2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
|
|
|
- Veronica Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology. e) biology. Answer: a Learning Objective 1: LO 1.1 Define anatomy and physiology. Section Reference 1: Section 1.1 Anatomy and Physiology Defined. 2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the a) chemical level. b) cellular level. c) tissue level. d) organ level. e) system level. Answer: d Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 3) A group of related organs that have a common function is called a(n) a) organ. b) system. c) tissue. d) group. e) organism. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body.
2 Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 4) The process by which unspecialized cells become specialized cells is called a) anabolism. b) catabolism. c) metabolism. d) differentiation. e) homeostasis. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 5) The sum of all chemical processes that occur in the human body is referred to as a) anabolism. b) catabolism. c) metabolism. d) differentiation. e) homeostasis. Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 6) All of the following are examples of organs EXCEPT a) stomach. b) heart. c) epithelium. d) brain. e) gallbladder. Answer: c Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 7) The maintenance of relatively stable conditions within the body is known as a) responsiveness.
3 b) homeostasis. c) differentiation. d) growth. e) All of the choices are correct. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. 8) All of the following are components of the negative feedback systems that control homeostasis EXCEPT a) control center. b) receptor. c) receiver. d) effector. e) All of these answer choices are basic components of the feedback system. Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 9) In a negative feedback system, the response of the effector to a stimulus a) enhances the original stimulus. b) eliminates the original stimulus. c) reverses the original stimulus. d) does not change the original stimulus. e) is not related to the original stimulus. Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 10) The life process of reproduction refers to a) an increase in the size of cells.
4 b) the formation of new cells. c) the production of a new individual. d) both formation of new cells and production of a new individual. e) both an increase in the size of cells and formation of new cells. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 11) Which of the following structures of a feedback system sends input to the control center? a) effector. b) receptor. c) affector. d) stimulus. e) None of the choices is correct. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 12) Baroreceptors in the feedback system that control blood pressure sense changes in a) the rate of blood flow through the aorta. b) the force of the blood as it presses against the walls of blood vessels. c) the temperature of the blood. d) the amount of stretch on the heart as it fills with blood. e) the amount of tissue damage inflicted by high blood pressure. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 13) Which of the following is a symptom of disease rather than a sign? a) nausea b) bleeding c) vomiting d) fever
5 e) rash Answer: a Learning Objective 2: LO Distinguish between symptoms and signs of a disease. 14) The science that deals with the treatment of disease using drugs is called a) physiology. b) anatomy. c) epidemiology. d) pharmacology. e) pathophysiology. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.8 Define various Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. Section Reference 1: Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. 15) In the anatomical position, the subject a) is lying face down. b) has his/her arms placed above the head. c) has his/her arms folded on the chest. d) is standing upright facing the observer with the palms backwards. e) is standing upright facing the observer with the palms forward. Answer: e Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the anatomical position. 16) A plane that divides the body into unequal left and right portions is called a(n) a) parasagittal plane. b) midsagittal plane. c) frontal plane. d) transverse plane. e) oblique plane. Answer: a
6 Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 17) A gluteal injection refers to an injection into the a) buttock. b) thigh. c) ankle. d) upper arm. e) abdomen. Answer: a Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 18) The sternum (breastbone) is to the heart. a) posterior b) anterior c) inferior d) lateral e) distal Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 19) The plane that divides the body into a superior and inferior portion is a a) parasagittal plane. b) midsagittal plane. c) transverse plane. d) oblique plane. e) frontal plane.
7 Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 20) Which of the following is NOT a basic tissue type? a) connective tissue b) epithelial tissue c) cartilage tissue d) nervous tissue e) muscle tissue Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 21) Which of the following organs does NOT belong to the digestive system? a) liver b) gallbladder c) ureter d) stomach e) salivary glands Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 22) The organ system that regulates the body's activities using chemical regulators called hormones is the a) digestive system. b) endocrine system. c) nervous system. d) cardiovascular system. e) integumentary system.
8 Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 23) The is the region between the lungs from the breastbone to the vertebral column. a) vertebral canal b) pericardium c) mediastinum d) pleural cavity e) manubrium Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 24) The organ system that transports fats from the gastrointestinal tract to the blood in the cardiovascular system is the a) digestive system. b) endocrine system. c) lymphatic system. d) urinary system. e) respiratory system. Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 25) The anatomical term which best describes a structure that is found toward the head is a) superficial. b) deep. c) inferior. d) superior. e) anterior. Answer: d
9 Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 26) In the anatomical position, the ring finger is to the little finger. a) lateral b) medial c) deep d) distal e) proximal Answer: a Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 27) The anatomical term for navel is a) crural. b) inguinal. c) umbilical. d) femoral. e) coxal. Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 28) Which of the following directional terms best describes structures found toward the back region of the body? a) ventral b) dorsal c) proximal d) distal e) medial
10 Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 29) The spleen and liver are located in the a) pelvic cavity. b) cranial cavity. c) abdominal cavity. d) thoracic cavity. e) vertebral cavity. Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 30) All of the following are found inferior to the diaphragm EXCEPT the a) thymus gland. b) gall bladder. c) large intestine. d) small intestine. e) urinary bladder. Answer: a Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 31) The body cavity containing the urinary bladder and portions of the large intestine is the a) pelvic cavity. b) abdominal cavity. c) mediastinum. d) pleural cavity. e) dorsal cavity.
