE UNSTOPPABLE Dual mode of action using the intensified effects of two actives with completely different properties
Pesticides and the Environment
 Section 3: Pesticides and the Environment Learning Objectives When you have completed this section, you should be able to:! indicate the relative residual activity of pesticides used for mosquito and black
Section 3: Pesticides and the Environment Learning Objectives When you have completed this section, you should be able to:! indicate the relative residual activity of pesticides used for mosquito and black
value as a medium for the in vivo cultivation of different
 THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
Mycotoxins and Poultry Health Natacha S. Hogan
 Mycotoxins and Poultry Health Natacha S. Hogan Department of Animal and Poultry Science, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK Toxicology Centre, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK Outline Fusarium
Mycotoxins and Poultry Health Natacha S. Hogan Department of Animal and Poultry Science, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK Toxicology Centre, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK Outline Fusarium
Expiry Date: yyyy-mm-dd Lot # XXXX-XXX This product is not to be sold or applied after the expiry date above.
 GROUP 1B INSECTICIDE UBG MALATHION GRAIN PROTECTOR DUST COMMERCIAL INSECTICIDE READ THE LABEL BEFORE USING FOR USE ON STORED GRAINS Protects against damage from Confused Flour Beetle, Granary Weevil, Saw-toothed
GROUP 1B INSECTICIDE UBG MALATHION GRAIN PROTECTOR DUST COMMERCIAL INSECTICIDE READ THE LABEL BEFORE USING FOR USE ON STORED GRAINS Protects against damage from Confused Flour Beetle, Granary Weevil, Saw-toothed
Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Organophosphorus Poisoning
 International Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry ISSN 0973-2691 Volume 14, Number 1 (2018) pp. 59-64 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients
International Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry ISSN 0973-2691 Volume 14, Number 1 (2018) pp. 59-64 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients
Original Article Bendiocarbamate Toxicity in the Chick Embryo
 Original Article Bendiocarbamate Toxicity in the Chick Embryo (carbamate / pesticides / embryotoxicity / reproduction / development) 1 E. PETROVOVÁ, 2,3 D. SEDMERA, 4 I. MÍŠEK, 4 F. LEŠNÍK, 1 L. LUPTÁKOVÁ
Original Article Bendiocarbamate Toxicity in the Chick Embryo (carbamate / pesticides / embryotoxicity / reproduction / development) 1 E. PETROVOVÁ, 2,3 D. SEDMERA, 4 I. MÍŠEK, 4 F. LEŠNÍK, 1 L. LUPTÁKOVÁ
Quiz 2: Organic Molecules. Multiple Choice (46 pts) Directions: Circle the best answer.
 Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Date: Quiz 2: Organic Molecules Multiple Choice (46 pts) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. Students digging near their school unearthed four objects. One of the objects was
Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Date: Quiz 2: Organic Molecules Multiple Choice (46 pts) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. Students digging near their school unearthed four objects. One of the objects was
5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176)
 Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Bayer Environmental Science
 Revision Date: 11/07/2005 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name MERIT 75 WSP INSECTICIDE MSDS Number 102000007120 EPA Registration No. 432-1318 Product Use Insecticide for foliar
Revision Date: 11/07/2005 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name MERIT 75 WSP INSECTICIDE MSDS Number 102000007120 EPA Registration No. 432-1318 Product Use Insecticide for foliar
Learning Objectives. Reduce Risk with Least Toxic Pesticides. When you have completed this section, you should be able to: LD 50 values
 Section 6: Human Health Learning Objectives When you have completed this section, you should be able to:! select pesticides for mosquito and black fly control on the basis of their oral and dermal LD 50
Section 6: Human Health Learning Objectives When you have completed this section, you should be able to:! select pesticides for mosquito and black fly control on the basis of their oral and dermal LD 50
Identification of Imidacloprid Metabolites in Onions Using High Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometry (LC/Q-TOF MS) and Accurate Mass Tools
