Vitamin K: New Issues in Cardiovascular Health, Renal Health, Osteoporosis, Diabetes, Liver & Colon Cancer, and Pregnancy.
|
|
|
- Ashley Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aunt Cathy s Guide to: Sanford Medical Center 2016 Vitamin K: New Issues in Cardiovascular Health, Renal Health, Osteoporosis, Diabetes, Liver & Colon Cancer, and Pregnancy. Cathy Breedon, PhD, RD, CSP, FADA Aunt Cathy Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist and Perinatal/Pediatric Nutrition Specialist Sanford Medical Center, and UND School of Medicine, Fargo, ND 1. Overview/Summary: Vitamin K Facts and Figures (All the important useful information is on pp. 1-12) 2. Just References from the Scientific Literature: Inadequacy of Vitamin K and Contribution to: I. Cardiovascular Disease and Arterial and Renal Calcinosis II. Unsafe Variability of Anticoagulation Therapy III. Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis IV. Liver Cancer and Colorectal Cancer V. Miscellaneous Health Issues: Non-warfarin-related hemorrhage Cholestasis Diarrhea Celiac disease Cystic fibrosis Short bowel syndrome Pregnancy This is the short form of this paper with just the references at the end. Another version is available that includes the abstracts of the referenced articles. As always, this paper is a review of new issues in the scientific literature and not intended to take the place of your personal health care provider. In particular, individuals using anticoagulant medications like Coumadin/warfarin must not make changes in their vitamin K intake without consulting their physician/pa/np. A separate paper for health professionals is available that discusses this issue in more detail. 1
2 Overview/Summary: Vitamin K Issues 1 Vitamin K has been found to be involved in carboxylation reactions in various tissues. It is now recognized as playing a critical role in bone health, growth, diabetes, pregnancy, cardiovascular health, renal health, and certain cancers, in addition to its well-known role in blood coagulation. Allowing (or inducing) vitamin K deficiency for any reason is clearly not benign. 2 Foods that are generous in vitamin K1 are also excellent sources of beneficial antioxidant phytochemicals. This includes lutein, a pigment in leafy greens that appears to have an additional unique potential benefit in the prevention or the slowing of the progression of blindness due to macular degeneration. These foods are also very low in calories and rich in other vitamins and minerals as well. However, many Americans eat very few of these foods and as a result, relative vitamin K inadequacy is not at all uncommon when it is actually checked. (It is currently only very rarely checked.) The most generous dietary vitamin K2 sources include bacterially fermented foods. One of the richest is natto a strong flavored soy bean product popular in Japan but considerably less so in the US. 3 Elderly people appear to require a regular intake of vitamin K above the 2001 Adequate Intake (AI) level in order to assure adequacy. Note that the recommended amounts for everyone (AIs, RDI, RDA, etc.) were set at a time when it was assumed that intestinal bacteria provided about half of one s requirements. As this source has been found to be more unreliable than was thought, it is very reasonable to aim toward an intake that is generous. People using the drug Coumadin need to discuss this issue with their physician as described below in #6 and #8 because of a drug/nutrient interaction. However, except for this well-known drug/nutrient interaction, there is no upper level of safety for vitamin K and foods rich in vitamin K are rich in many other nutrients as well. 4 Vitamin K as phylloquinone (K1) and menaquinone (K2) are not toxic, and for that reason there is no Upper Limit of Safety established for this vitamin. In contrast, menadione (K3) is potentially harmful and it is generally no longer used as a vitamin K supplement. 2
3 5 It was previously assumed that about half of a person s vitamin K requirements were met via production by intestinal bacteria. It is now clear that healthy people are in fact MUCH more dependent on vitamin K from foods and/or supplements to assure adequacy than we thought. 6 Misunderstanding about recommendations for vitamin K intake for people on anticoagulant therapy has resulted in many people avoiding all sources of vitamin K (instead of taking in a CONSISTENT but ADEQUATE amount of vitamin K as recommended by the drug manufacturers.) One result, for example, is the association seen between anticoagulant use and increased risk of osteoporosis and cardiac and renal calcification. Initially it was thought to be due to the drug itself, but it turned out to be related to the far too common inappropriate excessive restriction of vitamin K. 7 It appears that dangerous VARIABILITY of blood clotting among some patients taking anticoagulants can be controlled significantly by assuring a consistent daily intake of an adequate amount of vitamin K. Coagulation variability is a much greater problem among patients whose usual vitamin K status is low. Those are the people most greatly affected by fluctuations in vitamin K content of diet or supplements. Persons with a reliable adequate intake level are far less affected by additional intake in vitamin K. 8 Vascular calcification, a known cardiovascular risk factor, is another side effect related to the problem of inducing low vitamin K status in patients on anticoagulants and among the population at large. Failure to activate the hormone osteocalcin because of inadequate vitamin K results in failure to move calcium from the bloodstream into bone. Instead, calcium is deposited inappropriately in other tissues, such as blood vessel walls and the kidneys. This results in arteriocalcinosis (an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease.) It also results in renal calcinosis because increased calcium needs to be excreted. 9 Vitamin K inadequacy is now being identified even among healthy children when vitamin K status is evaluated however, at present it is only very rarely evaluated. People with conditions that result in malabsorption are at very high risk of deficiency. This includes conditions like cystic fibrosis, poorly controlled celiac disease, Crohn s disease (inflammatory bowel disease or IBD,) biliary atresia, short bowel syndrome and intractable diarrhea. 3
4 10. Others at particular risk of inadequacy of vitamin K include people using drugs that interfere with vitamin K such as salicylates (e.g. aspirin) and many seizure-control medications. Similarly, some renal medications used to bind phosphate in the intestine (e.g. sevelamer-hcl) can greatly impair vitamin K absorption. [Metal ion and vitamin adsorption profiles of phosphate binder ion-exchange resins. Clin Nephrol Jan;73(1): Assuring vitamin K adequacy in pregnant and breast-feeding women is an important new focus. Vitamin K inadequacy in pregnancy has recently been identified as a risk factor for pregnancy complications like hyperemesis gravidarum, pre-eclampsia, intracranial bleeding in the infant, and excessive blood loss at delivery. Although vitamin K transfer across the placenta is noted to be poor, relative inadequacy in pregnancy can also contribute to poor nutrient stores in infants. Whether more generous maternal stores of vitamin K might enhance the transfer to the fetus has not been evaluated. The recommendation of the American Academy of Pediatrics is to provide vitamin K to newborns. Additionally, breast-fed babies are noted to be at higher risk of inadequacy apparently for the same reason low vitamin K content of mother s milk. Again, whether relative maternal vitamin K inadequacy is a factor in the breastmilk vitamin K content has not been evaluated yet. [American Academy of Pediatrics Policy Statement: Controversies Concerning Vitamin K and the Newborn. Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Pediatrics Vol. 112 No. 1 July 2003, pp ] 12. New roles of vitamin K are being recognized. For example, failure to activate osteocalcin because of inadequate vitamin K appears to have a negative effect on energy metabolism, including insulin metabolism. A possible role of vitamin K inadequacy in diabetes and obesity is just beginning to be examined. This is in addition to the cardiovascular, bone, and renal health issues. 13. Assuring vitamin K adequacy appears to be a factor in some aspects in the prevention or treatment of cancers of the liver, colon/rectum, prostate, pancreas and ovaries. Other recent areas of investigation include a role of vitamin K inadequacy in hypertension (high blood pressure) and inflammatory diseases such as arthritis. Dietary vitamin K appears to have a role in sulfatide metabolism, myelin structure and behavior functions. 4
5 14. Big Point: All of the health concerns described above are made less severe by the same interventions: Assure adequacy of vitamin K status for everyone from foods and/or supplements. (Do not ASSUME adequacy.) If a person is on the anticoagulant medication Coumadin*, assure that the vitamin K is administered in a consistent manner each day and that the physician has approved any adjustments of vitamin K intake. Remember that inducing a vitamin K deficiency is common in this context, makes the drug use more dangerous, and causes damage to the cardiovascular system, the renal system, bone health and increases risk of certain cancers. *Note that many anticoagulants do not involve vitamin K in their function as Coumadin does, so it makes even less sense to restrict vitamin K with these medications. Adjust intake recommendations to compensate for conditions associated with malabsorption and the effects of aging. 5
6 Some Vitamin K Facts and Figures Adequate Intake (AI) for Vitamin K Life Stage Infants Infants Children Children Adolescents Adults * Age 0-6 months 7-12 months 1-3 years 4-13 years years 19 years and older mcg/day Males 120 Females 90 Pregnancy or Breastfeeding Pregnancy or Breastfeeding 18 years and younger years and older 90 [Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Vitamin K. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Washington D.C.: National Academy Press; 2001: ] *Older adults [for sure] may benefit from higher regular intakes than are listed in the Advisable Intakes (AIs.) These were developed with the assumption that intestinal production of usable vitamin K provided a more significant amount. Current AIs for other age groups have not been re-evaluated since the discovery that the intestinal bacterial sources are far less available than was believed, so it is not just the elderly who may be at risk. The rest have not been checked yet. Vitamin K status in the elderly. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care Jan;10(1):
