Effect of Hordeum vulgare Linn. Seeds on glycolic acid induced urolithiasis in rats
|
|
|
- Lydia Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pharmacognosy Communications Volume 2 Issue 2 Apr-Jun Research Article Effect of Hordeum vulgare Linn. Seeds on glycolic acid induced urolithiasis in rats Jignesh G. Shah 1 *, Dr. Bharat G. Patel 2, Sandip B. Patel 1, Ravindra Patel 1 1 Department of Pharmacology, Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, New Vallabh vidyanagar, Anand, Gujarat, India. 2 Institute of Science & Technology for Advanced studies & Research, Vallabh vidyanagar, Anand, Gujarat, India. ABSTRACT: Objective: To evaluate its anti-urolithic potential, the ethanolic extract of seeds of Hordeum vulgare was tested in an animal model of urolithiasis. Materials and Methods: Urolithiasis was induced by the addition of 3% glycolic acid to the normal diet of Wistar albino rats for a period of 42 days. Group I served as a normal control. Group II served as urolithiasis control. Group III, IV and V were treated with ethanolic extract of Hordeum vulgare (EHV) at 100, 250 and 500 mg/kg respectively. Group VI was treated with Cystone as a standard drug. The effects of EHV on various biochemical parameters were studied in urolithitic rats. Results: Glycolic acid induced hyperoxaluria in urolithiatic rats. And, there were significant elevated urine output, kidney weight loss and some renal injury markers in glycolic acid induced rats. In vivo antioxidant parameters including lipid peroxidation (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were also determined. oral administration of, 250 and 500 inhibited CaOx crystal disposition in renal tubules and protected against associated changes in polyurea and kidney weight loss. EHV significantly maintained the urinary excretion of the calcium, phosphate, uric acid, urea, and oxalate and increased the excretion of citrate as compared to glycolic acid control animals. The increased deposition of stone forming constituents in the kidneys of calculogenic rats were significantly lowered by treatment with EHV. The extract also induced a significant decrease in MDA which increased in urolithiatic control rats. The extract also significantly increased SOD and CAT in urolithiatic rats which were markedly decreased in glycolic acid induced urolithiasis in rats. Conclusion: This study demonstrates the anti-urolithic activity of Hordeum vulgare seeds and rationalizes their medicinal use for the treatment of urolithiasis. KEY WORDS: glycolic acid; Hordeum vulgare; urolithiasis. INTrODUCTION Hyperoxaluria is one of the major risk factors of human idiopathic calcium oxalate (CaOx) urolithiasis. Oxalate is a natural byproduct of metabolism and harmlessly excreted through the urine in normal individuals. However, increased urinary excretion of oxalate (hyperoxaluria) can be highly *Correspondence: Jignesh G. Shah, Assistant professor, Department of Pharmacology, Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, Post B. No. 53, Beyond G.I.D.C. Phase IV, Post Vithal udhyog Nagar, New Vallabh vidyanagar, Anand, Gujarat, India (M) , (O) jigneshshah_rx@yahoo.co.in DOI: /pc toxic because of its propensity to crystallize at physiologic ph and form CaOx. [1] Urolithiasis is a complex process that results from a succession of several physico-chemical events including supersaturation, nucleation, growth, aggregation, and retention within renal tubules. [2] Epidemiological data collected over several decades showed that the majority of stones (up to 80%) are composed mainly of calcium oxalate (CaOx). [3] Urine is always supersaturated with common stone forming minerals. The crystallization inhibiting capacity of urine does not allow urolithiasis to happen in most individuals, whereas this natural inhibition is in deficit in stone formers. [4] The majority of urinary calculi are made up of calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate, uric acid (urates) or magnesium ammonium phosphate. Many remedies have been employed through the ages to treat urolithiasis. In most cases, the management of urolithiasis involves both surgical and medical approaches, i.e., percutaneous nephrolithotomy 34 (c) Copyright 2011 EManuscript Publishing Services, India
2 (PCNL), extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and antibiotics [5]. However, these treatments are relatively costly, painful and require expert hands with availability of appropriate equipments. In spite of tremendous advances in the field of medicine, there is no truly satisfactory drug for the treatment of renal calculi. Hence, the search for herbo-mineral preparations is still ongoing. [6] A large number of Indian medicinal plants have been used in the treatment of urolithiasis and they are reported to be effective with no side effects. [7] Many Indian plants have been quoted to be useful as antilithiatic agents. They are effective with fewer side effects and are also inexpensive. Hence, the Indian plants are constantly being evaluated for possible antilithiatic effects in a systematic manner. [8] As per the indigenous system of Ayurveda medicine, the seeds of Hordeum vulgare Linn. have been reported to be useful in the treatment of a wide range of aliments, including urinary stones. [9] In the current study, an effort has been made to establish the scientific validity for the anti-urolithiatic activity of Hordeum vulgare seed extract using glycolic acid induced urolithiasis using male wistar albino rats. MATERIAL AND METHOD Animal selection For acute toxicity studies, albino mice of either sex weighing between gm and for the study of antiurolithisis activity adult male albino rats of Wistar strain ( gm) were procured form Zydus Research Centre, ahmedabad. The animals were acclimatized to standard laboratory conditions (temp: 23 ± 2 C) and maintained on 12-h light: 12-h dark cycle. They were provided with regular rat chow (VRK Nutritional Solutions, Pune, India) with free access to drinking water ad libitum for the period of 28 days. Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) approval (Protocol no.: IICP/PH/ /05 dated ) was obtained before the experiment and care of animal was taken as per guidelines of CPCSEA, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India. Chemicals Ethylene glycol was obtained from SD Fine Chemical Limited, Mumbai, India. Cystone (Himalaya Health Care, india) was procured from the local market. All other chemicals and reagents used were of analytical grade. Plant material The dried seeds of Hordeum vulgare Linn. were received from commercial supplier, Anand, Gujarat, India. The seeds were identified by Dr. G. C. Jadeja, Department of Agricultural Botany, B. A. College of Agriculture, Anand Agricutlture University, India. A Voucher specimen (voucher no. IICP/11-JGS/03-HV) was deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Pharmacognosy, Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, New Vallabh vidyanagar, India. Preparation of plant extract The air-dried powdered seeds (500 g) were extracted with ethanol in soxhlet apparatus for 24 h. The extract was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure to give solid residues. The residue was stored below 4 ºC for subsequent experiments. The yield of the extract was 4.82 % w/w. Acute toxicity studies The acute toxicity was performed as per WHO guideline and the Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) guideline for testing of chemicals (no.420) using albino mice of either sex prior to the evaluation of anti-urolithiatic activity. The EHV was tested using graded doses (500, 1000, 2000 and 5000 mg/kg) in mice. Furthermore, the general behaviour of mice was recorded continuously for 12 h, and daily for a further 2 weeks for any eventual mortality. [10] The EHV did not show mortality, or any remarkable symptoms of toxicity and/or any significant changes in general behaviour in mice. Experimental Design: Urolithiasis induced by glycolic acid model was used to study the anti-urolithiatic activity in Wistar albino rats. Animals were divided into six groups containing six animals in each. Animals of group I received the commercial diet and served as control, group II-IV was fed with a calculiproducing diet (CPD: commercial diet mixed with 3% glycolic acid) for 42 days. Group III, IV and V administered orally 100, 250 and 500 mg/kg b.w. of extract respectively. Group VI received standard anti-urolithiatic drug, cystone (750 mg/kg b.w.; p.o.). [11] All the extracts and standard drug were given once a day orally in addition to the CPD for the duration of 42 days. Collection and analysis of urine On the completion of treatment, all animals were kept in individual metabolic cages. Animals had free access to drinking water during the urine collection period. At the completion of treatment of 42 nd day, the urine sample of each animal was collected. Volume of urine and its ph were measured immediately after the collection of urine. The collected urine were admixed with a drop of concentrated hydrochloric acid and stored at 4 o C. urine was analyzed as previously described for calcium, [12] phosphate, [13] oxalate, [14] urea, [15] uric acid [16] and citrate. [17] Collection and analysis of serum Blood was collected by retro-orbital puncture under mild anesthetic conditions. Serum was separated by centrifugation at rpm for 20 min and analyzed for calcium, [12] phosphate, [13] urea, [15] uric acid [16] and creatinine. [18,19] 35
