Running footline: PPARδ activation attenuates hepatic steatosis and inflammation
|
|
|
- Noel McDonald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PPARδ ctivtion ttenutes heptic stetosis in Ldlr / mice y enhnced ft oxidtion, reduced lipogenesis nd improved insulin sensitivity Authors: Lzr A. Bojic, 1,2 Dwn E. Telford, 1,4 Morgn D. Fullerton, 5 Reecc J. Ford, 5 Brin G. Sutherlnd, 1 Jne Y. Edwrds, 1,4 Cynthi G. Swyez, 1,4, Roert Gros, 1,3 Bruce E. Kemp, 6 Gregory R. Steinerg, 5 nd Murry W. Huff, 1,2,4 Vsculr Biology, Rorts Reserch Institute 1, Deprtments of Biochemistry 2, Physiology nd Phrmcology 3 nd Medicine 4, The University of Western Ontrio, 1151 Richmond Street North, London, Ontrio, Cnd, N6A 5B7. 5 Division of Endocrinology nd Metolism, Deprtment of Medicine, McMster University, 128 Min Street West, Hmilton, Ontrio, Cnd, L8S 4K1. 6 St. Vincent s Institute of Medicl Reserch nd Deprtment of Medicine, University of Melourne, 41 Victori Prde, Fitzroy, Victori 365, Austrli Address correspondence to: Murry W. Huff, Rorts Reserch Institute, Rm 4222, The University of Western Ontrio, 1151 Richmond Street North, London, Ontrio, Cnd, N6A 5B7, Phone: 1 (519) FAX: 1 (519) Emil: mhuff@uwo.c Running footline: PPARδ ctivtion ttenutes heptic stetosis nd inflmmtion
2 2 Arevitions: ACC, cetyl CoAcroxylse; ACOX, cetylcoa oxidse; ADFP, dipocyte differentitionrelted protein; Akt, protein kinse B; AMPK, denosine monophosphtectivted protein kinse; ARG1, rginse 1; β1 /, AMPK β1 suunit knockout; CE, cholesterylester; CHOP, C/EBPhomologous protein; CCL2, chemokine (CC motif) lignd 2; CCL3, chemokine (CC motif) lignd 3; CLAMS, Comprehensive L Animl Monitoring System; CPT1α, crnitte plmitoyl trnsferse1 lph; EE, energy expenditure; ER, endoplsmic reticulum; FA, ftty cid; FAS, Fsn, ftty cid synthse; FOXO1, forkhed ox protein O1; GAPDH, glycerldehyde 3phosphte dehydrogense; GRP78, 78kD glucoseregulted protein; HFHC, highft, cholesterolcontining; ICAM1, intercellulr dhesion molecule 1; IL, interleukin; inos, inducile nitric oxide synthse; INSIG, insulin induced gene; IRS, insulin receptor sustrte; mtorc1, mmmlin trget of rpmycin complex 1; PCK1, phosphoenolpyruvte croxykinse 1; PGC1α, peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor gmm coctivtor 1 lph; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3kinse; PPAR, peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor; RER, respirtory exchnge rtio; SREBF, sterol regultory elementinding fctor; SREBP1c, sterol response element inding protein 1c; TC, totl cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; TNFα, tumor necrosis fctor lph; UPR, unfolded protein response; WT, wildtype.
3 3 Astrct The peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor (PPAR) δ regultes systemic lipid homeostsis nd inflmmtion ut its role in heptic lipid metolism remins uncler. Here, we exmine whether intervening with selective PPARδ gonist corrects heptic stetosis induced y highft, cholesterol contining (HFHC) diet. Ldlr / mice were fed chow or HFHC diet (42% ft,.2% cholesterol) for 4 weeks. For n dditionl 8 weeks, the HFHC group were fed HFHC or HFHC plus GW1516 (3mg/kg/d). GW1516intervention significntly ttenuted liver triglyceride ccumultion y induction of ftty cid (FA) βoxidtion nd ttenution of FA synthesis. In primry mouse heptocytes, GW1516tretment stimulted denosine monophosphtectivted protein kinse (AMPK) nd cetylcoa croxylse (ACC) phosphoryltion in wildtype (WT) heptocytes, ut not AMPKβ1 / heptocytes. However, FA oxidtion ws only prtilly reduced in AMPKβ1 / heptocytes, suggesting n AMPKindependent contriution to the GW1516 effect. Similrly PPARδmedited ttenution of FA synthesis ws prtilly due to AMPK ctivtion, s GW1516 reduced lipogenesis in WT heptocytes ut not AMPKβ1 / heptocytes. HFHCfed nimls were hyperinsulinemic nd exhiited selective heptic insulin resistnce, which contriuted to elevted fsting FA synthesis nd hyperglycemi. GW1516 intervention normlized fsting hyperinsulinemi nd selective heptic insulin resistnce, nd ttenuted fsting FA synthesis nd hyperglycemi. The HFHC diet polrized the liver towrds proinflmmtory M1 stte, which ws reversed y GW1516intervention.Thus, PPARδ gonist tretment inhiits the progression of preestlished heptic stetosis. Key Words: Heptic Triglyceride, Lipids, Insulin Resistnce, Inflmmtion, Intervention, Energy Expenditure
4 4 INTRODUCTION Heptic stetosis, defined s excessive lipid ccumultion in the liver, is oserved in greter thn 4% of ptients with type 2 dietes (1,2). Although cusl reltionship etween heptic stetosis nd insulin resistnce hs een difficult to define(1), inflmmtion hs een implicted s contriuting fctor to dysregulted heptic insulin signling (3). As consequence, hyperinsulinemimedited lipogenesis ensues which long with suppressed ftty cid (FA) oxidtion contriutes to ectopic lipid deposition(4). Prolonged heptic stetosis cn result in nonlcoholic stetoheptitis, cirrhosis nd eventully liver filure (3). However, few therpeutic strtegies exist tht effectively correct heptic stetosis in the setting of insulin resistnce. At moleculr level, insulin inding to its cognte receptor leds to receptormedited tyrosine phosphoryltion of insulin receptor sustrtes (IRS1 nd/or IRS2), which in turn ctivte phosphoinositide 3kinse (PI3K) to simulte the phosphoryltion nd ctivtion of protein kinse B (Akt) (5). Normlly, insulinstimulted Akt ctivtion results in the suppression of heptic gluconeogenesis due to phosphoryltion nd inctivtion of forkhed ox (Fox) O1, nd the promotion of de novo lipogenesis due to phosphoryltion nd ctivtion of the mmmlin trget of rpmycin complex (mtorc) 1 (6). However, in the insulin resistnt liver, Akt loses its ility to inctivte FoxO1, ut prdoxiclly mintins its ility to ctivte TORC1 (6). Consequently, mtorc1driven trnscription of the mster regultor of lipogenesis, sterol regultory element inding protein (SREBP)1c, remins chroniclly ctive (6). In ddition, insulin increses the mount of proteolyticlly processed ctive SREBP1c through mechnisms tht remin poorly understood (7). In this wy, hyperinsulinemi nd ccompnying heptic insulin resistnce leds to persistent FA synthesis nd eventully excessive heptic lipid ccumultion. In ddition to unregulted lipogenesis, decresed ft oxidtion excertes heptic lipid ccumultion during insulin resistnce (81). The denosine monophosphtectivted protein
5 5 kinse (AMPK) controls cellulr nd whole ody energy metolism (11,12). Specificlly, heptic AMPK is pivotl regultor of ft oxidtion nd synthesis, primrily vi direct phosphoryltion nd inhiition of cetylcoa croxylse (ACC) (1214). Biochemiclly, this reduces mlonyl CoA levels in the liver which (i) depletes ftty cid synthse (FAS) of sustrte in the lipogenic pthwy nd (ii) results in the derepression of crnitine plmitoyl trnsferse 1α (CPT1α) in the FA oxidtion pthwy (15). Thus, ctivtion of AMPK provides potentil mechnism for the ttenution of heptic stetosis. Peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor (PPAR) δ elongs to clss of lignddependent trnscription fctors involved in regultion of glucose nd lipid homeostsis(16). A numer of niml nd humn studies hve highlighted potentil role for ctivtion of this receptor in the tretment of metolic disese (17,18). In mice, genetic mnipultions of Pprδ s well s prevention experiments involving dministrtion of PPARδ gonists reveled tht ctivtion of this receptor ttenutes dyslipidemi nd hyperglycemi, improves wholeody insulin sensitivity nd prevents dietinduced oesity (1921). However, there re seemingly conflicting nd controversil reports with respect to PPARδctivtion nd heptic lipid metolism in mice (19,2225). The PPARδ gonist GW1516 ttenuted dietinduced heptic stetosis; however the 2fold increse in heptic Acox expression suggested PPARαdependent effect (22). Tnk et l. reported tht incresed expression of genes involved in heptic ft oxidtion resulted in reduced heptic lipid droplets in highft fed mice treted with GW1516 (2). Additionlly, in d/d mice injected with denovirl PPARδ (dpparδ), liver lipid droplets were reduced coincident with decresed SREBP1c processing, suggesting ttenuted lipogenesis (23). Despite reports suggesting reduced heptic stetosis, other studies hve demonstrted tht PPARδ ctivtion exerts either no effect (24), or induces liver triglyceride (TG) ccumultion (19,25). In d/d mice, GW1516 tretment resulted in incresed heptic TG s result of direct trnscriptionl ctivtion of cetylcoa croxylse β (Acc2), nd incresed
6 6 lipogenic gene expression (19). dpparδ gene delivery to highft fed Ldlr / mice incresed oth heptic lipogenic gene expression nd heptic TG ccumultion (25). None of these studies ctully mesured heptic FA oxidtion or synthesis. The clim tht PPARδ ctivtion increses heptic stetosis is counterintuitive since PPARδ gonists re known to improve wholeody insulin sensitivity nd lipid homeostsis, nd stimulte Cpt1medited ftty cid oxidtion in vriety of cell types nd tissues (1921). Furthermore, in muscle, GW1516 stimulted FA oxidtion due, in prt, to incresed AMPK ctivity (26,27). In model of heptic stetosis, GW1516 prevented dietinduced inctivtion of heptic AMPK (24). This suggests tht AMPK ctivtion y PPARδ gonists hs the ility to regulte heptic βoxidtion nd/or FA synthesis. The ojective of this study ws to determine whether PPARδ ctivtion cn reverse preestlished heptic stetosis nd insulin resistnce. We demonstrte tht intervention with GW1516 in Ldlr / mice fed high ft, cholesterolcontining diet, decresed heptic lipid deposition, result of ttenuted lipogenesis nd incresed FA oxidtion. Decresed FA synthesis ws due to GW1516medited correction of selective heptic insulin resistnce. In ddition, we provide evidence tht AMPK ctivtion ws required for the PPARδmedited ttenution of heptic de novo lipogenesis, ut ws not required for PPARδmedited induction of FA oxidtion. Furthermore, reduced liver TG content ws coupled to ttenuted heptic inflmmtion.
