UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date. Nutrition and Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Folate and Vitamin B
|
|
|
- Clifton Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Nutrition and Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Folate and Vitamin B Permalink Journal Nutrition Bytes, 5(2) ISSN X Author Edmonds, Zachary V. Publication Date Peer reviewed escholarship.org Powered by the California Digital Library University of California
2 Introduction Folate and vitamin B12 are important nutrients we must obtain from our diets in order to perform a number of cellular processes related to methylation and DNA synthesis. Vitamin B12 deficiency (often caused by pernicious anemia) and folate deficiency (often caused by inadequate dietary intake) are associated with well known hematological consequences, and occasionally, neurological symptoms. Recent evidence has associated abnormal levels of these vitamins with Alzheimer's disease, although there is currently debate as to whether they represent a casual factor or simply a consequence of the disease process. Folate and Vitamin B12Biochemistry Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in methylation (1-carbon metabolism) of nucleic acids and proteins, and in the biosynthesis of the purines and the pyramidine, thymine (1). Folic acid deficiency is probably the most common vitamin deficiency in the United States, particularly among pregnant women and alcoholics. Vitamin B12 is unique among all vitamins in that it is the largest and most complex, and because it contains a metal ion, cobalt. It is required for two essential enzymatic processes: the disposal of odd-numbered amino acids, and the synthesis of methionine in the methylation cycle (Figure 1). The main functions of these two vitamins are very interconnected, and it is difficult to distinguish a deficiency in one or the other. In humans, the majority of active folate is in the form of methyltetrahydrofolic acid (5-methyl THFA). Tetrahydrofolate (THFA), however, is needed in a number of different forms in order to perform its duties as a coenzyme: 1) in the formation of thymidylate (the rate-limiting step in DNA synthesis), 2) in catabolism or introconversion of some amino acids, 3) in purine, and 4) in protein synthesis (2). In order to convert 5-methyl THFA to THFA, a B12-mediated reaction converts homocysteine to methionine, which, in turn, is converted to
3 Figure 1. The role of folate and B12 in 1-carbon metabolism. *Serine is the source of most of the 1-carbon units involved in the methylation cycle. These methyl groups are used in the synthesis of thymidylate (a thymine precursor), purines, and methionine; THFA=tetetrahydrofolate. S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), the most common methyl-group donor in the body. In the absence of sufficient B12, folic acid accumulates in the 5-methyl THFA form and is unable to support synthesis of DNA, thus reducing cell proliferation. A similar situation arises in folic acid deficiency, where DNA synthesis is also reduced due to lack of THFA for thymidylate and purine synthesis. Those tissues most dependent on cell proliferation (including erythropoetic stem cells in bone marrow) are the first affected by a deficiency of THFA. The lack of DNA synthesis results in the formation of megaloblastic cells in the marrow (with sufficient cytoplasm but insufficient chromatin to divide), a condition known as megaloblastic anemia.
4 In addition to the haematological symptoms of B12/folate deficiency, there are a number of neurologic and psychiatric consequences, although they are much less understood (3). These vitamins are important in a number of metabolic pathways in the central nervous system, serving to generate methyl groups for the production of essential substances such as monoamine neurotransmitters and phospholipids. The most common CNS findings in severely vitamin B12 and folate deficient patients are peripheral neuropathy, demyelination, depression, and dementia. Current thinking proposes that these methylation reactions are central to the biochemical basis of these neuropsychiatric findings. The exact mechanisms, however, are unknown, but there are new theories related to pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease that have emerged recently, and will be discussed subsequently. Early Studies of B12 Deficiency in Alzheimer's Disease While it has been known for decades that severely low B12 levels can cause dementia, the first report of vitamin B12 deficiency in Alzheimer's patients emerged in the mid-80s. In a landmark study, Cole et al. found serum B12 levels to be lower in Alzheimer patients than those with non-alzheimer's type dementia (4). They conclude with some tentative hypotheses about the association of low B12 with AD, including damage to the Nuclues Basalis of Meynert (the source of many of the cholinergic projections that are destroyed in the disease), but are clearly left wondering about the causal nature of the relationship due to their small sample size. This study served to stimulate others working in the field to attempt clarification of this observed association between vitamin deficiency and one of the most common and costly diseases of the elderly. More recently, a number of studies have looked at the association of mental impairment and vitamin B12 deficiency in the elderly. Some authors have reported low serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) vitamin B12 levels in patients with Alzheimer's disease compared to a control group, and have suggested that patients with AD are particularly prone to vitamin B12 deficiency (5,6). Other investigators have found a low vitamin B12 level in cerebrospinal fluid but a normal serum vitamin B12 level in patients with AD (7). These results have not been reported by other studies, which fail to find any consistent correlation between B12 levels and Alzheimer's disease (8,9). Although blood and serum CSF levels of vitamin B12 in Alzheimer's patients have been controversial, some researchers have remained convinced of a vitamin B12/folate abnormality associated with this disease. This has lead investigators in the past few years to study the biochemistry of vitamin B12/folate metabolism more carefully in Alzheimer's patients, and assay some of the important metabolites involved in their biochemistry. An important study by Joosten et al. found levels of serum vitamin B12 and folate were very similar in Alzheimer patients