11 Answer: a Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 32) The pericardial cavity contains the a) lungs. b) thyroid glands. c) brain. d) heart. e) stomach. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 33) Which of the following is NOT one of the nine abdominopelvic regions? a) left lumbar region b) right upper region c) right inguinal region d) epigastric region e) pubic region Answer: b Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Explain why the abdominopelvic cavity is divided into regions and quadrants. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 34) Which of the following abdominopelvic regions contains portions of the stomach? a) right hypochondriac region b) left hypochondriac region c) epigastric region d) both right hypochondriac region and left hypochondriac region e) both left hypochondriac region and epigastric region
12 Answer: e Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 35) Failure of the body to maintain homeostasis will a) have no effect on health. b) cause illness and possibly death. c) always cause death. d) initiate positive feedback. e) enhance the immune response to pathogens. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Distinguish between symptoms and signs of a disease. 36) All of the following are controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, EXCEPT a) the skeletal muscle contractions used for walking. b) blood pressure. c) body temperature. d) blood sugar levels. e) breathing rate. Answer: a Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. 37) Which of the following physiological processes is controlled by positive feedback? a) regulation of blood sugar b) initiation of blood clotting c) control of blood pressure d) maintenance of body temperature e) control of breathing rate
13 Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Compare the operation of negative and positive feedback systems. 38) The organs found inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are commonly referred to as a) mediastinum. b) mammary glands. c) abdominal organs. d) viscera. e) pleural organs. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 39) All of the following are functions of the cardiovascular system EXCEPT a) oxygen transport. b) carbon dioxide transport. c) red blood cell production. d) mending damaged blood vessels. e) transport of nutrients and wastes. Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 40) The smallest living units within an organism are a) atoms. b) molecules. c) cells. d) tissues. e) organs. Answer: c
14 Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 41) Two or more atoms combine together to form a) cells. b) organs. c) organ systems. d) molecules. e) None of the choices is correct. Answer: d Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 42) The organ system that consists of skin, along with associated structures like hair and sweat glands, is the a) skeletal system. b) integumentary system. c) muscular system. d) endocrine system. e) cardiovascular system. Answer: b Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 43) The anatomical term used to describe the region of the neck is a) facial. b) brachial. c) cervical. d) thoracic. e) mental. Answer: c
15 Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 44) The splitting of proteins into amino acids which are then used to make new proteins is an example of the life process called a) responsiveness. b) reproduction. c) metabolism. d) differentiation. e) homeostasis. Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 45) Which of the following is NOT a change associated with aging? a) wrinkled skin b) diminished reflexes c) increased insulin production d) decreased muscle strength e) loss of bone mass Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.5 Describe some of the anatomical and physiological changes that occur with aging. Section Reference 1: Section 1.5 Aging and Homeostasis. 46) A disease that affects a limited area of the body is referred to as a(n) disease. a) systemic b) local c) systematic d) epidemic e) endemic Answer: b Learning Objective 1: LO 1.8 Define various Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. Section Reference 1: Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions.
16 47) The science that deals with medical problems and care of the elderly is called a) epidemiology. b) geriatrics. c) pathology. d) pharmacology. e) obstetrics. Answer: b Learning Objective 1: LO 1.8 Define various Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. Section Reference 1: Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. 48) The science that deals with the nature and causes of abnormal conditions, and the structural and functional changes that diseases produce is called a) epidemiology. b) geriatrics. c) pathology. d) pharmacology. e) obstetrics. Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.8 Define various Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. Section Reference 1: Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. 49) The release of insulin from pancreatic islet cells in response to an increase in the blood glucose concentration after a meal is an example of which of the following life processes? a) metabolism b) responsiveness c) movement d) growth e) differentiation Answer: b Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 50) The life process by which a hemocytoblast (unspecialized stem cell) becomes an erythroblast that will then mature into a red blood cell is called a) metabolism. b) movement.
17 c) growth. d) differentiation. e) reproduction. Answer: d Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 51) In the negative feedback system that controls the body s response to decreased body temperature, the skeletal muscles play the role of a) receptors. b) input signals. c) control centers. d) output signals. e) effectors. Answer: e Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 52) Otitis refers to inflammation in what region of the body? a) nose b) eye c) neck d) cheek e) ear Answer: e Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. Question type: True/False 53) Anatomy refers to both structure and function of the body.
18 Answer: False Learning Objective 1: LO 1.1 Define anatomy and physiology. Section Reference 1: Section 1.1 Anatomy and Physiology Defined. 54) The chemical level of structural organization includes all chemicals needed to maintain life. Answer: True Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 55) The integumentary system protects all the other body systems. Answer: True Learning Objective 2: LO Outline the body systems and explain how they relate to one another. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 56) Reproduction refers exclusively to the formation of new cells for growth, repair, and replacement. Answer: False Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 57) Stress can cause disruptions in homeostasis, because it creates an imbalance in the internal environment. Answer: True Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. 58) The control center determines the range within which a controlled condition needs to be maintained. Answer: True
19 Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 59) To describe the position of one body structure relative to another, anatomists use directional terms. Answer: True Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 60) A midsagittal plane always divides the body into equal superior and inferior portions. Answer: False Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 61) The spinal cord and the brain are located in the cranial cavity. Answer: False Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 62) The heart is located in the mediastinum. Answer: True Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities.
20 63) For practical purposes, clinicians prefer to use the quadrant system of dividing the abdominopelvic cavity instead of the nine region system used by anatomists. Answer: True Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Explain why the abdominopelvic cavity is divided into regions and quadrants. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 64) Childbirth is a good example of a positive feedback mechanism. Answer: True Learning Objective 2: LO Compare the operation of negative and positive feedback systems. 65) The heart is superior to the cranium. Answer: False Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 66) Aging is a normal process associated with a reduced ability to maintain homeostasis. Answer: True Learning Objective 1: LO 1.5 Describe some of the anatomical and physiological changes that occur with aging. Section Reference 1: Section 1.5 Aging and Homeostasis. 67) Aging affects all body systems. Answer: True
21 Learning Objective 1: LO 1.5 Describe some of the anatomical and physiological changes that occur with aging. Section Reference 1: Section 1.5 Aging and Homeostasis. 68) Aging can cause a decreased susceptibility to cancer. Answer: False Learning Objective 1: LO 1.5 Describe some of the anatomical and physiological changes that occur with aging. Section Reference 1: Section 1.5 Aging and Homeostasis. 69) Less efficient functioning of the digestive system and decreased function of the kidneys are changes often associated with aging. Answer: True Learning Objective 1: LO 1.5 Describe some of the anatomical and physiological changes that occur with aging. Section Reference 1: Section 1.5 Aging and Homeostasis. 70) Pathology is the science that deals with why, when and where diseases occur and how they are transmitted within a defined human population. Answer: False Learning Objective 1: LO 1.8 Define various Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. Section Reference 1: Section 1.8 Medical Terminology and Conditions. 71) The endocrine system would be the most likely control system for a homeostatic process that requires a rapidly induced change. Answer: False Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 72) The wrist is proximal to the fingers. Answer: True
22 Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. Question type: Text Entry 73) The science dealing with the structures of the human body is called. Answer: anatomy Learning Objective 1: LO 1.1 Define anatomy and physiology. Section Reference 1: Section 1.1 Anatomy and Physiology Defined. 74) All the body systems combined make up a(n). Answer: organism Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 75) Molecules combine to form structures at the level of organization. Answer: cellular Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 76) Largest level of organization within the human body is the level. Answer: organismal Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 77) Ability to detect and respond to changes in either the internal or external environment is called.
23 Answer: responsiveness Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 78) Maintenance of relatively stable conditions in the internal environment of the human body is called. Answer: homeostasis Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. 79) A life process by which unspecialized cells become specialized cells is called. Answer: differentiation Learning Objective 1: LO 1.3 Define the important life processes of humans. Section Reference 1: Section 1.3 Life Processes. 80) Blood pressure, which is the force of flowing blood against the walls of the arteries, is maintained within a narrow range by a feedback system. Answer: negative Learning Objective 2: LO Compare the operation of negative and positive feedback systems. 81) The basic component of a feedback system that receives output from the control center and produces a response is called the. Answer: effector Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system.
24 82) The component of a feedback system that monitors changes in the controlled condition is called the. Answer: receptor Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system. 83) The plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior segments is the plane. Answer: frontal (or coronal) Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 84) The fluid surrounding body cells within the tissues is called fluid. Answer: interstitial Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. 85) The stomach is to the lungs. Answer: inferior Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 86) The humerus is to the radius Answer: proximal
25 Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. 87) The abdominal and pelvic cavities combine to form the cavity. Answer: abdominopelvic Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 88) The correct anatomical term for the front of the elbow is. Answer: antecubital Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 89) All the bones of the body, their associated cartilages, and joints belong to the system. Answer: skeletal Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 90) Homeostasis is controlled by the and systems. Answer: nervous; endocrine Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the components of a feedback system.
26 91) The smallest structural units of matter that participate in chemical reactions within the human body are called. Answer: atoms Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. 92) The umbilical region of the abdominopelvic cavity is to the pubic region. Answer: superior Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 93) Using the quadrant system of dividing the abdominopelvic cavity, the liver is found primarily in the quadrant. Answer: right upper Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. Question type: Multiple Choice 94) Where on the diagram is the femoral area?
27 a) D b) E c) I d) J e) K Answer: a Difficulty: medium Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 95) Where on the diagram is the sacral area?
28 a) C b) D c) E d) I e) J Answer: d Difficulty: medium Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 96) Where on the diagram is the cervical area?
29 a) A b) B c) G d) F e) H Answer: b Difficulty: medium Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. 97) Where on the diagram is the brachial area?
30 a) C b) E c) I d) K e) D Answer: a Difficulty: medium Learning Objective 2: LO Identify the major regions of the body and relate the common names to the corresponding anatomical terms for various parts of the body. Question type: Essay 98) Name and briefly describe the six levels of structural organization in the human body. Answer:
31 Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the structural organization of the human body. Section Reference 1: Section 1.2 Levels of Organization and Body Systems. Solution: The chemical level: includes atoms and molecules. The cellular level: includes all different cells made of combinations of molecules. The tissue level: tissues consist of groups of similar cells. The organ level: organs are formed when different types of tissues join together. The system level: consists of related organs that have a common function. The organismal level: the highest level of structural organization includes all organ systems making up the entire organism. 99) Name and briefly describe the common planes used to describe anatomy of body parts that have been sectioned. Answer: Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body. Solution: A sagittal plane divides the body or body part into right and left portions. A midsagittal plane divides the body or body part into equal right and left portions. A parasagittal plane divides the body or body part into unequal right and left portions. A frontal (coronal) plane divides the body or body part into anterior and posterior portions. A transverse plane divides the body or body part into superior and inferior portions. An oblique plane passes through the body or body part at an angle between the planes mentioned above. 100) Define homeostasis. Answer: Learning Objective 2: LO Define homeostasis and explain its importance. Solution: Homeostasis is a condition in which the internal environment of the body is maintained within certain physiological limits. Question type: Multiple Choice 101) Which labeled cavity in the diagram can be subdivided into three smaller cavities called the pleural cavity, pericardial cavity, and mediastinum?
32 a) A b) B c) C d) E e) F Answer: c Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 102) Which of the labeled cavities in the diagram is lined with a serous membrane called the peritoneum?
33 a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E Answer: e Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities. 103) Which labeled cavity in the diagram contains the urinary bladder and the internal organs of reproduction?
34 a) A b) B c) C d) E e) F Answer: e Learning Objective 1: LO 1.7 Identify the four major body cavities, emphasizing the quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity. Learning Objective 2: LO Describe the principal body cavities and the organs they contain. Section Reference 1: Section 1.7 Body Cavities.
35 104) Which of the labeled planes in the diagram is a coronal (or frontal plane)? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E Answer: c Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body.
36 105) What type of plane is labeled E in the diagram? a) Oblique plane b) Transverse plane c) Frontal plane d) Midsagittal plane e) Parasagittal plane Answer: a Learning Objective 2: LO Define the directional terms and the anatomical planes and sections used to locate parts of the human body.
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
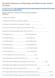
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13
 CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
The HUMAN BODY. Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
 The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Systemic The study of anatomy by body systems
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units
 hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
The Human Body: An Orientation
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Then think about these: Check your Packet- three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last?
 Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology
 Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
1. Define Anatomy and Physiology-
 Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
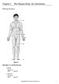 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later)
 Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
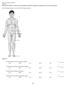 Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body
 Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body a. Anatomy the study of body structure -tomy means cutting or dissecting b. Physiology The study of body function; based on a Latin term meaning nature
Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body a. Anatomy the study of body structure -tomy means cutting or dissecting b. Physiology The study of body function; based on a Latin term meaning nature
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Link full download:
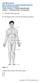 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
Figure 1.2. Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5) Umbilical region. Answer: C. 6) Right hypochondriac. Answer: B
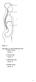 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B
 Human Anatomy & Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B 1) Thoracic cavity.
Human Anatomy & Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B 1) Thoracic cavity.
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
