Chapter 15 Homework Assignment
|
|
|
- Morgan Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 15 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 Chapter 15 1 Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Dynamic Steady State Fuels, such as glucose, enter a cell and waste products, such as CO 2, leave the cell. However, the mass and gross components of the cell do not change appreciatively The cell maintains a dynamic steady state For metabolic pathways, this means that as a product is produced by one reaction, it is used a the substrate of the next reaction at the same rate. ν A 1 ν S 2 P When ν1 = ν 2 [S] is constant Therefore, the concentration of the substrate remains constant. When this steady state is disturbed by some change in external circumstances or energy supply, the altered movement of compounds through the pathway (aka. the flux) triggers regulatory mechanisms intrinsic to each pathway. Chapter 15 3 Chapter 15 Principles of Metabolic Regulation Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Response to Metabolite Concentrations Flux through a biochemical pathway depends on the activities of the enzymes that catalyze each reaction in that pathway. For some steps, the reaction is close to equilibrium within the cell. For these reactions, small changes in the concentrations of the substrate or product can produce large changes in the net rate of the reaction, even favoring the reverse direction. These steps can be identified d by comparing the mass action ratio (Q) with the equilibrium constant (K eq ) If these two values are within a few orders of magnitude of one another, the reaction is near equilibrium If the two are not close then the reactions shifts to bring it closer to equilibrium Q > K eq System proceeds to form reactants. Q = K eq System is at equilibrium. Q < K eq System proceeds to form products Chapter
2 Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Response to Metabolite Concentrations of Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis Free Energy, kjou ule/mole Glycolysis: Free Energies A B G G-6-P F-6-P F-1,6-bP GA-3-P G-3-P 1,3-bPG 3-PG 2-PG PEP PYR C There are three irreversible steps during Glycolysis. Each of these is an excellent point for regulation A - Hexokinase: The first step of glycolysis B Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1): The committed step of glycolysis C- Pyruvate Kinase: The very last step of glycolysis Chapter 15 5 Chapter 15 7 Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Alteration of Enzyme Activity The activity of an enzyme can be modulated by changes in the number of enzyme molecules in the cell or by changes in the catalytic activity of each enzyme molecule already present. Change in the number of enzyme molecules is a relatively slow process whereas changes in the activity is a faster process. Mechanisms of flux regulation employ both reduction and enhancement of enzyme activity Regulation of activity can occur in one of four ways as shown above The upper two are used to regulate the activity of hexokinase IV (glucokinase). The lower two are combined to control pyruvate kinase, and the regulation by fructose- 2,6-bisphosphate. Isozymes (tissue-specific variants), feedback inhibition, and coordinate regulation are also employed Chapter 15 6 Isozymes An Aside Isozymes are different proteins that catalyze the same reaction These multiple forms may occur in the same species, in the same tissue, or even in the same cell The different forms generally differ in their kinetic and/or regulatory properties, in the cofactors they use or in their subcellular location Hexokinase, which catalyzes the conversion of Glucose to Glucose- 6-phosphate, is regulatory enzyme with four isozymes (Hexokinase I IV). Each of these isozymes is encoded by a different gene Hexokinases I III are found in muscle tissues (myocytes) Hexokinase IV (aka. Glucokinase) is found in liver cells (hepatocytes) The isozymes vary from one another in their K M values and their regulation Chapter
3 Hexokinase Regulation of Glycolysis Step 1 In MUSCLE Hexokinase-II K M = 0.1 mm Runs near V max unless glycolysis slows G6P will build up and thus inhibit the enzyme In LIVER Glucokinase (HK IV) K M = 10 mm Inhibition is mediated by glucokinase regulatory protein F6P stabilizes the interaction - glucose destabilizes it! Runs << V max, except after a meal rich in carbohydrate Blood glucose ~ 5 mm Chapter 15 9 PFK-1 Regulation of Glycolysis Step 3 High [ATP] signals energy needs are met; high citrate that TCA throughput is low either way, glycolysis slows Conversely, high [ADP] or [AMP] indicates more ATP is needed, and high F-2,6-BP signals high blood sugar (its levels are hormone-regulated) Chapter Glucokinase (HK IV) Regulation by Protein Association and Sequestration In the liver, glucokinase (hexokinase IV) is regulated by its high affinity for a nuclear regulator protein This complex cannot move into the cytosol where glycolysis takes place In the presence of high levels of F6P, this interaction is much tighter, keeping HK IV in the nucleus Glucose competes with F6P for binding, resulting in the release of the HK IV and its movement into the cytosol Unlike the muscle isozyme, glucokinase is not inhibited by glucose-6- phosphate Chapter Pyruvate Kinase Regulation of Glycolysis Step 3 There are at least 3 isozymes of PK found in vertebrates ATP, Acetyl CoA (first reactant of TCA) and long-chain fatty acids all signal that abundant energy is available, so that glycolysis can slow High [ATP] allosterically decreases the affinity of PK1 for PEP, raising the K M enough that the reaction is substantially slowed The liver form (L form) but not the muscle form (M form) is also subject to further regulation by phosphorylation in response to Glucagon signals Chapter