7 7 METHODS Mle Ldlr / mice on the C57BL/6 ckground (Jckson Lortory, Br Hror, MA), were housed in pirs in stndrd cges t 23 º C. The nimls were cred for in ccordnce with the Cndin Guide for the Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls. All experimentl procedures were pproved y the Animl Cre Committee t the University of Western Ontrio. Mice 112 weeks of ge (n=16) were fed d liitum, purified rodent chow diet (14% of clories from ft, Hrln Tekld TD864, Mdison WI) for 12 weeks. Another group of mice (112 weeks of ge, n=48) were fed highft cholesterolcontining western diet (HFHC 42% of clories from ft,.2% cholesterol, Hrln Tekld TD9268) for 4 weeks. For the susequent 8 weeks, hlf of these mice (n=24) remined on the HFHC diet; the other hlf (n=24) were fed the HFHC diet supplemented with 3mg/kg/dy GW1516 (Enzo Life Sciences, Ann Aror, MI). A similr dose of GW1516, dministered y orl gvge, hs een used previously in mice (24,28,29). In the present study, t the end of the drk cycle nd light cycle, nonfsting serum concentrtions for GW1516 were 64 ± 72 nmol/l nd 369 ± 26 nmol/l, respectively, for men concentrtion of 487 ± 5 nmol/l. This plsm concentrtion is ove the EC5 for murine PPARδ (2 nm), ut elow the EC5 for murine PPARγ (1 μm) nd well elow the EC5 for murine PPARα (2.5 μm) (3). Animls were fsted for 4h prior to nlyses or scrifice. For fsting/refeeding studies, nimls were either fsted for 16h prior to scrifice or fsted for 16h followed y 2h cute refeeding period of the experimentl diets prior to scrifice (31). Blood smples were otined s previously descried (9,32). Body weights nd cloric consumption were determined s descried previously (8). Activtion of AMPK in vivo Activtion of AMPK in vivo ws ssessed in chowfed Ldlr / mice following intrperitonel (i.p.) injection of GW1516 or A Animls were fsted overnight (15:7: h), followed y period of free ccess to food (chow) t 7: h for 2h. At 9: h, chow ws removed nd mice
8 8 were injected i.p. with vehicle (5% dimethyl sulfoxide in phosphteuffered sline), 3mg/kg GW1516 or 3mg/kg A (Selleck Bio, Houston, TX), synthetic ctivtor of AMPK (33). Anlyses of in vivo phosphoryltion of AMPK nd ACC were performed in liver smples isolted t scrifice y freezeclmp method, 9 minutes fter injection of the respective tretments, nd stored t 8 C until nlysis s descried (34). Energy Expenditure In the induction/intervention studies (week 11), nlyses of energy expenditure (EE) nd respirtory exchnge rtio (RER) were performed using the Oxymx Comprehensive L Animl Monitoring System (CLAMS, Columus Instruments, Columus, OH)(8). Mice were provided free ccess to food nd wter nd cclimtized to the system for 24h prior to 24h dt collection period, during which dt on O 2 consumption nd CO 2 production were collected every 1 minutes. EE nd RER were clculted s descried previously (8). Primry Mouse Heptocyte Isoltion, Lipogenesis nd Ftty Acid Oxidtion Primry mouse heptocytes were isolted from chowfed wildtype (WT) or AMPKβ1 / C57BL/6J mice y the collgense perfusion method s descried (35). AMPKβ1 suunit null mice on C57BL/6 ckground were generted using stndrd homologous recomintion techniques, s descried previously (35,36). AMPKβ1 / mice hve 9% reduction in liver AMPK ctivity, compred to WT mice. Studies in primry heptocytes from AMPKβ1 / mice were conducted y Dr. L.A. Bojic in the lortory of Dr. G.R. Steinerg, McMster University, Hmilton, Ontrio Cnd. Experiments were performed the dy following heptocyte isoltion. For mrna expression nlyses, heptocytes were incuted with either vehicle, GW1516 or A (t the indicted concentrtions) for 6 h prior to cell lysis in TRIzol regent. For lipogenesis nd FA oxidtion experiments, cells were wshed with PBS nd incuted in serumfree Medium 199 for 3 h. Lipogenesis ws ssessed y incuting cells for 4 h with serumfree Medium 199 contining [1 14 C]cette (.5 μci/ml) (Amershm Biosciences) nd.5 mm unleled sodium
9 9 cette, with or without GW1516 (1 nm) or A (1 µm). Susequently, cells were wshed twice with PBS nd hrvested y scrping cells into PBS. Lipids were extrcted using the Bligh nd Dyer method s descried (37,38). For FA oxidtion, cells were incuted for 4 h with serumfree Medium 199 contining [1 14 C]plmitic cid (.5 μci/ml) (Amershm Biosciences) nd.5 mm unleled plmitte, with or without GW1516 (1 nm) or A (1 µm). FA oxidtion ws determined y mesuring lelled CO 2 nd cidsolule metolites s descried (39). Plsm, Blood nd Tissue Anlyses Plsm insulin concentrtions were determined y ELISA (Alpco Dignostics, Slem, NH) in EDTAplsm ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions s descried previously (1). Blood glucose ws determined using n Ascensi Elite glucometer (Byer Helthcre, Toronto, Cnd) (1). Liver lipids were extrcted from 1 mg of tissue using the method of Folch et l. nd quntitted s descried previously (8,4). FA synthesis ws mesured following intrperitonel injection of [1 14 C]cetic cid s descried (9). Heptic FA oxidtion ws determined in tissue homogentes of fresh liver y conversion of [ 3 H]plmitte to 3 H 2 O (9). Immunolotting nd Densitometry Totl tissue or cell lystes were isolted from mouse liver or from primry mouse heptocytes s previously descried (41,42). Proteins were seprted y SDSPAGE, trnsferred to polyvinylidenedifluoride memrnes nd immunolotted (42). Memrnes were proed using ntiodies ginst mouse phosphorylted nd totl Akt, FoxO1, mtorc1, AMPK nd ACC s well s GRP78, CHOP nd βctin (Cell Signling, Dnvers, MA). The ntiphosphorylted ACC ntiody recognizes oth pacc1 Ser76 nd pacc2 Ser212, which recently hve een shown to hve overlpping functions (43). For SREBP1, liver lystes were seprted into postnucler nd nucler frctions s descried (41,42). Ech frction ws seprted y SDSPAGE (415% crylmide grdient) nd trnsferred to PVDF memrnes (42). Memrnes from oth frctions
10 1 were proed with monoclonl ntiody to SREBP1 (Neomrkers, Fremont, CA), stripped nd reproed with either the βctin ntiody for the postnucler frction or polyclonl lmin A/C ntiody (Snt Cruz Biotechnology, Snt Cruz, CA) for the nucler frction (41). Quntittion of protein on ll lots ws determined y densitometry s descried (41,42). Quntittive reltime PCR Gene Aundnce Anlyses Totl RNA ws isolted from liver tissue or primry mouse heptocytes using TRIzol regent (Life Technologies, Burlington, ON) s per mnufcturer s instructions. Specific mrna undnces (Pgc1, Ppr, Acox, Cpt1, Adfp, Sref1c, Fsn, Insig1, Insig2, Pck1, Tnf, Icm1, Il1, Ccl2, Ccl3, inos, Arg1, Hsp5 nd Gpdh) were mesured vi quntittive reltime PCR (qrtpcr) using n ABI Prism (79HT) Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) s previously descried (9,44). mrna undnces were clculted using the stndrd curve method. Primer nd proe sets were otined from Applied Biosystems (Streetsville, CA) inventoried gene expression rrys with the exception of murine Sref1c (Srep1c) which ws generted s descried previously (9,44) Sttisticl Anlyses Dt re expressed s mens / SEM. Student s pired ttest ws used to determine significnt differences etween two groups. Onewy ANOVA followed y pirwise comprisons y the Tukey s test ws used to determine differences etween three or more groups. For fsting/refeeding experiments nd experiments involving WT or AMPKβ1 / primry mouse heptocytes, twowy ANOVA followed y pirwise comprisons y the Tukey s test ws used to determine sttisticlly significnt differences nd interctions except for experiments where comprisons re mde to WT control. For these, twowy ANOVA followed y the Bonferroni test ws used. Significnce thresholds were P vlues less thn 5 nd mrked y different upper cse or lower cse letters s well s sterisks, s indicted in the figure legends.
