Editorial. The Role of Zinc in Child Health in Developing Countries: Taking the Science where it Matters
|
|
|
- Martin Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Editorial The Role of Zinc in Child Health in Developing Countries: Taking the Science where it Matters The role of zinc in human health has been recognized for almost half a century with the discovery of the syndrome of zinc deficiency, delayed sexual development and growth failure among adolescents in Iran(1). Following the discovery of this association however, despite sporadic studies of zinc supplementation in malnourished children and the recognition of the association between zinc deficiency, malnutrition and prolonged diarrhea(2), systematic evaluation of the role of zinc in child health and policy relevant research has been relatively slow. Zinc is widely recognized as an essential micronutrient with a catalytic role in over a 100 specific metabolic enzymes in human metabolism(3). These include all major enzyme-classes (oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lysases, isomerases and ligases). Zinc also chelates with the amino acids cysteine and histidine, forming zinc fingers that are important for protein transcription. Additional processes that are regulated by zinc include expression of the metallothionein gene, apoptosis and synaptic signaling. Zinc is one of the most ubiquitous of all trace elements involved in human metabolism and plays multiple roles in the perpetuation of genetic material, including transcription of DNA, translation of RNA, and ultimately cellular division. It is thus critical to understand the role of zinc in health and disease, especially during the vulnerable periods of growth and development(4). Unlike other essential micronutrients such as iron and vitamin A, there are no conventional tissue reserves of zinc that can be released or sequestered quickly in response to variations in dietary supply. It is recognized that the equivalent of approximately one-third (~450 mg) of total body zinc exchanges between the blood stream and other tissues(5). The major source of zinc intake is through diet, with the transcellular uptake occuring in the distal duodenum and proximal jejunum, potentially facilitated by specific transporters, such as zinc transporter protein-1 (ZnTP-1) (6). The intestine also serves as the major conduit for zinc elimination from the body with almost 50% of the daily zinc losses occurring in the gut. However, much of the zinc that is secreted into the intestine is subsequently reabsorbed, and this process serves as an important point of regulation of zinc balance. Other routes of zinc excretion include the urine, which accounts for approximately 15% of total zinc losses, and epithelial cell desquamation, sweat, semen, hair, and menstrual blood, which together account for approximately 17% of total zinc losses(7). Given the diverse array of biological functions of zinc, it is not surprising that multiple physiological and metabolic functions, such as physical growth, immunocompetence, reproductive function, and neurobehavioral development are all affected by zinc status. When the supply of dietary zinc is insufficient to support these functions, biochemical abnormalities and clinical signs may develop. The potential benefit of zinc on the immune system can be mediated via a variety of pathways including stabilization of the epithelial barrier, and function of neutrophils, natural killer cells, monocytes, INDIAN PEDIATRICS 429 VOLUME 41 MAY 17, 2004
2 and macrophages. In addition zinc status may affect lymphocyte counts and function occur, as well as alterations in the balance of T helper cell and TH1 and TH2 cytokines(8,9). Growth and Development Given the multiple metabolic roles of zinc and the earlier reports of the clinical association of zinc deficiency, there has been considerable interest in the potential growth benefits of zinc. Although the primary mechanisms whereby zinc influences growth are uncertain, there is a large body of literature indicating that zinc depletion limits growth and development. These include several studies of zinc supplementation among low birth weight infants (LBW) in developing countries indicating significant benefits on weight gain and some benefit on linear growth(10-12). Subsequent trials in Bangladesh (13, 14) have likewise found greater weight gain among severely malnourished inpatients who received supplemental zinc (10 mg/kg/day up to a maximum of 50 mg/day) during the course of nutritional rehabilitation. However, there have been relatively fewer reports of a positive effect of zinc supplementation on children's linear growth during recovery from severe malnutrition perhaps related to the duration of supplementation and pre-existing zinc status. A recent meta-analysis of 33 randomized intervention trials evaluating the effect of zinc supplementation on the growth of pre-pubertal children(15) concluded that zinc supplementation produced highly significant positive responses in linear growth and weight gain (mean effect sizes of SD units), with comparatively greater growth responses in children with low initial weightfor-age or height-for-age Z-scores. Effect of Zinc on Diarrhea Given the association and biological plausibility of the role of zinc in intestinal mucosal injury and recovery, a number of randomized controlled trials have demonstrated significant reduction in the incidence and duration of acute and persistent diarrhea in zinc-supplemented children compared to their placebo-treated counterparts (16,17). A pooled analysis of randomized, controlled trials of zinc supplementation performed in nine low-income countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, South and Southeast Asia, and the Western Pacific, demonstrated that supplemental zinc led to an 18% reduction in the incidence of diarrhea and a 25% reduction in the prevalence of diarrhea (18). While the pooled analysis did not find differences in the effect of zinc by age, baseline serum zinc status, presence of wasting, or sex, the relevance of zinc supplementation to various geographic regions of the world remained unclear. Recent studies from Africa using zinc supplementation in young children indicate significant benefit on diarrhea burden indicating that the effect may be consistent across various geographical regions(19,20) and even if zinc is administered with oral rehydration solution(21). Recent studies in Bangladesh of using zinc in the treatment of diarrhea in a community setting have also demonstrated substantial reduction in concomitant use of antibiotics by health-care providers(22), thus suggesting that there may be additional benefits to the use of zinc in the treatment of diarrhea. It is also anticipated that the forthcoming World Health Assembly will also ratify a joint UNICEF WHO statement that will strongly endorse the use of zinc supplements in young children with diarrhea. Respiratory Infections Despite advances in the recognition and management of acute respiratory infections (ARI), these account for over 20% of all child deaths globally(23). In preventive trials of zinc supplementation, a significant impact has been INDIAN PEDIATRICS 430 VOLUME 41 MAY 17, 2004