4 Gluconeogenesis Regulation The first regulatory point for gluconeogenesis is determination of the fate of pyruvate Does is move into the TCA cycle for energy production or does is get converted into glucose for export? This means regulation of two enzymes in tandem, Pyruvate dehydrogenase d (PDH) and pyruvate carboxylase (PCB) PDH is inhibited by high levels of Acetyl-CoA while PCB is positively modulated by high levels of Acetyl-CoA. Hormonal Regulation - Glucagon The liver is the overseer of blood glucose levels requiring additional regulatory mechanisms to coordinate glucose production and consumption within the hepatocytes We already know that the hormone Glucagon signals the liver to produce and release glucose into the blood. One source of glucose within the liver is within its glycogen molecules, the other source is via gluconeogenesis In addition to the enzyme cascade that leads to activation of Glycogen phosphorylase, glucagon also activates Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase- 2) FBPase-2 dephosphorylates fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, an allosteric effector of the enzymes PFK-1 and FBPase-1. Why should the same signal have these opposite effects? Chapter Chapter Gluconeogenesis Regulation FBPase-1 The second control point is the reaction catalyzed by FBPase-1 This reaction is inhibited by high [AMP] At the same time, high [AMP] stimulates phosphofructokinase-1 Hormonal Regulation F2,6BP Why would nature set the regulation of these reactions up in this manner? Chapter What does Glucagon signal? How does it effect the levels of F2,6BP? What do the varied levels of F2,6BP indicate? Should that favor Glycolysis or Gluconeogenesis? What hormone should have the opposite effect? Chapter
5 Hormonal Regulation F2,6BP PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzymatic activities of a single, bifunctional protein (one polypeptide chain, two activities!) Glucagon activates FBPase-2 activity via phosphorylation by a camp-dependent d protein kinase This activation reduces levels of the effector F2,6BP and favors gluconeogenesis Insulin has the opposite effect by stimulating the activity of a phosphoprotein phosphatase that dephosphorylates the PFK-2/FBPase-2 protein This removal activates the PFK-2 activity, producing F2,6BP, and favoring glycolysis Chapter Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen Storage In a wide range of organisms, excess glucose is stored in polymeric forms (e.g. Starch in plants and glycogen in animals) Glycogen can represent up to 10% of the weight of the liver and 1 2% of the weight of muscles. This polymeric storage keeps the concentration of glucose to ~ 0.01 µm The amount of glycogen in the muscles is there to provide a quick source of energy and can be exhausted in ~ 1 hour of vigourous exercise. In the liver, the glycogen serves as a reservoir of glucose for other tissues when dietary glucose is not available. This source can be depleted in hours Glycogen is stored in granules called β-particles which consists of up to 55K glucose residues with about 2000 reducing ends. These particles also include the enzymes needed for breakdown and synthesis as well as regulatory machinery. Chapter Alternative Uses for Glucose Glycogen Metabolism - Breakdown Breakdown Catalysis of Glycogen The glucose residues of the outer branches of glycogen enter glycolysis through the action of three enzymes: Glycogen Phosphorylase Glycogen Debranching Enzyme Phosphoglucomutase What do you think each enzyme does? Chapter Chapter
6 Glycogen Metabolism - Breakdown Glycogen Phosphorylase Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the phosphorolysis of the α (1 4) glycosidic bond between two glucose residues at the non-reducing end of glycogen. The bond undergoes attack by inorganic phosphate (P i ) producing Glucose-1- phophate and (Glycogen) n-1 Pyridoxal phosphate is an essential cofactor in this reaction Its phosphate acts as a general acid catalyst, promoting attack on the glycosidic bond GP acts continuously on a glycogen molecule until it reaches a point four residues away from a branch point where it stops. Further degradation can only continue after the Debranching enzyme catalyzed two successive reactions that transfer branches. Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Breakdown Phosphoglucomutase G1P, the end product of GP, is converted to G6P by phosphoglucomutase The enzyme is initially phosphorylated at a Ser residue and donates this group to the C- 6 position of the G1P, yielding the shortlived G1,6P The enzyme then accepts a P i group from the C-1 position, regenerating the enzyme and producing G6P. In the muscle, this product goes right into glycolysis for energy production. In the liver, the purpose of this product is to move glucose into the blood when levels have decreased. Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Breakdown Debranching Enzyme When an α (1 6) linkage is met, the phosphorylase cannot proceed A bifunctional debranching enzyme first transfers a block of 3 glucose residues to the nonreducing end of the chain by its transferase activity, Then employs its glucosidase α (1 6) activity to remove the glucose moiety at the branchpoint Glycogen phosphorylase then resumes its work on the now-linear (unbranched) polymer (until it hits the next branchpoint, if any) Glycogen Metabolism - Breakdown Glucose-6-Phosphatase Since the liver breaks down glycogen in an effort to increase blood glucose levels, the G6P must be dephosphorylated before movement into the blood. Glucose-6-phosphatase is found only in liver and kidney tissues and is responsible for this reaction The enzyme is an integral membrane protein with its active site facing the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Transporters move the reactants and products into and out of this area Chapter Chapter
7 Glycogen Metabolism - Synthesis Sugar Activation G1P Many of the reactions in which hexoses are transformed or polymerized involve sugar nucleotides These complexes have several properties that are useful for biosynthetic reactions The condensation reaction between a sugar phosphate (like Glu-1-P) and a nucleotide (like UTP) is irreversible ( G kj/mol due to PP i hydrolysis) The nucleotide moiety has many groups that can undergo non-covalent interactions with enzymes, adding free energy of binding to the mix The activated sugar carbon is primed for nucleophilic attack due to the presence of the excellent nucleotide leaving group The nucleotidyl tag marks such sugars for certain purposes (like glycogen synthesis), and prevents them from being used in other metabolic pathways (like glycolysis) Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Synthesis Glycogen Synthase Making glycogen begins with G6P (from where?) being converted to G1P by phosphoglucomutase G1P is then converted in turn by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase into UDP-glucose UDP-Glucose is added by the enzyme glycogen synthase in α (1 4) linkage to nonreducing ends of existing glycogen as long as the α (1 4) primer has at least 8 glucose residues Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Synthesis Initiation A 37 kd protein, glycogenin, is both the primer on which new chains are begun, and the enzyme that lengthens them Glycogenin acquires glucose by its glucosyltransferase activity from UDP-glu in a group transfer reaction; glucose becomes covalently attached to Tyr 194 Glycogen synthase then joins as a tight complex, and up to 7 more residues are added from UDPglu by glycogenin Glycogen synthase then takes over, extending the chain as it moves away from glycogenin A branching enzyme completes the glycogen particle, eventually dissociating, but glycogenin stays right there! 