|
|
|
- Oliver Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
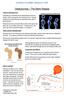
2 Osteoporosis Osteoporosis occurs when bones become thin and fragile. The result is that they break easily, even following a minor bump or fall from standing height. Worldwide, one in three women and one in five men over the age of 50 will suffer a fragility fracture (broken bone) due to osteoporosis. Although fractures can occur in any part of the body, they most commonly affect the wrists, spine and hips. Fractures due to osteoporosis are a major cause of pain, long-term disability and loss of independence among older adults, and can even result in premature death. ouch! Normal bone Osteoporotic bone
3 Setting the foundation for bone health throughout life They say you are what you eat and that s very true for your bones too. Bones, formed of living tissue, need the right nutrients to stay strong and healthy. A balanced diet, combined with regular exercise, will help to optimize your bone health at all ages and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. The size and the amount of bone contained in your skeleton changes significantly throughout life. Likewise, as you age, the specific nutritional needs of your skeleton change too. The goal of a bone-healthy diet is to help Children & Adolescents BUILD maximum peak bone mass Adults MAINTAIN healthy bones & avoid premature bone loss Seniors SUSTAIN mobility and independence
4 What are the key bone-healthy nutrients? 1. CALCIUM Calcium is a major building block of our skeleton, with 99% of the 1 kg of calcium found in the average adult body residing in our bones. Bone acts as a reservoir for maintaining calcium levels in the blood, which is essential for healthy nerve and muscle function. Calcium is a key nutrient for all age groups but the amount needed varies at different stages of life. Demands are particularly high during the rapid period of growth in teenagers. Dairy foods (milk, yoghurt, cheeses) are the most readily available sources of calcium in the diet, they also contain other important nutrients for growth. Additional food sources include certain green vegetables, whole canned fish with soft, edible bones such as sardines or pilchards, nuts and tofu set with calcium. Selection of calcium-rich foods
5 Food Serving size Calcium content 1. Milk 200 ml 240 mg 2. Yoghurt, natural 150 g 207 mg 3. Cheese, hard 30 g 240 mg 4. Broccoli (raw) 120 g 112 mg 5. Figs, dried 60 g 96 mg 6. Almonds 30 g 75 mg 7. Tofu, calcium-set 120 g 126 mg
6 2. VITAMIN D Vitamin D plays two key roles in the development and maintenance of healthy bones. It assists calcium absorption from food in the intestine and ensures correct renewal and mineralization of bone. Vitamin D is made in the skin when it is exposed to UV-B rays in sunlight. Due to our increasingly indoor lifestyles, low levels of vitamin D have become a worldwide problem as they can jeopardize bone and muscle health. Very few foods are naturally rich in vitamin D. As a result, in some countries certain food and drinks such as margarine, breakfast cereals and orange juice are fortified with vitamin D. Food Wild salmon Farmed salmon Sardines, canned Tuna, canned Shitake mushrooms, fresh Shitake mushrooms, sun-dried Egg yolk Vitamin D content* IU IU IU 236 IU 100 IU 1600 IU 20 IU per yolk *per 100g unless otherwise stated IU: International Unit
7 How much sun exposure do you need? Sunlight is not always a reliable source of vitamin D. The season and latitude, use of sunscreen, city smog, skin pigmentation, and a person s age are just some of the factors that will affect how much vitamin D your skin can produce through sunlight. Generally, you should try to get minutes of sun exposure to your bare skin (face, hands and arms) outside peak sunlight hours (before 10 AM and after 2 PM) daily without sunscreen and taking care not to burn. Selection of foods containing Vitamin D
8 3. PROTEIN Protein provides the body with a source of essential amino acids necessary for health. Low protein intake is detrimental both for the building of peak bone mass during childhood and adolescence (affecting skeletal growth) and for the preservation of bone mass with ageing. Protein undernutrition also leads to reduced muscle mass and strength in seniors, which is a risk factor for falls. Protein-rich foods include dairy products, meat, fish, poultry, lentils, beans and nuts. The acid-load claim Many people have been scared by claims that a high protein intake, including drinking milk, may cause increased calcium loss via the kidneys and therefore be bad for bone health. This claim has been disproved in many studies. Both plant and animal sources of protein promote strong bones and muscles. Milk and dairy products, as part of a balanced diet, are excellent sources of calcium, protein and other nutrients.
9 Micronutrients that support bone health Micronutrients are required in trace amounts for normal growth and development. Ongoing research suggests that several, listed below, are important to bone health: Vitamin K Found in leafy green vegetables, spinach, cabbage and kale, liver, some fermented cheeses, and dried fruit TIP Snack on prunes, a high source of vitamin K Magnesium Found in green vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, unrefined grains, fish and dried fruit TIP 50 g of almonds = up to 40% of your daily need Zinc Found in lean red meat, poultry, whole grain cereals, pulses, legumes and dried fruit TIP Beans and chickpeas are good plant sources Carotenoids precursors to vitamin A Found in many vegetables, including in leafy green vegetables, carrots and red peppers TIP 50 g of raw carrots meet your daily need
10 Building bones early in life Bone health starts early in life in fact it begins at the foetal stage, when good maternal nutrition helps optimize the development of the baby s skeleton. Childhood and adolescence is a critical time for bone building. It is during this period that both the size and strength of our bones increases significantly. Approximately half of our bone mass is accumulated during adolescence, with a quarter being built up during the two-year period of fastest growth. The process continues until our mid 20s. Although genetics will determine up to 80% of the variability in individual peak bone mass, factors such as nutritional intake and physical activity will help a child achieve optimal bone strength. This is beneficial in late adulthood as there is more bone in reserve
11 from which to draw; unlike in their younger years adults cannot replace bone tissue as quickly as they lose it. It is believed that a 10% increase in peak bone mineral density (BMD) one measure of bone strength could delay the development of osteoporosis by 13 years. Calcium and proteinrich nutrition boosts bone development Young people aged between 9 18 years have higher calcium and protein requirements, with the peak age for bone building being 14 years in boys and 12.5 years in girls. Milk and other dairy products provide up to 80% of dietary calcium intake for children from the second year of life onwards. Although calcium is a vital nutrient for bone development during this stage of life, children are consuming less milk than they did 10 years ago and are instead turning to sweetened beverages. This trend needs to be reversed and children encouraged to drink more milk. Young people also need enough protein to achieve their genetic potential for peak bone mass. Studies have shown a positive link between children who were given extra servings of milk in their diets which is high in protein and increases in a growth factor that enhances bone formation.
12 Getting enough of the sunshine vitamin Young people often don t get enough vitamin D. This is partly due to their increasingly indoor lifestyles. By ensuring that children spend more time participating in sports and outdoor physical activity and less time indoors in front of their computers or televisions parents can help them maintain a healthy level of this key vitamin. Recommended daily intake of key nutrients according to the Institute of Medicine (IOM) USA 4-8 years AGE 1000 mg CALCIUM 19 g PROTEIN 9-13 years AGE 1300 mg CALCIUM 34 g PROTEIN years AGE 1300 mg CALCIUM 46 g PROTEIN FOR GIRLS 52 g PROTEIN FOR BOYS 1-3 years AGE 700 mg CALCIUM 13 g PROTEIN Psst.. And we all need 600 IU of Vitamin D per day!
13 Exercise and lifestyle matter Nutrition and physical activity work hand in hand to enhance bone development in people of all ages, and at no stage in life is this more important than in youth. Young people who exercise regularly show a significant increase in bone mass. A healthy body weight during childhood and adolescence being neither too thin nor overweight contributes to optimal bone health. Anorexia has a serious and negative impact on BMD and skeletal strength in adolescents, while obese children are more likely to sustain fractures at the wrist. Bone-building tips for kids Snack Drink Eat Move on cheese, yoghurt, nuts and dried fruit milk-based beverages, fruit smoothies and mineral waters balanced meals that contain calcium and protein, as well as fruits and vegetables spend time outdoors on physical activities that involve running and jumping
14 Maintaining healthy bones as an adult Bone tissue loss generally begins at around the age of 40 years when we can no longer replace bone tissue as quickly as we lose it. At this stage in life you should take action to stem the tide of bone loss. Ensure bone-healthy nutrition, with sufficient calcium, protein, vitamin D and important micronutrients Engage in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercise Avoid negative lifestyle factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol use Adopting a bone-healthy lifestyle is of critical importance and adults need to pay particular attention at key points in their lives. In women, this is around the age of menopause when they experience a period of rapid bone loss due to a reduction in protective oestrogen levels. In men, bone loss accelerates after the age of 70 years.
15 Keep up your intake of dietary calcium Adults aged years should have a dietary calcium intake of 1,000 mg/day. For people who cannot get enough calcium through their diet, supplements (preferably combined with vitamin D) may be beneficial. These should however not exceed mg per day. Easy ways to boost your calcium intake: Consume dairy products as they are calcium rich; add low-fat cheeses to your meals Try calcium-set soy, which can be used as a substitute for meats Drink milk or calcium-enriched substitutes - and add to your coffees and tea Eat yoghurt regularly as a nutritious breakfast or snack Add wholegrains or seeds like quinoa and chia to your meals Snack on nuts or dried fruit Drink calcium-rich mineral water (check the labels) Choose vegetables that are especially calcium rich (such as cress, broccoli, okra) Add chickpeas, lentils and white beans to your meals
16 Are you at risk of vitamin D deficiency? The IOM recommended vitamin D allowance for adults aged is 600 IU per day. To maintain your vitamin D levels you need regular safe exposure to sunlight. Although sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, eating fatty fish regularly (e.g., salmon, sardines and tuna) or consuming vitamin D enriched food and drink, can help boost your levels. Adults at greater risk of deficiency include anyone who lives at latitudes with minimal exposure to sunlight and people who are obese, have a dark skin tone, cannot expose their skin to the sun Are you getting enough calcium? Calculate your average daily calcium intake in three easy steps. Available online and on mobile devices.
17 for medical or cultural reasons, or have diseases that reduce uptake of vitamin D from the intestine (e.g., Crohn s disease). If you have any of these risk factors, measurement of vitamin D, based on 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in the blood, may be advisable. Supplementation may then be prescribed if required. Proteins and healthy body weight The current recommended daily allowance for healthy adults is 0.8 g of protein per kilogram (kg) of body weight, per day. Adults should eat sufficient protein-rich foods such as dairy products, meats and fish, lentils, beans and nuts. Poor protein intake is often related to undernutrition. A person s body mass index (BMI) should ideally be between kg/m 2. A BMI below 19 kg/m 2 is a risk factor for osteoporosis. Knowing your risk factors ouch! Take the IOF One-Minute Osteoporosis Risk Test to find out whether you may have specific factors which place you at higher risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
18 Nutrition in seniors: stay strong and mobile In seniors, a bone-healthy diet is an essential ingredient in helping to slow the rate of bone thinning and preserve muscle function. This in turns helps reduce the risk of falls and fractures. Malnutrition is common among the elderly for a number of reasons. Seniors may have reduced appetite or be less inclined to cook balanced meals. Vitamin D levels may be lower because of less frequent exposure to sunlight, especially in seniors who are housebound. The skin s capacity to synthesize vitamin D also Daily dietary recommendations for seniors
19 decreases, as does the kidney s capacity to convert vitamin D to its active form. In addition, with age, the body is less able to absorb and retain calcium. More calcium, protein and vitamin D needed In addition to higher calcium intake, seniors need more dietary protein and vitamin D than the young. Both these nutrients help prevent muscle wasting (known as sarcopenia) and thereby help lower the risk of falls and fractures. Higher dietary intake of protein in older people who have been hospitalized with hip fracture has been shown to improve bone density, reduce the risk of complications and reduce rehabilitation time. Age Gender Calcium RDA Vitamin D RDA Protein RDA* years >70 years female 1200 mg 600 IU 46 g male 1000 mg 600 IU 56 g female 1200 mg 800 IU 46 g male 1200 mg 800 IU 56 g Based on IOM recommendations RDA: Recommended Dietary Allowances *According to IOF, a moderate increase in protein intake from 0.8 to g/kg per day is considered optimal for skeletal muscle health in older adults
20 The International Osteoporosis Foundation recommends that seniors aged 60 years and over take a Vitamin D supplement at a dose of IU/day. Vitamin D supplementation at these levels has been shown to reduce the risk of falls and fractures by about 20%. Exercise enhances the benefits of bone-healthy nutrition As at all stages of life, exercise is essential for bone health in seniors too. At this age, muscle strengthening exercises, suitable to individual needs and abilities, will help improve coordination and balance. This in turn helps to maintain mobility and reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
21 Treatment for those at high risk Although bone-healthy nutrition is important, drug therapies are critical for fracture prevention in people at high risk, including those who have already experienced a first fracture. Today, there are many proven and effective treatments which have been shown to reduce the risk of osteoporotic fracture by between 30 50%. If you re over aged 50 years and have broken a bone, or have other risk factors for osteoporosis ask your doctor for a clinical assessment. Controlling osteoporosis risk factors and complying with treatment regimens, where prescribed, can ensure people live mobile, independent, fracture-free lives for longer.
22 Non-age related nutritional factors Alcohol and caffeine: moderation is key Excessive alcohol intake more than two units per day can increase the risk of suffering a fragility fracture. As a rough guide: 1 unit would be the equivalent of 25 ml of spirits (40% alcohol) or 250 ml of beer (4% alcohol). If you enjoy drinking coffee or other caffeine-containing drinks you need to ensure that you are getting sufficient calcium. Caffeine intake at 330 mg per day (approximately 4 cups) could be associated with a 20% increase in risk of osteoporotic fractures. Coeliac disease and other disorders can affect nutritional status Diseases of the gastrointestinal system that affect nutrient absorption in people of all ages include inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn s disease and colitis) as well as coeliac
23 disease. People with these diseases may be at increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures and need to ensure an adequate intake of calcium (1,000 mg/day) and Vitamin D. In such cases it is recommended that individuals have their nutrient status checked as they may need supplements. Getting enough calcium despite lactose maldigestion or intolerance People with some degree of lactose maldigestion may avoid dairy products. As a result they often don t get enough calcium, which may increase their risk of osteoporosis. If you are sensitive to lactose you may not need to eliminate dairy consumption completely: lactose-reduced milks, yoghurts with live cultures, and some hard cheeses are normally tolerated. Another alternative is to take lactase tablets or drops along with dairy foods. People who are lactose intolerant should consult with their doctor to discuss the best way of ensuring adequate calcium intake, either through diet, or if necessary, through the use of supplements.
24 #LoveYourBones For further information about osteoporosis, consult your local osteoporosis patient or medical organization. You can find a list on Information is also available on the World Osteoporosis Day website International Osteoporosis Foundation rue Juste-Olivier, 9 CH-1260 Nyon Switzerland T F info@iofbonehealth.org International Osteoporosis Foundation DESIGN Gilberto D Lontro IOF
LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future IN CHILDREN & ADOLESCENTS
 LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future BUILDING STRONG BONES IN CHILDREN & ADOLESCENTS www.worldosteoporosisday.org Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease in which the skeleton becomes weak and fragile and
LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future BUILDING STRONG BONES IN CHILDREN & ADOLESCENTS www.worldosteoporosisday.org Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease in which the skeleton becomes weak and fragile and
4/25/2014. Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis. 1. Bone building nutrients. Nutrition and Bone Health
 Bones Nutrition and Bone Health Yvonne Chambers-Kozarov Registered Dietitian are constantly under construction certain cells break down bone tissue other cells use the calcium and nutrients in the foods
Bones Nutrition and Bone Health Yvonne Chambers-Kozarov Registered Dietitian are constantly under construction certain cells break down bone tissue other cells use the calcium and nutrients in the foods
Healthy Bodies Healthy Bones. Calcium. Connection. Food and activity choices that help you build and keep strong bones. HealthyEating.