3 shown on the incidence of acute lower respiratory infections(24-26). The recent pooled analysis of trials conducted in India, Jamaica, Peru and Vietnam indicated an overall 41% reduction in the incidence of pneumonia among zinc-supplemented children(27). More recently, the administration of zinc to children hospitalized with pneumonia in Bangladesh has been shown to reduce the severity and length of hospitalization (Brookes A, et al., Lancet 2004 in press). Malaria The benefits of zinc supplementation on the severity of disease and outcome of malaria are less straight forward. Bates, et al.(28) administered 70 mg zinc twice weekly for eighteen months to children in Gambia and were able to show 32 % reduction in clinic visits due to P. falciparum infections. Similarly a trial undertaken in Papua New Guinea among pre-school children(29) indicated a 38% reduction in clinic visits attributable to P. falciparum parasitemia as well as heavy parasitemia. In contrast a recent trial in Burkina Faso did not find any reduction in episodes of falciparum malaria among children who received daily supplementation with 10 mg zinc for six months(19). This variable effect of zinc in malarial areas may be related to an impact on the severity of disease rather than the incidence. Programmatic challenges: Atwater memorial lecture (King) The aforementioned evidence indicates the potential role of zinc for improving child health in public health settings(30). While much of the data derives from efficacy trials, they are largely restricted to well-controlled experimental situations, even in community settings. What is needed however, are large effectiveness trials in representative settings that may help understand and develop mechanisms for the use of zinc in health systems in a replicable and sustainable manner. The Bellagio child survival group estimated that the introduction of zinc in prophylactic and therapeutic public health programs could save as much as 9% of all under-5 deaths globally(31). Given the emerging evidence of the scale and magnitude of zinc deficiency in south Asia(32), it is important that these interventions be evaluated at the earliest. There is an additional unfinished research agenda that must also be pursued without holding zinc interactions back. It is also important to unravel several unanswered questions such as interactions with iron and multiple micronutrient deficiencies in susceptible populations, optimal delivery systems for zinc and frequency of administration as well as potential adverse effects(33). However, given the overwhelming evidence of the potential benefit of zinc for treatment of at risk children in susceptible populations, it is important to introduce this intervention in public health systems as soon as possible. Zulfiqar A. Bhutta, Husein Lalji Dewraj Professor of Pediatrics & Child Health, The Aga Khan University, P.O. Box 3500, Stadium Road, Karachi 74800, Pakistan. zulfiqar.bhutta@aku.edu Funding: None. Competing interests: None stated. REFERENCES 1. Prasad AS, Miale A Jr., Farid Z, Sandstead HH, Schulert AR. Zinc metabolism in patients with the syndrome of iron deficiency anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, dwarfism, and hypogonadism. J Lab Clin Med (1963); 116: Roy SK, Tomkins AM, Akramuzzaman SM, Behrens RH, Haider R, Mahalanabis D, et al. INDIAN PEDIATRICS 431 VOLUME 41 MAY 17, 2004
4 Randomised controlled trial of zinc supplementation in malnourished Bangladeshi children with acute diarrhoea. Arch Dis Child 1997; 77: Cousins RJ Zinc. In: Ziegler EE, & Filer Jr LJ, eds. Present Knowledge in Nutrition, 7th edition Washington, DC, ILSI Press. 4. International Zinc Nutrition Consultative Group (IZiNCG) Technical Document #1. Assessment of the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Populations and Options for its Control. Hotz C, Brown KH (Eds). Food and Nutrition Bulletin 2004: 25 (supplement 2) The United Nations University. 5. King JC, Shames DM Woodhouse LR. Zinc homeostasis in humans. J Nutr 2000; 130: 1360S-1366S. 6. McMahon RJ, Cousins RJ. Mammalian zinc transporters. J Nutr 1998;128: Food and Nutrition Board & Institute of Medicine (FNB/IOM). Dietary reference intakes of Vitamin A, Vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc Washington, DC, National Academy Press. 8. Shankar AH & Prasad AS. Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr 1998;68: 447S-463S. 9. Fraker PJ, King LE, Laakko T, Vollmer TL. The dynamic link between the integrity of the immune system and zinc status. J Nutr 2000;130: Castillo-Duran C, Rodriguez A, Venegas G, Alvarez P, & Icaza G. Zinc supplementation and growth of infants born small for gestational age. J Pediatr 1995; 127: Lira PI, Ashworth A, & Morris SS. Effect of zinc supplementation on the morbidity, immune function, and growth of low-birth-weight, fullterm infants in northeast Brazil. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 418S-424S. 12. Sur D, Gupta DN, Mondal SK, Ghosh S, Manna B, Rajendran K, et al. Impact of zinc supplementation on diarrheal morbidity and growth pattern of low birth weight infants in kolkata, India: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, community-based study. Pediatrics. 2003;112: Khanum S, Alam AN, Anwar I, Akbar Ali M, Mujibur Rahaman M. Effect of zinc supplementation on the dietary intake and weight gain of Bangladeshi children recovering from protein-energy malnutrition. Eur J Clin Nutr 1988; 42: Simmer K, Khanum S, Carlsson L, Thompson RP. Nutritional rehabilitation in Bangladesh-- the importance of zinc. Am J Clin Nutr 1988; 47: Brown KH, Peerson JM, Allen LH, Rivera J. Effect of supplemental zinc on the growth and serum zinc concentrations of pre-pubertal children: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: Ruel MT, Rivera JA, Santizo MC, Lonnerdal B, Brown K H. Impact of Zinc supplementation on morbidity from diarrhea and respiratory infections among rural Guatemalan Children. Pediatrics 1997; 99: Sazawal S, Black R, Bhan M, Bhandari N, Sinha A, Jalla S. Zinc supplementation in young children with acute diarrhea in India. New Engl J Med 1995; 333: Bhutta ZA, Black RE, Brown KH, Gardner JM, Gore S, Hidayat A, et al. Therapeutic effect of oral zinc in acute and persistent diarrhea in children in developing countries: pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 72: Müller O, Becher H, Baltussen van Zweeden A, Ye Y, Diallo DA, Konate AT, et al. Effect of zinc supplementation on malaria and other causes of morbidity in west African children: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial. BMJ 2001; 322: Umeta M, West CE, Haidar J, Deurenberg P, Hautvast JG..Zinc supplementation and stunted infants in Ethiopia: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2000; 355: Bhatnagar S, Bahl R, Sharma PK, Kumar GT, Saxena SK, Bhan MK. Zinc with oral INDIAN PEDIATRICS 432 VOLUME 41 MAY 17, 2004
5 rehydration therapy reduces stool output and duration of diarrhea in hospitalized children: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004; 38: Baqui AH, Black RE, El Arifeen S, Yunus M, Chakraborty J, Ahmed S, et al. Effect of zinc supplementation started during diarrhoea on morbidity and mortality in Bangladeshi children: community randomised trial. BMJ. 2002; 325: Black RE, Morris SS, Bryce J. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet 2003; 361: Ninh NX, Thissen JP, Collette L, Gerard G, Khoi HH, Ketelslegers JM. Zinc supplementation increases growth and circulating insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in growthretarded Vietnamese children. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 63: Sazawal S, Black RE, Jalla S, Mazumdar S, Sinha A, Bhan MK. Zinc supplementation reduces the incidence of acute lower respiratory infections in infants and preschool children: a double-blind, controlled trial. Pediatrics 1998;102: Mahalanabis D, Lahiri M, Paul D, Gupta S, Gupta A, Wahed MA, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the efficacy of treatment with zinc or vitamin A in infants and young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: Bhutta ZA, Black RE, Brown KH, Gardner JM, Gore S, Hidayat A, et al. Prevention of diarrhea and pneumonia by zinc supplementation in children in developing countries: pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Pediatr 1999;135: Bates CJ, Evans PH, Dardenne M, Prentice A, Lunn PG, Northrop-Clewes CA, et al. A trial of zinc supplementation in young rural Gambian children. Br J Nutr 1993; 69: Shankar AH, Genton B, Baisor M, Paino J, Tamja S, Adiguma T, et al. The influence of zinc supplementation on morbidity due to Plasmodium falciparum: a randomized trial in preschool children in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2000; 62: King J. Atwater Memorial Lecture, Federation of Experimental Biology annual meeting, April Jones G, Steketee RW, Black RE, Bhutta ZA, Morris SS. How many child deaths can we prevent this year? Lancet 2003; 362: Penny ME, Marin RM, Duran A, Peerson JM, Lanata CF, Lonnerdal B, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect of daily supplementation with zinc or multiple micronutrients on the morbidity, growth, and micronutrient status of young Peruvian children. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: Doherty CP, Sarkar MA, Shakur MS, Ling SC, Elton RA, Cutting A. Zinc and rehabilitation from severe protein-energy malnutrition: Higher- dose regimens are associated with increased mortality. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: INDIAN PEDIATRICS 433 VOLUME 41 MAY 17, 2004