7 Sources of Vitamin K Leafy Vegetable Food Sources Phylloquinone (vitamin K1) is a major dietary form of vitamin K, and the major food source is leafy green vegetables. Not all green vegetables are good sources... it s the darker leafy ones that have the most! Additional benefits of these foods are the extremely low calories and the generous provision of other vitamins (such as vitamin C and vitamin A as beta carotene) and potent antioxidant phytochemicals such as lutein. There are many excellent reasons to include these foods in one s diet. This is also true for people using anticoagulation medications like Coumadin (warfarin.) As described earlier, the goal is to assure both an adequate intake of vitamin K and a consistent level of intake. No one benefits from vitamin K deficiency. Food Serving Vitamin K1 (mcg) Seaweed, dulse dried 100g (3.5 oz) 1700 Kale, raw 1 cup (chopped) 547 Broccoli, cooked 1 cup (chopped) 420 Parsley, raw 1 cup (chopped) 324 Swiss chard, raw 1 cup (chopped) 299 Green tea, dried 1 oz (28 g) 199 Spinach, raw 1 cup (chopped) 120 Leaf lettuce, raw 1 cup (shredded) 118 Iceberg lettuce 1 leaf (20 g) 22 Watercress, raw 1 cup (chopped) (various refs) Pennington, JA. Bowes & Church s Food Values of Portions Commonly Used, Ed. 16 Phil: Lippincott Co.,
8 Oil Food Sources Some is available in vegetable oils, but they contribute far less vitamin K than leafy green vegetables. And, it is fairly impractical and also unwise to suggest that people attempt to meet their vitamin K requirements by increasing fat intake substantially. Additionally, hydrogenation of vegetable oils may decrease the absorption and biological effect of dietary vitamin K. (Effects of a hydrogenated form of vitamin K on bone formation and resorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74(6): ) Food Serving: 1 Tblsp Soybean oil Vitamin K1 (mcg) (various refs) Canola oil 20 Mayonnaise 12 Corn oil 0-7 (various refs) Olive oil 8 8
9 Animal Food Sources: Food Serving Vitamin K1 (mcg) Meat 3.5 oz 4 Raw Beef Liver (others less) 3.5 oz 104 Milk 8 oz 10 Egg Yolk 1 large 25 Fermented Food Sources: Food Natto (fermented soybeans) Serving Vitamin K2 (mcg) 1 oz 245 Curd Cheese 1 oz 20 Non-Food Sources: Intestinal Bacteria Bacteria that normally colonize the large intestine synthesize menaquinones (vitamin K2), which are active forms of vitamin K. Until recently it was thought that up to 50% of the human vitamin K requirement might be met by this bacterial synthesis. Recent research indicates that the contribution of intestinal bacterial synthesis is much less than previously thought, although the exact contribution remains unclear. Most of our menaquinones we actually make ourselves from phylloquinone. The likelihood is that even healthy people are more dependent on food sources of vitamin K than we previously believed. Individuals taking chronic antibiotics are far more dependent on food or supplement sources, of course, because these friendly colonic bacteria are killed by the medication as well. [Menaquinones, bacteria, and the food supply: the relevance of dairy and fermented food products to vitamin K requirements. Adv Nutr Jul 1;4(4): The importance of menaquinones in human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 1995;15: ) ] 9
10 Non-Food Sources: Supplements In the U.S. vitamin K1 is available without a prescription in multivitamin and other supplements in doses that generally range from mcg per dose. Vitamin K2 supplements are also available now. (PDR for Nutritional Supplements. Montvale: Medical Economics Company, Inc; 2001.) The amount of vitamin K associated with a decreased risk of hip fracture in the Framingham Heart Study was about 250 mcg/day. This can be obtained from a little more than 1/2 cup of chopped broccoli or a large salad of mixed greens every day. A multivitamin with minerals that provides at least the AI level of vitamin K would also be an excellent idea, and the label should be checked closely because vitamin K is notoriously variable between various products. Many vitamin supplement products contain none because of the earlier assumptions about the GI bacterial sources providing a significant amount. Some chewable calcium supplements provide some vitamin K and vitamin D. Again, check the label. A form of vitamin K2, menatetrenone (MK-4) has been used to treat osteoporosis in Japan and is currently under study in the U.S National Institutes of Health. K2 as MK-7 is the form produced in natto. Many earlier references state that vitamin K inadequacy is extremely unusual in adults. Testing for vitamin K inadequacy is also generally rare because inadequacy is assumed to not be a problem. Traditionally testing involves measuring prothrombin time. However, it appears that this hematological manifestation of inadequacy may not reflect adequacy of vitamin K for other functions. For example, newer studies use undercarboxylated osteocalcin or other measures as a marker of vitamin K inadequacy in bone and cardiovascular applications in particular. Vitamin K adequacy has not been in the public health radar or the radar of health care professionals. Consider, for example, the mypyramid.gov guidelines*, which are an effort to help people achieve an advisable intake of all nutrients over two weeks in 2000 kcals/day. Vitamin K is simply not included in the analysis. Vitamin D is missing as well. Apparently these nutrients are assumed to be adequate because you can make your own. In the case of vitamin D, this assumed adequacy 10
11 is now being discarded because of the overwhelming evidence that vitamin D deficiency is actually a huge but previously unrecognized public health problem. It is possible that the assumption of vitamin K adequacy may turn out to be similarly suspect. In any case, with the clear safety of generous vitamin K in normal circumstances, it would be advisable to simply assure adequacy rather than to assume it. *( Vitamin K Nomenclature Older nomenclature IUPAC (abbreviation) K1 K 2(n) K2(4) K2(35) K3 Phylloquinone (K) Menaquinone-n (MK-n) Menatetrenone (MK-4) Menaquinone-7 (MK-7) Menadione From Machlin, LJ. Handbook of Vitamins: Nutritional, Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.,1984 Toxicity Issues There is no known toxicity associated with high doses of phylloquinone (vitamin K1), or menaquinone (vitamin K2) forms of vitamin K. No tolerable upper level (UL) of intake of these forms of vitamin K has been established. [Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Vitamin K. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Washington DC: National Academy Press; 2001: ] 11
12 The same is not true for menadione (vitamin K3) and its derivatives. Menadione can interfere with the function of glutathione, one of the body's natural antioxidants, resulting in oxidative damage to cell membranes. Menadione given by injection has induced liver toxicity, jaundice, and hemolytic anemia (due to the rupture of red blood cells) in infants, and is no longer used for treatment of vitamin K deficiency. Contrary to popular belief, the fat-soluble status of vitamin K does NOT make it more likely to be toxic than water soluble vitamins. The toxicity traditionally ascribed somewhat globally to the fat soluble vitamins is in fact due to the fact that two of them (vitamins A and D) have actual hormonal messenger roles in the body. For this reason, relative inadequacy or excess of the active hormonal form of these two vitamins can actually induce metabolic changes to occur. The other two fat soluble vitamins (E and K) and the water soluble vitamins (C and the B vitamins) are much less likely to be toxic because they exert no hormonal influence on tissues. The fact that a substance dissolves in butter is not a measure of its potential toxicity, although most of us were taught that it is. This is an important big change in our understanding Memory Devices: I always find it hard to keep these kinds of terms and numbers straight, so I usually make up a little mnemonic device to help me out. Here s the one I use for remembering which form of vitamin K comes from which source, and which is K1 and which is K2 (Feel free to totally disregard this section and make up your own.) Phylloquinone starts with a P as in Plants. ( The vitamin K in leafy greens is Phylloquinone) I think of the kind made in people s intestines by bacteria or made in man from phylloquinone is menaquinone that is, the kind made in men. (The kind of vitamin K made in men is menaquinone. Women too, of course.) Because we convert phylloquinone to menaquinone for many of its uses, I think of phylloquinone (the spinach one) coming first (K1) and menaquinone (the kind made in man out of K1) as coming along secondarily (K2) 12
13 References by Topic: (A version with abstracts of these references is also available.) Inadequacy of Vitamin K: (General and interesting: J Nutr May;144(5): Dietary intake of vitamin K is inversely associated with mortality risk.) I. Contribution to Cardiovascular Disease: Arterial Calcinosis, Renal Calcinosis, Diabetes, Inflammation and Hypertension 2015 Diabetes Metab Res Rev Jan;31(1): Nutrients other than carbohydrates: their effects on glucose homeostasis in humans. Thromb Res Jan 26. Two enzymes catalyze vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase activity in mouse: VKORC1 is highly expressed in exocrine tissues while VKORC1L1 is highly expressed in brain. Thromb Res Feb 27. Plasma vitamin K concentrations depend on CYP4F2 polymorphism and influence on anticoagulation in Japanese patients with warfarin therapy. Development Mar 15;142(6): Vitamin K reduces hypermineralisation in zebrafish models of PXE and GACI. Atherosclerosis Feb 24;240(1): Prevention of vasculopathy by vitamin K supplementation: Can we turn fiction into fact? Transplant Proc Mar;47(2): Nutritional Status in Japanese Renal Transplant Recipients with Long-term Graft Survival. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol Jan;35(1): Increased vascular calcification in patients receiving warfarin. Nephrol Ther Mar 17. The matrix-gla protein awakening may lead to the demise of vascular calcification
