(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
|
|
|
- Kory White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery in the leg and blood taken from a vein in the leg. Give two differences in the composition of the blood.. 2. (2) (b) During operations patients can lose a lot of blood. Patients often need blood transfusions to keep them alive. The text shows information about a new artificial blood product. Page of 23
2 Suggest two possible advantages of using the new artificial blood, instead of using human blood for a transfusion in humans.. 2. (2) (Total 6 marks) Page 2 of 23
3 2 Fresh milk is a mixture of compounds including lipid, protein and about 5% lactose sugar. Lactose must be digested by the enzyme lactase, before the products can be absorbed. Lactase can be added to fresh milk to pre-digest the lactose. This makes lactose-free milk, which is suitable for people who do not produce enough lactase of their own. A student investigated the effect of changing ph and temperature on the digestion of lactose in milk. The results are shown in Tables and 2. Table Effect of ph Table 2 Effect of temperature ph Time taken to digest lactose in minutes Temperature in C Time taken to digest lactose in minutes No digestion (a) The label on a carton of lactose-free milk states: Lactase is normally produced in the stomach of mammals. The results in Table suggest that this statement is not true. Explain how. (2) Page 3 of 23
4 (b) Explain, as fully as you can, the results shown in Table 2. (3) (c) Bile is produced in the liver and is released into the small intestine. Bile helps the digestion of lipid in the milk. Describe how. (2) (Total 7 marks) 3 Drugs are used to treat cardiovascular diseases (diseases of the heart and blood vessels). (a) What is a drug? () Page 4 of 23
5 (b) People can be treated for cardiovascular diseases with statins or aspirin. Information about these two drugs is given in the table. STATINS Statins are only available on prescription from doctors. In studies, patients were monitored over several years. Statins were found to reduce the rate of non-fatal heart attacks by about 30%. Approximately 0.% of the patients suffered serious muscle damage and 0.0% suffered kidney failure. Statins reduce blood cholesterol which builds up in the walls of blood vessels. The cost of treating patients with statins can vary between 50 and 500 per year, depending on the type of cardiovascular disease being treated. ASPIRIN Aspirin can be bought over the counter. Treatment with aspirin costs up to 5 per year. In a study of 000 patients, aspirin was found to cause bleeding of the stomach in around 0.5% of patients and there was a slightly increased risk of poor blood clotting at cuts. There was a slightly increased risk of damage to the blood vessels in the brain in older patients. Aspirin was found to reduce the risk of non-fatal heart attacks by 3%. Page 5 of 23
6 Would you recommend statins or aspirin for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases? In your answer you should: give your recommendation use information from the table to support your recommendation by making comparisons of the two drugs. (5) (Total 6 marks) Page 6 of 23
7 4 Plants exchange substances with the environment. (a) Plant roots absorb water mainly by osmosis. Plant roots absorb ions mainly by active transport. Explain why roots need to use the two different methods to absorb water and ions. (4) (b) What is meant by the transpiration stream? (3) Page 7 of 23
8 (c) Students investigated the loss of water vapour from leaves. The students: cut some leaves off a plant measured the mass of these leaves every 30 minutes for 80 minutes. The graph shows the students results. (i) The rate of mass loss in the first 30 minutes was 7 milligrams per gram of leaf per minute. Calculate the rate of mass loss between 30 minutes and 80 minutes. Rate of mass loss = milligrams per gram of leaf per minute (2) The rate of mass loss between 0 and 30 minutes was very different from the rate of mass loss between 30 and 80 minutes. Suggest an explanation for the difference between the two rates. (2) (Total marks) Page 8 of 23
9 5 Plant leaves have many stomata. The diagram shows a stoma. (a) (b) Name cell X The table shows the mean widths of the stomata at different times of the day for two different species of plant. Species A grows in hot, dry deserts. Species B grows in the UK. () Time of day in hours Mean width of stomata as a percentage of their maximum width Species A Species B Dark Light Dark Page 9 of 23
10 The data in the table show that species A is better adapted than species B to living in hot, dry deserts. Explain how. (4) (Total 5 marks) 6 The leaves of most plants have stomata. (a) (i) Name the cells which control the size of the stomata. () Give one function of stomata. () Page 0 of 23
11 per mm 2 (2) (b) The image below shows part of the surface of a leaf. The length and width of this piece of leaf surface are both 0. mm. (i) Calculate the number of stomata per mm 2 of this leaf surface. A different plant species has 400 stomata per mm 2 of leaf surface. Having a large number of stomata per mm 2 of leaf surface can be a disadvantage to a plant. Give one disadvantage. () Page of 23
