Regulation of mutual inhibitory activities between AMPK and Akt with quercetin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
|
|
|
- Hilary Gibson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 24: , 2010 Regulation of mutual inhibitory activities between AMPK and Akt with quercetin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells YUN-KYOUNG LEE and OCK JIN PARK Department of Food and Nutrition, Hannam University Daedeok Valley Campus, Jeonmin-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon , Republic of Korea Received June 18, 2010; Accepted August 31, 2010 DOI: /or_ Abstract. In lieu of elucidating bidirectional connecting mechanism between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and survival signal Akt we applied MCF-7 breast cancer cells to determine whether AMPK modulation alters Akt signals and vice versa. Suppression of Akt activities with a synthetic Akt inhibitor alleviated AMPK activities suggesting that Akt is capable of inhibiting AMPK. Also the activation of AMPK with quercetin strongly abrogated Akt activities. Treating cancer cells with AMPK sirna or Compound C resulted in marked increment of Akt dephosphorylation indicating that AMPK has antagonistic activities towards Akt. However, quercetin exerted Akt inhibitory activities in the absence of AMPK activation. Quercetin induced partial co-localization of phospho-akt and phospho-ampk in the nucleus even though their interaction seems to be indirect since the immunoprecipitation data indicate there was no direct binding between total Akt and AMPK. These results suggest there is a mutual suppressive interaction between AMPK and Akt. The investigation of mutual suppression between Akt and AMPK by chemo-preventive agents such as quercetin may provide a mechanistic rational for controlling breast tumor cell growth. Introduction Akt, a serine/threonine protein kinase, is recognized as a significant regulator of multiple cellular processes, including cell growth, survival, apoptosis and cell cycle progression (1-3). Akt is activated by phosphorylation at Ser 473 or Thr 308 often as a downstream sequence of phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase (PI3K) in response to several growth factors, such as insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 or epidermal growth factor (EGF) (4). The aberrantly activated Akt is frequently found in many human cancers including breast cancer (5,6). A Correspondence to: Professor Ock Jin Park, Department of Food and Nutrition, Hannam University Daedeok Valley Campus, Jeonmin-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon , Republic of Korea ojpark@hnu.kr Key words: quercetin, AMP-activated protein kinase, Akt, mutual inhibition, MCF-7 breast cancer cells recent report suggests that Akt is a reliable biomarker for predicting the chemo-preventive effect of anti-cancer agents in breast cancer patients (7). Inhibition of apoptosis and stimulation of cell proliferation and metastasis have been shown to be carried out by the phosphorylation of Akt downstream targets including tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor), nuclear factor κb (NF-κB), Bad, and glycogen synthase kinase-3ß (GSK-3ß) (8,9). This may lead to continuous survival of cancer cells. Therefore, regulating Akt and Akt-regulated downstream pathways has emerged as a promising strategy for controlling cancer with chemo-preventive agents. Observations that AMPK activators are capable of dephosphorylating Akt evoked the importance of the regulation of AMPK/Akt pathway with chemo-preventive agents in cancer control (10-12). Furthermore, the Akt/TSC2/mTOR signaling pathway via the activation of AMPK has been proposed as a promising approach for tumor suppression. Several researchers have highlighted the controversial regulation between Akt and AMPK in several cancer cell models. In MDA-MB-231 cells, adiponectin-activated AMPK inhibits Akt through the activation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), which directly dephosphorylates Akt (11). In other cell models of MCF-7 it was shown that the activated AMPK with anti-cancer agent blocked phosphorylation of Akt (12). On the other hand, it has been shown that Akt negatively regulates AMPK by decreasing the AMP/ATP ratio (13). It has not been resolved whether direct interaction exists between Akt and AMPK, and further mutual suppression between these two proteins in a cancer cell system challenged with anti-cancer agents. In this study, we investigated the bidirectional regulatory mechanism between Akt and AMPK in quercetin-treated MCF-7 breast cancer cells. We found that Akt and AMPK do not directly bind to each other although they partially colocalized in the nucleus. We found that the activation of AMPK resulted in the suppression of Akt, and Akt was capable of inhibiting AMPK. These observations suggest that their interaction may occur with connecting signal(s) in both of positive suppression of AMPK on Akt and the negative regulation of Akt on AMPK. Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents. MCF-7 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and grown in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine
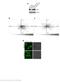
2 1494 LEE and PARK: THE MUTUAL INHIBITION OF AMPK AND Akt Figure 1. Quercetin decreases Akt activity and increases AMPK 1 activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. (A) The cells were treated with quercetin (0-200 μm) for 6 h. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and double stained with p-akt (green) and anti-mouse Alexa 488 secondary antibody or with p-ampk 1 (red) and antirabbit Alexa 546 secondary antibody. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (blue) and observed by confocal microscope. (B) The cells were treated with quercetin (0-200 μm) for 6 h, and total proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis using p-ampk 1 Thr172, AMPK 1, p-akt Ser473 and Akt antibodies. serum at 37 C in a 5% CO 2 atmosphere. Quercetin was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), and Compound C was obtained from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA, USA). LY was purchased from Tocris (Bristol, UK). Specific antibodies that recognize AMPK 1, Akt, ß-actin, and the phosphorylated forms of AMPK 1 Thr172, ACC Ser79 and Akt ser473 were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). Immunofluorescence staining. Cells were seeded on a 12- well plate with cover glasses. After treatment at the indicated time and dose, the cells were fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature (RT) and permeabilized in 0.2% Triton X-100 for 20 min at RT. Cells were blocked in 1% bovine serum albumin for 1 h and incubated overnight with primary antibodies directed against phospho-ampk 1 Thr172 and phospho-akt ser473. After washing, the cells were incubated with Alexa 546-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (Molecular Probes, OR, USA) and Alexa 488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (Molecular Probes) for 1 h at RT. Cell nuclei were stained with 10 μm of Hoechst for 10 min and observed under a confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY, USA). Western blot analysis. MCF-7 breast cancer cells were seeded into 6-well plates and treated with test compounds. Total proteins were extracted using RIPA lysis buffer [50 mm Tris-HCl (ph 8.0), 1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm PMSF] and subjected to Western blot analysis with specific antibodies. The proteins were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (Intron, Kyunggi, Korea) and detected using an LAS4000 chemiluminescence detection system (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan). Transient transfection with small interfering RNA. Small interfering RNAs (sirnas) were synthesized by Dharmacon Research (Dharmacon, Chicago, IL, USA). For transient
3 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 24: , transfection, the cells were seeded on a 6-well plate (2.5x10 5 cells/ml) in antibiotic-free medium. Following an overnight incubation, the targeting sirnas were transfected using DharmaFECT4 transfection reagent (Dharmacon) according to the manufacturer's instructions. After 72-h incubation, the cells were analyzed by Western blot analysis. Co-immunoprecipitation assay. Cells were seeded on 60-mm culture dishes and treated with quercetin. Cells were scraped into lysis buffer (1 M Tris-HCl, 0.5 M EDTA, 1 M NaCl, 1 M DTT, 10% NP-40, 10 mg/ml BSA, 0.1 M PMSF), and the lysates were precleared with protein G-beads (Zymed, San Francisco, CA, USA) for 4 h at 4 C. Proteins were then precipitated with protein G-bound primary antibody for 12 h at 4 C. After washing, protein interaction was observed by Western blot analysis. Results Dephosphorylation of Akt and activation of AMPK 1 by quercetin, and partial co-localization of Akt and AMPK 1 in the nucleus. To examine the effects of quercetin on Akt and AMPK 1 activities, cells were treated with different concentrations of quercetin for 6 h, and the levels of phospho-akt and AMPK 1 were examined by immunofluorescence staining. Akt was highly activated in the membrane and cytosol of MCF-7 breast cancer cells under serumcontaining conditions, but activated Akt was abolished in a dose-dependent manner following quercetin treatment. In addition, quercetin increased the levels of phospho-ampk 1 in the cytosol and nucleus, and activated AMPK 1 appeared to translocate to the nucleus following treatment with increasing concentrations of quercetin (Fig. 1A). Interestingly, partial co-localization was observed between phospho-akt and phospho-ampk 1 in nucleus. This is indicated by the appearance of yellow spots at concentrations of quercetin above 100 μm. The regulatory effects of quercetin on Akt and AMPK 1 were also confirmed by Western blotting. Quercetin effectively inhibited Akt through dephosphorylation but activated AMPK 1 in a dose-dependent manner in MCF-7 breast cancer cells (Fig. 1B). Akt and AMPK 1 have mutual inhibitory activities in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. To examine the regulatory mechanism between AMPK 1 and Akt, MCF-7 cells were treated with specific inhibitors of Akt and AMPK 1 (LY and Compound C, respectively) and quercetin. Inhibition of AMPK 1 by Compound C increased the