FISHERS HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TEST ANSWER KEY 2017
|
|
|
- Prosper Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FISHERS HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TEST ANSWER KEY 2017 Point Breakdown 52 Multiple Choice Questions- 1 point each: 52 points total Free Response Questions- 15 points total 1. 3 points 2. 2 points 3. 3 points 4. 3 points 5. 4 points Matching Questions: 14 points total 1-5 on antibodies: 5 points ( 1 point each) 1-9 on breathing patterns: 9 points ( 1 point each) Total points possible: 81 points
2 Complete the following multiple choice questions. (1 point each) 1. Which of the following nonrespiratory movements has the most similar mechanism to laughing? a. coughing b. crying c. yawning d. hiccuping 2. Which of the following disorders involves the alveolar walls breaking down and the surface of the lungs being reduced? a. asthma b. chronic bronchitis c. emphysema d. Pneumonia 3. Vibration due to exhaled air that results in speech is a function of the a. trachea b. epiglottis c. nasopharynx d. true vocal cords 4. Which description below describes the way 60% of carbon dioxide is transported in blood? a. as bicarbonate b. physically dissolved in plasma c. bound to Hb d. bound to another molecule of carbon dioxide 5. Which step below is the first step in external respiration? a. oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged between alveoli and blood by diffusion across pulmonary capillaries b. blood transports oxygen and carbon dioxide between lungs and tissues c. oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between tissue and blood by diffusion across systemic capillaries d. ventilation is flow of air into and out of lungs 6. Which of the following statements is false regarding the pharynx? a. 5 inches long b. commonly called the throat c. continuous with the nasal cavity via the internal nares d. plays a role in speech 7. What is tidal volume? a. amount of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions b. amount of air remaining in lungs after forced exhalation c. amount of air that can be inhaled during forced breathing
3 d. amount of air that can be exhaled during forced breathing 8. Which of the following equations best describes total lung capacity? a. TV + IRV + ERV b. VC + RV c. ERV + RV d. TV + IRV 9. Respiratory control center is located in the: a. brainstem b. midbrain c. frontal Lobe d. parietal Lobe 10. Shortness of breath associated with release of histamine is: a. asthma b. emphysema c. bronchitis d. pneumonia 11. Which statement below is not an effect of exercise on the respiratory system? a. The muscle cells produce increased amounts of carbon dioxide b. The brain tells the heart to beat faster c. The brain detects increasing levels of oxygen- a signal is sent to the lungs to decrease breathing d. Breathing rate and the volume of air in each breath increases 12. Which of the following describes the mucosa layer of the wall of the digestive system? a. Thick layer of connective tissue that provides distensibility and elasticity b. Lines the luminal surface of the digestive tract. c. Outer connective tissue covering; secretes serous fluid and prevents friction d. major smooth muscle coat of the digestive tract. 13. List the layers of the alimentary canal from the lumen to the outside. a. mucosa, muscularis externa, submucosa, serosa b. mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa c. submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa, mucosa d. Mucosa, submucosa, serosa, muscularis externa 14. What are the parts of the large intestine? a. colon, cecum, appendix, and rectum b. cecum, ileum, colon, appendix c. colon, cecum, jejunum, ileum d. ileum, jejunum, duodenum, colon
4 15. The posterior region of the tongue is attached to hyoid bone, it is covered with lymphatic tissue called a. Palatine Tonsils b. Lingual Tonsils c. Pharyngeal Tonsils d. Sublingual gland 16. This enzyme splits molecules of starch or glycogen into disaccharides a. Pancreatic Lipase b. Carboxypeptidase c. Pancreatic Amylase d. Trypsin 17. What are the four functions of the digestive system? a. Absorption, secretion, nutrition, motility b. Absorption, secretion, digestion, motility c. Secretion, digestion, motility, decomposition d. Secretion, absorption, nutrition, decomposition 18. What are the bacteria in the GI tract that aid in digestion called? a. Gut flora b. Spirillum c. Mycobaterium d. Bacillus 19. Where does the body store fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K? a. Stomach & liver b. Stomach & fatty tissue c. Liver & stomach d. Liver & fatty tissue 20. Malfunction of this sphincter results in Gastroesophageal reflux disease a. Upper esophageal sphincter b. Lower esophageal sphincter c. Pyloric Sphincter d. Hepatopancreatic sphincter 21. Extra Iron in the blood is mostly stored in a. Pancreas b. Stomach c. Liver d. Kidney
5 22. In addition to water, bile contains: a. Protein b. Carbohydrate c. Cholesterol d. Minerals 23. Contraction of gallbladder to release bile is controlled by: a. trypsin b. Chymotrypsin c. Cholecystokinin d. Lipase 24. A lack of Bile Salts results in: a. Poor lipid absorption b. Poor Carbohydrate absorption c. Poor Protein metabolism d. Electrolyte imbalance 25. The S shaped curve just below the rectum is the: a. Ascending colon b. Descending Colon c. Sigmoid colon d. Transverse colon 26. Lack of Vitamin A causes a. Weak Bones b. Effect on Skin and Vision c. Decreased immunity d. Impaired clotting 27. This mineral deficiency causes altered taste a. Mg b. Calcium c. Zinc d. Cobalt 28. Xerostomia means: a. Dry Mouth b. Dry Skin c. Dry Hair d. Dry Nose
6 29. This lipoprotein is responsible for removing cholesterol from tissues and delivering it to liver. a. LDL b. Triglycerides c. HDL d. VLDL 30. Most absorption happens in which part of GI tract: a. Large Intestine b. Stomach c. Small Intestine d. Liver 31. The jejunum and ileum are suspended from the posterior abdominal wall by a. Greater Omentum b. Lesser Omentum c. Mesentery d. Mucosa 32. What is the correct term to describe the migration of white blood cells toward bacteria? a. Chemotaxis b. Phagocytosis c. Metastasization d. Chemiosmosis 33. Which of the following statements does not describe a toxoid vaccine? a. The resultant protein product is used to provoke the immune system. b. A purified toxin produced by the antigen is used to elicit immune response. c. Genes for microbial antigens are inserted into a plasmid vector and are cloned in appropriate hosts. d. These vaccines contain all or part of the pathogen s DNA. 34. Which immune disease involves the thyroid gland producing excessive amounts of thyroxine? a. Grave s Disease b. Myasthenia gravis c. Multiple Sclerosis d. Rheumatoid arthritis 35. As one gets older, the thymus gland. a. Enlarges b. Shrinks c. Softens d. Hardens
7 36. What is the function of the thymus gland? a. Produce beta cells b. Produce T-cells c. Produce lymph d. Produce blood cells 37. Which cell type does not perform phagocytosis? a. Neutrophil b. Basophil c. Eosinophil d. Mast cell 38. Police : criminals as : a. Red Blood Cells : Oxygen b. Thrombocytes : antigens c. Antibodies: microbes d. Thrombocytes : neutrophils 39. What are the two immune systems that the human body has? a. Innate & Adaptive b. Acquired & Specific c. Innate & Responsive d. Acquired & Adaptive 40. Neutrophils are part of what immune system? a. Adaptive b. Innate c. Specific d. Responsive 41. Natural Killer T-Cells are considered part of what immune systems? a. Innate & Adaptive b. Acquired & Specific c. Innate & Responsive d. Acquired & Adaptive 42. What is the difference between humoral and cell-mediated immunity? a. Cell-mediated immunity focuses on using cell macromolecules to fight against microbes whereas humoral immunity revolves around the activation of phagocytes. b. Cell-mediated immunity is often referred to as antibody-mediated immunity while humoral immunity is often referred to as antigen-mediated immunity. c. Cell-mediated that does not involve antibodies, whereas humoral does. d. All of the above are true.
8 43. What is an example of an autoimmune disease? a. Sickle Cell Disease b. Alzheimer s c. Lou Gherig s Disease d. Multiple Sclerosis 44. The spleen s function is to. a. Produce antibodies b. Filter blood c. Create lymph fluid d. Filter urine 45. What is the function of Peyer s Patches? a. To generate memory lymphocytes for long-term immunity b. Remove pathogens from food or air c. Extract aged red blood cells d. Stores platelets 46. What are the 4 signs of short term inflammation? a. Swelling, heat, fever, pain b. Swelling, redness, heat, pus c. Redness, heat, swelling, pain d. Redness, heat, fever, pus 47. Which of the following explains diapedesis? a. Chemical signals prompt neutrophils to flatten out of capillaries b. Neutrophils migrate to site of injury c. Inflamed cells sprout cell adhesion molecules d. Chemicals from injured site attract natural killer cells 48. Which 2 cells secrete pyrogens? a. Natural killer cells, macrophages b. Leukocytes, macrophages c. Leukocytes, natural killer cells d. Eosinophils, macrophages 49. Which of the following does not describe basic antibody structure? a. Y or T shaped b. 4 heavy chains c. Each antibody has a constant region d. Each antibody has a variable region
9 50. Allografts are defined as: a. Tissue grafts transplanted from one genetically different individual to another b. Tissue grafts transplanted from one body site to another in the same person c. Tissue grafts transplanted from one species to another d. Tissue grafts transplanted from one genetically identical individual to another 51. What are cytokines? a. antibodies b. polypeptides c. carcinogens d. viruses 52. Which type of immunity is generally caused by vaccines? a. artificially acquired passive immunity b. naturally acquired passive immunity c. artificially acquired active immunity d. naturally acquired active immunity FRQ QUESTIONS- (Points vary per question) 1. Compare and contrast inspiration and expiration. (3 points: 1 point for discussing defining each term correctly, 1 point for similarity, 1 point for a difference) Inspiration is when the intrapleural pressure falls to 754 mm Hg, air moves down the pressure gradient and enters the lungs, air flows into the lungs because of the fall in intraalveolar pressure brought about by lung expansion. Lung expansion in not caused by movement of air into the lungs. During inspiration, enlargement of the thoracic cavity is primarily due to contraction and flattening of the diaphragm. Enlargement of the thoracic cavity lowers intra-pleural pressure. Expiration begins with passive relaxation of inspiratory muscles. Muscle relaxation plus the elastic recoil of alveoli decreases size of the thoracic cavity. This causes increase in intra-alveolar pressure. When pressure increases above atmospheric pressure, air is driven out. Forced expiration can occur by contraction of expiratory muscles. 2. What happens during heartburn? ( 2 points: 1 point for definition of heartburn, 1 point for elaboration) When one eats food, the food goes into the stomach and stomach acid is used to break down this food. The lower esophageal sphincter, the area at which the esophagus meets the stomach, closes to keep food from going up into the esophagus. If this sphincter doesn t work, acid can be refluxed into the esophagus causing that burning sensation in the chest.
10 3. Explain Lupus. What major body system does this disease involve and which population is most likely to get Lupus? (3 points) Lupus involves the immune system (1 point) Lupus is when the body s immune system attacks its own tissues and organs. (1 point) Women are more likely than men to develop Lupus (1 point) 4. Explain why there are different blood types. What would happen to a person if two different types were to be mixed? (3 points) Blood cells have antigens on their surfaces that determine the type of blood that they are, and some blood cells have antigen A, others have antigen B, some have both, and some have neither--creating the A, B, AB, and O (no antigens) blood types. (1 point for discussing antigens) If someone is given blood that is not the same type as theirs, that person s immune system will attack the blood cells that were transfused, as the body will treat these unknown cells as foreign invaders. (1 point for mentioning immune system will attack) The patient could suffer kidney failure or even death as a result. (1 point) 5. Discuss the role of fiber in the digestion process. What are the two types, and how does each affect the cycle in its own way? (4 points) Insoluble fibers draw water to the intestine. (1point) Increases the abundance and softness of waste products. (1 point) Soluble Fibers can be dissolved slowly and helps slow down the digestive process--allows stomach to stay fuller for longer. (1 point for dissolving slowly, 1 point for slowing down digestive process as a whole) Matching: Match the antibody with its function. (1 point for each correct match) 1.IgE D 2.IgD C 3.IgA B 4.IgM A 5.IgG E a. First released to blood by plasma cells b. Found in mucus; Prevents pathogens from entering the body c. Always bound to B cells d. Involved in allergies e. Can cross placenta; most abundant
11 Match the breathing pattern its definition (1 point for each correct match). 1. _C Eupnea a.shortness of breath 2. _G Apnea b.occurs when lying down 3. _E Hyperpnea c. normal, relaxed breathing 4. _H Hyperventilation d. Permanent cessation of breathing 5. _B Orthopnea e. increased rate and depth of breathing 6. _F Tachypnea f. Accelerated respiration 7. _A Dyspnea g. skipped breaths 8. _I_Hypoventilation h. increased pulmonary ventilation 9. _D Respiratory Arrest i.reduced pulmonary ventilation
FISHERS HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TEST 2017
 FISHERS HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TEST 2017 Point Breakdown 52 Multiple Choice Questions- 1 point each: 52 points total Free Response Questions- 15 points total 1. 3 points 2. 2 points 3. 3 points
FISHERS HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TEST 2017 Point Breakdown 52 Multiple Choice Questions- 1 point each: 52 points total Free Response Questions- 15 points total 1. 3 points 2. 2 points 3. 3 points
Anatomy and Physiology B Key. Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida
 Anatomy and Physiology B Key Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Tie breaker questions are 11,14, 35, 36, 41,43 Part 1- Respiratory System 1. Which of the following
Anatomy and Physiology B Key Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Tie breaker questions are 11,14, 35, 36, 41,43 Part 1- Respiratory System 1. Which of the following
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
Station A: YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament. Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5.