12 (c) A student investigated the loss of water from plant leaves. The student did the following: Step : took ten leaves from a plant Step 2: weighed all ten leaves Step 3: hung the leaves up in a classroom for 4 days Step 4: weighed all ten leaves again Step 5: calculated the mass of water lost by the leaves Step 6: repeated steps to 5 with grease spread on the upper surfaces of the leaves Step 7: repeated steps to 5 with grease spread on both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves. All the leaves were taken from the same type of plant. The table below shows the student s results. Treatment of leaves Mass of water the leaves lost in g No grease was used on the leaves 0.98 Grease on upper surfaces of the leaves 0.86 Grease on upper and lower surfaces of the leaves 0.0 (i) What mass of water was lost in 4 days through the upper surfaces of the leaves? Mass = g () Page 2 of 23
13 Very little water was lost when the lower surfaces of the leaves were covered in grease. Explain why. (3) (Total 9 marks) 7 Blood is part of the circulatory system. (a) (i) Give one function of white blood cells. () Which of the following is a feature of platelets? Tick ( ) one box. They have a nucleus. They contain haemoglobin. They are small fragments of cells. () Page 3 of 23
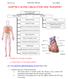
14 (b) Urea is transported by the blood plasma from where it is made to where the urea is excreted. Complete the following sentence. Blood plasma carries urea from where it is made in the to the where the urea is removed from the blood. (2) (c) The illustration shows a section through the human heart. Structure X is a valve. If valve X stops working, it may need to be replaced. A scientist is designing a new heart valve. The scientist knows that the valve must be the correct size to fit in the heart. Suggest two other factors the scientist needs to consider so that the newly designed valve works effectively in the heart. (2) (Total 6 marks) Page 4 of 23
15 8 During exercise, the heart beats faster and with greater force. The heart rate is the number of times the heart beats each minute.the volume of blood that travels out of the heart each time the heart beats is called the stroke volume. In an investigation, Person and Person 2 ran as fast as they could for minute. Scientists measured the heart rates and stroke volumes of Person and Person 2 at rest, during the exercise and after the exercise. The graph below shows the scientists results. (a) The cardiac output is the volume of blood sent from the heart to the muscles each minute. Cardiac output = Heart rate Stroke volume At the end of the exercise, Person s cardiac output = = cm 3 per minute. Use information from the figure above to complete the following calculation of Person 2 s cardiac output at the end of the exercise. At the end of the exercise: Person 2 s heart rate = beats per minute Person 2 s stroke volume = cm 3 Person 2 s cardiac output = cm 3 per minute (3) Page 5 of 23
16 (b) Person 2 had a much lower cardiac output than Person. (i) Use information from the figure above to suggest the main reason for the lower cardiac output of Person 2. () Person was able to run much faster than Person 2. Use information from the figure above and your own knowledge to explain why. (5) (Total 9 marks) Page 6 of 23
17 Mark schemes (a) (i) doesn t have valves allow veins have valves has a thicker wall or thicker layer of muscle allow has a smaller lumen ignore references to elastic (in walls) any two from: (artery has) more oxygen (artery has) more glucose allow (artery has) more amino acids / fatty acids (artery has) less carbon dioxide (artery has) less lactic acid ignore urea ignore reference to pressure accept converse for veins if veins is clearly stated 2 (b) any two from: no rejection allow no tissue matching required abundant supply low risk of infection allow named example ie HIV, CJD longer shelf life allow less space needed for storage ignore side effects 2 [6] 2 (a) stomach is acidic / has low ph allow any ph below 7 ignore stomach is not alkaline lactase works best / well in alkali / high ph / neutral / non-acidic conditions allow any ph of 7 and above accept works slowly in acid conditions allow figures from table with a comparison ignore reference to temperature Page 7 of 23
18 (b) any three from: (below 40( C)) increase in temperature increases rate / speed of reaction reference to molecules moving faster / colliding faster / harder / more collisions enzyme optimum / works best at 40 C allow value(s) in range ignore body temperature unless qualified high temperatures (above 40 C) / 45 C / 50 C enzyme denatured allow synonyms for denaturation, but do not allow killed denaturation at high and low temperature does not gain this mark ignore references to time / ph 3 (c) any two from: acid neutralised or conditions made neutral / alkali accept bile is alkaline (allow) emulsification / greater surface area (of lipid / fat) allow description of emulsification eg fat broken down / broken up into droplets do not accept idea of chemical breakdown lipase / enzymes (in small intestine) work more effectively / better allow better for enzymes ignore reference to other named enzymes 2 [7] 3 (a) (substance / chemical) that affects body chemistry / chemical reactions in the body Page 8 of 23