3 Kidney homogenate analysis The animals were sacrified by cerival dislocation. The abdomen was cut open to remove both kidneys from each animal. The weight of dry and wet kidney was measured. Isolated kidneys were cleaned of extraneous tissue and rinsed in ice-cold physiological saline. A sample of 100 mg of the dried kidney was boiled in 10 ml of 1N hydrochloric acid for 30 min and homogenized. The homogenate was centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 min and the supernatant was separated. The concentration of calcium, [12] phosphate [20] oxalate, [21] and uric acid [16] in kidney homogenate were determined. Enzyme assay A portion of kidney was taken from all the groups, and a 30% w/v homogenate was prepared in 0.9% buffered KCl (ph 7.4) for the estimation of protein, [22] superoxide dismutase (SOD), [23] catalase (CAT) [24] and malondialdehyde (MDA). [25] Statistical analysis Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Differences among data were determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison tests (Graphpad Prism software for Windows, Version ). p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS There were no any behavioral changes, signs of toxicity as well as any mortality were observed after the administration of a dose up to 5000 mg/kg. So, From the acute toxicity study, the LD 50 cut-off dose was found to be 5000 mg/kg body weight for the extract. Hence, the therapeutic dose was taken as 100 mg/kg, 250 mg/kg, and 500 mg/kg body weight for the ethanolic extract. In the present study, urolithiasis was induced by the supplementation of normal commercial diet with glycolic acid for the 42 days. Table 1 indicates the various physical parameters that were measured including the volume of urine collected at the end of the treatment, the ph of urine and the weight of dry and wet kidney. The volume of urine was reduced in calculi induced animals (Group II) as compared to normal control group. The treatment with (group V) and standard drug Cystone (Grop VI) increase the volume of urine in calculi induced animals when compared with control (Group II). The ph of urine of calculi controlled animals (Group II) were significantly (p<0.05) increased as compared to normal control rats which was slightly acidic. The treatment with was significantly (p<0.05) decreased the ph of urine near to neutral in calculi induced animals. There was a significant (p<0.05) increase in the kidney weight (both dry and wet weight) of animals receiving 3% glycolic acid which was significantly (p<0.05) reduced by the treatment with Cystone and the & 500. The kidney weight was significantly (p<0.05) higher in kidneys with crystal deposits. Due to the hyperurolxaluria there was an increased urinary excretion of calcium, phosphate, uric acid, urea and oxalate in calculi control animals (Table 2, Group II). However, supplementation with (Table 2, Group V) significantly (p<0.05) reserved these changes in urinary excretion of calcium, phosphate, uric acid, urea and oxalate Table 1: Effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of H. vulgare Linn. on various physical parameters of control and experimental animals I I Volume; ml/24 hr ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.08 ph 6.38 ± ± 0.07* 8.01 ± ± ± 0.12** 7.33 ± 0.11** Wet weight (g/100 g b.wt) 0.64 ± ± 0.01* 0.91 ± ± ± 0.04** 0.84 ± 0.03** Dry weight (g/100 g b.wt) 0.24 ± ± 0.03* 0.35 ± ± ± 0.07** 0.30 ± 0.01** Table 2: Effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of H. vulgare Linn. on various parameters in urine of control and experimental animals 36 I I Calcium 3.69 ± ± 0.54* 4.45 ± ± ± 0.41** 4.08 ± 0.22** Phosphate 3.11 ± ± 0.17* 7.18 ± ± ± 0.53** 4.23 ± 0.41** Uric acid 2.06 ± ± 0.37* 4.67 ± ± ± 0.37** 2.91 ± 0.35** urea 9.47 ± ± 1.04* ± ± ± 0.78** 9.72 ± 0.48** oxalate 3.48 ± ± 0.81* ± ± 0.79** 5.58 ± 0.61** 4.65 ± 0.39** Citrate ± ± 0.87* ± ± 0.92** ± 1.36** ± 1.87**
4 excretion dose-dependently in EHV treated animals (Table 2, Group III-V). Urinary citrate flow was decreased by glycolic acid inducing treatment. However, supplementation with and 500 (Table 2, Group IV, V) significantly (p<0.05) maintained the elevated level of citrate and restores it near to normal value. The observed results were comparable with cystone treated animals (Table 2, Group VI). Renal stone induction caused impairment of renal functions of the control (Group II) rats as evident from the markers of glomerular and tubular damage as reflected by the elevated levels of serum creatinin, uric acid and urea in calculi induced animals (Table 3, Group II), which were significantly (p<0.05) reduced in the animals treated with (Table 3, Group V). The serum calcium and inorganic phosphate were remarkably increased in calculiinduced animals (Table 3, Group II). However, treatment with mg/kg significantly (p < 0.05) lowered the elevated serum level of calcium and inorganic phosphate in calculi induced animals. Table 4 shows the parameters of the kidney homogenate. The calcium, phosphate, uric acid and oxalate level were significantly (p<0.05) increased in kidney homogenate of calculi induced animal group (Group II). The EHV (500 mg/ kg) and cystone treatment (p<0.05) maintained the levels of all parameters mentioned above. The EHV (100 and 250 mg/kg) failed to exhibit significant reduction in calcium, uric acid and oxalate level in kidney homogenate except phosphate level. For in vivo antioxidant activity, ethylene glycol treatment significantly (p<0.05) increased MDA and decreased SOD and CAT levels in calculi- induced animals as compared to normal animals (Table 5, Group II). The treatment with produced significant (p < 0.05) reduction in MDA and antioxidant enzymes like SOD and CAT as compared to control group. DISCUSSION In urolithiatic study, male rats were selected as a model system to induce renal stones because the urinary system of male rats resembles that of humans. [24] Here 3% glycolic acid used to provoke hyperoxaluria, which is known to be due to the ready conversion of glycolic acid to oxalate by Table 3: Effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of H. vulgare Linn. On various parameters in serum of control and experimental animals I I Cyston Treated Calcium 7.17 ± ± 0.98* ± ± ± 0.70** 7.52 ± 0.47** Phosphate 3.21 ± ± 0.40* ± ± ± 0.65** 4.35 ± 0.24** Uric acid 3.53 ± ± 0.60* 7.83 ± ± ± 0.48** 4.38 ± 0.30** Urea ± ± 2.88* ± ± ± 1.72** ± 2.04** Creatinin 0.83 ± ± 0.12* 1.82 ± ± ± 1.49** 1.02 ± 0.06** Table 4: Effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of H. vulgare Linn. on various parameters in kidney homogenate of control and experimental animals I I Calcium 3.04 ± ± 0.55* 5.88 ± ± ± 0.35** 3.67 ± 0.27** Phosphate 3.38 ± ± 0.60* 6.62 ± ± ± 0.42** 3.94 ± 0.37** oxalate 1.08 ± ± 0.20* 3.01 ± ± ± 0.30** 1.46 ± 0.26** Uric acid 1.85 ± ± 0.36* 4.40 ± ± ± 0.25** 1.90 ± 0.27** Table 5: Effect of ethanolic extract of seeds of H. vulgare Linn. on antioxidant enzymes of control and experimental animals I I Melondialdehyde ± ± 0.61* ± ± ± 0.14** ± 0.24** Superoxide dismutase ± ± 0.05* ± ± 0.11** ± 0.05** ± 0.04** Catalase ± ± 0.12* ± ± 0.08** ± 0.19** ± 0.22** 37