quercetin-induced inhibition of Akt activity compared to quercetin treatment alone, but the phospho-akt level was lower than the control group. These results indicate that quercetin-activated AMPK 1 exerts inhibitory effects on Akt, and suggests that quercetin could inhibit Akt activity through an AMPK 1-independent pathway. In addition, treatment with LY and quercetin inhibited Akt activity, but activated AMPK 1, more effectively than quercetin alone (Fig. 2A). Moreover, inhibition of Akt by LY alone caused activation of AMPK 1 and phosphorylation of ACC, a substrate of AMPK 1 (Fig. 2B). These results suggest that Akt has inhibitory effects on AMPK 1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and the suppression Figure 2. AMPK 1 and Akt exert mutual inhibitory effects in quercetintreated MCF-7 breast cancer cells. (A) The cells were pre-treated with 20 μm of LY or 10 μm of Compound C for 30 min and then treated with 100 μm of quercetin for 6 h. Proteins were subjected Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (B) The cells were treated with 20 μm of LY or 10 μm of Compound C for 6 h, and the molecular levels were examined by Western blot analysis. (C) The cells were transiently transfected with AMPK 1 sirna or non-specific sirna for 72 h. Transfected cells or MCF-7 cells were treated with quercetin (0-100 μm) for 6 h, followed by Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. of Akt activity leads to an increase in AMPK 1 activity. To determine whether quercetin activates AMPK 1 through suppressing Akt, we examined the effects of quercetin on Akt following suppression of AMPK 1 by sirna. Quercetin strongly inhibited Akt activity in the absence of AMPK 1 (Fig. 2C). Taken together, these results suggest that quercetin activates AMPK 1 by removing the inhibitory effects of Akt, and quercetin-activated AMPK 1 suppresses Akt. Direct binding between Akt and AMPK 1 proteins was not observed. To investigate whether the regulatory effects that occur between AMPK 1 and Akt are due to their direct binding, we performed a co-immunoprecipitation assay using Akt or AMPK 1 specific antibodies. We found that Akt
4 1496 LEE and PARK: THE MUTUAL INHIBITION OF AMPK AND Akt Figure 3. There is no direct binding between Akt and AMPK 1 in quercetintreated MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The cells were treated with 100 μm of quercetin for 6, 12, 24 h, and proteins were extracted. (A) Akt protein was precipitated with primary antibody and G-protein beads, and binding to AMPK 1 was detected by Western blot analysis using an AMPK 1 primary antibody. (B) AMPK 1 protein was precipitated with primary antibody and G-protein beads, and binding to Akt was detected by Western blot analysis using an Akt primary antibody. (C) The cells were treated with 100 μm of quercetin for 6, 12, 24 h, and total proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis. Figure 4. The regulation of Akt and AMPK 1 signaling by quercetin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. and AMPK 1 do not bind directly (Fig. 3A and B), but that quercetin effectively inhibited Akt and activated AMPK 1 in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 3C). We propose that the highly activated Akt signals observed in normal MCF-7 breast cancer cells may indicate inhibitory activity on AMPK 1 (Fig. 4A). In addition, quercetin could activate AMPK 1 by suppressing Akt activity or other Akt-independent pathways. Additionally, activated AMPK 1 is also involved in suppressing Akt activity, which may contribute to the apoptotic effects of quercetin in breast cancer (Fig. 4B). Discussion Quercetin, a well-investigated flavonoid, effectively inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis in various cancer cells (14-17). We previously reported that quercetin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through strong activation of AMPK that suppresses the expression of the anti-apoptotic molecule Cox-2 (18). Quercetin also induces apoptosis in several types of cancer cells by suppressing Akt-mediated anti-apoptotic activity, cell cycle progression, and cell survival-related pathways (15,19). In this study, we investigated the regulatory mechanism by which quercetin alters Akt and AMPK, two important apoptosis-regulating molecules, and the mutual regulatory mechanism between Akt and AMPK signals in quercetin-treated MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and our data indicated that quercetin was capable of activating AMPK by removing inhibitory activity of Akt on AMPK, and by direct activation on AMPK. These observations imply that Akt and AMPK have mutual inhibitory effects, and quercetin modulates both of these molecules through up- or downregulating ability in controlling cell growth or apoptosis. Recent reports have shown that suppression of Akt by AMPK is mediated through the activation of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) or PP2A, and the involvement of IRS-1 between Akt and AMPK was suggested (11,12,20). On the other hand, the inhibitory effect of Akt on AMPK
5 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 24: , was explained by either alteration of intracellular ATP by Akt or the regulatory activities of Akt on AMPK upstream kinases or phosphatases (13,21). Our results confirmed that Akt and AMPK signals have mutual inhibitory activities in MCF-7 cell system. Treating MCF-7 cells with Akt inhibitor LY or quercetin activated AMPK. The combination of quercetin and LY inhibited Akt while activating AMPK more strongly than quercetin treatment alone. The activated AMPK by quercetin exerted inhibitory effects on Akt as observed by elevated phosphorylation of Akt following inhibition of AMPK by Compound C. Because of the bidirectional relationship that occurs between Akt and AMPK following quercetin treatment, we hypothesized that quercetin may cause these two proteins to bind to each other. Immunofluorescence staining showed slight co-localization of Akt and AMPK 1 in the nucleus of quercetin-treated MCF-7 cells. However, co-immunoprecipitation revealed that Akt and AMPK do not bind to each other. These results suggest that there might exist another signaling molecule such as phosphatase down-regulating Akt and up-regulating AMPK activities by quercetin. In conclusion, we demonstrated that Akt and AMPK have mutual inhibitory activities, and quercetin regulated these signals through suppressing or stimulating their actions in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. These findings imply that quercetin strongly inhibits Akt activity, possibly through activating AMPK as well as through directing its suppressive effects against Akt. These observations suggest that anticancer agents, such as quercetin, have regulatory effects on both Akt and AMPK, and this could provide an effective strategy for preventing different types of cancers, including breast cancer. Acknowledgements This study was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. R ). References 1. Carnero A: The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer. Curr Pharm Des 16: 34-44, Bhaskar PT and Hay N: The two TORCs and Akt. Dev Cell 12: , Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, et al: Deregulation of the Akt pathway in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8: 27-36, Frech M, Andjelkovic M, Ingley E, Reddy KK, Falck JR and Hemmings BA: High affinity binding of inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides to the pleckstrin homology domain of RAC/protein kinase B and their influence on kinase activity. J Biol Chem 272: , Ghayad SE and Cohen PA: Inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: new hope for breast cancer patients. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 5: 29-57, Cicenas J: The potential role of Akt phosphorylation in human cancers. Int J Biol Markers 23: 1-9, Yang SX, Costantino JP, Kim C, et al: Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 predicts benefit of paclitaxel chemotherapy in nodepositive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28: , Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N and Koutsilieris M: The Akt pathway: molecular targets for anti-cancer drug development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: , Wang X, Chen W and Lin Y: Sensitization of TNF-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells by concurrent suppression of the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355: , Eto I: Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(kip1) expression: effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and retinoic acids. Cancer Cell Int 10: 3, Kim KY, Baek A, Hwang JE, et al: Adiponectin-activated AMPK stimulates dephosphorylation of AKT through protein phosphatase 2A activation. Cancer Res 69: , Zakikhani M, Blouin MJ, Piura E and Pollak MN: Metformin and rapamycin have distinct effects on the AKT pathway and proliferation in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123: , Hahn-Windgassen A, Nogueira V, Chen CC, Skeen JE, Sonenberg N and Hay N: Akt activates the mammalian target of rapamycin by regulating cellular ATP level and AMPK activity. J Biol Chem 280: , Kim YH and Lee YJ: TRAIL apoptosis is enhanced by quercetin through Akt dephosphorylation. J Cell Biochem 100: , Granado-Serrano AB, Angeles Martin M, Bravo L, Goya L and Ramos S: Time-course regulation of quercetin on cell survival/ proliferation pathways in human hepatoma cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 52: , Zhang Q, Zhao XH and Wang ZJ: Flavones and flavonols exert cytotoxic effects on a human oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell line (OE33) by causing G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 46: , Park CH, Chang JY, Hahm ER, Park S, Kim HK and Yang CH: Quercetin, a potent inhibitor against beta-catenin/tcf signaling in SW480 colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328: , Lee YK, Park SY, Kim YM, Lee WS and Park OJ: AMP kinase/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway regulates proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells treated with quercetin. Exp Mol Med 41: , Waite KA, Sinden MR and Eng C: Phytoestrogen exposure elevates PTEN levels. Hum Mol Genet 14: , Huang X, Wullschleger S, Shpiro N, et al: Important role of the LKB1-AMPK pathway in suppressing tumorigenesis in PTEN-deficient mice. Biochem J 412: , Kovacic S, Soltys CL, Barr AJ, Shiojima I, Walsh K and Dyck JR: Akt activity negatively regulates phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart. J Biol Chem 278: , 2003.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Quercetin Regulates Sestrin 2-AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway and Induces Apoptosis via Increased Intracellular ROS in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells
 JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2013 pissn 2288-3649 ㆍ eissn 2288-3657 Quercetin Regulates Sestrin 2-AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway and Induces Apoptosis via Increased Intracellular
JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2013 pissn 2288-3649 ㆍ eissn 2288-3657 Quercetin Regulates Sestrin 2-AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway and Induces Apoptosis via Increased Intracellular
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit
 AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0693 TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nandini Ghosh-Choudhury, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0693 TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nandini Ghosh-Choudhury, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy se
 A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
AMP kinase/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway regulates proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells treated with quercetin
 EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 41, No. 3, 201-207, March 2009 AMP kinase/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway regulates proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells treated with quercetin Yun-Kyoung Lee
EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 41, No. 3, 201-207, March 2009 AMP kinase/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway regulates proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells treated with quercetin Yun-Kyoung Lee
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(4):196-203 In Vitro Effect of Thai herbal extracts with
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(4):196-203 In Vitro Effect of Thai herbal extracts with
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
The PI3K/AKT axis. Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia. Introduction
 The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplemental Material:
 Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression. through inhibition of Hsp90
 Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
 Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples:
 Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line
 Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Trehalose, sucrose and raffinose are novel activators of autophagy in human. keratinocytes through an mtor-independent pathway
 Title page Trehalose, sucrose and raffinose are novel activators of autophagy in human keratinocytes through an mtor-independent pathway Xu Chen 1*, Min Li 1*, Li Li 1, Song Xu 1, Dan Huang 1, Mei Ju 1,
Title page Trehalose, sucrose and raffinose are novel activators of autophagy in human keratinocytes through an mtor-independent pathway Xu Chen 1*, Min Li 1*, Li Li 1, Song Xu 1, Dan Huang 1, Mei Ju 1,
Planar Waveguides: How Nano Layers Enable to Detect Zepto Moles of Macro Molecules in Pico Liter Spots on Micro Arrays
 Planar Waveguides: How Nano Layers Enable to Detect Zepto Moles of Macro Molecules in Pico Liter Spots on Micro Arrays Dr. Markus Ehrat Zeptosens A Division of Bayer Schweiz AG SSOM Meeting March 16 /17
Planar Waveguides: How Nano Layers Enable to Detect Zepto Moles of Macro Molecules in Pico Liter Spots on Micro Arrays Dr. Markus Ehrat Zeptosens A Division of Bayer Schweiz AG SSOM Meeting March 16 /17
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Catalog # Lot # 16875
 MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
ULTRARIPA kit for Lipid Raft. 1. Basic information
 ULTRARIPA kit for Lipid Raft 1. Basic information Background: Cell lysis buffers SDS-containing buffer Advantages - Strong extraction activity Fully extraction of cells Disadvantages - Denaturing protein
ULTRARIPA kit for Lipid Raft 1. Basic information Background: Cell lysis buffers SDS-containing buffer Advantages - Strong extraction activity Fully extraction of cells Disadvantages - Denaturing protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3
 Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
FOR REVIEW. BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission. Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: BMB
 BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Product Manual. [pser 473/474 ]Akt1/2 ELISA kit TABLE OF CONTENTS
![Product Manual. [pser 473/474 ]Akt1/2 ELISA kit TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Manual. [pser 473/474 ]Akt1/2 ELISA kit TABLE OF CONTENTS](/thumbs/91/106555455.jpg) [pser 473/474 ]Akt1/2 ELISA kit Catalog # ADI-900-162 96 well enzyme-linked immunoassay kit For use with cell lysates All reagents, except standard, should be stored at 4 C. Store standard at -20 C. Check
