Carbohydrates 4 th 5 th Grade Lesson Plan
|
|
|
- Candace Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Carbohydrates 4 th 5 th Grade Lesson Plan Goal: Introduce carbohydrates, identify their sources, and recognize what they do in our bodies. Objectives: 1. Students will be able to identify which food groups contain carbohydrates. 2. Students will be able to distinguish between refined and whole grain products. 3. Students will be able to identify where carbohydrates are found on the nutrition label. Materials Needed Captain Carbohydrate poster Pictures of food from the grains group Grains are seeds poster Wheat stalk Grain anatomy poster Wheat berries Making bread pictures Grinding wheat seeds equipment White/whole wheat flour models Cheerios food label poster Whole Grain or Refined Grain? PowerPoint Why is the grains group important? Poster Flashlight Sugar/water cup Senorita sugar puppet Cheerios Construction paper strips and tape Paper clips or black construction paper Canned beans and broccoli Parent handouts Student handouts Taste test Lesson Talking Points Materials/Activities/Notes Review Who remembers what we talked about last time I was here? Who remembers the challenge I gave you last time I was here? Mind Grabber Everyone up! Let s do 15 jumping jacks. Okay, let s stretch to the sky, now stretch to your toes. Alright, calmly take a seat. Today we are going to talk about the nutrient superhero that is your body s primary or first choice, for energy the energy we needed to do our jumping jacks and stretches. Who can tell me which nutrient superhero it is? That s right Captain Carbohydrate. Discussion Captain Carbohydrate s superpower (role) for your body Carbohydrates have two important functions in the body: 1. Supply energy to the body the energy you need to Show students Captain Carbohydrate.
2 stay alive, move your body, grow, think and learn. Our bodies do get energy from two other nutrients found in the foods we eat but Carbohydrate is your bodies preferred choice. We get 4 calories per gram from carbohydrate foods. 2. Supply fiber to the body fiber is the part of a plant that can t be broken down by our digestive system. Fiber keeps our bellies and hearts working well. Carbohydrates come primarily from plants. They are so important that most experts recommend that at least ½ of the calories in our daily diets come from carbohydrates. Believe it or not, carbohydrates are found in 4 different food groups on MyPlate and a few foods in the 5 th food group. Carbohydrates are in the Grains, Fruits, Vegetables and Dairy groups. In the Protein food group carbohydrates are in beans but not the meat. Which of these food groups come from plants? Which one of these food groups comes from an animal? Eating foods from several food groups is a great way to make sure you are getting plenty of carbohydrates. Because the grain group is an excellent source of carbohydrates, let s begin this lesson by focusing on this group. What are some of the foods in the grain group? Examples include whole wheat bread, cereal, pasta, corn tortillas, muffins, popcorn, oatmeal, and crackers. Do grains come from plants or animals? Plants! In fact, grains are seeds. Take a look at this poster I brought in with me and see how many different grains there are that we can eat. There are even more grains than this that we can eat, but these are some of the most common. We make the many different Grains group foods you know and eat from these grains (or seeds), such as bread, cereal, and noodles. Some of them we cook and eat the seed itself, like rice and oats. Many foods are made from grains and as you saw in the poster, most of the grains look a lot alike. So, how do we get from these seeds (grains) of plants to the Grain group foods you eat? I m going to tell you that story and I m going to use wheat as the example but the story is true of any of the grains. Remember, there are many different grains to choose from and no matter which grain you eat, it will give you the energy that your body needs to keep going each day. Eating foods made from the different kinds of grains is healthy way to give your body the energy it needs. To tell the story, let s go back to the wheat seed or the kernel as it is sometimes called. Take a look at this wheat stalk. This is how wheat grows. I m going to walk around with the wheat stalk and I need you to be very quiet so that you can hear it when I tap it. What do you think is on the inside, making that noise? Seeds, wheat seeds! Each wheat stalk has seeds on the inside! A wheat seed contains three parts: 1. Bran: The bran is what you see on the outside the other hard shell of the grain. It is the part of the seed that Using the MyPlate poster, point to each food group as they are mentioned to give the kids a visual. Show pictures of foods from the grains group. Show the Grains are Seeds poster with examples of real grains. Go over the poster and discuss the foods we get from each one of the seeds on the poster may also reinforce with picture or food models. Walk around with the wheat stalk and tap it for the students to hear. Show the students a bag of wheat seeds. Show students Grain Anatomy or seed model to illustrate the different parts of the seed. 2
3 provides the most fiber and B vitamins. 2. Germ: This is the baby plant. This part of the seed is packed with nutrients like vitamin E, some minerals, and antioxidants. 3. Endosperm: This is the soft, inner part of the grain. It contains some nutrients but not a lot. But, it does have a lot of the energy we get from these foods. Let s take a look at some real seeds. I have one wheat seed for each of you to examine. I want you all to be scientists and see if you can find all three parts of the seed. On the outside, you see the brown part, which is the protective coat, also called the bran. You can also see the baby plant beginning to sprout out of the seed. This is called the germ. Break open your seed and see what you find on the inside. The white part, also called the endosperm, is the food for the baby plant, which looks a bit like milk now that it is wet just like the food for baby people! Making Bread Does anyone know how we make bread from wheat seeds? First we have a picture of the wheat stalks growing in the field (picture 1). Notice that they are green. After a while, they turn brown or golden (picture 2). This means that they are ready to be harvested. Farmers use a big machine called a combine to cut down the wheat and take out all the seeds (picture 3). The machine pulls out the wheat seeds so that we can use them (picture 4). Then the wheat seeds are taken to a mill and ground up into little tiny pieces to make flour (picture 5). This is the flour that we use to make bread. Then, we mix the flour with other ingredients such as eggs, oil, and water to make dough (picture 6). Then we put it in a pan, bake it in the oven, and we get a loaf of bread (picture 7)! There are many different types of bread we can make. Here, we have a picture of white bread and whole wheat bread (picture 8). Can anybody tell me the difference between white bread and whole wheat bread? Which one do you think is healthier for you? (Grind wheat berries demo describing the important nutrients in each layer.) Now, which one do you think is healthier: White bread or whole wheat bread? o Whole grain foods are made using the whole seed. Because you are eating all 3 parts of the seed when you eat a whole grain food, you are getting all of the nutrients that whole grains offer (fiber, B vitamins, vitamin E, some minerals and some protein). o But refined grain foods, foods that aren t whole