 Calcium Healthy Bodies Healthy Bones Connection Food and activity choices that help you build and keep strong bones HealthyEating.org Yes No How do you measure up? Do you eat less than 3 servings of Dairy
Calcium Healthy Bodies Healthy Bones Connection Food and activity choices that help you build and keep strong bones HealthyEating.org Yes No How do you measure up? Do you eat less than 3 servings of Dairy
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Cooking for bone health
 Cooking for bone health An interactive cooking session that includes instruction on how to prepare simple and nutritious meals that support healthy bones. Why is bone health important? Bones play many
Cooking for bone health An interactive cooking session that includes instruction on how to prepare simple and nutritious meals that support healthy bones. Why is bone health important? Bones play many
Healthy Bones. How much calcium do I need each day? What can I do to keep my bones strong and healthy? How much vitamin D do I need each day?
 Healthy Bones Building and keeping strong, healthy bones continues throughout a person's life. Bones have many important roles in the body. They support your body, protect organs, help muscles work, and
Healthy Bones Building and keeping strong, healthy bones continues throughout a person's life. Bones have many important roles in the body. They support your body, protect organs, help muscles work, and
THROUGHOUT LIFE. Milk and dairy foods provide important nutrients for people of all ages and stages of life.
 Dairy AND YOUR MUSCLE AND BONE HEALTH Dairy, nutrition and health THROUGHOUT LIFE 2 A healthy lifestyle and good nutrition throughout life can help us live in better health for longer, with less illness
Dairy AND YOUR MUSCLE AND BONE HEALTH Dairy, nutrition and health THROUGHOUT LIFE 2 A healthy lifestyle and good nutrition throughout life can help us live in better health for longer, with less illness
Vegetarian Eating. Vegetarians consuming a varied and balanced diet will have no problem getting enough protein.
 Vegetarian or plant-based eating can offer many health benefits, including a reduced risk of cancer, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure and heart disease in fact, many vegetarian communities around
Vegetarian or plant-based eating can offer many health benefits, including a reduced risk of cancer, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure and heart disease in fact, many vegetarian communities around
31 Days to Stronger Bones
 31 Days to Stronger Bones May is National Osteoporosis Awareness & Prevention Month a time to remember the importance of preventing osteoporosis, a disease that causes bones to become weak and brittle.
31 Days to Stronger Bones May is National Osteoporosis Awareness & Prevention Month a time to remember the importance of preventing osteoporosis, a disease that causes bones to become weak and brittle.
Osteoporosis and Your Diet
 Osteoporosis and Your Diet Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to thinning and weakening in bones, causing bone density loss. Living with osteoporosis, you are susceptible to bone fractures and bone deterioration.
Osteoporosis and Your Diet Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to thinning and weakening in bones, causing bone density loss. Living with osteoporosis, you are susceptible to bone fractures and bone deterioration.
Basic Review of Digestion
 Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
Iron for Your Health
 Iron for Your Health Why do we need iron? Iron is an important mineral for health. Iron carries oxygen throughout the body. Most of the iron in the body is found in muscles, where it helps to store oxygen
Iron for Your Health Why do we need iron? Iron is an important mineral for health. Iron carries oxygen throughout the body. Most of the iron in the body is found in muscles, where it helps to store oxygen
FAST FACTS ABOUT OSTEOPOROSIS
 FAST FACTS ABOUT OSTEOPOROSIS Osteoporosis is a disease of the bone that makes a person s bones weak and more likely to break. Approximately 10 million Americans have osteoporosis and another 44 million
FAST FACTS ABOUT OSTEOPOROSIS Osteoporosis is a disease of the bone that makes a person s bones weak and more likely to break. Approximately 10 million Americans have osteoporosis and another 44 million
Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust. Love Your Bones. Diet and Osteoporosis. Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016
 Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Love Your Bones Diet and Osteoporosis Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016 Page 2 Measures to Reduce the Risk of Osteoporosis Nutrition: - Calcium - Vitamin D - Nutrients
Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Love Your Bones Diet and Osteoporosis Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016 Page 2 Measures to Reduce the Risk of Osteoporosis Nutrition: - Calcium - Vitamin D - Nutrients
Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis. Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet.
 Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet. Osteoporosis A disease affecting your bones Osteoporosis is known as the condition which affects bone health, and
Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet. Osteoporosis A disease affecting your bones Osteoporosis is known as the condition which affects bone health, and
LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future
 www.worldosteoporosisday.org LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future Know your risk for osteoporosis www.iofbonehealth.org Osteoporosis is a problem worldwide, and in many countries, up to one in three women
www.worldosteoporosisday.org LOVE YOUR BONES Protect your future Know your risk for osteoporosis www.iofbonehealth.org Osteoporosis is a problem worldwide, and in many countries, up to one in three women
Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health
 Virtual Education Forum Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health Presented by: Andrea Miller MHSc, RD 1 Outline: Optimizing Nutrition for Principles of Healthy Eating Bone Health Canada s Food Guide- A Review
Virtual Education Forum Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health Presented by: Andrea Miller MHSc, RD 1 Outline: Optimizing Nutrition for Principles of Healthy Eating Bone Health Canada s Food Guide- A Review
Healthy bones. Background information for course leader
 Background information for course leader Bones are made of collagen fibres filled in with calcium and other minerals to create a hard structure. During childhood and early adulthood they develop their
Background information for course leader Bones are made of collagen fibres filled in with calcium and other minerals to create a hard structure. During childhood and early adulthood they develop their
Functions of Food. To provide us with energy and keep us active. For growth and repair of the. body. To stop us from feeling hungry.
