Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
|
|
|
- Ernest Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill
2 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular organisms need a way to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the cells deep within tissues. Several organ systems help deliver oxygen, nutrients to and remove wastes from cells. Circulatory, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, and excretory systems 24-2
3 The Cardiovascular System 24-3 Pumps blood around the body Consists of Blood Fluid tissue that transports materials and heat The heart A muscular pump that forces fluid through the body Vessels Pipes that move blood through the body Arteries carry blood from the heart to the tissues. Capillaries are small vessels that carry blood through tissues. Veins carry blood from the tissues to the heart.
4 The Nature of Blood Consists of Several types of cells Called the formed elements Plasma Contains different kinds of dissolved molecules 24-4
5 Formed Elements Red blood cells Lack a nucleus Contain hemoglobin Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide Carbonic anhydrase converts carbon dioxide to bicarbonate that can be dissolved in the blood. Anemia is a lack of oxygen resulting from a lack of red blood cells. 24-5
6 Formed Elements White blood cells Also called leukocytes Lack hemoglobin Have a nucleus Include basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes Defend the body against microorganisms, damaging chemicals, and cancer 24-6
7 Formed Elements Platelets Not whole cells Fragments of white blood cells Important in blood clotting Collect at the site of a wound Release clotting factors Initiate a sequence of reactions that trap blood cells to form a clot Eventually the clots (scabs) are replaced by healthy, living tissue. 24-7
8 Plasma Liquid part of the blood Contains Salts that serve to Buffer and maintain blood ph Maintain osmotic balance Keeps the tissue fluid between cells at the right solute concentration so that it flows into the capillaries, maintaining blood pressure 24-8
9 Plasma Proteins Antibodies and other immune proteins Albumin to maintain osmotic balance Transports bilirubin from degraded RBCs to the liver Accumulated bilirubin can cause jaundice Nutrients Amino acids Sugars Lipoproteins carry fats and cholesterol Hormones 24-9
10 Composition of Blood 24-10
11 Functions of Blood Transports molecules, cells Oxygen, carbon dioxide Nutrients Waste products Immune cells and antibodies Hormones Regulates temperature If body temperature is too high, blood will be shunted to the body surface to radiate heat. If body temperature is too low, blood will be shunted to the body core to conserve heat.
12 The Heart Pumps the blood Generates the pressure necessary to move blood through vessels Blood must flow to move nutrients to tissues and waste away from tissues. Heart must repeatedly contract in order to keep blood moving
13 Mammalian Heart Has four chambers with four valves Two atria and two ventricles Ventricles Are larger and more muscular Force blood through the arteries to the body The aorta and pulmonary artery flow out of the ventricles. Atria Are smaller with thinner walls Pump blood into the ventricles 24-13
14 Mammalian Heart Atria and ventricles are separated by atrioventricular valves. Valves ensure that the blood only flows in one direction. Semilunar valves in the aorta and pulmonary arteries Act as check valves to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles when they relax Damaged valves causes inefficient pumping. Detected as heart murmurs because some of the blood is being pushed backward
15 The Anatomy of the Heart 24-15
16 Mammalian Heart Two different sides have different jobs The right atrium receives blood from the body. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs. Called pulmonary circulation Allows for the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the lungs The left atrium receives blood from the lungs. The left ventricle pumps blood to all other parts of the body. Called systemic circulation Allows for the delivery of oxygen, nutrient, and waste exchange in the tissues
17 Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation 24-17
18 Blood Vessels The tubes that transport blood from one place to another in the body Types of blood vessels Arteries Veins Capillaries 24-18
19 Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Contraction of the ventricles increases the pressure in the arteries. Called systolic blood pressure Relaxation of the ventricles decreases the pressure in the arteries. Called diastolic blood pressure 24-19
20 Arteries Blood pressure readings include both types of blood pressure. Systolic/diastolic 120/80 Have thick, muscular, and elastic walls Can stretch when pressure increases Branch into arterioles to take blood throughout the body 24-20
21 Veins Collect blood from the capillaries and return it to the heart Have very low pressure Walls not very muscular 24-21
22 Veins Have valves to prevent backflow Dysfunctional valves cause varicose veins. Contraction of leg muscles aids in pushing blood through veins. Sitting or standing for a long time can cause pooling of blood in the feet. Causes swelling Can cause fainting because the brain doesn t get enough blood 24-22
23 The Structure of Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries 24-23