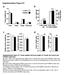
11 11 RESULTS GW1516tretment ttenutes heptic TG ccumultion, in prt, y stimulting ftty cid βoxidtion Mle C57BL/6 Ldlr / mice were dministered HFHC diet for 4 weeks to induce heptic stetosis. Susequently, mice were fed the HFHC diet supplemented with either vehicle or GW1516 (3mg/kg/dy) for n dditionl 8 weeks. In mice fed the HFHC diet for 4 weeks, prominent heptic stetosis developed, s evidenced y significntly incresed TG, totl cholesterol nd cholesteryl ester (Fig.1AC). These lipids continued to increse over the susequent 8 weeks in HFHCfed mice. In contrst, the ddition of GW1516 to the HFHC diet for 8 weeks decresed heptic lipids y 35% demonstrting significnt slowing of stetosis progression (Fig. 1AC). As we reported previously using similr protocol (45), GW1516 intervention reduced the rte of weight gin (6%), wheres cloric consumption ws unffected. (Fig. 1D,E). We resoned tht GW1516 ttenutes liver TG ccumultion vi incresed FA βoxidtion nd/or reduced ftty cid synthesis. With respect to FA oxidtion, suppressed Pgc1 expression in livers of mice fed the HFHCdiet for 12 weeks (2% compred to chowfed mice), ws not further ffected y GW1516tretment (Fig.2A). Furthermore, t 12 weeks, the expression of Ppr nd the PPARαtrget gene Acox were unffected y ny diet (Fig.2B,C). In contrst, Cpt1 mrna undnce ws significntly enhnced (35%) in livers isolted from GW1516 treted nimls, which ws ssocited with significnt 5% increse in FA oxidtion s compred to HFHCfed nimls (Fig.2D,E). Expression of the PPARδspecific trget gene dipocyte differentitionrelted protein (Adfp) (46) ws significntly incresed (~6%) in livers from GW1516treted nimls (Fig.2F). Collectively, these results suggest tht GW1516 ttenutes liver TG ccumultion prtly due to incresed heptic FA βoxidtion, primrily the consequence of ctivting the PPARδtrget gene Cpt1.
12 12 To further investigte the GW1516induced increse in heptic FA oxidtion, we ssessed energy lnce in metolic monitoring system. Totl energy expenditure (EE) ws significntly higher (16%) in mice receiving GW1516 compred to mice remining on the HFHC diet lone (Fig.2G). The respirtory exchnge rtio (RER) profiles, which reflect the reltive utiliztion of crohydrte (RER~1.) versus ft (RER~.7), were similr etween the HFHCfed nd GW1516intervention groups (Fig.2H). Given the significnt increse in totl EE in GW1516treted mice, the lck of difference in RER profiles suggests tht oth crohydrte nd ft utiliztion re incresed y PPARδ ctivtion. AMPK ctivtion is not required for the GW1516medited increse in ft oxidtion GW1516 hs een shown to ctivte AMPK in muscle (26). Given the GW1516induced stimultion of heptic FA oxidtion in vivo, we hypothesized tht AMPK ctivtion my e involved. To evlute the ility of GW1516 to cutely ctivte heptic AMPK in vivo, we employed fsting, feeding, injection nd refsting protocol (34). In livers isolted 9 minutes fter the injection of GW1516, we oserved significnt 2fold increse in phosphoryltion of AMPK nd its downstrem effector ACC (Fig.3A). Mice were lso injected with the potent synthetic AMPK ctivtor A (33), which incresed AMPK nd ACC phosphoryltion ~2 fold (Fig.3A). The requirement of AMPK for the GW1516medited stimultion of FA oxidtion ws determined in isolted primry mouse heptocytes from wild type (WT) or AMPKβ1 / mice (referred to s β1 / mice). Deletion of the AMPKβ1 suunit results in 9% loss of heptic AMPK ctivity (35). As depicted in Figure 3B, oth GW1516 nd A incresed phosphoryltion of AMPK nd ACC in WT heptocytes ut not in β1 / heptocytes. Furthermore, oth GW1516 nd A enhnced FA oxidtion in WT heptocytes y 3% (Fig.3C). The effect of A ws lost in β1 / heptocytes, consistent with n AMPKβ1dependent effect (36). However, s in WT cells, GW1516 ws le to increse FA oxidtion in β1 / heptocytes
13 13 pproximtely 3% (Fig.3C). To reconcile this, we exmined Cpt1 expression, PPARδ trget gene, in WT nd β1 / heptocytes. GW1516tretment significntly enhnced Cpt1 expression (~2fold) in oth WT nd β1 / heptocytes (Fig.3D). In contrst, A hd no effect on Cpt1 mrna undnce in heptocytes of either genotype (Fig.3D). The PPARδspecific trget gene Adfp ws incresed 2fold in isolted heptocytes from either genotype, wheres the PPARαspecific trget Acox ws unffected y genotype or tretment (Fig.3E,F). Tken together, these results demonstrte tht the GW1516induced increse in Cpt1medited FA oxidtion does not require AMPK ctivtion nd does not involve PPARα ctivtion. GW1516intervention ttenutes de novo lipogenesis, in prt, vi ctivtion of AMPK s well s correction of selective heptic insulin resistnce In ddition to regulting FA oxidtion, AMPK is known to regulte de novo lipogenesis (14). When incuted with WT heptocytes, GW1516 significntly inhiited de novo lipogenesis y ~3% (Fig.4A). This effect ws significntly ttenuted in β1 / heptocytes (Fig.4A). Consistent with n AMPKβ1specific effect, the 8% reduction in lipogenesis y A in WT heptocytes ws lost in β1 / heptocytes (Fig.4A). In WT heptocytes, GW1516 decresed the expression of Sref1c (24%) nd Fsn (18%, not significnt) nd incresed the expression of Insig1 (4%) (Fig.4B). Incresed expression of the PPARδtrget gene Insig1 hs een shown to inhiit the processing of SREBP1 to its ctive nucler form (nsrebp1) (23). Together, these dt demonstrte tht in isolted heptocytes, GW1516 inhiits de novo lipogenesis through ctivtion of AMPK. In vivo, selective heptic insulin resistnce contriutes to FA synthesis due to hyperinsulinemidriven mtorc1 ctivtion of SREBP1c (4). As we reported previously, (45) the HFHC diet resulted in continued progression of fsting hyperinsulinemi throughout the study (Fig.4C). Fsting hyperinsulinemi ws strongly ttenuted y intervention with GW1516 to the HFHC diet (Fig.4C). Selective heptic insulin resistnce ws evluted using fsting (16h)/refeeding
14 14 (2h) protocol. Compred to chowfed mice, phosphoryltion of heptic Akt ws significntly elevted in the fsted stte in HFHCfed mice, nd the response to feeding ws enhnced (Fig.4D). A similr pttern for pakt ws oserved in GW1516treted mice. However, in HFHCfed mice, the phosphoryltion of mtorc1 ws elevted in the fsted stte, nd the response to feeding ws exggerted. In contrst, GW1516intervention completely restored the fsting/refeeding responses of pmtorc1 to levels oserved in chowfed controls (Fig.4D). This is consistent with incresed sensitivity in the lipogenic mtorc1 rnch of the insulin signling cscde in HFHCfed mice (4), nd its normliztion following GW1516 tretment. Compred to chowfed controls, the hyperinsulinemi nd incresed heptic pmtorc1 oserved in fsted HFHCfed mice t 12 weeks ws ssocited with incresed expression of Sref1c, incresed nsrebp1, decresed expression of oth Insig1 nd Insig2 nd incresed expression of Fsn (Fig.4EH), s well s mrkedly enhnced FA synthesis (Fig.4I). GW1516 intervention ttenuted the expression of Sref1c, inhiited formtion of nsrebp1 nd incresed the expression of the PPARδtrget gene Insig1 (Fig. 4EG), which is known to lock processing of SREBP1c (23). The expression of Insig2, which is dependent on Akt signling (7), ws unffected y GW intervention (Fig. 4G). Reduced nsrebp1 ws ssocited with decrese in Fsn expression (Fig. 4F,H) nd ws coupled to complete inhiition of the HFHCinduced increse in FA synthesis from 4 to 12weeks of feeding (Fig. 4I). Together with results in primry mouse heptocytes, these dt indicte tht PPARδ ctivtion inhiits heptic lipogenesis through ctivtion of AMPK s well s correction of selective heptic insulin resistnce, oth of which contriute to the ttenution of liver TG ccumultion. PPARδ ctivtion restores dynmic regultion of heptic FoxO1, which slows the development of hyperglycemi Given tht PPARδ ctivtion improves heptic insulin sensitivity in d/d mice (19), we hypothesized tht the GW1516medited correction of the HFHC dietinduced ifurction in
15 15 heptic insulin signling would normlize FoxO1 signling. At 12 weeks, livers isolted from HFHCfed mice lost the ility to stimulte FoxO1 phosphoryltion nd suppress Pck1 expression in the fstingtofeeding trnsition (Fig.5A,B). This is consistent with our previous hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clmp studies in which the livers of Ldlr / mice fed high ft diet were insulin resistnt (1). In contrst, nimls receiving the GW1516intervention regined the ility to dynmiclly regulte fsting/refeeding of oth FoxO1 phosphoryltion nd Pck1 expression, similr to tht oserved in chowfed mice (Fig.5A,B). As we reported previously (45), fsting lood glucose levels were incresed (1.5fold) in mice fed HFHC for 12 weeks, which ws prtilly ttenuted y GW1516intervention (Fig.5C). These dt suggest tht the norml gluconeogenic rnch of insulin signling, resulting from dietinduced selective heptic insulin resistnce, is corrected y intervention with GW1516, leding to improved fsting lood glucose concentrtions. GW1516 inhiits heptic inflmmtion nd induction of ERstress Inflmmtion is prominent feture of heptic insulin resistnce nd stetosis (3). Given tht GW1516intervention ttenuted heptic stetosis nd corrected selective heptic insulin resistnce, we postulted tht this would e ssocited with reduced heptic inflmmtion. As shown in Fig.6A,B expression of the proinflmmtory M1 cytokines Tnf, Icm1, Il1, Ccl2, Ccl3 nd inos were mrkedly induced (2to 15fold) in livers of mice fed the HFHC diet t 12 weeks. In contrst, these cytokines were significntly ttenuted (5 to 65%) in livers from the GW1516intervention group (Fig.6A,B). Furthermore, HFHCfeeding strongly suppressed heptic expression of the M2 ntiinflmmtory mrker Arg1, resulting in gretly excerted inos/arg1 rtio compred to chowfed control mice (Fig. 6B). GW1516 intervention reversed or completely prevented this expression pttern (Fig. 6B). Together these dt suggest tht PPARδ ctivtion promotes n ntiinflmmtory M2 cytokine milieu in the liver. To ssess the direct effect of GW1516 on the inflmmtory response, we exmined the expression of
16 16 inflmmtory genes in primry heptocytes from chowfed mice incuted with GW1516. Of the cytokines exmined, the expression of Ccl3 (25%) nd Il1 (5%) were significntly decresed (Fig 6C). A similr response of these two cytokines to GW1516 ws reported in cultured mcrophges (47), suggesting tht direct effect of GW1516 on the expression of Ccl3 nd Il1 contriuted to their decresed expression in liver following GW intervention (Fig. 6A). Furthermore, it is likely tht the ttenuted heptic expression of Tnf, Icm1 nd Ccl2 were the consequence of reduced heptic stetosis. Inflmmtion is commonly interwoven with ERstress in the development of heptic insulin resistnce (3,48). Accordingly, HFHCfeeding significntly incresed heptic GRP78 (Fig.6D), mrker of the unfolded protein response (UPR), which is the precursor to the ERstress response (49). GW1516intervention completely normlized the dietinduced increse in GRP78 (Fig. 6D). CHOP, the downstrem effector of the ERstress response, ws not incresed y the HFHC diet nor ws it ffected y GW1516 (Fig. 6D). This suggests tht lthough the HFHC diet initited the UPR, GRP78 expression ws sufficient to prevent the full downstrem ERstress response. Nevertheless, PPARδ ctivtion ttenuted the HFHC dietinduction of the UPR. The expression of Hsp5, tht codes for GRP78, ws unffected y GW1516 in primry heptocytes (dt not shown), suggesting tht the GWinduced reduction in GRP78 in vivo ws secondry to decresed heptic stetosis.
17 17 DISCUSSION We evluted the ility of the PPARδ gonist GW1516 to ttenute the progression of dietinduced heptic stetosis. GW1516intervention inhiited the progression of liver TG ccumultion, the consequence of reduced FA synthesis nd incresed FA oxidtion. GW1516 ctivted heptic AMPK in vivo nd in vitro. Exposure of isolted heptocytes deficient in AMPK ctivity to GW1516 reveled tht inhiition of lipogenesis required AMPK, wheres the induction of FA oxidtion ws medited through incresed expression of Cpt1, rther thn y AMPK ctivtion. Heptic lipogenesis ws lso ttenuted through GW1516medited correction of selective heptic insulin resistnce, which ws ssocited with reduced heptic inflmmtion (Fig.7). The role of PPARδ ctivtion in liver TG metolism hs een controversil (19,2225). One study showed tht GW1516 prevented dietinduced suppression of heptic AMPK ctivtion, which ws ssocited with incresed expression of genes involved in FA oxidtion nd incresed plsm βhydroxyutyrte (24). Despite these oservtions, GW1516 did not ffect heptic TG content (24). Another study demonstrted tht injection of dpparδ into Ldlr / mice significntly incresed heptic AMPK phosphoryltion, which ws thought to contriute to glucose lowering (25). However, the impct of incresed heptic AMPK ctivtion on lipid metolism ws not explored (25). Here we provide direct evidence tht PPARδ ctivtion increses heptic AMPK nd ACC phosphoryltion in vivo s well s in primry mouse heptocytes. It is possile tht this effect ws due to chnges in denylte chrge (24). Nevertheless, the GW1516medited increse in pacc ws AMPKdependent s this effect ws lost in β1 / heptocytes. We demonstrte tht PPARδ ctivtion stimultes heptic FA oxidtion in vivo through PPARδspecific ctivtion of Cpt1. We recpitulted these results in primry mouse heptocytes, nd showed tht AMPK ctivtion is not requirement for
18 18 GW1516induced FA oxidtion, s enhnced Cpt1 expression nd FA oxidtion persisted in GW1516treted β1 / heptocytes. Studies which hve exmined the role PPARδ ctivtion in heptic de novo lipogenesis hve yielded oth positive nd negtive results (19,23,25). On one hnd, oth dpparδ injection nd GW1516tretment hve een shown to increse heptic expression of genes involved in lipogenesis, resulting in incresed liver TG ccumultion (19,25). On the other hnd, delivery of dpparδ or the synthetic PPARδ gonist GW742 hve demonstrted reduced SREBP1c processing, decresed lipogenic gene expression nd prevention of heptic stetosis (23). The dt presented here re consistent with, nd extend this ltter concept. We provide evidence tht intervention to HFHC diet with GW1516 in mice hlts progression of heptic stetosis nd corrects selective heptic insulin resistnce y normlizing signling through mtorc1, resulting in suppression of lipogenic gene expression. Not only ws Sref1c expression decresed, ut processing of SREBP1 to its ctive nucler form ws inhiited. The GW1516 induced expression of Insig1 likely contriutes to this inhiition (23). Other insulin regulted fctors known to influence SREBP1 processing were either unchnged (Insig2) or were not exmined (Gsk3B) nd (Lipin1) (7,23,5). Collectively, the GW1516induced suppression of the SREBP1cpthwy contriuted to the prevention of ny further increse in FA synthesis. Furthermore, GW1516 reduced de novo lipogenesis in WT primry mouse heptocytes, ut not in β1 / heptocytes, demonstrting tht inhiition of FA synthesis ws AMPKdependent. Although two different mechnisms contriute to the oserved reduction in lipogenesis y GW1516tretment, the reltive contriutions of these pthwys require further study. Coupled to hyperinsulinemi, the ifurction in insulin signling, in which FoxO1 ecomes insulin resistnt nd the mtorc1 SREBP1c pthwy mintins insulin sensitivity, contriutes to heptic stetosis, dyslipidemi nd hyperglycemi (4). In the present study, we provide evidence tht heptic insulin signling does in fct ifurcte in model of dietinduced insulin