19 (b) statin / aspirin / neither recommended no mark, may be implied. If no recommendation or implication, max 4 marks answers should be comparative any five from: argued evaluation in favour of aspirin or statin or neither answers could include reference to for statins: accept converse for statins / aspirin but not as advantage of one and disadvantage of other more people in studies so data / findings more repeatable accept reliable for repeatable ignore accurate / precise reduces cholesterol but aspirin doesn t allow reduces cholesterol but no evidence about aspirin aspirin (may) causes bleeding / poor clotting but statins do not allow aspirin causes bleeding / poor clotting but no evidence about statins smaller (total) percentage suffer side-effects monitored by doctor, aspirins not for aspirin: cheap er can be bought over the counter rather than prescribed statins cause serious damage / muscle damage / kidney failure but aspirins do not similarities: both have similar effect on reducing (non-fatal) heart attacks incidence of side-effects low in both allow (for aspirin) higher reduction of risk of heart attack 5 [6] 4 (a) solution in soil is more dilute (than in root cells) concentration of water higher in the soil (than in root cells) Page 9 of 23
20 so water moves from the dilute to the more concentrated region so water moves down (its) concentration gradient or water moves from a high concentration of water to a lower concentration concentration of ions in soil less (than that in root cells) so energy needed to move ions or ions are moved against concentration gradient the direction of the concentration gradient must be expressed clearly accept correct reference to water potential or to concentrations of water (b) any three from: movement of water from roots / root hairs (up stem) via xylem to the leaves (water) evaporates via stomata 3 (c) (i) 0.67/0.7 accept 0.66, or ⅔ or 0.6 correct answer gains 2 marks with or without working if answer incorrect allow evidence of for mark do not accept 0.6 or during the first 30 minutes any one from: it was warmer it was windier it was less humid there was more water (vapour) in the leaves Page 20 of 23
21 so there was more evaporation or ignore water loss stomata open during first 30 minutes or closed after 30 minutes () so faster (rate of) evaporation in first 30 min or reducing (rate of) evaporation after 30 min () [] 5 (a) guard cell ignore stoma / stomata (b) Species A : allow converse points for species B stomata open in dark / at night or close in light / in day stomata closed during warm(est) period or open when cool(er) heat (energy) /warmth increases evaporation / transpiration must give explicit link between heat and transpiration reduces water loss / evaporation / transpiration ignore photosynthesis [5] 6 (a) (i) guard (cells) allow phonetic spelling any one from: ignore reference to cells allow carbon dioxide to enter allow control loss / evaporation of water or control transpiration rate allow oxygen to leave. allow gaseous exchange (b) (i) 200 correct answer gains 2 marks with or without working allow mark for = 0.0 (mm 2 ) 2 Page 2 of 23
22 more / a lot of / increased water loss allow plant more likely to wilt (in hot / dry conditions) (c) (i) 0.2 the lower surface has most stomata stomata are now covered / blocked (by grease) so water cannot escape / evaporate from the stomata ignore waterproof to gain credit stomata must be mentioned at least once [9] 7 (a) (i) defence against or destroy pathogens / bacteria / viruses / microorganisms do not allow destroy disease accept engulf pathogen / bacteria / viruses / microorganism accept phagocytosis accept produce antibodies / antitoxins allow immune response (b) liver they are small fragments of cells in this order only kidney(s) (c) any two from: that it doesn t cause an immune response or isn t rejected / damaged by white blood cells whether it is a long lasting material / doesn t decompose / corrode / inert if it is strong (to withstand pressure) it will open at the right pressure that it doesn t cause clotting that it doesn t leak or it prevents backflow non toxic ignore correct size 2 [6] Page 22 of 23
23 8 (a) 5624 allow 2 marks for: correct HR = 48 and correct SV = 38 plus wrong answer / no answer or only one value correct and ecf for answer allow mark for: incorrect values and ecf for answer or only one value correct 3 (b) (i) Person 2 has low(er) stroke volume / SV / described eg Person 2 pumps out smaller volume each beat do not allow Person 2 has lower heart rate Person sends more blood (to muscles / body / lungs) (which) supplies (more) oxygen (and) supplies (more) glucose (faster rate of) respiration or transfers (more) energy for use ignore aerobic / anaerobic allow (more) energy release allow aerobic respiration transfers / releases more energy (than anaerobic) do not allow makes (more) energy removes (more) CO2 / lactic acid / heat allow less oxygen debt or less lactic acid made or (more) muscle contraction / less muscle fatigue if no other mark awarded, allow person is fitter (than person 2) for max mark [9] Page 23 of 23
2 Organisation higher (import)
 2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems
 Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level
Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level
cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical that can be used to preserve milk.
 Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Q1.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction.
 ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
A level Biology Preparation Work
 A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 1
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
GraspIT AQA GCSE Organisation Questions
 A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED
 Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules.
