The implementation of bioavailability in defining PNEC values for trace metals and metalloids in soil
|
|
|
- Dominic Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences Division of Soil and Water Management The implementation of bioavailability in defining PNEC values for trace metals and metalloids in soil Erik Smolders
2 Zn dose (mg/kg)
3 Main message in this talk 1. Metal toxicity depends on chemical properties of the soil. Data and models are needed to express the PNEC as a function of soil properties, i.e. regression slopes correct for differences among soils 2. Metal toxicity in laboratory spiked soils is generally larger than in the field because of lack of full equilibration in the lab (no ageing) and because metal salts induce artefacts that only disappear after sufficient leaching of the soil. A leaching-ageing correction is needed to make toxicity field relevant
4 Defining the thresholds 1.Standard laboratory toxicity tests with metal salt spiked soils Low High 2. Field experiments 3. Gradient studies in contaminated High Low fields relevance reproducibility clarity of causality
5 Most ecotoxicological soil limits (plants, invertebrates and microorganisms) based on standard ecotoxicological tests are within the natural background range HC 5 EU RAR* range of geogenic background Zn 26 mg/kg (added) mg/kg Cu ~30 mg/kg 2-50 mg/kg Ni 10 mg/kg mg/kg Pb 84 mg/kg mg/kg *EU Risk Assessment Report; limits without correction for biovailability NOEC Background Soil Ni (mg/kg)
6 Why total metal concentrations in soil are no robust index for available dose in toxicity tests 1.Speciation and mobility is different in different soils. Example: a soil with almost 100% sand and very little organic matter cannot immobilise metals, toxicity is very high; the opposite is true in a soil with larger % clay and organic matter 2.Short term effects in spiked soils overestimate long-term effects
7 Spiked soils are no good model for field contaminated soils because of differences in metal speciation Example: ageing reactions A. Diffusion in micro pores B. Inclusion in crystal structure of soil minerals C. Occlusion by precipitates D. Precipitation on soil surface E. Occlusion in organic matter
8 Starting idea: test toxicity differences between (1) (2) (3) different spiked soils aged&spiked field contaminated soils and spiked soils field Response % Response freshly spiked spiked and 15 months aged Response spiked soil 1 soil Total soil metal (mg Zn/kg) Total soil metal (mg Ni/kg) Total soil metal (mg Cu/kg) Zn toxicity to plants Ni toxicity to plants Cu toxicity to microbial In 2 different soils with or without ageing activity in spiked or 70 year old contaminated soil Smolders et al. Environ Toxicol Chem, 2009
9 1. Toxicity of metal between different freshly spiked soils
10 150 Response % soil 1 soil Total soil metal (mg Zn/kg)
11 NOEC (added Zn, mg Zn/kg) of spiked soils Soil plant growth nitrification glucose respiration maize residue respiration > > > > > Larger effect of soil type on NOEC than that of species
12 Tomato shoot growth in Cu salt spiked soils y=0.96x+1.47 R 2 =0.75 ecec= cation exchange capacity at soil ph; increases with % clay, %OM and ph
13 Folsomia candida reproduction in Ni spiked soils log ecec (cmol c /kg)
14 Interpretation of effects of soil properties for toxicity of cationic metals, e.g. Cu 2+ soil solids soil solution biota M 3 -OH -OH -OM -OM -OH -OH -OM -OH -OH H + H M 2+ M-DOM HO- HO- MO- HO- MO- HO- fixed labile metal metal Total metal in soil The terrestrial Biotic Ligand Model (t-blm): ion competition effects (nr. 2) are an extension of the free ion activity model (FIAM) t-blm has been used to model data of freshly spiked soils Thakali et al Environ. Sci. Technol.
15 Effects of soil properties on toxicity can be modelled with t-blm, however this model is too complicated to be adopted, therefore toxicity is normalised with the relative effect of soil property on toxicity, the slopes
16 Summary of all slopes for different metals and different species Slope=0.96
17 Using slopes to make limits depending on properties Example: limit is made for a reference soil (average properties in EU), e.g. soil with ecec=10 cmolc/kg Soil ecec ecec NOECmeasured NOEC in reference soil tested reference mg/kg mg/kg soil soil
18 Experimental ageing of spiked soils 2&3. Toxicity of metals as a function of ageing after spiking and difference with field contaminated soils METHODS Cu contaminated site at Hygum (Denmark)
19 Toxicity of Ni to barley root elongation 150 Response freshly spiked spiked and 15 months aged Total soil metal (mg Ni/kg) Rooney et al. unpublished
20 Toxicity of Cu in freshly spiked soils exceeds that in field contaminated soils Field transect Fresh spike
21 150 Response freshly spiked leaching-ageing factor aged Total soil metal (mg Ni/kg)
22 Summary of 110 leaching-ageing factors = EC10 EC10 aged, add freshlyspiked, add Horizontal lines: the empirical ageing factor selected for risk assessment. Example for Cu: factor 2
23 Soil chemical reactions explain the leaching and ageing effects Example: experimental ageing decreases the fraction of added Zn that remains labile as detected by isotope exchange Buekers et al. 2007, Eur. J. Soil Sci.
24 Larger mobility of metals in metal salt s-spiked soils compared to field contaminated soils can be related to difference in soil ph ph in soil solution spiked soils spiked & leached soils field transect soils Total Pb in soil (mg/kg) Source of Pb in the field is often PbO, in the lab it is PbCl 2
25 soil solids soil solution biota M 3 -OH -OH -OM -OM -OH -OH -OM -OH -OH H + H M 2+ M-DOM HO- HO- MO- HO- MO- HO- fixed labile metal metal Total metal in soil
26 Implementation of bioavailability in soil limits
27 Leaching-ageing (L/A) factors Cadmium 1.0 Copper 2.0 Lead 4.2 Zinc 3.0 Nickel 1 3 (increasing with ph) Cobalt (increasing with ph) Example for Cu Species Soil NOECadded NOECadded, aged mg Cu/kg mg Cu/kg 1 A B B
28 C b =background Cu in soil Example for Cu Spec. Soil NOEC added NOEC added,aged C b NOEC total,aged mg Cu/kg mg Cu/kg 1 A B B
29 NOEC reference = NOEC test abioticfactor abioticfactor reference test slope Reference: scenario for which threshold values must be derived Test: abiotic factors of the soil in which the NOEC or EC10 was derived Slope: slope of regression equation between log ECx and log soil properties
30
31 Species sensitivity distribution 100 Frequency of NOEC/EC10 values (%) not normalised normalised to ecec=5 normalised to ecec=35 PNEC Soil total Ni concentration (mg/kg) PNEC (Predicted No Effect Concentration) = 5 th percentile/ assessment factor
32 The biovailability corrections in the EU risk assessments Metals Data normalized with Leaching-Aging factor (L/A factor) Zn 2+ ecec, background Zn, 3 ph Cu 2+ ecec, %clay, %OC, 2 ph Ni 2+ ecec 1-3 (increasing as a function of ph) Cd
33 Zn Predicted No Effect Concentration PNEC (mg total metal/kg dry soil) Median sensitive soil * Highly sensitive soil* 24 (added) 28 (total) 94 (added) 111 (total) Weakly sensitive soil * 246 (added) 286 (total) Cu Ni Cd Soil properties:cec: 4, 15, and 35 cmol c /kg; ph: 4.5, 5.5, 7.0; %OC 1.0, 2.9, and 12%, %clay 5, 15, and 30% background Zn 8, 51, and 155 mg Zn/kg.