19 19 resistnce. Importntly, we demonstrte tht PPARδ ctivtion ttenutes the progression of the selective heptic insulin resistnt phenotype, s dynmic regultion of fstingtofeeding pmtor, pfoxo1 nd Pck1 expression ws restored in the GW1516intervention cohort. These dt elorte on the ody of evidence tht PPARδ ctivtion not only protects from insulin resistnce (1921), ut cn lso reverse preestlished heptic insulin resistnce. Liver inflmmtion hs een linked to heptic stetosis nd insulin resistnce (3,51). Vsculr chronic lowgrde inflmmtion is, in prt, medited y ortic lipid ccumultion nd insulin resistnce (52,53). Given the selective insulin resistnt phenotype nd TG cquisition in livers of HFHCfed nimls nd correction y GW1516intervention, it is tempting to hypothesize tht similr mechnisms govern induction nd ttenution of vsculr nd heptic inflmmtion. Moreover, Kupffer cellspecific deletion of Pprδ in mice resulted in incresed proinflmmtory cytokine expression nd reduced ntiinflmmtory cytokine expression, which ws coupled to incresed liver TG ccumultion nd heptic dysfunction (54). Therefore, our results re consistent with n ntiinflmmtory role for PPARδ ctivtion in the liver, similr to the effect in mcrophges nd the ort (28,45,47). The reltive impct of reduced inflmmtion versus correction of insulin sensitivity to the ttenution of heptic stetosis cnnot e discerned from the present experiments nd requires further elucidtion. Previous studies rise the possiility tht the reduction in heptic stetosis with GW1516 intervention ws n indirect consequence of ttenuted ody weight gin or the smll decrese in dipose tissue mss (~1%) (45), s GW1516 is known to lso trget dipose tissue (21). Wng et l reported tht dipose tissuespecific overexpression (3fold) of PPARδ expression vector in HFDfed C57BL/6 mice decresed diposity (~5%), primrily due to n increse in dipocyte Cpt1 expression nd enhnced ftty cid oxidtion (21). This ws ssocited with decrese in lipid droplets within liver sections. Using similr pproch, Qin et l reported tht heptic overexpression of PPARδ following injection of PPARδdenovirus in d/d mice
20 2 suppressed the heptic expression of genes involved in ftty cid synthesis, decresed SREBP 1c processing nd ttenuted oil red O stined heptic lipid (23). Although neither ftty cid oxidtion nor insulin resistnce were mesured, these ltter results re consistent with the concept tht direct heptic ctivtion of PPARδ is le to ttenute heptic stetosis. In the present study, we show in primry mouse heptocytes from chowfed mice nd in liver from HFHCfed mice tht PPARδ ctivtion y GW1516 increses the expression of the PPARδspecific trget gene Adfp. Furthermore, the PPARδ trget gene Cpt1 ws incresed directly or consequent to PPARδinduced AMPK ctivtion, leding to incresed ftty cid oxidtion. In ddition, GW1516 suppressed lipogenesis in heptocytes nd liver due to ctivtion of AMPK nd phosphoryltion of ACC, s well s decresed expression of Sref1c, nd suppression of SREBP1 processing to its ctive nucler form. The ltter ws ssocited with incresed expression of Insig1, considered to e direct trget of PPARδ (23). These results suggest tht the ttenution of heptic stetosis nd improved heptic insulin signling re the consequence of direct effect of GW1516 within the liver. In summry, the dt reported here provide physiologicl nd moleculr evidence tht intervention with PPARδspecific ctivtion in the liver llevites dietinduced heptic stetosis, insulin resistnce nd inflmmtion. We conclude tht PPARδ gonists my serve s therpeutic options for the tretment of ptients with heptic stetosis.
21 21 Acknowledgements This work ws primrily supported y grnts to MWH from the Cndin Institutes of Helth Reserch (MOP12645), the Hert nd Stroke Foundtion of Cnd (PRG5967) nd the University of Western Ontrio, Deprtment of Medicine (POEM). Additionl support ws provided y grnts from the Cndin Dietes Assocition (to GRS) nd the Cndin Foundtion for Innovtion (to GRS, RG). Cretion of Ampkβ1 / mice ws supported y grnts from the Ntionl Helth nd Medicl Reserch Council (to BEK, GRS) nd the Victorin Government s OIS Progrm (BEK). LAB held n Ontrio Grdute Scholrship.
22 22 REFERENCES 1. Frese, R. V., Jr., R. Zechner, C. B. Newgrd, nd T. C. Wlther The prolem of estlishing reltionships etween heptic stetosis nd heptic insulin resistnce. Cell Met. 15: Willimson, R. M., J. F. Price, S. Glncy, E. Perry, L. D. Nee, P. C. Hyes, B. M. Frier, L. A. Vn Look, G. I. Johnston, R. M. Reynolds, nd M. W. Strchn Prevlence of nd risk fctors for heptic stetosis nd nonlcoholic Ftty liver disese in people with type 2 dietes: the Edinurgh Type 2 Dietes Study. Dietes Cre. 34: Hummsti, S., nd G. S. Hotmisligil. 21. Endoplsmic reticulum stress nd inflmmtion in oesity nd dietes. Circ Res. 17: Brown, M. S., nd J. L. Goldstein. 28. Selective versus totl insulin resistnce: pthogenic prdox. Cell Met. 7: Kido, Y., J. Nke, nd D. Accili. 21. Clinicl review 125: The insulin receptor nd its cellulr trgets. J Clin Endocrinol Met. 86: Li, S., M. S. Brown, nd J. L. Goldstein. 21. Bifurction of insulin signling pthwy in rt liver: mtorc1 required for stimultion of lipogenesis, ut not inhiition of gluconeogenesis. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 17: Yecies, J. L., H. H. Zhng, S. Menon, S. Liu, D. Yecies, A. I. Lipovsky, C. Gorgun, D. J. Kwitkowski, G. S. Hotmisligil, C. H. Lee, nd B. D. Mnning Akt stimultes heptic SREBP1c nd lipogenesis through prllel mtorc1dependent nd independent pthwys. Cell Met. 14: Assini, J. M., E. E. Mulvihill, B. G. Sutherlnd, D. E. Telford, C. G. Swyez, S. L. Felder, S. Chhoker, J. Y. Edwrds, R. Gros, nd M. W. Huff Nringenin prevents cholesterolinduced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion, nd therosclerosis in Ldlr/ mice. J Lipid Res. 54: Mulvihill, E. E., E. M. Allister, B. G. Sutherlnd, D. E. Telford, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, J. M. Mrkle, R. A. Hegele, nd M. W. Huff. 29. Nringenin prevents dyslipidemi, polipoprotein B overproduction, nd hyperinsulinemi in LDL receptornull mice with dietinduced insulin resistnce. Dietes. 58: Mulvihill, E. E., J. M. Assini, J. K. Lee, E. M. Allister, B. G. Sutherlnd, J. B. Koppes, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, D. E. Telford, A. Chronneu, P. StPierre, A. Mrette, nd M. W. Huff Noiletin ttenutes VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemi, nd therosclerosis in mice with dietinduced insulin resistnce. Dietes. 6: Dzmko, N. L., nd G. R. Steinerg. 29. AMPKdependent hormonl regultion of wholeody energy metolism. Act Physiol (Oxf). 196:
23 Fullerton, M. D., G. R. Steinerg, nd J. D. Schertzer Immunometolism of AMPK in insulin resistnce nd therosclerosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 366: Kemp, B. E., D. Stpleton, D. J. Cmpell, Z. P. Chen, S. Murthy, M. Wlter, A. Gupt, J. J. Adms, F. Ktsis, B. vn Denderen, I. G. Jennings, T. Iseli, B. J. Michell, nd L. A. Witters. 23. AMPctivted protein kinse, super metolic regultor. Biochem Soc Trns. 31: Steinerg, G. R., nd B. E. Kemp. 29. AMPK in Helth nd Disese. Physiol Rev. 89: Sggerson, D. 28. MlonylCoA, key signling molecule in mmmlin cells. Annu Rev Nutr. 28: Evns, R. M., G. D. Brish, nd Y. X. Wng. 24. PPARs nd the complex journey to oesity. Nt Med. 1: Bojic, L. A., nd M. W. Huff Peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt: multifceted metolic plyer. Curr Opin Lipidol. 24: Reilly, S. M., nd C. H. Lee. 28. PPAR delt s therpeutic trget in metolic disese. FEBS Lett. 582: Lee, C. H., P. Olson, A. Hevener, I. Mehl, L. W. Chong, J. M. Olefsky, F. J. Gonzlez, J. Hm, H. Kng, J. M. Peters, nd R. M. Evns. 26. PPARdelt regultes glucose metolism nd insulin sensitivity. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 13: Tnk, T., J. Ymmoto, S. Iwski, H. As, H. Hmur, Y. Iked, M. Wtne, K. Mgoori, R. X. Iok, K. Tchin, Y. Wtne, Y. Uchiym, K. Sumi, H. Iguchi, S. Ito, T. Doi, T. Hmkuo, M. Nito, J. Auwerx, M. Yngisw, T. Kodm, nd J. Ski. 23. Activtion of peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt induces ftty cid etoxidtion in skeletl muscle nd ttenutes metolic syndrome. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 1: Wng, Y. X., C. H. Lee, S. Tiep, R. T. Yu, J. Hm, H. Kng, nd R. M. Evns. 23. Peroxisomeprolifertorctivted receptor delt ctivtes ft metolism to prevent oesity. Cell. 113: Ngsw, T., Y. Ind, S. Nkno, T. Tmur, T. Tkhshi, K. Mruym, Y. Ymzki, J. Kurod, nd N. Shit. 26. Effects of ezfirte, PPAR pngonist, nd GW51516, PPARdelt gonist, on development of stetoheptitis in mice fed methionine nd cholinedeficient diet. Eur J Phrmcol. 536: Qin, X., X. Xie, Y. Fn, J. Tin, Y. Gun, X. Wng, Y. Zhu, nd N. Wng. 28. Peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptordelt induces insulininduced gene1 nd suppresses heptic lipogenesis in oese dietic mice. Heptology. 48:
24 Brroso, E., R. RodriguezClvo, L. SerrnoMrco, A. M. Astudillo, J. Blsinde, X. Plomer, nd M. VzquezCrrer The PPARet/delt ctivtor GW51516 prevents the downregultion of AMPK cused y highft diet in liver nd mplifies the PGC1lphLipin 1PPARlph pthwy leding to incresed ftty cid oxidtion. Endocrinology. 152: Liu, S., B. Htno, M. Zho, C. C. Yen, K. Kng, S. M. Reilly, M. R. Gngl, C. Gorgun, J. A. Blschi, J. M. Ntmi, nd C. H. Lee Role of peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor δ/β in heptic metolic regultion. J Biol Chem. 286: Krmer, D. K., L. AlKhlili, B. Guigs, Y. Leng, P. M. GrciRoves, nd A. Krook. 27. Role of AMP kinse nd PPARdelt in the regultion of lipid nd glucose metolism in humn skeletl muscle. J Biol Chem. 282: Krmer, D. K., L. AlKhlili, S. Perrini, J. Skogserg, P. Wretenerg, K. Knnisto, H. WllergHenriksson, E. Ehrenorg, J. R. Zierth, nd A. Krook. 25. Direct ctivtion of glucose trnsport in primry humn myotues fter ctivtion of peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt. Dietes. 54: Brish, G. D., A. R. Atkins, M. Downes, P. Olson, L. W. Chong, M. Nelson, Y. Zou, H. Hwng, H. Kng, L. Curtiss, R. M. Evns, nd C. H. Lee. 28. PPARdelt regultes multiple proinflmmtory pthwys to suppress therosclerosis. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 15: Nrkr, V. A., M. Downes, R. T. Yu, E. Emler, Y. X. Wng, E. Bnyo, M. M. Mihylov, M. C. Nelson, Y. Zou, H. Juguilon, H. Kng, R. J. Shw, nd R. M. Evns. 28. AMPK nd PPARdelt gonists re exercise mimetics. Cell. 134: Oliver, W. R., Jr., J. L. Shenk, M. R. Snith, C. S. Russell, K. D. Plunket, N. L. Bodkin, M. C. Lewis, D. A. Winegr, M. L. Sznidmn, M. H. Lmert, H. E. Xu, D. D. Sternch, S. A. Kliewer, B. C. Hnsen, nd T. M. Willson. 21. A selective peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt gonist promotes reverse cholesterol trnsport. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 98: Lu, M., M. Wn, K. F. Levens, Q. Chu, B. R. Monks, S. Fernndez, R. S. Ahim, K. Ueki, C. R. Khn, nd M. J. Birnum Insulin regultes liver metolism in vivo in the sence of heptic Akt nd Foxo1. Nt Med. 18: Mulvihill, E. E., J. M. Assini, B. G. Sutherlnd, A. S. DiMtti, M. Khmi, J. B. Koppes, C. G. Swyez, S. C. Whitmn, nd M. W. Huff. 21. Nringenin decreses progression of therosclerosis y improving dyslipidemi in highftfed lowdensity lipoprotein receptornull mice. Arterioscler Throm Vsc Biol. 3: Cool, B., B. Zinker, W. Chiou, L. Kifle, N. Co, M. Perhm, R. Dickinson, A. Adler, G. Ggne, R. Iyengr, G. Zho, K. Mrsh, P. Kym, P. Jung, H. S. Cmp, nd E. Frevert. 26. Identifiction nd chrcteriztion of smll molecule AMPK ctivtor tht trets key components of type 2 dietes nd the metolic syndrome. Cell Met. 3:
25 Hwley, S. A., M. D. Fullerton, F. A. Ross, J. D. Schertzer, C. Chevtzoff, K. J. Wlker, M. W. Peggie, D. Zirov, K. A. Green, K. J. Mustrd, B. E. Kemp, K. Skmoto, G. R. Steinerg, nd D. G. Hrdie The ncient drug slicylte directly ctivtes AMPctivted protein kinse. Science. 336: Dzmko, N., B. J. vn Denderen, A. L. Hevener, S. B. Jorgensen, J. Honeymn, S. Glic, Z. P. Chen, M. J. Wtt, D. J. Cmpell, G. R. Steinerg, nd B. E. Kemp. 21. AMPK et1 deletion reduces ppetite, preventing oesity nd heptic insulin resistnce. J Biol Chem. 285: Scott, J. W., B. J. vn Denderen, S. B. Jorgensen, J. E. Honeymn, G. R. Steinerg, J. S. Okhill, T. J. Iseli, A. Koy, P. R. Gooley, D. Stpleton, nd B. E. Kemp. 28. Thienopyridone drugs re selective ctivtors of AMPctivted protein kinse et1 contining complexes. Chem Biol. 15: Steinerg, G. R., B. J. Michell, B. J. vn Denderen, M. J. Wtt, A. L. Crey, B. C. Fm, S. Andrikopoulos, J. Proietto, C. Z. Gorgun, D. Crling, G. S. Hotmisligil, M. A. Ferio, T. W. Ky, nd B. E. Kemp. 26. Tumor necrosis fctor lphinduced skeletl muscle insulin resistnce involves suppression of AMPkinse signling. Cell Met. 4: Wtt, M. J., N. Dzmko, W. G. Thoms, S. RoseJohn, M. Ernst, D. Crling, B. E. Kemp, M. A. Ferio, nd G. R. Steinerg. 26. CNTF reverses oesityinduced insulin resistnce y ctivting skeletl muscle AMPK. Nt Med. 12: Chen, M. B., A. J. McAinch, S. L. Mculy, L. A. Cstelli, E. O'Brien P, J. B. Dixon, D. CmeronSmith, B. E. Kemp, nd G. R. Steinerg. 25. Impired ctivtion of AMPkinse nd ftty cid oxidtion y gloulr diponectin in cultured humn skeletl muscle of oese type 2 dietics. J Clin Endocrinol Met. 9: Folch, J., M. Lees, nd G. H. Slone Stnley A simple method for the isoltion nd purifiction of totl lipides from niml tissues. J Biol Chem. 226: Beye, M. M., C. L. Heslop, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, J. G. Mrkle, R. A. Hegele, nd M. W. Huff. 27. Selective upregultion of LXRregulted genes ABCA1, ABCG1, nd APOE in mcrophges through incresed endogenous synthesis of 24(S),25 epoxycholesterol. J Biol Chem. 282: Rowe, A. H., C. A. Argmnn, J. Y. Edwrds, C. G. Swyez, O. H. Mornd, R. A. Hegele, nd M. W. Huff. 23. Enhnced synthesis of the oxysterol 24(S),25epoxycholesterol in mcrophges y inhiitors of 2,3oxidosqulene:lnosterol cyclse: novel mechnism for the ttenution of fom cell formtion. Circ Res. 93: Fullerton, M. D., S. Glic, K. Mrcinko, S. Sikkem, T. Pulinilkunnil, Z. P. Chen, H. M. O'Neill, R. J. Ford, R. Plnivel, M. O'Brien, D. G. Hrdie, S. L. Mculy, J. D. Schertzer, J. R. Dyck, B. J. vn Denderen, B. E. Kemp, nd G. R. Steinerg. 213.