[pser 473/474 ]Akt1/2 ELISA kit Catalog # ADI-900-162 96 well enzyme-linked immunoassay kit For use with cell lysates All reagents, except standard, should be stored at 4 C. Store standard at -20 C. Check
CELL DENSITY AFFECTS ERK SIGNALING HETEROGENEITY. Yen-Der Li School of Medicine and Department of Physics National Taiwan University
 1 CELL DENSITY AFFECTS ERK SIGNALING HETEROGENEITY Yen-Der Li School of Medicine and Department of Physics National Taiwan University Outline 2 Project summary Introduction Project scope & background Preliminary
1 CELL DENSITY AFFECTS ERK SIGNALING HETEROGENEITY Yen-Der Li School of Medicine and Department of Physics National Taiwan University Outline 2 Project summary Introduction Project scope & background Preliminary
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Supplementary Information. Table of contents
 Supplementary Information Table of contents Fig. S1. Inhibition of specific upstream kinases affects the activity of the analyzed readouts Fig. S2. Down-regulation of INCENP gene induces the formation
Supplementary Information Table of contents Fig. S1. Inhibition of specific upstream kinases affects the activity of the analyzed readouts Fig. S2. Down-regulation of INCENP gene induces the formation
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or
 Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
PI(3,4,5)P3 regulates the interaction between Akt and B23 in the nucleus
 BMB reports PI(3,4,5)P3 regulates the interaction between Akt and B23 in the nucleus Il-Sun Kwon 1,3, Kyung-Hoon Lee 2,3, *, Joung Woo Choi 1 & Jee-Yin Ahn 1,3, * 1 Department of Molecular Cell Biology,
BMB reports PI(3,4,5)P3 regulates the interaction between Akt and B23 in the nucleus Il-Sun Kwon 1,3, Kyung-Hoon Lee 2,3, *, Joung Woo Choi 1 & Jee-Yin Ahn 1,3, * 1 Department of Molecular Cell Biology,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
 Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Expanded View Figures
 MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
1 ml e.a. USD μl 30 e.a. USD ml 10 e.a. USD ml 100 e.a. USD 1700
 Data Sheet Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Full spectrum) A blend of pan-phosphatase inhibitors for protection of phosphorylation state. Catalog No. Size Price K5000 1 ml e.a. USD 37 100 μl 30 e.a. USD
Data Sheet Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Full spectrum) A blend of pan-phosphatase inhibitors for protection of phosphorylation state. Catalog No. Size Price K5000 1 ml e.a. USD 37 100 μl 30 e.a. USD
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates
 Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0011 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description
Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0011 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description
Supplemental Information. Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras. Promotes Basal Extrusion. of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P. Current Biology, Volume 24
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20 C
 Phospho-Stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20
Phospho-Stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation
 Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Bio-Plex Pro Cell Signaling Assays
 Acute Phase Response Cancer Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors Immunology/Inflammation Immunoglobulin Isotyping Cell Signaling Toxicology Bio-Plex Pro Cell Signaling
Acute Phase Response Cancer Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors Immunology/Inflammation Immunoglobulin Isotyping Cell Signaling Toxicology Bio-Plex Pro Cell Signaling
Human PKA (Protein Kinase A) Activity Assay Kit
 Human PKA (Protein Kinase A) Activity Assay Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2532 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The PKA (Protein Kinase A) Activity kit is designed to quantitatively measure PKA activity in a variety
Human PKA (Protein Kinase A) Activity Assay Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2532 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The PKA (Protein Kinase A) Activity kit is designed to quantitatively measure PKA activity in a variety
SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE
 SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE 45 CLINICAL CASES SERIAL DILUTION MULTIPLE PROTEIN CONCENTRATION QUANTITATIVE ASSAY PRODUCT NUMBER: PM1-001-N SOMAPLEX REVERSE
SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE 45 CLINICAL CASES SERIAL DILUTION MULTIPLE PROTEIN CONCENTRATION QUANTITATIVE ASSAY PRODUCT NUMBER: PM1-001-N SOMAPLEX REVERSE
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors
 Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3K isoform-selective inhibition
 Biochem. J. (2008) 415, 97 110 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20080639 97 A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3K
Biochem. J. (2008) 415, 97 110 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20080639 97 A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3K
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