 Identification of Imidacloprid Metabolites in Onions Using High Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometry (LC/Q-TOF MS) and Accurate Mass Tools Application ote Food Authors E. Michael Thurman and Imma Ferrer
Identification of Imidacloprid Metabolites in Onions Using High Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometry (LC/Q-TOF MS) and Accurate Mass Tools Application ote Food Authors E. Michael Thurman and Imma Ferrer
Biochemical alterations induced by the acute exposure to combination of chlorpyrifos and lead in Wistar rats
 Biochemical alterations induced by the acute exposure to combination of chlorpyrifos and lead in Wistar rats 1 H Krishna*, 2 AV Ramachandran 1 Dhirubhai Ambani Life Sciences Centre, Reliance Life Sciences
Biochemical alterations induced by the acute exposure to combination of chlorpyrifos and lead in Wistar rats 1 H Krishna*, 2 AV Ramachandran 1 Dhirubhai Ambani Life Sciences Centre, Reliance Life Sciences
COMPARISON OF ALBUMIN MEASUREMENTS BY ELECTROPHORESIS AND THE BROMOCRESOL GREEN METHOD IN CHICKEN PLASMA
 ZEBRA GRANT PROJECT COMPARISON OF ALBUMIN MEASUREMENTS BY ELECTROPHORESIS AND THE BROMOCRESOL GREEN METHOD IN CHICKEN PLASMA First published in the BVZS ZooMed Bulletin, March 2007 Shona Haydon This project
ZEBRA GRANT PROJECT COMPARISON OF ALBUMIN MEASUREMENTS BY ELECTROPHORESIS AND THE BROMOCRESOL GREEN METHOD IN CHICKEN PLASMA First published in the BVZS ZooMed Bulletin, March 2007 Shona Haydon This project
Bayer Environmental Science
 Revision Date: 08/24/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name CONTROL SUPER CONCENTRATE MSDS Number 102000015684 EPA Registration No. 72155-56 Bayer Environmental Science 2
Revision Date: 08/24/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name CONTROL SUPER CONCENTRATE MSDS Number 102000015684 EPA Registration No. 72155-56 Bayer Environmental Science 2
To improve the performance of a hatchery breeder operation, the baseline quality must first be determined.
 Breakout Analyses Guide for Hatcheries Reviewed by Jeanna L. Wilson, Extension Poultry Scientist Original manuscript by Joseph M. Mauldin, Former Extension Poultry Scientist To improve the performance
Breakout Analyses Guide for Hatcheries Reviewed by Jeanna L. Wilson, Extension Poultry Scientist Original manuscript by Joseph M. Mauldin, Former Extension Poultry Scientist To improve the performance
Pre-Empt Professional Cockroach Gel Bait MSDS Version 2.0
 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name Pre-Empt Professional Cockroach Gel Bait Chemical Name Common Name MSDS Number R000034193 Chemical Family Chemical Formulation EPA Registration
SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name Pre-Empt Professional Cockroach Gel Bait Chemical Name Common Name MSDS Number R000034193 Chemical Family Chemical Formulation EPA Registration
Cycloxydim CYCLOXYDIM (179)
 Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
INTRODUTION. from atropos, one of the three fates, who according to Greek mythology,
 Introduction INTRODUTION Atropine, a naturally occurring tertiary amine, derives its name from atropos, one of the three fates, who according to Greek mythology, chose how a person die. The atropine, a
Introduction INTRODUTION Atropine, a naturally occurring tertiary amine, derives its name from atropos, one of the three fates, who according to Greek mythology, chose how a person die. The atropine, a
TOXICITY EVALUATION (1)
 TOXICITY EVALUATION (1) ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY EMISSION TRANSPORT FATE EFFECT MAJOR CLASSES OF POLLUTANTS (CHEMICALS) INORGANIC IONS * metals & anions ORGANIC POLLUTANTS * hydrocarbons * polychlorinated
TOXICITY EVALUATION (1) ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY EMISSION TRANSPORT FATE EFFECT MAJOR CLASSES OF POLLUTANTS (CHEMICALS) INORGANIC IONS * metals & anions ORGANIC POLLUTANTS * hydrocarbons * polychlorinated
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY. Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NG NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NG NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0078265 -Session-1987-88 -Superclass- -Title- RH AVIAN PHYSIOLOGY
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NG NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0078265 -Session-1987-88 -Superclass- -Title- RH AVIAN PHYSIOLOGY
Name SID # NST11 Second Midterm-Version A. You have Version A. Please mark A for question 1.