grain, contain only the endosperm, so you miss out on a lot of vitamins and minerals. How can you tell if a food is made from whole grains or refined grains? When trying to figure out if a food is a whole grain, you need to read the ingredient list. If the first ingredient in a food uses the word whole, or words, 100% whole, it is a whole grain. For example, a whole grain food might list whole oats as its first Distribute sprouted wheat berries (or whole wheat berries) to each student to further illustrate the parts of the seed. (To sprout wheat berries, place a handful of wheat berries on a wet paper towel in a plastic container, uncovered. Keep at room temp and dampen as needed until sprouted (a few days) OR soak berries in water overnight, then drain and put into a strainer and rinse 1-2x a day until sprouted less likely to encourage mold growth; store in fridge.) Use Making Bread pictures to illustrate how bread is made from wheat berries. Use the grinder to grind wheat berries into flour and sift. Put a handful of wheat berries in the grinder and grind. When finished show the students what the flour looks like. Tell them that this is whole wheat flour because it used ALL three parts of the seed the WHOLE seed. Whole wheat flour results from grinding the seed and using all of it. Whole wheat flour is used for making whole wheat bread. Sift the flour into a bowl. The flour that comes through is white. This is white flour. Show to students and compare it to the color of the flour left in the sifter. The flour in the bowl should be whiter than what is left in the sifter. The white flour is the small part that falls through the sifter. This is the food inside the seed (or the endosperm). This is what we use to make white bread. The white flour is made up of only the endosperm and none of the bran or the germ. Remind students that the bran and the germ have more nutrients. OR show white flour and whole wheat flour models. Hold up the 8 x 11 Cheerios Breakfast Cereals poster and tell students that the first ingredient listed is whole oats (or can allow a student to read the first ingredient). Ask them if this is a whole grain cereal yes. Go through other breakfast cereals to provide 3
4 4 ingredient or it might say 100% whole wheat. We just spent a lot of time talking about the grains group, but remember carbohydrates are also found in the Fruit group, the Vegetable group, the Dairy group and beans from the Protein group. Game: Whole Grain or Refined Grain? We are going to play a game to see if you understand the difference between whole grains and refined grains. How much Grain group foods should we eat? Now that we know the difference between whole grain and refined grain foods from the Grains group let s take a look at MyPlate again. How much of your plate should be foods from the grain group? That s right! One quarter of your plate should be grains. That s a lot! examples. Divide the class into teams (or the whole class can answer the questions together) and ask the questions in the Whole Grain or Refined Grain PowerPoint. Show the MyPlate poster or plate model. Types of Carbohydrates There are 3 types of carbohydrates that we eat: 1. Sugars (or simple sugars) these carbohydrates dissolve easily in water and taste sweet when eaten. a) Naturally occurring sugars: such as the natural sugar found in fruit and milk. We don t add sugar to fruit and milk, it is naturally there. b) Added sugars: these are sugars we add to foods such as cake, candy, cookies, sweet breakfast cereals, sodas, and fruit canned in heavy syrup. Remember Senorita Sugar? Our nutrient superheroes make our bodies strong and healthy. Senorita Sugar is not a superhero! She is an added sugar and can cause all sorts of trouble. Why should we avoid sugar? Too much sugar can cause dental decay and weight gain. Sugar contains no vitamins and minerals. There are many names for sugar. Can you think of any? Some common names are sugar, brown sugar, honey, powdered sugar, corn syrup, and maple syrup. Also, any word that ends on ose is a sugar. 2. Starches Starches are the second type of carbohydrate. They do not dissolve in water and do not taste sweet. Starches are made and stored in plants in the seeds, stems, and roots. Rice, wheat, potatoes, corn, peas, and beans (pinto beans, kidney beans, and lima beans) are all examples of starchy foods. Our digestive system has to breakdown, (digest) the starches in food so body can get the energy out of the food. Optional Activity: Give each student a saltine cracker. The saltine contains some sugar and some starch. When you put it in your mouth, the sugar If you want you can put sugar in a container of water and allow students to see that by the end of class, the sugar has dissolved. Hold up Senorita Sugar puppet. Have the students look back to the handout from the label reading lesson, Read It Before You Eat It, to see other names for sugar. Place a handful of cheerios in water and allow students to observe that they do not completely dissolve. Using construction paper, link several chains together, show students and tell them starches are made of many glucose units. Show students the glucose and starch chains again. Remind them that our bodies use glucose for energy. The body is constantly breaking down chains of glucose and starch in order to get the energy it needs. Which chain is the quickest source of energy (which can be broken down in the body most quickly)? Glucose. Break apart the glucose chain to show that it doesn t take long. Foods that are pure
5 5 dissolves right away (remember it dissolves in water). The starch will break down eventually to glucose, but it takes awhile. The enzyme (amylase) in the saliva helps us to break the starch down into sugar. Have students hold the crackers in their mouths until they can taste the sweet sugar. 3. Fiber Fiber is the third type of carbohydrate. Fiber helps to give plants their shape so in a way, fiber is lake a plant s skeleton or bones. Vegetables, whole fruits, whole grains (remember the bran in the wheat seed contains fiber), beans and nuts are all good source of fiber. Do you remember that I said that starches are stored in the stems and roots of plants? Vegetables, like broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, and spinach are not starchy. This is because the stems and leafy portions of the plant do not contain much starch. Because we cannot digest fiber, it: 1. Helps us feel full so we will not eat as much food and we will not feel hungry too soon after eating the fiber containing food. 2. Keeps our digestive system healthy by helping move things through and getting rid of waste products (poop) regularly. 