34 PNEC calculator tool Based on all data and procedures of the EU RAR for Cd, Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn (so far) Calculates soil limits as a function of soil properties (ph, %OM, % clay, ) Microsoft Excel format Available at koen.oorts@arche-consulting.be
35 Main message in this talk 1. Metal toxicity depends on chemical properties of the soil. Data and models are needed to express the PNEC as a function of soil properties, i.e. regression slopes correct for differences among soils 2. Metal toxicity in laboratory spiked soils is generally larger than in the field because of lack of full equilibration in the lab (no ageing) and because metal salts induce artefacts that only disappear after sufficient leaching of the soil. A leaching-ageing correction is needed to make toxicity field-relevant
Application of improved scientific approaches in support of risk assessment within the European REACH and Biocides Regulations: A case study on metals
 Application of improved scientific approaches in support of risk assessment within the European REACH and Biocides Regulations: A case study on metals Koen Oorts, Katrien Delbeke, Chris Schlekat, Jasim
Application of improved scientific approaches in support of risk assessment within the European REACH and Biocides Regulations: A case study on metals Koen Oorts, Katrien Delbeke, Chris Schlekat, Jasim
Bioavailability Issues for Soil Organisms
 2015/SOM3/CD/WKSP/005 Bioavailability Issues for Soil Organisms Submitted by: University of Adelaide Workshop on Metals Risk Assessment Cebu, Philippines 28-29 August 2015 Bioavailability Issues for Soil
2015/SOM3/CD/WKSP/005 Bioavailability Issues for Soil Organisms Submitted by: University of Adelaide Workshop on Metals Risk Assessment Cebu, Philippines 28-29 August 2015 Bioavailability Issues for Soil
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties
 Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
ZINC CHLORIDE SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT
 ZINC CHLORIDE CAS No: 7646-85-7 EINECS No: 231-592-0 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared by the Ministry of Housing,
ZINC CHLORIDE CAS No: 7646-85-7 EINECS No: 231-592-0 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared by the Ministry of Housing,
ZINC SULPHATE SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT
 ZINC SULPHATE CAS No: 7733-02-0 EINECS No: 231-793-3 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared by the Ministry of Housing,
ZINC SULPHATE CAS No: 7733-02-0 EINECS No: 231-793-3 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared by the Ministry of Housing,
Inorganic Contaminants
 Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Ion-exchange technique (IET) for measuring Cu 2+, Ni 2+ and Zn 2+ activities in soils contaminated with metal mixtures
 , 14, 55 63 Supplementary material Ion-exchange technique (IET) for measuring Cu 2+, Ni 2+ and Zn 2+ activities in soils contaminated with metal mixtures D. M. Schwertfeger A,B and W. H. Hendershot A,C
, 14, 55 63 Supplementary material Ion-exchange technique (IET) for measuring Cu 2+, Ni 2+ and Zn 2+ activities in soils contaminated with metal mixtures D. M. Schwertfeger A,B and W. H. Hendershot A,C
Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
Soil Organic Matter. Unit 2. Forms of Soil Organic Matter: OM OC x (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor)
 Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
IBRACS. Integrating Bioavailability in Risk Assessment of Contaminated Soils: opportunities and feasibilities
 IBRACS Integrating Bioavailability in Risk Assessment of Contaminated Soils: opportunities and feasibilities Period: Oct 2011-Sep 2014; Total founding: 654 236 National founders: Formas & SGI (Sweden),
IBRACS Integrating Bioavailability in Risk Assessment of Contaminated Soils: opportunities and feasibilities Period: Oct 2011-Sep 2014; Total founding: 654 236 National founders: Formas & SGI (Sweden),
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SOIL PROPERTIES AND TOXICITY OF COPPER AND NICKEL TO BOK CHOY AND TOMATO IN CHINESE SOILS
 Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 2372 2378, 213 # 213 SETAC Printed in the USA RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SOIL PROPERTIES AND TOXICITY OF COPPER AND NICKEL TO BOK CHOY AND TOMATO
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 2372 2378, 213 # 213 SETAC Printed in the USA RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SOIL PROPERTIES AND TOXICITY OF COPPER AND NICKEL TO BOK CHOY AND TOMATO
Specific aspects for PNEC derivation for metals. P. Van Sprang, F. Verdonck, M. Vangheluwe
 Specific aspects for PNEC derivation for metals P. Van Sprang, F. Verdonck, M. Vangheluwe 1 2 Outline PNEC derivation Uncertainty management 3 PNEC DERIVATION 4 Effects assessment general framework PNEC
Specific aspects for PNEC derivation for metals P. Van Sprang, F. Verdonck, M. Vangheluwe 1 2 Outline PNEC derivation Uncertainty management 3 PNEC DERIVATION 4 Effects assessment general framework PNEC
