Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture
|
|
|
- Roland Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Neurosurg Spine 13: , 2010 Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture Clinical article Sa t o s h i Ka w a g u c h i, M.D., 1 Ke i k o Ho r i g o m e, M.D., 1 Hi d e k i Ya j i m a, M.D., 1 Ta k a s h i Od a, M.D., 1 Yu i c h i r o Kii, M.D., 1 Ka z u n o r i Id a, M.D., 2 Mi t s u n o r i Yo s h i m o t o, M.D., 2 Ko u s u k e Ib a, M.D., 2 Ts u n e o Ta k e b aya s h i, M.D., 2 a n d To s h i h i ko Ya m a s h i t a, M.D. 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asahikawa Kosei Hospital, Asahikawa; and 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan Object. The present study was designed to determine clinical and radiographic characteristics of unhealed osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVFs) and the role of fracture mobility and an intravertebral cleft in the regulation of pain symptoms in patients with an OVF. Methods. Patients who had persistent low-back pain for 3 months or longer and a collapsed thoracic or lumbar vertebra that had an intervertebral cleft and abnormal mobility were referred to as having unhealed OVFs. Twentyfour patients with an unhealed OVF and 30 patients with an acute OVF were compared with regard to several clinical and radiographic features including the presence of an intravertebral fluid sign. Subsequently, the extent of dynamic mobility of the fractured vertebra was analyzed for correlation with the patients age, duration of symptoms, back pain visual analog scale (VAS) score, and performance status. Finally, in cases of unhealed OVFs, the subgroup of patients with positive fluid signs was compared with the subgroup of patients with negative fluid signs. Results. Patients with an unhealed OVF were more likely to have a crush-type fracture, shorter vertebral height of the fractured vertebra, and a fracture with a positive fluid sign than those with an acute OVF. The extent of dynamic mobility of the vertebra correlated significantly with the VAS score in patients with an unhealed OVF. In addition, a significant correlation with the extent of dynamic vertebral mobility with performance status was seen in patients with an unhealed OVF and those with an acute OVF. Of the 24 patients with an unhealed OVF, 14 had a positive fluid sign in the affected vertebra. Patients with a positive fluid sign exhibited a statistically significantly greater extent of dynamic vertebral mobility, a higher VAS score, a higher performance status grade, and a greater likelihood of having a crush-type fracture than those with a negative fluid sign. All but 1 patient with an unhealed OVF and a positive fluid sign had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status Grade 3 or 4 (bedridden most or all of the time). In sharp contrast, all 10 patients with an unhealed OVF and a negative fluid sign were Grade 1 or 2. Conclusions. Unhealed OVFs form a group of fractures that are distinct from acute OVFs regarding radiographic morphometry and contents of the intravertebral cleft. Dynamic vertebral mobility serves as a primal pain determinant in patients with an unhealed OVF and potentially in those with an acute OVF. Fluid accumulation in the intravertebral cleft of unhealed OVFs likely reflects long-term bedridden positioning of the patients in daily activity. (DOI: / SPINE09364) Ke y Wo r d s vertebral fracture intravertebral cleft mobility osteoporosis back pain Ve rt e b r a l fractures are the most common type of osteoporotic fracture. 21 In the majority of patients with OVFs, acute back pain symptoms abate over a period of 6 8 weeks in line with the pace of fracture healing. However, a certain number of patients suffer Abbreviations used in this paper: ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; OVF = osteoporotic vertebral fracture; VAS = visual analog scale. persistent pain symptoms following an OVF. Various synonyms for this condition have been used in the literature, including Kümmell disease, avascular necrosis of the vertebra, vertebral fracture with intravertebral cleft, vertebral fracture with intraosseous vacuum phenomena, delayed vertebral collapse, vertebral pseudarthrosis, and intravertebral pseudarthrosis. 5,7,8,10,22 A common radiographic feature of the fractured vertebra in this group of patients is the presence of an intravertebral cleft that J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August
2 S. Kawaguchi et al. shows abnormal mobility. Although the primary pathogenesis of this condition is currently considered to be a failure of the fracture healing process, controversies exist regarding its nature, diagnosis, and therapeutic aspects. Intravertebral clefts, also called intravertebral vacuum phenomena and Kümmell signs, have been well documented in the imaging literature. 1,3,16,18,24,26,28 In radiographs, they are seen as an intravertebral transverse, linear, or semilunar radiolucent shadow. Magnetic resonance images reveal an accumulation of air or fluid in the cleft. 10,14,28 Abnormal mobility of the intravertebral cleft has been suggested as a cause of severe back pain during motion in patients with vertebral pseudarthrosis. 8,18 However, to our knowledge no study has addressed the symptomatic relevance of the intravertebral cleft. Furthermore, the clinical significance of fluid and gas accumulation in the intravertebral cleft remains under debate. 10,14,28 In the present study, we determined the diagnostic criteria of OVFs that failed to heal properly. We then compared patients with an unhealed OVF with those with an acute OVF with regard to clinical and radiographic features. Subsequently, we analyzed the symptomatic relevance of vertebral mobility and the intravertebral clefts in these groups of patients. Methods Patient Population Patients with low-back pain lasting 3 months or longer, a collapsed vertebra in the thoracic or lumbar spine showing mobility in flexion-extension or sitting-supine position radiographs, and an air- or fluid-containing intravertebral cleft in the collapsed vertebra were considered to have an unhealed OVF. Between June 2005 and November 2008, 24 patients met the diagnostic criteria of an unhealed OVF and were treated at our institutions (Table 1). There were 17 women and 7 men with a mean age of 77.0 years (range years). Two patients were younger than 65 years old. One of these patients (61 years old) had been treated with prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis, and the other (62 years old) suffered a compression fracture caused by a fall from a height of 1.5 m 6 months before referral to our institution. The affected vertebrae were distributed from T-11 to L-4. The duration of back pain symptoms ranged from 3 to 48 months (mean 9.3 months). As a control group, records of patients in whom an OVF had been diagnosed on plain radiographs and MR images obtained within 14 days after onset were reviewed. These fractures were referred to as acute OVFs. For the detection of an acute OVF, sagittal T1-weighted images, sagittal T2-weighted images, and sagittal STIR sequence images were used. Fractures caused by severe trauma and pathological fractures (tumor or infection) were excluded. Between May 2007 and April 2008, an acute OVF was diagnosed in 30 patients at one of our institutions. There were 21 women and 9 men with a mean age of 77.9 years (range years) (Table 1). Two of 3 patients younger than 65 years old (ages 54 and 60 years) had been treated with corticosteroids for dermatomyositis and aplastic TABLE 1: Clinical pictures