3eFig Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Synthesis Glycosyl-(4 6)-transferase Problem: Glycogen synthase cannot do α (1 6) branching This is the exclusive job of glycosyl-(4 6)-transferase, which removes 6-7 residues from a strand at least 11 long These residues are transfered to the C-6 carbon of a more interior glucose of the same (or another) chain, creating a new branch! Branches make glycogen more soluble, and allow for faster removal (or addition) of glucose, since there are more ends Chapter
8 Glycogen Metabolism - Synthesis A Glycogen Particle Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Glycogen Phosphorylase Isozymes hidden exposed About 55,000 glucose residues with a MW ~10 7 Chapter Fig The muscle and liver enzymes are isozymes: Muscle has no glucagon receptors, and the enzyme is allosterically stimulated by both AMP and calcium, present at high levels during muscle contraction Liver must mobilize glycogen breakdown for export of glucose Once blood glucose returns to normal levels, it occupies a unique site on this isozyme that both inhibits its activity and exposes Ser 14 -P to PP1 (itself activated by insulin) Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Glycogen Phosphorylase Stimulated by glucagon or epinephrine (via a camp cascade) Phosphorylation at Ser 14 allosterically activates its ability to break down glycogen (to G1P) This is reversible by the action of phosphoprotein phosphatase (PP1) Chapter The Role of Epinephrine and Glucagon in Glucose Liberation In the liver, Glucagon is the signal that activates the cascade for the production of glucose. This peptide hormone is a signal that the body is in a starvation stage and produced in pancreatic α cells in response to low blood glucose levels. Glucagon interacts with the Glucagon serpentine receptor WHY? that is very similar to the β- Adrenergic receptor of Ephinepherine The resulting camp acts as a second messenger. Just in case you forgot! Chapter
9 Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Glycogen Synthase Similar to GP, Glycogen Synthase can exist in either the phosphorylated or dephosphorylated form Phosphorylation of the hydroxyl side chain of several Ser residues of both subunits converts active GSa to inactive GSb This enzyme can be phosphorylated by at least 11 different protein kinases, with the most important one being Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 (GSK3) However, the action of GSK3 is hierarchical meaning that a different kinase (Casein kinase II; CKII) must phosphorylate certain residues before GSK3 can do its job (this is called priming) Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Effect of Insulin Are these effects logical? Chapter Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Effect of Insulin Glycogen Metabolism - Regulation Excellent Summary Did you miss this over break? Chapter Chapter
10 Glycogen Metabolism When Things Go Bad Chapter
Lecture 34. Carbohydrate Metabolism 2. Glycogen. Key Concepts. Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation
 Lecture 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Glycogen Key Concepts Overview of Glycogen Metabolism Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis What mechanisms
Lecture 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Glycogen Key Concepts Overview of Glycogen Metabolism Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis What mechanisms
Glycogen Metabolism. BCH 340 lecture 9
 Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet
 Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15)
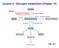 Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15) First. Fig. 15.1 Review: Animals use glycogen for ENERGY STORAGE. Glycogen is a highly-branched polymer of glucose units: Basic structure is similar to that
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15) First. Fig. 15.1 Review: Animals use glycogen for ENERGY STORAGE. Glycogen is a highly-branched polymer of glucose units: Basic structure is similar to that
Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Supplemental Reading
 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of glycogen metabolism - Biochemistry and regulation glycogen degradation - Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis - Control
Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of glycogen metabolism - Biochemistry and regulation glycogen degradation - Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis - Control
Carbohydrate. Metabolism
 Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS
 Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS Note: Even though we did not get through all of these slides during lecture, I advise you to look them all through because they will be helpful to you as you learn
Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS Note: Even though we did not get through all of these slides during lecture, I advise you to look them all through because they will be helpful to you as you learn
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
Highlights Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 Highlights Pentose Phosphate Pathway 1. The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is an interchange of metabolic pathways. 2. It is important to cells as a) an important source of NADPH, b) an important source
Highlights Pentose Phosphate Pathway 1. The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is an interchange of metabolic pathways. 2. It is important to cells as a) an important source of NADPH, b) an important source
Multiple choice: Circle the best answer on this exam. There are 12 multiple choice questions, each question is worth 3 points.
 CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHAPTER 16. Glycolysis
 CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis Net reaction of Glycolysis Converts: 1 Glucose Hexose stage 2 pyruvate - Two molecules of ATP are produced - Two molecules of NAD + are reduced to NADH Triose stage Glucose + 2 ADP
CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis Net reaction of Glycolysis Converts: 1 Glucose Hexose stage 2 pyruvate - Two molecules of ATP are produced - Two molecules of NAD + are reduced to NADH Triose stage Glucose + 2 ADP
Chapter 22. Before the class. 10 Steps of glycolysis. Outline. Can you tell the ten steps of glycolysis? Do you know how glucoses are
 Chapter 22 Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen metabolism, and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham 1 Before the class Can you tell the ten steps of glycolysis? Do you know how glucoses
Chapter 22 Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen metabolism, and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham 1 Before the class Can you tell the ten steps of glycolysis? Do you know how glucoses
PPP_glycogen_metabolism Part 2 الفريق الطبي األكاديمي. Done By: - Shady Soghayr
 PPP_glycogen_metabolism Part 2 الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Shady Soghayr لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ **How we get glucose-1-phosphate from glucose (source of glucose-1-
PPP_glycogen_metabolism Part 2 الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Shady Soghayr لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ **How we get glucose-1-phosphate from glucose (source of glucose-1-
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES. Carbohydrate Metabolism
 ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Glycolysis A. Pathway Regulation of glycolysis Hexokinase: Activated by glucose. Inhibited by G6P. 6-Phosphofructokinase: Inhibited by ATP, especially
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Glycolysis A. Pathway Regulation of glycolysis Hexokinase: Activated by glucose. Inhibited by G6P. 6-Phosphofructokinase: Inhibited by ATP, especially
Moh Tarek. Razi Kittaneh. Jaqen H ghar
 14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
Chapter 18: Carbohydrate Metabolism
 Vocabulary Biotin: a CO2 carrier molecule Cori Cycle: a pathway in carbohydrate metabolism that links glycolysis in the liver with gluconeogenesis in the liver Debranching Enzyme: an enzyme that hydrolyzes
Vocabulary Biotin: a CO2 carrier molecule Cori Cycle: a pathway in carbohydrate metabolism that links glycolysis in the liver with gluconeogenesis in the liver Debranching Enzyme: an enzyme that hydrolyzes
Final Review Sessions. 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office Hours
 Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Lecture 3: Phosphorylase (parts of Chapter 15 + Buchbinder et al. 2001) Discussion of paper and talk assignments.
 Lecture 3: Phosphorylase (parts of Chapter 15 + Buchbinder et al. 2001) Discussion of paper and talk assignments. Notes: A PDF of Buchbinder et al. 2001 will be posted on the course web site today. For
Lecture 3: Phosphorylase (parts of Chapter 15 + Buchbinder et al. 2001) Discussion of paper and talk assignments. Notes: A PDF of Buchbinder et al. 2001 will be posted on the course web site today. For
Glucose is the only source of energy in red blood cells. Under starvation conditions ketone bodies become a source of energy for the brain
 Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
Glycolysis. Degradation of Glucose to yield pyruvate
 Glycolysis Degradation of Glucose to yield pyruvate After this Lecture you will be able to answer: For each step of glycolysis: How does it occur? Why does it occur? Is it Regulated? How? What are the
Glycolysis Degradation of Glucose to yield pyruvate After this Lecture you will be able to answer: For each step of glycolysis: How does it occur? Why does it occur? Is it Regulated? How? What are the
Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways
 Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways Three stages of catabolism Glucose Synthesis of compounds e.g. lactose glycolipids Glucose-6-P Pentosephosphate Pathway Glycolysis Glycogenesis Acetyl-CoA
Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways Three stages of catabolism Glucose Synthesis of compounds e.g. lactose glycolipids Glucose-6-P Pentosephosphate Pathway Glycolysis Glycogenesis Acetyl-CoA
0.40. Biochemistry of Carbohydrates
 0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
BCH 4054 Chapter 23 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Chapter 23 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 23 Gluconeogenesis Glycogen Metabolism Pentose Phosphate Pathway 2 Gluconeogenesis Humans use about 160 g of glucose per day, about 75% for the brain. Body fluids
BCH 4054 Chapter 23 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 23 Gluconeogenesis Glycogen Metabolism Pentose Phosphate Pathway 2 Gluconeogenesis Humans use about 160 g of glucose per day, about 75% for the brain. Body fluids
Lecture 19: Review of regulation
 Chem*3560 Lecture 19: Review of regulation What is meant by cooperative allosteric regulation? Positive cooperativity - characteristic is the sigmoidal binding/activity curve T-state has weaker affinity,
Chem*3560 Lecture 19: Review of regulation What is meant by cooperative allosteric regulation? Positive cooperativity - characteristic is the sigmoidal binding/activity curve T-state has weaker affinity,
Biochemistry Team 437. Glycogen metabolism. Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights. Musculoskeletal block
 Glycogen metabolism Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights Biochemistry Team 437 ﺑ ﺳ م ﷲ اﻟرﺣﻣن اﻟرﺣﯾم Musculoskeletal block Objectives: By the end of this lecture,
Glycogen metabolism Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights Biochemistry Team 437 ﺑ ﺳ م ﷲ اﻟرﺣﻣن اﻟرﺣﯾم Musculoskeletal block Objectives: By the end of this lecture,
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels
 GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN LAJIDE LETURE NTENT INTRDUTIN GLYGEN BREAKDWN (Glycogenolysis) GLYGEN SYNTESIS (Glycogenesis) REGULATIN F GLYGEN METABLISM MAINTENANE F BLD GLUSE DIABETES MELLITUS AND INSULIN INTRDUTIN
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN LAJIDE LETURE NTENT INTRDUTIN GLYGEN BREAKDWN (Glycogenolysis) GLYGEN SYNTESIS (Glycogenesis) REGULATIN F GLYGEN METABLISM MAINTENANE F BLD GLUSE DIABETES MELLITUS AND INSULIN INTRDUTIN
Glycolysis Part 2. BCH 340 lecture 4
 Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
Biochemistry. Glycogenolysis. Metabolism of Carbohydrates. Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 24 Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 24 Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor
Dr. DerVartanian is ill and will likely not be able to give lectures this week.
 Dr. DerVartanian is ill and will likely not be able to give lectures this week. Today s slides will be put on-line today, and are designed to introduce you to glycolysis. You should use these slides, along
Dr. DerVartanian is ill and will likely not be able to give lectures this week. Today s slides will be put on-line today, and are designed to introduce you to glycolysis. You should use these slides, along
(de novo synthesis of glucose)
 Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Glycolysis. Glycolysis Expectations. Glycolysis 10/20/2015. Chapter 16, Stryer Short Course. Memorize/learn Figure 16.1
 Glycolysis Chapter 16, Stryer Short Course Glycolysis Expectations Memorize/learn Figure 16.1 Know overall reaction and stages Explain chemical/physiological purpose of each step Learn structures Reversible/Irreversible
Glycolysis Chapter 16, Stryer Short Course Glycolysis Expectations Memorize/learn Figure 16.1 Know overall reaction and stages Explain chemical/physiological purpose of each step Learn structures Reversible/Irreversible
Regulation of glycogen degradation
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 26 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Content Writer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor UGC-CAS Department
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 26 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Content Reviewer Content Writer Dr.S.K.Khare,Professor IIT Delhi. Dr. Ramesh Kothari,Professor UGC-CAS Department
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways
 METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
Gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009. Free energy changes in glycolysis 11/13/2009
 Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009 Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the
Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009 Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the
Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate. Chapter 16 Homework Assignment. Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
 Chapter 16 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 1, 3, 7, 10, 16, 19, 20 Additional Problem: Write out the eight reaction steps of the Citric Acid Cycle, using
Chapter 16 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 1, 3, 7, 10, 16, 19, 20 Additional Problem: Write out the eight reaction steps of the Citric Acid Cycle, using
Enzymes Part III: regulation II. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation II Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Advantage This is a major mechanism for rapid and transient regulation of enzyme activity. A most common mechanism is enzyme phosphorylation
Enzymes Part III: regulation II Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Advantage This is a major mechanism for rapid and transient regulation of enzyme activity. A most common mechanism is enzyme phosphorylation
CELLULAR GLYCOGEN Why Glycogen as an Energy Storage Molecule? Glycogenolysis NOT phosphorolysis
 CHM333 LECTURE 29 & 30: 4/12 15/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR GLYCOGEN Why Glycogen as an Energy Storage Molecule? 1. Fat cannot be as rapidly mobilized in skeletal muscle. 2. Fat
CHM333 LECTURE 29 & 30: 4/12 15/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR GLYCOGEN Why Glycogen as an Energy Storage Molecule? 1. Fat cannot be as rapidly mobilized in skeletal muscle. 2. Fat
Both pathways start with Glucose as a substrate but they differ in the product.
 Glycosis:may occur either with the presence or absence of -Glucose-.So with oxygen we have Aerobic glycolysis-, without the participation of oxygen Anaerobic glycolysis-(it occur in certain places) where
Glycosis:may occur either with the presence or absence of -Glucose-.So with oxygen we have Aerobic glycolysis-, without the participation of oxygen Anaerobic glycolysis-(it occur in certain places) where
2. What is molecular oxygen directly converted into? a. Carbon Dioxide b. Water c. Glucose d. None of the Above
 Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Carbohydrate Metabolism I
 Carbohydrate Metabolism I Outline Glycolysis Stages of glycolysis Regulation of Glycolysis Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview Enzyme Classification Dehydrogenase - oxidizes substrate using cofactors as
Carbohydrate Metabolism I Outline Glycolysis Stages of glycolysis Regulation of Glycolysis Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview Enzyme Classification Dehydrogenase - oxidizes substrate using cofactors as
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions.
 I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions.
 I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions
 CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
Energy storage in cells
 Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 14 Done by Dergam Al-Tarawneh Corrected by Maya Attarakih Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Glycogen metabolism Note: Everything written in orange is from the book not mentioned by the doctor. In
number 14 Done by Dergam Al-Tarawneh Corrected by Maya Attarakih Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Glycogen metabolism Note: Everything written in orange is from the book not mentioned by the doctor. In
Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules
 Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules of ATP Anaerobic no O 2 needed aerobic O 2 needed In
Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules of ATP Anaerobic no O 2 needed aerobic O 2 needed In
III. Metabolism Glucose Catabolism Part II
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism Glucose Catabolism Part II Slide 1 Metabolic Fates of NADH and Pyruvate Cartoon: Fate of pyruvate, the product of glycolysis.
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism Glucose Catabolism Part II Slide 1 Metabolic Fates of NADH and Pyruvate Cartoon: Fate of pyruvate, the product of glycolysis.
GLYCOGEN BEFORE THE LAB YOU HAVE TO READ ABOUT:
 GLYCGEN BEFRE THE LAB YU HAVE T READ ABUT:. Glycogen structure. 2. Glycogen synthesis and degradation (reactions with structural formulas and enzymes). 3. The role of glycogen in liver and muscles. INTRDUCTIN
GLYCGEN BEFRE THE LAB YU HAVE T READ ABUT:. Glycogen structure. 2. Glycogen synthesis and degradation (reactions with structural formulas and enzymes). 3. The role of glycogen in liver and muscles. INTRDUCTIN
The concentration of glucose residues stored as glycogen in liver is ~0.4M, Whereas, glycogen concentration is only 10 nm.
 The concentration of glucose residues stored as glycogen in liver is ~0.4M, Whereas, glycogen concentration is only 10 nm. IV: Large amount of glucose can be stored without affecting the osmolarity of
The concentration of glucose residues stored as glycogen in liver is ~0.4M, Whereas, glycogen concentration is only 10 nm. IV: Large amount of glucose can be stored without affecting the osmolarity of
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose. Jana Novotna
 Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 19 Glycolysis 2 aka = also known as verview of Glycolysis aka The Embden-Meyerhoff Pathway First pathway discovered Common to almost all living cells ccurs in
BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 19 Glycolysis 2 aka = also known as verview of Glycolysis aka The Embden-Meyerhoff Pathway First pathway discovered Common to almost all living cells ccurs in
PRINT your Name Student (FAMILY, first name) Midterm 7:00 P.M.
 PRINT your Name Student No. (FAMILY, first name) BIOCHEMISTRY 311A VERSION 1 (ONE) Midterm 7:00 P.M. Examiners: Dr. R. E. MacKenzie (69%) Dr. A. Storer (18%) Dr. W. Mushynski (13%) READ THE QUESTIONS CAREFULLY!!
PRINT your Name Student No. (FAMILY, first name) BIOCHEMISTRY 311A VERSION 1 (ONE) Midterm 7:00 P.M. Examiners: Dr. R. E. MacKenzie (69%) Dr. A. Storer (18%) Dr. W. Mushynski (13%) READ THE QUESTIONS CAREFULLY!!
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 16: Carbohydrate Metabolism
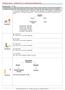 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 16: Carbohydrate Metabolism No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. Fill in the diagram below
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 16: Carbohydrate Metabolism No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. Fill in the diagram below
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS. Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions
 Handout Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions I. Kinetics A. Reaction rates 1. First order (reaction rate is
Handout Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions I. Kinetics A. Reaction rates 1. First order (reaction rate is
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2
 Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Glycolysis. Intracellular location Rate limiting steps
 Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
Pathway overview. Glucose + 2NAD + + 2ADP +2Pi 2NADH + 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2H 2 O + 4H +
 Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Fall 2005: CH395G - Exam 2 - Multiple Choice (2 pts each)
 Fall 2005: CH395G - Exam 2 - Multiple Choice (2 pts each) These constants may be helpful in some of your calculations: Avogadro s number = 6.02 x 10 23 molecules/mole; Gas constant (R) = 8.3145 x 10-3
Fall 2005: CH395G - Exam 2 - Multiple Choice (2 pts each) These constants may be helpful in some of your calculations: Avogadro s number = 6.02 x 10 23 molecules/mole; Gas constant (R) = 8.3145 x 10-3
Biochemistry - I SPRING Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) Lecture 16. Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat
 Biochemistry - I Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) SPRING 2017 Lecture 16 Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat 1 Catabolism of Di- and Polysaccharides Catabolism (digestion) begins
Biochemistry - I Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) SPRING 2017 Lecture 16 Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat 1 Catabolism of Di- and Polysaccharides Catabolism (digestion) begins
Integration Of Metabolism
 Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Regulation of Metabolism
 Regulation of Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 19 Regulation by Compartmentalization Form of reciprocal regulation Degradation vs biosynthesis Requires transporters 1 Specialization of organs Fuel
Regulation of Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 19 Regulation by Compartmentalization Form of reciprocal regulation Degradation vs biosynthesis Requires transporters 1 Specialization of organs Fuel
Fate of glucose in living systems. Glycolysis: Derived from Greek words; Glucose + 6O 2 = 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O δg o = kj/mol
 Glycolysis: Derived from Greek words; Glykys = Sweet, Lysis = splitting During this process one molecule of glucose (6 carbon molecule) is degraded into two molecules of pyruvate (three carbon molecule).
Glycolysis: Derived from Greek words; Glykys = Sweet, Lysis = splitting During this process one molecule of glucose (6 carbon molecule) is degraded into two molecules of pyruvate (three carbon molecule).
Name: Chem 351 Exam 3
 Multiple hoice: Pick the BEST answer and write it in the box at the end of the section. 1) The TA (Krebs) ycle depends on oxygen availability, though it does not directly use it. How can you best explain
Multiple hoice: Pick the BEST answer and write it in the box at the end of the section. 1) The TA (Krebs) ycle depends on oxygen availability, though it does not directly use it. How can you best explain
Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES
 Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES The video lecture covers basic principles you will need to know for the lectures covering enzymes and metabolism in Principles of Metabolism and elsewhere in the
Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES The video lecture covers basic principles you will need to know for the lectures covering enzymes and metabolism in Principles of Metabolism and elsewhere in the
Molecular Structure and Function Polysaccharides as Energy Storage. Biochemistry
 1 1.Objectives Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj To understand how polysaccharides act as energy source To understand the structure and energy generation process from glycogen To understand the structure
1 1.Objectives Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj To understand how polysaccharides act as energy source To understand the structure and energy generation process from glycogen To understand the structure
Integration of Metabolism 1. made by: Noor M. ALnairat. Sheet No. 18
 Integration of Metabolism 1 made by: Noor M. ALnairat Sheet No. 18 Data :24/11/2016 SLIDE 2: Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP,
Integration of Metabolism 1 made by: Noor M. ALnairat Sheet No. 18 Data :24/11/2016 SLIDE 2: Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP,
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-1
 Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-1 Using the following values, answer questions 1-3. ATP + H 2 O ADP + P i ΔG = -30 kj/mol Creatine-phosphate + H 2 O Creatine + P i ΔG = -12 kj/mol ½O 2 + 2H + + 2e - H
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-1 Using the following values, answer questions 1-3. ATP + H 2 O ADP + P i ΔG = -30 kj/mol Creatine-phosphate + H 2 O Creatine + P i ΔG = -12 kj/mol ½O 2 + 2H + + 2e - H
OVERVIEW OF THE GLYCOLYTIC PATHWAY Glycolysis is considered one of the core metabolic pathways in nature for three primary reasons:
 Glycolysis 1 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of the Glycolytic Pathway Glycolysis generates a small amount of ATP Preview of the ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions of glycolysis - Stage 1: ATP
Glycolysis 1 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of the Glycolytic Pathway Glycolysis generates a small amount of ATP Preview of the ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions of glycolysis - Stage 1: ATP
III. Metabolism - Gluconeogenesis
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism - Gluconeogenesis Carl & Gertrude Cori Slide 1 Carbohydrate Synthesis Lactate, pyruvate and glycerol are the important
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism - Gluconeogenesis Carl & Gertrude Cori Slide 1 Carbohydrate Synthesis Lactate, pyruvate and glycerol are the important
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 15 Done by BaraaAyed Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation Regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation involves two
number 15 Done by BaraaAyed Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation Regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation involves two
Glycolysis. Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights. Biochemistry Team 437