5 the oxalate synthesizing enzyme, glycolate oxidase in liver. Glycolic acid (the precursor of oxalic acid) is known to increase significantly the incidence of oxalate lithiasis. Our results are in concord with these studies, as shown by the significant increase in kidney weight. [13] As postulate in previous studies, following a stone-inducing regimen, volumes of 24 h urine and water intake were observed higher in the untreated group compared with those of the control animals and the urine ph was slightly reduced. [25] In the present investigation, the volume of urine and the ph were measured at the end of treatment. The volume of urine was not significantly reduced in the Cystone and the EHV treated animals. This indicates that the EHV had no diuretic activity. While, the ph were significantly affected by the drug treatment. There was a good correlation between wet tissue calcium and oxalate concentrations by compared to kidneys without CaOx crystals; in wet tissue such salt concentrations were observed significantly higher. Glycolic acid administration increased the urinary calcium level. It has been stated that hypercalciuria favors precipitation of calcium oxalate from urine [26] Thus, the high oxalate and calcium ion concentration in urine tends to form calcium oxalate crystals. According to previous reports, not only calcium and oxalate excretion but excretion of inorganic phosphate is also important in the formation of urinary stone. [27] In the present study, oxalate, calcium and phosphate excretion observed in glycolic acid treated rats is likely to have formed calcium phosphate crystals. Conversely, EHV declines the levels of oxalate, calcium as well as phosphate execretion which is known to prove valuable in preventing calculi formation due to supersaturation of these urolithiagenic substances. It has been reported that uric acid interferes with calcium oxalate solubility. It also reduces the inhibitory activity of glycosaminoglycans. [28] The predominance of uric acid crystals in calcium oxalate stones and the observation that uric acid binding proteins are capable of binding to calcium oxalate and modulate its crystallization also suggests its primary role in stone formation. [28,29] In comparison with normal controls there was significant increased in uric acid level in serum as well as in urine in glycolic acid control group. While in case of groups received treatment of standard and EHV, there was significant maintain the level of uric acid observed. In urine, citrate complexes calcium, reducing the free calcium- ion activity. This effect is ph-dependent, with maximum complex formation at or above ph 6.5. The citrate is as a specific inhibitor of crystal growth and aggregation. Citrate is one of the major inhibitors of calcium phosphate- crystal growth. In the calcium oxalate system, its effect is thought to be small and ph-dependent. [30] In the present study, EHV showed protective effect mediated by their influence on the urinary excretion of some citrate, in a model of experimental lithiasis in rats. In urolithiasis, the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreases due to the obstruction to the outflow of urine by stones in urinary system. thus the waste products particularly nitrogenous substances such as urea, uric acid and creatinin get accumulated in blood. [30] In comparison with the normal control there was significant increased in urea, uric acid and creatinine levels in serum as well as in urine in glycolic acid control group. While in case of groups received treatment of standard and EHV there was significant decreased in the level of urea, uric acid and creatinine. Elevated oxalate concentrations in urine has been reported to induce lipid peroxidation and cause renal damage by reacting with polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membrane. [26] The significant lowering of serum levels of accumulated waste products is attributed to the enhanced GFR and the anti-lipid peroxidative property. Stone inducing treatment caused hypertrophy and extensive calcium oxalate crystal deposition in kidneys of untreated rats accompanied by oxidative damage as reflected from increased levels of markers of oxidative injury: MDA and protein carbonyl content, and decreased activities of antioxidant enzymes and GSH levels in kidneys as well as deteriorated renal functions. [31] The systemic circulation may damage some part of the kidney, probably the mesengial or glomerular epithelial cells, and cause the kidney to produce more reactive oxygen species than systemic blood. Therefore, the excessive oxidative stress would have been completely compensated for by elevated antioxidant enzymes in the kidney during this period. [32] The decreased activities of catalase in the nephrolithiasis in this model may have led to more H 2 O 2 accumulation in the kidney, resulting in more hydroxyl radical formation; because catalase is the only enzyme that regulates the potent hydroxyl radical. [33] The may prevent the lipid peroxidation induced renal damage caused by calcium oxalate crystals deposition in the kidney. Hence, EHV prevented calcium oxalate crystal attachment as well as stone formation. And in addition, Administration of results in significant increase in the catalase and increase levels of SOD and CAT levels in kidney as compared to the control animals, which suggests its efficacy in preventing free radical-induced damage. CONCLUSION Overall, the presented data in this paper indicates that administration of seed extract of Hordeum vulgare Linn. to experimentally CaOx-induced nephrolithiasic rats reduced the deposition of crystals into kidneys confirming its 38
6 antilithiasic effect. This effect is possibly mediated through an antioxidant, nephroprotective property and lowering the concentration of urinary stone forming constituents. References 1. Pareta SK, Patra KC, Mazumder PM & Sasmal D. Aqueous extract of Boerhaavia diffusa root ameliorates ethylene glycol-induced hyperoxaluric oxidative stress and renal injury in rat kidney. Pharmaceutical Biol 2011; Khan SR. Interactions between stone-forming calcific crystals and macromolecules. Urologia Internationalis 1997; 59: Daudon M, Bader CA, Jungers P. Urinary calculi: review of classification methods and correlations with etiology. Scanning Microscopy 1993; 7: Tiselius HG, Hallin A, Lindbäck B. Crystallization properties in stone forming and normal subject s urine diluted using a standardized procedure to match the composition of urine in the distal part of the distal tubule and the middlepart of the collecting duct. Urol Res 2001; 29: Rivers K, Sheety S, Menon M. When and how to evaluate a patient with nephrolithiasis. Urol Clin N Amer 2000; 27 (2): Anderson EE, Rundles RW, Silberman HR, Metz EN. Allopurinol control of hyperuricosuria: A new concept in the prevention of uric acid stones. J of Urol 1967; 97: Nadkarni KM. Indian materia medica. In: K. M. Nadkarni, editor. 1 vols, 3 rd edn., Bombay: Popular book depot; p Christina AJM, Haja Najumadeen NA, Vimal Kumar S, Manikandan N, Tobin GC, Venkataraman S, Murugesh N. Antilithiatic Effect of Melia azedarach on Ethylene Glycol Induced Nephrolithiasis in Rats. Pharmaceutical Biology 2006; 44:6. p Khare CP. Indian medicinal plants - An illustrated Dictionary. In: C.P. Khare, editor. Heidelberg: Springer Publishers; p Ghosh MN. Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology. In: M.N. Ghosh, editor. 4 th edn., Calcutta: Hilten & company; p Mitra SK, Gopumadhavan S, Venkataranganna MV, Sundaram R. Effect of Cystone, a Herbal Formulation, on Glycolic Acid-induced Urolithiasis in Rats. Phytotherapy research 1998; 12: Caraway WT. Uric acid In. Standard Methods in Clinical Chemistry. 4 th ed. D. Selegson editors. New York: Academic Press; p Fossati P, Tarenghi G. & Musitelli C, Enzymatic Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Inorganic Phosphorus in Serum and Urine, J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem 1988 ; 26 : Young D. Effect of Preanalytical Variables on clinical Laboratory Tests. 2 nd ed. editor. Washington: AACC press; p Godkar PD, Godkar DB, Text book of medical laboratory technology. 2 nd ed., editor. Bhalani publishing home, India; p Hodgkinson A, Williams A. An improved colorimetric procedure for urine and kidney homogenate. Clinica Chimica Acta 1972; 36: Kaur T, Bijarnia RK, Singla SK, Tandon C. In vivo efficacy of Trachyspermum ammi anticalcifying protein in urolithiatic rat model. J of Ethnopharmacology 2009; 126: Toro G, Ackermann PG. practical chemistry. Editor: Little Brown & Co. Boston; p Fiske CH, Subbarow Y. The colorimetric determination of phosphate. J of Biological Chemistry 1925; 66: Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951; 193: Ohkawa I, Ohisi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 1979; 95: Aebi H, Catalase. Methods in Enzymol 1984; 105: Mishra H P, Fridovich I, The role of superoxide anion in the auto-oxidation of Epinephrine and a sample assay for superoxide dismutase. J Bio chem 1972; 24: Vermeulen CW. Experiments on causation of urinary calculi. In: Essays in Experimental Biology. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; p Fan J, Glass MA, Chandhoke PS. Impact of ammonium chloride administration on rat ethylene glycol urolithiasis model. Scanning Microsc 1997; 13: Lemann J Jr, Worcestor EM, Gray RW. Hypercalciuria and stones. American Journal of Kidney Disease 1991; 27: Asper R. Epidemiology and socioeconomic aspects of urolithiasis. Urol Res 1984; 12: Selvam R, Kalaiselvi P, Govindaraj A, Murugan VM, Satishkumar AS. Effect of A. lanata leaf extract and Vediuppu chunnam on the urinary risk factors of calcium oxalate urolithiasis during experimental hyperoxaluria. Pharmacol. Research 2001; 43: Meyer JL, Thomas WC Jr. Trace metalcitric acid complexes as inhibitors of calcification and crystal growth II. Effects of Fe (III), Cr(III) and Al(III) complexes on calcium oxalate crystal growth. J Urol 1998; 128(2): Ghodkar PB. Chemical tests in kidney disease. In: Textbook of Medical Laboratory Technology. 1 st ed., editor. P.B. Godkar. Bhalani Publishing House, Mumbai p Gadgeb NB, Karadi RV, Alagawadi KR, Savadi RV. Effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. root-wood on ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2006; 105: Huang HS, Ma MC, Chen J, Chen CF, Changes in the oxidant antioxidant balance in the kidney of rats with nephrolithiasis induced by ethylene glycol. Journal of Urology 2002; 167: Pippenger CE, Browne RW, Armstrong D.: Regulatory antioxidant enzymes. In: Free Radical and Antioxidant Protocols. D. Amstrong Editor. New Jersey: Humana Press, chapt p
Effect of Ethanolic Extract of HORDEUM VULGARE Seed on Calcium Oxalate Deposition by Surgericaly Induced Urolithiasis
 Effect of Ethanolic Extract of HORDEUM VULGARE Seed on Calcium Oxalate Deposition by Surgericaly Induced Urolithiasis Ravindrakumar Patel 1*, Jignesh G. Shah 2 1. Department of Pharmacology, Smt. S. M.Shah
Effect of Ethanolic Extract of HORDEUM VULGARE Seed on Calcium Oxalate Deposition by Surgericaly Induced Urolithiasis Ravindrakumar Patel 1*, Jignesh G. Shah 2 1. Department of Pharmacology, Smt. S. M.Shah
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS ABSTRACT
 EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
Curative potential of N. cadamba methanol fruit extract on experimentally induced urolithiasis in rats
 Journal of Innovations in Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences (JIPBS) ISSN: 2349-2759 Available online at www.jipbs.com Research article Curative potential of N. cadamba methanol fruit extract on experimentally
Journal of Innovations in Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences (JIPBS) ISSN: 2349-2759 Available online at www.jipbs.com Research article Curative potential of N. cadamba methanol fruit extract on experimentally
EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE AQUEOUS AND ALCOHOLIC EXTRACTS OF ROOTS OF BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA
 Page525 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2015 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE AQUEOUS AND ALCOHOLIC EXTRACTS OF ROOTS OF BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA Balaji L G
Page525 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2015 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE AQUEOUS AND ALCOHOLIC EXTRACTS OF ROOTS OF BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA Balaji L G
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2011) Anti-Urolithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Seeds of Benincasa Hispida (Thumb)
 Anti-Urolithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Seeds of Benincasa Hispida (Thumb) Patel RK 1 *, Patel SB 1, Shah JG 1 1 Department of Pharmacology, Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, New Vallabh
Anti-Urolithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Seeds of Benincasa Hispida (Thumb) Patel RK 1 *, Patel SB 1, Shah JG 1 1 Department of Pharmacology, Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, New Vallabh
EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF TRAPA NATANS L. FRUITS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF TRAPA NATANS L. FRUITS Mahesh Singh Rajpurohit
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF TRAPA NATANS L. FRUITS Mahesh Singh Rajpurohit
Vol-3, Issue-4, Suppl-3, Dec 2012 ISSN: Joshi et al PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES EFFECT OF RELITH ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS Joshi Nikhil * 1, Joshi Maya 1, Shah Rumit 2, Gajera Vipul 2
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES EFFECT OF RELITH ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS Joshi Nikhil * 1, Joshi Maya 1, Shah Rumit 2, Gajera Vipul 2
Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam
 Research Article Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam A.Tamil Selvan *1, B. Jayalaxmi, R. PAshvini, R.Suthakaran, Vishwanath 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Teegala Ram Reddy College of
Research Article Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam A.Tamil Selvan *1, B. Jayalaxmi, R. PAshvini, R.Suthakaran, Vishwanath 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Teegala Ram Reddy College of
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2010)
 Boerhaavia diffusa Linn AQUEOUS EXTRACT AS CURATIVE AGE T I ETHYLE E GLYCOL I DUCED UROLITHIASIS Surendra K. Pareta 1,2, Kartik Chandra Patra 2, Papiya Mitra Mazumder 1, Dinakar Sasmal 1 1 Department of
Boerhaavia diffusa Linn AQUEOUS EXTRACT AS CURATIVE AGE T I ETHYLE E GLYCOL I DUCED UROLITHIASIS Surendra K. Pareta 1,2, Kartik Chandra Patra 2, Papiya Mitra Mazumder 1, Dinakar Sasmal 1 1 Department of
PHYTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND ANTI LITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ABELMOSCHUS MOSCHATUS MEDIKUS
 Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 5, Issue 1, 2013 Research Article PHYTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND ANTI LITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ABELMOSCHUS
Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 5, Issue 1, 2013 Research Article PHYTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND ANTI LITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ABELMOSCHUS
G. Manish. et.al/ 1(4) pp
 Fractions from Coconut water (Cocos nucifera) influencing in vitro calcium oxalate crystal growth Manish Gandhi * 1, Tandon Chanderdeep 2, Puri Sanjeev 3, Singla Surindar *1, *1 Department of Biochemistry,
Fractions from Coconut water (Cocos nucifera) influencing in vitro calcium oxalate crystal growth Manish Gandhi * 1, Tandon Chanderdeep 2, Puri Sanjeev 3, Singla Surindar *1, *1 Department of Biochemistry,
Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Siddarthan, 6(6): June, 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN:
![Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Siddarthan, 6(6): June, 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN: Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Siddarthan, 6(6): June, 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN:](/thumbs/83/88578077.jpg) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES (Int. J. of Pharm. Life Sci.) Antilithiatic effect of Ethanolic extract of Crataeva religiosa on Wistar rats S. Siddarthan*, T. Gowri Thilagam, M.Mathivani,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES (Int. J. of Pharm. Life Sci.) Antilithiatic effect of Ethanolic extract of Crataeva religiosa on Wistar rats S. Siddarthan*, T. Gowri Thilagam, M.Mathivani,
ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF Saccharum spontaneum Linn. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS.
 ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF Saccharum spontaneum Linn. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS. M.Sathya Research scholar, Department of Biochemistry, Kongunadu Arts and Science College, Coimbatore-29
ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF Saccharum spontaneum Linn. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS. M.Sathya Research scholar, Department of Biochemistry, Kongunadu Arts and Science College, Coimbatore-29
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 372 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 2 2013 Research article Bioevaluation
372 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 2 2013 Research article Bioevaluation
Received: 19 Dec 2014, Revised and Accepted: 16 Dec 2014
 International Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014, Dec., Vol. 5 (4) ISSN: 0976-9390 IJCPS Antiurolithiatic activity of Stephania japonica Linn., leaves 1 Balasubramanian P *, 2 Senthamarai
International Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014, Dec., Vol. 5 (4) ISSN: 0976-9390 IJCPS Antiurolithiatic activity of Stephania japonica Linn., leaves 1 Balasubramanian P *, 2 Senthamarai
ACTIVITY OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS
 Research Article Sathya M,, 2012; Volume 1(5): 338-350 ISSN: 2277-8713 ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS M. SATHYA 1, Dr. R. KOKILAVANI 2
Research Article Sathya M,, 2012; Volume 1(5): 338-350 ISSN: 2277-8713 ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN. ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS M. SATHYA 1, Dr. R. KOKILAVANI 2
Mohammed Atif et al. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2014, 5 (7) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF HYDRO-ALCOHOLIC AND AQUEOUS LEAF EXTRACT OF BARLERIA PRIONITIS IN
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article EVALUATION OF ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF HYDRO-ALCOHOLIC AND AQUEOUS LEAF EXTRACT OF BARLERIA PRIONITIS IN
Evaluation of Ethanolic seed extract of Tribulus terrestris. Linn in serum electrolytes and urine oxalte of Urolithiatic male Albino Wistar rats
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Evaluation of Ethanolic seed extract of Tribulus terrestris. Linn in serum electrolytes and urine oxalte of Urolithiatic
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Evaluation of Ethanolic seed extract of Tribulus terrestris. Linn in serum electrolytes and urine oxalte of Urolithiatic
Rotula Aquatica Lour Aqueous Extract as Anti-Urolithiatic Agent in Experimentally Induced Urolithiatic Rat Model
 Available online on www.ijppr.com International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research 2017; 9(4); 553-558 DOI number: 10.25258/phyto.v9i2.8128 Research Article ISSN: 0975-4873 Rotula Aquatica
Available online on www.ijppr.com International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research 2017; 9(4); 553-558 DOI number: 10.25258/phyto.v9i2.8128 Research Article ISSN: 0975-4873 Rotula Aquatica
CHAPTER 7 EFFECT OF COSTUS IGNEUS STEM EXTRACT ON CALCIUM OXALATE UROLITHIASIS IN ALBINO RATS
 CHAPTER 7 EFFECT OF COSTUS IGNEUS STEM EXTRACT ON CALCIUM OXALATE UROLITHIASIS IN ALBINO RATS 7.1 INTRODUCTION Kidney stone disease is a common disorder estimated to occur in approximately 12% of the population,
CHAPTER 7 EFFECT OF COSTUS IGNEUS STEM EXTRACT ON CALCIUM OXALATE UROLITHIASIS IN ALBINO RATS 7.1 INTRODUCTION Kidney stone disease is a common disorder estimated to occur in approximately 12% of the population,
ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF SOLANUM VIRGINIANUM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS
 Page328 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF SOLANUM VIRGINIANUM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS Krishna Mohan Chinnala*, Srinivas
Page328 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF SOLANUM VIRGINIANUM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS Krishna Mohan Chinnala*, Srinivas
Available online at International Journal of Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology
 Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved Original Article Evaluation of Coleus barbatus
Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved Original Article Evaluation of Coleus barbatus
Summary 255 Research Summary
 Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
IN VITRO ANTILITHIATIC STUDIES ON DOLICHOS BIFLORUS LINN. (SEEDS) AND PARMELIA PERLATA ACH. (THALLUS)
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(3), 2008, 1324-1332 IN VITRO ANTILITHIATIC STUDIES ON DOLICHOS BIFLORUS LINN. (SEEDS) AND PARMELIA PERLATA ACH. (THALLUS) S. JHA, M. D. KHARYA a, P. P. SINGH b and P. K. JAIN b Department
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(3), 2008, 1324-1332 IN VITRO ANTILITHIATIC STUDIES ON DOLICHOS BIFLORUS LINN. (SEEDS) AND PARMELIA PERLATA ACH. (THALLUS) S. JHA, M. D. KHARYA a, P. P. SINGH b and P. K. JAIN b Department
Effect of astaxanthin on Diuresis and body composition in experimentalnephrolithiasis
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 5 May 2014 PP.17-22 Effect of astaxanthin on Diuresis and body composition in
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 5 May 2014 PP.17-22 Effect of astaxanthin on Diuresis and body composition in
Chitra Lekha Devi Adari and Raj Kiran K. / International Journal of Phytopharmacology. 7(2), 2016, International Journal of Phytopharmacology
 52 International Journal of Phytopharmacology Journal homepage: www.onlineijp.com e- ISSN 0975 9328 Print ISSN 2229 7472 IJP EFFECT OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PEEL OF PUNICA GRANATUM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL AND
52 International Journal of Phytopharmacology Journal homepage: www.onlineijp.com e- ISSN 0975 9328 Print ISSN 2229 7472 IJP EFFECT OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PEEL OF PUNICA GRANATUM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL AND
Lithotriptic Activity of Siddha Drug Megarajanga Chooranam on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Rats
 Research Article Lithotriptic Activity of Siddha Drug Megarajanga Chooranam on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Rats K. Kanakavalli 1, P. Parthiban 1, J. Anbu 2, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 3, R. Sathyavathy
Research Article Lithotriptic Activity of Siddha Drug Megarajanga Chooranam on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Rats K. Kanakavalli 1, P. Parthiban 1, J. Anbu 2, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 3, R. Sathyavathy
ISSN: Original Article Evaluation of Aerva Lanata Flower Extract for Its Antilithiatic Potential In Vitro and In Vivo
 Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science Research Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved ISSN: 2249-0337 Original Article
Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science Research Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved ISSN: 2249-0337 Original Article
Antiurolithiatic Activity of Whole-Plant Hydroalcoholic Extract of Pergularia daemia in Rats
 Pharmacognosy Antiurolithiatic Activity of Whole-Plant Hydroalcoholic Extract of Pergularia daemia in Rats Vyas BA, Vyas RB, Joshi SV, Santani DD 1 Maliba Pharmacy College, Gopal Vidyanagar, Tarsadi, Gujarat
Pharmacognosy Antiurolithiatic Activity of Whole-Plant Hydroalcoholic Extract of Pergularia daemia in Rats Vyas BA, Vyas RB, Joshi SV, Santani DD 1 Maliba Pharmacy College, Gopal Vidyanagar, Tarsadi, Gujarat
ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF TRIBULUS TERRESTRIS FRUITS AND PUNICA GRANATUM SEEDS IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED RAT MODELS.
 Page4605 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2013 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 Journal home page: http:///index.php/en/ INDO AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF
Page4605 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2013 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 Journal home page: http:///index.php/en/ INDO AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF
Induction of lipid peroxidation by oxalate in experimental rat urolithiasis
 J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 4, December 1987, pp. 367 373. Printed in India. Induction of lipid peroxidation by oxalate in experimental rat urolithiasis R. SELVAM and T. BIJI KURIEN Department of Medical
J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 4, December 1987, pp. 367 373. Printed in India. Induction of lipid peroxidation by oxalate in experimental rat urolithiasis R. SELVAM and T. BIJI KURIEN Department of Medical
Evaluation of anti lithiatic effect of Siruneer Kalluku Kudineer Chooranam (SKKC) on 1% ethylene glycol induced lithiasis in albino rats.