of patients with an unhealed OVF and those with an acute OVF* Variable Unhealed OVF Acute OVF no. of patients age (yr) 77.0 ± ± 9.4 male sex 7 (29) 9 (30) location T (0) 5 (17) T-11, T-12, & L-1 16 (67) 18 (60) L2 5 8 (33) 7 (23) duration of pain 9.3 ± 9.9 mos 4.1 ± 3.0 days VAS score (mm) 61.0 ± 22.3 ND ECOG Performance Status Grade 1 10 (42) 0 (0) 2 1 (4) 9 (30) 3 8 (33) 19 (63) 4 5 (21) 2 (7) fracture type normal 0 (0) 1 (3) wedge 12 (50) 27 (90) biconcave 1 (4) 2 (6) crush 11 (46) 0 (0) height of the vertebra (mm) sitting 8.1 ± ± 4.4 supine 15.7 ± ± 4.5 mobility 7.6 ± ± 3.0 presence of prevalent fracture(s) 15 (63) 13 (43) positive fluid sign 14 (59) 3 (10) * Values for age, duration of pain, VAS score, and height of the vertebra are described as mean ± SD. All other values are the number of patients with percentages in parentheses. Abbreviation: ND = not determined. Statistically significant difference between unhealed OVFs and acute OVFs (p < 0.01). anemia, respectively. Fractures were distributed from the T-7 to L-4 vertebrae. Seventeen fractures were caused by a simple fall, and 13 fractures occurred during daily activities. Evaluation Patients with an unhealed OVF were evaluated for severity of low-back pain by using the VAS and ECOG Performance Status. 20 In accordance with the ECOG Performance Status grade, Grade 1 indicates symptomatic but fully ambulatory, Grade 2 indicates symptomatic and up and about for more than 50% of waking hours, Grade 268 J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010
3 Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft TABLE 2: Clinical relevance of the fluid sign in patients with an unhealed OVF* Fluid Sign Variable Positive (14 patients) Negative (10 patients) patient age (yrs) 79.7 ± ± 6.7 male sex 4 (29) 3 (30) duration of pain (mos) 8.2 ± ± 13.9 VAS score (mm) 74.9 ± ± 15.0 ECOG Performance Status Grade 3.2 ± ± 0.3 crush-type fracture 10 (71) 1 (10) height on sitting radiographs (mm) 8.3 ± ± 3.9 height on supine radiographs (mm) 17.5 ± ± 3.9 dynamic mobility (mm) 9.2 ± ± 1.9 presence of prevalent fracture 9 (64) 6 (60) communication to intradiscal air 2 (17) 10 (100) * Values for age, duration of pain, VAS score, performance status, and height of anterior wall are described as the mean ± SD. All other values are the number of patients with percentages in parentheses. Statistically significant difference (p < 0.01) between the subgroups with positive and negative fluid signs. Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) between the subgroups with positive and negative fluid signs. 3 indicates symptomatic and being confined to bed or a chair for 50% or more of waking hours, and Grade 4 indicates being totally confined to bed or a chair. Patients with an acute OVF were also evaluated for performance status. Radiographic evaluation included classification of the fracture types, dynamic mobility of the affected vertebra, contents of the intravertebral cleft, prevalent vertebral fracture, and communication between air in the intravertebral cleft and air in the adjacent intervertebral disc. Fractures were classified into normal, wedge, biconcave, and crush types 4,6 using lateral decubitus-position radiographs (Fig. 1A). Dynamic mobility of the vertebra was determined by measuring the height of the affected vertebra manually in lateral radiographs obtained in the sitting and supine positions (Fig. 1B and C). 17 The radiographs were obtained at a film-focus distance of 1.1 m during the initial visit. Sitting lateral radiographs (Fig. 1B) and supine crosstable lateral radiographs (Fig. 1C) were compared with regard to the vertebral height that was measured to the nearest millimeter at the anterior border, the midpoint, and the posterior border of the vertebra. The region that indicated the largest difference of the vertebral height between the sitting lateral radiograph and the supine crosstable lateral radiograph was selected. The difference in the vertebral height in that region was referred to as the dynamic mobility of the vertebra. All cases with an acute OVF and 22 of 24 cases with an unhealed fracture were evaluated for dynamic fracture mobility using the aforementioned procedure. Accumulation of fluid in fractured vertebrae (fluid sign) was determined using MR imaging. In cases in which the signal intensity of an intravertebral lesion was equivalent to that of CSF on T2-weighted images, the vertebrae were defined as having a positive fluid sign. Intravertebral air and intradiscal air were defined as profound low-density lesions on sagittal reconstructed CT scans. Presence of intravertebral air, intradiscal air (vacuum disc), and communication between these 2 air lesions were determined using serial sagittal images of CT scans. A fluid sign was assessed in all 54 patients. Fig. 1. Evaluation of fracture type and dynamic mobility. This 91-year-old man had an unhealed fracture of the L-4 vertebra. Fractures are classified into normal, wedge, biconcave, and crush types by using lateral decubitus-position radiographs (A). The present case is classified as a crush type. The difference in the vertebral height at the anterior border of the affected vertebra between a sitting lateral radiograph (B) and a supine cross-table lateral radiograph (C) indicates the extent of dynamic fracture mobility. In the present case, the vertebral height is 7 mm in the sitting lateral radiograph and 21 mm in the supine lateral radiograph, indicating a dynamic fracture mobility of 14 mm. J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August
4 S. Kawaguchi et al. Fig. 2. Representative T1-weighted MR images (A, D, and G), T2-weighted MR images (B, E, and H), and reconstructed CT scans (C, F, and I) of unhealed OVFs. A C: Images obtained in an 89-year-old man with an unhealed crush-type fracture of the T-12 vertebra, showing an accumulation of fluid in the intravertebral cleft. There is a fracture line in the posterior wall of the T-12 vertebra, associated with a collapse of both anterior and posterior borders of the vertebra. Of our cases, 9 exhibited an accumulation of fluid alone in the cleft. D F: Images obtained in a 68-year-old man with an unhealed crush-type fracture of the L-1 vertebra, showing an accumulation of fluid and air in the intravertebral cleft. There is a fracture line in the posterior wall of the L-1 vertebra, associated with a collapse of both anterior and posterior borders of the vertebra. Of our cases, 5 had fluid and air in the cleft. G I: Images obtained in a 67-year-old man with an unhealed wedge-type fracture of the T-12 vertebra, showing a negative fluid sign. The intravertebral cleft is filled with air. The posterior wall of the vertebra has not collapsed, consistent with a wedge-type fracture. Of our cases, 10 showed an accumulation of air alone in the cleft (negative fluid sign). Intravertebral air was evaluated using CT scans in 22 of 24 patients with an unhealed OVF. Prevalent vertebral fractures were defined by MR images showing collapse with recovered signal intensity (high signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted images). All MR and CT images were analyzed by an author (S.K.) and an experienced radiologist working together. Analysis of Patient Groups Patients with an unhealed OVF and those with an acute OVF were compared with regard to clinical and radiographic features, including age, sex, duration of pain, performance status, fracture location, fracture classification, height of the affected vertebra, extent of dynamic vertebral mobility, presence of a fluid sign, and presence of prevalent vertebral fractures. The extent of dynamic mobility of the affected vertebra was analyzed for correlation with age, duration of symptoms, and performance status in all patients, and with VAS scores in patients with an unhealed OVF. The OVFs were divided into 2 subgroups on the basis of a fluid sign. Two subgroups (positive fluid sign and negative fluid sign) were compared with regard to age, sex, duration of pain, VAS score, performance status, number of cases with a crush-type fracture, height of the affected vertebra, extent of dynamic fracture mobility, presence of prevalent vertebral fracture, and communication between intravertebral air and intradiscal air. Statistical significance was determined using the Pearson correlation method, the Mann-Whitney test, and the Fisher exact probability test. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Groups containing fewer than 5 patients were not subjected to statistical analysis. Results Clinical and Radiographic Features of Unhealed OVFs and Acute OVFs To determine the clinical and radiographic features of unhealed OVFs, we analyzed 24 patients with putative diagnosis of an unhealed OVF and 30 patients with an 270 J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010
5 Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft Fig. 3. Representative T1-weighted (A, D, and G), T2-weighted (B, E, and H), and STIR (C, F, and I) MR images of acute OVFs. The intravertebral high signal intensity in STIR images (right panels) indicates an edematous change associated with acute fracture. A C: Images obtained in an 85-year-old woman with an acute wedge-type fracture of the T-11 vertebra, showing a square-shaped fluid sign. The posterior wall of the vertebra has not collapsed. Of our cases, only 1 showed a square-shaped fluid sign. D F: Images obtained in an 80-year-old woman with an acute wedge-type fracture of the L-1 vertebra, showing a linear fluid sign. The posterior wall of the vertebra has not collapsed. Of our cases, 2 exhibited a linear fluid sign. G I: Images obtained in an 84-year-old woman with an acute wedge-type fracture of the L-3 vertebra. There is no fluid sign in the vertebra. The posterior wall of the vertebra has not collapsed. Of our cases, 27 had a negative fluid sign. acute OVF comparatively. As depicted in Table 1, age, sex, and location of the fractures were comparable between the groups. The VAS score of patients with an unhealed OVF ranged from 20 to 100 mm (mean 61 mm). The ECOG Performance Status was Grade 1 in 10 patients, Grade 2 in 1 patient, Grade 3 in 8 patients, and Grade 4 in 5 patients. In patients with an acute OVF, the performance status was Grade 2 in 9 patients, Grade 3 in 19 patients, and Grade 4 in 2 patients. With respect to the fracture types, 12 patients with an unhealed OVF (50%) had a wedge-type fracture and 11 patients (46%) had a crush-type fracture (Figs. 1 and 2). In contrast, 27 patients with an acute OVF (90%) had a wedge-type fracture, and none of them had a crush-type fracture (Fig. 3). In sitting and supine cross-table lateral radiographs, the height of the affected vertebra was significantly shorter in unhealed OVFs than that in acute OVFs. The average mobility of the vertebra was 7.6 mm in unhealed OVFs and 5.2 mm in acute OVFs. The difference was not statistically significant. Prevalent fractures were found in 15 patients with an unhealed OVF (63%) and 13 patients with an acute OVF (43%). J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010 Intravertebral Accumulation of Fluid and Air Fourteen patients with an unhealed OVF (59%) and 3 patients with an acute OVF (10%) had a positive fluid sign in the affected vertebra (Table 1 and Figs. 2 and 3). The difference in the frequency of a positive fluid sign is statistically significant. Fluid was accumulated in a triangular/square shape in all 14 cases of an unhealed OVF (Fig. 2). In contrast, 2 of 3 acute OVFs showed fluid accumulation in a linear shape and the remaining fracture exhibited a triangular/square shape (Fig. 3). Accumulation of air in the vertebra was defined using reconstructed CT scans in 22 of 24 patients with an unhealed OVF. Of these, 5 patients showed fluid and air in the intravertebral cleft, and 10 patients had an air-filled intravertebral cleft (Fig. 2). Correlation of Dynamic Vertebral Mobility With Clinical Parameters Based on these clinical and radiographic findings, we conducted a correlation analysis between the extent of dynamic vertebral mobility and clinical parameters. In patients with an unhealed OVF, there was a significant 271
6 S. Kawaguchi et al. Fig. 4. Graphs showing the correlations of dynamic fracture mobility and clinical parameters in patients with an unhealed OVF. The x axes indicate dynamic mobility of the affected vertebra (mm). The y axes indicate VAS score (mm, A), ECOG Performance Status (grades, B), age (years, C), and duration of pain symptoms (months, D). The correlations of dynamic mobility with clinical parameters were analyzed and are presented with correlation coefficient (r) and probability (p) values. correlation between the extent of dynamic mobility and the VAS score (r = 0.54, p < 0.01) (Fig. 4). A significant correlation was also seen between the extent of dynamic mobility and performance status (r = 0.57, p < 0.01) (Fig. 4). In contrast, the extent of dynamic mobility was not significantly correlated with the patient s age and duration of symptoms. In patients with an acute OVF (Fig. 5), statistically significant correlations were seen between the extent of dynamic fracture mobility and performance status (r = 0.61, p < 0.01) and the patient s age (r = 0.49, p < 0.01). Also, there was a reverse correlation between the extent of dynamic mobility and duration of symptoms (r = 0.45, p < 0.02) (Fig. 5). Clinical Relevance of Intravertebral Fluid Sign Finally, we analyzed the clinical relevance of the fluid sign. Because only 3 patients with an acute OVF showed a positive fluid sign, analysis focused on patients with an unhealed OVF. As depicted in Table 2, there was no statistically significant difference between the subgroup with a positive fluid sign and that with a negative fluid sign with respect to patients age, sex, duration of symptoms, height of the affected vertebra in sitting and supine lateral radiographs, and the presence of prevalent fractures. In contrast, statistically significant differences were noted between these subgroups with respect to back pain VAS score, ECOG Performance Status grade, frequency of a crush-type fracture, extent of dynamic vertebral mobility, and frequency of communication between intravertebral air and intradiscal air. The VAS score, ECOG Performance Status grade, and the extent of dynamic vertebral mobility were larger in the subgroup with a positive fluid sign than that with a negative one. Notably, 13 of 14 patients with a positive fluid sign and an unhealed OVF had an ECOG Performance Status Grade 3 or 4, whereas all 10 patients with a negative fluid sign and an unhealed OVF had an ECOG Performance Status Grade 1 or 2. Communication between intradiscal air and intravertebral air was seen in all 10 patients with a negative fluid sign in an unhealed OVF and 2 of 12 patients with a positive fluid sign in an unhealed OVF examined with CT scans (Fig. 6). Discussion In the present study, we analyzed 24 patients with an unhealed OVF and 30 patients with an acute OVF. Patients with an unhealed OVF suffered various degrees of persistent pain for 3 months or longer and had a collapsed thoracic or lumbar vertebra that had an intravertebral cleft and mobility. Apart from these features, these patients were more likely to have a crush-type fracture, shorter vertebral height of the fractured vertebra, and a positive fluid sign fracture than those with an acute OVF. These findings support the claim that the fractures deemed as unhealed OVFs in this study form a distinct group of fractures from acute OVFs. The extent of dynamic vertebral mobility correlated significantly with back pain status (VAS score) in patients with an unhealed OVF. Dynamic mobility of the vertebra has been speculated as a cause of pain symptoms in patients with an unhealed OVF. 8,18 This assumption is based on the observation that operative stabilization of the intravertebral mobility in patients with an unhealed OVF leads to immediate pain relief. 7,9,10 Our findings serve as a more direct support for this assumption. In addition, 272 J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010
7 Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft Fig. 5. Graph showing the correlations of dynamic fracture mobility and clinical parameters in patients with an acute OVF. The x axes indicate dynamic mobility of the affected vertebra (mm). The y axes indicate ECOG Performance Status (grades, A), age (years, B), and duration of pain symptoms (days, C). The correlations of dynamic mobility with clinical parameters were analyzed and are presented with correlation coefficient (r) and probability (p) values. J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010 a significant correlation between the extent of dynamic fracture mobility and performance status grade was seen in patients with an unhealed OVF and those with an acute OVF. This indicates the possibility that dynamic fracture mobility serves as a primal pain determinant for patients with an unhealed OVF as well as those with an acute OVF. The clinical significance of fluid accumulation in the intravertebral clefts remains under debate. In the literature, Yu et al. 28 reported that vertebral collapse was more advanced in cases of unhealed OVFs with a negative fluid sign (that is, those that are air-filled) than unhealed OVFs with a positive fluid sign. This indicates that the contents (air or fluid) of the intravertebral cleft represent the severity of the vertebral collapse on radiographs. In contrast, Jang et al. 10 suggested that the contents of the intravertebral cleft denote the stages of unhealed OVFs, where fluid is accumulated in the early stages and converted into air in the later stages. Malghem, 16 Sarli, 26 and Linn 15 and their colleagues reported that supine positioning for a long time (more than 20 minutes) leads to fluid collection in the intravertebral cleft. They speculated that fluid may flow from blood into the intravertebral cleft by negative pressure created by widening of the affected vertebra during supine positioning. In this respect, all but 1 patient with an unhealed OVF that had a positive fluid sign in the present study had an ECOG Performance Status Grade 3 or 4, indicating that these patients were bedridden most of the time. In sharp contrast, all 10 patients with an unhealed OVF that had a negative fluid sign had an ECOG Performance Status Grade 1 or 2. Therefore, fluid accumulation in unhealed OVFs likely reflects long-term bedridden positioning of the patients. This theory, however, does not explain our finding that 18 of 27 patients with an acute OVF with a negative fluid sign had an ECOG Performance Status Grade 3 or 4. Communication between the intravertebral air and intradiscal air in the adjacent disc seen in the present study was previously reported by Lafforgue et al. 13 They found such communication in 83% of the 23 patients with an unhealed OVF with a negative fluid sign (air-filled). Lack of communication between the intravertebral cleft and intradiscal air in the adjacent disc in patients with an unhealed OVF was also demonstrated by Yu et al. 28 These observations, together with the findings in the present study, consistently suggest that the communication between the intravertebral cleft and the adjacent intradiscal air is likely to be pathognomic for air accumulation in the cleft. Of 24 patients with an unhealed OVF, 14 patients (58%) had positive fluid signs (including 5 patients showing both fluid and air) and the remaining 10 patients (42%) exhibited an air-filled cleft in the present study group. Similarly, Yu et al. 28 reported a positive fluid sign in 61% (fluid alone in 40% and fluid and air in 21%) and a negative fluid sign (air-filled clefts) in the remaining 39% of 112 patients with an unhealed OVF. In contrast, in the studies by Jang et al. 10 and Lane et al., 14 only 12.5% and 11.4%, respectively, of unhealed OVFs had an air-filled cleft. These low percentages of the air-filled types may be explained by the selection of patients as every participant in these studies was referred to them for percutane- 273
8 S. Kawaguchi et al. Fig. 6. Sagittal reconstructed CT scans showing communication of the air in the vertebra and the air in the adjacent intervertebral disc. A: Image obtained in a 67-year-old woman with an unhealed wedge-type fracture of the L-1 vertebra. The fluid sign in this case was negative. B: Image obtained in a 77-year-old woman with an unhealed wedge-type fracture of the L-3 vertebra. The fluid sign in this case was negative. ous vertebroplasty. In our study group, all but 1 of the 14 patients with a positive fluid sign in an unhealed OVF had been hospitalized for pain and disability before referral to our institutions. In contrast, all 10 individuals with a negative fluid sign (air-filled) unhealed OVF were outpatients. Thus, the number of patients with the airfilled unhealed OVF is likely to be low in referral-based orthopedic clinics. Because patients with an air-filled unhealed OVF visit clinics with relatively mild back pain, it is important that they are not misdiagnosed. In fact, some of the patients in our study group had been treated for osteoporosis-related chronic back pain elsewhere before presenting to our institutions. The presence of prevalent fractures may affect back pain status and performance status of patients with an acute OVF or an unhealed OVF. In this regard, frequency of the presence of prevalent fracture(s) was not significantly different between the patients with an unhealed OVF and those with an acute OVF (Table 1). Also, there was no significant difference in terms of frequency of prevalent fractures between unhealed OVFs with positive and negative fluid signs (Table 2). Patients who present for medical attention with back pain and have only a healed vertebral fracture may represent a suitable control group in the present study. However, in these patients, there is difficulty in determining whether healed OVF(s) are responsible for the pain symptoms. Unhealed OVFs with small dynamic vertebral mobility may be treated successfully with the long-term wearing of a body jacket. However, in the literature, unhealed OVFs have been treated surgically rather than conservatively. A variety of surgical procedures have been reported for the treatment of unhealed OVFs. These include osteosynthesis, 9 decompression and fusion surgeries via anterior, 11,19 posterior, 12,19,25 and anteroposterior 27 approaches, percutaneous vertebroplasty, 2,10,23 and percutaneous kyphoplasty. 