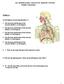 YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY
 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9.
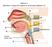 Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
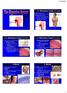 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad
 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz
 ate Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz p. 518 pp. 518 19 p. 517 1. The space between the vocal cords is the. palate.. glottis.. uvula.. pleura. 2. Which is the correct pathway of air as it enters the body?. nose,
ate Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz p. 518 pp. 518 19 p. 517 1. The space between the vocal cords is the. palate.. glottis.. uvula.. pleura. 2. Which is the correct pathway of air as it enters the body?. nose,
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
a. dissolved gases b. nutrients c. globulins d. surfactants e. hormones
 Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Anatomy and Physiology Aviation Invitational December 2017
 Anatomy and Physiology Aviation Invitational December 2017 True/False ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS (except short answer) on SCANTRON INCLUDE TEAM NAME/NUMBER ON SCANTRON FORM Indicate whether the statement is
Anatomy and Physiology Aviation Invitational December 2017 True/False ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS (except short answer) on SCANTRON INCLUDE TEAM NAME/NUMBER ON SCANTRON FORM Indicate whether the statement is
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion
 NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic Respiratory Systems Lymphatic Vessels, Tissue, Organs The Lymphatic System Consists of Lymphatic Lymphoid tissues Lymphatic system functions Transport fluids
Name: Date: Class: Unit 6 Outline: The Lymphatic Respiratory Systems Lymphatic Vessels, Tissue, Organs The Lymphatic System Consists of Lymphatic Lymphoid tissues Lymphatic system functions Transport fluids
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Tissues: systems of cells working together to perform specialized tasks. Ex muscles, nerves, blood
 Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Anatomy and Physiology C Test
 Anatomy and Physiology C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Tie breaker questions are 11,14, 35, 36, 41,43 Read the questions carefully and choose the best answer.
Anatomy and Physiology C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Tie breaker questions are 11,14, 35, 36, 41,43 Read the questions carefully and choose the best answer.
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption
 314 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Multiple Choice 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular system. 2. The digestive
314 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Multiple Choice 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular system. 2. The digestive
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food
 UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
 ROTATION SCHEME Year 1 Skeletal Muscular Integumentary (2016 and 2020) Year 2 Nervous Sense Organs Endocrine (2017 and 2021) Year 3 Respiratory Digestive Immune (2018 and 2022) Year 4 Cardiovascular Lymphatic
ROTATION SCHEME Year 1 Skeletal Muscular Integumentary (2016 and 2020) Year 2 Nervous Sense Organs Endocrine (2017 and 2021) Year 3 Respiratory Digestive Immune (2018 and 2022) Year 4 Cardiovascular Lymphatic
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Full file at
 An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
B cell response. B cell response. Immunological memory from vaccines. Macrophage and helper T cell involvement with initiating a B cell response:
 B cell response Macrophage and helper T cell involvement with initiating a B cell response: B cell response When specific B cells are activated, they multiply Some cells become memory cells, stored in
B cell response Macrophage and helper T cell involvement with initiating a B cell response: B cell response When specific B cells are activated, they multiply Some cells become memory cells, stored in
Al s 202 study guide answers Answers Respiratory System 1 External nares (nostrils) 33 Carina 2 Vestibule 34 Left primary bronchus 3 Nasal cavity 35
 Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
