Content Lecture 1 Lecture 2 - Amino acid Peptide and Polypeptide Lecture 3 Lecture 4
|
|
|
- Lee Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Good Morning Class!
2
3 Content Lecture 1 - Basic knowledge for Biochemistry - Cell: Structure and Function - Water Lecture 2 - Amino acid Peptide and Polypeptide Lecture 3 - Protein Structure and Function Lecture 4 - Metabolism of Protein and Amino acid - Protein structure determination (If time allow)
4 What do you really see here?
5 What are actually there? Composition? Membrane protein? Structural protein? Antibody? Transcription factor? Muscle? Chemicalreaction? Enzyme? Hormone? Receptor? Collagen? Metabolism? Ammonia & Urea?
6 What do you know about Protein and Amino acid? What are amino acids, peptide, polypeptide, protein? Where / How are they from / formed? What are major roles of them? What are their function? What force/bond make them? What are the differences, properties? What happen when them go wrong? When? Why? Help me!! How?
7 Amino acids and proteins Amino acids Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and a side-chain that is specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, serve as the building blocks of proteins. Proteins (3D polypeptide) Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides, which are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds, typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. Amino acid 1 Polypeptides Protein (Triose phosphate isomerase) 2 3
8 How many amino acids are there? n 20 amino acids are commonly found in human, called Proteinogenic or Standard amino acid 9 Essential amino acids 11 Nonessential amino acids What are they? Why?
9 What should you know about amino acid? Catabolism? Chemical bonds? Polarity? MW? n Structures? Electric charges? Optical isomer? Elements? Chiral center? Solubility? Ionization? Essential? Ketogenic or Glucogenic? Acidity? Melting temperature? Name & symbol? Functional groups? How many of them? Zwitterions? Biosynthesis?
10 Tetrahedral Isomerism Stereoisomers / Optical isomers / Enantiomers R R - Two optical isomer D (Right hand) and L (Left hand) amino acid (Except Glycine, R = H) - All proteinogenic amino acids are L-form. - Some D-amino acids can be found in some sea animla such as cone snail) or at cell wall of bacteria
11 Essential amino acids: Amino acids that animal cannot synthesize. Non-essential amino acids: Amino acids that animal can synthesize. Selenocysteine 21 st amino acid Pyrrolysine 22 nd amino acid Essential Nonessential Histidine Alanine Isolucine Arginine* Leucine Asparagine* Lysine Aspartate Methionine Cysteine Phenylalanine Glutamate Threonine Glutamine* Tryptophan Glycine* Valine Proline* Serine* Tyrosine* * Conditionally Essential Essential amino acids differ in animals.
12
13
14 Proteinogenic amino acid is -amino acid. O HO C CH 2 CH 2 β NH 2 CH O C OH Enzymes NH 2 CH 2 CH 2 β CH 2 O C OH Glutamic acid ( -amino acid) Proteinogenic amino acid GABA ( -amino butyric acid) Non Proteinogenic amino acid (neurotransmitter)
15 Properties and specific properties of amino acids depend on R-group Physical properties) - Optical * Light absorption R * Light polarization) NH2 - Structure: Stereo isoform + COOH + R NH2 + COOH + Chemical properties - Buffering because of Zwitter ion behabior NH2 + - Chemical reaction * Disulfide bond formation R * Interaction with Ninhydrin s regent NH2 * Interaction with FDNB (dinitrophynylated amino acid) * Interaction of SH with Hg 2+ of mercaptides R with Ag 2+ of ellman]s reagent Biological properties - Energy storage carbon + R - Intermediate in Nitrogen cycle - Intermediate in biological process NH2 + R NH2 R COOH + + COOH Because some amino acids have aromatic side chain. Because most amino acids have asymmetric carbon. Because sp3 of C is tetrahedral. NH2 R
16 Wiki!
17 pka ph in human body
18 Amino acid at physiological condition (ph 7.4 salt 150 mm) H 2 N : R C H C O OH : : + H 3 N R C H C O - O Non ionized structure Zwitterion Commonly found in human body..? Protonated gain H + Deprotonated lost H +
19 Zwitterionic form of amino acids
20 Resonance at the carboxyl group
21 Buffering ability of Glycine What happen at pka? Henderson Hasselbalch equation ph = pka + log [A - ] [HA] ph > pka : HA --> A - (Deprotonation) ph < pka : A - --> HA (Protonation) ph = pka : HA = A -
22 UV absorption of amino acids
23 UV absorption of aromatic amino acids
24 Fluorescent Characteristics of the Aromatic amino Acids
25 Roles of amino acids and its derivative Properties of amino acids depend on R (side chain) Function of standard amino acid - Building block of protein - Energy source (if necessary) - Precursor for Fatty acids synthesis (when excess) Non protein function of amino acids Derivative of amino acids
26 Non protein function of amino acids Tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. Tyrosine (and its precursor phenylalanine) are precursors of the catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Glycine is a precursor of porphyrins such as heme. Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide. Ornithine and S-adenosylmethionine are precursors of polyamines. Aspartate, glycine, and glutamine are precursors of nucleotides. Phenylalanine is a precursor of various phenylpropanoids, which are important in plant metabolism.
27 Derivative of amino acids β -aminobutyric acid (GABA) Neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It plays a role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. Brain development Beyond the nervous system including but not restrict to the intestine, stomach, pancreas, Fallopian tube, uterus, ovary, testis, kidney, urinary bladder, lung, and liver.
28 Derivative of amino acids Desmosine
29 Derivative of amino acids Thyroxine -alanine Homoserine Ornithine Homocysteine Statine
30 Derivative of amino acids Epinephrine Penicillamine Carnitine 5-hydroxylysine -Aminoadipic acid -carboxyglutamic acid
31 Derivative of amino acids 4-hydroxyproline Dopamine Sarcosine Citrulline Pyrrolysine Histamine
32 Derivative of amino acids 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid Lanthionine: antibiotic Alamethicin: antibiotic
33 Derivative of amino acids Nisin: antibiotic
34 Derivative of amino acids Alamethicin
35 Interesting information about amino acid Post-translation modification - Glucoxylation: Aspartic acid, Serine, Threnine - Carboxylation: Glutamic acid - Hydroxylation: Lysine, Proline - Sulfonation: Tyrosine - Methylation: Lysine - Phosphorylation: Serine, Threonine or Tyrosine residues (mostly in eukaryotes) Aspartic acid, Hstidine residues (mostly in prokaryotes). Proline: protogenic amino acid that side chain form ring with amino group interfere Helix structure (Helix preaker), often form unstructured region of protein involving in protein interaction
36 Peptide bonds, Peptide and Polypeptide Peptide bonds =? Peptide =? Polypeptide =?
37 Peptide bond formation C-terminus N-terminus
38 Peptide bond formation Hydrolysis (Break bond) N-terminus Condensation (bond formation) C-terminus
39 Physical properties of peptide
40 Resonance of peptide bond Behave like double ebon Majority isomer is Trans
41 Peptide and Polypeptide residue
42 Rotatable angle in peptideφ (phi) and Ψ(psi) Φ Ψ Φ Ψ Φ Ψ Φ phi Ψ psi Dihedral angles
43 Rotatable angle in peptideφ (phi) and Ψ(psi) Φ Ψ Φ Ψ Φ Ψ Φ Ψ Φ phi Ψ psi Dihedral angles
44 Ramachandran Plot Φ andψ angle effect conformation of peptide
45 Naming: Peptide Dipeptide Tripeptide R 1 O R O N 2 H CH C N CH C OH H Oligopeptide (> 3, < 50 residues) R 1 O N 2 H CH C N CH C N CH H H R 2 2 O R 3 O C OH N-terminus =? NH 2 -terminus Amino-terminus C-terminus =? COOH-terminus Carboxly-terminus N H R 1 CH O C N H R O R CH C N CH H O C N H R CH O Hexapeptide 6 residues R O R 5 6 C N CH C N CH H H O C
46 3 Types of peptide 1. Digestied protein - Milk - Peptone - Tryptone 2. Ribosomal peptide - Peptide hormone: Insulin, Glucagon, growth hormone, leptin, gastrin, prolactin, etc. - Prohormones
47 3.Non-Ribosomal Peptide Glutathion (tripeptide) -L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine (Antioxidation) Gramicidin S (antibiotic) is produced by Bacillus brevis, is a cyclodecapeptide. cyclo(-val-orn-leu-d-phe-pro-) 2
48 3.Non-Ribosomal Peptide (cont.) Bacitracin A S (antibiotic), is produced by Bacillus subtilis, is a mixture of related cyclic polypeptides produced by organisms of the licheniformis group of Bacillus subtilis var Tracy, isolation of which was first reported in These peptides disrupt both gram positive and gram negative bacteria, by interfering cell wall and phospholipid synthesis.
49 Do you have different view on the same picture?
50
51 NEXT!
52 Next! Protein Structure & Function Composition? Properties? Structure? Function? Interaction?
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Tala Saleh. Tamer Barakat. Diala Abu-Hassan
 13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Amino acids. You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures.
 Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
COO - l. H 3 N C a H l R 1
 COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Lecture 3: 8/24. CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids
 Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture -02 Amino Acids II
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture -02 Amino Acids II Ok, we start off with the discussion on amino acids. (Refer Slide Time: 00:48)
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture -02 Amino Acids II Ok, we start off with the discussion on amino acids. (Refer Slide Time: 00:48)
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية
 Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
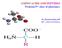 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids
 Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids *Essential and Non-essential * Glucogenic and Ketogenic 1 Essential Amino Acids Of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins 10 of them can be synthesized by
Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids *Essential and Non-essential * Glucogenic and Ketogenic 1 Essential Amino Acids Of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins 10 of them can be synthesized by
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Polypeptides. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Sheet #1 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 01/07/2014. Amino Acids
 Amino Acids Dr s office in physiology department in floor #1 Office hours: every day after 1 *How to study biochemistry for Dr. Mamoun s material: Slides will be sent before the lecture, try to read it
Amino Acids Dr s office in physiology department in floor #1 Office hours: every day after 1 *How to study biochemistry for Dr. Mamoun s material: Slides will be sent before the lecture, try to read it
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
0010 Amino Acids 40 Profile - Plasma
 Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
2018/9/24 AMINO ACIDS. Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information
 2018/9/24 AMINO ACIDS Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information Objectives: What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino
2018/9/24 AMINO ACIDS Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information Objectives: What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
O H 2 N. α H. Chapter 4 - Amino Acids
 hapter 4 - Amino Acids Introduction Several amino acids were produced in the electrical discharge in the reducing, primordial atmosphere that gave rise to the first biomolecules (see chapter 1). The importance
hapter 4 - Amino Acids Introduction Several amino acids were produced in the electrical discharge in the reducing, primordial atmosphere that gave rise to the first biomolecules (see chapter 1). The importance
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22
 Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
0010 Amino Acid Analysis - 40 Plasma
 770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
So where were we? But what does the order mean? OK, so what's a protein? 4/1/11
 So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions. Proteins
 Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks)
 Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Raghad Abu Jebbeh. Amani Nofal. Mamoon Ahram
 ... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Model 2: Aldohexoses, aldopentoses, ketohexoses and ketopentoses
 Model 1: D and L Sugars CHEM1405 Worksheet 13: Sugars and Amino Acids The simplest sugar is glyceraldehyde. This is a chiral molecule and the two enantiomers are shown opposite with wedges and dashes and
Model 1: D and L Sugars CHEM1405 Worksheet 13: Sugars and Amino Acids The simplest sugar is glyceraldehyde. This is a chiral molecule and the two enantiomers are shown opposite with wedges and dashes and
CHAPTER 29 HW: AMINO ACIDS + PROTEINS
 CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins
 UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins Significance of Proteins 1. Keep the cells and tissues growing, renewing and mending 2. Take part in some kinds of important physiological activities 3. Oxidation and supply
UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins Significance of Proteins 1. Keep the cells and tissues growing, renewing and mending 2. Take part in some kinds of important physiological activities 3. Oxidation and supply
Ali Yaghi مها أبو عجمية. Mamon Ahram
 13 Ali Yaghi مها أبو عجمية Mamon Ahram 0 P a g e This sheet is the last sheet we are supposed to study for the midterm exam. Let s begin. Biological significance of amino acids: Amino acids are used for
13 Ali Yaghi مها أبو عجمية Mamon Ahram 0 P a g e This sheet is the last sheet we are supposed to study for the midterm exam. Let s begin. Biological significance of amino acids: Amino acids are used for
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 11 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush July 3 rd 2013 Marah Dannoun Continuation of amino acids applications in life other than tryptophan and tyrosine: 1. Glutamate (glutamic acid): it s modified to give monosodium
11 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush July 3 rd 2013 Marah Dannoun Continuation of amino acids applications in life other than tryptophan and tyrosine: 1. Glutamate (glutamic acid): it s modified to give monosodium
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Protein Structure Klemens Wild, BZH,
 Protein Structure recommended books Proteins protein definition From gr. proteios (superior, erstrangig) 1836 JJ Berzelius Functions: structural, enzymes, muscle, transport immune system, Linear polymer
Protein Structure recommended books Proteins protein definition From gr. proteios (superior, erstrangig) 1836 JJ Berzelius Functions: structural, enzymes, muscle, transport immune system, Linear polymer
Review II: The Molecules of Life
 Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Learning goals: Structure and naming of amino acids Structure and properties of peptides Ionization behavior of amino acids and peptides Methods to characterize
CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Learning goals: Structure and naming of amino acids Structure and properties of peptides Ionization behavior of amino acids and peptides Methods to characterize
BCH 313 Metabolism of Amino acids and Proteins (3 UNITS)
 BCH 313 Metabolism of Amino acids and Proteins (3 UNITS) Proteins are polymers of amino acids, with each amino acid residue joined to its neighbour by a specific type of covalent bond. (The term residue
BCH 313 Metabolism of Amino acids and Proteins (3 UNITS) Proteins are polymers of amino acids, with each amino acid residue joined to its neighbour by a specific type of covalent bond. (The term residue
BCH302 [Practical] 1
![BCH302 [Practical] 1 BCH302 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/78/76808179.jpg) BCH302 [Practical] 1 Amino acids play a central role: i. As building blocks of proteins. ii. As intermediates in metabolism, converted to specialized products. There are 20 natural amino acids that are
BCH302 [Practical] 1 Amino acids play a central role: i. As building blocks of proteins. ii. As intermediates in metabolism, converted to specialized products. There are 20 natural amino acids that are
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics
 Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
AMINO ACIDS. Qualitative Tests
 AMINO ACIDS Qualitative Tests AMINO ACIDS Amino acid play A central role as building block of proteins. Amino acids also converted to specialized products. More than 300 different amino acids have been
AMINO ACIDS Qualitative Tests AMINO ACIDS Amino acid play A central role as building block of proteins. Amino acids also converted to specialized products. More than 300 different amino acids have been
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit
 Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM PHL-285 Biochemistry-2 Mahmoud N. Nagi, Ph.D. Professor of Biochemistry Overview of amino acid metabolism. Classification of amino acids. Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids.
AMINO ACID METABOLISM PHL-285 Biochemistry-2 Mahmoud N. Nagi, Ph.D. Professor of Biochemistry Overview of amino acid metabolism. Classification of amino acids. Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids.