 Name SID # NST11 Second Midterm-Version A You have Version A. Please mark A for question 1. In 2013, the Syrian president Bashar Al Asad used the Organophosphorus chemical warfare agent sarin against his
Name SID # NST11 Second Midterm-Version A You have Version A. Please mark A for question 1. In 2013, the Syrian president Bashar Al Asad used the Organophosphorus chemical warfare agent sarin against his
SHRIRAM INSTITUTE FOR INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH
 IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
MELTATOX POWDERY MILDEW FUNGICIDE FOR THE CONTROL OF POWDERY MILDEW ON GREENHOUSE ROSES AND FIELD-GROWN ROSES.
 03-JUN-2003 GROUP 5 FUNGICIDE MELTATOX POWDERY MILDEW FUNGICIDE FOR THE CONTROL OF POWDERY MILDEW ON GREENHOUSE ROSES AND FIELD-GROWN ROSES. COMMERCIAL (AGRICULTURAL) GUARANTEE: Dodemorph-acetate... 384
03-JUN-2003 GROUP 5 FUNGICIDE MELTATOX POWDERY MILDEW FUNGICIDE FOR THE CONTROL OF POWDERY MILDEW ON GREENHOUSE ROSES AND FIELD-GROWN ROSES. COMMERCIAL (AGRICULTURAL) GUARANTEE: Dodemorph-acetate... 384
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT PESTICIDES. What exactly is a Pesticide?
 THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT PESTICIDES What exactly is a Pesticide? Pesticides include insecticides, herbicides and fungicides, which are designed to kill insects, weeds and diseases respectively. Formulated
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT PESTICIDES What exactly is a Pesticide? Pesticides include insecticides, herbicides and fungicides, which are designed to kill insects, weeds and diseases respectively. Formulated
Environmental Science (SCBI 360) Environmental health and toxicology. Dr. Patompong Saengwilai SC2-306;
 Environmental Science (SCBI 360) Environmental health and toxicology Dr. Patompong Saengwilai SC2-306; patompong.sae@mahidol.ac.th Environmental Health Assesses environmental factors that influence human
Environmental Science (SCBI 360) Environmental health and toxicology Dr. Patompong Saengwilai SC2-306; patompong.sae@mahidol.ac.th Environmental Health Assesses environmental factors that influence human
Reproduction. Asexual vs Sexual
 Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
Safety Data Sheet European Format
 Safety Data Sheet European Format Preparation Date 05-Jan-2007 Revision Date Revision Number 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name Chemical Name Synonyms
Safety Data Sheet European Format Preparation Date 05-Jan-2007 Revision Date Revision Number 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name Chemical Name Synonyms
The Effect of Cyclosporin A on the Proliferating Chick Embryo Erythroblasts
 Physiol. Res. 43: 223-228, 1994 The Effect of Cyclosporin A on the Proliferating Chick Embryo Erythroblasts M. PETERKA, Z. LIKOVSKY, R. PETERKOVA Institute o f Experimental Medicine, Academy o f Sciences
Physiol. Res. 43: 223-228, 1994 The Effect of Cyclosporin A on the Proliferating Chick Embryo Erythroblasts M. PETERKA, Z. LIKOVSKY, R. PETERKOVA Institute o f Experimental Medicine, Academy o f Sciences
Bayer Environmental Science
 Revision Date: 06/12/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name PREMISE FOAM MSDS Number 102000011452 EPA Registration No. 432-1391 Product Use A ready-to-use formulation intended
Revision Date: 06/12/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name PREMISE FOAM MSDS Number 102000011452 EPA Registration No. 432-1391 Product Use A ready-to-use formulation intended
Toc H (RESIDENTIAL) PUBLIC SCHOOL PUNALUR. icbse.com CHEMISTRY PROJECT REPORT Name : Class : Reg. No :
 Name : Class : Reg. No : Toc H (RESIDENTIAL) PUBLIC SCHOOL PUNALUR CHEMISTRY PROJECT REPORT 2009-2010 Examiner Teacher-in charge. AIM T o s t u d y t h e p r e s e n c e o f I n s e c t i c i d e s a n
Name : Class : Reg. No : Toc H (RESIDENTIAL) PUBLIC SCHOOL PUNALUR CHEMISTRY PROJECT REPORT 2009-2010 Examiner Teacher-in charge. AIM T o s t u d y t h e p r e s e n c e o f I n s e c t i c i d e s a n
International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews
 Research article Available online www.ijsrr.org ISSN: 2279 0543 International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews Fatty Acid Metallic Salts and Pyrethroids - Environmental friendly Pesticides Jain
Research article Available online www.ijsrr.org ISSN: 2279 0543 International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews Fatty Acid Metallic Salts and Pyrethroids - Environmental friendly Pesticides Jain
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza
 Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
C3.1 What is the difference between intensive and organic farming? 1. Recall that many chemicals in living things are natural polymers
 C3 :Food matters C3.1 What is the difference between intensive and organic farming? 1. Recall that many chemicals in living things are natural polymers Potato, Pasta, Bread Carbohydrate Polymer = starch
C3 :Food matters C3.1 What is the difference between intensive and organic farming? 1. Recall that many chemicals in living things are natural polymers Potato, Pasta, Bread Carbohydrate Polymer = starch
BRIGAND. Leading the way in global pest control US A RODENTICIDES.