26 26 Single phosphoryltion sites in Acc1 nd Acc2 regulte lipid homeostsis nd the insulinsensitizing effects of metformin. Nt Med. 19: Beye, M. M., S. Reume, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, C. O'Neil, R. A. Hegele, J. G. Pickering, nd M. W. Huff The oxysterol 24(s),25epoxycholesterol ttenutes humn smooth musclederived fom cell formtion vi reduced lowdensity lipoprotein uptke nd enhnced cholesterol efflux. J Am Hert Assoc. 1: e Bojic, L. A., A. C. Burke, S. S. Chhoker, D. E. Telford, B. G. Sutherlnd, J. Y. Edwrds, C. G. Swyez, R. G. Tiron, H. Yin, J. G. Pickering, nd M. W. Huff Peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt gonist GW1516 ttenutes dietinduced ortic inflmmtion, insulin resistnce, nd therosclerosis in lowdensity lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Arterioscler Throm Vsc Biol. 34: Chwl, A., C. H. Lee, Y. Brk, W. He, J. Rosenfeld, D. Lio, J. Hn, H. Kng, nd R. M. Evns. 23. PPARdelt is very lowdensity lipoprotein sensor in mcrophges. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 1: Bojic, L. A., C. G. Swyez, D. E. Telford, J. Y. Edwrds, R. A. Hegele, nd M. W. Huff Activtion of peroxisome prolifertorctivted receptor delt inhiits humn mcrophge fom cell formtion nd the inflmmtory response induced y very lowdensity lipoprotein. Arterioscler Throm Vsc Biol. 32: Vn Beek, M., K. I. OrveczWilson, P. C. Delekt, S. Gu, X. Li, X. Jin, I. J. Apel, K. S. Konkle, Y. Feng, D. H. Teitelum, J. Rulnd, L. M. McAllisterLucs, nd P. C. Lucs Bcl1 links sturted ft overnutrition with heptocellulr NFkB ctivtion nd insulin resistnce. Cell Rep. 1: Kplowitz, N., T. A. Thn, M. Shinohr, nd C. Ji. 27. Endoplsmic reticulum stress nd liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 27: Peterson, T. R., S. S. Sengupt, T. E. Hrris, A. E. Crmck, S. A. Kng, E. Blders, D. A. Guertin, K. L. Mdden, A. E. Crpenter, B. N. Finck, nd D. M. Stini mtor complex 1 regultes lipin 1 locliztion to control the SREBP pthwy. Cell. 146: Gregor, M. F., nd G. S. Hotmisligil Inflmmtory mechnisms in oesity. Annu Rev Immunol. 29: Ling, C. P., S. Hn, T. Senokuchi, nd A. R. Tll. 27. The mcrophge t the crossrods of insulin resistnce nd therosclerosis. Circ Res. 1: Ts, I., A. Tll, nd D. Accili. 21. The impct of mcrophge insulin resistnce on dvnced therosclerotic plque progression. Circ Res. 16: 5867.
27 54. Odegrd, J. I., R. R. RicrdoGonzlez, A. Red Egle, D. Vts, C. R. Morel, M. H. Goforth, V. Surmnin, L. Mukundn, A. W. Ferrnte, nd A. Chwl. 28. Alterntive M2 ctivtion of Kupffer cells y PPARdelt meliortes oesityinduced insulin resistnce. Cell Met. 7:
28 28 Figure Legends Fig.1: GW1516 ttenutes dietinduced heptic stetosis nd ody weight gin, without chnge in cloric intke. Ldlr / mice were fed highft, cholesterolcontining diet (HFHC) for 4 weeks. For susequent 8 weeks, mice remined on HFHC lone or HFHC supplemented with GW51516 (GW1516) (3mg/kg/dy) (n=12/group). A, Heptic triglyceride (TG), B, heptic totl cholesterol (TC) nd C, heptic cholesteryl ester (CE) mss. D, Body weight nd E, cloric intke. Dt re presented s men / SEM. Different letters indicte significnt differences; onewy ANOVA with posthoc Tukey s test (P<5). Fig.2: GW1516 increses heptic ftty cid oxidtion nd wholeody energy expenditure. Aundnce of heptic Pgc1 (A), Ppr (B), Acox (C), Cpt1 (D)nd Adfp (F) ws mesured vi qrtpcr nd normlized to Gpdh. E, Heptic ftty cid βoxidtion ws determined s conversion of [ 3 H]plmitte to 3 H 2. Energy expenditure (G) nd respirtory exchnge rtio (H) (RER=VO2/VCO2) were mesured y indirect clorimetry (CLAMS) during 24h period. Mesurements were collected every 1 min. Men of ech prmeter during the 24h period is shown. Dt is presented s men / SEM. Different letters indicte significnt differences; onewy ANOVA with posthoc Tukey s test (P<5). Asterisk () indictes significnt different etween two groups; Student s pired ttest (P<5). Fig.3: GW1516 increses AMPK nd ACC phosphoryltion, which is not required for ftty cid oxidtion. A, Eight to ten weekold Ldlr / mice fed stndrd lortory chow were fsted overnight, fed t 7h for 2h nd refsted t 9h. Intrperitonel injection of vehicle, GW1516 (3mg/kg) or A (3mg/kg) (n=6/group) occurred t the eginning of the refsting period t 9h. Immunolots of AMPK nd ACC in freezeclmped liver lystes 9 minutes postinjection. Representtive immunolots with quntittions re shown. Asterisk () indictes significnt difference etween vehicle nd tretment; Student s pired ttest (P<5). BF, Primry heptocytes isolted from WT nd AMPKβ1 / mice. Cells were incuted for 1 h
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Naringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflammation, metabolic dysregulation and atherosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice.
 Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
PPAR activation attenuates hepatic steatosis in Ldlr
 / PPAR activation attenuates hepatic steatosis in Ldlr mice by enhanced fat oxidation, reduced lipogenesis, and improved insulin sensitivity Lazar A. Bojic, *, Dawn E. Telford, *, Morgan D. Fullerton,
/ PPAR activation attenuates hepatic steatosis in Ldlr mice by enhanced fat oxidation, reduced lipogenesis, and improved insulin sensitivity Lazar A. Bojic, *, Dawn E. Telford, *, Morgan D. Fullerton,
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
A. Kinoshita 1, L. Locher 2, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S. Dänicke 3, J. Rehage 4, K. Huber 5
 Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Inflammation adversely affects arterial wall biology. 1,2 Much
 Ftty cids Regulte Endothelil Lipse nd Inflmmtory Mrkers in Mcrophges nd in Mouse ort Role for PPRγ Un Ju Jung, Cludi Torrejon, Chuchun L. Chng, Hiroko Hmi, Till S. Worgll, Richrd J. Deckelum Ojective Mcrophge
Ftty cids Regulte Endothelil Lipse nd Inflmmtory Mrkers in Mcrophges nd in Mouse ort Role for PPRγ Un Ju Jung, Cludi Torrejon, Chuchun L. Chng, Hiroko Hmi, Till S. Worgll, Richrd J. Deckelum Ojective Mcrophge
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin
 Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Compound K attenuates glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis through AMPK-dependent pathways in type 2 diabetic OLETF rats
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 218;33:347-355 Compound K ttenutes glucose intolernce nd heptic stetosis through AMPK-dependent pthwys in type 2 dibetic OLETF rts Yoo-Cheol Hwng 1, D-Hee Oh 1, Moon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 218;33:347-355 Compound K ttenutes glucose intolernce nd heptic stetosis through AMPK-dependent pthwys in type 2 dibetic OLETF rts Yoo-Cheol Hwng 1, D-Hee Oh 1, Moon
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Combined deletion of SCD1 from adipose tissue and liver does not protect
 Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
Dietary fat source alters hepatic gene expression profile and determines the type of liver pathology in rats overfed via total enteral nutrition
 Physiol Genomics 44: 173 189, 212. First published September 18, 212; doi:1.1152/physiolgenomics.69.212. Dietry ft source lters heptic gene expression profile nd determines the type of liver pthology in
Physiol Genomics 44: 173 189, 212. First published September 18, 212; doi:1.1152/physiolgenomics.69.212. Dietry ft source lters heptic gene expression profile nd determines the type of liver pthology in
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of cholesterol-induced cytotoxicity in macrophages
 The endoplsmic reticulum is the site of cholesterol-induced cytotoxicity in mcrophges Bo Feng 1, Pin Mei Yo 1, Ynkun Li 1, Cecili M. Devlin 1, Djun Zhng 1, Hether P. Hrding 2, Michele Sweeney 3, Jmes X.
The endoplsmic reticulum is the site of cholesterol-induced cytotoxicity in mcrophges Bo Feng 1, Pin Mei Yo 1, Ynkun Li 1, Cecili M. Devlin 1, Djun Zhng 1, Hether P. Hrding 2, Michele Sweeney 3, Jmes X.