3. Helps us to fight disease. A high fiber diet helps to prevent heart disease by lowering cholesterol. A high fiber diet helps to fight diabetes by helping to control blood sugar (fiber changes the way our bodies respond to insulin) and a high fiber diet has been shown to prevent some types of cancer (colon). Finding Carbohydrates on the Nutrition Label Now let s talk about where carbohydrates are found on the nutrition label. o Total carbohydrates = sugars + starch + fiber in the food o Sugars = both naturally occurring and added sugars o Fiber = listed as dietary fiber. Some labels may also separate fiber into soluble and insoluble fiber. o Other carbohydrates = starch 4. Remember to also look at the ingredient list to find out if a food is a whole grain food or a refined grain food. Look for the word whole followed by one of the grain names (wheat, oats, barley, corn, rye) or look for brown rice listed as the first ingredient. Challenge Now that you know about the grains group, I challenge you to try two whole grain foods from the grain group every day until I come back. I ll ask you about them the next time I teach nutrition in your class. sugar, such as jelly beans or fruit juice give us quick energy but are not the healthiest choices because they don t stay with us long. We get hungry quickly after eating or drinking these sugary foods. Next break apart the starch chain. Our bodies break starches down into glucose. Ask students which will stay in our bodies longer and help us to feel full glucose or starchy foods? Starch foods. Remember that glucose or sugar dissolves in water, starches do not. Because starches are broken down more slowly, they give us energy over a longer period of time. Starches give us a steady supply of glucose whole sugars give us one quick gulp. Demonstration: Take a canned bean and smash it in between your fingers. The bean breaks down because it contains starch. Next take a piece of broccoli and smash it. Ask the students why it doesn t break down because it doesn t contain starch. It contains fiber. The stem of broccoli is like a skeleton, or bones. Using black construction paper (or paper clips); link together several chains to form fiber. Ask students to imagine that these chains are made of metal. Finally, pretend to pull the chain apart. It cannot be broken because we cannot digest the fiber. Remember it acts like a strong skeleton that can t be broken down. High fiber foods act like a scrub brush in our bodies and help to keep our digestive systems clean by moving food through and out. Using the Cheerios Food Label poster, show students where carbohydrates are located on the food label. Taste Test Ideas
6 6 Whole grain cereal mix Whole grain bagels with cream cheese Rice cakes and sunbutter Raisin bran muffins Popcorn Small Group Activities (10-15 minute activities) Teacher Activities: 1. Student worksheets 2. Whole Grain Helper Activity Nutritionist Activities: 1. Make whole grain cereal snack mix with the students. Additional Activities 1. White vs. Whole wheat: Using a food scale, weigh the difference between white and whole wheat bread. Why is one loaf of bread so much heavier than the other? Which bread do you think has the most nutrients and fiber? 2. Carbohydrates Foods Poster: Using Carbohydrates Foods poster (folded in half), have the students look at the continuum of foods from candy to starchy, high fiber vegetables. Ask them where they would find sugars on the poster. The left hand side shows foods with added sugars Senorita Sugar. The middle left contains foods with natural sugars milk and fruits. Ask students which foods on the poster contain starches and fiber (fruits, vegetables, beans). Ask them which foods are the healthiest and why - the right side of the poster contains starch and fiber and take longer to break down into glucose and, therefore will give us energy over and longer period of time. Next, show the bottom portion of the poster Grains. Ask them which foods contain sugars cookies, poptarts, and sweetened cereals. Which foods contain starch (all of them)? Which contain the most fiber (oatmeal, popcorn, corn tortillas, brown rice, and whole wheat bread)? Again ask them which foods on the poster are the healthiest and why. Then ask them to point out with foods are refined grain foods and which foods are whole grain foods. Which are the healthiest (whole grain foods)? Why? Because they contain all three parts of the seed and give us more vitamins, minerals, and fiber. 3. Find the Whole Grain Cereal: Divide the students into 4-5 groups. Have cereal food label sheets at different stations. Have the groups visit each station and fill out the What s in Your Cereal handout. Or, if the students are sitting in groups already, give a box to each group and rotate the boxes through the groups. Once each group is finished, discuss the answers to the handout and what they thought as a class. 4. Food label or Whole Grain Detective Handout Comparison: Pass out a food label and a whole grain detective handout to each student. Explain that a lot of foods try to disguise themselves as whole grains with tricky words like multi-grain, grain goodness, or 100% wheat. But these imposters will not fool us if we know what to look for. Don t look just at the color of the bread or the front of the label. The first place we should looks is the ingredient label. One the ingredient label, the very first item should say whole (wheat, oats, corn, rye, etc.) Show them the slide with breads A or B as an example. If using Whole Grain Detective handout, ask 3 students to read the 1 st ingredient and tell if it s a whole grain or not. Variation 1: Instead of passing labels around to students, just hold up cereal boxes, tell students what the first ingredient is and ask them if it s a whole grain. Variation 2: Have students rank the cereals lowest to highest in fiber content or sugar content to highlight that we want more fiber and less sugar in our grains. Student Handouts Carbohydrates Note s Page Whole Grain Detective Handout
7 7 Chef Solus Fiber Crossword Puzzle What is in Your Cereal Worksheet Grains Word Search Parent Handouts 10 Tips: Make Half Your Grains Whole (English & Spanish) The Truth about Carbohydrates (English & Spanish) Grains Handout (English & Spanish) Wellness Ways Whole Grain Foods (English & Spanish Lesson Roadmap Review Mind grabber- Jumping jacks Discussion o Carbohydrates overview; food groups that are good sources of carbohydrates o Grains group; Grains are seeds poster; Seed anatomy Making bread o Whole grains Why do we need carbohydrates? Energy &Fiber Types of carbohydrates: Sugar, Starches, Fiber Finding carbohydrates on the nutrition label: total CHO, sugars, fiber, other CHO Wrap up Challenge: Eat 2 whole grain foods each day Durham County Department of Public Health Nutrition Division (919) This material was funded by the SNAP-Ed Nutrition Education and Obesity Prevention Grant Program. In accordance with Federal law and U.S. Department of Agriculture policy, this institution is prohibited from discriminating on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, religion, political beliefs or disability. To file a complaint of discrimination, write USDA, Director, Offices of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington D.C or call (800) (voice) or (202) (TTY). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. SNAP, or Food and Nutrition Assistance, provides nutrition assistance to people with low income. It can help you buy nutritious foods for a better diet. To find out more, call (919)
Nutrition Label Detectives 4 th Grade Lesson
 1 Nutrition Label Detectives 4 th Grade Lesson Goal: Introduce the food label as a tool in choosing healthy meals and snacks Objectives: 1. Students will be able to distinguish between serving size and
1 Nutrition Label Detectives 4 th Grade Lesson Goal: Introduce the food label as a tool in choosing healthy meals and snacks Objectives: 1. Students will be able to distinguish between serving size and
Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates
 Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? There are 2 main types of carbohydrates: Simple carbohydrates include sugars found naturally in fruit, some vegetables, milk and milk
Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? There are 2 main types of carbohydrates: Simple carbohydrates include sugars found naturally in fruit, some vegetables, milk and milk
What is Fiber? Non-digestible part of plant foods. Important for maintaining good health. Most Americans only eat about half of the fiber they need!