Zinc and childhood infections:
 Norsk Epidemiologi 2005; 15 (2): 151-157 151 Zinc and childhood infections: From the laboratory to new treatment recommendations Tor A. Strand and Maria Mathisen Centre for International Health, University
Norsk Epidemiologi 2005; 15 (2): 151-157 151 Zinc and childhood infections: From the laboratory to new treatment recommendations Tor A. Strand and Maria Mathisen Centre for International Health, University
Zinc Supplementation for Prevention or Treatment of Childhood Pneumonia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
 E U R E C A Zinc Supplementation for Prevention or Treatment of Childhood Pneumonia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials JOSEPH L MATHEW From the Advanced Pediatrics Centre, PGIMER, Chandigarh
E U R E C A Zinc Supplementation for Prevention or Treatment of Childhood Pneumonia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials JOSEPH L MATHEW From the Advanced Pediatrics Centre, PGIMER, Chandigarh
Functional indicators for assessing zinc deficiency
 Functional indicators for assessing zinc deficiency Christa L. Fischer Walker and Robert E. Black Abstract Zinc is an essential micronutrient for growth and proper immune function. There is currently no
Functional indicators for assessing zinc deficiency Christa L. Fischer Walker and Robert E. Black Abstract Zinc is an essential micronutrient for growth and proper immune function. There is currently no
Effect of zinc supplementation on malaria and other causes of morbidity in west African children: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial
 Effect of zinc supplementation on malaria and other causes of morbidity in west African children: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial Olaf Müller, Heiko Becher, Anneke Baltussen van Zweeden,
Effect of zinc supplementation on malaria and other causes of morbidity in west African children: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial Olaf Müller, Heiko Becher, Anneke Baltussen van Zweeden,
Evidence for the Safety and Efficacy of Zinc Supplementation in the Management of Diarrhoea
 Evidence for the Safety and Efficacy of Zinc Supplementation in the Management of Diarrhoea A document prepared by the Department of Child and Adolescent Health and Development of the World Health Organization
Evidence for the Safety and Efficacy of Zinc Supplementation in the Management of Diarrhoea A document prepared by the Department of Child and Adolescent Health and Development of the World Health Organization
Preventive zinc supplementation among infants, preschoolers, and older prepubertal children
 Preventive zinc supplementation among infants, preschoolers, and older prepubertal children Kenneth H. Brown, Janet M. Peerson, Shawn K. Baker, and Sonja Y. Hess Abstract supplementation trials carried
Preventive zinc supplementation among infants, preschoolers, and older prepubertal children Kenneth H. Brown, Janet M. Peerson, Shawn K. Baker, and Sonja Y. Hess Abstract supplementation trials carried
Downloaded from:
 Baqui, AH; Black, RE; el Arifeen, S; Yunus, M; Chakraborty, Y; Ahmed, S; Vaughan, JP (2002) Effect of zinc supplementation started during diarrhoea on morbidity and mortality in Bangladeshi children: community
Baqui, AH; Black, RE; el Arifeen, S; Yunus, M; Chakraborty, Y; Ahmed, S; Vaughan, JP (2002) Effect of zinc supplementation started during diarrhoea on morbidity and mortality in Bangladeshi children: community
The ORION Medical Journal 2004 Jan;17:
 Zinc treatment for childhood diarrhoea A new and innovative project of ICDDR,B: Centre for Health and Population Research Larson CP, Ernst R The ORION Medical Journal 2004 Jan;17:136-138 Introduction In
Zinc treatment for childhood diarrhoea A new and innovative project of ICDDR,B: Centre for Health and Population Research Larson CP, Ernst R The ORION Medical Journal 2004 Jan;17:136-138 Introduction In
Zinc Deficiency: Descriptive Epidemiology and Morbidity among Preschool Children in Peri-urban Population in Delhi, India
 J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2009 Oct;27(5):632-639 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR DIARRHOEAL DISEASE RESEARCH, BANGLADESH Zinc Deficiency: Descriptive Epidemiology and Morbidity among Preschool
J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2009 Oct;27(5):632-639 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR DIARRHOEAL DISEASE RESEARCH, BANGLADESH Zinc Deficiency: Descriptive Epidemiology and Morbidity among Preschool
Overview of Zinc Nutrition
 Overview of Zinc Nutrition 1.1 Biological functions of zinc Zinc is ubiquitously present throughout all biologic systems and has abundant and varied functions within these systems. These characteristics
Overview of Zinc Nutrition 1.1 Biological functions of zinc Zinc is ubiquitously present throughout all biologic systems and has abundant and varied functions within these systems. These characteristics
Zinc is a vital micronutrient in humans and is
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Zinc Supplementation for Prevention of Acute Respiratory Infections in Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial AKASH MALIK, DAVENDRA K TANEJA, # NIVEDHITA DEVASENAPATHY AND *K
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Zinc Supplementation for Prevention of Acute Respiratory Infections in Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial AKASH MALIK, DAVENDRA K TANEJA, # NIVEDHITA DEVASENAPATHY AND *K
Role of zinc supplementation in acute respiratory tract infections in children aged 2 to 60 months
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Nair BT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Sep;4(5):1758-1762 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Nair BT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Sep;4(5):1758-1762 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 01 Page January 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i1.30 Effect of Zinc on Acute Diarrhea in Normal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i1.30 Effect of Zinc on Acute Diarrhea in Normal
MATERNAL FOOD SUPPLEMENTATION AND SGA
 BORN TOO SMALL : 32 MILLION BABIES ARE BORN SMALL-FOR-GESTATIONAL AGE IN LMIC EFFECT OF MATERNAL MULTIPLE MICRONUTRIENT SUPPLEMENTATION ON BIRTH OUTCOMES Parul Christian, SPO-Women s Nutrition Nutrition
BORN TOO SMALL : 32 MILLION BABIES ARE BORN SMALL-FOR-GESTATIONAL AGE IN LMIC EFFECT OF MATERNAL MULTIPLE MICRONUTRIENT SUPPLEMENTATION ON BIRTH OUTCOMES Parul Christian, SPO-Women s Nutrition Nutrition
Zinc deficiency is common in developing countries because of diets rich in phytate and fiber, a low intake of animal foods,
 IMPACT OF ZINC SUPPLEMENTATION ON MENTAL AND PSYCHOMOTOR SCORES OF CHILDREN AGED 12 TO 18 MONTHS: A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL SUNITA TANEJA, PHD, NITA BHANDARI, PHD, RAJIV BAHL, PHD, AND MAHARAJ KISHAN
IMPACT OF ZINC SUPPLEMENTATION ON MENTAL AND PSYCHOMOTOR SCORES OF CHILDREN AGED 12 TO 18 MONTHS: A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL SUNITA TANEJA, PHD, NITA BHANDARI, PHD, RAJIV BAHL, PHD, AND MAHARAJ KISHAN
Zinc Supplementation in Children Is Not Associated with Decreases in Hemoglobin Concentrations 1
 The Journal of Nutrition Community and International Nutrition Zinc Supplementation in Children Is Not Associated with Decreases in Hemoglobin Concentrations 1 Louise H. Dekker 2 * and Eduardo Villamor