7 The treatment procedure was determined depending on the severity of the fracture and neurological compromise and the surgeon s preference. Whereas osteosynthesis and fusion surgeries aim at solid bone union for stabilization of the affected vertebra, union status following percutaneous vertebroplasty or percutaneous kyphoplasty has not yet been addressed. Conclusions Unhealed OVFs form a group of fractures that are distinct from acute OVFs regarding radiographic morphometry and contents of the intravertebral cleft. Dynamic fracture mobility serves as a primal pain determinant of patients with an unhealed OVF and potentially those with an acute OVF. Fluid accumulation in the intravertebral cleft in unhealed OVFs likely reflects the positioning of patients in daily activity. Disclosure The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper. Author contributions to the study and manuscript preparation include the following. Conception and design: Kawaguchi. Acquisition of data: Horigome, Yajima, Oda, Kii, Ida, Yoshimoto, Iba, Takebayashi. Analysis and interpretation of data: Kawaguchi, Horigome, Yajima, Oda. Drafting the article: Kawaguchi, Oda. Critically revising the article: Oda, Takebayashi. Reviewed final version of the manuscript and approved it for submission: all authors. Administrative/technical/material support: Horigome, Yajima, Oda, Kii, Ida, Yoshimoto, Iba, Takebayashi. Study supervision: Yamashita. Acknowledgment The authors thank Dr. M. Tamakawa for his support and comments on imaging analysis. References 1. Bhalla S, Reinus WR: The linear intravertebral vacuum: a sign of benign vertebral collapse. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170: , Carlier RY, Gordji H, Mompoint DM, Vernhet N, Feydy A, Vallée C: Osteoporotic vertebral collapse: percutaneous vertebroplasty and local kyphosis correction. Radiology 233: , Dupuy DE, Palmer WE, Rosenthal DI: Vertebral fluid collection associated with vertebral collapse. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167: , Eastell R, Cedel SL, Wahner HW, Riggs BL, Melton LJ III: Classification of vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res 6: , Freedman BA, Heller JG: Kummel disease: a not-so-rare complication of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Am Board Fam Med 22:75 78, Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC: Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8: , Grohs JG, Matzner M, Trieb K, Krepler P: Treatment of intravertebral pseudarthroses by balloon kyphoplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech 19: , Hasegawa K, Homma T, Uchiyama S, Takahashi H: Vertebral pseudarthrosis in the osteoporotic spine. Spine 23: , Hasegawa K, Homma T, Uchiyama S, Takahashi HE: Osteosynthesis without instrumentation for vertebral pseudarthrosis in the osteoporotic spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79: , Jang JS, Kim DY, Lee SH: Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of intravertebral pseudarthrosis associated with noninfected avascular necrosis of the vertebral body. Spine 28: , Kaneda K, Asano S, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M: The 274 J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August 2010
9 Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft treatment of osteoporotic-posttraumatic vertebral collapse using the Kaneda device and a bioactive ceramic vertebral prosthesis. Spine 17 (8 Suppl):S295 S303, Kim KT, Suk KS, Kim JM, Lee SH: Delayed vertebral collapse with neurological deficits secondary to osteoporosis. Int Orthop 27:65 69, Lafforgue P, Chagnaud C, Daumen-Legré V, Daver L, Kasbarian M, Acquaviva PC: The intravertebral vacuum phenomenon ( vertebral osteonecrosis ). Migration of intradiscal gas in a fractured vertebral body? Spine 22: , Lane JI, Maus TP, Wald JT, Thielen KR, Bobra S, Luetmer PH: Intravertebral clefts opacified during vertebroplasty: pathogenesis, technical implications, and prognostic significance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23: , Linn J, Birkenmaier C, Hoffmann RT, Reiser M, Baur-Melnyk A: The intravertebral cleft in acute osteoporotic fractures: fluid in magnetic resonance imaging-vacuum in computed tomography? Spine 34:E88 E93, Malghem J, Maldague B, Labaisse MA, Dooms G, Duprez T, Devogelaer JP, et al: Intravertebral vacuum cleft: changes in content after supine positioning. Radiology 187: , McKiernan F, Faciszewski T: Intravertebral clefts in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Arthritis Rheum 48: , Mirovsky Y, Anekstein Y, Shalmon E, Peer A: Vacuum clefts of the vertebral bodies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , Mochida J, Toh E, Chiba M, Nishimura K: Treatment of osteoporotic late collapse of a vertebral body of thoracic and lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord 14: , Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, Mc- Fadden ET, et al: Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5: , Papaioannou A, Watts NB, Kendler DL, Yuen CK, Adachi JD, Ferko N: Diagnosis and management of vertebral fractures in elderly adults. Am J Med 113: , Pappou IP, Papadopoulos EC, Swanson AN, Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP: Osteoporotic vertebral fractures and collapse with intravertebral vacuum sign (Kümmel s disease). Orthopedics 31:61 66, Peh WC, Gelbart MS, Gilula LA, Peck DD: Percutaneous vertebroplasty: treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures with intraosseous vacuum phenomena. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180: , Resnick D, Niwayama G, Guerra J Jr, Vint V, Usselman J: Spinal vacuum phenomena: anatomical study and review. Radiology 139: , Saita K, Hoshino Y, Kikkawa I, Nakamura H: Posterior spinal shortening for paraplegia after vertebral collapse caused by osteoporosis. Spine 25: , Sarli M, Pérez Manghi FC, Gallo R, Zanchetta JR: The vacuum cleft sign: an uncommon radiological sign. Osteoporos Int 16: , Suk SI, Kim JH, Lee SM, Chung ER, Lee JH: Anterior-posterior surgery versus posterior closing wedge osteotomy in posttraumatic kyphosis with neurologic compromised osteoporotic fracture. Spine 28: , Yu CW, Hsu CY, Shih TT, Chen BB, Fu CJ: Vertebral osteonecrosis: MR imaging findings and related changes on adjacent levels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:42 47, 2007 Manuscript submitted April 28, Accepted March 26, Address correspondence to: Satoshi Kawaguchi, M.D., Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asahikawa Kosei Hospital, 111-3, 1-jo 24-chome, Asahikawa , Japan. kawaguch@sapmed. ac.jp. J Neurosurg: Spine / Volume 13 / August
An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review
 An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review C-H Li 1, M-C Chang 2, Z-P Ho 3, H-Y Chiu 4 ABSTRACT Osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVF) are most common injuries seen in elder people. The
An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review C-H Li 1, M-C Chang 2, Z-P Ho 3, H-Y Chiu 4 ABSTRACT Osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVF) are most common injuries seen in elder people. The
Bone Cement-Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation : An Effective Treatment for Kummell s Disease?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Intravertebral Clefts in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 5, May 2003, pp 1414 1419 DOI 10.1002/art.10984 2003, American College of Rheumatology Intravertebral Clefts in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Fergus McKiernan
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 5, May 2003, pp 1414 1419 DOI 10.1002/art.10984 2003, American College of Rheumatology Intravertebral Clefts in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Fergus McKiernan
What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Have on Further Compression and Clinical Outcome?