 Functions of Food To provide us with energy and keep us active. For growth and repair of the body. To stop us from feeling hungry. To keep us healthy and fight diseases. Nutrients Macro/Micro Nutrient
Functions of Food To provide us with energy and keep us active. For growth and repair of the body. To stop us from feeling hungry. To keep us healthy and fight diseases. Nutrients Macro/Micro Nutrient
Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian
 Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian Outline Benefits of healthy eating Meeting your nutritional requirements Using Canada s Food
Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian Outline Benefits of healthy eating Meeting your nutritional requirements Using Canada s Food
Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends. Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015
 Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015 Overview There are no foods that cause Juvenile Arthritis (JA) or that can cure
Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015 Overview There are no foods that cause Juvenile Arthritis (JA) or that can cure
Protein Power For Healthy Eating
 Protein Power For Healthy Eating What is Protein? Protein is: An essential nutrient. Used to build things in our bodies such as muscle. Made up of 20 amino acids, or building blocks. 9 of the 20 amino
Protein Power For Healthy Eating What is Protein? Protein is: An essential nutrient. Used to build things in our bodies such as muscle. Made up of 20 amino acids, or building blocks. 9 of the 20 amino
Information Sheet. Food and Mood. Accessible information about food and mood for adults with mental health problems
 Information Sheet Food and Mood Accessible information about food and mood for adults with mental health problems ? Introduction Over the years our relationship with food has become more complicated as
Information Sheet Food and Mood Accessible information about food and mood for adults with mental health problems ? Introduction Over the years our relationship with food has become more complicated as
Osteoporosis The Silent Disease
 Joel Johnson, Yr, Subtask, Biology ER., 7/9/5 Osteoporosis The Silent Disease What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a disease which causes bones to become brittle, which increases the risk of broken bones.
Joel Johnson, Yr, Subtask, Biology ER., 7/9/5 Osteoporosis The Silent Disease What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a disease which causes bones to become brittle, which increases the risk of broken bones.
Supplements That Work
 Supplements That Work Supplements can be confusing and expensive! Do they work? Do you need them? How should you take them? This guide is an introduction to supplements that most people need. Are supplements
Supplements That Work Supplements can be confusing and expensive! Do they work? Do you need them? How should you take them? This guide is an introduction to supplements that most people need. Are supplements
Nutrition Tips to Manage Your Diabetes
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
HEALTHY DIET = HEALTHY HAIR
 HEALTHY DIET = HEALTHY HAIR The best thing you can do for yourself and especially your hair is to eat a balanced diet. Experts agree that a healthy diet with the right mix of protein, iron, and other nutrients
HEALTHY DIET = HEALTHY HAIR The best thing you can do for yourself and especially your hair is to eat a balanced diet. Experts agree that a healthy diet with the right mix of protein, iron, and other nutrients
Osteoporosis, Fracture Risk Assessment and Promoting Healthy Bones
 Osteoporosis, Fracture Risk Assessment and Promoting Healthy Bones What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis means porous or brittle bones. Osteoporosis occurs when the solid parts of the bones weaken and lose
Osteoporosis, Fracture Risk Assessment and Promoting Healthy Bones What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis means porous or brittle bones. Osteoporosis occurs when the solid parts of the bones weaken and lose
Power of Protein After Surgery
 Power of Protein After Surgery What is Protein? Protein is: An essential nutrient. Used to build things in our bodies such as muscle. Made up of 20 amino acids, or building blocks. 9 of the 20 amino acids
Power of Protein After Surgery What is Protein? Protein is: An essential nutrient. Used to build things in our bodies such as muscle. Made up of 20 amino acids, or building blocks. 9 of the 20 amino acids
Chewing the fat about fat!
 Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals
 Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Macros and Micros. of a Healthy Diet. Macronutrients. Proteins
 Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Information on vitamins. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods.
 Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
The Food Guide Pyramid
 The Food Guide Pyramid In this lesson, you will Learn About n What influences a person s food choices. n How to use the Food Guide Pyramid to make healthful food choices. The Foods You Choose The foods
The Food Guide Pyramid In this lesson, you will Learn About n What influences a person s food choices. n How to use the Food Guide Pyramid to make healthful food choices. The Foods You Choose The foods
Goals for Eating Well, Living Well
 Goals for Eating Well, Living Well Fruit/Vegetable servings per day (rainbow of colors) Dairy/Calcium-rich foods per day (1300 mg/day) Large servings of water per day Hours of screen time (texting, computer,
Goals for Eating Well, Living Well Fruit/Vegetable servings per day (rainbow of colors) Dairy/Calcium-rich foods per day (1300 mg/day) Large servings of water per day Hours of screen time (texting, computer,
Following Dietary Guidelines
 LESSON 26 Following Dietary Guidelines Before You Read List some things you know and would like to know about recommended diet choices. What You ll Learn the different food groups in MyPyramid the Dietary
LESSON 26 Following Dietary Guidelines Before You Read List some things you know and would like to know about recommended diet choices. What You ll Learn the different food groups in MyPyramid the Dietary
Lactose Free Eating Guide
 The great thing about Metabolic Jumpstart is that you can go dairy-free as long as you make a few adjustments to ensure you are eating nutrient-rich and on your targets. This shows you how to get the optimum
The great thing about Metabolic Jumpstart is that you can go dairy-free as long as you make a few adjustments to ensure you are eating nutrient-rich and on your targets. This shows you how to get the optimum
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health. By Dr. Isaac Eliaz
 6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks?
 CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some concerns about diet drinks? CHFFF
CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some examples of sweetened drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 Why are 100% fruit juice and flavored milk the only slow drinks? CHFFF Lesson 1 What are some concerns about diet drinks? CHFFF
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource
 Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
Helpful information about bone health & osteoporosis Patient Resource Every year In the United States, 2.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis. Out of these, 330,000 are hip fractures, and half
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Guide to good nutrition and hydration in older age
 Guide to good nutrition and hydration in older age Registered charity no. 1016437 Registered charity no. 226064 Introduction The Friends of the Elderly Group has partnered with the British Dietetic Association
Guide to good nutrition and hydration in older age Registered charity no. 1016437 Registered charity no. 226064 Introduction The Friends of the Elderly Group has partnered with the British Dietetic Association
All about. Osteoporosis
 All about Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bone. It is a condition that causes bones to become thin and fragile, decreasing bone strength and making them more prone
All about Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bone. It is a condition that causes bones to become thin and fragile, decreasing bone strength and making them more prone
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Essential Standard. 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness.
 Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Stand up for your Bones Osteoporosis - A Guide to Bone Health
 Stand up for your Bones Osteoporosis - A Guide to Bone Health What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a condition where the bones become thin and weak and break easily. These broken bones, commonly known
Stand up for your Bones Osteoporosis - A Guide to Bone Health What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a condition where the bones become thin and weak and break easily. These broken bones, commonly known
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups:
 The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
Nutrition Solutions For a Better You! Melissa Wdowik, PhD, RD The Nutrition CSU
 Nutrition Solutions For a Better You! Melissa Wdowik, PhD, RD The Nutrition Center @ CSU Introduction About Me The Nutrition Center @ CSU Food Science and Human Nutrition Department Outline I. Better Brain
Nutrition Solutions For a Better You! Melissa Wdowik, PhD, RD The Nutrition Center @ CSU Introduction About Me The Nutrition Center @ CSU Food Science and Human Nutrition Department Outline I. Better Brain
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Bethesda, Maryland 20892 Dear Parent/Guardian, As Director
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Bethesda, Maryland 20892 Dear Parent/Guardian, As Director
Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn
 Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your
Professor Popcorn Grade 2, Lesson 1: Visual 2:1A The Professor Popcorn What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
What s. on your plate? ChooseMyPlate.gov. Vegetables. Fruits. Protein. Grains. Dairy. plate fruits and vegetables. Make half your
 What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your protein food choices. Make at least half your grains whole. Before you
What s Protein Grains Dairy on your plate? Fruits Vegetables ChooseMyPlate.gov Make half your plate fruits and vegetables. Vary your protein food choices. Make at least half your grains whole. Before you
Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living
 December 2018 Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living Research shows that living a healthy lifestyle can add a Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health conducted a study of
December 2018 Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living Research shows that living a healthy lifestyle can add a Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health conducted a study of
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH
 eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D.
 Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D. 2 types of nutrients Macronutrients Carbohydrate Fats Protein Micronutrients Vitamins Minerals 1 Occur when the quantity or quality of food is not sufficient to meet a persons
Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D. 2 types of nutrients Macronutrients Carbohydrate Fats Protein Micronutrients Vitamins Minerals 1 Occur when the quantity or quality of food is not sufficient to meet a persons
Name Hour. Nutrition Notes
 Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
 NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Dear Parent, Your child s bones are growing every day, and growing bones need lots of calcium. Milk is an excellent
NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Dear Parent, Your child s bones are growing every day, and growing bones need lots of calcium. Milk is an excellent
By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating. Canada s Food Guide. Healthier Food Choices Are...
 Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating Lesson #1 Making Healthier Food Choices Healthier Food Choices Are... follow Eating Well with, By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Apply health knowledge
Healthy Living Unit #1 Healthy Eating Lesson #1 Making Healthier Food Choices Healthier Food Choices Are... follow Eating Well with, By the end of the lesson students will be able to: Apply health knowledge
AGING GRACEFULLY WITH THE RIGHT NUTRITION
 AGING GRACEFULLY WITH THE RIGHT NUTRITION Pamela Er Dietitian Department of Dietetics National University Hospital Introduction Elderly people above the age of 65 years old, with good nutritional status
AGING GRACEFULLY WITH THE RIGHT NUTRITION Pamela Er Dietitian Department of Dietetics National University Hospital Introduction Elderly people above the age of 65 years old, with good nutritional status
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Fresh BaBy s eat Like a MyPlate Super HERO
 Audience 3 rd and 4 th Grade Setting Small Group Fresh BaBy s eat Like a MyPlate Super HERO MyPlate Messages Eating a variety of foods provides the body with a variety of essential vitamins, minerals and
Audience 3 rd and 4 th Grade Setting Small Group Fresh BaBy s eat Like a MyPlate Super HERO MyPlate Messages Eating a variety of foods provides the body with a variety of essential vitamins, minerals and
Warm up # 76. What do you think the difference is between fruits and vegetables? Warm up # 77
 Warm up # 76 What do you think the difference is between fruits and vegetables? Warm up # 77 Which of these are vegetables and which of these are fruits? Apples Tomatoes Onions Pumpkin Lettuce Broccoli
Warm up # 76 What do you think the difference is between fruits and vegetables? Warm up # 77 Which of these are vegetables and which of these are fruits? Apples Tomatoes Onions Pumpkin Lettuce Broccoli
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Energy Needs & Requirements Food is the only source of body which undergoes Metabolism and liberate / Generates Energy required for vital activities
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Energy Needs & Requirements Food is the only source of body which undergoes Metabolism and liberate / Generates Energy required for vital activities
Nutrients and Wound Healing
 Nutrients and Wound Healing UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what nutrients are how they help your body heal wounds the different kinds of nutrients what else you
Nutrients and Wound Healing UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what nutrients are how they help your body heal wounds the different kinds of nutrients what else you
Healthy Food. You are part of it! Healthier, fitter, safer.