The Journal of Nutrition Community and International Nutrition Zinc Supplementation in Children Is Not Associated with Decreases in Hemoglobin Concentrations 1 Louise H. Dekker 2 * and Eduardo Villamor
THE PREVALENCE OF MALNUTRITION IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES: A REVIEW ABSTRACT
 THE PREVALENCE OF MALNUTRITION IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES: A REVIEW Yasser Hussein Issa Mohammed, Noor Fathima Khanum, S. V. Mamatha, Mahima Jyothi, Zabiulla,Fares Hezam Al-Ostoot and Shaukath Ara Khanum
THE PREVALENCE OF MALNUTRITION IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES: A REVIEW Yasser Hussein Issa Mohammed, Noor Fathima Khanum, S. V. Mamatha, Mahima Jyothi, Zabiulla,Fares Hezam Al-Ostoot and Shaukath Ara Khanum
Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial
 Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial Nazia Shehzad (1), Muhammd Irfan Anwar (2), Tahira Muqaddas (1) (1) Lahore
Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial Nazia Shehzad (1), Muhammd Irfan Anwar (2), Tahira Muqaddas (1) (1) Lahore
MALNUTRITION. At the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 MALNUTRITION 1 MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lecture students should be able to: Define and classify malnutrition Enumerate causes and effects of malnutrition Identify strategies for prevention
MALNUTRITION 1 MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lecture students should be able to: Define and classify malnutrition Enumerate causes and effects of malnutrition Identify strategies for prevention
Maternal, infant, and young child nutrition: a global perspective
 Maternal, infant, and young child nutrition: a global perspective Kenneth H. Brown, MD Department of Nutrition, and Program in International and Community Nutrition University of California, Davis PICN
Maternal, infant, and young child nutrition: a global perspective Kenneth H. Brown, MD Department of Nutrition, and Program in International and Community Nutrition University of California, Davis PICN
Low-dose weekly supplementation of iron and/or zinc does not affect growth among Bangladeshi infants
 (2009) 63, 87 92 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low-dose weekly supplementation of iron and/or zinc does not affect growth
(2009) 63, 87 92 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low-dose weekly supplementation of iron and/or zinc does not affect growth
Summary p. 1 What Are Dietary Reference Intakes? p. 2 Approach for Setting Dietary Reference Intakes p. 7 Nutrient Functions and the Indicators Used
 Summary p. 1 What Are Dietary Reference Intakes? p. 2 Approach for Setting Dietary Reference Intakes p. 7 Nutrient Functions and the Indicators Used to Estimate Requirements p. 10 Criteria and Proposed
Summary p. 1 What Are Dietary Reference Intakes? p. 2 Approach for Setting Dietary Reference Intakes p. 7 Nutrient Functions and the Indicators Used to Estimate Requirements p. 10 Criteria and Proposed
The Lancet Series on Maternal and Child Nutrition Launch Symposium 6 June, 2013
 The Lancet Series on Maternal and Child Nutrition Launch Symposium 6 June, 2013 Imperial College St Mary s Campus Rothschild Lecture Hall, School of Medicine Norfolk Place, London Maternal and Child Undernutrition
The Lancet Series on Maternal and Child Nutrition Launch Symposium 6 June, 2013 Imperial College St Mary s Campus Rothschild Lecture Hall, School of Medicine Norfolk Place, London Maternal and Child Undernutrition
Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives
 TECHNICAL BRIEF Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives Amy L. Rice, PhD INTRODUCTION Over half a million women around the world die each year from conditions related to pregnancy and
TECHNICAL BRIEF Vitamin A Deficiency: Counting the Cost in Women s Lives Amy L. Rice, PhD INTRODUCTION Over half a million women around the world die each year from conditions related to pregnancy and
Iron deficiency anaemia in young children (6 to 23 months) in relation to complementary feeding practices in rural Telangana, India
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Sailaja K et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Jul;4(4):1240-1244 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Sailaja K et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Jul;4(4):1240-1244 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Therapeutic Evaluation of Zinc and Copper Supplementation in Acute Diarrhea in Children: Double Blind Randomized Trial
 Therapeutic Evaluation of Zinc and Copper Supplementation in Acute Diarrhea in Children: Double Blind Randomized Trial Archana B. Patel, *Leena A. Dhande and *Manwar S. Rawat From the Clinical Epidemiology
Therapeutic Evaluation of Zinc and Copper Supplementation in Acute Diarrhea in Children: Double Blind Randomized Trial Archana B. Patel, *Leena A. Dhande and *Manwar S. Rawat From the Clinical Epidemiology
Effect of zinc supplementation on growth in West African children: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial in rural Burkina Faso
 IJE vol.32 no.6 International Epidemiological Association 2003; all rights reserved. International Journal of Epidemiology 2003;32:1098 1102 DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyg190 PAEDIATRIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Effect of zinc
IJE vol.32 no.6 International Epidemiological Association 2003; all rights reserved. International Journal of Epidemiology 2003;32:1098 1102 DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyg190 PAEDIATRIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Effect of zinc
Short-term supplementation with zinc and vitamin A has no significant effect on the growth of undernourished
 Short-term supplementation with zinc and vitamin A has no significant effect on the growth of undernourished Bangladeshi children 1 3 Mohammad M Rahman, Fahmida Tofail, Mohammad A Wahed, George J Fuchs,
Short-term supplementation with zinc and vitamin A has no significant effect on the growth of undernourished Bangladeshi children 1 3 Mohammad M Rahman, Fahmida Tofail, Mohammad A Wahed, George J Fuchs,
Update on the nutrition situation in the Asia Pacific region
 Update on the nutrition situation in the Asia Pacific region Mike Toole 13 th National Rural Health Conference, Darwin, 24-27 May 2015 Source: DFAT, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea Conceptual framework
Update on the nutrition situation in the Asia Pacific region Mike Toole 13 th National Rural Health Conference, Darwin, 24-27 May 2015 Source: DFAT, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea Conceptual framework
Protein Energy Malnutrition
 Protein Energy Malnutrition Cindy Howard, MD, MPHTM Associate Director University of Minnesota November 8, 2008 Time Magazine, August, 2008 The percentage of under five mortality worldwide caused in part
Protein Energy Malnutrition Cindy Howard, MD, MPHTM Associate Director University of Minnesota November 8, 2008 Time Magazine, August, 2008 The percentage of under five mortality worldwide caused in part
A C T I O N T O A D D R E S S P N E U M O N I A A N D D I A R R H O E A
 A C T I O N T O A D D R E S S P N E U M O N I A A N D D I A R R H O E A Integrated Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea: Frequently Asked Questions Document for
A C T I O N T O A D D R E S S P N E U M O N I A A N D D I A R R H O E A Integrated Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea: Frequently Asked Questions Document for
by Ruchika Kumar, 1 Praveen Kumar, 1 S. Aneja, 1 Virendra Kumar, 1 and Harmeet S. Rehan 2
 Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 2015, 61, 435 441 doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmv054 Advance Access Publication Date: 27 August 2015 Original Paper Safety and Efficacy of Low-osmolarity ORS vs. Modified Rehydration
Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 2015, 61, 435 441 doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmv054 Advance Access Publication Date: 27 August 2015 Original Paper Safety and Efficacy of Low-osmolarity ORS vs. Modified Rehydration
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Impact of Training Workshop on Knowledge and Attitude for Zinc and Its Role in Management of
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Impact of Training Workshop on Knowledge and Attitude for Zinc and Its Role in Management of
Understanding copper homeostasis in humans and copper effects on health
 Biol Res 39: 183-187, 2006 BR 183 Understanding copper homeostasis in humans and copper effects on health MAGDALENA ARAYA, FERNANDO PIZARRO, MANUEL OLIVARES, MIGUEL ARREDONDO, MAURICIO GONZÁLEZ and MARCO
Biol Res 39: 183-187, 2006 BR 183 Understanding copper homeostasis in humans and copper effects on health MAGDALENA ARAYA, FERNANDO PIZARRO, MANUEL OLIVARES, MIGUEL ARREDONDO, MAURICIO GONZÁLEZ and MARCO
Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency in Elementary School Children of South Khorasan Province (East Iran)
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:249-254 Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency in Elementary School Children of South Khorasan Province (East Iran) Azita Fesharakinia* 1, MD; Asghar
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:249-254 Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency in Elementary School Children of South Khorasan Province (East Iran) Azita Fesharakinia* 1, MD; Asghar
EFFICACY OF ZINC AS ADJUNCT IN THE TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN LESS THAN FIVE YEARS: A META-ANALYSIS
 2 EFFICACY OF ZINC AS ADJUNCT IN THE TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN LESS THAN FIVE YEARS: A META-ANALYSIS AUTHORS: Kathlynne Anne Caling Abat, MD, Jacinto Blas V. Mantaring III, MD University of the
2 EFFICACY OF ZINC AS ADJUNCT IN THE TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN LESS THAN FIVE YEARS: A META-ANALYSIS AUTHORS: Kathlynne Anne Caling Abat, MD, Jacinto Blas V. Mantaring III, MD University of the
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION
 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION This part reflects the scientific knowledge and the information about this product available at the time of prequalification. Thereafter, updates may have become necessary which are
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION This part reflects the scientific knowledge and the information about this product available at the time of prequalification. Thereafter, updates may have become necessary which are
1978 WHO primary health care 2000
 2008 Vol. 20 No. 2183 1 20 3 1911 1 17 19 1 2 1978 WHO primary health care 2000 2 Key wordsmdg 222 0036 3211 184 2008 1 1 2015 1 1 1990 1 2 2015 1990 2 3 4 5 2015 5 1990 3 1 5 6 HIV 7 HIV 2015 8 2015 7
2008 Vol. 20 No. 2183 1 20 3 1911 1 17 19 1 2 1978 WHO primary health care 2000 2 Key wordsmdg 222 0036 3211 184 2008 1 1 2015 1 1 1990 1 2 2015 1990 2 3 4 5 2015 5 1990 3 1 5 6 HIV 7 HIV 2015 8 2015 7
Int.J.Curr.Res.Aca.Rev.2016; 4(6): Impact of Mid Day Meal on Nutritional Status of School Going Children with Special Emphasis on Zinc
 Impact of Mid Day Meal on Nutritional Status of School Going Children with Special Emphasis on Zinc Iram Khan* and Sangeeta Pandey Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Mount Carmel College, No.58, Palace
Impact of Mid Day Meal on Nutritional Status of School Going Children with Special Emphasis on Zinc Iram Khan* and Sangeeta Pandey Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Mount Carmel College, No.58, Palace
Evidence Based Interventions for Improving Maternal and Child Nutrition: What Can be Done and at What Cost? Lancet, vol 382, , 2013
 Evidence Based Interventions for Improving Maternal and Child Nutrition: What Can be Done and at What Cost? Lancet, vol 382, 452 77, 2013 Dr. S.K Roy Senior Scientist Chairperson, Bangladesh Breastfeeding
Evidence Based Interventions for Improving Maternal and Child Nutrition: What Can be Done and at What Cost? Lancet, vol 382, 452 77, 2013 Dr. S.K Roy Senior Scientist Chairperson, Bangladesh Breastfeeding
Sunil Sazawal 1,2, Usha Dhingra 2, Saikat Deb 2, Maharaj K. Bhan 3, Venugopal P. Menon 2, and Robert E. Black 1
 J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2007 Mar;25(1):62-66 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 Effect of Zinc Added to Multi-vitamin Supplementation Containing Low-dose Vitamin A on Plasma Retinol Level in Children A Double-blind
J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2007 Mar;25(1):62-66 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 Effect of Zinc Added to Multi-vitamin Supplementation Containing Low-dose Vitamin A on Plasma Retinol Level in Children A Double-blind
NUTRITION and. Child Growth & Development. Washington, DC May 2-3, Kay Dewey. UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive
 Clean, Fed & Nurtured: Joining forces to promote child growth and development NUTRITION and Child Growth & Development Washington, DC May 2-3, 2013 Kay Dewey UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive Nutrition Basics
Clean, Fed & Nurtured: Joining forces to promote child growth and development NUTRITION and Child Growth & Development Washington, DC May 2-3, 2013 Kay Dewey UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive Nutrition Basics
Community and International Nutrition
 Community and International Nutrition Effects of Iron and Zinc Supplementation in Indonesian Infants on Micronutrient Status and Growth 1 Marjoleine A. Dijkhuizen,* Frank T. Wieringa,* Clive E. West,*
Community and International Nutrition Effects of Iron and Zinc Supplementation in Indonesian Infants on Micronutrient Status and Growth 1 Marjoleine A. Dijkhuizen,* Frank T. Wieringa,* Clive E. West,*
Zinc: An Essential Trace Element with Potential Benefits to Soldiers*
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 170, 12:1048, 2005 Zinc: An Essential Trace Element with Potential Benefits to Soldiers* Guarantor: James P. McClung, PhD Contributors: James P. McClung, PhD; Angus G. Scrimgeour, PhD
MILITARY MEDICINE, 170, 12:1048, 2005 Zinc: An Essential Trace Element with Potential Benefits to Soldiers* Guarantor: James P. McClung, PhD Contributors: James P. McClung, PhD; Angus G. Scrimgeour, PhD
Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs
 Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs November/December 2002 A research-based newsletter prepared by the University of California for professionals interested in maternal and infant nutrition Recent Trends
Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs November/December 2002 A research-based newsletter prepared by the University of California for professionals interested in maternal and infant nutrition Recent Trends
Information Gaps for Scaling-up Programs to Improve Zinc Nutrition
 TECHNICAL BRIEF for Scaling-up Programs to Improve Zinc Nutrition Kenneth H. Brown, MD BACKGROUND This document focuses on the existing gaps in information needed to design large-scale programs to enhance
TECHNICAL BRIEF for Scaling-up Programs to Improve Zinc Nutrition Kenneth H. Brown, MD BACKGROUND This document focuses on the existing gaps in information needed to design large-scale programs to enhance
Effects of maternal zinc supplementation on pregnancy and lactation outcomes
 Effects of maternal zinc supplementation on pregnancy and lactation outcomes Sonja Y. Hess and Janet C. King Abstract Observational studies in human populations suggest that maternal zinc deficiency during
Effects of maternal zinc supplementation on pregnancy and lactation outcomes Sonja Y. Hess and Janet C. King Abstract Observational studies in human populations suggest that maternal zinc deficiency during
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status
 Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Monika Blössner WHO Department of Nutrition for Health and Development Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry?