 Glycolysis Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights Biochemistry Team 437 ﺑ ﺳ م ﷲ اﻟرﺣﻣن اﻟرﺣﯾم Objectives: Recognize glycolysis as the major oxidative pathway of
Glycolysis Color index: Doctors slides Notes and explanations Extra information Highlights Biochemistry Team 437 ﺑ ﺳ م ﷲ اﻟرﺣﻣن اﻟرﺣﯾم Objectives: Recognize glycolysis as the major oxidative pathway of
CH395 G Exam 2 Multiple Choice - Fall 2004
 C395 G Exam 2 Multiple Choice - Fall 2004 1. Which of the following fatty acids has the lowest melting point? a. Fatty acids with sites of unsaturation with cis double bonds b. Fatty acids with sites of
C395 G Exam 2 Multiple Choice - Fall 2004 1. Which of the following fatty acids has the lowest melting point? a. Fatty acids with sites of unsaturation with cis double bonds b. Fatty acids with sites of
Chem Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis
 Chem 352 - Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis Introduction Carbohydrate metabolism involves a collection of pathways. Glycolysis Hexoses 3-Carbon molecules Gluconeogenesis 3-Carbon molecules
Chem 352 - Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis Introduction Carbohydrate metabolism involves a collection of pathways. Glycolysis Hexoses 3-Carbon molecules Gluconeogenesis 3-Carbon molecules
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Biochemistry of carbohydrates
 Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Carbohydrate metabolism 3. Atip Likidlilid
 Carbohydrate metabolism 3 Atip Likidlilid Glycogenolysis muscle glycogen (1-2 % by weight) liver glycogen (6-10 % by weight) Glycogen for energy storage > fat 1. Muscles cannot mobilize fat as rapid as
Carbohydrate metabolism 3 Atip Likidlilid Glycogenolysis muscle glycogen (1-2 % by weight) liver glycogen (6-10 % by weight) Glycogen for energy storage > fat 1. Muscles cannot mobilize fat as rapid as
Ahmad Ulnar. Faisal Nimri ... Dr.Faisal
 24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 12 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Mamoon Mohammad Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Lactate production 1 P a g e Advantages of producing lactate Lactate is produced anaerobically to meet the following
number 12 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Mamoon Mohammad Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Lactate production 1 P a g e Advantages of producing lactate Lactate is produced anaerobically to meet the following
Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life
 Chapter 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Activation Energy and the Metastable State Many thermodynamically feasible reactions in a cell that could
Chapter 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Activation Energy and the Metastable State Many thermodynamically feasible reactions in a cell that could
Metabolism. Metabolic pathways. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism
 Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism 70 Stage 1: Digestion of Carbohydrates In Stage 1, the digestion of carbohydrates Begins in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller
Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism 70 Stage 1: Digestion of Carbohydrates In Stage 1, the digestion of carbohydrates Begins in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller
Tala Saleh. Ahmad Attari. Mamoun Ahram
 23 Tala Saleh Ahmad Attari Minna Mushtaha Mamoun Ahram In the previous lecture, we discussed the mechanisms of regulating enzymes through inhibitors. Now, we will start this lecture by discussing regulation
23 Tala Saleh Ahmad Attari Minna Mushtaha Mamoun Ahram In the previous lecture, we discussed the mechanisms of regulating enzymes through inhibitors. Now, we will start this lecture by discussing regulation
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2. Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system
 Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
Chapter 10. Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002
 Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Exam 3 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone 8:00. V max = k cat x E t. ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]
![Exam 3 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone 8:00. V max = k cat x E t. ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S] Exam 3 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone 8:00. V max = k cat x E t. ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]](/thumbs/75/71985573.jpg) Exam 3 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone 8:00 Name There are 106 possible points (6 bonus points) on this exam. There are 8 pages. v o = V max x [S] k cat = kt e - ΔG /RT V max = k cat x E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]
Exam 3 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone 8:00 Name There are 106 possible points (6 bonus points) on this exam. There are 8 pages. v o = V max x [S] k cat = kt e - ΔG /RT V max = k cat x E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]
Last time we talked about glucagon and epinephrine
 Last time we talked about glucagon and epinephrine *Glucagon it's very important hormone, its nature is a protein look like a polypeptide chain. *Epinephrine hormone it's nature is an amino acid derivative.
Last time we talked about glucagon and epinephrine *Glucagon it's very important hormone, its nature is a protein look like a polypeptide chain. *Epinephrine hormone it's nature is an amino acid derivative.
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Metabolism
 Metabolic Pathways and Energy Metabolism Last Week Energy Metabolism - The first thing a living organism has got to be able to do is harness energy from the environment - Plants do it by absorbing sunlight
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Metabolism Last Week Energy Metabolism - The first thing a living organism has got to be able to do is harness energy from the environment - Plants do it by absorbing sunlight
Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003
 Enzymes & Kinetics IV Regulation and Allostery ENZYME-SUBSTRATE INTERACTIONS THE LOCK & KEY MODEL Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A perfect match between enzyme and substrate can explain enzyme specificity
Enzymes & Kinetics IV Regulation and Allostery ENZYME-SUBSTRATE INTERACTIONS THE LOCK & KEY MODEL Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A perfect match between enzyme and substrate can explain enzyme specificity
Glycogen Metabolism Dr. Mohammad Saadeh
 Glycogen Metabolism Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry II Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy I. overview Glucose is energy source for Brain.
Glycogen Metabolism Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry II Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy I. overview Glucose is energy source for Brain.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
 Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
Chapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
