Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
|
|
|
- Gordon Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
2 Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week of Life BAPEN Leeds, November 27, 2007 Patti Thureen, MD, Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Health Sciences Center and the Children s Hospital of Denver patti.thureen@uchsc.edu Financial Disclosures: No relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests
3 Objectives Discuss the arguments for and against early amino acid nutrition in preterm infants Review the safety and efficacy of Early Aggressive Parenteral Amino Acid Nutrition Discuss new data on benefits of early amino acids Present controversies and unresolved issues with early parenteral amino acid administration in preterm infants
4 Why Not Give Early Aggressive Parenteral Nutrition? i Persistent concerns regarding protein intolerance and toxicity Potential adverse outcomes with early amino acids delivery to preterm infants (e.g. cholestasis) Until very recently, few data to indicate that this strategy has long-term benefit on growth or developmental outcomes
5 Why Give Early Aggressive Parenteral Amino Acid Nutrition? Cost Effective? Minimal nutritional reserves in preterms Nationally and internationally we are producing postnatal growth retardation that t is not reversed by the time of hospital discharge
6
7 What Should be the Goals of Early Parenteral Nutrition? Maximize growth and developmental outcome Define minimal acceptable intakes Clarify maximal acceptable intakes: avoid nutrient t toxicity it Wean off parenteral amino acids to enteral nutrition as soon as possible
8
9 Our Approach to Early Aggressive Parenteral Nutrition The Very Preterm Newborn: A NUTRITIONAL EMERGENCY Glucose stores of only 200 kcal Catabolic: net protein loss With IV glucose alone, lose 1% body protein/day 10% loss of protein stores = protein malnutrition
10 Protein Losses In Infants Receiving Glucose Without Amino Acids Gestational Age (g/kg/d) Protein Loss Term weeks weeks Denne, JCI 1996; Clark, Pediatr Res 1997; Poindexter, Am J Physiol 1997
11 Our Primary Nutrition Goal in Very Preterm Infants is Protein Accretion There is increasing evidence that the amount of protein intake early in life correlates with improved developmental outcome Protein gain is the best indicator of real growth Greatest rate of relative protein gain throughout life occurs prior to birth
12 Highest rate of protein gain/kg/d occurs prior to 32 weeks gestation Nutritional needs of Micheliet et al,,in ŅNutritional needs of the preterm infant, Tsang, 1993
13 *Protein Accretion Protein deposition depends on: 1) Protein quantity and quality 2) Energy intake 3) Underlying disease state (sepsis) 4) Medications (steroids, narcotics)
14 Protein Quantity is the Primary Determinant of Protein Accretion Minimum Parenteral Amino Acid Intake Zero Balance (i.e. not catabolic) Can be achieved with g/kg/d protein Initial goal of limiting catabolism and preserving endogenous protein stores can be easily accomplished if parenteral AAs are initiated on the first day of life in ELBW infants, even if caloric intake is low
15 Protein Quantity is the Primary Determinant of Protein Accretion Maximal Parenteral Intake Yet to be defined, limited by concerns of toxicity If goal is to achieve fetal delivery rates (Ziegler): weeks g/kg/d weeks 3.5 g/kg/d 32 weeks 3.2 g/kg/d Term infants g/kg/d
16 How Much Protein and How Quickly? Are Early High Amino Acid Intakes Safe? Current markers used to determine parenteral amino acid intolerance: Metabolic acidosis High ammonia concentration Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) Abnormal plasma amino acid levels *Reliable and sensitive markers of amino acid intolerance still need to be defined
17 How Much Protein and How Quickly? Low vs High Amino Acid Intake Study Hypothesis: Thureen et al, Pediatr Res 53, 2003 In ELBW infants in the first 48 hours of life receiving Low (1 g/kg/d) versus High (3 g/kg/d) IV amino acid intake, the High intake would be: 1) More efficacious (improved protein accretion) 2) Safe : no significant acidosis, elevated BUN, abnormal amino acid concentrations
18 Subject Demographic and Clinical Features 1 g/kg/d 3 g/kg/d Number of infants Birth Wt (g) Gestational Age (wk) Birth to start of TPN (h) Time on TPN at study (h) SNAP Score NTISS Score mean + sem, no significant differences between groups
19 24-hour Nutrient Intake During Experimental Study 1 g/kg/d 3 g/kg/d Amino acids (g/kg/d)c /d) * Glucose (mg/kg/min) Lipid (g/kg/d) Non-protein caloric intake (kcal/kg/d) mean + sem; *significant difference between groups. p<
20 Protein Balance By Nitrogen Balance 1.5 alance d) gen Ba g/kg/d Nitrog (g p= gm/kg/d 3 gm/kg/d -1 AA Intake
21 Protein Balance By Leucine 1.60 Stable Isotope Method Protei n Bal ance (gm m/kg/d d) p= gm/kg/d 3.0 gm/kg/d AA Intake
22 Serum BUN UN mg/d l p= g/kg/d 3g/kg/d B AA Intake
23 Essential Amino Acids ** 1 g/kg/d amino acid intake 3 g/kg/d amino acid intake id Conce entration n (umol/m ml) Am mino Ac ** ns ** ** ** ns * * p<0.05 ** p< VAL LEU ILEU THR PHE MET LYS HIS
24 Essential Amino Acids Amino Ac cid Conce entration n (umol/l L) 400 ELBW, 3 g/kg/d AA Cetin et al, Fetal 2nd Trimester Cetin et al, Fetal 3rd Trimester VAL LEU ILEU THR PHE MET LYS HIS
25 Study Conclusions Efficacy: ELBW neonates on 3 g/kg/d parenteral amino acids immediately after birth have significantly greater rates of protein accretion compared to those on 1 g/kg/d Safety: Based on BUN and plasma amino acid measurements, 3 g/kg/d amino acid IV amino acid intake appears to be tolerated t immediately after birth in ELBW neonates
26 Benefits of Early Amino Acids Administration for LBW Infants STUDY Anderson (1979) Saini (1989) van Lingen (1992) Rivera (1993) Kashyap (1994) van Goudover (1995) Thureen (1998) Thureen (2003) Ibrahim (2004) te Braake (2005) AA SOLUTION Aminosyn Vamin-9 Aminovenous Aminosyn-PF Trophamine Primene Trophamine Trophamine Trophamine Primene
27 Outcomes with Early Amino Acids The majority of reported positive outcomes are from studies showing 1) short-term term increase in nitrogen balance 2) evidence of growth Poindexter et al, J Pediatr 2006, Dinerstein i et al, J Perinatol, 2006 Retrospective and prospective studies: 1) shorter time to regain birth weight 2) suggestion of lower incidence of BPD with early amino acids Ho MY et al, Nutrition, 2003; Porcelli,JPGN,, 2002
28 Outcomes with Early Amino Acids NICHD Studies Early Provision of Parenteral Amino Acids in ELBW Infants: Relationship to Growth and Neurodevelopmental Outcome at 18 Months Corrected Age Initially suggested improved neurodevelopmental outcomes, but not borne out in final analyses Poindexter, J Pediatr 2006
29 Parenteral AA Intake over the first 20 days of life 3.5 Pare enteral AA Intake (g/ /kg/d) Grams per kilo per day Early A A Late AA A ge (days) Days of life From: Poindexter, J Pediatr 2006
30 Growth at 36 weeks CA in ELBW Infants Stratified by Early or Late AAs Early (n=182) Late (n=836) p-value or OR Weight (g) ± 383 Wt <10th 127 (82%) ± 320 p< (82%) 681 (95%) OR 4.2 Length(cm) 41.7 ± ±2.3 p= HC (cm) 30.9 ± ±1.6 p< From: Poindexter, J Pediatr 2006
31 Growth at months CA in ELBW Infants Stratified by Early or Late AAs Early (n=182) Late (n=836) p-value or OR (95% CI) Weight (kg) 10.7 ± ±1.5 NS Wt <10th 70 (47%) 311 (44%) 0.9 ( ) Length(cm) 81.0 ± ±3.9 NS HC (cm) 47.1 ± ±2.0 NS HC < 5th 15 (10%) 124 (17%) 22(1 2.2 ( ) 41) At 18 months CA there were no differences in weight, length or neurodevelopment. However, males in the late group were twice as likely to have head circumference <10th %. Poindexter, J Pediatr 2006
32 Effect of Amino Acid Intake on Hyperglycemia In our 1 vs 3 g/kg/d amino acid intake study, insulin concentrations correlated with amino acid intake. Our incidence of neonatal hyperglycemia has dramatically decreased since starting early parenteral amino acids. Though correlation of decreased incidence of hyperglycemia with increased amino acid intake has been noted, the only publication regarding this was reported by Micheli et al, 1994.
33 Number of infants < 1000 g 60 with hyperglycemia Š hyperkalemia 50 41% 34% 43% 5% 7% 0% simple glucose infusion amino acids + glucose Micheli et al, Seminars in Neonatal Nutrition and Metabolism, 1994
34 Controversies and Unresolved Issues with Early Amino Acids in Preterm Infants TPN Issues Current and ideal amino acid solutions Conditionally essential amino acids Markers of Amino Acid Toxicity i TPN complications Role of TPN in Cholestasis
35 Quality of Parenteral AA Intake to Maximize Protein growth Maximal protein accretion depends on providing the perfect balance of amino acids The optimal ratio of all amino acids in parenteral nutrition of the preterm infant is unknown In theory, deficiency of one essential amino acid will limit overall protein synthesis, and all other amino acids will be in relative excess and will be preferentially oxidized (used for energy)
36 Essential Amino Acids Amino Acid Co oncentrat tion (umo ol/l) 400 ELBW, 3 g/kg/d g AA Cetin et al, Fetal 2nd Trimester Cetin et al, Fetal 3rd Trimester VAL LEU ILEU THR PHE MET LYS HIS
37 Neonatal Amino Acid Solutions Three generations of development: 1) Casein hydrolysates 2) Crystalline amino acid mixtures (Aminosyn, FreAmine III, Travasol) 3) Special pediatric preparations of the crystalline amino acids (Aminosyn PF, Trophamine, Primene, Neopham) *None of the above specifically designed for the ELBW infant
38 Neonatal Amino Acid Solutions Trophamine (Premasol identical in composition) originally formulated to produce plasma amino acid concentrations of healthy, term, breast-fed infants Aminosyn Aminosyn-PF designed to produce AA levels within a normal range of concentrations from breast-fed + parenterally-fed infants Primene derived d from fetal and neonatal cord blood amino acid concentrations
39 Essential or Indispensable AA Cannot be synthesized by humans so must be added Aminosyn-PF (Abbott) Trophamine (B. Braun) Primene (Baxter) Valine Leucine Isoleucine Threonine Phenylalanine Methionine Lysine Histidine Tryptophan AA conc. in mg/dl; AA mixtures shown are 10% solutions
40 Non-Essential AA Can be synthesized from other amino acids or from other precursors Aminosyn- PF Trophamin e Primene Serine Glycine Alanine Tyrosine * 45 Glutamine Glutamic acid Aspartic acid Asparagine - - AA conc. in mg/dl; AA mixtures shown are 10% solutions
41 Conditionally Essential or Semi-Essential AA These are non-essential AAs that become essential under certain circumstances (e.g.sepsis) These amino acids can be synthesized from other AAs Aminosyn-PF Trophamine Primene Glycine *Proline *Arginine Tyrosine * 45 Cysteine - <16 189?Taurine *Some debate exists about the conditional essentiality of arginine and proline AA conc. in mg/dl; AA mixtures shown are 10% solutions
42 Stock or Starter Amino Acid (AA) Solutions Parenteral AA and Dextrose Solution Once prepared it is stable for up to two weeks if refrigerated and with no vitamins, minerals or lipids added We use as initial intravenous fluid after birth
43 Example Stock or Starter Amino Acid (AA) Solutions 2% AA in D10W at 60 ml//kg/d 1.2 g/kg/d AA 2% AA in D10W at 80 ml//kg/d 1.6 g/kg/d AA 5% AA in D7.5W at 60 ml//kg/d 3.0 g/kg/d AA If you start with 5% AA you can t increase the fluid rate! Additional fluids can be co-infused if glucose and/or electrolyte requirements change
44 Complications of Parenteral Nutrition: Parenteral Nutrition Associated Cholestasis (PNAC) Etiology of PNAC is unknown and likely to be multifactorial Risk Factors: Younger gestational ti age» Significantly increased if infants <1000g at birth Duration of TPN Perhaps earlier initiation of TPN Absence of enteral feeding Sepsis, cholangitis, bacterial translocation
45 Parenteral Nutrition Associated Cholestasis (PNAC) Risk Factors: Could lipid infusion be a risk for parenteral nutrition-associated i t cholestasis in LBW infants? Eur J Pediatr, 2007 Significant correlation with duration of TPN, duration of fasting, days of antibiotic use, positive C-reative protein, total t amino acid intake, and total lipid intake Prenatal desamethasone was a significant protective factor for PNAC
46 PNAC Potential Predisposing Factors/Causes Immaturity of the neonatal liver and GI tract Reduced total bile salt pool in preterm neonates Decreased hepatic uptake tk and synthesis of bile salts Reduced enterohepatic circulation Deficient sulfation (important step in the solubilization of toxic bile salts)
47 PNAC Toxicity of TPN components Animal studies: Decreased bile flow with glucose infusions Cholestatic effect of amino acid infusions (esp. methionine, sulfur containing amino acids) Choline dfii deficiency causes steatosis t in rats Human studies Hepatic dysfunction with infusion of excessive calories Cholestatic effect of amino acid infusions (tryptophan, methionine, excess homocystine) Impaired bilirubin excretion in adults receiving high dose intravenous lipids Free radical production is increased by administration of TPN in infants
48 PNAC Potential Therapies in Neonates Parenteral taurine supplementation in specific subgroups of neonatal patients: JPEN, 2005 Significantly reduced PNAC in neonates with NEC Demonstrated a trend to decreased incidence of PNAC in preterm infants versus those without taurine supplementation Conclusions: Infants with NEC or severe prematurity are most likely to benefit from taurine supplementation
49 PNAC Potential Therapies Avoid glucose overload Early detection ti and treatment t t of infections Oral refeeding as soon as possible Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) Chen, et al Pediatr 2004;317 Prevent free radical production (cover lipid and TPN to avoid photo-oxidation) oxidation) Increase anti-oxidant capacities of TPN solutions
50 Toxicity of Early Amino Acids Is BUN an Appropriate Marker for Determining i Protein Intolerance? Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) may increase when administered protein is not completely utilized. This may be accompanied by hyperammonemia (? Bad BUN ) However, urea production may also be a by- product of amino acid oxidation (i.e. amino acids are used as an energy source) (? Good BUN )
51 Fetal Amino Acid (AA) Metabolism Fetal AA uptake from the placenta greatly exceeds protein accretion requirements Excess fetal AA can be used as an energy source (oxidation) It is estimated that 25-50% 50% of energy in the fetal sheep comes from oxidation of AA Animal and human studies show that the normal fetus produces BUN at a high level
52 Human Neonatal Amino Acid (AA) Metabolism In our studies, there is evidence that ELBW neonates who do not tolerate glucose and lipid (i.e., high serum glucose and triglyceride levels at low glucose and lipid id intakes) may use amino acids as an energy source In this case, elevated BUN may reflect a beneficial utilization of AA for energy and not intolerance of protein intake
53 Predictors of Increased BUN Ridout E, Thureen P et al, Journal of Perinatology, December, 2004 Retrospective p review of 4 studies of BUN concentrations in parenterally fed neonates in the first 3 days of life: 122 neonates, 137 BUN values Mean GA: weeks Mean BWt: g
54 Effect of Amino Acid Intake on BUN /d) mg/kg/ BUN (m BUN = AA Intake = r 2 P value NS = Amino Acid Intake (g/kg/d) Adapted from: Ridout, et al. Journal of Perinatology 25:130, 2005
55 Conclusions Early yp parenteral amino acid nutrition in very preterm neonates is associated with both desirable and adverse outcomes There are still many unanswered questions regarding the amount, duration and ideal composition of parenteral amino acid solutions in very preterm neonates
56
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PRIMENE 10% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each litre of the infusion solution contains: L-Isoleucine L-Leucine L-Valine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PRIMENE 10% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each litre of the infusion solution contains: L-Isoleucine L-Leucine L-Valine
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE
 EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 258-265 J. Chung, S.D. Carter,C.V.
EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 258-265 J. Chung, S.D. Carter,C.V.
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
Post Discharge Nutrition. Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP
 Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT ml of the solution for infusion contain:
 Title Page Information June 1999 1 (5) Aminoven infant 10% 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminoven infant 10% 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only
Title Page Information June 1999 1 (5) Aminoven infant 10% 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminoven infant 10% 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE. Authors: J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C.
 EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates:
 Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates: A Randomized Trial Investigating Glutathione Synthesis Stephen B. Shew, M.D. UCLA Division of Pediatric Surgery Nov 29, 2006 Background
Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates: A Randomized Trial Investigating Glutathione Synthesis Stephen B. Shew, M.D. UCLA Division of Pediatric Surgery Nov 29, 2006 Background
GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction
 Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Department of Pediatrics 2 Wesley Medical Center, Department of Neonatology
 Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
0010 Amino Acids 40 Profile - Plasma
 Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Proteins and Amino Acids. Benjamin Caballero, MD, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Test de aminoácidos. Orina.
 SPECIMEN VALIDITY per creatinine INTERVAL 2.5 th 16 th 50 th 84 th 97.5 th Creatinine 57 mg/dl 15-120 Glutamine/Glutamate 4.3 5-160 Ammonia Level (NH 4 ) 42800 μm/g 18000-100000 Specimen Validity Index
SPECIMEN VALIDITY per creatinine INTERVAL 2.5 th 16 th 50 th 84 th 97.5 th Creatinine 57 mg/dl 15-120 Glutamine/Glutamate 4.3 5-160 Ammonia Level (NH 4 ) 42800 μm/g 18000-100000 Specimen Validity Index
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant. J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
 Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
0010 Amino Acid Analysis - 40 Plasma
 770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Evaluation of a taurine containing amino acid
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1991; 66: 21-25 21 Coombe Lying-In Hospital, Dublin 8, Republic of Ireland L Thornton E Griffim Correspondence to: Dr Griffm. Accepted 26 July 199 Evaluation of a taurine
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1991; 66: 21-25 21 Coombe Lying-In Hospital, Dublin 8, Republic of Ireland L Thornton E Griffim Correspondence to: Dr Griffm. Accepted 26 July 199 Evaluation of a taurine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
Maximizing Milk Components and Metabolizable Protein Utilization through Amino Acid Formulation
 Maximizing Milk Components and Metabolizable Protein Utilization through Amino Acid Formulation CHUCK SCHWAB PROFESSOR EMERITUS, ANIMAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE PRE- CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM 71
Maximizing Milk Components and Metabolizable Protein Utilization through Amino Acid Formulation CHUCK SCHWAB PROFESSOR EMERITUS, ANIMAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE PRE- CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM 71
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Development and Evaluation of a New Precision-Fed Chick Assay for Determining Amino Acid Digestibility and Metabolizable Energy of Feed Ingredients
 Development and Evaluation of a New Precision-Fed Chick Assay for Determining Amino Acid Digestibility and Metabolizable Energy of Feed Ingredients C.M. Parsons University of Illinois 1207 W. Gregory Drive
Development and Evaluation of a New Precision-Fed Chick Assay for Determining Amino Acid Digestibility and Metabolizable Energy of Feed Ingredients C.M. Parsons University of Illinois 1207 W. Gregory Drive
Speaker: Paul De Smet. Thursday June 4th 2015
 Speaker: Paul De Smet Thursday June 4th 2015 Your logo Stress Support: the nutritional answer to stress, infection and disease Thursday June 4th 2015 Table of content Stress Support: the nutritional answer
Speaker: Paul De Smet Thursday June 4th 2015 Your logo Stress Support: the nutritional answer to stress, infection and disease Thursday June 4th 2015 Table of content Stress Support: the nutritional answer
M1 - Renal, Fall 2007
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2007-09 M1 - Renal, Fall 2007 Lyons, R.; Burney, R. Lyons, R., Burney, R. (2008, August 07). Renal. Retrieved from Open.Michigan - Educational Resources
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2007-09 M1 - Renal, Fall 2007 Lyons, R.; Burney, R. Lyons, R., Burney, R. (2008, August 07). Renal. Retrieved from Open.Michigan - Educational Resources
Amino Acids: essential nonessential
 Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit?
 Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit? T. R. Overton and L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell University As our understanding of the biology underlying specifics of protein nutrition
Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit? T. R. Overton and L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell University As our understanding of the biology underlying specifics of protein nutrition
Outline. Ø Standard Recommendations. Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins
 Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Product Information: Phenex -1
 Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
R. O. Gottlob, J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokach, R. D. Goodband, J. L. Nelssen, S. S. Dritz 2, C. W. Hastad, K. R. Lawrence, and D. A.
 Swine Day 2004 DETERMINATION OF THE APPARENT AND TRUE ILEAL AMINO ACID DIGESTIBILITY AND DIGESTIBLE AND METABOLIZABLE ENERGY OF SPECIALTY PROTEIN SOURCES INTENDED FOR NURSERY PIG DIETS 1 R. O. Gottlob,
Swine Day 2004 DETERMINATION OF THE APPARENT AND TRUE ILEAL AMINO ACID DIGESTIBILITY AND DIGESTIBLE AND METABOLIZABLE ENERGY OF SPECIALTY PROTEIN SOURCES INTENDED FOR NURSERY PIG DIETS 1 R. O. Gottlob,
Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 7%, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection pediatric formula) is a
Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 7%, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection pediatric formula) is a
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid
Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD
 Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Product Information: Tyrex -1
 Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
Soy Protein. Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging. May 9, Mark Cope, PhD
 Soy Protein Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging May 9, 2017 Mark Cope, PhD Blending Proteins to Provide Better Muscle Health Importance of Muscle Health The Benefits
Soy Protein Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging May 9, 2017 Mark Cope, PhD Blending Proteins to Provide Better Muscle Health Importance of Muscle Health The Benefits
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update?
 Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update? Rajavel Elango Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, School of Population and Public Health University of British Columbia Scientist Level 1 Nutrition
Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update? Rajavel Elango Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, School of Population and Public Health University of British Columbia Scientist Level 1 Nutrition
PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN Praveen Goday MBBS CNSC Associate Professor Pediatric Gastroenterology Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI Parenteral Nutrition-Associated
PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN Praveen Goday MBBS CNSC Associate Professor Pediatric Gastroenterology Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI Parenteral Nutrition-Associated
Product Information: Ketonex -1
 Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Fetal Growth Retardation Caused by Maternal Dietary Amino Acid Imbalance
 Nutritional Adaptation of the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Newborn, edited by N. Kretchmer and A. Minkowski. Nestle, Vevey/Raven Press, New York 1983. Fetal Growth Retardation Caused by Maternal Dietary
Nutritional Adaptation of the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Newborn, edited by N. Kretchmer and A. Minkowski. Nestle, Vevey/Raven Press, New York 1983. Fetal Growth Retardation Caused by Maternal Dietary
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition. Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health
 Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
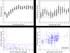 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
 Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Product Information: Propimex -1
 Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
Minimal Enteral Nutrition
 Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D.
 What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane
 Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane Latvian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition September, 2013 Introduction Food contains one or more of the following nutrients: Water Carbohydrate Lipids
Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane Latvian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition September, 2013 Introduction Food contains one or more of the following nutrients: Water Carbohydrate Lipids
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes Read all of this leaflet carefully. It provides a summary of information about your medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes Read all of this leaflet carefully. It provides a summary of information about your medicine.
Threonine Is More Limiting Than Valine in Diets of Lactating Sows with High Rates of Body Protein Loss
 Threonine Is More Limiting Than Valine in Diets of Lactating Sows with High Rates of Body Protein Loss Kevin T. Soltwedel, Robert A. Easter, and James E. Pettigrew Department of Animal Sciences University
Threonine Is More Limiting Than Valine in Diets of Lactating Sows with High Rates of Body Protein Loss Kevin T. Soltwedel, Robert A. Easter, and James E. Pettigrew Department of Animal Sciences University
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Impact of Dietary Crude Protein, Synthetic Amino Acid and Keto Acid Formulation on Nitrogen Excretion
 International Journal of Poultry Science (8): 49-46, 04 ISSN 68-856 Asian Network for Scientific Information, 04 Impact of Dietary Crude Protein, Synthetic Amino Acid and Keto Acid Formulation on Nitrogen
International Journal of Poultry Science (8): 49-46, 04 ISSN 68-856 Asian Network for Scientific Information, 04 Impact of Dietary Crude Protein, Synthetic Amino Acid and Keto Acid Formulation on Nitrogen
STANDARD FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS
 STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide
 Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide Quantitative Amino acids Plasma Plasma. Container/Tube: Preferred EDTA, Place immediately in ice. Acceptable: lithium heparin, sodium heparin. Patient preparation:
Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide Quantitative Amino acids Plasma Plasma. Container/Tube: Preferred EDTA, Place immediately in ice. Acceptable: lithium heparin, sodium heparin. Patient preparation:
Age-related reference ranges
 Authoriser: Peter Beresford Page 1 of 6 Age-related reference ranges Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) IU/L Both less than 14 days 90 273 Both 14 days
Authoriser: Peter Beresford Page 1 of 6 Age-related reference ranges Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) IU/L Both less than 14 days 90 273 Both 14 days
Vamin 18 EF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION
 ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS
 ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
COMPARISON OF INTERNATIONAL PROTEIN CORPORATION 740 FISH MEAL AND SPECIAL SELECT MENHADEN FISH MEAL IN NURSERY PIG DIETS
 Swine Day 2001 Contents COMPARISON OF INTERNATIONAL PROTEIN CORPORATION 740 FISH MEAL AND SPECIAL SELECT MENHADEN FISH MEAL IN NURSERY PIG DIETS M. G. Young, M. D. Tokach, R. D. Goodband, J. L. Nelssen,
Swine Day 2001 Contents COMPARISON OF INTERNATIONAL PROTEIN CORPORATION 740 FISH MEAL AND SPECIAL SELECT MENHADEN FISH MEAL IN NURSERY PIG DIETS M. G. Young, M. D. Tokach, R. D. Goodband, J. L. Nelssen,
BENEFITS OF COLLAGEN
 ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE/TENDON/MUSCLE Alanine: Alanine is an important source of energy for muscle tissue. Helps to convert sugar into glucose for energy. Asparagine: Asparagine may increase endurance and
ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE/TENDON/MUSCLE Alanine: Alanine is an important source of energy for muscle tissue. Helps to convert sugar into glucose for energy. Asparagine: Asparagine may increase endurance and
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals
 Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports
 Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 0 Issue 10 Swine Day (1968-2014) Article 1092 2004 Determination of the apparent and true ileal amino acid digestibility and digestible and
Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 0 Issue 10 Swine Day (1968-2014) Article 1092 2004 Determination of the apparent and true ileal amino acid digestibility and digestible and
Aminosyn-PF 10% An Amino Acid Injection Pediatric Formula. Essential Amino Acids (mg/100 ml)
 Aminosyn -PF 10% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 10%, Sulfite-Free,
Aminosyn -PF 10% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 10%, Sulfite-Free,
EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION. of 7 September 2009
 European Medicines Agency Doc. Ref. EMEA/551360/2009 P/175/2009 EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION of 7 September 2009 on the acceptance of a modification of an agreed Paediatric Investigation Plan for
European Medicines Agency Doc. Ref. EMEA/551360/2009 P/175/2009 EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION of 7 September 2009 on the acceptance of a modification of an agreed Paediatric Investigation Plan for
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Amanda Hernandez FND Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011
 Amanda Hernandez FND 430-001 Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011 1. HP needs TPN because he has short bowel syndrome and his GI tract is not functional. His entire jejunum was and proximal
Amanda Hernandez FND 430-001 Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011 1. HP needs TPN because he has short bowel syndrome and his GI tract is not functional. His entire jejunum was and proximal
Amino acid Catabolism
 Enzymatic digestion of dietary proteins in gastrointestinal-tract. Amino acid Catabolism Amino acids: 1. There are 20 different amino acid, they are monomeric constituents of proteins 2. They act as precursors
Enzymatic digestion of dietary proteins in gastrointestinal-tract. Amino acid Catabolism Amino acids: 1. There are 20 different amino acid, they are monomeric constituents of proteins 2. They act as precursors
Food for special medical purposes. phenylketonuria (PKU) Important notice: Suitable only for individuals with proven phenylketonuria.
 PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
Metabolism of Amino Acids in Aquatic Animals II
 Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 26 pp. 45-48 (1977) Metabolism of Amino Acids in Aquatic Animals II The effect of an amino acid supplemented casein diet on the growth rate of carp Yoshito Tanaka,
Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 26 pp. 45-48 (1977) Metabolism of Amino Acids in Aquatic Animals II The effect of an amino acid supplemented casein diet on the growth rate of carp Yoshito Tanaka,
Protein: Amino Acids. Chapter 6
 Protein: Amino Acids Chapter 6 Chemist s View of Protein Amino Acid Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Each amino acid has an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a side group. It
Protein: Amino Acids Chapter 6 Chemist s View of Protein Amino Acid Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Each amino acid has an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a side group. It
Overview of AMINO ACIDS
 Overview of AMINO ACIDS Amino Acids are the chemical units or "building blocks" of the body that make up proteins. Protein substances make up the muscles, tendons, organs, glands, nails, and hair. Growth,
Overview of AMINO ACIDS Amino Acids are the chemical units or "building blocks" of the body that make up proteins. Protein substances make up the muscles, tendons, organs, glands, nails, and hair. Growth,
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health
 Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Quantity Per Serving. 27 grams
 Whey Protein Isolate Nutrient Details Certain nutrients are included or omitted in our Regular Whey Isolate formula for specific reasons backed by scientific research and development Nutrient Type Protein
Whey Protein Isolate Nutrient Details Certain nutrients are included or omitted in our Regular Whey Isolate formula for specific reasons backed by scientific research and development Nutrient Type Protein
Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Amino acids. Ing. Petrová Jaroslava. Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, , Ankara. Turkey ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1
 Amino acids Ing. Petrová Jaroslava Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, 6. 7. 12. 2011, Ankara. Turkey 6.12.2011 ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1 Content of this presentation 1. Function of amino acids
Amino acids Ing. Petrová Jaroslava Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, 6. 7. 12. 2011, Ankara. Turkey 6.12.2011 ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1 Content of this presentation 1. Function of amino acids
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines
 Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
24-HOUR URINE AMINO ACIDS
 24-HOUR URINE AMINO ACIDS PATIENT: Sample Patient SEX: Male AGE: 14 CLIENT#: 12345 DOCTOR: Doctor's Data, Inc. 3755 Illinois Ave. St. Charles, IL 60174 SPECIMEN VALIDITY SPECIMEN RESULT REFERENCE PERCENTILE
24-HOUR URINE AMINO ACIDS PATIENT: Sample Patient SEX: Male AGE: 14 CLIENT#: 12345 DOCTOR: Doctor's Data, Inc. 3755 Illinois Ave. St. Charles, IL 60174 SPECIMEN VALIDITY SPECIMEN RESULT REFERENCE PERCENTILE
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Dietary Amino Acid Responses of Layers. W. A. Dozier, III Associate Professor Department of Poultry Science, Auburn University Auburn, AL, USA
 Dietary Amino Acid Responses of Layers W. A. Dozier, III Associate Professor Department of Poultry Science, Auburn University Auburn, AL, USA Egg Production Per Hen-Housed 20 to 60 Weeks of Age Elliot,
Dietary Amino Acid Responses of Layers W. A. Dozier, III Associate Professor Department of Poultry Science, Auburn University Auburn, AL, USA Egg Production Per Hen-Housed 20 to 60 Weeks of Age Elliot,
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention
 Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Objectives. Background 4/23/2015. What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition. Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP.
 What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP Objectives Background Indications in the NICU Risks and Complications What is in the bag? Protein Carbohydrate Fats Others
What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP Objectives Background Indications in the NICU Risks and Complications What is in the bag? Protein Carbohydrate Fats Others