 RODENTICIDES Leading the way in global pest control US A www.pelgar-usa.com BROMADIOLONE BAITS Bromadiolone is a second generation anticoagulant which is highly effective in the control of rats and mice.
RODENTICIDES Leading the way in global pest control US A www.pelgar-usa.com BROMADIOLONE BAITS Bromadiolone is a second generation anticoagulant which is highly effective in the control of rats and mice.
AGREEMENT OF THE MEMBER STATE COMMITTEE ON THE IDENTIFICATION OF 4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL A) AS A SUBSTANCE OF VERY HIGH CONCERN
 AGREEMENT OF THE MEMBER STATE COMMITTEE ON THE IDENTIFICATION OF 4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL A) AS A SUBSTANCE OF VERY HIGH CONCERN According to Articles 57 and 59 of Regulation (EC) 1907/2006
AGREEMENT OF THE MEMBER STATE COMMITTEE ON THE IDENTIFICATION OF 4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL A) AS A SUBSTANCE OF VERY HIGH CONCERN According to Articles 57 and 59 of Regulation (EC) 1907/2006
Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN
 Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN 1017-8139 EFFECTS OF GARLIC CLOVE, NEEM AND EUCALYPTUS LEAF EXTRACT ON MATING BEHAVIOUR, OVIPOSITION AND ADULT EMERGENCE OF PULSE BEETLE, Callosobruchus maculatus
Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN 1017-8139 EFFECTS OF GARLIC CLOVE, NEEM AND EUCALYPTUS LEAF EXTRACT ON MATING BEHAVIOUR, OVIPOSITION AND ADULT EMERGENCE OF PULSE BEETLE, Callosobruchus maculatus
Frumkin, 2e Part 4: Environmental Health on a Local Scale. Chapter 25: Children
 Frumkin, 2e Part 4: Environmental Health on a Local Scale Chapter 25: Children Children and the Environment It is now understood that the environment, on both the micro (chemical) and the macro (structural)
Frumkin, 2e Part 4: Environmental Health on a Local Scale Chapter 25: Children Children and the Environment It is now understood that the environment, on both the micro (chemical) and the macro (structural)
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER CROP SCIENCE P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-0013 TRANSPORTATION EMERGENCY NON-TRANSPORTATION CALL CHEMTREC: 800-424-9300 BAYER EMERGENCY PHONE...: (800)
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER CROP SCIENCE P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-0013 TRANSPORTATION EMERGENCY NON-TRANSPORTATION CALL CHEMTREC: 800-424-9300 BAYER EMERGENCY PHONE...: (800)
EFFECT OF DIETARY LUTEIN ON IMMUNE RESPONSE OF BREEDERS AND BROILER CHICKS. Holly Pizzey
 EFFECT OF DIETARY LUTEIN ON IMMUNE RESPONSE OF BREEDERS AND BROILER CHICKS INTRODUCTION Lutein is a xanthophyll carotenoid found naturally in marigold flowers, corn, and dark-green leafy vegetables. Recent
EFFECT OF DIETARY LUTEIN ON IMMUNE RESPONSE OF BREEDERS AND BROILER CHICKS INTRODUCTION Lutein is a xanthophyll carotenoid found naturally in marigold flowers, corn, and dark-green leafy vegetables. Recent
Bayer Environmental Science
 Revision Date: 04/13/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name MSDS Number 102000014898 EPA Registration No. 72155-68 Bayer Environmental Science 2 T.W. Alexander Drive Research
Revision Date: 04/13/2006 SECTION 1. CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name MSDS Number 102000014898 EPA Registration No. 72155-68 Bayer Environmental Science 2 T.W. Alexander Drive Research
EVALUATION OF PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ERYTHRINA VARIEGATA AND SPIRULINA PLATENSIS IN COCKERELS INTOXICATED WITH IMIDACLOPRID
 Research Article EVALUATION OF PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ERYTHRINA VARIEGATA AND SPIRULINA PLATENSIS IN COCKERELS INTOXICATED WITH IMIDACLOPRID ABSTRACT MAYANK GUPTA 1, S.P. SINGH 2 AND N.K. PANKAJ 3 1 Department
Research Article EVALUATION OF PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ERYTHRINA VARIEGATA AND SPIRULINA PLATENSIS IN COCKERELS INTOXICATED WITH IMIDACLOPRID ABSTRACT MAYANK GUPTA 1, S.P. SINGH 2 AND N.K. PANKAJ 3 1 Department
DDT (General Fact Sheet) For more technical information, please refer to the Technical Fact Sheet
 This fact sheet was created in 1999; some of the information may be out-of-date. NPIC is not planning to update this fact sheet. More pesticide fact sheets are available here. Please call NPIC with any
This fact sheet was created in 1999; some of the information may be out-of-date. NPIC is not planning to update this fact sheet. More pesticide fact sheets are available here. Please call NPIC with any
ENVIRONMENT AND HEALTH
 ENVIRONMENT AND HEALTH Infection and Immunity in Broiler Chicken Breeders Vaccinated with a Temperature-Sensitive Mutant of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Impact on Performance of Offspring E. K. Barbour,*,1
ENVIRONMENT AND HEALTH Infection and Immunity in Broiler Chicken Breeders Vaccinated with a Temperature-Sensitive Mutant of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Impact on Performance of Offspring E. K. Barbour,*,1
N-Methylneodecanamide (MNDA)
 United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA-730-F-99-008 Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances July 1999 Agency (7505C) New Pesticide Fact Sheet Description of the Chemical N-Methylneodecanamide (MNDA)
United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA-730-F-99-008 Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances July 1999 Agency (7505C) New Pesticide Fact Sheet Description of the Chemical N-Methylneodecanamide (MNDA)
Science Policy Notice
 Science Policy Notice SPN2002-01 Children s Health Priorities within the Pest Management Regulatory Agency (publié aussi en français) January 3, 2002 This document is published by the Submission Coordination
Science Policy Notice SPN2002-01 Children s Health Priorities within the Pest Management Regulatory Agency (publié aussi en français) January 3, 2002 This document is published by the Submission Coordination
A. No. There are no current reports of avian influenza (bird flu) in birds in the U.S.
 Bird Flu FAQ 2 Frequently Asked Avian Influenza Questions Avian influenza in birds Q. What is avian influenza? A. Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza
Bird Flu FAQ 2 Frequently Asked Avian Influenza Questions Avian influenza in birds Q. What is avian influenza? A. Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza
New Pesticide Fact Sheet
 United States Prevention, Pesticides Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances May 2005 Agency (7505C) New Pesticide Fact Sheet Picaridin Description of the Chemical Use Patterns and Formulations Generic
United States Prevention, Pesticides Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances May 2005 Agency (7505C) New Pesticide Fact Sheet Picaridin Description of the Chemical Use Patterns and Formulations Generic
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE A Business Group of BAYER CROPSCIENCE, LP 95 Chestnut Ridge Road Montvale, NJ 07645 For MEDICAL, TRANSPORTATION or Other EMERGENCY call 1-800-334-7577
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE A Business Group of BAYER CROPSCIENCE, LP 95 Chestnut Ridge Road Montvale, NJ 07645 For MEDICAL, TRANSPORTATION or Other EMERGENCY call 1-800-334-7577
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Environmental exposures and health impacts of PFAS
 Environmental exposures and health impacts of PFAS Andrew B. Lindstrom U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National Exposure Research Laboratory, Research Triangle Park, NC Christopher Lau U.S. Environmental
Environmental exposures and health impacts of PFAS Andrew B. Lindstrom U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National Exposure Research Laboratory, Research Triangle Park, NC Christopher Lau U.S. Environmental
Chemicals in the Diet
 Chemicals in the Diet Recognize chemicals in the diet associated with adverse health outcomes from: Fish & Seafood Synthetic Chemicals Natural Toxins Review common chemicals found in drinking water: Arsenic
Chemicals in the Diet Recognize chemicals in the diet associated with adverse health outcomes from: Fish & Seafood Synthetic Chemicals Natural Toxins Review common chemicals found in drinking water: Arsenic
NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM. Somatic nervous system. Brain Spinal Cord Autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic nervous system
 SYNAPTIC NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Spinal Cord Autonomic nervous system Somatic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous
SYNAPTIC NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Spinal Cord Autonomic nervous system Somatic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous
JOURNAL OF VETERINARY CLINICAL RESERCH
 JOURNAL OF VETERINARY CLINICAL RESERCH Vol.7. No.2. 2017 '' Abstracts '' ** Contents ** Rapid cataract induction by Sodium Selenite in rabbit... III Voria Tohidi, Saeed Azimpour Clinical reaction and hematological
JOURNAL OF VETERINARY CLINICAL RESERCH Vol.7. No.2. 2017 '' Abstracts '' ** Contents ** Rapid cataract induction by Sodium Selenite in rabbit... III Voria Tohidi, Saeed Azimpour Clinical reaction and hematological
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents
 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Cholinergic agents, Cholinomimetic drugs,
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Cholinergic agents, Cholinomimetic drugs,
Mistake Correction!!!!!