 Fill Up On Fiber! Project Sponsors USDA project funded through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program School District of Philadelphia Department of Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University What is
Fill Up On Fiber! Project Sponsors USDA project funded through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program School District of Philadelphia Department of Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University What is
KCAS Health, Nutrition 2.31, 3.2, 3.5 Health, Psychomotor Skills 2.35 Health, Lifetime Personal Wellness 3.2 Health, Safety 5.4
 KCAS Health, Nutrition 2.31, 3.2, 3.5 Health, Psychomotor Skills 2.35 Health, Lifetime Personal Wellness 3.2 Health, Safety 5.4 1. Interest Approach Review goal-setting from last time. Ask, What successes
KCAS Health, Nutrition 2.31, 3.2, 3.5 Health, Psychomotor Skills 2.35 Health, Lifetime Personal Wellness 3.2 Health, Safety 5.4 1. Interest Approach Review goal-setting from last time. Ask, What successes
Carbohydrates and Weight Loss
 Carbohydrates and Weight Loss A Macronutrient Our Body Uses for Energy Provides energy for the body to function properly by every cell in the body, even the brain. Carbohydrate: Calories of Macronutrients:
Carbohydrates and Weight Loss A Macronutrient Our Body Uses for Energy Provides energy for the body to function properly by every cell in the body, even the brain. Carbohydrate: Calories of Macronutrients:
Lesson 1: Getting the Most Nutrition From Your Food. Lesson Highlights. Getting Started: Objective
 Lesson 1: Getting the Most Nutrition From Your Food Lesson Highlights Objective Students will: Review the content of MyPyramid for Kids, identifying food groups and important nutrition messages relating
Lesson 1: Getting the Most Nutrition From Your Food Lesson Highlights Objective Students will: Review the content of MyPyramid for Kids, identifying food groups and important nutrition messages relating
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will understand the important food and non-food uses of the major grains grown in Maryland. OBJECTIVES: Students will identify several types of grains grown in
Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will understand the important food and non-food uses of the major grains grown in Maryland. OBJECTIVES: Students will identify several types of grains grown in
CHOOSE HEALTH: FOOD, FUN, AND FITNESS. Read the Label!
 POSTER 1-1: REPLACE SWEETENED DRINKS Read the Label! Nutrition Facts 20 oz. cola Serving Size: 1 bottle (591mL) Servings Per Container: 1 Amount Per Serving Calories 240 Calories from Fat 0 % Daily Value
POSTER 1-1: REPLACE SWEETENED DRINKS Read the Label! Nutrition Facts 20 oz. cola Serving Size: 1 bottle (591mL) Servings Per Container: 1 Amount Per Serving Calories 240 Calories from Fat 0 % Daily Value
Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion, United States Department of Agriculture
 Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion, United States Department of Agriculture G e t on the ntrai O 0. e a t enough w,9 "Js? How m a. H.I man K' v WHOLE.'! '.f " W h a 9ra/ tar ~-/- «s do I eat?" E
Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion, United States Department of Agriculture G e t on the ntrai O 0. e a t enough w,9 "Js? How m a. H.I man K' v WHOLE.'! '.f " W h a 9ra/ tar ~-/- «s do I eat?" E
Lesson 3 Assessing My Eating Habits
 Lesson 3 Assessing My Eating Habits Overview This lesson introduces the federal guidelines for healthy eating. Students assess their eating habits against these guidelines and make suggestions for improvement.
Lesson 3 Assessing My Eating Habits Overview This lesson introduces the federal guidelines for healthy eating. Students assess their eating habits against these guidelines and make suggestions for improvement.
EatHealthy. SUBJECTS: Health Science English Language Arts listening, speaking, and writing Math. Healthy
 Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument for Family Child Care
 Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument for Family Child Care Date: Your Name: Child Care Program Name: Child Nutrition Go NAP SACC is based on a set of best practices that stem from the latest research
Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument for Family Child Care Date: Your Name: Child Care Program Name: Child Nutrition Go NAP SACC is based on a set of best practices that stem from the latest research
NUTRITION EDUCATION LESSON CODE FG MyPyramid: Simple Steps for Healthy Living
 \ NUTRITION EDUCATION LESSON CODE FG-000-06 MyPyramid: Simple Steps for Healthy Living LESSON DESCRIPTION In this video and activity lesson class participants will explore the different food groups in
\ NUTRITION EDUCATION LESSON CODE FG-000-06 MyPyramid: Simple Steps for Healthy Living LESSON DESCRIPTION In this video and activity lesson class participants will explore the different food groups in
Activity Breaks. Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities
 Activity Breaks Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities Studies show students can benefit both physically and academically from physical activity breaks*: Helps meet recommended daily physical
Activity Breaks Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities Studies show students can benefit both physically and academically from physical activity breaks*: Helps meet recommended daily physical
CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks?
 CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some concerns about diet drinks? CHFFF
CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some concerns about diet drinks? CHFFF
DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan
 1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
Health Basics Start with
 Health Basics Start with GRAINS TIME 50 minutes BACKGROUND INFORMATION GRAINS - MyPlate recommends six ounces of grains per day. One slice of bread is typically one ounce of grain. An ounce is also equal
Health Basics Start with GRAINS TIME 50 minutes BACKGROUND INFORMATION GRAINS - MyPlate recommends six ounces of grains per day. One slice of bread is typically one ounce of grain. An ounce is also equal
Nutrition Tips to Manage Your Diabetes
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
Student Book. Grains: 5 10 ounces a day (at least half whole grains) Self-Check
 ETR Associates Middle School I read and followed directions. My work is neat and complete. This is my best work. HealthSmart Actions Lesson at a Glance Student Book The HealthSmart Actions student book
ETR Associates Middle School I read and followed directions. My work is neat and complete. This is my best work. HealthSmart Actions Lesson at a Glance Student Book The HealthSmart Actions student book
HEALTHY FAMILIES MAKING HEALTHY CHOICES
 HEALTHY FAMILIES MAKING HEALTHY CHOICES HEALTHY FAMILIES MAKING HEALTHY CHOICES We know that keeping your family healthy is important to you. Eating right and being active are big parts of staying healthy.
HEALTHY FAMILIES MAKING HEALTHY CHOICES HEALTHY FAMILIES MAKING HEALTHY CHOICES We know that keeping your family healthy is important to you. Eating right and being active are big parts of staying healthy.
Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument
 Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument Date: Program Name: Enrollment ID#: Child Nutrition Go NAP SACC is based on a set of best practices that stem from the latest research and guidelines in the field.
Go NAP SACC Self-Assessment Instrument Date: Program Name: Enrollment ID#: Child Nutrition Go NAP SACC is based on a set of best practices that stem from the latest research and guidelines in the field.
Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 1: Serve up Your Grains, Vegetables and Fruits. Educator(s) Name (s): Sub-Contractor:
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 1: Serve up Your Grains, Vegetables and Fruits Educator Self-Assessment
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 1: Serve up Your Grains, Vegetables and Fruits Educator Self-Assessment
MyPlate. Lesson. By Carone Fitness. MyPlate
 Lesson By Carone Fitness Nutrition is the study of how the health of your body is influenced by the foods you eat. The foods that you consume provide your body with energy, build and maintain organs and
Lesson By Carone Fitness Nutrition is the study of how the health of your body is influenced by the foods you eat. The foods that you consume provide your body with energy, build and maintain organs and
Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Kidney Disease and Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease where your body cannot properly store and use food for energy. The energy that your body needs is called glucose (sugar). Glucose comes
Kidney Disease and Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease where your body cannot properly store and use food for energy. The energy that your body needs is called glucose (sugar). Glucose comes
Lesson 6. MyPlate. Estimated Class Time Part A Q & A: 20 minutes Total Time: 20 minutes. Part B Poster Activity: 20 minutes Total Time: 20 minutes
 Lesson 6 MyPlate Objectives Students will: recognize the importance of energy balance and moderation identify the food groups and other features of MyPlate, as well as foods within each group* create posters
Lesson 6 MyPlate Objectives Students will: recognize the importance of energy balance and moderation identify the food groups and other features of MyPlate, as well as foods within each group* create posters
Healthy Snacks Kindergarten 1 st Grade Lesson Plan
 1 Healthy Snacks Kindergarten 1 st Grade Lesson Plan Goal: Students will realize the importance of eating snacks and making healthy snack choices. Objectives: 1. Students will be able to differentiate
1 Healthy Snacks Kindergarten 1 st Grade Lesson Plan Goal: Students will realize the importance of eating snacks and making healthy snack choices. Objectives: 1. Students will be able to differentiate
Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn
 Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1B Why We Eat 7 6 5 4 3 2 Hungry 1 Growth Stay healthy Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson
Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1B Why We Eat 7 6 5 4 3 2 Hungry 1 Growth Stay healthy Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson
(teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them?
 Grains (teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them? Grain products are foods such as breads, cereals, rice and pasta. You need about 6 ounces (6 servings)
Grains (teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them? Grain products are foods such as breads, cereals, rice and pasta. You need about 6 ounces (6 servings)
Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn
 Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your
Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your
The Lunch Box. Learning From Labels
 Learning From Labels Handout B The Lunch Box Food labels can help you choose healthy foods for your child s lunch. Today s food labels provide information about ingredients and nutrient content. Read the
Learning From Labels Handout B The Lunch Box Food labels can help you choose healthy foods for your child s lunch. Today s food labels provide information about ingredients and nutrient content. Read the
Level 1 MyPyramid Lessons for Grades 1 and 2 Teamnutrition.usda.gov
 Teamnutrition.usda.gov Level 1 Lessons for Grades 1 and 2 United States Department of Agriculture Food and Nutrition Service FNS-384 September 2005 The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination
Teamnutrition.usda.gov Level 1 Lessons for Grades 1 and 2 United States Department of Agriculture Food and Nutrition Service FNS-384 September 2005 The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination
August-September, Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions
 August-September, 2015 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet despite
August-September, 2015 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet despite
What Does My Body Need to Grow?
 What Does My Body Need to Grow? If you want to be healthy and have the energy for all your favorite games and activities, then you need to eat food that is good for you and that will make you strong. How
What Does My Body Need to Grow? If you want to be healthy and have the energy for all your favorite games and activities, then you need to eat food that is good for you and that will make you strong. How
(teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them?
 Grains (teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them? Grain products are foods such as breads, cereals, rice and pasta. You need about 6 ounces (6 servings)
Grains (teacher) Sample question: What grain foods are you familiar with and how do you prepare them? Grain products are foods such as breads, cereals, rice and pasta. You need about 6 ounces (6 servings)
Welcome & Introduction Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 5 Lesson 4: Make Half Your Grains Whole Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 5 Lesson 4: Make Half Your Grains Whole Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
What s. on your plate? ChooseMyPlate.gov. Vegetables. Fruits. Protein. Grains. Dairy. plate fruits and vegetables. Make half your
 What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your protein food choices. Make at least half your grains whole. Before you
What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your protein food choices. Make at least half your grains whole. Before you
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH
 eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
Lose It To Win It Weekly Success Tip. Week 1
 Lose It To Win It Weekly Success Tip Week 1 Writing down your goals will keep you on track. Revise or add to your goals at any time. Start by setting a long-term weight loss goal. Next, set a goal for
Lose It To Win It Weekly Success Tip Week 1 Writing down your goals will keep you on track. Revise or add to your goals at any time. Start by setting a long-term weight loss goal. Next, set a goal for
Ready, Set, Start Counting!
 Ready, Set, Start Counting! Carbohydrate Counting a Tool to Help Manage Your Blood Glucose When you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose in a healthy range can help you feel your best today and in
Ready, Set, Start Counting! Carbohydrate Counting a Tool to Help Manage Your Blood Glucose When you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose in a healthy range can help you feel your best today and in
Exploring MyPlate with Professor Popcorn
 Exploring MyPlate with Professor Popcorn Grade 4: Energized by Food Grade 4: Lesson 1 (4:1) MyPlate Objectives Upon completion of Lesson 1, youth will: 1. State that food and physical activity are important
Exploring MyPlate with Professor Popcorn Grade 4: Energized by Food Grade 4: Lesson 1 (4:1) MyPlate Objectives Upon completion of Lesson 1, youth will: 1. State that food and physical activity are important
Lesson #5: Finding the Energy
 Lesson #5: Finding the Energy Chapter Five Although Cristina has introduced her family to ways to eat healthier, she is still confused about one thing. The doctor arranged for her grandmother to talk to
Lesson #5: Finding the Energy Chapter Five Although Cristina has introduced her family to ways to eat healthier, she is still confused about one thing. The doctor arranged for her grandmother to talk to
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA
 UNIVERSITY F CALIFRNIA Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources http://anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu Publication 8108 Learning from Labels Food labels can help you choose healthy foods for your child s lunch.
UNIVERSITY F CALIFRNIA Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources http://anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu Publication 8108 Learning from Labels Food labels can help you choose healthy foods for your child s lunch.
