FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
|
|
|
- Bruce Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN Vol. 1, No. 3, July IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE Manoj Kr Gautam 1 and Varsha Deva 1* *Corresponding Author: Varsha Deva, varsha.moon@gmail.com The objective of the present investigation was to prepare and evaluate floating drug delivery system1,2,4 consisting of ranitidine hydrochloride (RH). Formulation of various concentration and grades were prepared with HPMC K4M, guar gum and xantham gum as sustained release polymers, and in-vitro floating profile was studied. As the result non- effervescent floating drug delivery system was achieved by in-vitro buoyancy with polymer HPMC K4 M8,9, but xantham gum, and guar gum did not exhibit sufficient swelling to provide in vitro buoyancy. So an effervescent approach was adopted, in which sodium bicarbonate was added as gas generating agent. Keywords: Radiation emission, Dwelling zone, Ailments, Moody, Blood pressure INTRODUCTION Oral administration is the most convenient and preferred means of any drug delivery to the systematic circulation (Arora et al., 2005; and Dave et al., 2004). Oral controlled release drug delivery have recently been of increasing interest in pharmaceutical field to achieve improved therapeutic advantages, such as ease of dosing administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation (Korsemeyer et al., 1983; and Martindale, 2002). Drugs that are easily absorbed from gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and have short half-lives are eliminated quickly from the systemic circulation. Frequent dosing of these drugs are required to achieve suitable therapeutic activity. To avoid this limitation, the development of oral sustained-controlled release formulations is an attempt to release the drug slowly into the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and maintain an effective drug concentration in the systemic circulation for a long time. After oral administration, such a drug delivery would be retained in the stomach and release the drug in a controlled manner, so that the drug could be supplied continuously to its absorption sites the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). These drug delivery systems suffer from mainly two adversities: the short gastric retention time (GRT) and unpredictable short gastric emptying time (GET), which can result in incomplete drug release from 1 Department of Pharmacy, Shri Ram Murti Smarak College of Enggineering and Technology, Bareilly, UP. 142
2 the dosage form in the absorption zone (stomach or upper part of small intestine) leading to diminished efficacy of administered dose. To formulate a site-specific orally administered controlled release dosage form, it is desirable to achieve a prolonged gastric residence time by the drug delivery. Prolonged gastric retention improves bioavailability, increases the duration of drug release, reduces drug waste, and improves the drug solubility that are less soluble in a high ph environment (Danbrow and Samuelov, 1980; and Miyazaki et al., 2000). Also prolonged gastric retention time (GRT) in the stomach could be advantageous for local action in the upper part of the small intestine e.g. treatment of peptic ulcer (Miyazaki et al., 2003; and Nunamaker et al., 2007) etc. Gastroretentive drug delivery is an approach to prolong gastric residence time, thereby targeting site-specific drug release in the upper gastrointestinal tract (GIT) for local or systemic effects. Gastroretentive dosage forms can remain in the gastric region for long periods and hence significantly prolong the gastric retention time (GRT) of drugs. Over the last few decades, several gastroretentive drug delivery approaches being designed and developed, including: high density (sinking) systems that is retained in the bottom of the stomach, low density (floating) systems that causes buoyancy in gastric fluid, mucoadhesive systems that causes bioadhesion to stomach mucosa, unfoldable, extendible, or swellable systems which limits emptying of the dosage forms through the pyloric sphincter of stomach superporous hydrogel systems magnetic systems etc. The current review deals with various gastroretentive approaches that have recently become leading methodologies in the field of site-specific orally administered controlled release drug delivery systems. FACTORS CONTROLLING GAS- TRIC RETENTION OF DOSAGE FORMS The stomach anatomy and physiology contain parameters to be considered in the development of gastroretentive dosage forms. To pass through the pyloric valve in to the small intestine the particle size should be in the range of 1 to 2 mm. The most important parameters controlling the gastric retention time (GRT) of oral dosage forms include : density, size and shape of the dosage form, food intake and its nature, caloric content and frequency of intake, posture, gender, age, sex, sleep, body mass index, physical activity and diseased states of the individual (e.g., chronic disease, diabetes, etc.) and administration of drugs with impact on gastrointestinal transit time for example drugs acting as anticholinergic agents (e.g., atropine, propantheline), Opiates (e.g., codeine) and prokinetic agents (e.g., metclopramide, cisapride). The molecular weight and lipophilicity of the drug depending on its ionization state are also important parameters. Density of Dosage Forms The density of a dosage form also affects the gastric emptying rate and determines the location of the system in the stomach. Dosage forms having a density lower than the gastric contents can float to the surface, while high density systems sink to bottom of the stomach. Both positions may isolate the dosage system from the pylorus. Density of <1.0 gm/cm 3 is required to exhibit floating property. 143
3 Shape and Size of the Dosage Form Shape and size of the dosage forms are important in designing indigestible single unit solid dosage forms. The mean gastric residence times of nonfloating dosage forms are highly variable and greatly dependent on their size, which may be large, medium and small units. In most cases, the larger the dosage form the greater will be the gastric retention time (GRT) due to the larger size of the dosage form would not allow this to quickly pass through the pyloric antrum into the intestine. Dosage forms having a diameter of more than 7.5 mm show a better gastric residence time compared with one having 9.9 mm. Ring-shaped and tetrahedron-shaped devices have a better gastric residence time as compared with other shapes. Retention time (GRT) due to the larger size of the dosage form would not allow this to quickly pass through. Food Intake and Its Nature Food intake, viscosity and volume of food, caloric value and frequency of feeding have a profound effect on the gastric retention of dosage forms. The presence or absence of food in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) influences the gastric retention time (GRT) of the dosage form. Usually the presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) improves the gastric retention time (GRT) of the dosage form and thus, the drugs absorption increases by allowing its stay at the absorption site for a longer period. Again, increase in acidity and caloric value shows down gastric emptying time (GET), which can improve the gastric retention of dosage forms. Effect of Gender, Posture and Age Generally females have slower gastric emptying rates than male. The effect of posture does not have any significant difference in the mean gastric retention time (GRT) for individuals in upright, ambulatory and supine state. In case of elderly persons, gastric emptying is slowed down (Higuchi, 1963; Indian pharmacopoeia, 1996; and Miyazaki et al., 2000). Floating Drug Delivery Systems Floating drug delivery systems is one of the important approaches to achieve gastric retention to obtain sufficient drug bioavailability. These delivery systems are desirable for drugs with an absorption window in the stomach or in the upper small intestine. This has a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period and the drug is released slowly as a desired rate from the system. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. This result in an increased gastric retention time (GRT) and a better control of the fluctuation in plasma drug concentration. The major requirements for floating drug delivery system are (Paulo and Jose, 2001; and Shabaraya and Narayanacharyulu, 2003): It should release contents slowly to serve as a reservoir. It must maintain specific gravity lower than gastric contents ( gm/cm3). It must form a cohesive gel barrier. The inherent low density can be provided by the entrapment of air (e.g., hollow chambers) or by the incorporation of low density materials (e.g., fatty materials or oils, or foam powder). These following approaches have been used for the design of floating dosage forms of single and multiple-unit systems. Recently a single-unit floating system was proposed consisting of 144
4 polypropylene foam powder. Matrix forming polymers, drug and filler (Sahoo et al., 2007; and Singh and Known, 2000). The good floating behavior of these systems could be successfully combined with accurate control of the resulting drug release patterns. Single-unit dosage forms are associated with problems such as sticking together or being obstructed in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) which may produce irritation. On the other hand multiple-unit floating systems may be an attractive alternative since they have been shown to reduce the inter- and intra-subject availabilities in drug absorption as well as to lower the possibility of dose dumping. Various multipleunit floating system like air compartment multipleunit system, hollow microspheres (microballoons) prepared by the emulsion solvent diffusion method, microparticles based on low density foam powder, beads prepared by emulsion gelatin method etc. can be distributed widely throughout the GIT, providing the possibility of achieving a longer lasting and more reliable release of drugs. Based on the mechanism of buoyancy two distinctly different technologies, i.e., non-effervescent and effervescent systems have been utilized in the development of floating drug delivery system. Non-Effervescent Systems Non-effervescent floating drug delivery systems are normally prepared from gel-forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides or matrix forming polymers like polyacrylate, polycarbonate, polystyrene and polymethacrylate. In one approach, intimate mixing of drug with a gel forming hydrocolloid which results in contact with gastric fluid after oral administration and maintain a relative integrity of shape and a bulk density less than unity within the gastric environment. The air trapped by the swollen polymer confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. Excipients used most commonly in these systems include hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) polyacrylates, polyvinyl acetate, carbopol, agar, sodium alginate, calcium chloride, polyethylene oxide and polycarbonate. This system can be further divided into the subtypes. 1. Hydrodynamically balanced systems 2. Microballoons/Hollow microspheres 3. Alginate beads 4. Microporous compartment system (Figure 1) Figure 1: Microporous Compartment System and Effervescent Systems 145
5 5. Effervescent systems 6. Bioadhesive or Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems (Figure 2) 7. Expandable, unfoldable and swellable systems (Figure 3) 8. Super porous hydrogel systems and 9. Magnetic Systems MATERIALS AND METHODS (Arora et al., 2005; Dave et al., 2004; Santucci et al., 1996; Shilpa et al., 2003; and Whitehead et al., 2004) Materials Ranitidine hydrochloride was received as a gift sample from Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Ahmedabad, India. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose Figure 2: Bioadhesive or Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems Figure 3: Drug Release From Swellable Systems 146
6 (HPMC K4 M), guar gum, and xanthan gum were received as gift samples from Zydus-Cadila Healthcare Ltd, Ahmedabad, India. Sodium bicarbonate, stearic acid, and citric acid anhydrous (hereafter referred to as citric acid) were purchased from SD. Fine-Chem. Ltd., Ahmedabad, India. All other ingredients were of laboratory grades. Methods (Santucci et al., 1996; Shilpa et al., 2003; Whitehead et al., 2004; and United States Pharmacopoeia, 1999) Preparation of floating drug delivery system of ranitindine hydrochloride (United States Pharmacopoeia, 1999): Firstly RH was mixed with the required quantities of HPMC K4 M by geometric mixing. Then blended Then RH was dispersed in chloroformic solution of the required quantity of stearic acid. And the with stearic acid and magnesium stearate (1% wt/wt) and purified talc (1% wt/wt). Then a tablet is punched using multistation puching machine. The same procedure was repeated with Guar gum and Xanthum gum (Table 1). Another set of formulation was prepared using sodium bicarbonate and citric acid for effervescence. For which RH was mixed with the required quantities of Xantham gum sodium bicarbonate, and citric acid dispersion was stirred and chloroform was evaporated to form an RHcitric. This mixture was then blended with other ingredients like lubricants, magnesium stearate Formulation Table 1: Table Showing Various Formulations Prepared Ingredients (1% wt/wt) and guar gum (Table 2). This may improves the floating properties of the formulations. Table 2: Second Set of Formulation Formulation Ingredients F1 F2 In-Vitro Studies RH, guar gum, sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, magnesium stearate and talc. RH, Xantham gum, sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, magnesium stearate and talc Floating Properties The floating properties of the formulation were done in USP dissolution apparatus (paddle type), with 0.1 N Hcl. The floating time was calculated for each formulation separately. Drug Release Profile purified talc (1% wt/wt). The same procedure was repeated with The drug release profile was studied through the dissolution study in U.S.P. dissolution apparatus basket type and the rate of release of drug from the polymer matrix is mathematically calculated. And swelling was also monitored after every hour by measuring the diameter of the tablet. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The RH tablets prepared using polymers such as HPMC K4 M, and then guar gum, and xanthan gum. The xanthan gum and guar gum did not exhibit sufficient swelling to provide in vitro buoyancy. A1 A2 A3 RH and Guar gum Rh and Xantham gum RH and HPMC K 4 M Floating Properties A1 shows the excellent floating properties. The result was shown in Table
7 Formulation A1 A2 A3 F1 F2 Table 3: Floating Time Floating Time 169 min 35 min. 26 min. 143 min. 138 min. Drug Release Profile and Swelling Properties The result of the dissolution studies shows the following result as shown in the Table 4. The drug content, entrapment efficiency and change in the size of the diameter given in the Table 4. In formulation A1 i.e., having HPMC only shows the prominent change in size, the entrapment efficiency and drug content is quite high as compared to other formulations of guar gum and xanthum gum. Adding sodium bicarbonate, citric acid and stearic acid changes the swelling properties only as not much changes is seen in case of drug content and entrapment efficiency. Table 4: The Results of Dissolution Studies Formulation Drug Change in Entrapment Content (%) Diameter Efficiency (%) A A A F F Non-effervescent floating drug delivery was achieved by in vitro buoyancy. The RH tablets were prepared using polymers such as HPMC K4 M, and then guar gum, and xanthan gum. The xanthan gum and guar gum did not exhibit sufficient swelling to provide in vitro buoyancy. An effervescent approach was then adopted. Another set of formulation was prepared using guar gum, and xanthan gum. Sodium bicarbonate was added as a gas generating agent. Sodium bicarbonate induced CO 2 generation in the presence of dissolution medium (0.1 N HCl). The gas generated was trapped and protected within the gel, formed by hydration of polymer, thus decreasing the density of the tablet. As the density of the tablet falls below 1, the tablet becomes buoyant. Whitehead et al. (2000) have demonstrated good correlation between in vitro buoyancy of floating dosage forms. Three types of formulation were prepared i.e., A1, A2 and A3, A1 and A2 containing guar gum and xanthan gum, failed to form a gel with sufficient strength, while A3 with HPMC K4 M produced tablets with good gel strength, imparting stable and persistent buoyancy. To study the effect of sodium bicarbonate concentration on floating lag time, another formulation F1 and F2 was developed. Demonstrates sodium bicarbonate (50 mg per tablet) was essential to achieve optimum in vitro buoyancy. CONCLUSION The preparation of gastroretentive tablets of Ranitidine hydrochloride was studied and evaluated carefully. The study suggested that the effervescent based floating drug delivery was a promising approach to achieve in vitro buoyancy. The addition of gel-forming polymer HPMC K4 M and gas-generating agent sodium bicarbonate was essential to achieve in vitro buoyancy. Addition of citric acid, to achieve buoyancy under the elevated ph of the stomach, caused an enhancement in drug release that was retarded by incorporation of stearic acid in the formulation. Thus, by selecting a suitable composition of 148
8 release rate enhancer (citric acid) and release rate retardant (stearic acid), the desired dissolution profile can be achieved. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors are grateful in expressing their sincere thanks to our management, of S.R.M.S.C.E.T. Bareilly, Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd, and Zydus-Cadila Healthcare Ltd, Ahmedabad, India, for providing the Ranitidine hydrochloride samples, guar gum and xantham gum for this research respectively. Last but not the least, thankful to friends, colleagues and parents for the efforts in motivating us for the work. REFERENCES 1. Arora S, Ali J and Ahuja A (2005), Floating Drug Delivery System: A Review, AAPS Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Vol. 6, pp. E372-E Dave B S, Amin A F and Patel M M (2004), Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System of Ranitidine Hydrochloride Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation, AAPS Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Vol. 5, p Danbrow M and Samuelov Y (1980), Zero Order Drug Delivery From Double Layered Porous Films: Release Rate Profiles From Ethyl Cellulose, Hydroxypropyl Cellulose and Polyethylene Glycol Mixtures, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Vol. 32, pp Higuchi T (1963), Mechanism of Sustainedaction Medication: Theoretical Analysis of Rate of Release of Solid Drugs Dispersed in Solid Matrices, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 52, pp Korsemeyer R W, Gurny R, Doelker E M, Buri P and Peppas N A (1983), Mechanism of Solute Release from Porous Hydrophilic Polymers, International Journal of Pharmacy, Vol. 15, pp Martindale (2002), The Complete Drug Reference, 33 rd Edition, Pharmaceutical Press, p. 1245, London. 7. Mishra B, Jayanta B and Sankar C (2003), Development of Chitosan-Alginate Microcapsules for Colon Specific Delivery of Metronidazole, Indian Drugs, Vol. 40, No. 12, pp Miyazaki S, Whitehead K and Attwood D (2000), Oral Sustained Delivery of Theophylline Using In Situ Gelation of Sodium Alginate, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 67, pp Miyazaki S, Whitehead K and Attwood D (2003), Oral Sustained Delivery of Paracetamol from In Situ Gelling Gellan and Sodium Alginate, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 258, pp Nunamaker E A, Purcell E K and Kipke D R (2007), In Vivo Stability and Biocompatibility of Implanted Calcium Alginate Disks, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, Vol. 83, pp Paulo C and Jose M S L (2001), Modeling and Comparison of Dissolution Profiles, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 13, pp Sahoo S K, Dalai S R, Pani N R and Barik B B (2007), Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Alginate Beads of Aceclofanac by Ionotropic Gelation Technique, Indian Drugs, Vol. 44, pp
9 13. Santucci E, Alhaique F, Carafa M, Coviello T, Murtas E and Riccieri F M (1996), Gelletion for the Formulation of Sustained Release Beads, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 42, pp Shabaraya A R and Narayanacharyulu R (2003), Design and Evaluation of Chitosan Microspheres of Metoprolol Tatarate for Sustained Release, Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, Vol. 65, No. 3, pp Shilpa A, Agrawal S S and Ray A R (2003), Controlled Delivery of Drugs from Alginate Matrix, Journal of Macromoleculer Science Part C-Polymer Reviews, Vol. 43, p Singh B N and Known H (2000), Review of Floating Drug Delivery Systems: An Approach To Oral Controlled Drug Delivery Via Gastric Retention, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 63, pp Whitehead K, Miyazaki S, Dairaku M, Togashi M, Mikami R and Attwood D (2004), Oral Sustained Delivery Of Ambroxol From In Situ Gelling Pectin Formulations, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 271, pp United States Pharmacopoeia 24/National Formulary 19, USP Convention, Rockville,
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Formulation and evaluation of sustained release atenolol
 9 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of sustained release layer of atenolol Atenolol is a cardioselective β-blocker widely prescribed for asymptomatic condition such as hypertension. It is poorly
9 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of sustained release layer of atenolol Atenolol is a cardioselective β-blocker widely prescribed for asymptomatic condition such as hypertension. It is poorly
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION SPRAY DRYING TECHNIQUE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Patel Krunal M et al. IRJP 2 (2)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 223 87 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF MODIFIED RELEASE TABLET OF MONTELUKAST SODIUM BY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 223 87 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF MODIFIED RELEASE TABLET OF MONTELUKAST SODIUM BY
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
FORMULATION AND EVALUATIONOF AMOXYCILLIN: THREE-LAYER GUAR GUM MATRIX TABLET
 Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
 Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Research Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF GLIPIZIDE AS FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM WITH NATURAL POLYMER (GUAR-GUM)
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF GLIPIZIDE AS FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM WITH NATURAL POLYMER (GUAR-GUM)
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE
 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design.
 Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design. Adenike Okunlola a, Oluwatoyin A. Odeku a* and Rakesh P. Patel b a Department of Pharmaceutics
Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design. Adenike Okunlola a, Oluwatoyin A. Odeku a* and Rakesh P. Patel b a Department of Pharmaceutics
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
The objective of the present investigation is to design and evaluate controlled release tablets of carvedilol, employing
 Research Article Preparation and evaluation of controlled release tablets of carvedilol M L Varahala Setti, J Vijaya Ratna Division of Pharmaceutical Technology, University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Research Article Preparation and evaluation of controlled release tablets of carvedilol M L Varahala Setti, J Vijaya Ratna Division of Pharmaceutical Technology, University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Sivakasi , Tamil Nadu, India. ABSTRACT KEYWORDS:
 276 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 4(1): January-February 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
276 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 4(1): January-February 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
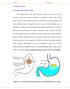 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2013, 4(4):141-150 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Development and in-vitro evaluation of intra gastric cefadroxil monohydrate
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2013, 4(4):141-150 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Development and in-vitro evaluation of intra gastric cefadroxil monohydrate
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of effervescent floating tablets of an antiulcer agent
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(2):1066-1073 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of effervescent
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(2):1066-1073 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of effervescent
Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Floating Microspheres of Anti-Diabetic Drug Prepared by Solvent Evaporation Method
 Research Article Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Floating Microspheres of Anti-Diabetic Drug Prepared by Solvent Evaporation Method Vadaliya SK 1*, Vadaliya KR 1, Desai HT 1 and Patel JK 2 1 School
Research Article Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Floating Microspheres of Anti-Diabetic Drug Prepared by Solvent Evaporation Method Vadaliya SK 1*, Vadaliya KR 1, Desai HT 1 and Patel JK 2 1 School
Bahadur S. et al /J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol.1(4), 2009,
 Abstract: In the present work, we developed an effective mucoadhesive tablets of omeprazole(diomeprazole magnesium powder and omeprazole pellets) by direct punch method with excellent mucoadhesive force
Abstract: In the present work, we developed an effective mucoadhesive tablets of omeprazole(diomeprazole magnesium powder and omeprazole pellets) by direct punch method with excellent mucoadhesive force
CHAPTER 8 HYDROGEL PLUG FORMULATION AND EVAUATION
 CHAPTER 8 HYDROGEL PLUG FORMULATION AND EVAUATION 8.1 Preparation of erodible tablet plug (Hydrogel Plug) Direct compression method was used to prepare the erodible tablet plug. The compositions of different
CHAPTER 8 HYDROGEL PLUG FORMULATION AND EVAUATION 8.1 Preparation of erodible tablet plug (Hydrogel Plug) Direct compression method was used to prepare the erodible tablet plug. The compositions of different
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ACECLOFENAC SODIUM BILAYER SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.1, No.4, pp 1381-1385, Oct-Dec 2009 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ACECLOFENAC SODIUM BILAYER SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.1, No.4, pp 1381-1385, Oct-Dec 2009 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ACECLOFENAC SODIUM BILAYER SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS
Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.3 (2), April-June, 2013
 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF IN SITU NASAL GEL UMESH D.SHIVHARE*, SACHIN R.THAWKAR, Sharad Pawar College of Pharmacy, Wanadongri, Hingna road, Nagpur-441110. (M. S.) INDIA Corresponding author
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF IN SITU NASAL GEL UMESH D.SHIVHARE*, SACHIN R.THAWKAR, Sharad Pawar College of Pharmacy, Wanadongri, Hingna road, Nagpur-441110. (M. S.) INDIA Corresponding author
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND IN-VITRO CHARACTERIZATION OF BILAYER TABLETS OF AMOXICILLIN AND FAMOTIDINE
 ISSN: 2395 1338 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND IN-VITRO CHARACTERIZATION OF BILAYER TABLETS OF AMOXICILLIN AND FAMOTIDINE B. Venkateswara Reddy *, K. Navaneetha Department of Pharmaceutics, St.Paul s College
ISSN: 2395 1338 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND IN-VITRO CHARACTERIZATION OF BILAYER TABLETS OF AMOXICILLIN AND FAMOTIDINE B. Venkateswara Reddy *, K. Navaneetha Department of Pharmaceutics, St.Paul s College
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Research 2011;1(1):67-74 An Official Publication of Association of Pharmacy Professionals
 Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Research 2011;1(1):67-74 An Official Publication of Association of Pharmacy Professionals ISSN: 2249-6041 (Print); ISSN: 2249-9245 (Online) RESEARCH ARTICLE FORMULATION AND EVALUATION
Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Research 2011;1(1):67-74 An Official Publication of Association of Pharmacy Professionals ISSN: 2249-6041 (Print); ISSN: 2249-9245 (Online) RESEARCH ARTICLE FORMULATION AND EVALUATION
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating drug delivery system of Atenolol
 2014; 3(5): 11-18 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(5): 11-18 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 05-06-2014 Accepted: 12-06-2014 Kameswara Rao Sankula Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics,
2014; 3(5): 11-18 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(5): 11-18 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 05-06-2014 Accepted: 12-06-2014 Kameswara Rao Sankula Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics,
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Formulation and evaluation of oro-dispersible tablets of lafutidine
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):226-235 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):226-235 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate
 Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Gastroretentive floating drug delivery systems (GFDDS) of metformin hydrochloride, an antidiabetic drug with an oral
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE Lavanya Asula* Neelima Rani 1, Praveen
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE Lavanya Asula* Neelima Rani 1, Praveen
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE COLON TARGETED TABLETS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE COLON TARGETED TABLETS G. Subba Rao
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE COLON TARGETED TABLETS G. Subba Rao
2. LITERATURE REVIEW.
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Sonia Pandey et al., (2010), formulated Carvedilol bilayered buccal tablet in order to avoid the first-pass effect and decrease the drug loss using different polymers and excipients.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Sonia Pandey et al., (2010), formulated Carvedilol bilayered buccal tablet in order to avoid the first-pass effect and decrease the drug loss using different polymers and excipients.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2010) Newsletter Rathi et al.
 EVALUATION OF DELONIX REGIA ENDOSPERMIC MUCILAGE AS GASTRIC MUCOADHESIVE AGENT Rathi.S.N*,Zate.S.U, Bhutada.D.K, Gawande.V.S, Kolhe.R.C, Bhagure.K.B, Aher.A.N, Pal.S.C. Department of Pharmacognosy,MVP
EVALUATION OF DELONIX REGIA ENDOSPERMIC MUCILAGE AS GASTRIC MUCOADHESIVE AGENT Rathi.S.N*,Zate.S.U, Bhutada.D.K, Gawande.V.S, Kolhe.R.C, Bhagure.K.B, Aher.A.N, Pal.S.C. Department of Pharmacognosy,MVP
Pharma & Food Solutions. POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency
 Pharma & Food Solutions POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX * are nonionic poly (ethylene oxide) polymers that meet all the specifications
Pharma & Food Solutions POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX * are nonionic poly (ethylene oxide) polymers that meet all the specifications
GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Suppl 2, 2011 Research Article GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY JUÁREZ
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Suppl 2, 2011 Research Article GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY JUÁREZ
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLET OF ATENOLOL FOR GASTRO-RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY
 Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Suppl 3, 2012 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLET OF ATENOLOL FOR
Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Suppl 3, 2012 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLET OF ATENOLOL FOR
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Drug Delivery System of Atenolol
 DOI:10.2126/ijprhs.2016.0.06 H Kaur et al. CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-646 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article
DOI:10.2126/ijprhs.2016.0.06 H Kaur et al. CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-646 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article