 Tuzzy Talk # 7: Effects of Oil, Dispersants and Dispersed Oil on Organisms Part 1: Introduction to Toxicology (Continued) November 1, 2014 Nancy E. Kinner University of New Hampshire Center for Spills
Tuzzy Talk # 7: Effects of Oil, Dispersants and Dispersed Oil on Organisms Part 1: Introduction to Toxicology (Continued) November 1, 2014 Nancy E. Kinner University of New Hampshire Center for Spills
The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure. Cindy Zheng
 The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure Cindy Zheng WInSTEP Research Paper 2018 AP Biology, Kohler High School, Kohler, Wisconsin [1] The Increase
The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure Cindy Zheng WInSTEP Research Paper 2018 AP Biology, Kohler High School, Kohler, Wisconsin [1] The Increase
Effects of resistance genes and insecticidal seed treatments on soybean. aphid population growth and development
 Effects of resistance genes and insecticidal seed treatments on soybean aphid population growth and development Jiaqi Guo, Christian Krupke 1 1 Department of Entomology, Purdue University, 901 W. State
Effects of resistance genes and insecticidal seed treatments on soybean aphid population growth and development Jiaqi Guo, Christian Krupke 1 1 Department of Entomology, Purdue University, 901 W. State
Frequently Asked Questions About Bird Flu
 Frequently Asked Questions About Bird Flu Q1: What is Bird flu or Avian flu? A: It is a form of infection caused by a virus that affects birds (fowls, ducks, etc) and leads to their death. The new virus
Frequently Asked Questions About Bird Flu Q1: What is Bird flu or Avian flu? A: It is a form of infection caused by a virus that affects birds (fowls, ducks, etc) and leads to their death. The new virus
Update on Pesticides in Washington. Northwest Center for Alternatives to Pesticides Megan Dunn November 2016
 Update on Pesticides in Washington Northwest Center for Alternatives to Pesticides Megan Dunn November 2016 Outline-A Public Health Check of Cannabis and Pesticides Who is NCAP What pesticides? How do
Update on Pesticides in Washington Northwest Center for Alternatives to Pesticides Megan Dunn November 2016 Outline-A Public Health Check of Cannabis and Pesticides Who is NCAP What pesticides? How do
Applicators and Pesticide Toxicity
 Applicators and Pesticide Toxicity Moire Creek Manager, Toxicology Valent USA Corporation Toxicology: The Science of Poison All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison. The right dose
Applicators and Pesticide Toxicity Moire Creek Manager, Toxicology Valent USA Corporation Toxicology: The Science of Poison All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison. The right dose
5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253)
 Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER CROP SCIENCE P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-0013 TRANSPORTATION EMERGENCY NON-TRANSPORTATION CALL CHEMTREC: 800-424-9300 BAYER EMERGENCY PHONE...: (800)
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET BAYER CROP SCIENCE P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-0013 TRANSPORTATION EMERGENCY NON-TRANSPORTATION CALL CHEMTREC: 800-424-9300 BAYER EMERGENCY PHONE...: (800)
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Anatomy and Physiology of Poultry Lesson 2: Skeletal Structure of Poultry Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1.