 Healthy Food You are part of it! Healthier, fitter, safer. It is vital that you look after your own health and wellbeing at sea and ashore. Make healthy, nutritious food choices and ensure a balanced diet
Healthy Food You are part of it! Healthier, fitter, safer. It is vital that you look after your own health and wellbeing at sea and ashore. Make healthy, nutritious food choices and ensure a balanced diet
Part 1: Cronometer Food Diary. Date. Add Food. Part 2: Cronometer Nutrition Report
 This assignment has 3 parts: 1) Food Diary: Cronometer (https://cronometer.com) is a free diet analysis tool. You will record your food & beverage intake for 3-5 days. Entering your exercise is optional.
This assignment has 3 parts: 1) Food Diary: Cronometer (https://cronometer.com) is a free diet analysis tool. You will record your food & beverage intake for 3-5 days. Entering your exercise is optional.
Parkinson s Disease. Diagnostic Symptoms
 Parkinson s Disease What is Parkinson s disease? Parkinson s disease (PD) is a progressive disease that affects an individual s movement and motor skills. It is progressive in that symptoms of the disease
Parkinson s Disease What is Parkinson s disease? Parkinson s disease (PD) is a progressive disease that affects an individual s movement and motor skills. It is progressive in that symptoms of the disease
BARBADOS FOOD BASED DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR. Revised Edition (2017)
 FOOD BASED DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR BARBADOS ma fro ni m Foods O ts & ils Fa Fruits Le gum es al s Revised Edition (2017) V e eg ta bles les ap St These guidelines aim to encourage healthy eating habits
FOOD BASED DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR BARBADOS ma fro ni m Foods O ts & ils Fa Fruits Le gum es al s Revised Edition (2017) V e eg ta bles les ap St These guidelines aim to encourage healthy eating habits
Beverage Guidelines: 1 up to 3 Years
 Beverage Guidelines: nutritionally-equivalent nondairy beverages like soy, rice, or lactose-free milks with medical permission). nutritionally-equivalent nondairy beverages like soy, rice, or lactose-free
Beverage Guidelines: nutritionally-equivalent nondairy beverages like soy, rice, or lactose-free milks with medical permission). nutritionally-equivalent nondairy beverages like soy, rice, or lactose-free
F. To provide energy, to spare body protein, to prevent ketosis. G. Food sources include breads, vegetables, fruit, and milk.
 Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
HEALTHY EATING. What you need to know for a long and healthy life. March National Nutrition Month
 HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
Term Year 7 HPE (B, E, F, G, J, M) Nutrition
 Term 1 2019 Year 7 HPE (B, E, F, G, J, M) Nutrition Personal, social and community health Food for life Year 7 Unit 1 Assessment task Food for life Name: PCG: Teacher: Genre: In class project Assignment
Term 1 2019 Year 7 HPE (B, E, F, G, J, M) Nutrition Personal, social and community health Food for life Year 7 Unit 1 Assessment task Food for life Name: PCG: Teacher: Genre: In class project Assignment
I know what I eat affects my health, so how do I ensure I m meeting all my nutritional needs? Improve your nutrition. Improve your life.
 YOUR GUIDE TO NUTRITION DURING I know what I eat affects my health, so how do I ensure I m meeting all my nutritional needs? Improve your nutrition. Improve your life. HEALING AT It s time to return home
YOUR GUIDE TO NUTRITION DURING I know what I eat affects my health, so how do I ensure I m meeting all my nutritional needs? Improve your nutrition. Improve your life. HEALING AT It s time to return home
Diet Charts for Teenagers as per Gender and Level of Activity
 Diet Charts for Teenagers as per Gender and Level of Activity Zohra Jabeen Diet Adolescence is the age of 11 to 18 years when both the male and the female body experiences a lot of physical changes and
Diet Charts for Teenagers as per Gender and Level of Activity Zohra Jabeen Diet Adolescence is the age of 11 to 18 years when both the male and the female body experiences a lot of physical changes and
Vitamin A. What Is It Good For?
 Vitamin A What Is It Good For? Vitamin A is important for normal vision, your immune system, and to help your heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs work properly. Where Can You Find It? Vitamin A is
Vitamin A What Is It Good For? Vitamin A is important for normal vision, your immune system, and to help your heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs work properly. Where Can You Find It? Vitamin A is
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory
 Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
2002 Learning Zone Express
 1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
Vitamins and Minerals
 Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn
 Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1B Why We Eat 7 6 5 4 3 2 Hungry 1 Growth Stay healthy Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson
Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1A Professor Popcorn Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson 1: Visual 3:1B Why We Eat 7 6 5 4 3 2 Hungry 1 Growth Stay healthy Professor Popcorn Grade 3, Lesson
Heart health and diet. Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart.
 Heart health and diet Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart. What you eat can have an impact on the health of your heart. Eating a healthy diet
Heart health and diet Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart. What you eat can have an impact on the health of your heart. Eating a healthy diet
In addition to bone health, emerging science reveals a non-skeletal benefit of vitamin D for several other health outcomes.
 Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Calcium Supplement Guidelines
 Supplement Guidelines Item Type text; Book Authors Houtkooper, Linda; Farrell, Vanessa A. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 24/07/2018 09:13:03 Item License
Supplement Guidelines Item Type text; Book Authors Houtkooper, Linda; Farrell, Vanessa A. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 24/07/2018 09:13:03 Item License
Essential Standard. 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness.