 Int. J. Curr. Res. Chem. Pharm. Sci. (2017). 4(9): 9-14 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps
Int. J. Curr. Res. Chem. Pharm. Sci. (2017). 4(9): 9-14 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps
USHAKIRAN CH*, PUSHPA VALLI MURTHY P, SAI LAKSHMI P, MOUNIKA V, MANI JYOTHI N and ANITHA P
 EVALUATION AND ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF RAPHANUS SATIVUS EXTRACT BY IN-VIVO ON EXPERIMENTALY INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS USHAKIRAN CH*, PUSHPA VALLI MURTHY P, SAI LAKSHMI P, MOUNIKA V, MANI JYOTHI
EVALUATION AND ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF RAPHANUS SATIVUS EXTRACT BY IN-VIVO ON EXPERIMENTALY INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS USHAKIRAN CH*, PUSHPA VALLI MURTHY P, SAI LAKSHMI P, MOUNIKA V, MANI JYOTHI
RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks
 Mayo Clinic O Brien Urology Research Center RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES 2017 Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks John C Lieske, MD July 27, 2017 What types
Mayo Clinic O Brien Urology Research Center RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES 2017 Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks John C Lieske, MD July 27, 2017 What types
Evaluation of different urinary constituent ratios in renal stone formers
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (3) : 50-55 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Evaluation of
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (3) : 50-55 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Evaluation of
Urolithiasis. Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery
 Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
BERGENIA CILIATA EXTRACT PREVENTS ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE KIDNEY
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 68 No. 5 pp. 711ñ715, 2011 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society BERGENIA CILIATA EXTRACT PREVENTS ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 68 No. 5 pp. 711ñ715, 2011 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society BERGENIA CILIATA EXTRACT PREVENTS ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development Vol.1 (6) Nov. Dec. 2013: 62-69
 Chayva Pavitra et al www.ajprd.com 61 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development (An International Peer-Reviewed Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development) www.ajprd.com ISSN 2320-4850
Chayva Pavitra et al www.ajprd.com 61 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development (An International Peer-Reviewed Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development) www.ajprd.com ISSN 2320-4850
FREE RADICAL CHANGES IN METHANOL TOXICITY
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2003; 47(2) (2) : 207 211 Methanol and Free Radicals 207 FREE RADICAL CHANGES IN METHANOL TOXICITY ESTHER M. PAULA, D. C. MATHANGI AND A. NAMASIVAYAM* Department of Physiology,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2003; 47(2) (2) : 207 211 Methanol and Free Radicals 207 FREE RADICAL CHANGES IN METHANOL TOXICITY ESTHER M. PAULA, D. C. MATHANGI AND A. NAMASIVAYAM* Department of Physiology,
Anti-Urolithiatic Evaluation of Siddha formulation Seenakara Parpam against Zinc Disc Implantation induced Urolithiasis in Wistar Albino Rats
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 3, Issue 12-2016 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2016.03.12.002
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 3, Issue 12-2016 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2016.03.12.002
Evaluation of Diuretic Effect of Aqueous Extract of Dolichos biflorus Seeds against Ethylene Glycol Induced Renal Stone in Experimental Rats
 Journal of Animal Research: v.5 n.4, p. 773-777. December 2015 DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2015.00128.X Evaluation of Diuretic Effect of Aqueous Extract of Dolichos biflorus Seeds against Ethylene Glycol Induced
Journal of Animal Research: v.5 n.4, p. 773-777. December 2015 DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2015.00128.X Evaluation of Diuretic Effect of Aqueous Extract of Dolichos biflorus Seeds against Ethylene Glycol Induced
Management of common uroliths through diet
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Priyanka Kantivan Goswami et al. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2015, 6 (12) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ROOT EXTRACT OF NOTHOSAERVA BRACHIATA WIGHT IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIATIC RATS
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ROOT EXTRACT OF NOTHOSAERVA BRACHIATA WIGHT IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIATIC RATS
Prophylactic Role of Boerhaavia diffusa in Ethylene Glycol Induced Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis
 African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 2, 2011 28-36 Original article Prophylactic Role of Boerhaavia diffusa in Ethylene Glycol Induced Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis S. K. Pareta 1,2, K. C.
African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 2, 2011 28-36 Original article Prophylactic Role of Boerhaavia diffusa in Ethylene Glycol Induced Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis S. K. Pareta 1,2, K. C.
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 1 Jan-Mar-2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access ANTIUROLITHIATIC
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 1 Jan-Mar-2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access ANTIUROLITHIATIC
Evaluation of Antiurolithiatic Potentials of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Cucumis sativus L.
 Evaluation of Antiurolithiatic Potentials of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Cucumis sativus L. Original Article Shriram Ramesh Pethakar 1 *, Pramod Jayadevappa Hurkadale 1, Ravindra Durdundayya Hiremath 2
Evaluation of Antiurolithiatic Potentials of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Cucumis sativus L. Original Article Shriram Ramesh Pethakar 1 *, Pramod Jayadevappa Hurkadale 1, Ravindra Durdundayya Hiremath 2
Effect of Sarva Noi Linga Chenduram for anti urolithiatic activity in ethylene glycol induced animal model.
 Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. (2017). 4(2): 50-59 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 4, Issue
Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. (2017). 4(2): 50-59 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 4, Issue
ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF Peperomia tetraphylla ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN RATS
 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF Peperomia tetraphylla ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL
ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF THE PLANT EXTRACTS OF Peperomia tetraphylla ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL
School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR
 1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
Effect of Aqueous, Ethanol and Petroleum Ether Extracts of Amaranthus viridis L on Nephrolithiasic Wistar Rats
 Human Journals Research Article May 2018 Vol.:12, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Somayeh Afsah Vakili et al. Effect of Aqueous, Ethanol and Petroleum Ether Extracts of Amaranthus viridis L on Nephrolithiasic
Human Journals Research Article May 2018 Vol.:12, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Somayeh Afsah Vakili et al. Effect of Aqueous, Ethanol and Petroleum Ether Extracts of Amaranthus viridis L on Nephrolithiasic
EVALUATION OF ANTI-UROLITHIATIC POTENTIAL OF NOVEL SIDDHA FORMULATION SEENAKARAPARPAM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL-INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN WISTAR ALBINO RATS
 EVALUATION OF ANTI-UROLITHIATIC POTENTIAL OF NOVEL SIDDHA FORMULATION SEENAKARAPARPAM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL-INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN WISTAR ALBINO RATS A.Mariappan *, G.Ganapathy, V.Bhanumathi * Lecturer,
EVALUATION OF ANTI-UROLITHIATIC POTENTIAL OF NOVEL SIDDHA FORMULATION SEENAKARAPARPAM ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL-INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN WISTAR ALBINO RATS A.Mariappan *, G.Ganapathy, V.Bhanumathi * Lecturer,
Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn.
 Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn. R.Mythreyi 1, N.Rajkumar 1* and E.Sasikala 2 1 Maharaji College of Pharmacy, Besant Nagar, Chennai-90. 2 Central Research Institute for Siddha,
Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn. R.Mythreyi 1, N.Rajkumar 1* and E.Sasikala 2 1 Maharaji College of Pharmacy, Besant Nagar, Chennai-90. 2 Central Research Institute for Siddha,
Study on In vitro antiurolithiatic activity of Bryophyllum pinnatum and Ocimum gratissimum leaves
 RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research Article Study on In vitro antiurolithiatic
RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research Article Study on In vitro antiurolithiatic
EQUILIBRIUM VERSUS SUPERSATURATED URINE HYPOTHESIS IN CALCIUM SALT UROLITHIASIS: A NEW THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL APPROACH TO A CLINICAL PROBLEM
 Scanning Microscopy Vol. 13, No. 2-3, 1999 (Pages 261-265) 0891-7035/99$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago Equilibrium (AMF O Hare), model for IL calcium 60666 USA salt urolithiasis EQUILIBRIUM
Scanning Microscopy Vol. 13, No. 2-3, 1999 (Pages 261-265) 0891-7035/99$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago Equilibrium (AMF O Hare), model for IL calcium 60666 USA salt urolithiasis EQUILIBRIUM
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist
 The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
In vitro study of aqueous leaf extract of Raphanus Sativus var. for inhibition of calcium oxalate crystallization
 Bioscience Discovery, 8(2):153-157, April - 2017 RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research
Bioscience Discovery, 8(2):153-157, April - 2017 RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research
NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention
 NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Epidemiology Prevalence 2-3%, maybe in
NEPHROLITHIASIS Etiology, stone composition, medical management, and prevention Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Epidemiology Prevalence 2-3%, maybe in
MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL STUDY OF URINARY CALCULI
 MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL STUDY OF URINARY CALCULI Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 303 F.D. Khan, M.S. Memon, A.F. Ansari ( Department of Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry, University of
MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL STUDY OF URINARY CALCULI Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 303 F.D. Khan, M.S. Memon, A.F. Ansari ( Department of Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry, University of
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
Curative Effect of Extractive Phytoconstituents of Psidium Guajava Leaves on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Experimental Animals
 31 Original Article Curative Effect of Extractive Phytoconstituents of Psidium Guajava Leaves on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Experimental Animals Hemant K. Nagar a, *, Harinarayan S. Chandel
31 Original Article Curative Effect of Extractive Phytoconstituents of Psidium Guajava Leaves on Ethylene Glycol Induced Urolithiasis in Experimental Animals Hemant K. Nagar a, *, Harinarayan S. Chandel
GUIDELINES ON UROLITHIASIS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLITHIASIS (Text updated May 2005) H.G. Tiselius (chairman), D. Ackermann, P. Alken, C. Buck, P. Conort, M. Gallucci, T. Knoll Eur Urol 2001;40:362-371 Introduction Urinary stone disease
GUIDELINES ON UROLITHIASIS (Text updated May 2005) H.G. Tiselius (chairman), D. Ackermann, P. Alken, C. Buck, P. Conort, M. Gallucci, T. Knoll Eur Urol 2001;40:362-371 Introduction Urinary stone disease
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI)
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(1), 2013, 457463 ISSN 0972768X www.sadgurupublications.com PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI) SUMAN PARIHAR a, PRASOON HADA
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(1), 2013, 457463 ISSN 0972768X www.sadgurupublications.com PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF URINARY STONES (PATHARI) SUMAN PARIHAR a, PRASOON HADA
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009) ewsletter Kumar et al.