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 181-188, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 181-188, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic
The spinal vacuum sign or vacuum phenomenon. Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion?
 An Original Study Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion? Arjun A. Dhawale, MD, Steven Falcone, MD, Barth A. Green, MD, and Nathan H. Lebwohl, MD
An Original Study Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion? Arjun A. Dhawale, MD, Steven Falcone, MD, Barth A. Green, MD, and Nathan H. Lebwohl, MD
Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease
 Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease Poster No.: C-1570 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. D'Anastasi, C.
Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease Poster No.: C-1570 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. D'Anastasi, C.
The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
 Abstract The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Kyu Sung Lee, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pochun Joongmoon Medical School Study design : Radiographic findings of vertebral
Abstract The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Kyu Sung Lee, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pochun Joongmoon Medical School Study design : Radiographic findings of vertebral
Ja Yeon You, MD, Joon Woo Lee, MD, Jung Eun Kim, MD, Heung Sik Kang, MD
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.503 Magnetic Resonance Enhancement Patterns at the Different Ages of Symptomatic Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures 유증상골다공증성척추압박골절에서골절시기에따른자기공명영상의조영증강유형
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.503 Magnetic Resonance Enhancement Patterns at the Different Ages of Symptomatic Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures 유증상골다공증성척추압박골절에서골절시기에따른자기공명영상의조영증강유형
Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse Takashi Ohnishi 1)2), Akira Iwata 1)2), Masahiro Kanayama
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse Takashi Ohnishi 1)2), Akira Iwata 1)2), Masahiro Kanayama
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Early Bone Marrow Edema Pattern of the Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture : Can Be Predictor of Vertebral Deformity Types and Prognosis?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.2.137 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59 (2) : 137-142, 2016 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2016 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.2.137 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59 (2) : 137-142, 2016 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2016 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Byung Jik Kim, M.D., Jin Hwan Kim, M.D., Jeong Gook Seo #, M.D., Young Chul Kim, M.D.
 Comparison of the Results of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture and Posttraumatic Vertebral Collapse (Kummell s disease) Abstract Byung Jik Kim, MD, Jin
Comparison of the Results of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture and Posttraumatic Vertebral Collapse (Kummell s disease) Abstract Byung Jik Kim, MD, Jin
Intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in osteoporotic compression fracture: report of 67 cases with quantitative evaluation of intravertebral instability
 J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:24 31, 2004 Intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in osteoporotic compression fracture: report of 67 cases with quantitative evaluation of intravertebral instability DONG-YUN KIM,
J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:24 31, 2004 Intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in osteoporotic compression fracture: report of 67 cases with quantitative evaluation of intravertebral instability DONG-YUN KIM,
Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft and Its Varied Locations within Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E979-E986 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft and Its Varied Locations within Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E979-E986 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft and Its Varied Locations within Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures. Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC
 Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic Spinal Compression Fractures
 J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
Correlation Between Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI in Degenerative Disks
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research D Anastasi et al. Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI of Degenerative Disks Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Melvin D Anastasi 1 Christof Birkenmaier
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research D Anastasi et al. Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI of Degenerative Disks Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Melvin D Anastasi 1 Christof Birkenmaier
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Treatment of Painful Vertebral Compression Fractures with Intraosseous Vacuum Phenomena
 Wilfred C. G. Peh 1,2 Michael S. Gelbart 2 Louis. Gilula 2 Dallas D. Peck 2,3 Received January 17, 2002; accepted after revision October 22, 2002. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General
Wilfred C. G. Peh 1,2 Michael S. Gelbart 2 Louis. Gilula 2 Dallas D. Peck 2,3 Received January 17, 2002; accepted after revision October 22, 2002. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture. Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD
 Pain Physician 2012; 15:E527-E532 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD From: Department
Pain Physician 2012; 15:E527-E532 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD From: Department
Vertebroplasty has been widely accepted as an effective
 Published June 26, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1186 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.E. Rad D.F. Kallmes Pain Relief Following Vertebroplasty in Patients with and without Localizing Tenderness on Palpation BACKGROUND AND
Published June 26, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1186 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.E. Rad D.F. Kallmes Pain Relief Following Vertebroplasty in Patients with and without Localizing Tenderness on Palpation BACKGROUND AND
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse of a Lumbar Spine Vertebral Body
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 682075, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/682075 Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 682075, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/682075 Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When
 Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
REFERENCE DOCTOR Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
Kanji Mori, Kazuya Nishizawa, Akira Nakamura, and Shinji Imai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty
 KYPHON Results from a randomized controlled study comparing KYPHON to nonsurgical care for treatment of vertebral compression fractures Relief. Mobility. Quality of Life. What is? KYPHON is a minimally
KYPHON Results from a randomized controlled study comparing KYPHON to nonsurgical care for treatment of vertebral compression fractures Relief. Mobility. Quality of Life. What is? KYPHON is a minimally
Osteoporosis and Spinal Fractures
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
The role of imaging procedures before percutaneous vertebroplasty
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H.J. Voormolen W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski Y. van der Graaf L.E.H. Lampmann P.N.M. Lohle J.R. Juttmann Pain Response in the First Trimester after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.H.J. Voormolen W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski Y. van der Graaf L.E.H. Lampmann P.N.M. Lohle J.R. Juttmann Pain Response in the First Trimester after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
 Pain Physician 2015; 18:373-381 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Evaluation Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
Pain Physician 2015; 18:373-381 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Evaluation Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
Fracture REduction Evaluation (FREE) Study
 Fracture REduction Evaluation (FREE) Study Efficacy and Safety of Balloon Kyphoplasty Compared with Non-surgical Care for Vertebral Compression Fracture (FREE): A Randomised Controlled Trial Wardlaw Lancet