Food. Food Groups & Nutrients
 Food Food Groups & Nutrients Grains Group Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Examples: bread,
Food Food Groups & Nutrients Grains Group Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Examples: bread,
History of the. Food Guide Systems
 History of the Food Guide Systems 1940 A guide to good eating, the basic 7 Focus on nutritional adequacy, specific servings from each food group 1956-1970 Food For Fitness: Daily Food Guide Basic 4 1979
History of the Food Guide Systems 1940 A guide to good eating, the basic 7 Focus on nutritional adequacy, specific servings from each food group 1956-1970 Food For Fitness: Daily Food Guide Basic 4 1979
MANAGING DIABETES. with a healthy diet
 MANAGING DIABETES with a healthy diet Getting Started For many people with diabetes, the keys to controlling blood glucose are: 1) choosing the right amount of healthy foods 2) getting enough exercise
MANAGING DIABETES with a healthy diet Getting Started For many people with diabetes, the keys to controlling blood glucose are: 1) choosing the right amount of healthy foods 2) getting enough exercise
Orange-Pineapple Smoothie Module 6
 Ingredients: 1 banana 1-15oz can pineapple chunks (packed in their own juice, not in syrup) 1 cup 100% orange juice (not orange drink ) ¼ cup non-fat (skim) or low-fat (1%) milk 4-5 ice cubes Orange-Pineapple
Ingredients: 1 banana 1-15oz can pineapple chunks (packed in their own juice, not in syrup) 1 cup 100% orange juice (not orange drink ) ¼ cup non-fat (skim) or low-fat (1%) milk 4-5 ice cubes Orange-Pineapple
Tips for making healthy food choices
 Tips for making healthy food choices A diabetic diet is all about balance and the choices you make. It works best when you eat a variety of foods in the right portions and at the same times each day. It
Tips for making healthy food choices A diabetic diet is all about balance and the choices you make. It works best when you eat a variety of foods in the right portions and at the same times each day. It
The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet
 The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet # Name Information Picture 1 Water The single most essential component that represents 80% of your body and 65% of your weight 2 Beans Top ranked carbohydrates
The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet # Name Information Picture 1 Water The single most essential component that represents 80% of your body and 65% of your weight 2 Beans Top ranked carbohydrates
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages
 Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Diabetes. Page 1 of 12. English
 Diabetes English These materials were developed by the Nutrition Education for New Americans project of the Department of Anthropology and Geography at Georgia State University, Atlanta, Georgia. Funded
Diabetes English These materials were developed by the Nutrition Education for New Americans project of the Department of Anthropology and Geography at Georgia State University, Atlanta, Georgia. Funded
Be a Food Label Detective!
 Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
Diabetes Prevention Presentation: Walk the Walk! Talk the Talk! See Your Doc! Target Audience: 6 10 year olds People with special needs Older adults
 Diabetes Prevention Presentation: Walk the Walk! Talk the Talk! See Your Doc! Flesch Kincaid Reading Level: 4.0 without proper names, numbers, presenter instructions and terms diabetes, type 1 diabetes,
Diabetes Prevention Presentation: Walk the Walk! Talk the Talk! See Your Doc! Flesch Kincaid Reading Level: 4.0 without proper names, numbers, presenter instructions and terms diabetes, type 1 diabetes,
Youth4Health Project. Student Food Knowledge Survey
 Youth4Health Project Student Food Knowledge Survey Student ID Date Instructions: Please mark your response. 1. Are you a boy or girl? Boy Girl 2. What is your race? Caucasian (White) African American Hispanic
Youth4Health Project Student Food Knowledge Survey Student ID Date Instructions: Please mark your response. 1. Are you a boy or girl? Boy Girl 2. What is your race? Caucasian (White) African American Hispanic
A common sense approach to taking control of your diet
 Welcome Wellness Warriors! Carbohydrate Counting: A common sense approach to taking control of your diet Today we will discuss The different food groups and how they affect blood sugar Which foods increase
Welcome Wellness Warriors! Carbohydrate Counting: A common sense approach to taking control of your diet Today we will discuss The different food groups and how they affect blood sugar Which foods increase
U.S. Army Center for Health Promotion & Preventive Medicine
 A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. Army Center for Health Promotion & Preventive Medicine Directorate of Health Promotion and Wellness Oral Fitness Program Aberdeen Proving Ground Maryland, 21010-5403
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. Army Center for Health Promotion & Preventive Medicine Directorate of Health Promotion and Wellness Oral Fitness Program Aberdeen Proving Ground Maryland, 21010-5403
Using the Nutrition Facts Table to Make Heart Healthy Food Choices
 Using the Table to Make Heart Healthy Food Choices Most packaged food products that you purchase contain a Table on the label. The Table lists information on nutrients that are found in the food product.
Using the Table to Make Heart Healthy Food Choices Most packaged food products that you purchase contain a Table on the label. The Table lists information on nutrients that are found in the food product.
Activity #5: The Glycemic Index
 Activity #5: The Glycemic Index Cristina shares with her grandmother the information she has learned about reading nutrition labels and checking the total amount of sugar and fiber per serving. She is
Activity #5: The Glycemic Index Cristina shares with her grandmother the information she has learned about reading nutrition labels and checking the total amount of sugar and fiber per serving. She is
Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber
 Dining with Diabetes 6:1 Chapter 6 Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber Lesson Plans Learning Objectives Participants will state the benefits of low-fat dairy products and exercise on osteoporosis
Dining with Diabetes 6:1 Chapter 6 Session Four: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fiber Lesson Plans Learning Objectives Participants will state the benefits of low-fat dairy products and exercise on osteoporosis
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy
 My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and s throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and s throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
Jump in for Healthy Choices
 Jump in for Healthy Choices Grade Level: K-3 Lesson Overview Objectives: Students will be able to Recognize the importance of eating a variety of fruits and vegetables Green and Healthy Kids - People Topic
Jump in for Healthy Choices Grade Level: K-3 Lesson Overview Objectives: Students will be able to Recognize the importance of eating a variety of fruits and vegetables Green and Healthy Kids - People Topic
Replace Refined Grains with Whole Grains
 Power House: Group Experience Maintenance Session Replace Refined Grains with Whole Grains Session Objectives 1. Participants will engage in 45 minutes of physical activity. 2. Participants will verbalize
Power House: Group Experience Maintenance Session Replace Refined Grains with Whole Grains Session Objectives 1. Participants will engage in 45 minutes of physical activity. 2. Participants will verbalize
Child Nutrition & Wellness Kansas State Department of Education Presents. Whole Grain Choo-Choo Train Lesson Plan
 Child Nutrition & Wellness Kansas State Department of Education Presents Whole Grain Choo-Choo Train Lesson Plan This class was developed by Child Nutrition & Wellness, Kansas State Department of Education.