14 Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol Jul;34(7): Sequence variation in vitamin K epoxide reductase gene is associated with survival and progressive coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets Nov 10. Vitamins And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Med Monatsschr Pharm Aug;37(8):284-92; quiz Micronutrients in diabetology: complementary medicine update World J Cardiol May 26;6(5): Are there ways to attenuate arterial calcification and improve cardiovascular outcomes in chronic kidney disease? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol Jul;34(7): Sequence variation in vitamin K epoxide reductase gene is associated with survival and progressive coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease. Postgrad Med Mar;126(2): The molecular biology and pathophysiology of vascular calcification. Public Health Nutr Jan 2:1-9. Evaluating the diet of children at increased risk for type 1 diabetes: first results from the TEENDIAB study Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci Sep;17(18): Something more to say about calcium homeostasis: the role of vitamin K2 in vascular calcification and osteoporosis. Trends Mol Med Apr;19(4): Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla-protein: a crucial switch to control ectopic mineralization. Bone Dec;57(2): Prevention of arterial calcification corrects the low bone mass phenotype in MGP-deficient mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol Jan 8;12:7. Association between dietary phylloquinone intake & peripheral metabolic risk markers related to insulin resistance and diabetes in elderly subjects at high cardiovascular risk. Diabetes Care Nov;36(11): Matrix Gla protein species and risk of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients. J Dev Phys Disabil Dec 1;25(6). Diet Quality of Overweight and Obese Adults with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities as Measured by the Healthy Eating Index Diabetologia Sep;56(9): The vitamin K-dependent Gla proteins and risk of type 2 diabetes Am J Clin Nutr Nov;96(5): Dietary phylloquinone intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in elderly subjects at high risk of cardiovascular disease. 14
15 Clin Experiment Ophthalmol Sep-Oct;40(7): Predictive value of the vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 G-1639A and C1173T single nucleotide polymorphisms in retinal vein occlusion. Am J Kidney Dis Feb;59(2): Effect of vitamin K2 supplementation on functional vitamin K deficiency in hemodialysis patients: a randomized trial Adv Nutr Mar 1;3(2): The role of vitamin K in soft-tissue calcification. Ups J Med Sci Aug;117(3): Amelioration of pregnancy-associated osteoporosis after treatment with vitamin K₂: a report of four patients Diabetes Res Clin Pract Nov;94(2):236-41Association of VKORC G>A polymorphism with carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Rev Mar;69(3): Bone quality and vitamin K2 in type 2 diabetes: review of preclinical and clinical studies. Nutr Rev Jun;68(6): Role of vitamins and minerals in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care Aug;33(8): Dietary phylloquinone and menaquinones intakes and risk of type 2 diabetes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol Feb 4. The circulating inactive form of matrix GLA Protein is a surrogate marker for vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: a preliminary report. J Nutr Biochem Feb 8. Vitamin K suppresses the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in cultured macrophage-like cells via the inhibition of the activation of nuclear factor kappab through the repression of IKKalpha/beta phosphorylation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol Feb 18 Vitamins K and D status in stages 3-5 chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Oct 20. The dualistic role of vitamin D in vascular calcifications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol Apr;5(4): The circulating inactive form of matrix gla protein is a surrogate marker for vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: a preliminary report. Thromb Haemost Oct;104(4): Characterisation and potential diagnostic value of circulating matrix Gla protein (MGP) species. Urol Int Jul;85(1):94-9. Activity and expression of vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase in patients with calcium oxalate urolithiasis. Thromb Haemost Apr;101(4): Relation of circulating Matrix Gla-Protein and anticoagulation status in patients with aortic valve calcification. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol Apr;5(4):590-7 Vitamins K and D status in stages 3-5 chronic kidney disease Kidney Int Sep 22 Recent progress in the treatment of vascular calcification. Clin Nephrol Jan;73(1):30-5. Metal ion and vitamin adsorption profiles of phosphate binder ion- exchange resins. 15
16 Clin Exp Immunol Dec 17. Vitamin K(3) attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappab activation. J Mal Vasc Apr 2. Origin of the mediacalcosis in kidney failure Nephrol Dial Transplant Jul;24(7): Association of kidney function and uncarboxylated matrix GLA protein: data from the Heart and Soul Study. J Thromb Haemost Feb;101(2): Uncarboxylated matrix GLA protein (ucmgp) is associated with coronary artery calcification in haemodialysis patients. J Thromb Haemost 2009;Sept 28. Warfarin use and the risk of valvular calcification. Int J Artif Organs Feb;32(2): Coagulation meets calcification: The vitamin K system. J Bone Miner Res Vitamin k and bone: past, present, and future. Br J Nutr Apr 1:1-16 Minerals and vitamins in bone health: the potential value of dietary enhancement. Osteoporos Int Mar 12Prior treatment with vitamin K(2) significantly improves the efficacy of risedronate. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(3): Short-term menatetrenone therapy increases gammacarboxylation of osteocalcin with a moderate increase of bone turnover in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized prospective study. Bioorg Med Chem Lett Feb 15;19(4): Elucidation of the mechanism producing menaquinone-4 in osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res Jun;24(6): Vitamin k treatment reduces undercarboxylated osteocalcin but does not alter bone turnover, density, or geometry in healthy postmenopausal north american women. J Mal Vasc Apr 2. Origin of the mediacalcosis in kidney failure. Am J Clin Nutr Jul;88(1): Phylloquinone intake, insulin sensitivity, and glycemic status in men and women. Thromb Res. 2008;122(3): High dietary menaquinone intake is associated with reduced coronary calcification. Effects of the blood coagulation vitamin K as an inhibitor of arterial calcification. J Vasc Res Apr 10;45(5): The Circulating Inactive Form of Matrix Gla Protein (ucmgp) as a Biomarker for Cardiovascular Calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol Apr;28(4): Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) polymorphism and aortic calcification: the Rotterdam Study. Am J Epidemiol Feb 1;167(3): Vitamin K and vitamin D status: associations with inflammatory markers in the Framingham Offspring Study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol May 21. Vitamin K-dependent Proteins, Warfarin, and Vascular Calcification. Am J Clin Nutr Jul;88(1): Phylloquinone intake, insulin sensitivity, and glycemic status in men and women. Cell Cycle Jun;7(11): Does the absence of ABCC6 (multidrug resistance protein 6) in patients with Pseudoxanthoma elasticum prevent the liver from providing sufficient vitamin K to the periphery? J Pharm Pharmacol Jul;60(7): Mechanisms underlying the biphasic effect of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) on arterial blood pressure. Curr Opin Lipidol Feb;19(1): Vitamin K intake and atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb Dec;14(6): Treatment with vitamin k(2) combined with bisphosphonates synergistically inhibits calcification in cultured smooth muscle cells. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol Oct;3(10):522-3 Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: the role of vitamin K. 16
17 Rhinology Sep;45(3): Vitamin D3, vitamin K2, and warfarin regulate bone metabolism in human paranasal sinus bones. Thromb Haemost Jul;98(1): Vitamin K: The coagulation vitamin that became omnipotent. Exp Anim Jul;56(4): Vitamin K Deficiency of Germfree Mice Caused by Feeding Standard Purified Diet Sterilized by gamma-irradiation.. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis Jan;17(1): Phylloquinone intake and risk of cardiovascular diseases in men. Blood Nov 30; Regression of warfarin-induced medial elastocalcinosis by high intake of vitamin K in rats. Am J Health Syst Pharm Aug 1;62(15): Vitamin K in the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis and arterial calcification Eur J Clin Nutr Feb;59(2): Phylloquinone intake as a marker for coronary heart disease risk but not stroke in women. II. Inadequacy of Vitamin K: Contribution to Unsafe Variability of Anticoagulation Therapy Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol Jan;35(1): Increased vascular calcification in patients receiving warfarin. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther Mar 22:1-7New oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists before cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of data from 4 randomized trials. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol Mar 22:1-12. Pharmacodynamic profile and drug interactions with non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants: implications for patients with atrial fibrillation. Drugs R D Mar;15(1): Budget impact analysis of warfarin reversal therapies among hip fracture patients in Finland. Thromb Res Feb 27. Plasma vitamin K concentrations depend on CYP4F2 polymorphism and influence on anticoagulation in Japanese patients with warfarin therapy. Semin Thromb Hemost Feb 19 Oral Anticoagulant Drugs and the Risk of Osteoporosis: New Anticoagulants Better than Old? Am J Ther Warfarin use and prevalence of coronary artery calcification assessed by multislice computed tomography. Dtsch Med Wochenschr May;138(21): Medial calcific sclerosis under long-term anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists. Adv Nutr Jul 1;4(4): Menaquinones, bacteria, and the food supply: the relevance of dairy and fermented food products to vitamin K requirements. 17