24 Capillaries Tiny vessels, one-cell thick RBC go through capillaries single file Have thin walls Only one-cell thick Allows materials to diffuse into and out of the blood Allows liquid to be exchanged between the blood and tissue fluid Are numerous All cells in the body have a capillary nearby. Flow of blood through capillaries is slow Allows time for diffusion and fluid exchange
25 Capillaries 24-25
26 The Lymphatic System A second circulatory system A collection of thin-walled vessels Called lymph vessels Branch throughout body and lymph organs Functions Moves fat from digestive system to blood stream Transports excess fluid back to cardiovascular system Carries immune cells
27 The Lymphatic System 24-27
28 The Lymphatic System Lymph Fluid tissue that is moved through the lymph organs via lymph vessels Emptied into large veins near the heart Moved through lymph vessels by muscle contraction Edema Accumulation of fluid in tissues 24-28
29 Lymph Organs Lymph nodes Filter lymph Contain large numbers of white blood cells Remove microorganisms and foreign particles from the lymph When an infection is active, the lymph nodes enlarge Tonsils Near the throat Contain the tonsils and the adenoids Filter pathogens that enter through the mouth and nose
30 Lymph Organs Spleen Contains a large number of white blood cells Filters the blood Cleans out pathogens and dying RBCs Located just below the diaphragm Thymus Produces WBCs called T-lymphocytes Most active in children Shrinks as one ages
31 Lymph Organs Red bone marrow Found in children s bones Reduced in adult bones Produces RBCs, WBCs, and platelets 24-31
32 The Respiratory System Moves air into and out of the body Lungs Allow gas exchange between air and blood Trachea A tube that carries air into and out of the lung Branches into bronchi then into bronchioles Bronchioles end in alveoli Alveoli are small sacs where gas exchange takes place Air-transport pathway Includes the nose, mouth, and throat Pulls air into the trachea
33 Respiratory Anatomy 24-33
34 Breathing System Regulation Breathing is the process of moving air into and out of the lungs. Involves the diaphragm A large muscle that separates the chest cavity (containing lungs) from the abdominal cavity When contracted, the diaphragm moves down Creates negative pressure in the chest cavity Pulls air into the lungs When relaxed, the diaphragm resumes its normal position Generates positive pressure in the chest cavity Pushes air out of the lungs
35 Breathing Movements 24-35
36 Breathing During Exercise Exercise increases the body s demand for oxygen. Requires faster gas exchange in lungs Accomplished by Increased breathing rate Can involve greater diaphragm contraction to pull in more air 24-36
37 Breathing During Exercise Can also involve contraction of abdominal muscles to fully empty the lungs This happens when carbon dioxide concentration increases in the blood and blood ph. Sensed by brain, then brain causes increased contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles Increased air exchange volume in each breath 24-37
38 The Control of Breathing Rate 24-38
39 Lung Function Lungs are specialized so that blood and air can come very close together. This facilitates gas exchange between them. Blood flows through capillaries in the lungs that come very close to the air in the alveoli. Oxygen and carbon dioxide cross the alveoli and capillary walls. Therefore, the surface area of the alveoli must be very large (collectively). This is why there are so many alveoli.
40 The Association of Capillaries with Alveoli 24-40
41 Lung Function Gas exchange is facilitated by blood and air movement. Blood enters the lungs high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen. Air enters the lungs high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide. Therefore, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood to the air and oxygen diffuses from the air to the blood
42 Disrupting Lung Function Interfering with blood flow or gas exchange will reduce the efficiency of the organism. A poorly pumping heart reduces the amount of blood that is sent to the lungs. Constriction of bronchioles (asthma) reduces the amount of air that can enter the alveoli. Reducing the number of alveoli (emphysema) reduces the surface area for gas exchange
43 The Digestive System Responsible for processing and distributing nutrients Mechanical processing Chemical processing Nutrient uptake Chemical alteration Consists of A muscular tube Glands that secrete digestive juices
44 The Digestive System 24-44
45 Mechanical and Chemical Processing The process of taking large pieces of food and breaking them down into individual molecules that can be absorbed Mechanical processing Chewing in the oral cavity generates a food bolus. Increases surface area of food Allows digestive enzymes greater access to the food 24-45
46 Mechanical and Chemical Processing Salivary glands produce saliva containing some digestive enzymes. Chewing mixes the food with the saliva. Salivary amylase begins to break down starch. Tongue Tastes food Pushes food back toward throat 24-46
47 Mechanical and Chemical Processing Food bolus passes through the esophagus to the stomach Moves from mouth to the pharynx into the esophagus Contractions of the pharynx move the food toward the stomach. In the stomach, food is churned. Mixes food with digestive juices Pepsin breaks down proteins. Low ph denatures proteins The food then moves to the small intestine where chemical breakdown is completed.