Child Nutrition & Wellness Kansas State Department of Education Presents Whole Grain Choo-Choo Train Lesson Plan This class was developed by Child Nutrition & Wellness, Kansas State Department of Education.
Oral Health Education
 e C ity Fre v a K I DS Oral Health Education for Pregnant Women, Children Birth through Age Five, and Their Families TM A Quick Reference for Home Visitors TM Cavity Free K I DS Cavity Free Kids Oral Health
e C ity Fre v a K I DS Oral Health Education for Pregnant Women, Children Birth through Age Five, and Their Families TM A Quick Reference for Home Visitors TM Cavity Free K I DS Cavity Free Kids Oral Health
Essential Standard. 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness.
 Essential Standard 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness. 8.NPA.1.3 Implement meal plans that are consistent with Dietary Guidelines. Warm Up Without
Essential Standard 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness. 8.NPA.1.3 Implement meal plans that are consistent with Dietary Guidelines. Warm Up Without
November National Diabetes Month
 Diabetes can cause serious health problems, including blindness, nerve damage, and kidney disease. November 2017 It is one of the leading causes of disability and death in the United States. The disease
Diabetes can cause serious health problems, including blindness, nerve damage, and kidney disease. November 2017 It is one of the leading causes of disability and death in the United States. The disease
Healthy Foods Café. EatHealthy. 5 Classroom Materials
 Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
2-3 class periods, time outside of class to track foods and beverages consumed for one day
 MyPlate is Great! Time Frame: 2-3 class periods, time outside of class to track foods and beverages consumed for one day Overview: Students will create and categorize an alphabetical list of foods into
MyPlate is Great! Time Frame: 2-3 class periods, time outside of class to track foods and beverages consumed for one day Overview: Students will create and categorize an alphabetical list of foods into
Department of Nutrition, University of California, Davis; University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources
 Labels Food The United States Food and Drug Administration requires most packaged foods and beverages to have a Nutrition Facts label to help consumers make informed choices about the foods they eat. Serving
Labels Food The United States Food and Drug Administration requires most packaged foods and beverages to have a Nutrition Facts label to help consumers make informed choices about the foods they eat. Serving
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan
 Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
Welcome & Introduction Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 2: Serve up Your Dairy and Protein Foods Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 2: Serve up Your Dairy and Protein Foods Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
TRACKS Lesson Plan. Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Girls Club
 TRACKS Lesson Plan Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Girls Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related to eating and physical
TRACKS Lesson Plan Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Girls Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related to eating and physical
TRACKS Lesson Plan. Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Boys Club
 TRACKS Lesson Plan Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Boys Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related to eating and physical
TRACKS Lesson Plan Snacks Snack Attack Grades 5 8 Boys Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related to eating and physical
If adaptations were made or activity was not done, please describe what was changed and why. Please be as specific as possible.
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition Grade 6 Lesson 1: Make Your Calories Count Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition Grade 6 Lesson 1: Make Your Calories Count Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
CONCEPTS: OBJECTIVES: MATERIALS:
 CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
How to Fight Diabetes and Win. Meal. Planning NUTURNA. Advance Diabetic Support
 How to Fight Diabetes and Win Meal Planning NUTURNA TM Advance Diabetic Support Meal Planning Well-balanced and portion-controlled meals are vital to the control of blood sugar levels and management of
How to Fight Diabetes and Win Meal Planning NUTURNA TM Advance Diabetic Support Meal Planning Well-balanced and portion-controlled meals are vital to the control of blood sugar levels and management of
Diabetic Monthly Newsletter
 JULY 2013 Diabetic Monthly Newsletter Gunnison Valley Diabetes Self -Management Education Program 45 East 100 North Gunnison, Utah 84634 Inside This Issue 1 Support Group Topic 1 Support Group Schedule
JULY 2013 Diabetic Monthly Newsletter Gunnison Valley Diabetes Self -Management Education Program 45 East 100 North Gunnison, Utah 84634 Inside This Issue 1 Support Group Topic 1 Support Group Schedule
Glycemic Index. Mean Incremental Blood Glucose Responses in Healthy Subjects (65-70 years) Time (Minutes)
 Glycemic Index How to use the glycemic index By making careful food choices, you can influence your hunger and energy as well as blood sugar levels, cholesterol and triglyceride levels. If you have problems
Glycemic Index How to use the glycemic index By making careful food choices, you can influence your hunger and energy as well as blood sugar levels, cholesterol and triglyceride levels. If you have problems
Reading Food Labels A few questions before we start. Questions Continued. After this session, you will be able to:
 A few questions before we start Reading Food Labels 1. A healthy food might have lots of: a) Cholesterol b) Sugar c) Fibre d) Saturated fat Questions Continued 2. Fibre is healthy because it: a) Helps
A few questions before we start Reading Food Labels 1. A healthy food might have lots of: a) Cholesterol b) Sugar c) Fibre d) Saturated fat Questions Continued 2. Fibre is healthy because it: a) Helps
TRACKS Lesson Plan. MyPlate and Whole Grains Food For Thought Grades 5 8 Boys Club
 TRACKS Lesson Plan MyPlate and Whole Grains Food For Thought Grades 5 8 Boys Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related
TRACKS Lesson Plan MyPlate and Whole Grains Food For Thought Grades 5 8 Boys Club I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance related
Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy
 Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy A Healthy Diet and Our Body If our bodies are human machines food is our fuel. How well we eat, affects how well our bodies work, and how long we live. It is especially
Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy A Healthy Diet and Our Body If our bodies are human machines food is our fuel. How well we eat, affects how well our bodies work, and how long we live. It is especially
LiveWell Kids Nutrition
 3rd Grade, Module 2 Fruits and Vegetables Did You Know? LiveWell Kids Nutrition Grade: 3rd Module 2: Fruits & Vegetables Fruits and vegetables are important sources of vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium and
3rd Grade, Module 2 Fruits and Vegetables Did You Know? LiveWell Kids Nutrition Grade: 3rd Module 2: Fruits & Vegetables Fruits and vegetables are important sources of vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium and
Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Whole Grains: How Much for YOUR Plate?