 Essential Standard 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness. 8.NPA.1.3 Implement meal plans that are consistent with Dietary Guidelines. Warm Up Without
Essential Standard 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness. 8.NPA.1.3 Implement meal plans that are consistent with Dietary Guidelines. Warm Up Without
Facts that you need to know
 NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
Prevent and/or reduce overweight and obesity through improved eating and physical activity.
 A summary of the key recommendations to healthier living for Americans of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines and a weight-loss guide to combat obesity are offered by the May 2011 issue of the Tufts Health & Nutrition
A summary of the key recommendations to healthier living for Americans of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines and a weight-loss guide to combat obesity are offered by the May 2011 issue of the Tufts Health & Nutrition
Nutrition And You. An Orange a Day
 Nutrition And You Anatomy of The Healthy Eating Pyramid Healthy Eating Pyramid s 9 Food Groups An Orange a Day Anatomy of the Healthy Eating Pyramid. Activity is represented as the foundation of this pyramid.
Nutrition And You Anatomy of The Healthy Eating Pyramid Healthy Eating Pyramid s 9 Food Groups An Orange a Day Anatomy of the Healthy Eating Pyramid. Activity is represented as the foundation of this pyramid.
Nutrition - What Should We Eat?
 Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
 Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Food group Food Guide Serving Food Guide Servings per day Builds a healthy Women age 14 to 18 Women age 19 to 50 baby Vegetables and
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Food group Food Guide Serving Food Guide Servings per day Builds a healthy Women age 14 to 18 Women age 19 to 50 baby Vegetables and
Make your. first break. your last.
 www.iofbonehealth.org Make your first break your last WHAT IS OSTEOPOROSIS? Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become more fragile and weak, leading to an increased risk of fractures (broken bones).
www.iofbonehealth.org Make your first break your last WHAT IS OSTEOPOROSIS? Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become more fragile and weak, leading to an increased risk of fractures (broken bones).
Notes: A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or
 A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans Mary M. McGrane, PhD Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion February 25, 2015 Agenda for Commodity Supplemental Food Program (CSFP) Brief history and description
2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans Mary M. McGrane, PhD Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion February 25, 2015 Agenda for Commodity Supplemental Food Program (CSFP) Brief history and description
14 Superfoods for your baby and how to serve them
 Your baby needs a variety of macro and micronutrients to grow and thrive. Here are some of the important ones: Protein: Protein suppliers our bodies structural blocks and it is extremely important for
Your baby needs a variety of macro and micronutrients to grow and thrive. Here are some of the important ones: Protein: Protein suppliers our bodies structural blocks and it is extremely important for
NUTRITION E- Book. Guru Mann CERTIFIED Nutritionist. San Francisco California, UNITED STATES
 NUTRITION E- Book San Francisco California, UNITED STATES OVERVIEW Thyroid hormones help control your growth, repair and metabolism. As a result, people who suffer from hypothyroidism may experience tiredness,
NUTRITION E- Book San Francisco California, UNITED STATES OVERVIEW Thyroid hormones help control your growth, repair and metabolism. As a result, people who suffer from hypothyroidism may experience tiredness,
Twin and triplet pregnancy: Healthy eating and nutrition
 Twin and triplet pregnancy: Healthy eating and nutrition Healthy eating for a multiple pregnancy Nuts & seeds 1 serve per day 1 serve = a handful Cereals & reads 6+ serves or more per day 1 serve = 1 slice
Twin and triplet pregnancy: Healthy eating and nutrition Healthy eating for a multiple pregnancy Nuts & seeds 1 serve per day 1 serve = a handful Cereals & reads 6+ serves or more per day 1 serve = 1 slice
What should my toddler be eating?
 Contents What should my toddler be eating? 1 Can my toddler eat the same food as us? 2 Semi-skimmed and skimmed milk 3 What foods should be avoided? 4 Sweet drinks 5 Food allergy 6 Vegetarian diets 7 Where
Contents What should my toddler be eating? 1 Can my toddler eat the same food as us? 2 Semi-skimmed and skimmed milk 3 What foods should be avoided? 4 Sweet drinks 5 Food allergy 6 Vegetarian diets 7 Where
LESSON 2 BUILD FOODS DEVELOPED AT THE OHSU BOB AND CHARLEE MOORE INSTITUTE FOR NUTRITION & WELLNESS
 LESSON 2 BUILD FOODS DEVELOPED AT THE OHSU BOB AND CHARLEE MOORE INSTITUTE FOR NUTRITION & WELLNESS Lesson Plan 2: MyPlate Build Foods The Build Your Body groups - protein and dairy Summary of needed materials
LESSON 2 BUILD FOODS DEVELOPED AT THE OHSU BOB AND CHARLEE MOORE INSTITUTE FOR NUTRITION & WELLNESS Lesson Plan 2: MyPlate Build Foods The Build Your Body groups - protein and dairy Summary of needed materials
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
JUST ME TEA AUSTRALIA MEAL PLAN GUIDE
 JUST ME TEA AUSTRALIA MEAL PLAN GUIDE MEAL PLAN GUIDE Important notes: It is essential that you use this eating plan in conjunction with our weight loss tea range and your normal exercise routine. Additionally,
JUST ME TEA AUSTRALIA MEAL PLAN GUIDE MEAL PLAN GUIDE Important notes: It is essential that you use this eating plan in conjunction with our weight loss tea range and your normal exercise routine. Additionally,
The eatwell plate is based on the Government s Eight Guidelines for a Healthy Diet, which are:
 The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
