Animal Nutrition AP Biology
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Lisa Wheeler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal Nutrition
2 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides food O 2 ATP energy for synthesis ATP
3 Nutritional requirements Animals are heterotrophs need to take in food Why? fulfills 3 needs fuel = chemical energy for production of ATP raw materials = carbon source for synthesis essential nutrients = animals cannot make elements (N, P, K, Fe, Na, K, Ca...), NAD, FAD, etc.
4 How do animals get their food? filter (suspension) feeding substrate feeding fluid feeding bulk feeding
5
6 Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms Herbivores eat mainly plants gorillas, cows, rabbits, snails Carnivores eat other animals sharks, hawks, spiders, snakes Omnivores eat animals & plants cockroaches, bears, raccoons, humans humans evolved as hunters, scavengers & gatherers
7
8 Getting & Using Food Ingest Digest Absorb taking in food mechanical digestion breaking up food into smaller pieces chemical digestion breaking down food into molecules small enough to be absorbed into cells enzymes (hydrolysis) absorb across cell membrane diffusion active transport Eliminate undigested extracellular material passes out of digestive system intracellular digestion extracellular digestion
9 Digestive systems Everybody s got one!
10 Human digestive system Alimentary Canal
11 Common processes & structures Movement & Control peristalsis push food along by rhythmic waves of smooth muscle contraction in walls of digestive system sphincters muscular ring-like valves, regulate the passage of material between sections of digestive system Accessory glands salivary glands, pancreas, liver & gall bladder secrete digestive juices (enzymes & fluid)
12 Swallowing (& not choking) Epiglottis problem: breathe & swallow through same orifice flap of cartilage closes trachea (windpipe) when swallowing food travels down esophagus Esophagus move food along to stomach by peristalsis AP Biology
13 Ingestion Mouth mechanical digestion teeth breaking up food chemical digestion saliva amylase enzyme digests starch mucin slippery protein (mucus) protects soft lining of digestive system lubricates food for easier swallowing buffers neutralizes acid to prevent tooth decay anti-bacterial chemicals kill bacteria that enter mouth with food
14 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs
15 Stomach Functions food storage can stretch to fit ~2L food disinfect food HCl = ph 2 kills bacteria breaks apart cells chemical digestion pepsin enzyme breaks down proteins secreted as pepsinogen activated by HCl Ooooooh! Zymogen! But the stomach is made out of protein! What stops the stomach from digesting itself? mucus secreted by stomach cells protects stomach lining
16 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs stomach kills germs store food break up food digest proteins cardiac sphincter pyloric sphincter
17 Ulcers Used to think ulcers were caused by stress tried to control with antacids Now know ulcers caused by bacterial infection of stomach Helicobacter pylori now cure with antibiotics inflammatory proteins (CagA) cytokines neutrophil cells Coevolution of parasite & host Colonized by H. pylori inflammation of stomach H. pylori Free of H. pylori inflammation of esophagus cell damaging proteins (VacA) helper T cells white blood cells
18 Revolutionizing healthcare "for their discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer disease" Helicobacter pylori J. Robin Warren Barry Marshall
19 Small intestine Function major organ of digestion & absorption chemical digestion digestive enzymes absorption through lining over 6 meters! small intestine has huge surface area = 300m 2 (~size of tennis court) Structure 3 sections duodenum = most digestion jejunum = absorption of nutrients & water ileum = absorption of nutrients & water
20 Duodenum 1st section of small intestines acid food from stomach mixes with digestive juices from accessory glands: pancreas liver gall bladder
21 Pancreas Digestive enzymes peptidases trypsin trypsinogen chymotrypsin chimotrypsinogen carboxypeptidase procarboxypeptidase pancreatic amylase Buffers reduces acidity alkaline solution rich in bicarbonate (HCO 3 -) buffers acidity of material from stomach What stops pancreas Ooooooh! from Zymogen! digesting itself small intestines Explain how this is a molecular example of structure-function theme.
22 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & starch
23 Liver Digestive System Functions produces bile stored in gallbladder until needed breaks up fats act like detergents to breakup fats Circulatory System Connection bile contains colors from old red blood cells collected in liver = iron in RBC rusts & makes feces brown
24 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & starch
25 Digestive enzymes
26 Absorption by Small Intestines Absorption through villi & microvilli finger-like projections increase surface area for absorption Ooooh Structure-Function theme!
27 Absorption of Nutrients Passive transport fructose Active (protein pumps) transport pump amino acids, vitamins & glucose against concentration gradients across intestinal cell membranes allows intestine to absorb much higher proportion of nutrients in the intestine than would be possible with passive diffusion worth the cost of ATP! nutrients are valuable grab all you can get!
28 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & starch stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food small intestines breakdown all foods - proteins - starch - fats - nucleic acids absorb nutrients
29 1. Which of the following is the most direct result of the presence of acid chyme in the small intestine? (A) The liver produces insulin. (B) The pancreas produces hydrolytic enzymes. (C) The stomach produces pepsin. (D)The intestinal lining produces the hormone secretin. (E) The gall bladder releases bile.
30 Large intestines (colon) Function re-absorb water use ~9 liters of water every day in digestive juices > 90% of water reabsorbed not enough water absorbed back to body diarrhea too much water absorbed back to body constipation
31 Flora of large intestines You ve got company! Living in the large intestine is a rich flora of harmless, helpful bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) a favorite research organism bacteria produce vitamins vitamin K; biotin, folic acid & other B vitamins generate gases by-product of bacterial metabolism methane, hydrogen sulfide
32 Why do we fart? Flatulence contains nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, methane, and hydrogen sulfide. These are created by the fermentation of undigested foods such as bean skins and vegetable fiber. The hydrogen sulfide and other compounds make the released gases smell bad. Humans actually expel little methane compared to ruminants such as cows and sheep!
33 Rectum Last section of colon (large intestines) Tell them about the rabbits, George! eliminate feces undigested materials extracellular waste salts mainly cellulose from plants roughage or fiber masses of bacteria appendix
34 mouth break up food moisten food digest starch kill germs liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & carbs stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food small intestines breakdown food - proteins - starch - fats absorb nutrients large intestines absorb water
35 Appendix Vestigial organ
36 Hungry for Information? Ask Questions!
AP Biology. Animal Nutrition
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food oxygen food Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food oxygen food Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms. Mouth
 Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion. Regents Biology
 38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Digestion & Nutrition
 Digestion & Nutrition Ch. 41 Lecture Animal Nutrition 2006-2007 Big Ideas (Unity and Diversity of Life) 1.B.1: Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed
Digestion & Nutrition Ch. 41 Lecture Animal Nutrition 2006-2007 Big Ideas (Unity and Diversity of Life) 1.B.1: Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition
 Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
1. Animals are heterotrophs that require food for fuel, carbon skeletons, and essential nutrients: an overview
 1. Animals are heterotrophs that require food for fuel, carbon skeletons, and essential nutrients: an overview A nutritionally adequate diet satisfies three needs: fuel (chemical energy) for all the cellular
1. Animals are heterotrophs that require food for fuel, carbon skeletons, and essential nutrients: an overview A nutritionally adequate diet satisfies three needs: fuel (chemical energy) for all the cellular
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
This is descriptive - general zoologists might be interested in this: Suspension feeders - whales, gills, clams.
 Nutrition: How to obtain food: This is descriptive - general zoologists might be interested in this: Suspension feeders - whales, gills, clams. Eat little particles suspended in the water. Substrate feeders
Nutrition: How to obtain food: This is descriptive - general zoologists might be interested in this: Suspension feeders - whales, gills, clams. Eat little particles suspended in the water. Substrate feeders
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
UNIT I - DIGESTION Chapter 21
 UNIT I - DIGESTION Chapter 21 OBJECTIVES Core: I can describe the structure and function of the digestive tract. I can outline the chemical digestion of the 3 main macromolecules. I can explain the absorption
UNIT I - DIGESTION Chapter 21 OBJECTIVES Core: I can describe the structure and function of the digestive tract. I can outline the chemical digestion of the 3 main macromolecules. I can explain the absorption
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
(*) (*) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. Uptake of nutrients by body cells (intestine)
 Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition. Omnivores regularly consume animals as well as plants or algae
 Ch 41 Animal Nutrition Need to Feed Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae
Ch 41 Animal Nutrition Need to Feed Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells.
 Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Topic: Human Digestive System Page 1 of 13. The Chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
digestion basic needs budgets chapter 41 ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS FOR ADULTS
 digestion chapter 41 basic needs Nutritional Requirements A nutritionally adequate diet satisfies three needs: Fuel (chemical energy) organic raw materials organic carbon organic nitrogen Essential nutrients
digestion chapter 41 basic needs Nutritional Requirements A nutritionally adequate diet satisfies three needs: Fuel (chemical energy) organic raw materials organic carbon organic nitrogen Essential nutrients
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff
 Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Mouth. Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion. breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces.
 Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Rebel Biology - Nutrition. organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities. carbs, proteins. vitamins, water,
 Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
Digestion, Absorption, and Transport
 Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion
 NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics
 Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition
 Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2015
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
The Digestive System. Functions of the Digestive System
 The Digestive System THINK ABOUT IT When you re hungry, your whole body needs food. But the only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So, how does food get to the rest
The Digestive System THINK ABOUT IT When you re hungry, your whole body needs food. But the only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So, how does food get to the rest
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
The Digestive System: Basics. WedNesday October 24th All organisms need energy to survive. > Use energy to reproduce, grow, and repair
 WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Mar 27 9:53 AM. Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Human Digestion. Junior Science
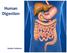 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