18 Br J Haematol Feb 11. Influence of dietary vitamin K intake on subtherapeutic oral anticoagulant therapy. Am J Transl Res Jul 15;1(4): Activated protein C: a potential cardioprotective factor against ischemic injury during ischemia/reperfusion. J Manag Care Pharm Apr;15(3): Meta-analysis to assess the quality of warfarin control in atrial fibrillation patients in the United States. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis Apr 3. Erythrocyte folate and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate levels decline during 6 months of oral anticoagulation with warfarin. J Thromb Haemost Dec;7(12): Warfarin use and the risk of valvular calcification. Hamostaseologie Feb;28(1-2):44-50 New insight in therapeutic anticoagulation by Coumarin Derivatives. J Thromb Haemost Jul;6(7): Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1 ) polymorphism influences the anticoagulation response subsequent to vitamin K intake: a pilot study Vitam Horm. 2008;78: Vitamin K and thrombosis J Thromb Haemost Oct;5(10): Daily vitamin K supplementation improves anticoagulant stability. Thromb Haemost Jul;98(1): Vitamin K: The coagulation vitamin that became omnipotent. INRJ Thromb Thrombolysis Feb 24; Prospective study of supplemental vitamin K therapy in patients on oral anticoagulants with unstable international normalized ratios. J Am Diet Assoc Nov;107(11):2022.Vitamin K: what are the current dietary recommendations for patients taking coumadin? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care Jan;10(1):1-5. Dietary vitamin K intake & anticoagulation in elderly patients. Blood Nov 16 Vitamin K supplementation can improve stability of anticoagulation for patients with unexplained variability in response to warfarin. Int J Vitam Nutr Res Mar;76(2): Dietary vitamin K variability affects International Normalized Ratio (INR) coagulation indices Pharmacotherapy Dec;25(12): Low-dose vitamin K to augment anticoagulation control. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004;4(1): The use of vitamin K in patients on anticoagulant therapy: a practical guide
19 III. Inadequacy of Vitamin K: Contribution to Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, Bone Development, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Related Conditions 2015 Exp Toxicol Pathol Mar 12. Characterization of bone turnover and energy metabolism in a rat model of primary and secondary osteoporosis. J Cell Biol Mar 16;208(6): GGCX and VKORC1 inhibit osteocalcin endocrine functions. Drugs R D Mar;15(1): Budget impact analysis of warfarin reversal therapies among hip fracture patients in Finland. Semin Thromb Hemost Feb 19. Oral Anticoagulant Drugs and the Risk of Osteoporosis: New Anticoagulants Better than Old? Endocrine Jan 20. Effect of 1-year dietary supplementation with vitaminized olive oil on markers of bone turnover and oxidative stress in healthy post-menopausal women. Nutr Res Feb;35(2): Vitamin K3 increased BMD at 1 and 2 months post-surgery and the maximum stress of the middle femur in the rat Glob J Health Sci Jul 14;6(6):82-7. Assessment of vitamin K2 levels in osteoporotic patients: a case control study. Mol Nutr Food Res Aug;58(8): Vitamin K and musculoskeletal health in postmenopausal women. Clin Nutr May 28.. Vitamin K deficiency evaluated by serum levels of undercarboxylated osteocalcin in patients with anorexia nervosa with bone loss. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2014;23(2): Vitamin K nutritional status and undercarboxylated osteocalcin in postmenopausal osteoporotic women treated with bisphosphonates. Nutrients May 16;6(5): Vitamin K₂ therapy for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9: Menatetrenone versus alfacalcidol in the treatment of Chinese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, double-dummy, positive drug-controlled clinical trial. Maturitas Mar;77(3): Effects of vitamin K in postmenopausal women: mini review. J Bone Miner Metab May;32(3): Effects of risedronate alone or combined with vitamin K2 on serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin and osteocalcin levels in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab Mar;32(2): Low-dose vitamin K2 (MK-4) supplementation for 12 months improves bone metabolism and prevents forearm bone loss in postmenopausal Japanese women. 19
20 Geriatr Gerontol Int Jan;14(1):1-7. Vitamin K: novel molecular mechanisms of action and its roles in osteoporosis Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2013;52 Suppl 1:43-8.Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Role of vitamin K in the prevention of osteoporosis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2013;22(4): Effects of gamma-glutamyl carboxylase gene polymorphism (R325Q) on the association between dietary vitamin K intake and gamma-carboxylation of osteocalcin in young adults. J Clin Densitom Oct-Dec;16(4): Vitamin K and bone health. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci Sep;17(18): Something more to say about calcium homeostasis: the role of vitamin K2 in vascular calcification and osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int Sep;24(9): Three-year low-dose menaquinone-7 supplementation helps decrease bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women Clin Chem Lab Med Aug;51(8): Trace elements and bone health. Clin Nutr Dec;32(6): High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and osteoporosis in out-patients with intestinal failure. Endocrinol Nutr Apr;60(4): Update on nutrients involved in maintaining healthy bone. Crit Rev Biotechnol Sep 18. Vitamin K series: current status and future prospects. J Clin Biochem Nutr Sep;53(2): Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) &K2 (menaquinone-4) supplementation improves bone formation in a high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Pancreatology May-Jun;13(3): The prevalence of fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies and a decreased bone mass in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Crit Rev Biotechnol Sep 18. Vitamin K series: current status and future prospects. PLoS One Aug 16;8(8):e71665 Effects of multi-deficiencies-diet on bone parameters of peripheral bone in ovariectomized mature rat. Mod Rheumatol Sep;23(5): Vitamin K2 administration is associated with decreased disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int Mar;33(3): Dietetic issues in antiphospholipid syndrome Osteoporos Int Nov;23(11): Vitamin K supplementation for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fractures: is it cost-effective and is future research warranted? Calcif Tissue Int Apr;90(4): Changes in parameters of bone metabolism in postmenopausal women following a 12-month intervention period using dairy products enriched with calcium, vitamin D, and phylloquinone (vitamin K(1)) or menaquinone-7 (vitamin K (2)): the Postmenopausal Health Study II. Ups J Med Sci Aug;117(3): Amelioration of pregnancy-associated osteoporosis after treatment with vitamin K₂: a report of four patients. 20
21 Transplantation Feb 27;89(4): Dietary vitamin K2 supplement improves bone status after lung and heart transplant. Proc Nutr Soc Feb;69(1): Session 2:Other diseases: Dietary management of osteoporosis throughout the life course. J Bone Miner Metab Dec 19. Hop rho iso-alpha acids, berberine, vitamin D(3) and vitamin K(1) favorably impact biomarkers of bone turnover in postmenopausal women in a 14-week trial. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): Clinical implications of undercarboxylated osteocalcin. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): Anti-fracture efficacy of vitamin K. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): Effect of vitamin K on bone material properties. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): Biological effects of vitamin K2 on bone quality. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): In vivo metabolism of vitamin K: in relation to the conversion of vitamin K1 to MK-4. Clin Calcium Dec;19(12): Vitamin K function mediated by activation of steroid and xenobiotic receptor Curr Osteoporos Rep Dec;7(4): Osteoporosis prevention and nutrition. J Orthop Sci Nov;14(6): Association of low dietary vitamin K intake with radiographic knee osteoarthritis in the Japanese elderly population: dieary survey in a population-based cohort of the ROAD study. Nutr Res Apr;29(4): High-dose vitamin K supplementation reduces fracture incidence in postmenopausal women: a review of the literature. Br J Nutr May 19:1-8. The effect of menaquinone-7 (vitamin K2) supplementation on osteocalcin carboxylation in healthy prepubertal children. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) Feb;55(1): Effect of low dose vitamin K2 (MK-4) supplementation on bio-indices in postmenopausal Japanese women. Calcif Tissue Int Aug;83(2): Effects of vitamin k(2) and risedronate on bone formation and resorption, osteocyte lacunar system, & porosity in the cortical bone of glucocorticoidtreated rats. Ann Rheum Dis Jul 14 Vitamin K in hand osteoarthritis: results from a Randomized Clinical Trial. Bone Aug;43(2): Uptake of postprandial lipoproteins into bone in vivo: Impact on osteoblast function. Br J Nutr Feb 18:1-7. Vitamin K status is associated with childhood bone mineral content. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(3): Response of serum carboxylated and undercarboxylated osteocalcin to alendronate monotherapy and combined therapy with vitamin K2 in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr May;87(5): Vitamin K1 intake is associated with higher bone mineral density and reduced bone resorption in early postmenopausal Scottish women: no evidence of gene-nutrient interaction with apolipoprotein E polymorphisms. J Pharmacol Sci Apr;106(4): Pharmacological topics of bone metabolism: recent advances in pharmacological management of osteoporosis. 21