 A TIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACTS OF ASPARAGUS RACEMOSUS WILLD. A D TAMARI DUS I DICA LI. I RATS Satish Kumar M. C 1, Udupa A.L 2, Sammodavardhana K 1, Rathnakar U.P 3, Shvetha Udupa 1, Prabhath
A TIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACTS OF ASPARAGUS RACEMOSUS WILLD. A D TAMARI DUS I DICA LI. I RATS Satish Kumar M. C 1, Udupa A.L 2, Sammodavardhana K 1, Rathnakar U.P 3, Shvetha Udupa 1, Prabhath
Pharmacological evaluation of ethanolic extract of Kigelia pinnata fruit against ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 1, (1):63-7 SSN : 49-741 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Pharmacological evaluation of ethanolic extract of Kigelia pinnata
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 1, (1):63-7 SSN : 49-741 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Pharmacological evaluation of ethanolic extract of Kigelia pinnata
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths
 Published in IVIS with the permission of the editor Close window to return to IVIS ROYAL CANIN VIEWPOINT Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths KEY POINTS
Published in IVIS with the permission of the editor Close window to return to IVIS ROYAL CANIN VIEWPOINT Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths KEY POINTS
Anti-Urolithiatic Activity of Melia Azedarach Linn Leaf Extract in Ethylene Glycol-Induced Urolithiasis in Male Albino Rats
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research March 2014; 13 (3): 391-397 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research March 2014; 13 (3): 391-397 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
EVALUATION ON ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF BRYOPHYLLUM PINNATUM OF RATS
 EVALUATION ON ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF BRYOPHYLLUM PINNATUM OF RATS Ayaz Ahmad* 1, Ram Garg 1, Sonu Sharma 1 1. Nims institute of pharmacy, Nims university, Shobha Nagar Jaipur, INDIA *Corresponding
EVALUATION ON ANTIUROLITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF BRYOPHYLLUM PINNATUM OF RATS Ayaz Ahmad* 1, Ram Garg 1, Sonu Sharma 1 1. Nims institute of pharmacy, Nims university, Shobha Nagar Jaipur, INDIA *Corresponding
The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones. Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019
 The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019 Urinary Calculi Prevalence and incidence of kidney stones increasing across the world Environmental
The Nuts and Bolts of Kidney Stones Soha Zouwail Consultant Chemical Pathology UHW Renal Training Day 2019 Urinary Calculi Prevalence and incidence of kidney stones increasing across the world Environmental
Research Article. Protective effect of methanolic extract of Abelmoschus moschatus seeds against calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):269-278 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Protective effect of methanolic extract of Abelmoschus
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):269-278 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Protective effect of methanolic extract of Abelmoschus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017, 1715 1720 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFICACY OF PUNARNAVA (BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA) IN THE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017, 1715 1720 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFICACY OF PUNARNAVA (BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA) IN THE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF
Evaluation of anti lithiatic effect of Maavilinga Kudineer Chooranam (MKC) on 1% ethylene glycol induced lithiasis in albino rats
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps Coden: IJCROO(USA) Volume 4, Issue 6-2017
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps Coden: IJCROO(USA) Volume 4, Issue 6-2017
Effect of Methanolic Extract of Triblus Terrestris in Ethylene Glycol Induced Crystalluric Rats
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2016), PP 98-102 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Methanolic Extract of Triblus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2016), PP 98-102 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Methanolic Extract of Triblus
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research Article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Nephrotoxicity and Urolithiasis Activity of Solanum nigrum C. Hema Harika
Research Article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Nephrotoxicity and Urolithiasis Activity of Solanum nigrum C. Hema Harika
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences Vol 2, Issue 1, 2010
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences Vol 2, Issue 1, 2010 ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVITY OF CLEOME VISCOSA SEED EXTRACTS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE. Amrita Mishra 1,2, Arun K Mishra 1, Sanjay
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences Vol 2, Issue 1, 2010 ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVITY OF CLEOME VISCOSA SEED EXTRACTS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE. Amrita Mishra 1,2, Arun K Mishra 1, Sanjay
ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE
 Ancient Science of Life Vol. : XXVI (1&) July, August, September, October, November, December 006 ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE T.ANITHA AND S.MOHANDASS Received
Ancient Science of Life Vol. : XXVI (1&) July, August, September, October, November, December 006 ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE T.ANITHA AND S.MOHANDASS Received
Antiurolithiatic Effects of Solanum xanthocarpum Fruit Extract on Ethylene-Glycol-Induced Nephrolithiasis in Rats
 Pharmacognosy Antiurolithiatic Effects of Solanum xanthocarpum Fruit Extract on Ethylene-Glycol-Induced Nephrolithiasis in Rats Patel PK, Patel MA, Saralai MG, Gandhi TR 1 Department of Pharmacology, C.
Pharmacognosy Antiurolithiatic Effects of Solanum xanthocarpum Fruit Extract on Ethylene-Glycol-Induced Nephrolithiasis in Rats Patel PK, Patel MA, Saralai MG, Gandhi TR 1 Department of Pharmacology, C.
In vitro antiurolithiatic activity of Strychnos potatorum L.F.