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Monika Blössner WHO Department of Nutrition for Health and Development Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry?
Effect of zinc supplementation on mortality in children aged 1 48 months: a community-based randomised placebocontrolled
 Effect of zinc supplementation on mortality in children aged 1 48 months: a community-based randomised placebocontrolled trial Sunil Sazawal, Robert E Black, Mahdi Ramsan, Hababu M Chwaya, Arup Dutta,
Effect of zinc supplementation on mortality in children aged 1 48 months: a community-based randomised placebocontrolled trial Sunil Sazawal, Robert E Black, Mahdi Ramsan, Hababu M Chwaya, Arup Dutta,
WHO Child Growth Standards
 WHO Child Growth Standards Implications for everyday practice Dr Mercedes de Onis Department of Nutrition World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland 1 year 2 years 3 years 4 years 5 years WHO Child
WHO Child Growth Standards Implications for everyday practice Dr Mercedes de Onis Department of Nutrition World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland 1 year 2 years 3 years 4 years 5 years WHO Child
Chapter 8. Chapter 8: Protein-energy Malnutrition
 Chapter 8 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 8: Protein-energy Malnutrition Press the space bar or click the mouse to build
Chapter 8 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 8: Protein-energy Malnutrition Press the space bar or click the mouse to build
(Black et a., 2013) How can livestock interventions affect nutrition outcomes?
 Improving diets and nutrition through an integrated poultry value chain and nutrition intervention (SELEVER) in Burkina Faso: A cluster randomised control trial. Livestock, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Child
Improving diets and nutrition through an integrated poultry value chain and nutrition intervention (SELEVER) in Burkina Faso: A cluster randomised control trial. Livestock, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Child
Zinc supplementation as an adjunct to antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia in children 2 to 59 months of age
 ecommons@aku Woman and Child Health Division of Woman and Child Health October 2011 Zinc supplementation as an adjunct to antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia in children 2 to 59 months of age Batool
ecommons@aku Woman and Child Health Division of Woman and Child Health October 2011 Zinc supplementation as an adjunct to antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia in children 2 to 59 months of age Batool
Environmental Health and Child Survival:
 Environmental Health and Child Survival: Epidemiology and Economics Presentation by Anjali Acharya Senior Environmental Specialist World Bank What do children die from? Diarrhea kills an estimated 1.6
Environmental Health and Child Survival: Epidemiology and Economics Presentation by Anjali Acharya Senior Environmental Specialist World Bank What do children die from? Diarrhea kills an estimated 1.6
Nutrition News for Africa 05/2017
 Predictors and pathways of language and motor development in four prospective cohorts of young children in Ghana, Malawi, and Burkina Faso. Prado EL, Abbeddou S, Adu-Afarwuah S, et al. Journal of Child
Predictors and pathways of language and motor development in four prospective cohorts of young children in Ghana, Malawi, and Burkina Faso. Prado EL, Abbeddou S, Adu-Afarwuah S, et al. Journal of Child
Systematic review of the efficacy and effectiveness of complementary feeding interventions
 Systematic review of the efficacy and effectiveness of complementary feeding interventions Kathryn G. Dewey, PhD Seth Adu-Afarwuah Afarwuah,, PhD Program in International and Community Nutrition University
Systematic review of the efficacy and effectiveness of complementary feeding interventions Kathryn G. Dewey, PhD Seth Adu-Afarwuah Afarwuah,, PhD Program in International and Community Nutrition University
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR. Eduard Bos The World Bank
 IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition
 Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition February 2016 Meera Shekar Global Lead for Nutrition 1 Global Stunting Rates 159 million children stunted worldwide
Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition February 2016 Meera Shekar Global Lead for Nutrition 1 Global Stunting Rates 159 million children stunted worldwide
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI REMARKS MADE BY PROF. PETER M. F. MBITHI, DEPUTY VICE-CHANCELLOR (A&F) DURING THE INSTAPA PROJECT ANNUAL MEETING HELD ON JUNE 22, 2009 Project Description AIM: To identify novel staple
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI REMARKS MADE BY PROF. PETER M. F. MBITHI, DEPUTY VICE-CHANCELLOR (A&F) DURING THE INSTAPA PROJECT ANNUAL MEETING HELD ON JUNE 22, 2009 Project Description AIM: To identify novel staple
Undernutrition & risk of infections in preschool children
 Indian J Med Res 130, November 2009, pp 579-583 Undernutrition & risk of infections in preschool children Prema Ramachandran & Hema S. Gopalan Nutrition Foundation of India, New Delhi, India Received April
Indian J Med Res 130, November 2009, pp 579-583 Undernutrition & risk of infections in preschool children Prema Ramachandran & Hema S. Gopalan Nutrition Foundation of India, New Delhi, India Received April
Child Survival Basic Training
 INTRODUCTION: Child Survival Basic Training for Community Outreach Teams - Sahel Version 1 Copyright 2010 MAMA Project, Inc. Revised 2013 (slide 3) This material is intended solely for non-commercial,
INTRODUCTION: Child Survival Basic Training for Community Outreach Teams - Sahel Version 1 Copyright 2010 MAMA Project, Inc. Revised 2013 (slide 3) This material is intended solely for non-commercial,
The multiple burden of malnutrition and healthy diets
 The multiple burden of malnutrition and healthy diets F.Branca Director Department of Nutrition for Health and development WHO/HQ Acting Executive Secretary SCN 1 Leading risk factors for global burden
The multiple burden of malnutrition and healthy diets F.Branca Director Department of Nutrition for Health and development WHO/HQ Acting Executive Secretary SCN 1 Leading risk factors for global burden
Early life predictors of motor, cognitive, and language development: a pooled multi-country analysis
 Early life predictors of motor, cognitive, and language development: a pooled multi-country analysis Ayesha Sania Christopher Sudfeld Dana McCoy Goodarz Danaei Günther Fink Majid Ezzati Wafaie Fawzi Background
Early life predictors of motor, cognitive, and language development: a pooled multi-country analysis Ayesha Sania Christopher Sudfeld Dana McCoy Goodarz Danaei Günther Fink Majid Ezzati Wafaie Fawzi Background