22 Proc Nutr Soc May;67(2): Importance of calcium, vitamin D and vitamin K for osteoporosis prevention and treatment. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents Jan-Mar;22(1): Vitamin K and D association stimulates in vitro osteoblast differentiation of fracture site derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Pediatr Mar;15(3): Recommendations for the management of bone demineralization in cystic fibrosis J Clin Endocrinol Metab Apr;93(4): Effect of vitamin K supplementation on bone loss in elderly men and women. Clin Calcium Feb;18(2): Genomic approaches to bone and joint diseases. New insights into molecular mechanisms underlying protective effects of vitamin K on bone health Eur J Epidemiol. 2008;23(3): Association of hip fracture incidence and intake of calcium, magnesium, vitamin D, and vitamin K. J Cyst Fibros Jul;7(4): Undercarboxylated osteocalcin and bone mass in 8-12 year old children with cystic fibrosis. J Nutr Jan;138(1):172S-177S. The balance of bone health: tipping the scales in favor of potassium-rich, bicarbonate-rich foods. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(1): Low plasma phylloquinone concentration is associated with high incidence of vertebral fracture in Japanese women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(1):9-12. Steroid and xenobiotic receptor mediates a novel vitamin K2 signaling pathway in osteoblastic cells. Br J Nutr Jan;99(1): Nutrition and bone health projects funded by the UK Food Standards Agency: have they helped to inform public health policy? Clin Exp Rheumatol May-Jun;26(3): Extremes in vitamin K status of bone are related to bone ultrasound properties in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Mayo Clin Health Lett Nov;25(11):4. Vitamin K linked to bone strength. Pediatr Res Mar;61(3): Pronounced elevation of undercarboxylated osteocalcin in healthy children. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) Dec;53(6): Vitamin K content of foods and dietary vitamin K intake in Japanese young women. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) Oct;53(5): Nutritional effects of gamma-glutamyl carboxylase gene polymorphism on the correlation between the vitamin K status and gamma- carboxylation of osteocalcin in young males. Clin Calcium Nov;17(11): Experience of vitamin K2 in Thailand Clin Calcium Nov;17(11): Clinical application of undercarboxylated osteocalcin Clin Calcium Nov;17(11): Measurement of serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin by ECLIA with the "Picolumi ucoc" kit. Osteoporos Int Jul;18(7): Vitamin K2 supplementation improves hip bone geometry and bone strength indices in postmenopausal women. Int J Cardiol Jun 12;118(3): Fracture risk in users of oral anticoagulants: a nationwide case-control study. Thromb Haemost Jul;98(1): Vitamin K: The coagulation vitamin that became omnipotent. Curr Rheumatol Rep Apr;9(1): Not just calcium and vitamin D: other nutritional considerations in osteoporosis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care Jan;10(1):20-3. Vitamin K status in the elderly. Int J Cardiol Jun 12;118(3): Fracture risk in users of oral anticoagulants: a nationwide case-control study. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol May 29; Vitamin K deficiency inhibits mineralization & enhances deformity in vertebrae of haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus L.) 22
23 Br J Nutr Apr;97(4): Serum percentage undercarboxylated osteocalcin, a sensitive measure of vitamin K status, and its relationship to bone health indices in Danish girls. Exp Anim Apr;56(2): Additive effect of vitamin K2 and risedronate on long bone mass in hypophysectomized young rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2007;25(1): Effect of vitamin K2 and growth hormone on the long bones in hypophysectomized young rats: a bone histomorphometry study. Am J Kidney Dis Mar;49(3): Subclinical vitamin K deficiency in hemodialysis patients. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) Jun;53(3): vitamin K2 (menaquinone-4) on intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity in rats. Curr Drug Saf Jan;1(1):87-97Role of vitamin K2 in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin Calcium Sep;16(9): and Nutrition Jul-Aug;22(7-8): (same article in both journals) Protective effects of vitamin K against osteoporosis and its pleiotropic actions J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) Oct;52(5): Beneficial effect of pretreatment and treatment continuation with risedronate and vitamin K2 on cancellous bone loss after ovariectomy in rats: a bone histomorphometry study. Arthritis Rheum Apr;54(4): Low vitamin K status is associated with osteoarthritis in the hand and knee. Calcif Tissue Int Nov;79(5): Synergistic effect of vitamin K2 and prostaglandin E2 on cancellous bone mass in hypophysectomized young rats. Clin Calcium Dec;16(12): Present knowledge in nutritional aspects of fracture. Am J Clin Nutr Feb;83(2): Vitamin K status of healthy Japanese women: age-related vitamin K requirement for gamma-carboxylation of osteocalcin. Int J Vitam Nutr Res Nov;76(6): A preliminary assessment of vitamin K1 intakes and serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin levels in year old Irish girls. Br J Nutr May;95(5):982-8 Phylloquinone (vitamin K1) intakes and serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin levels in Irish postmenopausal women. Am J Health Syst Pharm Aug 1;62(15): Vitamin K in the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis and arterial calcification. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(21): Effects of vitamin K2 on osteoporosis. IV. Inadequacy of Vitamin K: Cancer: Liver, Colorectal, Prostate, Ovarian, Pancreatic and Cancer Risk in General Med Hypotheses Mar;84(3): Vitamin K: The missing link to prostate health. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;6C:95-9. Primary colon cancer with a high serum PIVKA-II level. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: Gla-rich protein is a potential new vitamin K target in cancer: evidences for a direct GRP-mineral interaction. 23
24 Ultrastruct Pathol Apr;38(2): Synergistic antitumor cytotoxic actions of ascorbate and menadione on human prostate (DU145) cancer cells in vitro: nucleus and other injuries preceding cell death by autoschizis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant Mar;20(3): Serial profile of vitamins and trace elements during the acute phase of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Clin Colorectal Cancer Mar;13(1):62-7. Pilot clinical trial on the efficacy of prophylactic use of vitamin K1-based cream (Vigorskin) to prevent cetuximab-induced skin rash in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer J Endourol Dec;27(12): Alternative therapeutic approach to renal-cell carcinoma: induction of apoptosis with combination of vitamin K3 and D-fraction. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9): Menadione (Vitamin K3) induces apoptosis of human oral cancer cells and reduces their metastatic potential by modulating the expression of epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers and inhibiting migration. Toxicology Jan 7;303: Resveratrol inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncol Rep Jun;29(6): Curcumin reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pacreatic cancer cells by inhibiting the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Anticancer Res May;33(5): Quercetin inhibits migration and invasion of SAS human oral cancer cells through inhibition of NF-κB and matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 signaling pathways. Pharmazie Jun;68(6): Vitamin K4 induces tumor cytotoxicity in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells via the mitochondria-related apoptotic pathway.plos One. 2013;8(3):e Postoperative use of the chemopreventive vitamin K2 analog in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Dermatol Jan-Feb;23(1): Topical vitamin K1 may not be effective in preventing acneiform rash during cetuximab treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol Dec 15;273(3):611-22CR108, a novel vitamin K3 derivative induces apoptosis and breast tumor inhibition by reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e Alpha-tocopheryl succinate inhibits autophagic survival of prostate cancer cells induced by vitamin K3 and ascorbate to trigger cell death.and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e Berberine induces caspase-independent cell death in colon tumor cells through activation of apoptosis-inducing factor. Anticancer Res Dec;32(12): Effect of menatetrenone, a vitamin k2 analog, on recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Gastroenterol Nov 29;12:170. Role of vitamin K2 in preventing the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clinics (Sao Paulo) Sep;67(9): Synergistic growth inhibition by sorafenib and vitamin K2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Surg Oncol Apr 21;10:60. Vitamin K1 enhances sorafenib-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of human malignant glioma cells by blocking the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. 24
Vitamin K. Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz
 Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
Vitamin K. Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz
 Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron,
Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron,
Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz
 Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz Did you know that vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 are different types of vitamin K? Before 2006, the USDA
Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz Did you know that vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 are different types of vitamin K? Before 2006, the USDA
Vitamin K. Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib
 Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION
 NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION As we have all known for several years now, the presence of optimal amounts of vitamin D is essential for maintaining optimal bone health and bone calcification, as noted by
NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION As we have all known for several years now, the presence of optimal amounts of vitamin D is essential for maintaining optimal bone health and bone calcification, as noted by
Vitamin K --Focus on the Vitamin K and
 Aunt Cathy s Guide to Nutrition Sanford Medical Center Vitamin K --Focus on the Vitamin K and Warfarin/Coumadin Anticoagulant Drug Issue Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP, FADA Clinical and Metabolic Nutrition
Aunt Cathy s Guide to Nutrition Sanford Medical Center Vitamin K --Focus on the Vitamin K and Warfarin/Coumadin Anticoagulant Drug Issue Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP, FADA Clinical and Metabolic Nutrition
Sultan Qaboos University. College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences. Vitamin K. Lecture Summary
 Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
Biochemistry of Vitamin K
 Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
Vitamin K Snapshot Monograph
 vitamins minerals nutrients Vitamin K Snapshot Monograph Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2 Most Frequent Reported Uses: Blood clotting Anticoagulant reversal; bleeding disorders Osteoporosis prevention Arthritis,
vitamins minerals nutrients Vitamin K Snapshot Monograph Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2 Most Frequent Reported Uses: Blood clotting Anticoagulant reversal; bleeding disorders Osteoporosis prevention Arthritis,
Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency
 Sanford Medical Center Aunt Cathy s Guide to: Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP,FADA Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist Perinatal/Pediatric Nutrition Specialist Sanford
Sanford Medical Center Aunt Cathy s Guide to: Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP,FADA Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist Perinatal/Pediatric Nutrition Specialist Sanford
Life Change Checklist (2 slides)
 Life Change Checklist (2 slides) Have You Made Changes? If you are a long-time listener I hope you have: Switched out hydrogenated oils for olive or coconut oil Cut or eliminated your intake of refined
Life Change Checklist (2 slides) Have You Made Changes? If you are a long-time listener I hope you have: Switched out hydrogenated oils for olive or coconut oil Cut or eliminated your intake of refined
Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients
 Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients Alpha Lineoleic Acid (Omega 3) 1 ensures the optimal cerebral and cognitive development of the infant the presence of large quantities of EPA and DHA
Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients Alpha Lineoleic Acid (Omega 3) 1 ensures the optimal cerebral and cognitive development of the infant the presence of large quantities of EPA and DHA
The most important human clinical trials on Vitamin K2
 References update The most important human clinical trials on Vitamin K2 REFERENCES UPDATE Cardiovascular Health Bone Health Kidney Health Other (Efficacy, Dose Finding, Absorption, etc.) Beneficial Effects
References update The most important human clinical trials on Vitamin K2 REFERENCES UPDATE Cardiovascular Health Bone Health Kidney Health Other (Efficacy, Dose Finding, Absorption, etc.) Beneficial Effects
Vitamin K (Phylloquinone)
 Vitamin K (Phylloquinone) What is Vitamin K? Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin which plays a key role in blood coagulation. Its name comes from the German name, Koagulationsvitamin. There are three forms,
Vitamin K (Phylloquinone) What is Vitamin K? Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin which plays a key role in blood coagulation. Its name comes from the German name, Koagulationsvitamin. There are three forms,
A Vitamin B12 Update 2016 ( Minimal References Version)
 Aunt Cathy s Guide to Nutrition: Sanford Medical Center A Vitamin B12 Update 2016 ( Minimal References Version) Aunt Cathy Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP, FADA Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist and Prenatal/Pediatric
Aunt Cathy s Guide to Nutrition: Sanford Medical Center A Vitamin B12 Update 2016 ( Minimal References Version) Aunt Cathy Cathy Breedon PhD, RD, CSP, FADA Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist and Prenatal/Pediatric
Vitamins and Minerals
 Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity.
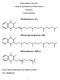
 D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis
 Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Disclosures. Nutrition & Menopause. What changes? Mindless Eating 10/6/2017. I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Disclosures Nutrition & Menopause Making changes when you can t eat like a 25 year old, and get away with it.. What changes? Social situation Family and family meals Activity levels
I have no disclosures Disclosures Nutrition & Menopause Making changes when you can t eat like a 25 year old, and get away with it.. What changes? Social situation Family and family meals Activity levels
LABORATORY REPORT SAMPLE. Summary of Deficient Test Results. Vitamin B12 Pantothenate Biotin Spectrox Immunidex
 LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
DISCUSSION OF RESEARCH RECOMMENDATIONS. Presenter: Robert M. Russell
 6 Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silver, Vanadium, and Zinc 1 In this session, Robert Russell of Tufts
6 Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silver, Vanadium, and Zinc 1 In this session, Robert Russell of Tufts
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by Jerry Casados
 What are Fat-Soluble Vitamins? FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by y Casados Fat soluble vitamins are essential to your health, and each one has its one very important function in the body. Vitamins A, D, E and K
What are Fat-Soluble Vitamins? FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by y Casados Fat soluble vitamins are essential to your health, and each one has its one very important function in the body. Vitamins A, D, E and K
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health. By Dr. Isaac Eliaz
 6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
COURSE OUTLINE - Module I
 Module II MEDICAL DISCLAIMER The information in this program is for educational purposes only. It is meant to as a guide towards health and does not replace the evaluation by and advice of a qualified
Module II MEDICAL DISCLAIMER The information in this program is for educational purposes only. It is meant to as a guide towards health and does not replace the evaluation by and advice of a qualified
ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary
 ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary Date Range : JAN 2017 through DEC 2017 COMPREHENSIVE MAJOR MEDICAL Print Date : 1/19/2018 9:43:49AM Page 1 of 1 Month Year Single 2 Person : Emp/Spouse 2 Person :
ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary Date Range : JAN 2017 through DEC 2017 COMPREHENSIVE MAJOR MEDICAL Print Date : 1/19/2018 9:43:49AM Page 1 of 1 Month Year Single 2 Person : Emp/Spouse 2 Person :
Minerals and water. Minerals 10/23/2017
 Minerals and water MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What are some major functions of water in the body? For each mineral, what are the best dietary sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the
Minerals and water MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What are some major functions of water in the body? For each mineral, what are the best dietary sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the
Nutrients. Macronutrients. Micronutrients. Others. Carbohydrates Proteins Fats. Vitamins Minerals. Fiber, water
 Nutrition Human Nutrition - The science of food, the nutrients and other substances contained therein, their action, interaction, and balance in relation to health and disease Normal Nutrition - caloric
Nutrition Human Nutrition - The science of food, the nutrients and other substances contained therein, their action, interaction, and balance in relation to health and disease Normal Nutrition - caloric
Vitamin K The Forgotten Vitamin
 Vitamin K The Forgotten Vitamin Ask anybody what vitamins they know about, and you re likely to hear Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and many people will even know that there are multiple vitamins called
Vitamin K The Forgotten Vitamin Ask anybody what vitamins they know about, and you re likely to hear Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and many people will even know that there are multiple vitamins called
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Calcium Supplement Guidelines
 Supplement Guidelines Item Type text; Book Authors Houtkooper, Linda; Farrell, Vanessa A. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 24/07/2018 09:13:03 Item License
Supplement Guidelines Item Type text; Book Authors Houtkooper, Linda; Farrell, Vanessa A. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 24/07/2018 09:13:03 Item License
American Journal of Human Genetics. American Journal of Hypertension. American Journal of Neuroradiology
 A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
Can mineral content in diet influence mineralization in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE)?
 Can mineral content in diet influence mineralization in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE)? Eliza Duvall September 2016 Abstract Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) is a rare genetic disorder with no effective
Can mineral content in diet influence mineralization in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE)? Eliza Duvall September 2016 Abstract Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) is a rare genetic disorder with no effective
Vitamin K1, 2 & 3. Version June 2014
 Vitamin K1, 2 & 3. Version 1.1 28 June 2014 These are not well known, but have an important place in health. Dr Mercola - There are three types of vitamin K Vitamin K1, or phylloquinone, is found naturally
Vitamin K1, 2 & 3. Version 1.1 28 June 2014 These are not well known, but have an important place in health. Dr Mercola - There are three types of vitamin K Vitamin K1, or phylloquinone, is found naturally
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri
![VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri](/thumbs/88/115610056.jpg) VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
Chapter. The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals. Images shutterstock.com
 Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
Parapharmaceuticals Dr Eman A. Ha H mmad
 Parapharmaceuticals DrEmanA. Hammad 1 What do you think? 3 Introduction Vitamins are defined as organiccompounds that are intended to supplement the diet and cannot be synthesized by humans Multivitamin
Parapharmaceuticals DrEmanA. Hammad 1 What do you think? 3 Introduction Vitamins are defined as organiccompounds that are intended to supplement the diet and cannot be synthesized by humans Multivitamin
regulates the opening of blood vessels, important for unhindered blood flow.