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Molecular Analysis of BRCA1 in Human Breast Cancer. Cells Under Oxidative Stress
 Moleculr Anlysis of BRCA1 in Humn Brest Cncer Cells Under Oxidtive Stress Brin L. Gilmore 1, Ynping Ling 1, Crly E. Winton 1,2, Ky Ptel 1, Vsile Krgeorge 1, A. Cmeron Vrno 1,3, Willim Dernley 1, Zhi Sheng
Moleculr Anlysis of BRCA1 in Humn Brest Cncer Cells Under Oxidtive Stress Brin L. Gilmore 1, Ynping Ling 1, Crly E. Winton 1,2, Ky Ptel 1, Vsile Krgeorge 1, A. Cmeron Vrno 1,3, Willim Dernley 1, Zhi Sheng
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Northern blot analysis
 Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Effects of Rosiglitazone on Inflammation in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
 Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:191-199 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.3.191 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Rosiglitzone on Inflmmtion in Otsuk Long-Evns Tokushim Ftty Rts Jin Woo Lee 1, Il Seong
Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:191-199 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.3.191 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Rosiglitzone on Inflmmtion in Otsuk Long-Evns Tokushim Ftty Rts Jin Woo Lee 1, Il Seong
The role of insulin and glucose in goose primary hepatocyte triglyceride accumulation
 1553 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 212, 1553-1558 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 2009 doi:10.1242/je.022210 The role of insulin nd glucose in goose primry heptocyte triglyceride ccumultion Chunchun
1553 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 212, 1553-1558 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 2009 doi:10.1242/je.022210 The role of insulin nd glucose in goose primry heptocyte triglyceride ccumultion Chunchun
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
Hypoxia-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion in human adipose tissue stromovascular cells
 Dietologi (211) 54:148 149 DOI 1.17/s125-11-213-y ARTICLE Hypoxi-induced inflmmtory cytokine secretion in humn dipose tissue stromovsculr cells R. W. O Rourke & A. E. White & M. D. Metclf & A. S. Olivs
Dietologi (211) 54:148 149 DOI 1.17/s125-11-213-y ARTICLE Hypoxi-induced inflmmtory cytokine secretion in humn dipose tissue stromovsculr cells R. W. O Rourke & A. E. White & M. D. Metclf & A. S. Olivs
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE
 THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Responses of skeletal muscle lipid metabolism in rat gastrocnemius to hypothyroidism and iodothyronine administration: a putative role for FAT/CD36
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
Adrenaline-stimulated glycogen breakdown activates glycogen synthase and. increases insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in epitrochlearis muscles
 Articles in PresS. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met (Decemer 2, 214). doi:1.1152/jpendo.282.214 1 2 Adrenline-stimulted glycogen rekdown ctivtes glycogen synthse nd increses insulin-stimulted glucose uptke
Articles in PresS. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met (Decemer 2, 214). doi:1.1152/jpendo.282.214 1 2 Adrenline-stimulted glycogen rekdown ctivtes glycogen synthse nd increses insulin-stimulted glucose uptke
Research Article Carvacrol Protects against Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet by Enhancing SIRT1-AMPK Signaling
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 3, Article ID 9, pges http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/9 Reserch Article Crvcrol Protects ginst Heptic Stetosis in Mice Fed High-Ft
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 3, Article ID 9, pges http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/9 Reserch Article Crvcrol Protects ginst Heptic Stetosis in Mice Fed High-Ft
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Society of Nephrology sic reserch The protective roles of GLP-1R signling in dietic nephropthy: possile mechnism nd therpeutic potentil Hiroki Fujit
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Society of Nephrology sic reserch The protective roles of GLP-1R signling in dietic nephropthy: possile mechnism nd therpeutic potentil Hiroki Fujit
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
Critical role of c-kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model
 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
Altered adrenal gland cholesterol metabolism in the apoe-deficient mouse
 Altered drenl glnd cholesterol metolism in the poe-deficient mouse Fynne E. Thorngte,* Penelope A. Strockine,* Sndr K. Erickson, nd Dvid L. Willims 1, * Deprtment of Phrmcologicl Sciences,* University
Altered drenl glnd cholesterol metolism in the poe-deficient mouse Fynne E. Thorngte,* Penelope A. Strockine,* Sndr K. Erickson, nd Dvid L. Willims 1, * Deprtment of Phrmcologicl Sciences,* University
R-α-Lipoic acid and acetyl-l-carnitine complementarily promote mitochondrial biogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes
 Dietologi (28) 51:165 174 DOI 1.17/s125-7-852-4 ARTICLE R-α-Lipoic cid nd cetyl-l-crnitine complementrily promote mitochondril iogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 dipocytes W. Shen & K. Liu & C. Tin & L. Yng &
Dietologi (28) 51:165 174 DOI 1.17/s125-7-852-4 ARTICLE R-α-Lipoic cid nd cetyl-l-crnitine complementrily promote mitochondril iogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 dipocytes W. Shen & K. Liu & C. Tin & L. Yng &
Research Article Total 4EBP1 Is Elevated in Liver of Rats in Response to Low Sulfur Amino Acid Intake
 Journl of Amino Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 864757, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/864757 Reserch Article Totl 4EBP1 Is Elevted in Liver of Rts in Response to Low Sulfur Amino Acid Intke Angelos
Journl of Amino Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 864757, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/864757 Reserch Article Totl 4EBP1 Is Elevted in Liver of Rts in Response to Low Sulfur Amino Acid Intke Angelos
Bruna Paola Murino Rafacho 1,2, Camilla Peach Stice 1, Chun Liu 1, Andrew S. Greenberg 3, Lynne M. Ausman 1,4, Xiang-Dong Wang 1,4.
 Originl Article Inhiition of diethylnitrosmine-initited lcohol-promoted heptic inflmmtion nd precncerous lesions y flvonoid luteolin is ssocited with incresed sirtuin ctivity in mice Brun Pol Murino Rfcho,2,
Originl Article Inhiition of diethylnitrosmine-initited lcohol-promoted heptic inflmmtion nd precncerous lesions y flvonoid luteolin is ssocited with incresed sirtuin ctivity in mice Brun Pol Murino Rfcho,2,
Metformin Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in the Mouse: Critical Role of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 26;13:299 2112 Metformin Prevents AlcoholInduced Liver Injury in the Mouse: Criticl Role of Plsminogen Activtor Inhibitor1 INA BERGHEIM,* LUPING GUO,* MOLLY ANNE DAVIS,* JASON C. LAMBERT,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 26;13:299 2112 Metformin Prevents AlcoholInduced Liver Injury in the Mouse: Criticl Role of Plsminogen Activtor Inhibitor1 INA BERGHEIM,* LUPING GUO,* MOLLY ANNE DAVIS,* JASON C. LAMBERT,*
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via
 Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Flaxseed Lignan Increased Glucose Uptake by Human Red Blood Cells
 The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via b-endorphin Signaling in the Skeletal Muscles of Fructose-Fed Rats
 ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
Abstract. Introduction. V.I. Lushchak 1,*, T.V. Bagnyukova 1,*, J.M. Storey 2 and K.B. Storey 2
 Brzilin Journl of Medicl nd Biologicl Reserch (2001) 34: 1055-1064 Effect of exercise on glycolytic enzymes in fish tissues ISSN 0100-879X 1055 Influence of exercise on the ctivity nd the distriution etween
Brzilin Journl of Medicl nd Biologicl Reserch (2001) 34: 1055-1064 Effect of exercise on glycolytic enzymes in fish tissues ISSN 0100-879X 1055 Influence of exercise on the ctivity nd the distriution etween
Effect of Oral Administration of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrations in Periparturient Dairy Cows
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Research Article Antidiabetic Effect of Morindacitrifolia (Noni) Fermented by Cheonggukjang in KK-A y Diabetic Mice
 Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 163280, 8 pges doi:10.1155/2012/163280 Reserch Article Antidietic Effect of Morindcitrifoli (Noni) Fermented y Cheonggukjng in
Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 163280, 8 pges doi:10.1155/2012/163280 Reserch Article Antidietic Effect of Morindcitrifoli (Noni) Fermented y Cheonggukjng in
Arachidonic acid induces ERK activation via Src SH2 domain association with the epidermal growth factor receptor
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 6 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Archidonic cid induces ERK ctivtion vi Src SH2 domin ssocition with the epiderml growth fctor receptor LD Alexnder
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 6 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Archidonic cid induces ERK ctivtion vi Src SH2 domin ssocition with the epiderml growth fctor receptor LD Alexnder
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Accepted 10 January 2006
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 9, - Pulished y The Compny of Biologists doi:./je. Glycerol production in rinow smelt (Osmerus mordx) my e triggered y low temperture lone nd is ssocited with the ctivtion
The Journl of Experimentl Biology 9, - Pulished y The Compny of Biologists doi:./je. Glycerol production in rinow smelt (Osmerus mordx) my e triggered y low temperture lone nd is ssocited with the ctivtion