Fracture REduction Evaluation (FREE) Study Efficacy and Safety of Balloon Kyphoplasty Compared with Non-surgical Care for Vertebral Compression Fracture (FREE): A Randomised Controlled Trial Wardlaw Lancet
Evaluation of prognostic scoring systems for bone metastases using single center data
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 3: 1361-1370, 2015 Evaluation of prognostic scoring systems for bone metastases using single center data HIROFUMI SHIMADA 1, TAKAO SETOGUCHI 2, SHUNSUKE NAKAMURA 1, MASAHIRO
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 3: 1361-1370, 2015 Evaluation of prognostic scoring systems for bone metastases using single center data HIROFUMI SHIMADA 1, TAKAO SETOGUCHI 2, SHUNSUKE NAKAMURA 1, MASAHIRO
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment
 Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
Balloon kyphoplasty is now considered as minimally invasive
 Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3424 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE In Not Only Vertebroplasty but Also Kyphoplasty, the Resolution of Vertebral Deformities Depends on Vertebral Mobility K. Yokoyama,
Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3424 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE In Not Only Vertebroplasty but Also Kyphoplasty, the Resolution of Vertebral Deformities Depends on Vertebral Mobility K. Yokoyama,
Percutaneous vertebroplasty has been in clinical use in the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.T. Trout D.F. Kallmes J.I. Lane K.F. Layton W.F. Marx Subsequent Vertebral Fractures after Vertebroplasty: Association with Intraosseous Clefts BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Patients with
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.T. Trout D.F. Kallmes J.I. Lane K.F. Layton W.F. Marx Subsequent Vertebral Fractures after Vertebroplasty: Association with Intraosseous Clefts BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Patients with
Kümmell s Disease: Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients Inclusion Criteria
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 288 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, 288-297 Open Access Kümmell s Disease: Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients Inclusion Criteria Charalampos
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 288 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, 288-297 Open Access Kümmell s Disease: Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients Inclusion Criteria Charalampos
Vertebral body fractures after transpsoas interbody fusion procedures
 The Spine Journal 11 (2011) 1068 1072 Case Report Vertebral body fractures after transpsoas interbody fusion procedures Justin E. Brier-Jones, BS a, Daniel K. Palmer, BS b, Serkan Inceoglu, PhD a, Wayne
The Spine Journal 11 (2011) 1068 1072 Case Report Vertebral body fractures after transpsoas interbody fusion procedures Justin E. Brier-Jones, BS a, Daniel K. Palmer, BS b, Serkan Inceoglu, PhD a, Wayne
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE
 YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE Sudden-onset back pain could signal a spinal fracture. TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR If you have tried treatments like rest and oral medication for more than a few days
YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE Sudden-onset back pain could signal a spinal fracture. TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR If you have tried treatments like rest and oral medication for more than a few days
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
 Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 02/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient;
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 02/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient;
Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction: a case report
 Cumming et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:189 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction:
Cumming et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:189 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction:
Vertebroplasty has been widely and successfully used in the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.M. Knavel K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Traumatic Nonosteoporotic Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Vertebroplasty is commonly used for osteoporotic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.M. Knavel K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Traumatic Nonosteoporotic Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Vertebroplasty is commonly used for osteoporotic
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous
Author's response to reviews Title: Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
Reporting of Spinal Fractures
 Reporting of Spinal Fractures Poster No.: P-0026 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Al-Chalabi, C. Groves; Bradford/UK Osteoporosis, Structured reporting, Observer performance,
Reporting of Spinal Fractures Poster No.: P-0026 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Al-Chalabi, C. Groves; Bradford/UK Osteoporosis, Structured reporting, Observer performance,
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study
 Total Disc Replacement IDE Clinical Study Study Design TDR vs. circumferential fusion: Multi-center, prospective, randomized trial 17 centers, 292 patients 162 patients 80 fusion patients 50 non-randomized
Total Disc Replacement IDE Clinical Study Study Design TDR vs. circumferential fusion: Multi-center, prospective, randomized trial 17 centers, 292 patients 162 patients 80 fusion patients 50 non-randomized
OSTEOPOROSIS IS a disease characterized by low bone
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 2, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Perspective Calling All Vertebral Fractures Classification of Vertebral Compression Fractures:
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 2, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Perspective Calling All Vertebral Fractures Classification of Vertebral Compression Fractures:
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion Andrei Stefan Iencean ROMANIA DOI:
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion Andrei Stefan Iencean ROMANIA DOI:
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty (BKP) 1 is an interventional
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Saliou D.R. Rutgers E.M. Kocheida G. Langman A. Meurin H. Deramond P. Lehmann Balloon-Related Complications and Technical Failures in Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Fractures BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Saliou D.R. Rutgers E.M. Kocheida G. Langman A. Meurin H. Deramond P. Lehmann Balloon-Related Complications and Technical Failures in Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Fractures BACKGROUND
1. Introduction. Correspondence should be addressed to Sumihisa Orita;
 Hindawi Pain Research and Management Volume 2017, Article ID 9265259, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9265259 Research Article A Clinical Prospective Observational Cohort Study on the Prevalence and
Hindawi Pain Research and Management Volume 2017, Article ID 9265259, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9265259 Research Article A Clinical Prospective Observational Cohort Study on the Prevalence and
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1595 1600, June/July 2005 MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty David M. Dansie, Patrick H. Luetmer, John I. Lane, Kent R. Thielen, John T. Wald, and David F. Kallmes BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1595 1600, June/July 2005 MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty David M. Dansie, Patrick H. Luetmer, John I. Lane, Kent R. Thielen, John T. Wald, and David F. Kallmes BACKGROUND
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study
 MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
ASJ. Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 294 Kee-Yong Clinical Ha et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.294 Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Asian Spine Journal 294 Kee-Yong Clinical Ha et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.294 Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative. International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011
 Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
OVCF of the thoracic and lumbar spine can be a source of
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging has been used extensively