 Vitamin E AT A GLANCE Introduction The term vitamin E describes a family of eight related, fat-soluble molecules. Among these, alphatocopherol has the highest biological activity and is the most abundant
Vitamin E AT A GLANCE Introduction The term vitamin E describes a family of eight related, fat-soluble molecules. Among these, alphatocopherol has the highest biological activity and is the most abundant
 Food, Supplements and Healthy Lifestyles in Slowing and Preventing Macular Degeneration Julie Mares, Professor For the Nutrition and Eye Health Research Team http://nutritionforeyes.ophth.wisc.edu Preserving
Food, Supplements and Healthy Lifestyles in Slowing and Preventing Macular Degeneration Julie Mares, Professor For the Nutrition and Eye Health Research Team http://nutritionforeyes.ophth.wisc.edu Preserving
Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency
 Aunt Cathy s Guide to: Sanford Medical Center 5-16 Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency Aunt Cathy Cathy Breedon PhD, RD,CSP, FADA, FAND Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist and Perinatal/Pediatric
Aunt Cathy s Guide to: Sanford Medical Center 5-16 Nutrition Support of Iron Deficiency Aunt Cathy Cathy Breedon PhD, RD,CSP, FADA, FAND Clinical/Metabolic Nutrition Specialist and Perinatal/Pediatric
- Spontaneous hemorrhaging increase
 MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
Vitamin K & Antioxidants. NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018
 Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Index. B BMC. See Bone mineral content BMD. See Bone mineral density Bone anabolic impact, Bone mass acquisition
 A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
Amani Alghamdi. Slide 1
 Minerals in the body Amani Alghamdi Slide 1 The Minerals Small, naturally occurring, inorganic, chemical elements Serve as structural components Minerals classification The minerals present in the body
Minerals in the body Amani Alghamdi Slide 1 The Minerals Small, naturally occurring, inorganic, chemical elements Serve as structural components Minerals classification The minerals present in the body
Kimberly Tierney Bio-Nutrition
 Kimberly Tierney Bio-Nutrition Analysis, evaluation and conclusion of nutrient content and formulation of three separate multivitamins and assessing the adequacy for a thirty year old male and a twenty
Kimberly Tierney Bio-Nutrition Analysis, evaluation and conclusion of nutrient content and formulation of three separate multivitamins and assessing the adequacy for a thirty year old male and a twenty
Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines
 Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTICHOICE 1. Which of the following statements best describes the recommended dietary allowances (RDA)? (A) they are average nutrient intake goals that
Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTICHOICE 1. Which of the following statements best describes the recommended dietary allowances (RDA)? (A) they are average nutrient intake goals that
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
Mineral, Health and Vitality Formula
 Mineral, Health and Vitality Formula Maintaining optimal mineral levels, enjoying peak health and increasing your body s vitality are now more accessible than ever. OptimALL Nutrition balance is an allnatural,
Mineral, Health and Vitality Formula Maintaining optimal mineral levels, enjoying peak health and increasing your body s vitality are now more accessible than ever. OptimALL Nutrition balance is an allnatural,
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions
 Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Featured Topic: Get Digestive Relief (and more) with Probiotics (4 slides)
 Featured Topic: Get Digestive Relief (and more) with Probiotics (4 slides) 3 things you need to know about probiotics Probiotics are helpful bacteria Probiotics prevent disease, they don t cause it (bad
Featured Topic: Get Digestive Relief (and more) with Probiotics (4 slides) 3 things you need to know about probiotics Probiotics are helpful bacteria Probiotics prevent disease, they don t cause it (bad
Vitamin K2 Key To. Health. Special Report VITAMIN K2. look good. feel good be well
 Vitamin K2 Key To Health Special Report VITAMIN K2 Readers, I believe this newsletter contains among the most important new health information that I have ever written for you. In many ways it is the longawaited
Vitamin K2 Key To Health Special Report VITAMIN K2 Readers, I believe this newsletter contains among the most important new health information that I have ever written for you. In many ways it is the longawaited
Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis
 Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 10 Inflammation Markers The 19 Deadly Sins of Heart Disease 1. Excess LDL 2. Excess Total cholesterol 3. Low HDL 4. Excess Triglycerides 5. Oxidized LDL
Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 10 Inflammation Markers The 19 Deadly Sins of Heart Disease 1. Excess LDL 2. Excess Total cholesterol 3. Low HDL 4. Excess Triglycerides 5. Oxidized LDL
Building Our Evidence Base
 Plant-Based Diets Neal D. Barnard, MD, FACC Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine Washington, DC Building
Plant-Based Diets Neal D. Barnard, MD, FACC Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine Washington, DC Building
The Better Health News2
 October, 2016 Volume11, Issue 10 The Better Health News2 Special Interest Articles: Menopause and Bioflavonoids Osteoporosis and Exercise Bone Health: More than Calcium & Vitamin D Flax Seeds and Menopause
October, 2016 Volume11, Issue 10 The Better Health News2 Special Interest Articles: Menopause and Bioflavonoids Osteoporosis and Exercise Bone Health: More than Calcium & Vitamin D Flax Seeds and Menopause
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Infants. Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants. Infants Metabolic Rate. Age 0-1 yrs. Massive weight gain. Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are high
 Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Age 0-1 yrs Infants Massive weight gain Weight doubles by 5 months Weight triples by 12 months Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are
Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Age 0-1 yrs Infants Massive weight gain Weight doubles by 5 months Weight triples by 12 months Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water
 Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Shopping for Health: Vegetarian Diets 1
 FSHN11-06 1 Lauren Foster and Wendy J. Dahl 2 A Healthy Choice: Vegetarianism Well-balanced vegetarian diets can be nutritious and provide a variety of health benefits. Vegetarians are less likely to develop
FSHN11-06 1 Lauren Foster and Wendy J. Dahl 2 A Healthy Choice: Vegetarianism Well-balanced vegetarian diets can be nutritious and provide a variety of health benefits. Vegetarians are less likely to develop
LifePak Health Benefits. LifePak is optimum supplementation for:
 LifePak What is LifePak? Our comprehensive nutritional wellness program delivering the optimum amounts of all essential and generally beneficial nutrients for long-term health and well-being. LifePak Health
LifePak What is LifePak? Our comprehensive nutritional wellness program delivering the optimum amounts of all essential and generally beneficial nutrients for long-term health and well-being. LifePak Health
Chapter 2-Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines
 Chapter 2-Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is an appropriate use for dietary reference intakes (DRI)? a. ensuring that maximum nutrient requirements are
Chapter 2-Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is an appropriate use for dietary reference intakes (DRI)? a. ensuring that maximum nutrient requirements are
Soy and Soy Extract. James Meschino DC, MS,ND
 Soy/Soy Extract 1 Soy and Soy Extract James Meschino DC, MS,ND General Features Soybeans contain a variety of biologically active components that are associated with the prevention of certain cancers,
Soy/Soy Extract 1 Soy and Soy Extract James Meschino DC, MS,ND General Features Soybeans contain a variety of biologically active components that are associated with the prevention of certain cancers,
Classes of Nutrients A Diet
 Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Vitamin dan Mineral. Vitamin. General Concepts
 Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
?Pairing peanuts with other healthy foods can actually help you. Nutrient Density. Peanuts Improve Nutrient Intake %RDA %RDA
 Peanuts Improve Nutrient Intake snacking on peanuts improves intake of healthy nutrients. One serving of peanuts provides many of the essential nutrients we need each day. These include vitamin E, magnesium,
Peanuts Improve Nutrient Intake snacking on peanuts improves intake of healthy nutrients. One serving of peanuts provides many of the essential nutrients we need each day. These include vitamin E, magnesium,
The effect of supplementation with vitamin D on recurrent ischemic events and sudden cardiac death in patients with acute coronary syndrome
 CRC IRB Proposal Matthew Champion PGY-1 8/29/12 The effect of supplementation with vitamin D on recurrent ischemic events and sudden cardiac death in patients with acute coronary syndrome Study Purpose
CRC IRB Proposal Matthew Champion PGY-1 8/29/12 The effect of supplementation with vitamin D on recurrent ischemic events and sudden cardiac death in patients with acute coronary syndrome Study Purpose
In addition to bone health, emerging science reveals a non-skeletal benefit of vitamin D for several other health outcomes.
 Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Understanding Cholesterol Holistically
 Understanding Cholesterol Holistically Dr. Molly Force & Dr. Alicia McCubbins 213 Decatur Street, Port Townsend www.prospernaturalhealth.com (360)385-5375 This presentation is meant for educational use
Understanding Cholesterol Holistically Dr. Molly Force & Dr. Alicia McCubbins 213 Decatur Street, Port Townsend www.prospernaturalhealth.com (360)385-5375 This presentation is meant for educational use
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins
 Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
MILK. Nutritious by nature. The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods
 MILK Nutritious by nature The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods Weight control Contrary to the popular perception that dairy foods are fattening, a growing body of
MILK Nutritious by nature The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods Weight control Contrary to the popular perception that dairy foods are fattening, a growing body of
Protecting Bone and Arterial Health with Vitamin k2
 http://www.lef.org/ LE Magazine March 2008 Protecting Bone and Arterial Health with Vitamin k2 By William Davis, MD Millions of people take calcium supplements to maintain healthy bone. Yet few patients
http://www.lef.org/ LE Magazine March 2008 Protecting Bone and Arterial Health with Vitamin k2 By William Davis, MD Millions of people take calcium supplements to maintain healthy bone. Yet few patients
Bone Health. Written by the Editors of Examine.com
 Written by the Editors of Examine.com Updated June 24, 2014 Medical Disclaimer & Important Note This guide is a general health-related information product, intended for healthy adults over the age of 18.
Written by the Editors of Examine.com Updated June 24, 2014 Medical Disclaimer & Important Note This guide is a general health-related information product, intended for healthy adults over the age of 18.
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test
 Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
Austin Quan Yin Newsletter The Better Health News
 September, 2009 Volume 1, Issue 7 Austin Quan Yin Newsletter The Better Health News Special Interest Articles: Black cohosh and menopause B 12 and strokes Otitis media Pain and the cost of health care
September, 2009 Volume 1, Issue 7 Austin Quan Yin Newsletter The Better Health News Special Interest Articles: Black cohosh and menopause B 12 and strokes Otitis media Pain and the cost of health care
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals
 Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Micronutrients in parenteral nutrition T. Nguyen (NZ) Micronutrients in Parenteral Nutrition Truc Nguyen Counties Manukau
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Micronutrients in parenteral nutrition T. Nguyen (NZ) Micronutrients in Parenteral Nutrition Truc Nguyen Counties Manukau
Lecture 3. Nutrition
 Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Nutraceuticals & Lifestyle Changes That Can Halt The Progression Of Alzheimer s. by Dr. Gregory Smith
 Nutraceuticals & Lifestyle Changes That Can Halt The Progression Of Alzheimer s by Dr. Gregory Smith DIET: Studies of dietary influences on Alzheimer's disease do not yet provide clear evidence. Also the
Nutraceuticals & Lifestyle Changes That Can Halt The Progression Of Alzheimer s by Dr. Gregory Smith DIET: Studies of dietary influences on Alzheimer's disease do not yet provide clear evidence. Also the
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake
 Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 GLUCERNA THERAPEUTIC NUTRITION SHAKE has CARBSTEADY, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose
Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 GLUCERNA THERAPEUTIC NUTRITION SHAKE has CARBSTEADY, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose
Principles of nutrition Lesson B
 Principles of nutrition Lesson B Sam - ID 38359016 Unit: Applying the principles of nutrition to a physical activity programme Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will:
Principles of nutrition Lesson B Sam - ID 38359016 Unit: Applying the principles of nutrition to a physical activity programme Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will:
PCOS DIET. By Juliana Kassianos, Natural Fertility Therapist. The School of Fertility
 PCOS DIET By Juliana Kassianos, Natural Fertility Therapist The School of Fertility One of the biggest thing of PCOS suffers is that sugar effects us more, so we need to be cautious with this Madeleine
PCOS DIET By Juliana Kassianos, Natural Fertility Therapist The School of Fertility One of the biggest thing of PCOS suffers is that sugar effects us more, so we need to be cautious with this Madeleine
Vitamins. Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD
 Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
Vitamins. Vitamins (continued) Lipid-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K) Vitamins Serve Important Roles in Function of Body
 Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Contemporary Nutrition 6 th. th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals
 Contemporary Nutrition 6 th th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals Minerals Various functions in the body Major Minerals Require >100 mg /day Calcium, phosphorus Trace Minerals Require < 100 mg/day Iron, zinc Bioavailability
Contemporary Nutrition 6 th th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals Minerals Various functions in the body Major Minerals Require >100 mg /day Calcium, phosphorus Trace Minerals Require < 100 mg/day Iron, zinc Bioavailability
Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber
 Dining with Diabetes 6:1 Chapter 6 Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber Lesson Plans Learning Objectives Participants will state the benefits of low-fat dairy products and exercise on osteoporosis
Dining with Diabetes 6:1 Chapter 6 Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber Lesson Plans Learning Objectives Participants will state the benefits of low-fat dairy products and exercise on osteoporosis
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups:
 The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
Chapter Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients
 Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
What is survivorship? Late effects of treatment. Concerns of survivorship
 Choices to enhance vitality!!!and survival!!!!!!!!! (and how to make it work in the real world)! What is survivorship? Multiple definitions! Anyone living with cancer at any stage since diagnosis! Anyone
Choices to enhance vitality!!!and survival!!!!!!!!! (and how to make it work in the real world)! What is survivorship? Multiple definitions! Anyone living with cancer at any stage since diagnosis! Anyone
Information on vitamins. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods.
 Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
Coordinator of Post Professional Programs Texas Woman's University 1
 OSTEOPOROSIS Update 2007-2008 April 26, 2008 How much of our BMD is under our control (vs. genetics)? 1 2 Genetic effects on bone loss: longitudinal twin study (Makovey, 2007) Peak BMD is under genetic
OSTEOPOROSIS Update 2007-2008 April 26, 2008 How much of our BMD is under our control (vs. genetics)? 1 2 Genetic effects on bone loss: longitudinal twin study (Makovey, 2007) Peak BMD is under genetic
2002 Learning Zone Express
 1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
Nutrients Empty calorie foods DRI
 Nutrients are life-sustaining chemical substances that nourish and promote the growth of the human body. No one food contains all of the nutrients necessary for the body to function effectively; therefore,
Nutrients are life-sustaining chemical substances that nourish and promote the growth of the human body. No one food contains all of the nutrients necessary for the body to function effectively; therefore,
DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165. External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay
 DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165 External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay NOTE: THIS EXAM PAPER CONSISTS OF SIX (6) PAGES PLUS A MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONNAIRE (MCQ) ANSWER BOOKLET
DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165 External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay NOTE: THIS EXAM PAPER CONSISTS OF SIX (6) PAGES PLUS A MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONNAIRE (MCQ) ANSWER BOOKLET
Introduction to Nutrition
 Introduction to Nutrition What is meant by Nutrition Definition:- It means that food is taken in and uses for many purposes (maintenance and production). Introduction to Nutrition: what you will learn
Introduction to Nutrition What is meant by Nutrition Definition:- It means that food is taken in and uses for many purposes (maintenance and production). Introduction to Nutrition: what you will learn
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
 Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
RD COURSE OUTLINE NUTRITION SCIENCE
 RD COURSE OUTLINE NUTRITION SCIENCE Macro Nutrients: 1. Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins Food Sources Composition Digestion, absorption, transport and metabolism Recommended Daily Intake Effect of Deficiency
RD COURSE OUTLINE NUTRITION SCIENCE Macro Nutrients: 1. Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins Food Sources Composition Digestion, absorption, transport and metabolism Recommended Daily Intake Effect of Deficiency
Vitamin D & Cardiovascular Disease
 Vitamin D & Cardiovascular Disease Disclosures None Vitamin D Objectives: Discuss the basics of vitamin D metabolism Discuss the role of vitamin D deficiency in the development of coronary disease Review
Vitamin D & Cardiovascular Disease Disclosures None Vitamin D Objectives: Discuss the basics of vitamin D metabolism Discuss the role of vitamin D deficiency in the development of coronary disease Review
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
There are three major types of omega-3 fatty acids that are ingested in foods and used by the body:
 Long-chain fatty acids (LC-PUFAs: ARA, DHA and EPA) AT A GLANCE Introduction LC-PUFAs or long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids are mainly found in the form of two families of conditionally essential fatty
Long-chain fatty acids (LC-PUFAs: ARA, DHA and EPA) AT A GLANCE Introduction LC-PUFAs or long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids are mainly found in the form of two families of conditionally essential fatty
Calcium Marie Dunford, PhD, MD, Nutrition Consultant, Kingsburg, CA
 Calcium Marie Dunford, PhD, MD, Nutrition Consultant, Kingsburg, CA Calcium is an essential mineral and a major nutrient needed for proper bone health. Absorption of calcium in adults is low. Vitamin D
Calcium Marie Dunford, PhD, MD, Nutrition Consultant, Kingsburg, CA Calcium is an essential mineral and a major nutrient needed for proper bone health. Absorption of calcium in adults is low. Vitamin D
