Explain what is meant by the term cephalization
|
|
|
- Piers Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Learning Outcomes and for Biology 104 Chapter 29 Introduction to Invertebrates Learning Outcome 29.a. Knowledge of the evolution of animals List the criteria for the classification of animals Explain what is meant by the term cephalization Distinguish between acoelmates, pseudocoelomates, and coelomates Learning Outcome 29.b. Knowledge of multicellularity Describe the major characteristics of sponges that make them a group of animals at the cellular level of organization Describe sponge dispersal Explain the sponge skeleton Learning Outcome 29.c. Knowledge of true tissue layers Distinguish between radial and bilateral symmetry Describe organisms of the phylum Ctenophora Describe organisms of the phylum Cnidaria Learning Outcome 29.d. Knowledge of bilateral symmetry Distinguish between a sac body plan and a tube-withina-tube body plan Describe the organisms of the phylum Platyhelminthes List some adaptations in tapeworms and flukes that allow them to be parasitic organisms Learning Outcome 29.e. Knowledge of pseudocoelomates Describe the pseudocoelom Chapter 30 More Invertebrates List the two phyla containing pseudocoelomate organisms Identify methods of transmission of Ascaris roundworms List some conditions/diseases that may result from infection with other roundworm species
2 Learning Outcome 30.a. Knowledge of the coelomates Distinguish between protostomes and deuterostomes Define coelome List the advantages of having a coelom Learning Outcome 30.b. Knowledge of Mollusks List the three parts of the mollusk body plan Describe the composition of the shell of a bivalve Describe cephalopod predation and movement Describe the different types of organisms found in the class Gastropoda Describe developmental torsion as seen in the gastropods Define hermaphroditism List advantages of hermaphroditism in slow-moving organisms Learning Outcome 30.c. Knowledge of Annelids Distinguish between polychaetes and oligochaetes What are setae and what is their purpose List the evidence of segmentation found in earthworms What is a hydrostatic skeleton Describe reproduction in earthworms Learning Outcome 30.d. Knowledge of Arthropods Describe the arthropod skeleton What are disadvantages associated with the arthropod skeleton List the characteristics that make arthropods the most successful group of animals List the three main body segments of the arthropods
3 List major characteristic associated with the Uniramians Describe the major characteristic and adaptations found in the Chelicerates Learning Outcome 30.e. Knowledge of Echinoderms Describe the symmetry found in echinoderms Describe the eater vascular system Describe the role of the coelom in the exchange and movement of gases and wastes in the echinoderms Chapter 31 Vertebrates Learning Outcome 31.a. Knowledge of Chordates Describe the four principal characteristics of chordates Compare and contrast the non-vertebrate chordates and the vertebrate chordates Learning Outcome 31.b. Knowledge of Vertebrates List the major characteristics shared by all vertebrates Chapter 32 Human Evolution How do jawless fishes differ from the other vertebrates Explain characteristics involved in the evolution of terrestrial organisms from aquatic organisms How do amphibians differ from all of the other terrestrial vertebrates Explain how reptiles have adapted for life on land Describe the amniotic egg and which groups of organisms produce this type of egg List special adaptations found in birds to accommodate flight List the major characteristics found in all mammals Differentiate between marsupials, monotremes and placental mammals
4 Learning Outcome 32.a. Knowledge of the evolution of primates List the major characteristics of all primates What is the major advantage of binocular vision Learning Outcome 32.b. Knowledge of the evolution of hominids List some characteristics that distinguish hominids from other primates What is bipedalism Describe adaptation of the human skeleton to allow for standing erect Describe the major characteristics of Australopithecines Learning Outcome 32.c. Knowledge of humans What is culture List the accomplishments of early Homo sapiens Describe the Out-of-Africa hypothesis Describe the multiregional continuity hypothesis List some evidence to support the hypothesis that Homo sapiens evolved from Homo erectus Describe cultural advancements seen in Neanderthals and Cro-magnons Chapter 33 Animal Organization and Homeostasis Learning Outcome 33.a. Knowledge of tissue types Understand how vertebrate cells are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems List the major tissue types found in vertebrates Describe the general characteristic and functions of epithelial tissues List and describe the different epithelial tissue types Describe the functions of connective tissues
5 Describe the specialized connective tissues Differentiate among smooth, striated, and cardiac muscle tissues Be able to label the major parts of a neuron Describe the function and location of nervous tissue Learning Outcome 33.b. Knowledge of organs and organ systems Describe the integumentary system Describe the functions of skin in humans Identify the components contained within the different regions of the skin List some accessory organs to the skin and their functions Label the different mammalian body cavities Learning Outcome 33.c. Knowledge of homeostasis What is homeostasis Explain how organ systems in the human body contribute to homeostasis Describe negative feedback homeostatic mechanisms; give an example these Describe positive feedback homeostatic mechanisms; give an example of these Chapter 34 Circulation and Cardiovascular System Learning Outcome 34.a. Knowledge of transport in invertebrates Describe circulation in invertebrates that do not have a circulatory system. Distinguish between the terms blood and hemolymph Distinguish between an open circulatory system and a closed circulatory system Learning Outcome 34.b. Knowledge of transport in vertebrates Describe the three types of blood vessels
6 Compare and contrast the circulatory pathways that exist among different vertebrates Define the term cardiovascular system Learning Outcome 34.c. Knowledge of transport in humans Describe the structure of the human heart Trace the path of blood flow through the heart Describe the heartbeat and the normal cardiac cycle Describe the two major circular pathways of the human cardiovascular system Describe human blood pressure and how it is measured Learning Outcome 34.d. Knowledge of cardiovascular disorders Explain the causes of hypertension and identify two genes that may be associated with this disorder Explain the causes of the disorder atherosclerosis Distinguish between an embolus and a thrombus Describe the causes and symptoms of a heart attack and a stroke Learning Outcome 34.e. Knowledge of blood as a transport medium Identify the two main components of the blood of mammals. List and describe the three types of formed elements found in blood Describe the process of blood clotting Describe the role of vitamin K in the blood Define the term tissue fluid Explain how osmotic pressure and blood pressure control the movement of fluid through the capillary walls Chapter 35 - Lymph Transport and Immunity
7 Learning Outcome 35.a. Lymphatic system Describe the lymphatic vessels Explain what causes edema Define lymph Distinguish between the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic duct List and describe the lymphoid organs Describe the role of the lymphatic system in defending the body against diseases Distinguish between red pulp and white pulp Describe the function of the tonsils and the peyer s patches Learning Outcome 35.b. Nonspecific and specific defenses Define the term immunity Distinguish between nonspecific and specific defenses List and describe the four nonspecific defenses Identify four symptoms of an inflamed area What are natural killer cells? Distinguish between B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes Describe antibody-mediated immunity Define the term apoptosis Describe the structure of an antibody List and describe the types of antibodies Describe cell-mediated immunity List and describe the types of T-cells
8 Learning Outcome 35.c. Induced immunity Distinguish between active and passive immunity What are cytokinins? Describe and diagram hydrogen bonding between water molecules Describe how interferon and interleukins are used in the fight against cancer What are monoclonal antibodies? Describe how they are produced Learning Outcome 35.d. Immunity side effects Distinguish between the terms allergy and allergen Distinguish between an immediate and a delayed allergic response Describe the ABO system and the four blood types Explain what causes agglutination Distinguish between Rh positive and Rh negative. Explain why Rh factor is important during pregnancy Explain what causes tissue rejection to occur and what can be done to prevent it from occurring Define the term autoimmune diseases Chapter 36 Digestive System and Nutrition Learning Outcome 36.a. Knowledge of Digestive tracts Compare and contrast a complete and incomplete digestive tract Distinguish between continuous and discontinuous feeders Distinguish among omnivores, herbivores, and carnivores. Describe the dentition of mammals according to their mode of nutrition. Learning Outcome 36.b. Knowledge of the human digestive tract
9 List and describe the function of each part of the digestive system Describe the enzymes associated with the process of digestion List and describe the function of the three accessory organs associated with the digestive system Describe the function of the pancreas as an exocrine gland and as an endocrine gland Learning Outcome 36.c. Knowledge of digestive enzymes Describe the function of salivary amylase Identify the enzyme associated with protein digestion. Describe protein digestion Describe the enzymatic breakdown of starch, protein, nucleic acids, and fats by the small intestine Learning Outcome 36.d. Knowledge of nutrition Distinguish among the eating disorders obesity, anorexia nervosa, and bulimia nervosa Distinguish between soluble and insoluble fiber Identify the number of different amino acids required for protein synthesis Identify the three subunits of the phospholipid molecule. What are the components of a triglyceride or fat molecule? Distinguished between saturated and unsaturated fats. What is meant by polyunsaturated? Identify the three atoms found in carbohydrates and indicate the molecular ratio of these atoms. Define monosaccharide and give some examples of this group of carbohydrates.
10 What are vitamins? Describe how sodium and calcium affect the body Describe the function of antioxidants. Identify how antioxidants can be acquired Chapter 37 Respiratory System Learning Outcome 37.a. Knowledge of gas exchange surfaces Describe respiration of aquatic organisms and terrestrial organisms Describe the role of the gills in the process of respiration Describe the function of the lungs and the diaphragm in the process of respiration Learning Outcome 37.b. Knowledge of the human respiratory system Trace the path of air flow from the nose to the alveoli Describe the gas exchange that occurs between air in the alveoli and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries Describe the process of transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of respiration Learning Outcome 37.c. Knowledge of respiration and health List and describe some upper respiratory tract infections Distinguish among the lower respiratory tract disorders acute bronchitis, Pneumonia, and Pulmonary Tuberculosis Identify the causes of respiratory disorders such as chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis, emphysema, asthma, and lung cancer Chapter 38 Body Fluid Regulation and Excretory System
11 Learning Outcome 38.a. Knowledge of body fluid regulation Describe how the regulation of body fluid concentrations can be achieved by regulating the water and ions in body fluids. Describe how marine environments can promote water loss while fresh water can promote the gain of water Describe how osmolarity can affect the movement of water Learning Outcome 38.b. Knowledge of nitrogenous waste products Describe how the breakdown of nucleic acids and amino acids can result in nitrogenous wastes Describe the excretion of nitrogenous wastes in terrestrial amphibians and mammals. Explain the urea cycle Describe how uric acid is synthesized Learning Outcome 38.c. Knowledge of the organs of excretion Describe the functions of flame cells, nephridia, and malpighian tubules in the process of excretion Learning Outcome 38.d. Knowledge of the urinary system in humans Describe the four parts of the human urinary system Describe the structure of the kidney Describe the process of urine formation, glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion Describe the role of antidiuretic hormones (ADH) Distinguish between the terms diuresis and antidiuresis Describe the process of salt reabsorption Explain how the acid-base balance is maintained Chapter 39 - Neurons And Nervous Systems Learning Outcome 39.a. Knowledge of evolution of the nervous system
12 Trace the evolution of the nervous system by contrasting its organization in hydras, planarians, earthworms, and humans. Learning Outcome 39.b. Knowledge of nervous tissue Describe the structure of a neuron, and give a function for each part mentioned. Name three types of neurons, and give a function for each. What are the major events of an action potential, and what ion changes are associated with each event? Describe the mode of action of a neurotransmitter at a synapse, including how it is stored and how it is destroyed. Learning Outcome 39.c. Knowledge of the Central Nervous System: Brain and Spinal Cord Name the major parts of the human brain, and give a principal function for each part. Describe the limbic system, and discuss its possible involvement in learning and memory. Learning Outcome 39.d. Knowledge of the Peripheral Nervous System Discuss the structure and function of the peripheral nervous system. Trace the path of a spinal reflex. Contrast the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic system. Chapter 40 - Sense Organs Learning Outcome 40.a. Knowledge of the chemical senses Discuss the structure and function of human chemoreceptors. Learning Outcome 40.b. Knowledge of the sense of vision In general, how does the eye in arthropods differ from that in humans? What types of animals have eyes that are constructed like the human eye? Name the parts of the human eye, and give a function for
13 each part. Explain focusing and accommodation in terms of the anatomy of the human eye. Contrast the location and the function of rod cells to those of cone cells. Explain the process of integration in the retina and the brain. Learning Outcome 40.c. Knowledge of the sense of hearing and balance. Describe the structure of the human ear. Describe how we hear. Describe the role of the semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule in balance. Chapter 41 Locomotion and Support Systems Learning Outcome 41.a. Knowledge of the diversity of skeletons What are the three types of skeletons found in the animal kingdom and how do they differ? Cite animals that have these types of skeletons. Learning Outcome 41.b. Knowledge of the human skeletal system Give several functions of the skeletal system in humans. How does the skeletal system contribute to homeostasis? Contrast compact bone with spongy bone. Explain how bone grows and is renewed. Distinguish between axial and appendicular skeletons. List the bones of the pectoral girdle and upper limb; the pelvic girdle and lower limb. How are joints classified? Describe the anatomy of a freely movable joint. Learning Outcome 41.c. Knowledge of the Human Muscular System Give several functions of the muscular system in humans. How does the muscular system contribute to homeostasis? Describe how muscles are attached to bones. What is
14 accomplished by muscles acting in antagonistic pairs? Discuss the microscopic structural features of a muscle fiber and a sarcomere. What is the sliding filament model? Discuss the availability and the specific role of ATP during muscle contraction. What is oxygen debt, and how is it repaid? Describe the structure and function of a neuromuscular junction. Describe the cyclical events as myosin pulls actin toward the center of a sarcomere. Chapter 42 - Hormones and Endocrine Systems Learning Outcome 42.a. Knowledge of Endocrine Glands Categorize chemical signals into three groups based on the distance between site of secretion and site of reception, and give examples for each group. Explain how steroid hormones and peptide hormones affect the metabolism of the cell. Learning Outcome 42.b. Knowledge of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary Glands Explain the relationship of the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary gland and to the anterior pituitary gland. List the hormones secreted by the posterior and the anterior pituitary gland. Give an example of the negative feedback relationship among the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary, and the other endocrine glands. Discuss the effect of there being too much or too little growth hormone when a young person is growing. What is the result if the anterior pituitary produces growth hormone in an adult. Learning Outcome 42.c. Knowledge of other Endocrine Glands and Hormones
15 What two types of goiters are associated with a malfunctioning thyroid? Explain each type. How do the thyroid and the parathyroid work together to control the blood calcium level. How do the adrenal glands respond to stress? What hormones are secreted by the adrenal medulla and what effects do these hormones have? Name the most significant glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid, and discuss the function of each. Explain the symptom of Addison disease and Cushing syndrome. Draw a diagram to explain how insulin and glucagons maintain the blood glucose level. Use your diagram to explain three major symptoms of type I diabetes mellitus. Name the other endocrine glands cited in your reading, and discuss the functions of the hormones they secrete. Also discuss the hormones not produced by endocrine glands. Chapter 43 - Reproductive Systems Learning Outcome 43.a. Knowledge of how Animals Reproduce Contrast asexual reproduction with sexual reproduction, reproduction in water with reproduction on land, and the life history of an insect with that of a bird. Learning Outcome 43.b. Knowledge of the male reproductive system Trace the path of sperm in a human male. What glands contribute fluids to semen? Name the endocrine glands involved in maintaining the sex characteristics of males and the hormones produced by each. Learning Outcome 43.c. Knowledge of the Female Reproductive System Trace the path of an oocyte in a human female. Where do fertilization and implantation occur? Name two functions of the vagina.
16 Describe the external genital organs in females. Discuss the anatomy and physiology of the ovaries. Describe the ovarian cycle and ovulation. Describe the uterine cycle, and relate it to the ovarian cycle. In what way is menstruation prevented if pregnancy occurs? What events occur at fertilization? Name three function of the female sex hormones, aside from their involvement in the uterine cycle. Describe the anatomy and physiology of the breast Learning Outcome 43.d. Knowledge of Control of Reproduction Which means of birth control require surgery, use of hormones, use of barrier methods, or are dependent on none of these? If couples are infertile, what assisted reproductive technologies are available? Learning Outcome 43.e. Knowledge of Sexually Transmitted Diseases List the cause, symptoms, and treatment for the most common types of sexually transmitted diseases.
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water
 Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Performance Objective Critical Attributes Benchmarks/Assessment. Can the student identify structures and functions of whole systems?
 Curriculum Standard One: Organization of the Human Body The student will understand how structure and function compliment each other, the nature of homeostasis, and the language of Anatomy. 1A. The student
Curriculum Standard One: Organization of the Human Body The student will understand how structure and function compliment each other, the nature of homeostasis, and the language of Anatomy. 1A. The student
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review. 3 weeks A&P1, A&P2
 Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
6) An animal with the cross section shown above has a: a) Gastrovascular cavity b) Pseudocoelom c) Coelom
 1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
29-2 Form and Function in Invertebrates Slide 1 of 52
 29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview
 Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
 Warm-up Introduction to the Animal Kingdom What characteristics are common to all animals? Eukaryotic cells NO cell wall Multicellular Cell specialization Heterotrophic Reproduction/Development Categories
Warm-up Introduction to the Animal Kingdom What characteristics are common to all animals? Eukaryotic cells NO cell wall Multicellular Cell specialization Heterotrophic Reproduction/Development Categories
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Elaine N. Marieb Katja N. Hoehn Ninth Edition
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Katja N. Hoehn Ninth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Katja N. Hoehn Ninth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
Homeostasis. Thermoregulation. Osmoregulation. Excretion. how organisms regulate their body temperature
 Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 AP Exam Chapters 44 Osmosregulation and 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the following structural
AP Exam Chapters 44 Osmosregulation and 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the following structural
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
General Anatomy & Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
STRUCTURES OF PLANTS/ANIMALS THAT HELP MAXIMIZE EXCHANGE OF MATERIALS WITH THE CELLS ENVIRONMENT:
 ANIMAL & PLANT PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURES OF PLANTS/ANIMALS THAT HELP MAXIMIZE EXCHANGE OF MATERIALS WITH THE CELLS ENVIRONMENT: 1. root extensions that increase surface area to maximize 2. sacs in the lungs
ANIMAL & PLANT PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURES OF PLANTS/ANIMALS THAT HELP MAXIMIZE EXCHANGE OF MATERIALS WITH THE CELLS ENVIRONMENT: 1. root extensions that increase surface area to maximize 2. sacs in the lungs
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion. Chapter 36
 Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2
 The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION
 1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Test Review: Animal Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Topic 5: Animal Systems Ch.22,23. Nutrition Types p Food Processing p.476
 Topic 5: Animal Systems Ch.22,23 Fig. 21.11 Nutrition Types p. 476 Herbivore Organism that eats plants. Carnivore Organism that consumes meat. Omnivore Organism that eats both plants and animals. Food
Topic 5: Animal Systems Ch.22,23 Fig. 21.11 Nutrition Types p. 476 Herbivore Organism that eats plants. Carnivore Organism that consumes meat. Omnivore Organism that eats both plants and animals. Food
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
How do heterotrophs obtain energy from their environment? How do heterotrophs depend on autotrophs for their energy and matter?
 ecurriculum System emap Licensed to: TRUMBULL PUBLIC SCHOOLS COURSE: Honors Biology CODE: UNIT: Unit 9: Animal and Human Biology MAP LEVEL: CONTACT: Doug Winters; Denise Weed; Marty Schaivone GRADE: TIME
ecurriculum System emap Licensed to: TRUMBULL PUBLIC SCHOOLS COURSE: Honors Biology CODE: UNIT: Unit 9: Animal and Human Biology MAP LEVEL: CONTACT: Doug Winters; Denise Weed; Marty Schaivone GRADE: TIME
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary, digestive, urinary, respiratory and reproductive systems
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2008 UNIT 2 Key Concepts: REVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS A. OVERVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS 1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2008 UNIT 2 Key Concepts: REVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS A. OVERVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS 1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary,
Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) What are the three levels of behavior? Please describe and give an example for each.
 Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) 20.1 1. How does a Biblical worldview and recognition that others are made in the image of God alter how we treat one another? What are the three levels
Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) 20.1 1. How does a Biblical worldview and recognition that others are made in the image of God alter how we treat one another? What are the three levels
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME
 セ @セ@ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION
セ @セ@ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vp5jeap3k4 27 2012 2012 Welcome back! Please write a response to the following: Imagine a time that you have been stressed, please describe the physical sensations that
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vp5jeap3k4 27 2012 2012 Welcome back! Please write a response to the following: Imagine a time that you have been stressed, please describe the physical sensations that
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Unit 3 - Homeostasis in the Human Body
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours. Animal Form. AP Biology Rapid Learning Series
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Osmoregulation. 19 th March 2012
 Osmoregulation 19 th March 2012 1 Outline Body Fluid Regulation Aquatic Animals Marine Bony Fish Freshwater Bony Fish Terrestrial Animals Nitrogenous Waste Products Organs of Excretion Urinary System in
Osmoregulation 19 th March 2012 1 Outline Body Fluid Regulation Aquatic Animals Marine Bony Fish Freshwater Bony Fish Terrestrial Animals Nitrogenous Waste Products Organs of Excretion Urinary System in
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Body Structure and Function
 Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
water balance water nitrogen chapter 42
 water balance chapter 42 water osmoregulation water and dissolved solutes adjusting the composition of internal body fluids in arthropods -- hemolymph in vertebrates -- interstitial fluid transport epithelia
water balance chapter 42 water osmoregulation water and dissolved solutes adjusting the composition of internal body fluids in arthropods -- hemolymph in vertebrates -- interstitial fluid transport epithelia
Chapter 44. Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review. 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,,
 Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III Chapter 41 1. Distinguish between herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. 2. Describe the following feeding mechanisms and give examples of animals that use each:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III Chapter 41 1. Distinguish between herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. 2. Describe the following feeding mechanisms and give examples of animals that use each:
Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I
 Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Chapter 8 Human Organization
 Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Circulatory Systems AP Biology
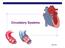 Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
A2 Level Paper 2 and 3 Topics 5-8
 A2 Level Paper 2 and 3 Topics 5-8 Section 3.5: Energy transfers in and between organisms 3.5.1 Photosynthesis 3.5.2 Respiration 3.5.3 Energy and ecosystems 3.5.4 Nutrient cycles Section 3.6 Organisms respond
A2 Level Paper 2 and 3 Topics 5-8 Section 3.5: Energy transfers in and between organisms 3.5.1 Photosynthesis 3.5.2 Respiration 3.5.3 Energy and ecosystems 3.5.4 Nutrient cycles Section 3.6 Organisms respond
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
Chapter 16. Urinary System and Thermoregulation THERMOREGULATION. Homeostasis
 Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