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging has been used extensively
Akira Iwata 1,2*, Masahiro Kanayama 1, Fumihiro Oha 1, Tomoyuki Hashimoto 1 and Norimasa Iwasaki 2
 Iwata et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:148 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1509-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of teriparatide (rh-pth 1 34) versus bisphosphonate on the healing of osteoporotic vertebral
Iwata et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:148 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1509-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of teriparatide (rh-pth 1 34) versus bisphosphonate on the healing of osteoporotic vertebral
Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine
 Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
Value of Bone Scan Imaging in Predicting Pain Relief from Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1807 1812, November/December 2000 Value of Bone Scan Imaging in Predicting Pain Relief from Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures A. Stanley Maynard,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1807 1812, November/December 2000 Value of Bone Scan Imaging in Predicting Pain Relief from Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures A. Stanley Maynard,
ASJ. Quality of Life in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Quality Asian of Spine life in J 2014;8(5):653-658 the patient with osteoporotic http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.5.653 vertebral fracture Quality
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Quality Asian of Spine life in J 2014;8(5):653-658 the patient with osteoporotic http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.5.653 vertebral fracture Quality
Treatment of painful vertebral hemangioma with alcohol, cement or both
 Treatment of painful vertebral hemangioma with alcohol, cement or both Poster No.: C-0746 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Zauner, S. PEREZ, A. Marin; Sabadell/ES Keywords: Haemangioma,
Treatment of painful vertebral hemangioma with alcohol, cement or both Poster No.: C-0746 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Zauner, S. PEREZ, A. Marin; Sabadell/ES Keywords: Haemangioma,
Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 180~187, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.180 Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Myung-Ho
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 180~187, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.180 Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Myung-Ho
Epiconus syndrome induced only in the erect standing position in a patient with L1 compression fracture: a representative case report
 CASE EPOT Epiconus syndrome induced only in the erect standing position in a patient with compression fracture: a representative case report Kenji Kubota, Koki Abe, Sumihisa Orita, Kazuhide Inage, Miyako
CASE EPOT Epiconus syndrome induced only in the erect standing position in a patient with compression fracture: a representative case report Kenji Kubota, Koki Abe, Sumihisa Orita, Kazuhide Inage, Miyako
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Input-dms SPINE Volume 31, Number 13, pp 000 000 2006, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing
Input-dms SPINE Volume 31, Number 13, pp 000 000 2006, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing
Vertebral Body Augmentation
 Vertebral Body Augmentation Nitin Sekhri MD Department of Anesthesiology Department of Radiology Westchester Medical Center Maria Fareri Children's Hospital Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology New York
Vertebral Body Augmentation Nitin Sekhri MD Department of Anesthesiology Department of Radiology Westchester Medical Center Maria Fareri Children's Hospital Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology New York
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical
 Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures
 Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Available online at Open Access at PubMed Central. The Journal of Biomedical Research, 2016, 30(5):
 Available online at www.jbr-pub.org Open Access at PubMed Central The Journal of Biomedical Research, 2016, 30(5):419-426 Original Article The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height
Available online at www.jbr-pub.org Open Access at PubMed Central The Journal of Biomedical Research, 2016, 30(5):419-426 Original Article The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height
Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage posterior surgery: a case report
 Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report -
 CASE REPORT Vol. 19, No. 1, 2012 Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report - Kyung-Soon Park, Dong-Hyun Lee, Indra Peni, Taek-Rim Yoon * Department of Orthopaedic
CASE REPORT Vol. 19, No. 1, 2012 Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report - Kyung-Soon Park, Dong-Hyun Lee, Indra Peni, Taek-Rim Yoon * Department of Orthopaedic
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Kummell s disease: literature update and challenges ahead
 Page 1 of 7 Spinal Surgery Kummell s disease: literature update and challenges ahead N Jindal 1 *, R Sharma 2, R Jindal 1, SK Garg 1 Abstract Introduction Osteonecrosis of the vertebral body, also known
Page 1 of 7 Spinal Surgery Kummell s disease: literature update and challenges ahead N Jindal 1 *, R Sharma 2, R Jindal 1, SK Garg 1 Abstract Introduction Osteonecrosis of the vertebral body, also known
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip.
 Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones lose calcium. Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty C. Xu, H.-X. Liu, and H.-Z. Xu ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty C. Xu, H.-X. Liu, and H.-Z. Xu ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Cement augmentation in spinal tumors: a systematic review comparing vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
 35 35 43 Cement augmentation in spinal tumors: a systematic review comparing vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty Authors Josh E Schroeder¹, Erika Ecker², Andrea C Skelly², Leon Kaplan¹ Institutions ¹ Orthopedic
35 35 43 Cement augmentation in spinal tumors: a systematic review comparing vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty Authors Josh E Schroeder¹, Erika Ecker², Andrea C Skelly², Leon Kaplan¹ Institutions ¹ Orthopedic
Medical Coverage Policy Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Scaroplasty
 Medical Coverage Policy Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Scaroplasty EFFECTIVE DATE: 02 01 2011 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 07 02 2013 OVERVIEW Percutaneous vertebroplasty is an interventional technique involving
Medical Coverage Policy Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Scaroplasty EFFECTIVE DATE: 02 01 2011 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 07 02 2013 OVERVIEW Percutaneous vertebroplasty is an interventional technique involving
PERCUTANEOUS BALLOON KYPHOPLASTY, RADIOFREQUENCY KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION
 KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures,
KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures,
Lateral Mass and Pedicle Screws Fixation of Cervical Spine
 Lateral Mass and Pedicle Screws Fixation of Cervical Spine Anderson Spine 1991 Paul A Anderson University of Wisconsin AAOS Biomedical Engineering Committee Co-chair ASTM F05-24 Purpose Anatomy Surgical
Lateral Mass and Pedicle Screws Fixation of Cervical Spine Anderson Spine 1991 Paul A Anderson University of Wisconsin AAOS Biomedical Engineering Committee Co-chair ASTM F05-24 Purpose Anatomy Surgical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
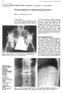 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
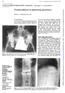 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2011 Sep;18(3): Originally published online September 30, 2011;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Delayed Paraplegia after Successful Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in a Patient with Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: A Case Report Yong-Chan Kim, M.D., Won-Su
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Delayed Paraplegia after Successful Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in a Patient with Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: A Case Report Yong-Chan Kim, M.D., Won-Su
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