 South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 174 178 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article In vitro antiurolithiatic activity of Strychnos potatorum L.F. Thermadum Vareed Binu 1,*, Bhavaniamma
South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 174 178 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article In vitro antiurolithiatic activity of Strychnos potatorum L.F. Thermadum Vareed Binu 1,*, Bhavaniamma
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 6.805
 SJIF Impact Factor 6.805 Volume 5, Issue 2, 1721-1735. Research Article ISSN 2277 7105 EVALUATION OF ANTI-UROLITHIATIC EFFECT OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF PARSLEY (PETROSELINUM SATIVUM) USING ETHYLENE GLYCOL-INDUCED
SJIF Impact Factor 6.805 Volume 5, Issue 2, 1721-1735. Research Article ISSN 2277 7105 EVALUATION OF ANTI-UROLITHIATIC EFFECT OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF PARSLEY (PETROSELINUM SATIVUM) USING ETHYLENE GLYCOL-INDUCED
ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT OF BOERHAAVIA DIFFUSA ROOTS ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED LITHIASIS IN RATS
 Academic Sciences International Chitra Journal et al. of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Issue 2, 2012 Research Article ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT OF BOERHAAVIA
Academic Sciences International Chitra Journal et al. of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Issue 2, 2012 Research Article ANTILITHIATIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT OF BOERHAAVIA
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2011, 2 (1): 129-134 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Studies on diuretic activity of three plants from Menispermaceae family
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2011, 2 (1): 129-134 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Studies on diuretic activity of three plants from Menispermaceae family
Effect of hydro alcoholic extract of Vernonia cinerea Less. against ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats
 Research Article Access this article online Quick Response Code: Website: www.ijp online.com DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.186211 Effect of hydro alcoholic extract of Vernonia cinerea Less. against ethylene glycol
Research Article Access this article online Quick Response Code: Website: www.ijp online.com DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.186211 Effect of hydro alcoholic extract of Vernonia cinerea Less. against ethylene glycol
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009) Diuretic, Laxative and Toxicity Studies of Viola odorata Aerial Parts
 Diuretic, Laxative and Toxicity Studies of Viola odorata Aerial Parts A. Vishal a,, K. Parveen a, S. Pooja b, N. Kannappan c*, Shakun Kumar d a G.V.M College of Pharmacy, Sonepat, Haryana, India b R.K.S.D
Diuretic, Laxative and Toxicity Studies of Viola odorata Aerial Parts A. Vishal a,, K. Parveen a, S. Pooja b, N. Kannappan c*, Shakun Kumar d a G.V.M College of Pharmacy, Sonepat, Haryana, India b R.K.S.D
1. LITERATURE REVIEW
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Baheti D. G., (2013) reported antiurolithiatic activity of a polyherbal formulation against calcium oxalate induced urolithiasis in rats and a polyherbal formulation constituted
1. LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Baheti D. G., (2013) reported antiurolithiatic activity of a polyherbal formulation against calcium oxalate induced urolithiasis in rats and a polyherbal formulation constituted
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 21, 2(3):374-38 ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 Anti gastric ulcer activity of Plectranthus amboinicus
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 21, 2(3):374-38 ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 Anti gastric ulcer activity of Plectranthus amboinicus
SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine
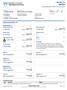 1-800-533-1710 SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine Patient ID Patient Name SAMPLEREPORT, SAT24 NORMAL Birth Date 1976-05-13 Gender M Age 40 Order Number Client Order Number Ordering Physician
1-800-533-1710 SAT24 Supersaturation Profile, 24 Hour, Urine Patient ID Patient Name SAMPLEREPORT, SAT24 NORMAL Birth Date 1976-05-13 Gender M Age 40 Order Number Client Order Number Ordering Physician
Antiurolithiatic Activity of Extract and Oleanolic Acid Isolated from the Roots of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Pharmacology Volume 2013, Article ID 951795, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951795 Research Article Antiurolithiatic Activity of Extract and Oleanolic Acid Isolated
Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Pharmacology Volume 2013, Article ID 951795, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951795 Research Article Antiurolithiatic Activity of Extract and Oleanolic Acid Isolated
Effect of Aerva lanata on calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats
 Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, December 2006, pp. 981-986 Effect of Aerva lanata on calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats P Soundararajan #, R Mahesh, T Ramesh $ & V Hazeena Begum* Department
Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, December 2006, pp. 981-986 Effect of Aerva lanata on calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats P Soundararajan #, R Mahesh, T Ramesh $ & V Hazeena Begum* Department
TEPZZ _6 76A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ _6 76A_T (11) EP 3 162 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 03.0.17 Bulletin 17/18 (21) Application number: 172173.0
(19) TEPZZ _6 76A_T (11) EP 3 162 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 03.0.17 Bulletin 17/18 (21) Application number: 172173.0
Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca Tel (714) Fax (714) Kidney Stone Disease in Adults
 Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc. 11160 Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca 92708 Tel (714)549-3333 Fax (714)549-3334 Kidney Stone Disease in Adults Overview Kidney stones are one of the most painful
Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc. 11160 Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca 92708 Tel (714)549-3333 Fax (714)549-3334 Kidney Stone Disease in Adults Overview Kidney stones are one of the most painful
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Research Article Pharmacognosy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF SEMECARPUS ANACARDIUM FRUIT EXTRACTS AGAINST CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY
Research Article Pharmacognosy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF SEMECARPUS ANACARDIUM FRUIT EXTRACTS AGAINST CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY
PREVENTIVE EFFECT OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN.AGAINST GLYCOLIC ACID INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN MALE WISTAR ALBINO RATS ABSTRACT
 Research Article Biochemistry ISSN 0975-6299 PREVENTIVE EFFECT OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN.AGAINST GLYCOLIC ACID INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN MALE WISTAR ALBINO RATS M,SATHYA 1 * AND DR. R.KOKILAVANI 2 1 Research
Research Article Biochemistry ISSN 0975-6299 PREVENTIVE EFFECT OF SACCHARUM SPONTANEUM LINN.AGAINST GLYCOLIC ACID INDUCED UROLITHIASIS IN MALE WISTAR ALBINO RATS M,SATHYA 1 * AND DR. R.KOKILAVANI 2 1 Research
Alkaline citrate reduces stone recurrence and regrowth after shockwave lithotripsy and percutaneous nephrolithotomy
 Clinical Urology Alkaline citrate and stone recurrence International Braz J Urol Vol. 37 (5): 611-616, September - October, 2011 Alkaline citrate reduces stone recurrence and regrowth after shockwave lithotripsy
Clinical Urology Alkaline citrate and stone recurrence International Braz J Urol Vol. 37 (5): 611-616, September - October, 2011 Alkaline citrate reduces stone recurrence and regrowth after shockwave lithotripsy
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2010)
 THERAPEUTIC ROLE OF ANTI-OXIDANT PROPERTIES OF EMBLICA OFFICINALIS (AMLA) IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED TYPE I DIABETIC RATS P. R. Tirgar* 1, P. D. Jadav 2, D. B. Sheth 3, T. R. Desai 4 Authors addresses Pravin
THERAPEUTIC ROLE OF ANTI-OXIDANT PROPERTIES OF EMBLICA OFFICINALIS (AMLA) IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED TYPE I DIABETIC RATS P. R. Tirgar* 1, P. D. Jadav 2, D. B. Sheth 3, T. R. Desai 4 Authors addresses Pravin
Journal of Pharmacreations
 Journal of Pharmacreations Pharmacreations Vol. 1 Issue 1 Mar - 2014 Journal Home page: Review article Open Access Animal Models For Urolithiasis A Short Review T.Vijaya, Nallani Venkata Rama Rao*, A.Narendra
Journal of Pharmacreations Pharmacreations Vol. 1 Issue 1 Mar - 2014 Journal Home page: Review article Open Access Animal Models For Urolithiasis A Short Review T.Vijaya, Nallani Venkata Rama Rao*, A.Narendra
Effect of Vitamin A Deficiency on Urinary Calculus
 J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 8, 51-60, 1990 Effect of Vitamin A Deficiency on Urinary Calculus Formation in Rats Ravi Kumar KANCHA and Adoni ANASUVA* National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical
J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 8, 51-60, 1990 Effect of Vitamin A Deficiency on Urinary Calculus Formation in Rats Ravi Kumar KANCHA and Adoni ANASUVA* National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood
 Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
Pharmacological and Clinical Study on Cystone
 [Probe (1977): (XVII), 1, 25-29] Pharmacological and Clinical Study on Cystone Phukan, D.P., M.D., Professor and Head of the Department of Pharmacology, (Mrs.) Deka, A., M.D., Demonstrator of Pharmacology
[Probe (1977): (XVII), 1, 25-29] Pharmacological and Clinical Study on Cystone Phukan, D.P., M.D., Professor and Head of the Department of Pharmacology, (Mrs.) Deka, A., M.D., Demonstrator of Pharmacology