 The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
UR Revision Guide. igcse Biology. Page 1
 UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Draw one line from each type of respiration in human cells to the correct information. Aerobic respiration Uses oxygen
 1 Respiration can happen aerobically or anaerobically. Respiration transfers energy from glucose. (a) Draw one line from each type of respiration in human cells to the correct information. Type of respiration
1 Respiration can happen aerobically or anaerobically. Respiration transfers energy from glucose. (a) Draw one line from each type of respiration in human cells to the correct information. Type of respiration
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Gold Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Gold Level Mark Scheme
GCSE Biology. BL3HP Mark scheme June Version 1.0: Final Mark Scheme
 GCSE Biology BL3HP Mark scheme 440 June 206 Version.0: Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
GCSE Biology BL3HP Mark scheme 440 June 206 Version.0: Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
Name: B2 Organisation. Class: 35 Questions. Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Brookvale Groby Learning Trust
 B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance
 Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Tuesday 15 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Tuesday 15 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
M1. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine 1
 M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
BYA6 Physiology and the Environment
 version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
Name: BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS. Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 59
 BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 59 In a living organism, the cells are organised into organs, systems and tissues. (a) Use words from the box to complete the list
BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 59 In a living organism, the cells are organised into organs, systems and tissues. (a) Use words from the box to complete the list
COMBINED SCIENCE GCSE. Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier. Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes. Materials. For this paper you must have: Instructions all
 GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
HSC Biology. Year 2016 Mark Pages 46 Published Jan 18, Biology Notes. By James (99.05 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
Mark Scheme (Results) March GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes:
 Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
The scientists made measurements of blood flow to different organs of:
 Q1.Scientists investigated how exercise affects blood flow to different organs in the body. The scientists made measurements of blood flow to different organs of: a person resting in a room at 20 C the
Q1.Scientists investigated how exercise affects blood flow to different organs in the body. The scientists made measurements of blood flow to different organs of: a person resting in a room at 20 C the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
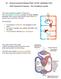 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Name: Paper 1 exp skills. Class: Date: 128 minutes. Time: 126 marks. Marks: Comments:
 Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
L1. Photosynthesis photosynthesis Photosynthesis endothermic carbon dioxide + water (+ light energy) glucose + oxygen chloroplasts chlorophyll
 L1. Photosynthesis Green plants and algae make their own food in a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is an endothermic process. Almost all life on Earth depends upon this process. Photosynthesis
L1. Photosynthesis Green plants and algae make their own food in a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is an endothermic process. Almost all life on Earth depends upon this process. Photosynthesis
GCSE Biology Flying Start
 GCSE Biology Flying Start 1. Figure 1 shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure 1 Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D 1.1 Into
GCSE Biology Flying Start 1. Figure 1 shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure 1 Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D 1.1 Into
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
Mark Scheme (Results)
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
remove solution / liquid (on outside of worm) allow water variable amounts removed from each worm ignore reference to length of timing 1
 M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
Mark Scheme (Results) January Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2B
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper B Pearson Edexcel Certificate in Biology (KBI0) Paper B Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Mark Scheme (Results) January 016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper B Pearson Edexcel Certificate in Biology (KBI0) Paper B Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Animal Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Questions
 Animal Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Questions Q1. Figure 1 shows a diagram of the human heart. Figure 1 (a) What part of the heart is labelled A? Tick one box. Aorta Atrium Valve Ventricle (b) Where