and controls (10). However, differences were found with respect to serum methylmalonyl-coa (MMA) and homocysteine (Hcy) levels (the assessment of MMA and Hcy levels more accurately reflects intracellular levels of vitamin B12 and folate), with those in the AD group demonstrating elevated levels. MMA accumulates in vitamin B12 deficiency because the conversion of methylmalonyl-coa to succinyl-coa requires this vitamin. Homocysteine, on the other hand, builds up in cases of folate deficiency due to a lack of methyl THFA. This finding lead to the conclusion that interpretation of vitamin B12 and folate status in patients with AD depends on the methodology (serum vitamins versus metabolite levels), and that metabolic abnormalities (MMA and Hcy) can be masked by apparently normal levels of vitamin B12 and folate. Furthermore, examining the levels of MMA and Hcy are potentially more useful and specific because they assess the intracellular state of affairs rather than blood in general. Recent focus has confirmed the association of these metabolic abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease, and examined whether such abnormalities play a role in pathogenesis or are simply consequences of the disease process. Studies Implicating Correlation but not Causation Kristensen et. al confirmed the high levels of methlymalonyl-coa in Alzheimer patients compared to patients with other types of dementia and controls, but found no association between these high levels and the severity of dementia (11). This finding motivated a conclusion that elevated MMA levels are an associated finding with Alzheimer's disease, but are not related to etiology or pathogenesis. They hypothesize that AD patients have a predisposition to develop B12 deficiency which may add to cognitive
5 burden of the disease process by leading to demyelinating lesions in the brain, and should thus be corrected with supplements. A study by Levitt et. al examined the relationship between folate, vitamin B12, other metabolites, and the severity of cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer's disease (12). Low folate/b12 and high metabolite (MMA and homocysteine) levels were associated with dementia in some, but not all cases. They cite the lack of a relationship between these metabolic abnormalities and dementia, combined with failure of replacement therapy to have any positive effect on cognition, as evidence that these biochemical findings in Alzheimer's disease represent consequences of the disease process rather than etiological factors. They propose that the underlying disease process may lead to decreased absorption or storage of B12, or increased rates of utilization or excretion. Thus, while metabolic indicators of low folate/b12 may correlate highly with AD, these authors suggest such findings are consequences of the disease process. Studies Implicating Causation Trolin et al. have looked at the biochemistry of vitamin B12 methylation pathways, and provide good evidence that disorders of such physiology may be involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer-type dementia (13). They found that methionine S-adenosyltransferase, the enzyme that converts methionine to the major methyl donor molecule in the body (S-adenosylmethionine), has reduced activity in erythrocytes of AD patients, and correlates with low vitamin B12 levels and elevated homocysteine values. Although deficiencies in transmethylation in the CNS have been hypothesized to represent a pathogenic mechanism in the general development of dementia, this study directly links such deficiencies to the erythrocytes of Alzheimer patients. Due to the low metabolic activity of the erythrocytes, the functional role of SAM is relatively limited, while in brain, it is involved in the synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters, membrane phospholipids, proteins, and in DNA methylation. These findings support the notion that abnormalities in the transmethylating systems may be involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer-type dementia. The most exciting study in this area emerged last November, and also implicates nutritional deficiency in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (14). Clarke et al demonstrated significantly elevated serum homocysteine levels in patients with histologically confirmed AD (which is more specific diagnosis than can be made on clinical grounds alone); an association that was independent of age, sex, apoe e 4, and social class. They propose a number of consequences to elevated levels of homocysteine in the pathogenesis of dementia. Homocysteine has been shown to activate the NMDA receptor, and thus, high Hcy levels in these patients may lead to excitotoxic cell death of neurons. Homocysteine may also be converted to homocysteic acid, which also has excitotoxic effects on neurons. In addition, elevated Hcy levels are strongly associated with cerebrovascular disease, which many are beginning to regard as common in AD. They suggest that microvascular disease may play a role in the cause of "pure" AD. For instance, small vessel disease (arising as a consequence of high Hcy levels), may result in the deposition of b -amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles that are the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer-type dementia. Further evidence for high Hcy levels being a cause and not a consequence of the disease include the stability of homocysteine levels in patients in varying stages of the disease and lack of relationship with duration of symptoms. Conclusion Although it has proven difficult to establish a global deficiency of vitamin B12 and folate in patients with Alzheimer's disease, more careful examination of the biochemistry of these nutrients has uncovered more consistent metabolic abnormalities. The study of homocysteine, in particular, has suggested that abnormally high levels may contribute to the pathogenesis of AD. However, despite the plausible mechanisms, further work is required to establish whether the observed associations are causal or consequential as they relate to the disease process. If an etiological role for elevated homocysteine is established, the potential for supplementation of folate as a preventive measure represents an exciting possibility. If the maintenance of normal folate levels throughout life turns out to be protective for Alzheimer's disease, wider efforts than are currently being made to supplement diets with folate should be untertaken.