Unit B: Anatomy and Physiology of Poultry Lesson 2: Skeletal Structure of Poultry Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1.
BIOL Week 6. Nervous System. Transmission at Synapses
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds What is Avian Influenza? The disease commonly referred to as bird flu is an animal infection caused by the H5N1 virus. The virus occurs naturally among
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds What is Avian Influenza? The disease commonly referred to as bird flu is an animal infection caused by the H5N1 virus. The virus occurs naturally among
5.24 TRIAZOLE FUNGICIDE METABOLITES
 Triazole metabolites 355 5.24 TRIAZOLE FUNGICIDE METABOLITES TOXICOLOGY 1,2,4-Triazole, triazole alanine, triazole acetic acid, triazole pyruvic acid and triazole lactic acid are the common metabolites
Triazole metabolites 355 5.24 TRIAZOLE FUNGICIDE METABOLITES TOXICOLOGY 1,2,4-Triazole, triazole alanine, triazole acetic acid, triazole pyruvic acid and triazole lactic acid are the common metabolites
Safety Data Sheet European Format
 Safety Data Sheet European Format Preparation Date 09-Jan-2007 Revision Date Revision Number 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name Common Name Chemical
Safety Data Sheet European Format Preparation Date 09-Jan-2007 Revision Date Revision Number 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name Common Name Chemical
Tentative Syllabus for BIO2233 Mammalian Anatomy
 Tentative Syllabus for BIO2233 Mammalian Anatomy Lecturer: Dr. Frank Nelson tue26441@temple.edu Lab Instructor: Dr. Uloma Opara-Osuoha opara-osuoha@temple.edu Lab Coordinator: Dr. Rob Jennings tug07799@temple.edu
Tentative Syllabus for BIO2233 Mammalian Anatomy Lecturer: Dr. Frank Nelson tue26441@temple.edu Lab Instructor: Dr. Uloma Opara-Osuoha opara-osuoha@temple.edu Lab Coordinator: Dr. Rob Jennings tug07799@temple.edu
R.E.D. FACTS. Limonene. Pesticide Reregistration. Use Profile
 United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA-738-F-94-030 Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances September 1994 Agency (7508W) R.E.D. FACTS Pesticide Reregistration Use Profile Limonene All pesticides
United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA-738-F-94-030 Environmental Protection And Toxic Substances September 1994 Agency (7508W) R.E.D. FACTS Pesticide Reregistration Use Profile Limonene All pesticides
EFFECT OF ENDOSULFAN AND CHLORPYRIFOS ON PROTEASE ACTIVITY IN THE CULTIVATED SOIL Sumit Kumar*
 Research Article EFFECT OF ENDOSULFAN AND CHLORPYRIFOS ON PROTEASE ACTIVITY IN THE CULTIVATED SOIL Sumit Kumar* Address for Correspondence * Biotechnology Engineering Department, V.V.P. Engineering College,
Research Article EFFECT OF ENDOSULFAN AND CHLORPYRIFOS ON PROTEASE ACTIVITY IN THE CULTIVATED SOIL Sumit Kumar* Address for Correspondence * Biotechnology Engineering Department, V.V.P. Engineering College,
Bendi 800. Insecticide 200GM GENERAL INFORMATION ACTIVE INGREDIENT
 WARNING KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN Ecotoxic. Read safety directions before opening or using. Bendi 800 Insecticide GENERAL INFORMATION A non-repellent, residual spray for control of a wide range of
WARNING KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN Ecotoxic. Read safety directions before opening or using. Bendi 800 Insecticide GENERAL INFORMATION A non-repellent, residual spray for control of a wide range of
ES/RP 531 Fundamentals of Environmental Toxicology Fall 2005
 ctober 10, 2005 Lecture 13 eurotoxicity II I. Toxicants Acting at the Level of the Synapse (continued) A. Another mechanism of acetylcholine receptor agonism is mimicking acetylcholine by binding directly
ctober 10, 2005 Lecture 13 eurotoxicity II I. Toxicants Acting at the Level of the Synapse (continued) A. Another mechanism of acetylcholine receptor agonism is mimicking acetylcholine by binding directly
U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook.
 U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Aflatoxins 1. Name of Toxin: Aflatoxins 2. Name of Acute Disease:
U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Aflatoxins 1. Name of Toxin: Aflatoxins 2. Name of Acute Disease:
