Biological evaluation of analogues of an insect neuropeptide proctolin
|
|
|
- Kerry Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. 51 No. 1/ QUARTERLY Biological evaluation of analogues of an insect neuropeptide proctolin Iwona Woźnica 1, Wioletta Szeszel-Fedorowicz 1, Grzegorz Rosiński 2 and Danuta Konopińska 1 1 Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wrocław, Wrocław, Poland; 2 Department of Animal Physiology, A. Mickiewicz University, Poznań, Poland Received: 31 October, 2003; revised: 23 January, 2004; accepted: 06 February, 2004 Key words: proctolin, insect myotropic peptide proctolin, proctolin analogues Continuing our studies on proctolin (Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr) we performed the synthesis and biological evaluation of 52 analogues substituted in position 2, 3, 4, and 5 of the peptide chain. The peptides were bioassayed for cardiotropic activity in vitro on Tenebrio molitor and myotropic activity on foregut of Schistocerca gregaria. Twenty analogues retained 20 80% of proctolin activity. Continuing our studies on structure/function relationship of proctolin ( Konopiñska & Rosiñski, 1999) (Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr) we performed the synthesis of four groups of analogues modified in position 2, 3, 4, or 5 by natural or non-natural amino-acid residues, such as: 1/ H-Arg-X 2 -Leu-Pro-Thr-OH, where X 2 = Hpa (1), Hpa(4-NO 2 ) (2), Hpa(4-NH 2 ) (3), Hpa(4-N,N-Me 2 ) (4), Phg (5), D-Phg (6), Phg(4-NO 2 ) (7), D-Phg(4-NO 2 ) (8), Phg(4-NH 2 ) To whom correspondence should be addressed: Danuta Konopińska, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wrocław, Wrocław, Poland; dk@wchuwr.chem.uni.wroc.pl Abbreviations: The symbols of amino acids, peptides, and their derivatives are in accordance with the IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature Recommendation, 1983 (Eur J Biochem.; 138: 9, (1984); and J Pept Sci. 5: 465 (1999); J Pept Sci. 9: 1 (2003)). -Abu, -aminobutyric acid; Boc-, t-butoxycarbonyl; BOP, benzotriazolyl-n-oxytrisdimethylaminophosphonium hexafluorophosphate; HOBt, hydroxybenztriazole; HPLC, high pressure liquid chromatography; DCC, N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide; Hpa, L-homo-phenylalanine; Hpa(p-NO 2 ), 4-nitro-L-homo-phenylalanine; Hpa(p-NH 2 ), 4-amino-L-homo-phenylalanine; Hpa(NMe 2 ), 4- p-n,n-dimethyl-l-phenylglycine; Me, methyl; Nva, L-norvaline; Phg, L-phenylglycine; Sar, sarcosine; Phg(p-OH), 4-hydroxy-L-phenylglycine; D-Phg(p-OH), 4-hydroxy-D-phenylglycine; Phg(p-NO 2 ), 4-nitro-L-phenylglycine; D-Phg(p-NO 2 ), 4-nitro-D-phenylglycine; Phg(p-NH 2 ), 4-amino-L-phenylglycine; D-Phg(p-NH 2 ), 4-amino-D-phenylglycine; Phg(p-NMe 2 ), 4-p-N,N-dimethyl-L-phenylglycine; D-Phg(p-NMe 2 ), 4-N,N-dimethyl-D-phenylglycine.
2 116 I. Woźnica and others 2004 (9), D-Phg(4-NH 2 ) (10), Phg(4-OH) (11), D-Phg(4-OH) (12), Phg (4-N,N-Me 2 ) (13), D-Phg (4-N,N-Me 2 ) (14); 2/H-Arg-Tyr-X 3 -Pro- Thr-OH, where X 3 = Ile (15), Phe (16), Lys (17), Glu (18), Gln (19), Asn (20), Asp (21), Nva (22), Nle (23), -Abu (24), Arg (25), Sar (26); 3/ H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-X 4 -Thr-OH, where X 4 = Phg (27), Phe (28), Ala(N-Me) (29); 4/ H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-X 5 -OH, where X 5 = Val (30), D-Val (31), Ile (32), D-Ile (33), Ala (34), D-Ala (35), Ser (36), Asn (37), Gln (38), Asp (39), Glu (40), Arg (41), D-Arg (42), Lys (43), Gly (44); 5/ Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-NH(R ), where R = isobutyl (45), S-1-methyl-1-phenylmethyl (46), R-1-methyl-1-phenylmethyl (47), R-2-hydroxy-1-methylethyl (48), S-2-hydroxy- 1-methylethyl (49), R-2-hydroxypropyl (50), S-2-hydroxypropyl (51), 1-hydroxy-n-propyl (52) (Table 1). In the first group of analogues the Tyr residue in position 2 was replaced by L-Hpa and its derivatives or by L- and D-Phg derivatives. In contrast to native Tyr-2, Phg is an amino acid which is deprived of the methylene group between the C- atom and the benzene ring, whereas Hpa have two methylene groups between the C- atom and the benzene ring. The aim of these modifications was to explain the influence of lack of the methylene system or presence of an additional methylene group in the side chain of amino acids in position 2 on the myotropic activity in insects. Because the role of Leu in position 3 and Pro in position 4 has not been sufficiently established in the previous investigations (Konopiñska & Rosiñski, 1999) of the structure-biological function relationship, we performed the synthesis of further proctolin analogues where Leu-3 and Pro-4 were replaced for protein or non-protein amino-acid residues. We also synthesized of proctolin analogues modified in position 5 (30 52) to check the role of the C-terminal Thr on the biological activity in insects. In this group, Thr in position 5 was substituted with other amino acids. Especially interesting in these studies were analogues modified in position 5 by a residue with an isosteric structure of the side chain relative to Thr, such as [Val 5 ]- and [Ile 5 ]-proctolin as well as analogues deprived of the carboxyl group at the C-terminal end of proctolin. In these analogues, Thr 5 was replaced by a series of S- and R- hydroxyamines or phenyl amines. We also obtained analogues 50 and 51, with amines isosteric to the structure of the side chain of Thr in position 5. The purpose of these studies was to explain the role of the C-terminal carboxyl group for proctolin myotropic properties in insects. MATERIALS AND METHODS Syntheses of the peptides were carried out by the solid-phase standard method (Kuczer et al., 1996). All peptides were synthesized by the classical solid-phase Boc (tert-butoxycarbonyl) procedure. Chloromethylated classical Merrifield resin containing mmol Cl/g resin was obtained by the standard caesium salt procedure. The protected amino acid was coupled to the resin with diisopropylcarbodiimide or dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) in the presence of HOBt or BOP as coupling reagents. The Boc-protecting group was removed by 30% CF 3 COOH in CH 2 Cl 2. Peptides were released from the resin using CF 3 SO 3 H, the nitro group was reduced by hydrogenation over Pd/C as a catalyst. All free peptides were desalted with Amberlite CG-4B and then purified on a Sephadex G-15 column, with 5% acetic acid as eluent, according to (Kuczer et al., 1996). Final purification was carried out by preparative HPLC on a C-18 column (Beckman). Purity and homogeneity of the free peptides were determined by analytical HPLC, amino acid analysis, and optical activity. The purity of all peptides was about 100%. All peptides were bioassayed in vitro on semi-isolated hearts of yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) using a cardioexcitatory test elaborated by Gäde and Rosiñski (1988). Peptides 5 14 and were bioassayed on the locust (Schistocerca gregaria) foregut
3 Vol. 51 Insect neuropeptide proctolin analogues 117 (Gray et al., 1994). Results of biological investigation are presented in Table 1. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Among the proctolin analogues modified in position 2 of the peptide chain studied for cardiotropic activity in T. molitor only peptides 1 4 retained weak 20% proctolin activity at the physiological range of concentrations ( M). Analogues 5 12 modified by D- or L-Phg and their derivatives were inactive. In the myotropic test performed on proctolin modified in position 2 of the peptide chain by L-homophenylalanine or its derivatives, there is a longer distance between the side chain aromatic ring at position 2 and the peptide chain. Thus, the presence of only one methylene group next to the benzene ring of the amino-acid residue at position 2 is essential for myotropic activity in insects. The myotropic effects observed in insects depend probably on the structural properties of the amino-acid residue at position 2 of the proctolin molecule. The biological activity of proctolin analogues modified at position 3 of the peptide chain tested (Table 1) on the Table 1. Selected proctolin analogues with myotropic activity in insect *nd, no data the foregut of S. gregaria, analogues modified in position 2 of the peptide chain (5 12) were inactive. The lack of myotropic activity of proctolin analogues containing L-or D-phenylglycine (5 12) is probably a result of the lack of the CH 2 group in the side chain of the Phg residue. It is probably an important element of structure for creation of myotropic activity in insects. In the analogues of T. molitor heart showed that the presence of hydrophobic residues in position 3 is not so important for myotropic properties in insects as we postulated in our earlier paper (Konopińska & Rosiński, 1999). Only [Val 3 ]-proctolin, described earlier (Konopińska & Rosiński, 1999), and [Ile 3 ]-proctolin (15) presented here both with a branched side chain, retain a high cardiostimulatory activity.
4 118 I. Woźnica and others 2004 Proctolin analogues containing hydrophobic amino acids without a branched side chain, such as: Phe (16), Sar (26), Nva (22), Nle (23), and -Abu (24) were practically inactive. On the other hand, proctolin analogues modified at position 3 by basic amino-acids, such as (17) and (25), retained more than 60% of proctolin activity. Analogues containing acidic amino-acid residues at position 3, like Asp (21) or Glu (18), had 70% and 30% of the native peptide activity, respectively. The exchange of Thr for amines also pointed out that the presence of the C-terminal carboxyl group is important for the myotropic activity. Peptides 30, 32, 34, 41, 43, 51, and 52 retained about 20 60% of the proctolin activity in T. molitor. We found that analogues 33, 30 and 32 retained about 30 60% of the proctolin-like activity in the myotropic test on the foregut of S. gregaria whereas peptides 34 and 36 had weak stimulatory properties in the test evaluating contraction of the locust foregut at the peptide concentration ranging from 10 7 to 10 6 M. Other peptides had neither agonistic nor antagonistic activity. This is interesting that analogues 30 and 32, containing Val or Ile with the side chain isosteric in relation to Thr, stimulated the heart-beat frequency in T. molitor and contraction of the S. gregaria foregut. It testifies that the presence of methyl or ethyl groups isosteric with the threonine side chain is sufficient for preservation of the myotropic effect in insects. In addition, it should be pointed out that proctolin analogue 51, containing R-1-amino-2-propanol in position 5, and analogue 52, containing 1-amino-n-propanol with the side chain isosteric with the side chain of Thr, retained about 50% of proctolin myotropic activity in T. molitor. Moreover, species specificity was observed in the case of [D-Ile 5 ]-(33) and [Gln 5 ]-proctolin (38). These different myotropic effects, observed in two insect species, depend probably on the structural requirement for a specific amino-acid residue in position 5 of the proctolin molecule in the species tested. For instance, a peptide with Ala in position 5 of the proctolin chain (analogue 34) weakly stimulated the heart of the yellow mealworm. The same analogue showed no stimulatory effect in the test performed on the foregut of S. gregaria. Similar species specificity was observed in the case of analogues 33 and 38, which contained D-Ile and Gln, respectively, instead of Thr-5. These analogues preserved 30% and 80% of the proctolin activity in the locust, respectively, while lacked this activity in the yellow mealworm. The different activities of the investigated peptides in the two insect species is probably a consequence of structurally different requirement of receptors in the T. molitor heart and S. gregaria foregut. CONCLUSION From analysis of the myotropic effects of proctolin analogues 1 52 in insects the following conclusions can be drawn: 1. The biological results pointed out that the presence of a methylene group between the C- atom and the aromatic ring of the side chain of the amino-acid residue at position 2 of the peptide chain is important for myotropic activity in insects. 2. Probably, elongation of the side chain at position 2 and bringing the aromatic ring further away from the peptide chain changes the peptide conformation and leads to inactive analogues. 3. The presence of a hydrophobic amino-acid residue with a branched side chain at position 3 is important for cardiotropic activity in the yellow mealworm. 4. The basic or acidic character of residues at position 3 of proctolin does not destroy the myotropic activity on the insect heart. 5. The lack of activity of most analogues containing amines instead of Thr in position 5, except for analogues 51 and 52 which retained 60 50% proctolin activity, testifies that the presence of the carboxyl group at the C-terminus as well as of the -OH group in the
5 Vol. 51 Insect neuropeptide proctolin analogues 119 side chain plays an essential role for the myotropic properties in insects. REFERENCES Gray AS, Osborne RH, Jewess PJ. (1994) Pharmacology of proctolin receptors in the isolated foregut of the locust Schistocerca gregaria identification of [N-methyl-L-tyrosine 2 ]-proctolin as a potent receptor antagonist. J Insect Physiol.; 40: Konopińska D, Rosiński G. (1999) Proctolin an insect neuropeptide. J Pept Sci.; 5: Kuczer M, Rosiński G, Lisowski M, Picur B, Konopińska D. (1996) New proctolin analogues modified by D-amino acids in the peptide chain and their high cardioexcitatory effect on Tenebrio molitor. Int J Peptide Protein Res.; 48: Rosiński G, Gäde G. (1988) Hyperglycaemic and myoactive factors in the corpora cardiaca of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor. J Insect Physiol.; 33:
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Biol 405 Molecular Medicine 1998 Crystal structure of phenylalanine hydroxylase solved. The polypeptide consists of three regions: Regulatory
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Biol 405 Molecular Medicine 1998 Crystal structure of phenylalanine hydroxylase solved. The polypeptide consists of three regions: Regulatory
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
Third Exam Practice Test
 Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Electronic Supplementary Information. Table of Contents
 Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 4 Protein Sequence
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
paper and beads don t fall off. Then, place the beads in the following order on the pipe cleaner:
 Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology:
 The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease
 Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry The Renin-Angiotensin Pathway Dr Anna Barnard - Spring 2017 Course Overview Lecture 1: Overview of the
Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry The Renin-Angiotensin Pathway Dr Anna Barnard - Spring 2017 Course Overview Lecture 1: Overview of the
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Previous Class. Today. Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism. Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties
 Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Saccharomyces cerevisiae*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 1988 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Vol. 263, No. 29, Issue of October 15, pp. 14948-14955, 1988 Printed in U.S.A. Purification
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 1988 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Vol. 263, No. 29, Issue of October 15, pp. 14948-14955, 1988 Printed in U.S.A. Purification
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions. Proteins
 Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Organic Chemistry 3540
 rganic Chemistry 3540 December 8, 2004 (8 Pages, 13 Parts) ame 1. (8%) Many organic compounds found in living systems are complex molecules which can be characterized, in part, by simply listing the chemical
rganic Chemistry 3540 December 8, 2004 (8 Pages, 13 Parts) ame 1. (8%) Many organic compounds found in living systems are complex molecules which can be characterized, in part, by simply listing the chemical
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular
 Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
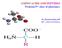 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
Ynamides as racemization-free coupling reagents for amide and peptide synthesis
 Ynamides as racemization-free coupling reagents for amide and peptide synthesis Long Hu, Silin Xu, Zhenguang Zhao, Yang Yang, Zhiyuan Peng, Ming Yang, Changliu Wang, Junfeng Zhao* Key Laboratory of Chemical
Ynamides as racemization-free coupling reagents for amide and peptide synthesis Long Hu, Silin Xu, Zhenguang Zhao, Yang Yang, Zhiyuan Peng, Ming Yang, Changliu Wang, Junfeng Zhao* Key Laboratory of Chemical
Calpain Assays, Nerve injury and Repair
 Calpain Assays, Nerve injury and Repair Annual Progress Report (G-3 3-Y44) April 2001 James C. Powers School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0400 (404) 894-4038
Calpain Assays, Nerve injury and Repair Annual Progress Report (G-3 3-Y44) April 2001 James C. Powers School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0400 (404) 894-4038
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
Electronic supplementary information Poly(vinyl)chloride supported palladium nanoparticles: Catalyst for rapid hydrogenation reactions
 Electronic supplementary information Poly(vinyl)chloride supported palladium nanoparticles: Catalyst for rapid hydrogenation reactions Hosahalli P. Hemantha and Vommina V. Sureshbabu* Peptide Research
Electronic supplementary information Poly(vinyl)chloride supported palladium nanoparticles: Catalyst for rapid hydrogenation reactions Hosahalli P. Hemantha and Vommina V. Sureshbabu* Peptide Research
An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis
 An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis Lisa Sapp Clinical Research and Forensic Toxicology Product Manager Mass Spectrometry Systems Amino Acid Analysis Using itraq Reagents
An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis Lisa Sapp Clinical Research and Forensic Toxicology Product Manager Mass Spectrometry Systems Amino Acid Analysis Using itraq Reagents
Protein Investigator. Protein Investigator - 3
 Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis. Chemistry M3LC
 Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates. Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager
 Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager Cheese composition Cheese consists of proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, goat,
Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager Cheese composition Cheese consists of proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, goat,
mm C3a. 1 mm C3a Time (s) C5a. C3a. Blank. 10 mm Time (s) Time (s)
 125 I-C5a (cpm) Fluorescnece Em 520nm a 4000 3000 2000 1000 c 0 5000 4000 3000 2000 Blank C5a C3a 6 0.3 mm C3a 7 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 0.3 mm C5a 0 300 600 900 1200 Time (s) 17 Fluorescnece Em 520nm Fluorescnece
125 I-C5a (cpm) Fluorescnece Em 520nm a 4000 3000 2000 1000 c 0 5000 4000 3000 2000 Blank C5a C3a 6 0.3 mm C3a 7 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 0.3 mm C5a 0 300 600 900 1200 Time (s) 17 Fluorescnece Em 520nm Fluorescnece
Protein Modification Overview DEFINITION The modification of selected residues in a protein and not as a component of synthesis
 Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
Cahn - Ingold - Prelog system. Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009. The Fischer Convention (1) G (2) (3)
 Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Chemistry of Insulin. Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, (1959)
 Chemistry of Insulin Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, 1340-1344 (1959) Human Insulin The Sanger Method The DNP- amino acids are bright yellow substances and can be separated from
Chemistry of Insulin Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, 1340-1344 (1959) Human Insulin The Sanger Method The DNP- amino acids are bright yellow substances and can be separated from
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon. Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011
 Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM
 SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. Cell 7.5
 Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
 Acta Univ. Sapientiae, Alimentaria, 1 (2008) 49 60 Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
Acta Univ. Sapientiae, Alimentaria, 1 (2008) 49 60 Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid as the reductive thiol-containing reagent employed for the derivatization of amino acids with o-phthaldialdehyde analysis
PAPER No. : 16, Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 22, Mechanism of enzyme catalyst reaction (I) Chymotrypsin
 Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Bio Factsheet. Proteins and Proteomics. Number 340
 Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
TEPZZ 757_Z7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 77_Z7A_T (11) EP 2 77 7 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.07.14 Bulletin 14/ (21) Application number: 12831927.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 77_Z7A_T (11) EP 2 77 7 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.07.14 Bulletin 14/ (21) Application number: 12831927.4 (22)
Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information.
 Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of TRBV25-1 + and TRBV25-1 - CD1d-α-GalCerreactive cells.
Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of TRBV25-1 + and TRBV25-1 - CD1d-α-GalCerreactive cells.
Supporting Information. Recyclable hypervalent-iodine-mediated solid-phase peptide
 Supporting Information Recyclable hypervalent-iodine-mediated solid-phase peptide synthesis and cyclic peptide synthesis Dan Liu, Ya-Li Guo, Jin Qu and Chi Zhang* for Address: State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic
Supporting Information Recyclable hypervalent-iodine-mediated solid-phase peptide synthesis and cyclic peptide synthesis Dan Liu, Ya-Li Guo, Jin Qu and Chi Zhang* for Address: State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic