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Investigating the versatility of a primary fish gill cell culture system for environmental monitoring
 Investigating the versatility of a primary fish gill cell culture system for environmental monitoring Matteo Minghetti, Sabine Schnell, Christer Hogstrand, Nic Bury Fish Gill In vitro Cell culture System
Investigating the versatility of a primary fish gill cell culture system for environmental monitoring Matteo Minghetti, Sabine Schnell, Christer Hogstrand, Nic Bury Fish Gill In vitro Cell culture System
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001
 Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Assessment of surface water monitoring data: Application of biotic ligand modelbased software tools to address the bioavailability of metals
 Assessment of surface water monitoring data: Application of biotic ligand modelbased software tools to address the bioavailability of metals Heinz Rüdel Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied
Assessment of surface water monitoring data: Application of biotic ligand modelbased software tools to address the bioavailability of metals Heinz Rüdel Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied
Postprint. Copyright 2007 NERC. This version available at
 Postprint de Vries, Wim; Lofts, Steve; Tipping, Ed; Meili, Markus; Groenenberg, Jan E.; Schütze, Gudrun. 2007 Impact of soil properties on critical concentrations of cadmium, lead, copper, zinc and mercury
Postprint de Vries, Wim; Lofts, Steve; Tipping, Ed; Meili, Markus; Groenenberg, Jan E.; Schütze, Gudrun. 2007 Impact of soil properties on critical concentrations of cadmium, lead, copper, zinc and mercury
Matching analytical methods with EQS values for water and sediment
 Matching analytical methods with EQS values for water and sediment Frank Van Assche International Zinc Association 168 Avenue de Tervueren 1150 Brussels contents Monitoring metals in water total versus
Matching analytical methods with EQS values for water and sediment Frank Van Assche International Zinc Association 168 Avenue de Tervueren 1150 Brussels contents Monitoring metals in water total versus
Solubility and toxicity of antimony trioxide
 Solubility and toxicity of antimony trioxide (Sb 2 O 3 ) in soil Koen Oorts, Erik Smolders *, Fien Degryse, Jurgen Buekers, Gabriel Gascó, Geert Cornelis and Jelle Mertens SUPPORTING INFORMATION Page S3:
Solubility and toxicity of antimony trioxide (Sb 2 O 3 ) in soil Koen Oorts, Erik Smolders *, Fien Degryse, Jurgen Buekers, Gabriel Gascó, Geert Cornelis and Jelle Mertens SUPPORTING INFORMATION Page S3:
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Environmental Risks of Cadmium The European Perspective
 Environmental Risks of Cadmium The European Perspective Erik Smolders Laboratory of Soil and Water Management, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium European Regulations on environmental Cd Cd limits
Environmental Risks of Cadmium The European Perspective Erik Smolders Laboratory of Soil and Water Management, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium European Regulations on environmental Cd Cd limits
Need for Specific approaches for Environmental Hazard and Exposure assessments for metals and inorganics
 Need for Specific approaches for Environmental Hazard and Exposure assessments for metals and inorganics H. Waeterschoot (Eurometaux-ICMM) (with contributions from C. Schlekat (NIPERA)) Paris, September
Need for Specific approaches for Environmental Hazard and Exposure assessments for metals and inorganics H. Waeterschoot (Eurometaux-ICMM) (with contributions from C. Schlekat (NIPERA)) Paris, September
ZINC DISTEARATE SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT
 ZINC DISTEARATE CAS No: 557-05-1 & 91051-01-3 EINECS No: 209-151-9 & 293-049-4 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared
ZINC DISTEARATE CAS No: 557-05-1 & 91051-01-3 EINECS No: 209-151-9 & 293-049-4 SUMMARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PART I - ENVIRONMENT Final report, May 2008 The Netherlands This document has been prepared
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in
 Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Nutrient level (EC) in a pot is like a bank
 Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Appendix C Metal Speciation
 Appendix C Metal Speciation GHD Report for Vista Gold Australia - Mt Todd Gold Mine, 43/22187 SPECIATION MODELLING OF METALS IN SURFACE WATERS OF THE EDITH RIVER DURING WET SEASON DISCHARGE OF WASTEWATER
Appendix C Metal Speciation GHD Report for Vista Gold Australia - Mt Todd Gold Mine, 43/22187 SPECIATION MODELLING OF METALS IN SURFACE WATERS OF THE EDITH RIVER DURING WET SEASON DISCHARGE OF WASTEWATER
Models for the field-based toxicity of copper and zinc salts to wheat in eleven Australian soils and comparison to laboratorybased
 0 Models for the field-based toxicity of copper and zinc salts to wheat in eleven Australian soils and comparison to laboratorybased models Michael StJ Warne a, Diane Heemsbergen a, Mike McLaughlin a,
0 Models for the field-based toxicity of copper and zinc salts to wheat in eleven Australian soils and comparison to laboratorybased models Michael StJ Warne a, Diane Heemsbergen a, Mike McLaughlin a,
DISCREPANCY OF THE MICROBIAL RESPONSE TO ELEVATED COPPER BETWEEN FRESHLY SPIKED AND LONG-TERM CONTAMINATED SOILS
 Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 845 853, 2006 2006 SETAC Printed in the USA 0730-7268/06 $12.00.00 DISCREPANCY OF THE MICROBIAL RESPONSE TO ELEVATED COPPER BETWEEN FRESHLY SPIKED
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 845 853, 2006 2006 SETAC Printed in the USA 0730-7268/06 $12.00.00 DISCREPANCY OF THE MICROBIAL RESPONSE TO ELEVATED COPPER BETWEEN FRESHLY SPIKED
Incorporation of bio-availability for the freshwater compartment Cu-example
 Incorporation of bio-availability for the freshwater compartment Cu-example OECD Meeting, 7-8 September 2011 K Delbeke Aim Importance of bioavailability for copper effects to freshwater organisms BLM developments
Incorporation of bio-availability for the freshwater compartment Cu-example OECD Meeting, 7-8 September 2011 K Delbeke Aim Importance of bioavailability for copper effects to freshwater organisms BLM developments
REPORT SNO PNEC for metals in the marine environment derived from species sensitivity distributions
 REPORT SNO 5336-2007 PNEC for metals in the marine environment derived from species sensitivity distributions Norwegian Institute for Water Research REPORT an institute in the Environmental Research Alliance
REPORT SNO 5336-2007 PNEC for metals in the marine environment derived from species sensitivity distributions Norwegian Institute for Water Research REPORT an institute in the Environmental Research Alliance
Soil acidity. Kiyoshi Tsutsuki
 Soil acidity Kiyoshi Tsutsuki http://timetraveler.html.xdomain.jp H = log (H+) oriba Home page ph and crop growth (vegetables and root crops) Low ph tolerance strong (4.0~5.0) A little strong (4.5~6.0)
Soil acidity Kiyoshi Tsutsuki http://timetraveler.html.xdomain.jp H = log (H+) oriba Home page ph and crop growth (vegetables and root crops) Low ph tolerance strong (4.0~5.0) A little strong (4.5~6.0)
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 DATE REPORTED: 11/04/2014 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.52 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.48 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.76 1.63 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.08 0.17 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
DATE REPORTED: 11/04/2014 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.52 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.48 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.76 1.63 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.08 0.17 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 DATE REPORTED: 09/14/2015 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.88 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.12 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.87 1.88 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.10 0.21 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
DATE REPORTED: 09/14/2015 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.88 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.12 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.87 1.88 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.10 0.21 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
How to assess effects data sets for metals hazard identification and risk characterization.
 How to assess effects data sets for metals hazard identification and risk characterization. OECD Meeting, 7-8 September 2011 K Delbeke Aims Metal characteristics, critical to assessing environmental effects
How to assess effects data sets for metals hazard identification and risk characterization. OECD Meeting, 7-8 September 2011 K Delbeke Aims Metal characteristics, critical to assessing environmental effects
Effects of Biochars on ecotoxicological indicators
 Effects of Biochars on ecotoxicological indicators Biochars characteristics Feedstock and origins: Biochar Code Feedstocks Production Scale Pyrolysis Temperature BC1 R1501017 PmW-BC Poultry manure and
Effects of Biochars on ecotoxicological indicators Biochars characteristics Feedstock and origins: Biochar Code Feedstocks Production Scale Pyrolysis Temperature BC1 R1501017 PmW-BC Poultry manure and
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Table S1. Analytical methods used to determine selected characteristics of the three reference soils. Property Detail Reference ph 1:5 (w/v) soil suspension using 0.01 M CaCl2.
Supplemental Information Table S1. Analytical methods used to determine selected characteristics of the three reference soils. Property Detail Reference ph 1:5 (w/v) soil suspension using 0.01 M CaCl2.
Cd, Pb and Zn oral bioaccessibility in urban soils in the vicinity of two lead and zinc smelters
 Cd, Pb and Zn oral bioaccessibility in urban soils in the vicinity of two lead and zinc smelters Roussel H., Waterlot C., Pruvot C., Douay F. Laboratory of Soils and Environment, Institut Supérieur d Agriculture,
Cd, Pb and Zn oral bioaccessibility in urban soils in the vicinity of two lead and zinc smelters Roussel H., Waterlot C., Pruvot C., Douay F. Laboratory of Soils and Environment, Institut Supérieur d Agriculture,
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Analysis Report For: Copy To: Merlyn Akhtar Ulster County Resource Recovery Agency LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C09238 01/13/2017 Finished Compost Static
Analysis Report For: Copy To: Merlyn Akhtar Ulster County Resource Recovery Agency LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C09238 01/13/2017 Finished Compost Static
Molybdenum-Enriched Compound Fertilisers in Acidic and Alkaline Soils
 Reactions of Fluid and Granular Copper and Molybdenum-Enriched Compound Fertilisers in Acidic and Alkaline Soils Ganga Hettiarachchi hi 1, Mike McLaughlin 12 1,2, Kirk Scheckel 3, David Chittleborough
Reactions of Fluid and Granular Copper and Molybdenum-Enriched Compound Fertilisers in Acidic and Alkaline Soils Ganga Hettiarachchi hi 1, Mike McLaughlin 12 1,2, Kirk Scheckel 3, David Chittleborough
Discuss the importance of healthy soils Soil properties, physical, chemical and biological that one can manage for soil health How organics play a
 Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Lecture 14. More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils
 Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Analysis Report For: Copy To: Greg Gelewski OCRRA LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY Jamesville 1/2" C06659 9/27/2013 Screened Compost Finished Compost Windrow
Analysis Report For: Copy To: Greg Gelewski OCRRA LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY Jamesville 1/2" C06659 9/27/2013 Screened Compost Finished Compost Windrow
Interpreting Soils Report. Beyond N P K
 Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.37 - SOIL.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
!! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
The importance of dissolved organic carbon in the assessment of environmental quality standard compliance for copper and zinc
 The importance of dissolved organic carbon in the assessment of environmental quality standard compliance for copper and zinc by Water Framework Directive - United Kingdom Technical Advisory Group (WFD-UKTAG)
The importance of dissolved organic carbon in the assessment of environmental quality standard compliance for copper and zinc by Water Framework Directive - United Kingdom Technical Advisory Group (WFD-UKTAG)
DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS
 DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin - Madison Basic concepts of soil fertility How plants
DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin - Madison Basic concepts of soil fertility How plants
AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged.
 AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged. Criteria for Essential Elements A. B. C. Essential Elements (17): Nonmineral (3): Mineral (14):
AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged. Criteria for Essential Elements A. B. C. Essential Elements (17): Nonmineral (3): Mineral (14):
Transition Metals Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Hg, and Pb
 Transition Metals Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Hg, and Pb 4 Mycorrhizal fungi acquire essential macronutrients, such as phosphorus (Burgess et al. 1993), and are efficient at taking up and accumulating microelements
Transition Metals Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Hg, and Pb 4 Mycorrhizal fungi acquire essential macronutrients, such as phosphorus (Burgess et al. 1993), and are efficient at taking up and accumulating microelements
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS
 Originators of Your Crop's Dieticians 4915 West Monte Cristo Road Edinburg, Texas 78541 Telephone: 956-383-0739 Facsimile: 956-383-0730 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS TPSL 's Daubeny Carbon
Originators of Your Crop's Dieticians 4915 West Monte Cristo Road Edinburg, Texas 78541 Telephone: 956-383-0739 Facsimile: 956-383-0730 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS TPSL 's Daubeny Carbon
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON TOXICITY, ECOTOXICITY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (CSTEE)
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C Public Health and Risk Assessment C7 Risk assessment Brussels, C7/VR/csteeop/Cr/100903 D(03) SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON TOXICITY,
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C Public Health and Risk Assessment C7 Risk assessment Brussels, C7/VR/csteeop/Cr/100903 D(03) SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON TOXICITY,
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Analysis Report For: Copy To: Loren Martin Terra-Gro Inc LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C08481 032016 Proselect 4/7/2016 GWD Finished Compost Windrow Lancaster
Analysis Report For: Copy To: Loren Martin Terra-Gro Inc LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C08481 032016 Proselect 4/7/2016 GWD Finished Compost Windrow Lancaster
MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES
 MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES MGGA Convention Great Falls December 1, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Clickers are better than cell phones because: A. You don t listen
MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES MGGA Convention Great Falls December 1, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Clickers are better than cell phones because: A. You don t listen
Welcome. Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories
 Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Bob Watts LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: C09017 10/4/2016 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids 56.6 % Organic Matter Total
Bob Watts LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: C09017 10/4/2016 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids 56.6 % Organic Matter Total
The European Union Risk Assessment on Zinc and Zinc Compounds: The Process and the Facts
 Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management Volume 1, Number 4 pp. 301 319 Ó 2005 SETAC 301 The European Union Risk Assessment on Zinc and Zinc Compounds: The Process and the Facts Charles W.M.
Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management Volume 1, Number 4 pp. 301 319 Ó 2005 SETAC 301 The European Union Risk Assessment on Zinc and Zinc Compounds: The Process and the Facts Charles W.M.