 Page 1 Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Whole Grains: How Much for YOUR Plate? Task Topic: Task Title: Teaching Message(s): Resources: Whole Grains Whole Grains: How Much for YOUR Plate? When consuming
Page 1 Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Whole Grains: How Much for YOUR Plate? Task Topic: Task Title: Teaching Message(s): Resources: Whole Grains Whole Grains: How Much for YOUR Plate? When consuming
Elementary Program Unit 5.3
 Elementary Program Unit 5.3 Lesson: Knowledge is Power Goals: Students will be able to identify the number of grams or milligrams of fat, sugar, fiber, and sodium in one serving by reading the nutrition
Elementary Program Unit 5.3 Lesson: Knowledge is Power Goals: Students will be able to identify the number of grams or milligrams of fat, sugar, fiber, and sodium in one serving by reading the nutrition
CHILD AND ADULT MEALS
 UPDATED CHILD AND ADULT CARE FOOD PROGRAM MEAL PATTERNS: CHILD AND ADULT MEALS USDA recently revised the CACFP meal patterns to ensure children and adults have access to healthy, balanced meals throughout
UPDATED CHILD AND ADULT CARE FOOD PROGRAM MEAL PATTERNS: CHILD AND ADULT MEALS USDA recently revised the CACFP meal patterns to ensure children and adults have access to healthy, balanced meals throughout
Eating Healthy To Be Healthy
 Just A Reminder what is healthy food? Healthy Eating Healthy To Be Healthy Fruit Vegetables Fish & Meat Eggs, Cheese & Milk Unhealthy Food Chocolate Crisps chips Cake Sweets A Guide To Healthy Eating Being
Just A Reminder what is healthy food? Healthy Eating Healthy To Be Healthy Fruit Vegetables Fish & Meat Eggs, Cheese & Milk Unhealthy Food Chocolate Crisps chips Cake Sweets A Guide To Healthy Eating Being
Food Science. Grains Unit Handouts
 Food Science Grains Unit Handouts Whole Grains: The Inside Story Article Questions 1. How many servings of whole grains does the USDA recommend is consumed each day? a. How many servings does the average
Food Science Grains Unit Handouts Whole Grains: The Inside Story Article Questions 1. How many servings of whole grains does the USDA recommend is consumed each day? a. How many servings does the average
Aim for a healthy weight. Be physically active each day.
 Diet Principles and Dietary these two items should be considered each time we make a choice of what goes into our mouth Guidelines Diet Planning 6 basic diet planning principles adequacy enough energy
Diet Principles and Dietary these two items should be considered each time we make a choice of what goes into our mouth Guidelines Diet Planning 6 basic diet planning principles adequacy enough energy
Nutrition - What Should We Eat?
 Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Making Meals Matter. Tips to feed 6-12 year olds. Healthy eating for your school-age child
 Making Meals Matter Tips to feed 6-12 year olds Healthy eating for your school-age child Your child learns healthy eating from you. Your elementary- school child needs you to guide them and to model healthy
Making Meals Matter Tips to feed 6-12 year olds Healthy eating for your school-age child Your child learns healthy eating from you. Your elementary- school child needs you to guide them and to model healthy
Welcome & Review Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 3 Lesson 4: Vitamins, Minerals and Water Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 3 Lesson 4: Vitamins, Minerals and Water Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
VENN DIAGRAM. November Appendix
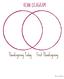 VENN DIAGRAM Thanksgiving Today First Thanksgiving NOVEMBER Soybean Information Sheet Soy products come from the soybean, a legume native to northern China. The United States is now the world s largest
VENN DIAGRAM Thanksgiving Today First Thanksgiving NOVEMBER Soybean Information Sheet Soy products come from the soybean, a legume native to northern China. The United States is now the world s largest
By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating. Canada s Food Guide. Healthier Food Choices Are...
 Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating Lesson #1 Making Healthier Food Choices Healthier Food Choices Are... follow Eating Well with, By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Apply health knowledge
Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating Lesson #1 Making Healthier Food Choices Healthier Food Choices Are... follow Eating Well with, By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Apply health knowledge
Coach on Call. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics.
 Coach on Call Planning Healthy Snacks for Diabetes It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions
Coach on Call Planning Healthy Snacks for Diabetes It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions
Nutrition for Rehab Patients
 Nutrition for Rehab Patients Michelle Ray, RD Michelle Ray, RD Michelle Ray MS, RD, LDN Making healthcare remarkable Why is nutrition important for our patients? Adequate nutrition protects quality of
Nutrition for Rehab Patients Michelle Ray, RD Michelle Ray, RD Michelle Ray MS, RD, LDN Making healthcare remarkable Why is nutrition important for our patients? Adequate nutrition protects quality of
ALIGNING MENUS: 2010 DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS
 ALIGNING MENUS: FOR AMERICANS Child and Adult Care Food Program Illinois State Board of Education Nutrition and Wellness Programs August 2013 ALIGNING MENUS WITH Institute of Medicine Recommendations:
ALIGNING MENUS: FOR AMERICANS Child and Adult Care Food Program Illinois State Board of Education Nutrition and Wellness Programs August 2013 ALIGNING MENUS WITH Institute of Medicine Recommendations:
Weight Loss, Healthy Eating and Energy Balance
 Weight Loss, Healthy Eating and Energy Balance Diet and weight loss is an area that everyone has an opinion on. Every person is different and like exercise one diet does not fit everyone. The following
Weight Loss, Healthy Eating and Energy Balance Diet and weight loss is an area that everyone has an opinion on. Every person is different and like exercise one diet does not fit everyone. The following
Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment Fidelity Team Assessment. Educator(s) Name (s): Sub-Contractor: Region: County: Date of Lesson:
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Eat Healthy, Be Active Community Workshops: Workshop 1 Enjoy Healthy Food That Tastes Great Educator Self-Assessment
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Eat Healthy, Be Active Community Workshops: Workshop 1 Enjoy Healthy Food That Tastes Great Educator Self-Assessment
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in My Daily Food Needs. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
Healthy Futures Newsletter
 Healthy Futures Newsletter Wassaja Memorial Health Center Spring Cleaning Your Eating Habits Winter is over and spring time is here! We remember to spring clean our homes, but have you thought about spring
Healthy Futures Newsletter Wassaja Memorial Health Center Spring Cleaning Your Eating Habits Winter is over and spring time is here! We remember to spring clean our homes, but have you thought about spring
Step Up and Celebrate
 Step Up and Celebrate Physical Activity Physical Activity Healthy Eating Goals Met Rewards Goals Met 1. 1. Handout 12-1 Healthy Eating Rewards 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6. Choose an appropriate reward
Step Up and Celebrate Physical Activity Physical Activity Healthy Eating Goals Met Rewards Goals Met 1. 1. Handout 12-1 Healthy Eating Rewards 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6. Choose an appropriate reward
