Digestive System. Lecture Overview (Lectures 7 & 8) Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition
|
|
|
- Caitlin Casey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 21 - Digestive System I, II Lectures 7 & 8 1 Lecture Overview (Lectures 7 & 8) Introduction to the digestive system General characteristics of the alimentary canal The mouth and tongue Salivary glands Pharynx and esophagus Stomach Pancreas 2 Functions of Digestive System ingestion Digestive System mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into a form that cells can absorb absorption excretion defecation 3 1
2 Major Organs of Digestive System Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill, 2007 Organs can be divided into the: -Digestive tract (primary) (alimentary canal); tube extending from mouth to anus (about 30 ft.) -Accessory organs; teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas 4 The Greater and Lesser Omenta Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill, The Mesentery Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill,
3 The Abdominal Cavity & Peritoneum Notice that the pancreas, duodenum, and rectum are retroperitoneal Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, Alimentary Canal Continuous tube modified along its length to carry out specialized, regional functions. Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and anal canal are lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium Stomach and intestines are lined by simple columnar epithelium. Why? 8 Alimentary Canal Wall Know the 4 layers of the alimentary canal Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
4 Alimentary Canal Wall 10 Movements Through the Alimentary Canal mixing movements (segmentation) peristalsis - The wavelike muscular contractions of the alimentary canal or other tubular structures by which contents are forced onward toward the opening. (Triggered by pacesetter cells.) 11 Innervation of the Alimentary Canal The alimentary canal has extensive sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation - mainly in the muscularis externa - regulates its tone and the strength, rate, and velocity of muscular contractions submucosal plexus controls secretions/blood flow myenteric plexus controls gastrointestinal motility/sphincters parasympathetic division of ANS increases activities of digestive system and relaxes sphincters sympathetic division of ANS generally inhibits digestive actions and contracts sphincters 12 4
5 Mouth (Oral or Buccal cavity) (Labium) ingestion mechanical digestion prepares food for further chemical digestion (Labium) Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill, Tongue Very muscular; muscles run in several directions Covered by mucous membranes Blast from the past - Root of tongue is anchored to the hyoid bone 1. Tastebuds 2. Friction for food handling 3. Secretes lingual lipase 14 Palate roof of oral cavity (adenoids) Important in separating the nasopharynx from the pharynx during swallowing 15 5
6 Secondary (Permanent) Teeth Total of 32 secondary (permanent) teeth Watch for incoming ICBMs!!! Know the order of these 16 Primary (Deciduous, Baby, Milk) Teeth (Mastication = chewing) 8 incisors 4 cuspids 8 molars 20 total All primary teeth are lost, generally between ages 6 and Section of a Tooth Oh no! Not again! What type of articulation is this? Know this diagram for exam 18 6
7 Moistens food Binds food particles Functions of Saliva Dissolves food for tasting Begins chemical digestion of complex CHO (amylase) Cleans teeth and mouth (ph = ) Anti-microbial (IgA and lysozyme) 19 Salivary Glands 20 Secretions of Salivary Glands Secretions are slightly acidic and continual due to basal parasympathetic stimulation, but increase after - presence, or anticipation of, food; - parasympathetic stimulation (watery, large volume) - sympathetic stimulation (viscous, small volume) Parotid glands clear primarily water, serous fluid rich in amylase mumps virus typically attacks here Submandibular glands primarily serous fluid some mucus, amylase Sublingual glands primarily mucus most viscous 21 7
8 Pharynx Pharynx aids swallowing by grasping food and moving it toward the esophagus. 22 Three Phases of the Swallowing Reflex Only voluntary phase is the buccal (oral) phase, i.e., the initiation of swallowing, then soft palate and uvula raise hyoid bone and larynx elevate epiglottis closes off top of trachea longitudinal muscles of pharynx contract inferior constrictor muscles relax and esophagus opens peristaltic waves push food through pharynx Pharyngeal phase reflexive Esophageal phase 23 Swallowing Mechanism 24 8
9 Esophagus Veins drain into hepatic portal vein (via gastric veins) Lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter prevents reflux (backup) of stomach acid into the esophagus. Esophagus conveys food from pharynx to stomach by peristalsis 25 Stomach M Gastric glands Stomach can hold about liters of material Rugae flatten as stomach fills M G cells D cells Greater curvature Stomach Functions: - Mixing - Reservoir - Secretion of gastric juice - Digestion, anti-bacterial action, facilitates absorption of vitamin B 12 - Secretion of gastrin, somatostatin 26 Blood Supply and Drainage of Stomach Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
10 Lining and Gastric Glands of Stomach Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, mucus (cardia) from goblet cells and mucous glands protective to stomach wall pepsinogen from chief cells inactive form of pepsin pepsin from pepsinogen in presence of HCl protein splitting enzyme Gastric Secretions INFANTS ONLY rennin (chymosin) gastric lipase hydrochloric acid from parietal cells needed to convert pepsinogen to pepsin p in parietal and p in ph intrinsic factor from parietal cells required for vitamin B 12 absorption mucus, gastrin, somatostatin from pyloric glands protective to stomach wall gastrin and somatostatin are hormones 29 Secretion of H by Parietal Cells Important functions of the stomach ph ( ) - kills microorganisms - denatures proteins - breaks down plant material and CT in meats - activates pepsin Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
11 Three Phases of Stomach Control Cephalic phase triggered by smell, taste, sight, or thought of food begin secretion and digestion Gastric phase triggered by distension, presence of food, and rise in ph in stomach enhances secretion and digestion Intestinal phase triggered by distension of small intestine and ph change controls rate of gastric emptying; may slow emptying NOTE that all these phases control activity in the STOMACH Know what each phase does (shown in red) 31 Cephalic Phase of Gastric Secretion Emotional states can exaggerate or inhibit this phase Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, Gastric Phase of Gastric Secretion Proteins, alcohol, and caffeine can markedly increase secretions by stimulating gastric chemoreceptors Histamine stimulates acid secretion by parietal cells Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
12 Intestinal Phase of Gastric Secretion Enterogastric reflex (inhibits gastric activity) reduces gastric motility, stimulates contraction of pyloric sphincter (pylorus) Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, Overview of Gastric Control/Secretion Key Stimulation ph < 3.0 Emptying of Stomach ( [H ]) (intestinal phase) Fats in Small Intestine D cells Somatostatin Stomach Molility (Segmentation/Peristalsis) ph > 3.0 (dilution of H ) - Food in Stomach (cephalic/gastric phases) Parasympathetic NS G cells Gastrin Stretch of stomach Both Mucous Cells Peptides Protein Breakdown Fat Breakdown ECL Cells Histamine Parietal Cells Chief Cells Lipases - Inhibition Endocrine Factor Exocrine Factor Intrinsic Factor HCO 3- (alkaline tide) Pepsinogen H Cl - Pepsin B Mixing and Emptying Actions 36 12
13 Gastric Absorption Gastric absorption is very limited due to: - blanket of mucus covering cells - epithelial cells lack specialized transport mechanisms - tight junctions between adjacent epithelial cells - gastric lining is relatively impermeable to water - chyme usually contains only partially digested material Some substances can be absorbed by the stomach: some water certain salts certain lipid-soluble drugs, e.g., aspirin alcohol (slowed by presence of fats) 37 Pancreas Exocrine (digestive) and endocrine (metabolic) functions Completes digestion of proteins that was started in the stomach 38 Blood Supply and Drainage of Pancreas Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
14 Pancreatic Juice pancreatic amylase splits glycogen into disaccharides pancreatic lipases break down triglycerides pancreatic nucleases digest nucleic acids bicarbonate ions make pancreatic juice alkaline (ph = 8) and neutralize acid coming from stomach Pancreatic proteolytic enzymes 40 Pancreatic Proteolytic Enzymes Enteropeptidase (Enterokinase) (brush border of sm. intestine) Know this chart Trypsinogen Trypsin Pancreas Chymotrypsinogen yp Procarboxypeptidase Proelastase (Proenzymes, Zymogens) Chymotrypsin yp Carboxypeptidase Elastase (Active enzymes) Dipeptides, tripeptides, amino acids Proteins Purpose of proteolytic enzymes is continued breakdown of proteins that began in the stomach 41 Regulation of Pancreatic Secretions acidic chyme stimulates release of secretin secretin stimulates release of watery pancreatic juice with bicarbonate and phosphate (= buffers; to ph) CCK and parasympathetic NS stimulate production and secretion of pancreatic enzymes and zymogens 42 14
15 Secretin Bile and Pancreatic ducts Regulation of Pancreas/Intestinal Digestion HCO 3-, PO 4 3- ph to 8 (req. for enzyme action) Lacteals Gallbladder Contraction Bile Triglycerides Cholesterol Fat Soluble Vitamins Acidic Chyme Enters Duodenum Cholecystokinin (CCK) Relaxation of hepatopancreatic sphincter Lipases (emulsification) Fatty acids, monoglycerides (brush border) Enterokinase Trypsinogen Trypsin Pancreas Chymotrypsinogen Trypsinogen Procarboxypeptidase Proelastase Carboxypeptidase Elastase Nucleases (DNA, RNA) Nucleotides Portal Vein (proenzymes, zymogens) Amylase (glycogen, starches) Proteins Mono-, di-, trisaccharides Action of brush border enzymes Key Di- and tripeptides Stimulation Subclavian vein Conversion to chylomicrons Monosaccharides Amino acids 43 Alimentary canal (direct contact with food) Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, anal canal Accessory structures (no direct contact with food, but provide secretions) Sli Salivary glands, liver, gall llbldd bladder, pancreas Four layers of the alimentary canal Mucosa absorption, secretion, protection Submucosa nutrition and transport Muscularis movement Serosa protection, lubrication 44 Wave-like movement of alimentary canal is called peristalsis Results from stretching Bowel sounds Innervation of the alimentary canal (enteric nervous system) Parasympathetic increases activity Sympathetic decreases activity Mouth Mastication mechanical processing of food and mixing with saliva 45 15
16 Tongue Lined by mucous membranes Thick, skeletal muscle Papillae function in food handling and taste Lingual frenulum Lingual tonsils Lingual glands secrete lingual lipase Palate (roof of oral cavity) Hard palate (Palatine proc. of maxillary bones) Soft palate Uvula is suspended from this Uvula closes opening to nasal cavity (nasopharynx) 46 Tonsils Lingual (back of tongue) Palatine (lateral to tongue) Pharyngeal (posterior wall of pharynx; adenoids) Teeth Teeth Primary teeth (deciduous teeth; baby teeth) 6 months to 2-4 years 20 total Secondary (permanent teeth) 6 yrs to years 32 total 47 Teeth (continued) Incisors sharp for biting Cuspids (canine) for grasping/tearing Bicuspids and molars grinding Structure Crown above gum line Root below gum line Outer covering is enamel hardest substance in body NOT replaceable Inner substance is dentin (alive) Pulp cavity Periodontal ligament 48 16
17 Alimentary canal (direct contact with food) Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, anal canal Accessory structures (no direct contact with food) Sli Salivary glands, liver, gall llbldd bladder, pancreas Four layers of the alimentary canal Mucosa absorption, secretion, protection Submucosa nutrition and transport Muscularis movement Serosa protection, lubrication 49 Wave-like movement of alimentary canal is called peristalsis Results from stretching Bowel sounds Innervation of the alimentary canal (enteric nervous system) Parasympathetic increases activity Sympathetic decreases activity Mouth Mastication mechanical processing of food and mixing with saliva 50 Tongue Lined by mucous membranes Thick, skeletal muscle Papillae function in food handling and taste Lingual frenulum Lingual tonsils Lingual glands secrete lingual lipase Palate (roof of oral cavity) Hard palate (Palatine proc. of maxillary bones) Soft palate Uvula is suspended from this Uvula closes opening to nasal cavity (nasopharynx) 51 17
18 Tonsils Lingual (back of tongue) Palatine (lateral to tongue) Pharyngeal (posterior wall of pharynx; adenoids) Teeth Primary teeth (deciduous teeth; baby teeth) 6 months to 2-4 years 20 total Secondary (permanent teeth) 6 yrs to years 32 total 52 Teeth (continued) Incisors sharp for biting Cuspids (canine) for grasping/tearing Bicuspids and molars grinding Structure Crown above gum line Root below gum line Outer covering is enamel hardest substance in body NOT replaceable Inner substance is dentin (alive) Pulp cavity Periodontal ligament 53 Salivary glands produce saliva which Moistens food Binds food particles Begins chemical digestion of CHO Dissolves food (for taste) Cleanses mouth and teeth; antibacterial i Three pairs of salivary glands Parotid; front of ear, watery fluid rich in amylase Submandibular; floor of mouth, viscous fluid Sublingual; below tongue, thick, stringy secretion 54 18
19 Salivary glands Sympathetic stimulation small quantity of viscous saliva Parasympathetic stimulation large volume of watery saliva Pharynx Cavity connecting mouth with esophagus Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx Muscles Inner circular constriction Outer longitudinal movement of food bolus 55 Swallowing Initiation is voluntary; act of swallowing is NOT it s a reflex Three stages Chewing and rolling of food into oropharynx (voluntary, buccal) Swallowing reflex (pharyngeal) Epiglottis closes over larynx Muscles in lower pharynx relax Esophagus opens and food moves in Peristalsis in esophagus transports food to stomach (esophageal) Esophagus Muscular tube connects to cardiac region of stomach Esophageal hiatus Lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter 56 Stomach Cardiac, fundus, body, pylorus Mixes food and begins digestion of protein Limited absorption (alcohol) Moves food into small intestine Pyloric sphincter (entrance to small intestine) Rugae and gastric pits Gastric glands Mucous cells (goblet) secrete mucous Chief cells (peptic) secrete digestive enzymes, esp. pepsinogen Parietal cells (oxyntic) secrete HCl (Parietal, ph) Infants only - Gastric lipase and rennin 57 19
20 Regulation of gastric activity Cephalic phase (primarily neural) Prior to food entry into stomach Increased motility and production of gastric juice Gastric phase Neural: Food entering stomach / ph rising Hormonal: gastrin release Local: histamine release (stimulates parietal cells) Intestinal phase Neural: distension of duodenum (enterogastric reflex) Hormonal: CCK, GIP, and secretin, gastrin Reduction (slowing) of gastric emptying 58 Pancreas Both exocrine and endocrine functions Main source of intestinal digestive enzymes Pancreatic amylase (starches) Pancreatic lipase (fats) Nucleases Proteolytic proenzymes / enzymes Regulation of pancreatic activity Acid chyme stimulates secretin Secretin stimulates watery buffering secretion Parasympathetic NS and CCK stimulate production and secretion of digestive enzymes 59 20
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Chapter 24, Part 1! The Digestive System!
 Chapter 24, Part 1! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-1! The digestive system, consisting of the digestive tract and accessory organs, has overlapping food utilization functions! 2 1! Functions! 1. Ingestion!
Chapter 24, Part 1! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-1! The digestive system, consisting of the digestive tract and accessory organs, has overlapping food utilization functions! 2 1! Functions! 1. Ingestion!
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Digestive System. Digestive Processes. The Digestive System. Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells
 The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract
 16 The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract The Digestive System Consists of the muscular digestive tract assisted by various accessory organs Digestive functions include: Ingestion Mechanical
16 The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract The Digestive System Consists of the muscular digestive tract assisted by various accessory organs Digestive functions include: Ingestion Mechanical
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System CHAPTER 14
 Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Chapter 16. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
the serous membranes lining the peritoneal cavity continuously produce what?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Sunday 29th January. Day 1: The Digestive Tract. From Anatomy to Treatment. A Nutritional Approach MPS.
 Sunday 29th January Day 1: The Digestive Tract From Anatomy to Treatment A Nutritional Approach MPS www.osteopathicea.com mike@osteopathicea.com AKA Digestive Tract, Alimentary Canal, Enteron, or Gut Body
Sunday 29th January Day 1: The Digestive Tract From Anatomy to Treatment A Nutritional Approach MPS www.osteopathicea.com mike@osteopathicea.com AKA Digestive Tract, Alimentary Canal, Enteron, or Gut Body
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
EXTRA CREDIT DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - Suggested Answer/Outline
 EXTRA CREDIT DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - Suggested Answer/Outline ASSIGNMENT: You have just eaten a balanced meal. The meal contained the macromolecules protein, carbohydrates, and fat as well as a vitamin B12
EXTRA CREDIT DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - Suggested Answer/Outline ASSIGNMENT: You have just eaten a balanced meal. The meal contained the macromolecules protein, carbohydrates, and fat as well as a vitamin B12
Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition
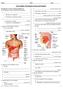 Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition The Digestive System: Mouth and Pharynx The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Breakdown of ingested Absorption of nutrients into
Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition The Digestive System: Mouth and Pharynx The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Breakdown of ingested Absorption of nutrients into
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
 Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Chapter 15 Digestive System and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestive System and Nutrition 15.1 Introduction (Fig. 15.1) A. Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. B. The digestive
Chapter 15 Digestive System and Nutrition 15.1 Introduction (Fig. 15.1) A. Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. B. The digestive
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. Digestive system organs fall into two main groups: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. (pp. 857 858; Fig. 23.1) 1. The
The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. Digestive system organs fall into two main groups: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. (pp. 857 858; Fig. 23.1) 1. The
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
 Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Lu Anne Clark Professor of Science, Lansing Community College Chapter 15 Lecture Outlines* *See PowerPoint
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Lu Anne Clark Professor of Science, Lansing Community College Chapter 15 Lecture Outlines* *See PowerPoint
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestion and absorption (I)
 Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Chapter 9 Digestive System. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
10/24/2016. Introduction
 Introduction Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Main portion of the digestive system is a long tube extending
Introduction Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Main portion of the digestive system is a long tube extending
Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 13 Digestive System 1 Mouth to Stomach Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of the digestive system
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 13 Digestive System 1 Mouth to Stomach Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of the digestive system
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Chapter 15 The Digestive System
 Chapter 15 The Digestive System 3 major macromolecules are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Carbohydrates are polymers of simple monosacharides. Fats are polymers of glycerol and fatty acids. Proteins
Chapter 15 The Digestive System 3 major macromolecules are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Carbohydrates are polymers of simple monosacharides. Fats are polymers of glycerol and fatty acids. Proteins
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Chapter 25
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
Chapter 23: The Digestive System
 Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Digestive System Chapter 22. Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs
 13 Bio104 Lecture Outline Digestive System Chapter 22 Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs è Module 22.1: Overview of the Digestive System INTRODUCTION Digestive system
13 Bio104 Lecture Outline Digestive System Chapter 22 Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs è Module 22.1: Overview of the Digestive System INTRODUCTION Digestive system
Chapter 14 The Digestive System
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System Foods are used as metabolic fuel (energy) Foods are oxidized and transformed into ATP ATP = Chemical energy the drives cellular activities Energy value of food is measured
Chapter 14 The Digestive System Foods are used as metabolic fuel (energy) Foods are oxidized and transformed into ATP ATP = Chemical energy the drives cellular activities Energy value of food is measured