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Analysis Report For: Erth Products Copy To: Mandy Walls 561 Dogwood Trail Tyrone GA 30290 LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C07987 Jul 2015 STA 7/30/2015
Analysis Report For: Erth Products Copy To: Mandy Walls 561 Dogwood Trail Tyrone GA 30290 LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C07987 Jul 2015 STA 7/30/2015
Mineral Nutrition. Criteria for Essentiality
 Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
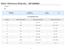 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Essential Elements. Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics
 Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
BIOTIC LIGAND MODELS (BLMS) FOR ASSESSING BIOAVAILABILITY OF SELECTED METALS IN FRESHWATERS: CURRENT VALIDATION BOUNDARIES AND ON-GOING INITIATIVES
 BIOTIC LIGAND MODELS (BLMS) FOR ASSESSING BIOAVAILABILITY OF SELECTED METALS IN FRESHWATERS: CURRENT VALIDATION BOUNDARIES AND ON-GOING INITIATIVES Biotic Ligand Models (BLMs) for predicting the chronic
BIOTIC LIGAND MODELS (BLMS) FOR ASSESSING BIOAVAILABILITY OF SELECTED METALS IN FRESHWATERS: CURRENT VALIDATION BOUNDARIES AND ON-GOING INITIATIVES Biotic Ligand Models (BLMs) for predicting the chronic
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Immobilizing Arsenic in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates
 Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article
 Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development
 Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Approximating Solubility/Availability & Communicating Information
 Approximating Solubility/Availability & Communicating Information Wayne P. Robarge Professor (Emeritus) Soil Physical Chemistry Department of Crop and Soil Sciences NC State University, Raleigh, NC Presented
Approximating Solubility/Availability & Communicating Information Wayne P. Robarge Professor (Emeritus) Soil Physical Chemistry Department of Crop and Soil Sciences NC State University, Raleigh, NC Presented
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY
 NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
Importance of micronutrients in crop nutrition
 Importance of micronutrients in crop nutrition R.W. Bell, B. Dell, and L. Huang We thank Prof. B. Rerkasem, R. Brennan, ACIAR, ARC Outline Essential elements Classical approach for assessing micronutrient
Importance of micronutrients in crop nutrition R.W. Bell, B. Dell, and L. Huang We thank Prof. B. Rerkasem, R. Brennan, ACIAR, ARC Outline Essential elements Classical approach for assessing micronutrient
WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES. Certificate of Analysis. International Soil-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL
 WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES Certificate of Analysis International Soil-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL ISE sample 946 $Dd General Information Certificate of Analysis
WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES Certificate of Analysis International Soil-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL ISE sample 946 $Dd General Information Certificate of Analysis
Greenhouse Horticulture
 Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Figure 1. Location of 43 benchmark sites across Alberta.
 1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS. Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions
 COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions are diluted water solutions containing one or more inorganic
COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions are diluted water solutions containing one or more inorganic
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide. Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University
 Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
DEVELOPMENT AND FIELD VALIDATION OF A BIOTIC LIGAND MODEL PREDICTING CHRONIC COPPER TOXICITY TO DAPHNIA MAGNA
 Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 165 175, 2004 2004 SETAC Printed in the USA 070-7268/04 $12.00.00 DEVELOPMENT AND FIELD VALIDATION OF A BIOTIC LIGAND MODEL PREDICTING CHRONIC
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 165 175, 2004 2004 SETAC Printed in the USA 070-7268/04 $12.00.00 DEVELOPMENT AND FIELD VALIDATION OF A BIOTIC LIGAND MODEL PREDICTING CHRONIC
The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai
 The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai Email: p_natthawoot@yahoo.com (advisor) woranan_n@yahoo.com Phytoremediation
The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai Email: p_natthawoot@yahoo.com (advisor) woranan_n@yahoo.com Phytoremediation
FACTORS AFFECTING WATER QUALITY
 TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
Salts and Chlorides Remediation
 Salts and Chlorides Remediation The remediation of salts and chlorides is not a process of consumption but rather a process of binding, buffering, immobilization, detoxification, filtering, or conversion
Salts and Chlorides Remediation The remediation of salts and chlorides is not a process of consumption but rather a process of binding, buffering, immobilization, detoxification, filtering, or conversion
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Soils and Soil Fertility Management
 Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Applying Biotic Ligand Models and Bayesian Techniques: Ecological Risk Assessment of Copper and Nickel in Tokyo Rivers
 Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management Volume 9, Number 1 pp. 63 69 ß 2012 SETAC 63 Applying Biotic Ligand Models and Bayesian Techniques: Ecological Risk Assessment of Copper and Nickel in
Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management Volume 9, Number 1 pp. 63 69 ß 2012 SETAC 63 Applying Biotic Ligand Models and Bayesian Techniques: Ecological Risk Assessment of Copper and Nickel in
Acad. M. Popov Institute of Plant Physiology, Acad. G. Bonchev Str., Bl. 21, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria 2
 12 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 12 23 GROWTH, YIELD, LEAD, ZINC AND CADMIUM CONTENT OF RADISH, PEA AND PEPPER PLANTS AS INFLUENCED BY LEVEL OF SINGLE AND MULTIPLE CONTAMINATION OF SOIL. III.
12 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 12 23 GROWTH, YIELD, LEAD, ZINC AND CADMIUM CONTENT OF RADISH, PEA AND PEPPER PLANTS AS INFLUENCED BY LEVEL OF SINGLE AND MULTIPLE CONTAMINATION OF SOIL. III.
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ
 Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ Micronutrients ARE NOT miracle workers Follow the season Mg/Micros Assess N (& S) Look at P (& K) Get the soil right Clearly
Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ Micronutrients ARE NOT miracle workers Follow the season Mg/Micros Assess N (& S) Look at P (& K) Get the soil right Clearly
Fertilization Programming
 Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Micronutrient Management. Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management
 Micronutrient Management Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Essential Nutrients Thirteen essential nutrients Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur Iron, manganese,
Micronutrient Management Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Essential Nutrients Thirteen essential nutrients Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur Iron, manganese,
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations...
 Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Trace Elements in Manure
 Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES. Certificate of Analysis. International Plant-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL
 WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES Certificate of Analysis International Plant-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL IPE sample 561 $Dd General Information Certificate of Analysis
WAGENINGEN EVALUATING PROGRAMS FOR ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES Certificate of Analysis International Plant-Analytical Exchange REFERENCE MATERIAL IPE sample 561 $Dd General Information Certificate of Analysis
Nutrient Sources. Third International Conference on EEF SOLUBILITY VS. AVAILABILITY. Latin America-Everris. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil March 12-13, 2013
 Third International Conference on EEF Rio de Janeiro, Brazil March 12-13, 2013 The Potential Benefits for Controlled Release Phosphorus and Potassium in Specialty Agriculture A. Amilcar Ubiera, PhD Latin
Third International Conference on EEF Rio de Janeiro, Brazil March 12-13, 2013 The Potential Benefits for Controlled Release Phosphorus and Potassium in Specialty Agriculture A. Amilcar Ubiera, PhD Latin
FACT SHEET. Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation
 Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
REMEDIATE. Cipullo S., Negrin I., Claveau L., Snapir B., Tardif, S., Pulleyblank C., Prpich G., Campo P., Coulon F.
 REMEDIATE Linking bioavailability and toxicity changes of complex chemicals mixture to support decision making for remediation endpoint of contaminated soils Cipullo S., Negrin I., Claveau L., Snapir B.,
REMEDIATE Linking bioavailability and toxicity changes of complex chemicals mixture to support decision making for remediation endpoint of contaminated soils Cipullo S., Negrin I., Claveau L., Snapir B.,
Zinc isotopes in the Seine River water, France: a probe of. anthropogenic contamination
 Zinc isotopes in the Seine River water, France: a probe of anthropogenic contamination Jiubin Chen*, Jérôme Gaillardet and Pascale Louvat Equipe Géochimie et Cosmochimie, Institut de Physique du Globe
Zinc isotopes in the Seine River water, France: a probe of anthropogenic contamination Jiubin Chen*, Jérôme Gaillardet and Pascale Louvat Equipe Géochimie et Cosmochimie, Institut de Physique du Globe
PT-2017-NRL-TE-FASFC Determination of As, Asi, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in chocolate
 CODA-CERVA Belgian National Reference Laboratory for Trace Elements in Food and Feed PT-2017-NRL-TE-FASFC Determination of As, Asi, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in chocolate Final report on the 2017 Proficiency Test
CODA-CERVA Belgian National Reference Laboratory for Trace Elements in Food and Feed PT-2017-NRL-TE-FASFC Determination of As, Asi, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in chocolate Final report on the 2017 Proficiency Test
Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium
 MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