Animal Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Questions Q1. Figure 1 shows a diagram of the human heart. Figure 1 (a) What part of the heart is labelled A? Tick one box. Aorta Atrium Valve Ventricle (b) Where
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Name: ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2. Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 35
 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2 Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 35 The table shows the amounts of energy used in running and in walking at different speeds by people of
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2 Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 35 The table shows the amounts of energy used in running and in walking at different speeds by people of
Movement of substances
 1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI2F) Paper 01
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2014 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI2F) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2014 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI2F) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Homeostasis. Mark Scheme 1. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Level GCSE (9-1) Exam Board 4.5 Homeostasis and Response. Booklet Mark Scheme 1
 Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
B3 Essential Questions - Answers
 B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
NAME.. Figure 1 shows the concentrations of glucose and of lactic acid in the athlete s blood at the start and at the end of the run.
 ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.An athlete ran as fast as he could until he was exhausted. (a) Figure shows the concentrations of glucose and of lactic acid in the athlete s blood at the
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.An athlete ran as fast as he could until he was exhausted. (a) Figure shows the concentrations of glucose and of lactic acid in the athlete s blood at the
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided
 GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice
 AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
Where in the cell are proteins made? Which part of a cell controls its activities? ribosomes. nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur?
 Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Year 9 Biology Learning Cycle 2 Overview What are our bodies capable of?
 Learning Cycle Overview: Year 9 Biology Learning Cycle 2 Overview Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis 3: How do substances move in and out of our cells? The rate of diffusion cannot
Learning Cycle Overview: Year 9 Biology Learning Cycle 2 Overview Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis 3: How do substances move in and out of our cells? The rate of diffusion cannot
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
 3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
Exchange of materials
 Exchange of materials 1 During marathon races, athletes are advised to drink sports drinks. Choose the correct words from the list below to complete the sentences. alcohol fat ions protein starch sugar
Exchange of materials 1 During marathon races, athletes are advised to drink sports drinks. Choose the correct words from the list below to complete the sentences. alcohol fat ions protein starch sugar
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1)
 Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Trial Examination VCE Biology Unit 1. Written Examination. Question and Answer Booklet. Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes
 Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Theory (Core) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:80 Published This mark scheme is published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Theory (Core) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:80 Published This mark scheme is published
G.T. College G10 Term One Biology Form Test 2
 G.T. College 2018 19 G10 Term One Biology Form Test 2 Total marks: 40 marks Time allowed: 35 minutes Date: Name: Class: ( ) Section A: Multiple choice questions (10 marks@ 1 mark each) 1. Given a solution
G.T. College 2018 19 G10 Term One Biology Form Test 2 Total marks: 40 marks Time allowed: 35 minutes Date: Name: Class: ( ) Section A: Multiple choice questions (10 marks@ 1 mark each) 1. Given a solution
Question What is the function of the immune system? Answer:
 Q1 How quickly do bacteria reproduce in ideal conditions? Every 20 minutes. Q2 If you start with 1 bacterium that reproduces every 20 minutes, how many bacteria will you have after 5 hours? 32768 Q3 Give
Q1 How quickly do bacteria reproduce in ideal conditions? Every 20 minutes. Q2 If you start with 1 bacterium that reproduces every 20 minutes, how many bacteria will you have after 5 hours? 32768 Q3 Give
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]
![name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6] name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]](/thumbs/79/79061016.jpg) Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
Biology BLY3H Unit Biology B3 Written Paper Thursday 14 January am to 9.45 am For this paper you must have: Time allowed Instructions all
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January 2010 1 2 Biology
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January 2010 1 2 Biology
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