48 Mechanical and Chemical Processing Chemical processing in the small intestine Also known as the duodenum Receives digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions from the pancreas Digestive enzymes complete the chemical processing of food. Bicarbonate neutralizes the low ph of the food coming from the stomach. Receives bile from the liver by way of the gall bladder Emulsifies fat into smaller fat globules Allows digestive enzymes greater access to the fats
49 Mechanical and Chemical Processing Finally, the remainder of the undigested food passes from the small intestine to the large intestine (colon). 1.5 meters long Water is reabsorbed. Contains bacteria that utilize the undigested food These bacteria produce vitamins that we need
50 Digestive Enzymes 24-50
51 Nutrient Uptake Once food is broken down into individual macromolecules, they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Absorption occurs through the lining of the small intestine. Requires a large surface area The small intestine is very long (6 to 8 meters). The lining of the small intestine has fingerlike projections called villi
52 Nutrient Uptake Each villus contains Several capillaries A lymphatic vessel called a lacteal Involves diffusion Water and small ions move into blood via simple diffusion. Sugars and amino acids move into blood via carrier proteins. Fatty acids and glycerol enter intestinal cells where they are built into fats and transported into the lacteals
53 Chemical Alterations: The Role of the Liver The nutrient-rich blood leaves the intestine and goes straight to the liver. Moves through the hepatic portal vein In the liver Enzymes modify the nutrient molecules. Foreign organisms are filtered out
54 Chemical Alterations: The Role of the Liver Toxic substances are detoxified Ethyl alcohol Plant toxins Excess glucose is collected and stored as glycogen. Excess amino acids are converted to Other types of amino acids Glucose and stored Urea and sent to the kidneys 24-54
55 The Excretory System (The Urinary System) Responsible for the processing and elimination of metabolic waste Urea Toxic substances Hydrogen ions Water Salts Consists of Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra
56 The Urinary System 24-56
57 Kidney Structure 24-57
58 Kidney Function In order to filter out waste, kidney must have a close association with bloodstream Exchange of waste occurs across a surface Requires large surface area Glomerulus represents a large surface area 24-58
59 Kidney Function Major activities in kidney Filtration Blood enters glomerulus under pressure as the heart contracts. Glomerular capillaries are porous. Glucose, amino acids, ions, and water are pushed through the pores into the nephron tubules
60 Kidney Function Reabsorption Not everything that is filtered into the nephron needs to be excreted. Some molecules are reabsorbed into capillaries around the nephron. Amino acids, glucose, sodium Occurs mostly in the proximal convoluted tubule Water is reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle. Occurs because of osmotic gradients that exist in the kidney Concentrates the urine and conserves water
61 Kidney Function Secretion Additional waste is moved from the capillaries around the nephron into the distal convoluted tubule
62 Specific Functions of the Nephron 24-62
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Mouth. Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion. breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces.
 Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
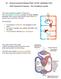 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Anatomy and Physiology. Part 1
 Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 Anatomy - the study of the structure and relationship between body parts Physiology - the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole. Overview and Homeostasis
Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 Anatomy - the study of the structure and relationship between body parts Physiology - the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole. Overview and Homeostasis
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
You start digesting your food the moment you start chewing. This process involves several body structures along the digestive tube.
 The Digestive System This may sound strange, but your digestive system is basically one big tube that starts at your mouth and ends at your anus. The shape of the tube changes along its length, getting
The Digestive System This may sound strange, but your digestive system is basically one big tube that starts at your mouth and ends at your anus. The shape of the tube changes along its length, getting
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM
 CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets
 The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms. Mouth
 Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange. d = t 2
 Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