6 REFERENCES 1. Brody T. Nutritional Biochemistry. Academic Press: New York, Champe PC. Biochemistry. J.B. Lippincott Company: Philadelphia, Bottiglieri T. Folate, vitamin B12, and neuropyschiatric disorders. Nutrion Reveiws 1996;54: Cole MG, Prchal JF. Low serum vitamin B12 in Alzheimer-type dementia. Age Ageing 1984;13: Karnaze DS, Carmel R. Low serum cobalamin level in primary degenerative dementia. Do some patients harbor atypical cobalamin deficiency states? Arch Intern Med 1987;147: Ikeda T, Furukama Y, Mashimoto S, Takahashi K, Yamad M. Vitamin B12 levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of people with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Psych Scand, 1990;82: Bottiglieri T, Godfrey P, Flynn T, et al. Cerebrosinal fluid S-adnosylmethionine in depression and dementia: effects of treatment with parenteral and oral S-adenosylmethionine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1990;53: Basun H, Fratiglioni L, Winblad B. Cobalamin levels are not reduced in Alzheimer's disease: results from a population based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 1994;42: Crystal HA, Ortof E, Frishman WH, Gruber A, Hershman D, Aronson M. Serum vitamin B12 levels and incidence of dementia in a healthy elderly population: a report from the Bronx longitudinal aging study. J Am Geriatric Soc 1994;42: Joosten E, Lesaffre E, Riezler R, Ghekiere V, Dereymaeker L, Pelemans W, Dejaeger E. Is metabolic evidence for vitamin B12 and folate deficieny more frequen in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease? J Gerontology Med Sci 1997;52A:M76-M Kristensen MO, Gulmann NC, Chrsitensen JEJ, Ostergaard K, Rasmussen K. Serum cobalamin and methylmalonic acid in Alzheimer dementia. Acta Neurol Scand 1993;87: Levitt AJ, Karlinsky H. Folate, vitamin B12 and cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Psych Scand 1992;86: Trolin CG, Regland B, Oreland L. Decreased methionine adensyltransferas activity in erythrocytes of patients with dementia disoders. European Neuropyschopharmacology 1995;5: Clarke R, Smith AD, Jobst KA, Refsum H, Surron L, Ueland PU. Folate, vitamin B12, and serum total homocysteine levels in confirmed Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 1998;55:
Folic Acid and vitamin B12
 Folic Acid and vitamin B12 ILOs: by the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1. Understand that vitamins are crucial nutrients that are important to health. 2. Know that folic acid and vitamin B12
Folic Acid and vitamin B12 ILOs: by the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1. Understand that vitamins are crucial nutrients that are important to health. 2. Know that folic acid and vitamin B12
LECTURE-4 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE
 LECTURE-4 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE-20-12-2018 VITAMIN B 12 VITAMIN B-12 COBALAMIN (COBALT ATOM IN CORRIN RING)
LECTURE-4 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE-20-12-2018 VITAMIN B 12 VITAMIN B-12 COBALAMIN (COBALT ATOM IN CORRIN RING)
Nutritional Megaloblastic Anemias DR. NABIL BASHIR HLS, 2018
 Nutritional Megaloblastic Anemias DR. NABIL BASHIR HLS, 2018 Definition: Macrocytic Anemia MCV>100fL Impaired DNA formation due to lack of: B12 or folate in ultimately active form use of antimetabolite
Nutritional Megaloblastic Anemias DR. NABIL BASHIR HLS, 2018 Definition: Macrocytic Anemia MCV>100fL Impaired DNA formation due to lack of: B12 or folate in ultimately active form use of antimetabolite
Folic Acid. Ameer Saadallah Al-Zacko Ahmad Ausama Al-Kazzaz Ahmad Maan Al-Hajar
 Folic Acid Ameer Saadallah Al-Zacko Ahmad Ausama Al-Kazzaz Ahmad Maan Al-Hajar Now with Ahmad Maan Al-Hajar Folic acid Folic acid is a water soluble Vitamin which has many forms include folate, vitamin
Folic Acid Ameer Saadallah Al-Zacko Ahmad Ausama Al-Kazzaz Ahmad Maan Al-Hajar Now with Ahmad Maan Al-Hajar Folic acid Folic acid is a water soluble Vitamin which has many forms include folate, vitamin
Biochemistry Vitamins B6 and B12
 HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
??? A Vitamin only produced by bacteria
 A Vitamin only produced by bacteria Both animals and humans must get this vitamin from food or supplements as it can not be naturally produced by the body.??? Active- B 12 (Holotranscobalamin) N C H 2
A Vitamin only produced by bacteria Both animals and humans must get this vitamin from food or supplements as it can not be naturally produced by the body.??? Active- B 12 (Holotranscobalamin) N C H 2
LECTURE-3 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE
 LECTURE-3 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE-20-12-2018 FOLATE or FOLIC ACID FOLATE Other names Folic acid Folacin Pteroylglutamic
LECTURE-3 VITAMINS DR PAWAN TOSHNIWAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR BIOCHEMISTRY ZYDUS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, DAHOD, GUJARAT DATE-20-12-2018 FOLATE or FOLIC ACID FOLATE Other names Folic acid Folacin Pteroylglutamic
Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function. B-vitamins and aging. Nafisa Jadavji, PhD
 Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function B-vitamins and aging Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Answer to questions from last class Homocysteine Vitamin B9:
Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function B-vitamins and aging Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Answer to questions from last class Homocysteine Vitamin B9:
a. Cofactors involved in CPR activity are FAD and FMN, which are derived from riboflavin (B2).
 MED 562 Fall 2017 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochrome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What cofactor
MED 562 Fall 2017 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochrome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What cofactor
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 MEDCH 402 FALL 2007 PRBLEM SET #4 WATER SLUBLE VITAMIS I. MATCH THE VITAMI R MIERAL WITH THE CRRESPDIG AMUT AD UIT. Answer (DV) Amount Unit 1. Thiamin g,x a) 20 x) mg 2. Biotin b,x b) 0.3 y) µg 3. Folacin
MEDCH 402 FALL 2007 PRBLEM SET #4 WATER SLUBLE VITAMIS I. MATCH THE VITAMI R MIERAL WITH THE CRRESPDIG AMUT AD UIT. Answer (DV) Amount Unit 1. Thiamin g,x a) 20 x) mg 2. Biotin b,x b) 0.3 y) µg 3. Folacin
VITAMIN B12 UPDATE. Rosemary S. Browne, MD Southern Arizona VA Healthcare System College of Medicine The University of Arizona
 VITAMIN B12 UPDATE Rosemary S. Browne, MD Southern Arizona VA Healthcare System College of Medicine The University of Arizona Learning Objectives: Relate the history of Vitamin B12 since the beginning
VITAMIN B12 UPDATE Rosemary S. Browne, MD Southern Arizona VA Healthcare System College of Medicine The University of Arizona Learning Objectives: Relate the history of Vitamin B12 since the beginning
B vitamins, homocysteine, and neurocognitive function in the elderly 1 4
 B vitamins, homocysteine, and neurocognitive function in the elderly 1 4 Jacob Selhub, Laura C Bagley, Joshua Miller, and Irwin H Rosenberg ABSTRACT Evidence of the importance of the B vitamins folic acid,
B vitamins, homocysteine, and neurocognitive function in the elderly 1 4 Jacob Selhub, Laura C Bagley, Joshua Miller, and Irwin H Rosenberg ABSTRACT Evidence of the importance of the B vitamins folic acid,
Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status
 Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status Dr. Attila Bezzegh Semmelweis Medical University, Instutute for Laboratory Medicine, Budapest, Hungary 2017 Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status Dr. Attila Bezzegh Semmelweis Medical University, Instutute for Laboratory Medicine, Budapest, Hungary 2017 Vitamin B12
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN. Nafisa Jadavji, PhD
 HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
IMPORTANCE OF EVALUATING VITAMIN B12 STATUS IN DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY DISORDERS
 Psychiatry Case Series International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. IMPORTANCE OF EVALUATING VITAMIN
Psychiatry Case Series International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. IMPORTANCE OF EVALUATING VITAMIN
UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date. Calcium and Hypertension. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss
 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Calcium and Hypertension Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss Journal Nutrition Bytes, 4(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author Martinez, Christina Publication Date 1998-01-01
UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Calcium and Hypertension Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss Journal Nutrition Bytes, 4(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author Martinez, Christina Publication Date 1998-01-01
Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases.
 Chapter 7 Vitamins Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1 Key Concept Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases. Dietary Reference
Chapter 7 Vitamins Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1 Key Concept Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases. Dietary Reference
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Folate, Vitamin B 12, and Serum Total Homocysteine Levels in Confirmed Alzheimer Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Folate, Vitamin B 12, and Serum Total Homocysteine Levels in Confirmed Alzheimer Disease Robert Clarke, MD; A. David Smith, DPhil; Kim A. Jobst, DM; Helga Refsum, MD; Lesley Sutton,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Folate, Vitamin B 12, and Serum Total Homocysteine Levels in Confirmed Alzheimer Disease Robert Clarke, MD; A. David Smith, DPhil; Kim A. Jobst, DM; Helga Refsum, MD; Lesley Sutton,
Hematopoiesis, The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid.
 Hematopoiesis, 200 billion new blood cells per day The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid. hematopoietic growth factors, proteins that regulate the proliferation
Hematopoiesis, 200 billion new blood cells per day The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid. hematopoietic growth factors, proteins that regulate the proliferation
Elements for a Public Summary. Overview of Disease Epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of Disease Epidemiology Toxicity of Folic acid antagonists Despite having a low frequency of major toxicity, low dose Methotrexate (MTX, folic acid antagonist)
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of Disease Epidemiology Toxicity of Folic acid antagonists Despite having a low frequency of major toxicity, low dose Methotrexate (MTX, folic acid antagonist)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Folic acid acts on megaloblastic bone marrow to produce a normoblastic marrow.
 Folic Acid Tablets, USP Rx Only DESCRIPTION Folic acid, USP, N-[p-[[(2-amino-4- hydroxy-6-pteridinyl) methyl]- amino] benzoyl]-lglutamic acid, is a B complex vitamin containing a pteridine moiety linked
Folic Acid Tablets, USP Rx Only DESCRIPTION Folic acid, USP, N-[p-[[(2-amino-4- hydroxy-6-pteridinyl) methyl]- amino] benzoyl]-lglutamic acid, is a B complex vitamin containing a pteridine moiety linked
B-vitamins and prevention of dementia
 Proceedings of the Nutrition Society (8), 67, 75 81 g The Author 8 DOI:1.117/S2966518646 The Summer Meeting of the Nutrition Society, hosted by the Irish Section, was held at the University of Ulster,
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society (8), 67, 75 81 g The Author 8 DOI:1.117/S2966518646 The Summer Meeting of the Nutrition Society, hosted by the Irish Section, was held at the University of Ulster,
B Vitamins, Cognition, and Aging: A Review
 Journal of Gerontology: PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCES 2001, Vol. 56B, No. 6, P327 P339 Copyright 2001 by The Gerontological Society of America B Vitamins, Cognition, and Aging: A Review Eva Calvaresi and Janet
Journal of Gerontology: PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCES 2001, Vol. 56B, No. 6, P327 P339 Copyright 2001 by The Gerontological Society of America B Vitamins, Cognition, and Aging: A Review Eva Calvaresi and Janet
CNB12 Plus. by ChiroNutraceutical. Recommended for:
 CNB12 Plus by ChiroNutraceutical Recommended for: Increased Metabolism Nervous System Repair & Support Anti-Brain Aging Anemia Parkinson s, Alzheimer s and Multiple Sclerosis What is Methylcobalamin? Methylcobalamin
CNB12 Plus by ChiroNutraceutical Recommended for: Increased Metabolism Nervous System Repair & Support Anti-Brain Aging Anemia Parkinson s, Alzheimer s and Multiple Sclerosis What is Methylcobalamin? Methylcobalamin
EFFECT OF FOLATE AND VITAMIN B12 STATUS AND RELATED GENETIC POLYMORPHISMS ON CONGENITAL HEART DEFECT RISK: A PILOT STUDY
 EFFECT OF FOLATE AND VITAMIN B12 STATUS AND RELATED GENETIC POLYMORPHISMS ON CONGENITAL HEART DEFECT RISK: A PILOT STUDY By YOUNIS ALI SALMEAN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
EFFECT OF FOLATE AND VITAMIN B12 STATUS AND RELATED GENETIC POLYMORPHISMS ON CONGENITAL HEART DEFECT RISK: A PILOT STUDY By YOUNIS ALI SALMEAN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Metabolism of. Sulfur Containing Amino Acids
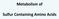 Metabolism of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids Methionine S CH 3 CH 2 cysteine CH 2 SH CH 2 CHNH 2 COOH CHNH 2 COOH Essential amino acid Non-polar amio acid Glucogenic amino acid Methionine IMPORTANCE: As
Metabolism of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids Methionine S CH 3 CH 2 cysteine CH 2 SH CH 2 CHNH 2 COOH CHNH 2 COOH Essential amino acid Non-polar amio acid Glucogenic amino acid Methionine IMPORTANCE: As
Coenzymes. Coenzymes 9/15/2014. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
9/16/2015. Coenzymes. Coenzymes. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins. Types of cofactors
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
Drugs Used in Anemia
 Drugs Used in Anemia Drugs of Anemia Anemia is defined as a below-normal plasma hemoglobin concentration resulting from: a decreased number of circulating red blood cells or an abnormally low total hemoglobin
Drugs Used in Anemia Drugs of Anemia Anemia is defined as a below-normal plasma hemoglobin concentration resulting from: a decreased number of circulating red blood cells or an abnormally low total hemoglobin
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins
 3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy
 UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy Title Vitamin C and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5xg9t04z Journal Nutrition Noteworthy, 4(1) ISSN 1556-1895 Author Chang, Angela
UCLA Nutrition Noteworthy Title Vitamin C and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5xg9t04z Journal Nutrition Noteworthy, 4(1) ISSN 1556-1895 Author Chang, Angela
!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
 LAB #: Sample Report PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: SEX: Female DOB: 01/01/1985 AGE: 33 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Sample Doctor Doctors Data Inc 3755 Illinois Ave St. Charles, IL 60174 U.S.A.!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
LAB #: Sample Report PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: SEX: Female DOB: 01/01/1985 AGE: 33 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Sample Doctor Doctors Data Inc 3755 Illinois Ave St. Charles, IL 60174 U.S.A.!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
c. NADPH can reduce FAD or FMN, thus the cofactors should be converted to their colorless forms.
 MEDCH 562 Fall 2018 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochorome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What
MEDCH 562 Fall 2018 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochorome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 30 Outline Amino acids are obtained from the
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 30 Outline Amino acids are obtained from the
Screening for vitamin B-12 and folate deficiency in older persons 1 3
 Screening for vitamin B-12 and folate deficiency in older persons 1 3 Robert Clarke, Helga Refsum, Jacqueline Birks, John Grimley Evans, Carole Johnston, Paul Sherliker, Per M Ueland, Joern Schneede, Joseph
Screening for vitamin B-12 and folate deficiency in older persons 1 3 Robert Clarke, Helga Refsum, Jacqueline Birks, John Grimley Evans, Carole Johnston, Paul Sherliker, Per M Ueland, Joern Schneede, Joseph
Vitamin B 12 Deficiency in the Elderly
 Benign Hematological Disorders Vitamin B 12 Deficiency in the Elderly Sudeep S. Gill, MD, FRCP(C), Research Fellow, Division of Geriatric Medicine, University of Toronto and Kunin-Lunenfeld Applied Research
Benign Hematological Disorders Vitamin B 12 Deficiency in the Elderly Sudeep S. Gill, MD, FRCP(C), Research Fellow, Division of Geriatric Medicine, University of Toronto and Kunin-Lunenfeld Applied Research
Nitrous Oxide induced Elevation of Plasma Homocysteine and Methylmalonic Acid Levels and their Clinical Implications
 SHORT COMMUNICATION JIACM 2005; 6(1): 48-52 Abstract Nitrous Oxide induced Elevation of Plasma Homocysteine and Methylmalonic Acid Levels and their Clinical Implications Pramood C Kalikiri*, Reena G Sachan*
SHORT COMMUNICATION JIACM 2005; 6(1): 48-52 Abstract Nitrous Oxide induced Elevation of Plasma Homocysteine and Methylmalonic Acid Levels and their Clinical Implications Pramood C Kalikiri*, Reena G Sachan*
HYPERHOMOCYSTEINEMIA: RELATION TO CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (PDF) HOMOCYSTEINE AND RELATED B-VITAMIN STATUS IN COELIAC
 PDF HYPERHOMOCYSTEINEMIA: RELATION TO CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (PDF) HOMOCYSTEINE AND RELATED B-VITAMIN STATUS IN COELIAC 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 homocysteine related vitamins pdf Hyperhomocysteinemia: Relation
PDF HYPERHOMOCYSTEINEMIA: RELATION TO CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (PDF) HOMOCYSTEINE AND RELATED B-VITAMIN STATUS IN COELIAC 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 homocysteine related vitamins pdf Hyperhomocysteinemia: Relation
Ranking Nutritional Supplements Botanical Medicine Primary
 Your Monthly Update Dear Colleague Welcome to the October newsletter from Pure Bio Ltd. Did you know...? The UK organic market grew by 30% and averaged sales of 7million a week in 2005! Our topic for this
Your Monthly Update Dear Colleague Welcome to the October newsletter from Pure Bio Ltd. Did you know...? The UK organic market grew by 30% and averaged sales of 7million a week in 2005! Our topic for this
Physiological Role: B-vitamins are coenzymes of many enzymes systems of body metabolism. Thiamine {B 1 }
 Food Constituents [continued] Micronutrients B-Vitamins The B group of vitamin {water soluble} includes: Thiamine: vitamin B 1, ant beriberi vitamin. Riboflavin: vitamin B 2. Niacin: nicotinic acid, PP
Food Constituents [continued] Micronutrients B-Vitamins The B group of vitamin {water soluble} includes: Thiamine: vitamin B 1, ant beriberi vitamin. Riboflavin: vitamin B 2. Niacin: nicotinic acid, PP
T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S
 W H O L E H E A L T H A M E R I C A. C O M Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present J U L Y, 2 0 1 3 V O L U M E 1 0, I S S U E 7 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S P R O T E C T F R O M
W H O L E H E A L T H A M E R I C A. C O M Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present J U L Y, 2 0 1 3 V O L U M E 1 0, I S S U E 7 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S P R O T E C T F R O M
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY AND CHRONIC ILLNESS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY AND CHRONIC ILLNESS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 vitamin b12 deficiency and chronic illness vitamin b12 deficiency and pdf vitamin b12 deficiency and chronic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY AND CHRONIC ILLNESS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 vitamin b12 deficiency and chronic illness vitamin b12 deficiency and pdf vitamin b12 deficiency and chronic
Metabolism of Nucleotides
 Metabolism of Nucleotides Outline Nucleotide degradation Components of Nucleobases Purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis Hyperuricemia Sources Nucleotide degradation The nucleotides are among the most complex
Metabolism of Nucleotides Outline Nucleotide degradation Components of Nucleobases Purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis Hyperuricemia Sources Nucleotide degradation The nucleotides are among the most complex
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Robert Lyons, Ph.D., 008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the reative ommons Attribution Share Alike.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/bysa/.0/
Author: Robert Lyons, Ph.D., 008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the reative ommons Attribution Share Alike.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/bysa/.0/
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 31 Amino Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 31 Outline Although the atmosphere is approximately 80% nitrogen,
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 31 Amino Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 31 Outline Although the atmosphere is approximately 80% nitrogen,
At one time, the diagnosis of a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folate was considered to
 REVIEW ARTICLE Laboratory Diagnosis of Vitamin B 12 and Folate Deficiency A Guide for the Primary Care Physician Christopher F. Snow, MD At one time, the diagnosis of a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folate
REVIEW ARTICLE Laboratory Diagnosis of Vitamin B 12 and Folate Deficiency A Guide for the Primary Care Physician Christopher F. Snow, MD At one time, the diagnosis of a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folate
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
Name of Policy: Serum Holotranscobalamin as a Marker of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Status
 Name of Policy: Serum Holotranscobalamin as a Marker of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Status Policy #: 448 Latest Review Date: August 2013 Category: Medicine/Laboratory Policy Grade: Effective 08/29/2013: Active
Name of Policy: Serum Holotranscobalamin as a Marker of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Status Policy #: 448 Latest Review Date: August 2013 Category: Medicine/Laboratory Policy Grade: Effective 08/29/2013: Active
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Homocysteine, vitamin B-12, and folic acid and the risk of cognitive decline in old age: the Leiden 85-Plus Study 1 3
 Homocysteine, vitamin B-12, and folic acid and the risk of cognitive decline in old age: the Leiden 85-Plus Study 1 3 Simon P Mooijaart, Jacobijn Gussekloo, Marijke Frölich, Jelle Jolles, David J Stott,
Homocysteine, vitamin B-12, and folic acid and the risk of cognitive decline in old age: the Leiden 85-Plus Study 1 3 Simon P Mooijaart, Jacobijn Gussekloo, Marijke Frölich, Jelle Jolles, David J Stott,
Coenzymes. Coenzymes 9/11/2018. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN
 EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN Financial Disclosure: Consultant to DaVinci Labs AGENDA Overview of the following: Methylation Telomere
EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN Financial Disclosure: Consultant to DaVinci Labs AGENDA Overview of the following: Methylation Telomere
Why Use Genetic Testing in Practice?
 Pure Encapsulations is committed to producing the most complete line of research-based nutritional supplements. Available through health professionals, finished products are pure and hypoallergenic to
Pure Encapsulations is committed to producing the most complete line of research-based nutritional supplements. Available through health professionals, finished products are pure and hypoallergenic to
Extrafolate-S (6S)-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Salt
 Extrafolate-S (6S)-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Salt Folate and the misleading concept The terms folic acid and folate are often erroneously used interchangeably for the water-soluble B-complex vitamin.
Extrafolate-S (6S)-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Salt Folate and the misleading concept The terms folic acid and folate are often erroneously used interchangeably for the water-soluble B-complex vitamin.
2) What are the main types of reactions that use folates as a cofactor?
 MED 562 Fall 2017 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochorome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What cofactor
MED 562 Fall 2017 Water Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 2 1) Cytochorome P450 Reductase (CPR) is an enzyme responsible for the reduction of a large portion of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. a. What cofactor
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
DATA SHEET QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 1 DATA SHEET PRODUCT NAME Solution for injection 1 mg/ml QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Hydroxocobalamin acetate 1 mg/ml For full list of excipients, see section 6.1 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Solution
1 DATA SHEET PRODUCT NAME Solution for injection 1 mg/ml QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Hydroxocobalamin acetate 1 mg/ml For full list of excipients, see section 6.1 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Solution
METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS
 Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders. Dr. Ron Grabowski
 Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders Dr. Ron Grabowski Statistics Depression is a common mental disorder with a complex etiology. Depressive disorders affect 121 million people worldwide and are
Nutritional Considerations and Mood Disorders Dr. Ron Grabowski Statistics Depression is a common mental disorder with a complex etiology. Depressive disorders affect 121 million people worldwide and are
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three
 Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Review Fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids are converted into carboxylic
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Review Fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids are converted into carboxylic
Package Insert. Raricap. 4. Clinical particulars 4.1 Therapeutic indications For the prevention and treatment of Iron deficiency anaemias
 Package Insert Raricap Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Raricap 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each film coated tablet contains: Ferrous Calcium Citrate Complex (Equivalent
Package Insert Raricap Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Raricap 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each film coated tablet contains: Ferrous Calcium Citrate Complex (Equivalent
and animals in which cobalamin had been inactivated by nitrous oxide, made it possible to test a much wider range of folate analogues (Deacon
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (October 1981) 57, 611-616 The effect of folate analogues on thymidine utilization by human and rat marrow cells and the effect on the deoxyuridine suppression test ROSEMARY
Postgraduate Medical Journal (October 1981) 57, 611-616 The effect of folate analogues on thymidine utilization by human and rat marrow cells and the effect on the deoxyuridine suppression test ROSEMARY
Summary HTA. The role of Homocysteine as a predictor for coronary heart disease. Lühmann D, Schramm S, Raspe H. HTA-Report Summary
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary The role of Homocysteine as a predictor for coronary heart disease. Lühmann D, Schramm S, Raspe H DAHTA@DIMDI Waisenhausgasse 36-38a D-50676 Köln Tel.: +49 221 4724-525 Fax
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary The role of Homocysteine as a predictor for coronary heart disease. Lühmann D, Schramm S, Raspe H DAHTA@DIMDI Waisenhausgasse 36-38a D-50676 Köln Tel.: +49 221 4724-525 Fax
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
Methylation. Taking the guesswork out of diagnosis. Proper functioning of the methylation cycle helps to reduce the risk of:
 Methylation The methylation cycle is a biochemical pathway that manages or contributes to a wide range of crucial bodily functions. Methylation is not just one specific reaction, there are hundreds of
Methylation The methylation cycle is a biochemical pathway that manages or contributes to a wide range of crucial bodily functions. Methylation is not just one specific reaction, there are hundreds of
PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS
 PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID CATABOLISM After removing of amino group the carbon skeletons of amino acids are transformed into metabolic
PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID CATABOLISM After removing of amino group the carbon skeletons of amino acids are transformed into metabolic
Homocysteine. Related Vitamins and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Homocysteine Related Vitamins and Neuropsychiatric Disorders Springer Paris Berlin Heidelberg New York Hong Kong London Milan Tokyo Christina Bolander-Gouaille Teodoro Bottiglieri Homocysteine Related
Homocysteine Related Vitamins and Neuropsychiatric Disorders Springer Paris Berlin Heidelberg New York Hong Kong London Milan Tokyo Christina Bolander-Gouaille Teodoro Bottiglieri Homocysteine Related
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines
 Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date
 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Whey Protein- The Role of Protein Supplementation in Resistance Training Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/07p2v5wd Journal Nutrition Bytes, 10(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author
UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Whey Protein- The Role of Protein Supplementation in Resistance Training Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/07p2v5wd Journal Nutrition Bytes, 10(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Dietary Folate and Vitamin B 12 Intake and Cognitive Decline Among Community-Dwelling Older Persons
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dietary Folate and Vitamin B 12 Intake and Cognitive Decline Among Community-Dwelling Older Persons Martha Clare Morris, ScD; Denis A. Evans, MD; Julia L. Bienias, ScD; Christine
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dietary Folate and Vitamin B 12 Intake and Cognitive Decline Among Community-Dwelling Older Persons Martha Clare Morris, ScD; Denis A. Evans, MD; Julia L. Bienias, ScD; Christine
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
CBS Deficient Homocystinuria.
 CBS Deficient Homocystinuria. Kenneth N. Maclean PhD University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics The methionine cycle Alternative metabolic fates for Hcy Extrusion into the extracellular
CBS Deficient Homocystinuria. Kenneth N. Maclean PhD University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics The methionine cycle Alternative metabolic fates for Hcy Extrusion into the extracellular
MTHFR & Genetic Basics
 MTHFR & Genetic Basics The Answers You Need to Take Control of Your Health By Dr. Doni Wilson Genetics + Stress = Health Footnote What are Stresses? Major Life Stresses Daily Stresses Food Sensitivities
MTHFR & Genetic Basics The Answers You Need to Take Control of Your Health By Dr. Doni Wilson Genetics + Stress = Health Footnote What are Stresses? Major Life Stresses Daily Stresses Food Sensitivities
9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism
 9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism M.V. Martinov 1,V.M.Vitvitsky 1,E.V.Mosharov 2,R.Banerjee 2,F.I.Ataullakhanov 1 1 National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia 125167 2
9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism M.V. Martinov 1,V.M.Vitvitsky 1,E.V.Mosharov 2,R.Banerjee 2,F.I.Ataullakhanov 1 1 National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia 125167 2
V i t a m i n s Vitamins Organic micronutrients required for reproduction, development, growth, & maintenance of body functions.
 V i t a m i n s MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What is a vitamin? For each vitamin, what are the best food sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the results of deficiency? what are the results
V i t a m i n s MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What is a vitamin? For each vitamin, what are the best food sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the results of deficiency? what are the results
Folate and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Paradigm Shift after Forty Years of Research
 Folate and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Paradigm Shift after Forty Years of Research From Holland to Jamaica; from the 18th Century to 1988 In the 18th century, a midwife in Friesland, in the northern part
Folate and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Paradigm Shift after Forty Years of Research From Holland to Jamaica; from the 18th Century to 1988 In the 18th century, a midwife in Friesland, in the northern part
Composition: Each Tablet Contains. L-Methylfolate. Pyridoxal 5 -phosphate. Pharmacokinetic properties:
 Composition: Each Tablet Contains L-Methylfolate Mecobalamin Pyridoxal 5 -phosphate 1mg 1500 mcg 0.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: L-methylfolate is a water soluble molecule which is primarily excreted
Composition: Each Tablet Contains L-Methylfolate Mecobalamin Pyridoxal 5 -phosphate 1mg 1500 mcg 0.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: L-methylfolate is a water soluble molecule which is primarily excreted
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Vitamin B12 and mercury
 Dr. med. Jürg Eichhorn Allgemeine Innere Medizin FMH Praxis für Allgemeine und Erfahrungsmedizin Traditionelle Chinesische Medizin ASA Sportmedizin SGSM Neuraltherapie SANTH & SRN Manuelle Medizin SAMM
Dr. med. Jürg Eichhorn Allgemeine Innere Medizin FMH Praxis für Allgemeine und Erfahrungsmedizin Traditionelle Chinesische Medizin ASA Sportmedizin SGSM Neuraltherapie SANTH & SRN Manuelle Medizin SAMM
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
UPDATE. Compiled by Dr Bevan Hokin
 UPDATE Advances and controversies in B-vitamins and Choline: A report on the Leipzig Conference March 5-8 2012 Introduction An International Conference of scientists and clinicians was held at Leipzig
UPDATE Advances and controversies in B-vitamins and Choline: A report on the Leipzig Conference March 5-8 2012 Introduction An International Conference of scientists and clinicians was held at Leipzig
Faculty of Medicine Dr. Tariq Aladily
 Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Vitamin B-12 and cognition in the elderly 1 4
 Vitamin B-12 and cognition in the elderly 1 4 A David Smith and Helga Refsum ABSTRACT Vitamin B-12 deficiency is often associated with cognitive deficits. Here we review evidence that cognition in the
Vitamin B-12 and cognition in the elderly 1 4 A David Smith and Helga Refsum ABSTRACT Vitamin B-12 deficiency is often associated with cognitive deficits. Here we review evidence that cognition in the
Role of homocysteine, cystathionine and methylmalonic acid measurement for diagnosis of vitamin deficiency in high-aged subjects
 European Journal of Clinical Investigation (2000) 30, 1083±1089 Role of homocysteine, cystathionine and methylmalonic acid measurement for diagnosis of vitamin deficiency in high-aged subjects W. Herrmann
European Journal of Clinical Investigation (2000) 30, 1083±1089 Role of homocysteine, cystathionine and methylmalonic acid measurement for diagnosis of vitamin deficiency in high-aged subjects W. Herrmann
T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S
 Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present V O L U M E 7, I S S U E 2 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S F E B R U A R Y, 2 0 1 0 D E M E N T I A A N D E X E R C I S E L E T S H E A R I T F
Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present V O L U M E 7, I S S U E 2 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S F E B R U A R Y, 2 0 1 0 D E M E N T I A A N D E X E R C I S E L E T S H E A R I T F
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease
 What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
Toxicity of Inorganic Copper from Drinking Water in the Causation of Alzheimer s Disease
 Toxicity of Inorganic Copper from Drinking Water in the Causation of Alzheimer s Disease George J Brewer, M.D. Professor Emeritus University of Michigan Sellner Professor Emeritus of Human Genetics Senior
Toxicity of Inorganic Copper from Drinking Water in the Causation of Alzheimer s Disease George J Brewer, M.D. Professor Emeritus University of Michigan Sellner Professor Emeritus of Human Genetics Senior
K-9 Kraving Brand Training
 K-9 Kraving Brand Training What s In The Mix? Session Preview Complete & Balanced Diets Breakdown Vitamin, Mineral & Trace Mineral Mix What s In It and Why? Dietary Supplements Raw Diet Dog Foods are:
K-9 Kraving Brand Training What s In The Mix? Session Preview Complete & Balanced Diets Breakdown Vitamin, Mineral & Trace Mineral Mix What s In It and Why? Dietary Supplements Raw Diet Dog Foods are:
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR
 Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
Micronutrients: History of the Word Vitamin. INE: Micronutrients - Vitamins: Introduction to Vitamins.
 Micronutrients: Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not
Micronutrients: Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
BCH 471 Experiment (7) HEMOGIOBIN AND ANEMIA, ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) AND HEMATOCRIT (HCT)
 BCH 471 Experiment (7) HEMOGIOBIN AND ANEMIA, ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) AND HEMATOCRIT (HCT) OBJECTIVES 1) Quantitative determination of hemoglobin in a blood sample. 2) Determination of erythrocyte
BCH 471 Experiment (7) HEMOGIOBIN AND ANEMIA, ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) AND HEMATOCRIT (HCT) OBJECTIVES 1) Quantitative determination of hemoglobin in a blood sample. 2) Determination of erythrocyte
Medical Policy Vitamin B12 Screening & Testing
 Medical Policy Vitamin B12 Screening & Testing Subject: Vitamin B12 Screening & Testing Background: Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is required for proper red blood cell formation, neurological
Medical Policy Vitamin B12 Screening & Testing Subject: Vitamin B12 Screening & Testing Background: Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is required for proper red blood cell formation, neurological
Subject Review. The Biochemical Basis of Cobalamin Deficiency
 Subject Review The Biochemical Basis of Cobalamin Deficiency AYALEW TEFFERI, M.D., AND RAJIV K. PRUTHI, M.D. Objective: In this report, our goal was to summarize the current knowledge of the biochemical
Subject Review The Biochemical Basis of Cobalamin Deficiency AYALEW TEFFERI, M.D., AND RAJIV K. PRUTHI, M.D. Objective: In this report, our goal was to summarize the current knowledge of the biochemical
STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING
 How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca REMINDER! Purpose of Course To present information about how nutrition
How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca REMINDER! Purpose of Course To present information about how nutrition
Identification and Validation of Biomarkers in Disease States
 Identification and Validation of Biomarkers in Disease States Patrick J. Stover, PhD Vice Chancellor and Dean for Agriculture and Life Sciences Disclosures AFFILIATION/FINANCIAL INTERESTS (prior 12 months)
Identification and Validation of Biomarkers in Disease States Patrick J. Stover, PhD Vice Chancellor and Dean for Agriculture and Life Sciences Disclosures AFFILIATION/FINANCIAL INTERESTS (prior 12 months)