Serum Levels of Trace Elements (Zinc and Coppper) in Malnourished Children in Bangladesh
 Serum Levels of Trace Elements (Zinc and Coppper) in Malnourished Children in Bangladesh Pages with reference to book, From 251 To 255 S.A.M. Khairul Bashar, Lamia Sharmeen ( Department of Biochemistry,
Serum Levels of Trace Elements (Zinc and Coppper) in Malnourished Children in Bangladesh Pages with reference to book, From 251 To 255 S.A.M. Khairul Bashar, Lamia Sharmeen ( Department of Biochemistry,
Preventive zinc supplementation for children, and the effect of additional iron: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Preventive zinc supplementation for children, and the effect of additional iron: a systematic review and meta-analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Preventive zinc supplementation for children, and the effect of additional iron: a systematic review and meta-analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY
 RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 59 To 61 Inayat Hussain Thaver ( Department of Community Health Sciences, Aga
RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 59 To 61 Inayat Hussain Thaver ( Department of Community Health Sciences, Aga
Agriculture and Nutrition Global Learning and Evidence Exchange (AgN-GLEE)
 This presentation is part of the Agriculture and Nutrition Global Learning and Evidence Exchange (AgN-GLEE) held in Bangkok, Thailand from March 19-21, 2013. For additional presentations and related event
This presentation is part of the Agriculture and Nutrition Global Learning and Evidence Exchange (AgN-GLEE) held in Bangkok, Thailand from March 19-21, 2013. For additional presentations and related event
Global Distribution and Disease Burden Related to Micronutrient Deficiencies
 World Nutrition Situation Black RE, Singhal A, Uauy R (eds): International Nutrition: Achieving Millennium Goals and Beyond. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 78, pp 21 28, ( DOI: 10.1159/000354932 )
World Nutrition Situation Black RE, Singhal A, Uauy R (eds): International Nutrition: Achieving Millennium Goals and Beyond. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 78, pp 21 28, ( DOI: 10.1159/000354932 )
Nutrition in the Post-2015 Context. Lynnda Kiess Head, Nutrition and HIV Unit, WFP
 Nutrition in the Post-2015 Context Lynnda Kiess Head, Nutrition and HIV Unit, WFP Presentation Different Dimensions of Malnutrition Consequences Food Security and Nutrition Looking forward Key Points Nutrition
Nutrition in the Post-2015 Context Lynnda Kiess Head, Nutrition and HIV Unit, WFP Presentation Different Dimensions of Malnutrition Consequences Food Security and Nutrition Looking forward Key Points Nutrition
Early Nutrition and Adult Noncommunicable. that must be broken
 Early Nutrition and Adult Noncommunicable diseases: A vital link that must be broken Commonwealth Health Ministers Meeting WHO, Geneva May 14, 2011 Anna Lartey (Associate Professor) Department of Nutrition
Early Nutrition and Adult Noncommunicable diseases: A vital link that must be broken Commonwealth Health Ministers Meeting WHO, Geneva May 14, 2011 Anna Lartey (Associate Professor) Department of Nutrition
Zinc for severe pneumonia in very young children: double-blind placebo-controlled trial
 Zinc for severe pneumonia in very young children: double-blind placebo-controlled trial ARTICLES W Abdullah Brooks, M Yunus, Mathuram Santosham, M A Wahed, Kamrun Nahar, Sultana Yeasmin, Robert E Black
Zinc for severe pneumonia in very young children: double-blind placebo-controlled trial ARTICLES W Abdullah Brooks, M Yunus, Mathuram Santosham, M A Wahed, Kamrun Nahar, Sultana Yeasmin, Robert E Black
ISSN X (Print) Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1D):267-271 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1D):267-271 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
GAIN S GLOBAL STRATEGY ON FOOD FORTIFICATION TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH ASIA HIGHLIGHTS. Regina Moench-Pfanner, PhD Director, Singapore GAIN
 GAIN S GLOBAL STRATEGY ON FOOD FORTIFICATION TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH ASIA HIGHLIGHTS Regina Moench-Pfanner, PhD Director, Singapore GAIN 1 GAIN - Introduction GAIN was founded at a UN global summit on
GAIN S GLOBAL STRATEGY ON FOOD FORTIFICATION TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH ASIA HIGHLIGHTS Regina Moench-Pfanner, PhD Director, Singapore GAIN 1 GAIN - Introduction GAIN was founded at a UN global summit on
Stop stunting: situation and way forward to improve maternal, child and adolescent nutrition in Afghanistan 1
 Commentary DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12288 Stop stunting: situation and way forward to improve maternal, child and adolescent nutrition in Afghanistan 1 Ariel Higgins-Steele *, Piyali Mustaphi *, Sherin Varkey
Commentary DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12288 Stop stunting: situation and way forward to improve maternal, child and adolescent nutrition in Afghanistan 1 Ariel Higgins-Steele *, Piyali Mustaphi *, Sherin Varkey
DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING
 DEFEATDD.ORG DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING PATH developed these messages for use by anyone interested in communicating the impact of diarrhea on the health and development of children and families around
DEFEATDD.ORG DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING PATH developed these messages for use by anyone interested in communicating the impact of diarrhea on the health and development of children and families around
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Determinants of Zinc Status of 2-3-Year-Old Children in Laguna, Philippines
 Mal J Nutr 23(1): Determinants 9-16, 2017 of Zinc Status of 2-3-Year-Old Children in Laguna, Philippines 9 Determinants of Zinc Status of 2-3-Year-Old Children in Laguna, Philippines Rodesa T Naupal-Forcadilla
Mal J Nutr 23(1): Determinants 9-16, 2017 of Zinc Status of 2-3-Year-Old Children in Laguna, Philippines 9 Determinants of Zinc Status of 2-3-Year-Old Children in Laguna, Philippines Rodesa T Naupal-Forcadilla
Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015
 1 Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015 Dr Mercedes de Onis SCN Annual Session, Hanoi, Viet Nam 2008 2 Intergenerational cycle of growth failure Child
1 Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015 Dr Mercedes de Onis SCN Annual Session, Hanoi, Viet Nam 2008 2 Intergenerational cycle of growth failure Child
Vitamin K. Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz
 Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC.
 Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
Factors affecting child development in developing countries
 Factors affecting child development in developing countries S Grantham-McGregor Centre for Health and Development, Institute of Child Health, University College London Figure 1.1 The Lancet series: The
Factors affecting child development in developing countries S Grantham-McGregor Centre for Health and Development, Institute of Child Health, University College London Figure 1.1 The Lancet series: The
Effect of Consuming Zinc-Fortified Bread on Serum Zinc and Iron Status of Zinc-Deficient Women: A Double Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
 IJPM Effect of Consuming Zinc-Fortified Bread on Serum Zinc and Iron Status of Zinc-Deficient Women: A Double Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial Akbar Badii, Niloufar Nekouei, Mohammad Fazilati, Mohammad
IJPM Effect of Consuming Zinc-Fortified Bread on Serum Zinc and Iron Status of Zinc-Deficient Women: A Double Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial Akbar Badii, Niloufar Nekouei, Mohammad Fazilati, Mohammad
Women by area: Urban F Women by area: Rural F
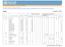 Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Vitamin A Deficiency The Vitamin A Deficiency database includes data by country based on xerophthalmia and/or serum or plasma
Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Vitamin A Deficiency The Vitamin A Deficiency database includes data by country based on xerophthalmia and/or serum or plasma
Launch of a supplement in Health Policy and Planning. Dr. Joy Lawn Mary Kinney Anne Pfitzer On behalf of the team
 A Decade of Change for Newborn Survival Launch of a supplement in Health Policy and Planning Dr. Joy Lawn Mary Kinney Anne Pfitzer On behalf of the team Overview of the supplement Editorial Gary Darmstadt,
A Decade of Change for Newborn Survival Launch of a supplement in Health Policy and Planning Dr. Joy Lawn Mary Kinney Anne Pfitzer On behalf of the team Overview of the supplement Editorial Gary Darmstadt,
Global Update. Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases. infant feeding, including exclusive breastfeeding.
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
nutrition to high global political and fiscal priority
 Emerging opportunity to raise nutrition to high global political and fiscal priority Edward Frongillo Health Promotion, Education, and Behavior February 25, 2011 Nutrition in 20 th century 1912 Vitamin,
Emerging opportunity to raise nutrition to high global political and fiscal priority Edward Frongillo Health Promotion, Education, and Behavior February 25, 2011 Nutrition in 20 th century 1912 Vitamin,
CHILD HEALTH. There is a list of references at the end where you can find more information. FACT SHEETS
 SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
A Randomized Open Label Comparative Clinical Study of a Probiotic against a Symbiotic in the Treatment of Acute Diarrhoea in Children
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
Effects of micronutrient supplementation and fortification interventions on the health and nutritional status of young children: a systematic review
 Effects of micronutrient supplementation and fortification interventions on the health and nutritional status of young children: a systematic review Emily Keats, Jai Das, Zulfiqar A. Bhutta Submitted to
Effects of micronutrient supplementation and fortification interventions on the health and nutritional status of young children: a systematic review Emily Keats, Jai Das, Zulfiqar A. Bhutta Submitted to
Leader. Micronutrients and immune function: some recent developments. (IL)-2 production, higher antibody response,
 _J Clin Pathol 1997;50:887-891 Leader Human Nutrition Research Group, School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Ulster, Coleraine, UK; email: di.thurnham@ ulst.ac.uk Accepted for publication 28 July
_J Clin Pathol 1997;50:887-891 Leader Human Nutrition Research Group, School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Ulster, Coleraine, UK; email: di.thurnham@ ulst.ac.uk Accepted for publication 28 July
Proportion (%) of population with haemoglobin below:
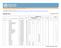 Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Anaemia The database on Anaemia includes data by country on prevalence of anaemia and mean haemoglobin concentration BURKINA
Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Anaemia The database on Anaemia includes data by country on prevalence of anaemia and mean haemoglobin concentration BURKINA
Oral Killed Whole Cell Vaccines: review of available evidence of vaccine effectiveness and safety across different settings and age groups
 Oral Killed Whole Cell Vaccines: review of available evidence of vaccine effectiveness and safety across different settings and age groups Francisco J. Luquero On behalf of the OCV- SAGE working group:
Oral Killed Whole Cell Vaccines: review of available evidence of vaccine effectiveness and safety across different settings and age groups Francisco J. Luquero On behalf of the OCV- SAGE working group:
Strategic Plan. Briefing. Strategic Plan Annual Results. Briefing. Associate Director, Nutrition 15 June 2015 Danny Kaye. Associate Director
 2014 2014 Strategic Plan Strategic Plan Annual Annual Results Results Briefing Briefing Nutrition Werner Werner Schultink Schultink Associate Director Associate Director, 15 June 2015 Nutrition 15 June
2014 2014 Strategic Plan Strategic Plan Annual Annual Results Results Briefing Briefing Nutrition Werner Werner Schultink Schultink Associate Director Associate Director, 15 June 2015 Nutrition 15 June
Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition
 35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition
 The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition Marie Ruel Director, Poverty, Health and Nutrition, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) October
The global evidence-base for what different sectors can do to contribute to undernutrition Marie Ruel Director, Poverty, Health and Nutrition, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) October
Statement. Consensus Statement of IAP National Task Force: Status Report on Management of Acute Diarrhea
 Statement Consensus Statement of IAP National Task Force: Status Report on Management of Acute Diarrhea Writing Committee: Shinjini Bhatnagar Nita Bhandari U.C. Mouli M.K. Bhan Several important developments
Statement Consensus Statement of IAP National Task Force: Status Report on Management of Acute Diarrhea Writing Committee: Shinjini Bhatnagar Nita Bhandari U.C. Mouli M.K. Bhan Several important developments
Balance Sheets 1. CHILD HEALTH... PAGE NUTRITION... PAGE WOMEN S HEALTH... PAGE WATER AND ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION...
 Balance Sheets A summary of the goals, gains and unfinished business of the 1990-2000 decade as included in the Report of the Secretary-General, 'We the Children: End-decade review of the follow-up to
Balance Sheets A summary of the goals, gains and unfinished business of the 1990-2000 decade as included in the Report of the Secretary-General, 'We the Children: End-decade review of the follow-up to
NUTRITION In action. 11 June Diane E. Holland Nutrition Section, Programme Division, UNICEF
 NUTRITION In action 11 June 2018 Diane E. Holland Nutrition Section, Programme Division, UNICEF Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable Development Goals: Global context UNICEF for every child, nutrition
NUTRITION In action 11 June 2018 Diane E. Holland Nutrition Section, Programme Division, UNICEF Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable Development Goals: Global context UNICEF for every child, nutrition
Common Virus and Senseless Killer: A Briefing Paper on Rotavirus
 Common Virus and Senseless Killer: A Briefing Paper on Rotavirus Diarrhea kills. Mothers in the world s poorest countries know this all too well. It s a fact few people in wealthier nations realize. Rotavirus
Common Virus and Senseless Killer: A Briefing Paper on Rotavirus Diarrhea kills. Mothers in the world s poorest countries know this all too well. It s a fact few people in wealthier nations realize. Rotavirus
